FH-1 Phantom on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The McDonnell FH Phantom is a
 When the first XFD-1, serial number ''48235'', was completed in January 1945, only one Westinghouse 19XB-2B engine was available for installation. Ground runs and taxi tests were conducted with the single engine, and such was the confidence in the aircraft that the first flight on 26 January 1945 was made with only the one turbojet engine.Francillon 1979, p. 382. During flight tests, the Phantom became the first U.S. Navy aircraft to exceed 500 mph (434 kn, 805 km/h). With successful completion of tests, a production contract was awarded on 7 March 1945 for 100 FD-1 aircraft. With the end of the war, the Phantom production contract was reduced to 30 aircraft, but was soon increased back to 60.''Air International'' November 1987, p. 258.
The first prototype was lost in a fatal crash on 1 November 1945,Angelucci and Bowers 1987, pp. 297–298. but the second and final Phantom prototype ( serial number ''48236'') was completed early the next year and became the first purely jet-powered aircraft to operate from an American aircraft carrier, completing four successful takeoffs and landings on 21 July 1946, from near Norfolk, Virginia. At the time, she was the largest carrier serving with the U.S. Navy, allowing the aircraft to take off without assistance from a catapult. The second prototype crashed on 26 August 1946.
Production Phantoms incorporated a number of design improvements. These included provisions for a flush-fitting centerline
When the first XFD-1, serial number ''48235'', was completed in January 1945, only one Westinghouse 19XB-2B engine was available for installation. Ground runs and taxi tests were conducted with the single engine, and such was the confidence in the aircraft that the first flight on 26 January 1945 was made with only the one turbojet engine.Francillon 1979, p. 382. During flight tests, the Phantom became the first U.S. Navy aircraft to exceed 500 mph (434 kn, 805 km/h). With successful completion of tests, a production contract was awarded on 7 March 1945 for 100 FD-1 aircraft. With the end of the war, the Phantom production contract was reduced to 30 aircraft, but was soon increased back to 60.''Air International'' November 1987, p. 258.
The first prototype was lost in a fatal crash on 1 November 1945,Angelucci and Bowers 1987, pp. 297–298. but the second and final Phantom prototype ( serial number ''48236'') was completed early the next year and became the first purely jet-powered aircraft to operate from an American aircraft carrier, completing four successful takeoffs and landings on 21 July 1946, from near Norfolk, Virginia. At the time, she was the largest carrier serving with the U.S. Navy, allowing the aircraft to take off without assistance from a catapult. The second prototype crashed on 26 August 1946.
Production Phantoms incorporated a number of design improvements. These included provisions for a flush-fitting centerline

 The first Phantoms were delivered to USN fighter squadron VF-17A (later redesignated VF-171) in August 1947;''Air International'' November 1987, p. 259. the squadron received a full complement of 24 aircraft on 29 May 1948. Beginning in November 1947, Phantoms were delivered to
The first Phantoms were delivered to USN fighter squadron VF-17A (later redesignated VF-171) in August 1947;''Air International'' November 1987, p. 259. the squadron received a full complement of 24 aircraft on 29 May 1948. Beginning in November 1947, Phantoms were delivered to
"The FH-1 Phantom."
''The McDonnell FH-1 Phantom & F2H Banshee'', 1 November 2010. Retrieved: 10 May 2011. The team's name was an obvious play on the name of the recently formed U.S. Navy
 ;FH-1
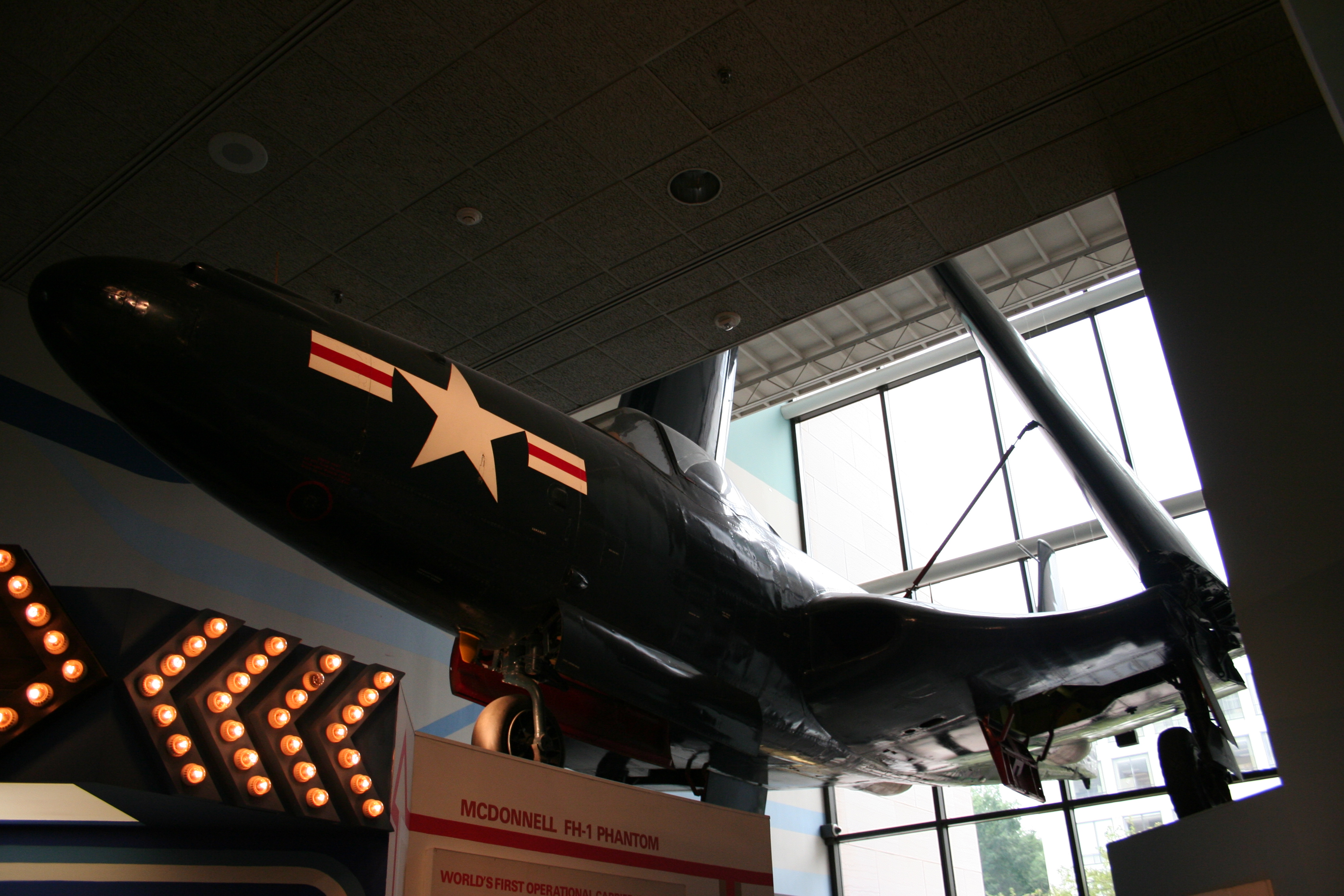
*BuNo 111759 - National Air and Space Museum of the
;FH-1
*BuNo 111759 - National Air and Space Museum of the "FH-1 Phantom/111793."
''National Museum of Naval Aviation.'' Retrieved: 15 January 2015. This aircraft was accepted by the navy on 28 February 1948. After flying for a brief time with Marine Fighter Squadron (VMF) 122, the first Marine jet squadron, at Marine Corps Air Station Cherry Point, North Carolina, it was stricken from the naval inventory in 1949. The museum acquired the aircraft from National Jets, Inc., of Fort Lauderdale, Florida, in 1983.
"Part 6: Postwar Years: 1946–1949"
''United States Naval Aviation 1910–1995''. Washington, D.C.: Naval Historical Center, 1997. . * Hamilton, Hayden. "The McDonnell FH-1 Phantom: the Forgotten Phantom". ''AAHS Journal'', Vol. 55, No. 2, Summer 2010. * Mesko, Jim. ''FH Phantom/F2H Banshee in action''. Carrollton, Texas: Squadron/Signal Publications, Inc., 2002. . * Mills, Carl. ''Banshees in the Royal Canadian Navy''. Willowdale, Ontario, Canada: Banshee Publication, 1991. . * "Mr Mac's First Phantom: The Story of the McDonnell FH-1". '' Air International'' Vol. 33, No. 5, November 1987, pp. 231–235, 258–260. Bromley, UK: Fine Scroll. . * Wagner, Ray. ''American Combat Planes''. New York: Doubleday, third edition, 1982. .
"Phantom Development"
a 1947 ''Flight'' article by
twinjet
A twinjet or twin-engine jet is a jet aircraft powered by two engines. A twinjet is able to fly well enough to land with a single working engine, making it safer than a single-engine aircraft in the event of failure of an engine. Fuel efficien ...
fighter aircraft designed and first flown during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
for the United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
. The Phantom was the first purely jet-powered aircraft to land on an American aircraft carrier and the first jet deployed by the United States Marine Corps
The United States Marine Corps (USMC), also referred to as the United States Marines, is the maritime land force service branch of the United States Armed Forces responsible for conducting expeditionary and amphibious operations through combi ...
. Although only 62 FH-1s had been built by the end of the war it helped prove the viability of carrier-based jet fighters. As McDonnell's first successful fighter, it led to the development of the follow-on F2H Banshee
The McDonnell F2H Banshee (company designation McDonnell Model 24) is an American single-seat carrier-based jet fighter aircraft deployed by the United States Navy and United States Marine Corps from 1948 to 1961. A development of the FH Phanto ...
, which was one of the two most important naval jet fighters of the Korean War
, date = {{Ubl, 25 June 1950 – 27 July 1953 (''de facto'')({{Age in years, months, weeks and days, month1=6, day1=25, year1=1950, month2=7, day2=27, year2=1953), 25 June 1950 – present (''de jure'')({{Age in years, months, weeks a ...
; combined, the two established McDonnell as an important supplier of navy aircraft.
McDonnell chose to bring the name back with the Mach 2–class McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom II
The McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom II is an American tandem two-seat, twin-engine, all-weather, long-range supersonic jet interceptor and fighter-bomber originally developed by McDonnell Aircraft for the United States Navy.Swanborough and B ...
, the most versatile and widely used western combat aircraft of the Vietnam War era.
The FH Phantom was originally designated the FD Phantom, but this was changed as the aircraft entered production.
Design and development
In early 1943, aviation officials at the United States Navy were impressed with McDonnell's audacious XP-67 Bat project. McDonnell was invited by the navy to cooperate in the development of a shipboard jet fighter, using an engine from the turbojets under development byWestinghouse Electric Corporation
The Westinghouse Electric Corporation was an American manufacturing company founded in 1886 by George Westinghouse. It was originally named "Westinghouse Electric & Manufacturing Company" and was renamed "Westinghouse Electric Corporation" in ...
. Three prototypes were ordered on 30 August 1943 and the designation XFD-1 was assigned. Under the 1922 United States Navy aircraft designation system
From 1922 until 1962, the United States Navy, the United States Marine Corps and the United States Coast Guard used a system to designate their aircraft that included information about a craft's role and its manufacturer. For a listing of all such ...
, the letter "D" before the dash designated the aircraft's manufacturer. The Douglas Aircraft Company had previously been assigned this letter, but the USN elected to reassign it to McDonnell because Douglas had not provided any fighters for navy service in years.Mesko 2002, p. 7.
McDonnell engineers evaluated a number of engine combinations, varying from eight 9.5 in (24 cm) diameter engines down to two engines of 19 inch (48 cm) diameter. The final design used the two 19 in (48 cm) engines after it was found to be the lightest and simplest configuration.''Air International'' November 1987, p. 233. The engines were buried in the wing root to keep intake and exhaust ducts short, offering greater aerodynamic efficiency than underwing nacelle
A nacelle ( ) is a "streamlined body, sized according to what it contains", such as an engine, fuel, or equipment on an aircraft. When attached by a pylon entirely outside the airframe, it is sometimes called a pod, in which case it is attached ...
s,''Air International'' November 1987, p. 234. and the engines were angled slightly outwards to protect the fuselage
The fuselage (; from the French ''fuselé'' "spindle-shaped") is an aircraft's main body section. It holds crew, passengers, or cargo. In single-engine aircraft, it will usually contain an engine as well, although in some amphibious aircraf ...
from the hot exhaust blast. Placement of the engines in the middle of the airframe allowed the cockpit with its bubble-style canopy to be placed ahead of the wing, granting the pilot excellent visibility in all directions. This engine location also freed up space under the nose, allowing designers to use tricycle gear
Tricycle gear is a type of aircraft undercarriage, or ''landing gear'', arranged in a tricycle fashion. The tricycle arrangement has a single nose wheel in the front, and two or more main wheels slightly aft of the center of gravity. Tricycle ...
, thereby elevating the engine exhaust path and reducing the risk that the hot blast would damage the aircraft carrier deck.Mesko 2002, p. 5. The construction methods and aerodynamic design of the Phantom were fairly conventional for the time; the aircraft had unswept wings, a conventional empennage
The empennage ( or ), also known as the tail or tail assembly, is a structure at the rear of an aircraft that provides stability during flight, in a way similar to the feathers on an arrow.Crane, Dale: ''Dictionary of Aeronautical Terms, third e ...
, and an aluminum
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It ha ...
monocoque
Monocoque ( ), also called structural skin, is a structural system in which loads are supported by an object's external skin, in a manner similar to an egg shell. The word ''monocoque'' is a French term for "single shell".
First used for boats, ...
structure with flush riveted aluminum skin. Folding wing
A folding wing is a wing configuration design feature of aircraft to save space and is typical of carrier-based aircraft that operate from the limited deck space of aircraft carriers. The folding allows the aircraft to occupy less space in a con ...
s were used to reduce the width of the aircraft in storage configuration. Provisions for four .50-caliber (12.7 mm) machine gun
A machine gun is a fully automatic, rifled autoloading firearm designed for sustained direct fire with rifle cartridges. Other automatic firearms such as automatic shotguns and automatic rifles (including assault rifles and battle rifles) ar ...
s were made in the nose, while racks for eight 5 in (127 mm) High Velocity Aircraft Rockets could be fitted under the wings, although these were seldom used in service. Adapting a jet to carrier use was a much greater challenge than producing a land-based fighter because of slower landing and takeoff speeds required on a small carrier deck. The Phantom used split flaps on both the folding and fixed wing sections to enhance low-speed landing performance,''Air International'' November 1987, pp. 234–235. but no other high-lift device
In aircraft design and aerospace engineering, a high-lift device is a component or mechanism on an aircraft's wing that increases the amount of lift produced by the wing. The device may be a fixed component, or a movable mechanism which is deplo ...
s were used. Provisions were also made for Rocket Assisted Take Off (RATO) bottles to improve takeoff performance.
 When the first XFD-1, serial number ''48235'', was completed in January 1945, only one Westinghouse 19XB-2B engine was available for installation. Ground runs and taxi tests were conducted with the single engine, and such was the confidence in the aircraft that the first flight on 26 January 1945 was made with only the one turbojet engine.Francillon 1979, p. 382. During flight tests, the Phantom became the first U.S. Navy aircraft to exceed 500 mph (434 kn, 805 km/h). With successful completion of tests, a production contract was awarded on 7 March 1945 for 100 FD-1 aircraft. With the end of the war, the Phantom production contract was reduced to 30 aircraft, but was soon increased back to 60.''Air International'' November 1987, p. 258.
The first prototype was lost in a fatal crash on 1 November 1945,Angelucci and Bowers 1987, pp. 297–298. but the second and final Phantom prototype ( serial number ''48236'') was completed early the next year and became the first purely jet-powered aircraft to operate from an American aircraft carrier, completing four successful takeoffs and landings on 21 July 1946, from near Norfolk, Virginia. At the time, she was the largest carrier serving with the U.S. Navy, allowing the aircraft to take off without assistance from a catapult. The second prototype crashed on 26 August 1946.
Production Phantoms incorporated a number of design improvements. These included provisions for a flush-fitting centerline
When the first XFD-1, serial number ''48235'', was completed in January 1945, only one Westinghouse 19XB-2B engine was available for installation. Ground runs and taxi tests were conducted with the single engine, and such was the confidence in the aircraft that the first flight on 26 January 1945 was made with only the one turbojet engine.Francillon 1979, p. 382. During flight tests, the Phantom became the first U.S. Navy aircraft to exceed 500 mph (434 kn, 805 km/h). With successful completion of tests, a production contract was awarded on 7 March 1945 for 100 FD-1 aircraft. With the end of the war, the Phantom production contract was reduced to 30 aircraft, but was soon increased back to 60.''Air International'' November 1987, p. 258.
The first prototype was lost in a fatal crash on 1 November 1945,Angelucci and Bowers 1987, pp. 297–298. but the second and final Phantom prototype ( serial number ''48236'') was completed early the next year and became the first purely jet-powered aircraft to operate from an American aircraft carrier, completing four successful takeoffs and landings on 21 July 1946, from near Norfolk, Virginia. At the time, she was the largest carrier serving with the U.S. Navy, allowing the aircraft to take off without assistance from a catapult. The second prototype crashed on 26 August 1946.
Production Phantoms incorporated a number of design improvements. These included provisions for a flush-fitting centerline drop tank
In aviation, a drop tank (external tank, wing tank or belly tank) is used to describe auxiliary fuel tanks externally carried by aircraft. A drop tank is expendable and often capable of being jettisoned. External tanks are commonplace on modern ...
, an improved gunsight, and the addition of speed brakes. Production models used Westinghouse J30
The Westinghouse J30, initially known as the Westinghouse 19XB, was a turbojet engine developed by Westinghouse Electric Corporation. It was the first American-designed turbojet to run, and only the second axial-flow turbojet to run outside German ...
-WE-20 engines with 1,600 lbf (7.1 kN) of thrust per engine. The top of the vertical tail had a more square shape than the rounder tail used on the prototypes, and a smaller rudder
A rudder is a primary control surface used to steer a ship, boat, submarine, hovercraft, aircraft, or other vehicle that moves through a fluid medium (generally air or water). On an aircraft the rudder is used primarily to counter adve ...
was used to resolve problems with control surface clearance discovered during test flights. The horizontal tail surfaces were shortened slightly, while the fuselage was stretched by 19 in (48 cm). The amount of framing in the windshield was reduced to enhance pilot visibility.
Halfway through the production run, the navy reassigned the designation letter "D" back to Douglas, with the Phantom being redesignated FH-1. Including the two prototypes, a total of 62 Phantoms were finally produced, with the last FH-1 rolling off the assembly line in May 1948.
Realizing that the production of more powerful jet engines was imminent, McDonnell engineers proposed a more powerful variant of the Phantom while the original aircraft was still under development – a proposal that would lead to the design of the Phantom's replacement, the F2H Banshee
The McDonnell F2H Banshee (company designation McDonnell Model 24) is an American single-seat carrier-based jet fighter aircraft deployed by the United States Navy and United States Marine Corps from 1948 to 1961. A development of the FH Phanto ...
. Although the new aircraft was originally envisioned as a modified Phantom, the need for heavier armament, greater internal fuel capacity, and other improvements eventually led to a substantially heavier and bulkier aircraft that shared few parts with its agile predecessor.Mesko 2002, p. 10. Despite this, the two aircraft were similar enough that McDonnell was able to complete its first F2H-1 in August 1948, a mere three months after the last FH-1 had rolled off the assembly line.
Operational history

 The first Phantoms were delivered to USN fighter squadron VF-17A (later redesignated VF-171) in August 1947;''Air International'' November 1987, p. 259. the squadron received a full complement of 24 aircraft on 29 May 1948. Beginning in November 1947, Phantoms were delivered to
The first Phantoms were delivered to USN fighter squadron VF-17A (later redesignated VF-171) in August 1947;''Air International'' November 1987, p. 259. the squadron received a full complement of 24 aircraft on 29 May 1948. Beginning in November 1947, Phantoms were delivered to United States Marine Corps
The United States Marine Corps (USMC), also referred to as the United States Marines, is the maritime land force service branch of the United States Armed Forces responsible for conducting expeditionary and amphibious operations through combi ...
squadron VMF-122
Marine Fighter Attack Squadron 122 (VMFA-122) is a United States Marine Corps fighter attack squadron flying the F-35B Lightning II. The squadron is based out of Marine Corps Air Station Yuma, AZ and falls under the command of Marine Aircraft Gr ...
, making it the first USMC combat squadron to deploy jets. VF-17A became the USN's first fully operational jet carrier squadron when it deployed aboard on 5 May 1948.Grossnick 1997, p. 171.
The Phantom was one of the first jets used by the U.S. military for exhibition flying. Three Phantoms used by the Naval Air Test Center were used by a unique demonstration team called the Gray Angels, whose members consisted entirely of naval aviators holding the rank of rear admiral (Daniel V. Gallery
Daniel Vincent Gallery (July 10, 1901 – January 16, 1977) was a rear admiral in the United States Navy. He saw extensive action during World War II, fighting U-boats during the Battle of the Atlantic, where his most notable achievement was t ...
, Apollo Soucek
Apollo Soucek (February 24, 1897 – July 22, 1955) was a vice admiral in the United States Navy, who was a record-breaking test pilot during 1929 and 1930, served in World War II, and was commander of Carrier Division Three during the Korean ...
and Edgar A. Cruise.)Goebel, Greg"The FH-1 Phantom."
''The McDonnell FH-1 Phantom & F2H Banshee'', 1 November 2010. Retrieved: 10 May 2011. The team's name was an obvious play on the name of the recently formed U.S. Navy
Blue Angels
The Blue Angels is a flight demonstration squadron of the United States Navy.
, who were still flying propeller-powered Grumman F8F Bearcats at the time. The "Grays" flew in various air shows during the summer of 1947, but the team was abruptly disbanded after their poorly timed arrival at a September air show in Cleveland, Ohio, nearly caused a head-on low-altitude collision with a large formation of other aircraft; their Phantoms were turned over to test squadron VX-3
Air Development Squadron 3 or VX-3 was a United States Navy air test and evaluation squadron established on 20 November 1948 and disestablished on 1 March 1960.
Operational history
VX-3 was established by the merger of the assets of VA-1L and V ...
. The VMF-122 Phantoms were later used for air show demonstrations until they were taken out of service in 1949, with the team being known alternately as the Marine Phantoms
Marine is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the sea or ocean.
Marine or marines may refer to:
Ocean
* Maritime (disambiguation)
* Marine art
* Marine biology
* Marine debris
* Marine habitats
* Marine life
* Marine pollution
Militar ...
or the Flying Leathernecks
''Flying Leathernecks'' is a 1951 American Technicolor action war film directed by Nicholas Ray, produced by Edmund Grainger, (who had produced ''Sands of Iwo Jima'') and starring John Wayne and Robert Ryan. The movie details the exploits an ...
.
The Phantom's service as a frontline fighter would be short-lived. Its limited range and light armament – notably, its inability to carry bombs – made it best suited for duty as a point-defence
Point defence (or point defense; see spelling differences) is the defence of a single object or a limited area, e.g. a ship, building or an airfield, now usually against air attacks and guided missiles. Point defence weapons have a smaller range i ...
interceptor aircraft
An interceptor aircraft, or simply interceptor, is a type of fighter aircraft designed specifically for the defensive interception role against an attacking enemy aircraft, particularly bombers and reconnaissance aircraft. Aircraft that are c ...
. However, its speed and rate of climb were only slightly better than existing propeller-powered fighters and fell short of other contemporary jets, such as the Lockheed P-80 Shooting Star
The Lockheed P-80 Shooting Star was the first jet fighter used operationally by the United States Army Air Forces (USAAF) during World War II. Designed and built by Lockheed in 1943 and delivered just 143 days from the start of design, prod ...
, prompting concerns that the Phantom would be outmatched by future enemy jets it might soon face. Moreover, recent experience in World War II had demonstrated the value of naval fighters that could double as fighter-bombers, a capability the Phantom lacked. Finally, the aircraft exhibited some design deficiencies – its navigational avionics
Avionics (a blend of ''aviation'' and ''electronics'') are the electronic systems used on aircraft. Avionic systems include communications, navigation, the display and management of multiple systems, and the hundreds of systems that are fit ...
were poor, it could not accommodate newly developed ejection seat
In aircraft, an ejection seat or ejector seat is a system designed to rescue the pilot or other crew of an aircraft (usually military) in an emergency. In most designs, the seat is propelled out of the aircraft by an explosive charge or rock ...
s, and the location of the machine guns in the upper nose caused pilots to be dazzled by muzzle flash
Muzzle flash is the light — both visible and infrared — created by a muzzle blast, which is caused by the sudden release and expansion of high-temperature, high-pressure gases from the muzzle of a firearm during shooting. Both the blast ...
.
The F2H Banshee and Grumman F9F Panther
The Grumman F9F Panther is one of the United States Navy's first successful carrier-based jet fighters, as well as Grumman’s first jet fighter. A single-engined, straight-winged day fighter, it was armed with four cannons and could carry a wi ...
, both of which began flight tests around the time of the Phantom's entry into service, better satisfied the navy's desire for a versatile, long-range, high-performance jet. Consequently, the FH-1 saw little weapons training, and was primarily used for carrier qualifications to transition pilots from propeller-powered fighters to jets in preparation for flying the Panther or Banshee. In June 1949, VF-171 (VF-17A) re-equipped with the Banshee, and their Phantoms were turned over to VF-172; this squadron, along with the NATC, VX-3, and VMF-122, turned over their Phantoms to the United States Naval Reserve
The United States Navy Reserve (USNR), known as the United States Naval Reserve from 1915 to 2005, is the Reserve Component (RC) of the United States Navy. Members of the Navy Reserve, called Reservists, are categorized as being in either the Se ...
by late 1949 after receiving F2H-1 Banshees. The FH-1 would see training duty with the USNR until being replaced by the F9F Panther in July 1954; none ever saw combat, having been retired from frontline service prior to the outbreak of the Korean War
, date = {{Ubl, 25 June 1950 – 27 July 1953 (''de facto'')({{Age in years, months, weeks and days, month1=6, day1=25, year1=1950, month2=7, day2=27, year2=1953), 25 June 1950 – present (''de jure'')({{Age in years, months, weeks a ...
.
Civilian use
In 1964, Progressive Aero, Incorporated of Fort Lauderdale, Florida purchased three surplus Phantoms, intending to use them to teach civilians how to fly jets. A pair were stripped of military equipment and restored to flying condition, but the venture was unsuccessful, and the aircraft were soon retired once again.Mesko, 2002 p. 8.Variants
;XFD-1 : Prototype aircraft powered by Westinghouse 19XB-2B engines (J-30). Two built.Angelucci and Bowers 1987, p. 268. ;FH-1 (FD-1): Production version with Westinghouse J30-WE-20 engines (originally designated FD-1). 60 built.Operators
; *United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
** VX-3
Air Development Squadron 3 or VX-3 was a United States Navy air test and evaluation squadron established on 20 November 1948 and disestablished on 1 March 1960.
Operational history
VX-3 was established by the merger of the assets of VA-1L and V ...
** VF-171 (VF-17A)
** VF-172
** Naval Air Reserve
* United States Marine Corps
The United States Marine Corps (USMC), also referred to as the United States Marines, is the maritime land force service branch of the United States Armed Forces responsible for conducting expeditionary and amphibious operations through combi ...
** VMF-122
Marine Fighter Attack Squadron 122 (VMFA-122) is a United States Marine Corps fighter attack squadron flying the F-35B Lightning II. The squadron is based out of Marine Corps Air Station Yuma, AZ and falls under the command of Marine Aircraft Gr ...
** VMF-311
Marine Fighter Attack Squadron 311 (VMFA-311) is a United States Marine Corps fighter attack squadron consisting of F-35C Lightning II. Known as the "Tomcats", the squadron is based at Marine Corps Air Station Miramar, California and falls under t ...
Aircraft on display
Smithsonian Institution
The Smithsonian Institution ( ), or simply the Smithsonian, is a group of museums and education and research centers, the largest such complex in the world, created by the U.S. government "for the increase and diffusion of knowledge". Founded ...
in Washington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...
, United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
. This aircraft served with Marine Fighter Squadron 122 (VMF-122). It was retired in April 1954, with a total of 418 flight hours. The aircraft was transferred to the Smithsonian by the U.S. Navy in 1959.Hamilton, Hayden. "The McDonell FH-1 Phantom: the Forgotten Phantom". ''AAHS Journal,'' Vol. 55, No. 2, Summer 2010.
*BuNo 111768 - Pima Air & Space Museum
The Pima Air & Space Museum, located in Tucson, Arizona, is one of the world's largest non-government funded aerospace museums. The museum features a display of nearly 300 aircraft spread out over 80 acres (320,000 m²) on a campus oc ...
, Tucson, Arizona
, "(at the) base of the black ill
, nicknames = "The Old Pueblo", "Optics Valley", "America's biggest small town"
, image_map =
, mapsize = 260px
, map_caption = Interactive map ...
, on loan from the National Museum of the Marine Corps
The National Museum of the Marine Corps is the historical museum of the United States Marine Corps. Located in Triangle, Virginia near MCB Quantico, the museum opened on November 10, 2006, and is now one of the top tourist attractions in the st ...
, Triangle, Virginia
Triangle is a census-designated place (CDP) in Prince William County, Virginia, United States. The population was 8,188 at the 2010 census. It is bounded to the south by the Marine Corps Base Quantico, which surrounds the town of Quantico.
Geogr ...
. It has had a busy post-retirement life. Formerly a Progressive Aero aircraft c/n 456 (civil registration N4283A) it was placed on display at the Marine Corps Museum
The Marine Corps Museum was located on the first floor of the Marine Corps Historical Society in Building 58 of the Washington Navy Yard, 9th and M Streets (southeast), Washington, D.C. It housed a wide variety of exhibits with artifacts relatin ...
. The aircraft was later transferred to the St. Louis Aviation Museum, and then the National Warplane Museum
The National Warplane Museum is a warbird and military history museum currently located on the grounds of the Geneseo Airport in Geneseo, New York. Founded in 1994, the museum restores, flies, and displays vintage military aircraft from the Seco ...
in Geneseo, New York
Geneseo is a town in Livingston County in the Finger Lakes region of New York, United States. It is at the south end of the five-county Rochester Metropolitan Area. The population of the town was 10,483 at the 2010 census.
The English name ...
. In 2006 the aircraft was moved to the Wings of Eagles Discovery Center
Elmira Corning Regional Airport is in Chemung County, New York, seven miles northwest of Elmira and eight miles east of Corning. It is in the town of Big Flats but its mailing address is Horseheads, New York. The airport was formerly Elmira ...
in Horseheads, New York
Horseheads is a town in Chemung County, New York, United States. The population was 19,412 at the 2020 census. The name of the town is derived from the number of bleached horses' skulls once found there.
Horseheads is north of the city of Elmira ...
., and moved to Tucson in 2016.
*BuNo 111793 - National Naval Aviation Museum
The National Naval Aviation Museum, formerly known as the National Museum of Naval Aviation and the Naval Aviation Museum, is a military and aerospace museum located at Naval Air Station Pensacola, Florida.
Founded in 1962 and moved to its cur ...
at Naval Air Station Pensacola
Naval Air Station Pensacola or NAS Pensacola (formerly NAS/KNAS until changed circa 1970 to allow Nassau International Airport, now Lynden Pindling International Airport, to have IATA code NAS), "The Cradle of Naval Aviation", is a United State ...
, Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and to ...
.''National Museum of Naval Aviation.'' Retrieved: 15 January 2015. This aircraft was accepted by the navy on 28 February 1948. After flying for a brief time with Marine Fighter Squadron (VMF) 122, the first Marine jet squadron, at Marine Corps Air Station Cherry Point, North Carolina, it was stricken from the naval inventory in 1949. The museum acquired the aircraft from National Jets, Inc., of Fort Lauderdale, Florida, in 1983.
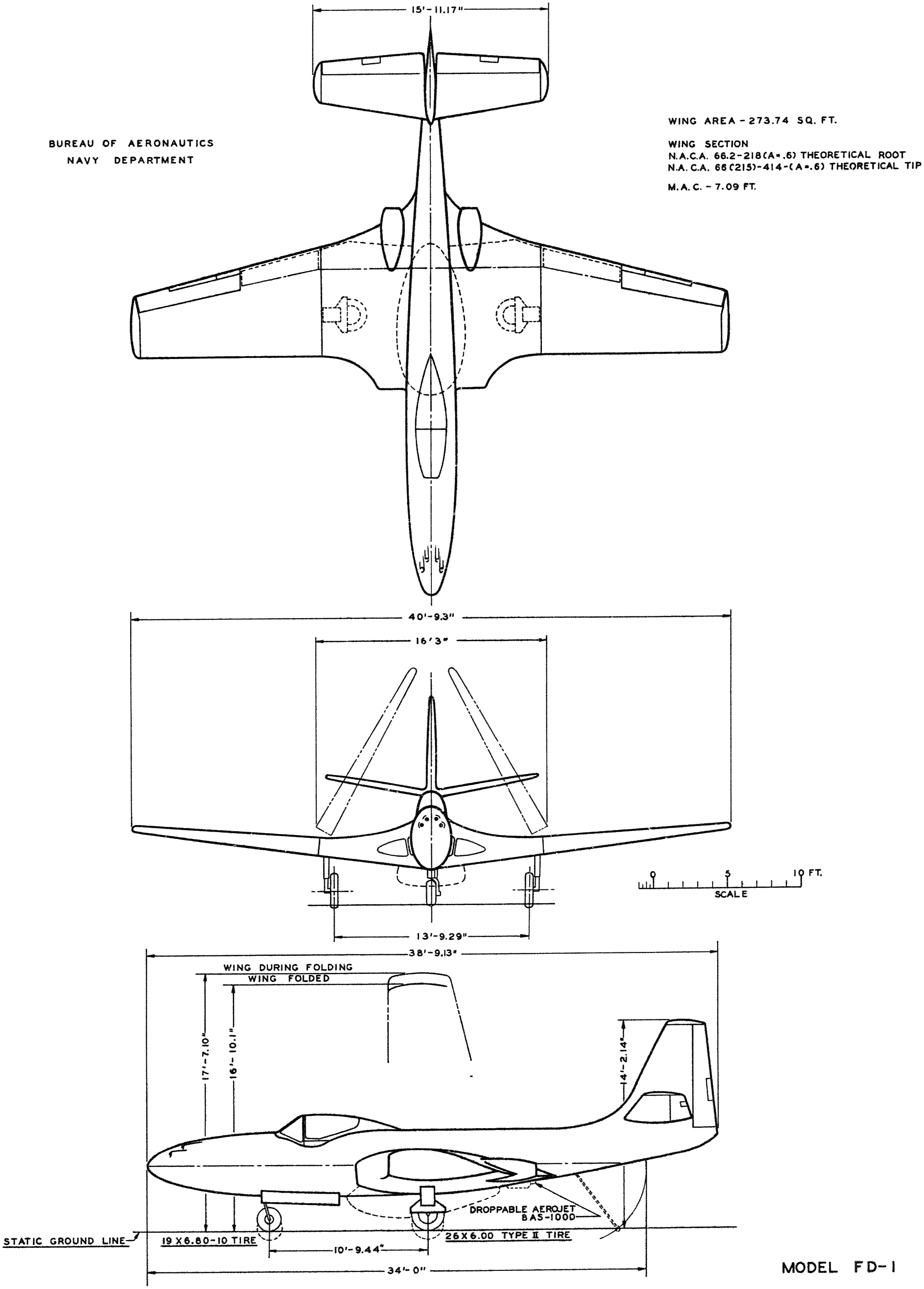
Specifications (FH-1 Phantom)

See also
References
Notes
Citations
Bibliography
* Angelucci, Enzo and Peter M. Bowers. ''The American Fighter''. Sparkford, Somerset, UK: Haynes Publishing Group, 1987. . * * Francillon, René J. ''McDonnell Douglas Aircraft since 1920''. London: Putnam & Company, Ltd, 1979. . * Green, William. ''War Planes of the Second World War, Volume Four: Fighters''. London: MacDonald & Co. (Publishers) Ltd., 1961 (sixth impression 1969). . * Green, William and Gordon Swanborough. ''WW2 Aircraft Fact Files: US Navy and Marine Corps Fighters''. London: Macdonald and Jane's, 1976. . * Grossnick, Roy A"Part 6: Postwar Years: 1946–1949"
''United States Naval Aviation 1910–1995''. Washington, D.C.: Naval Historical Center, 1997. . * Hamilton, Hayden. "The McDonnell FH-1 Phantom: the Forgotten Phantom". ''AAHS Journal'', Vol. 55, No. 2, Summer 2010. * Mesko, Jim. ''FH Phantom/F2H Banshee in action''. Carrollton, Texas: Squadron/Signal Publications, Inc., 2002. . * Mills, Carl. ''Banshees in the Royal Canadian Navy''. Willowdale, Ontario, Canada: Banshee Publication, 1991. . * "Mr Mac's First Phantom: The Story of the McDonnell FH-1". '' Air International'' Vol. 33, No. 5, November 1987, pp. 231–235, 258–260. Bromley, UK: Fine Scroll. . * Wagner, Ray. ''American Combat Planes''. New York: Doubleday, third edition, 1982. .
External links
"Phantom Development"
a 1947 ''Flight'' article by
John W. R. Taylor
John William Ransom Taylor, OBE Hon DEng FRAeS FRHistS AFIAA, (8 June 1922 – 12 December 1999) was a British aviation expert and editor. He edited '' Jane's All the World's Aircraft'' for three decades during the Cold War. He retired as edit ...
{{DEFAULTSORT:Mcdonnell Fh Phantom
Carrier-based aircraft
F1H Phantom
McDonnell F1H Phantom
World War II jet aircraft of the United States
Cruciform tail aircraft
Twinjets
Aircraft first flown in 1945