Extreme points of Greenland on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Permanent crops:'' Approximately 0%
''Other:'' 100% (2012 est.) The total population comprises around 56,000 inhabitants, of whom approximately 18,000 live in the capital,


 Greenland's climate is a
Greenland's climate is a
''Los Angeles Times'', June 25, 2006 If the ice melted, the interior bedrock below sea level would be covered by water. It is not clear whether this water would be at sea level or a lake above sea level. If it would be at sea level it could connect to the sea at Ilulissat Icefjord, in Baffin Bay and near
www.geus.dk
Geological map of Greenland from the Geological Survey of Denmark and Greenland (GEUS).
"Times Atlas reviews Greenland map accuracy after climate change row"
– ''The Guardian'', 22 September 2011 {{DEFAULTSORT:Geography Of Greenland
Greenland
Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland i ...
is located between the Arctic Ocean
The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceans. It spans an area of approximately and is known as the coldest of all the oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, a ...
and the North Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
, northeast of Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
and northwest of Iceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its s ...
. The territory comprises the island
An island (or isle) is an isolated piece of habitat that is surrounded by a dramatically different habitat, such as water. Very small islands such as emergent land features on atolls can be called islets, skerries, cays or keys. An island ...
of Greenland—the largest island in the world—and more than a hundred other smaller islands (see alphabetic list). Greenland has a 1.2 kilometre (0.75 mi) long border with Canada on Hans Island. A sparse population is confined to small settlements along certain sectors of the coast. Greenland possesses the world's second-largest ice sheet
In glaciology, an ice sheet, also known as a continental glacier, is a mass of glacial ice that covers surrounding terrain and is greater than . The only current ice sheets are in Antarctica and Greenland; during the Last Glacial Period at La ...
.
Greenland sits atop the Greenland plate, a subplate of the North American plate
The North American Plate is a tectonic plate covering most of North America, Cuba, the Bahamas, extreme northeastern Asia, and parts of Iceland and the Azores. With an area of , it is the Earth's second largest tectonic plate, behind the Pacif ...
. The Greenland craton
A craton (, , or ; from grc-gre, κράτος "strength") is an old and stable part of the continental lithosphere, which consists of Earth's two topmost layers, the crust and the uppermost mantle. Having often survived cycles of merging an ...
is made up of some of the oldest rocks on the face of the earth. The Isua greenstone belt in southwestern Greenland contains the oldest known rocks on Earth, dated at 3.7–3.8 billion years old.
The vegetation is generally sparse, with the only patch of forested land being found in Nanortalik Municipality in the extreme south near Cape Farewell.
The climate is arctic to subarctic, with cool summers and cold winters. The terrain is mostly a flat but gradually sloping icecap that covers all land except for a narrow, mountainous, barren, rocky coast. The lowest elevation is sea level
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical datuma standardise ...
and the highest elevation is the summit of Gunnbjørn Fjeld
Gunnbjørn Fjeld is the tallest mountain in Greenland, the Kingdom of Denmark, and north of the Arctic Circle. It is a nunatak, a rocky peak protruding through glacial ice.
Geography
Gunnbjørn Fjeld is located in the Watkins Range, an area o ...
, the highest point in the Arctic
The Arctic ( or ) is a polar region located at the northernmost part of Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean, adjacent seas, and parts of Canada (Yukon, Northwest Territories, Nunavut), Danish Realm (Greenland), Finland, Iceland, N ...
at . The northernmost point of the island of Greenland is Cape Morris Jesup
Cape Morris Jesup ( da, Kap Morris Jesup) is a headland in Peary Land, Greenland.
Geography
Cape Morris Jesup is the northernmost point of mainland Greenland. It is from the geographic North Pole. It is located in Johannes V. Jensen Land, abo ...
, discovered by Admiral Robert Peary in 1900. Natural resource
Natural resources are resources that are drawn from nature and used with few modifications. This includes the sources of valued characteristics such as commercial and industrial use, aesthetic value, scientific interest and cultural value. ...
s include zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodi ...
, lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cu ...
, iron
Iron () is a chemical element with Symbol (chemistry), symbol Fe (from la, Wikt:ferrum, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 element, group 8 of the periodic table. It is, Abundanc ...
ore, coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal is formed when ...
, molybdenum, gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile me ...
, platinum
Platinum is a chemical element with the symbol Pt and atomic number 78. It is a dense, malleable, ductile, highly unreactive, precious, silverish-white transition metal. Its name originates from Spanish , a diminutive of "silver".
Pla ...
, uranium
Uranium is a chemical element with the symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Uranium is weak ...
, hydropower
Hydropower (from el, ὕδωρ, "water"), also known as water power, is the use of falling or fast-running water to produce electricity or to power machines. This is achieved by converting the gravitational potential or kinetic energy of a w ...
and fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of ...
.
Area
''Total area:'' 2,166,086 km2 ''Land area:'' 2,166,086 km2 (410,449 km2 ice-free, 1,755,637 km2 ice-covered) Maritime claims: ''Territorial sea:'' ''Exclusive fishing zone:''Land use
''Arable land:'' approximately 6%; some land is used to growsilage
Silage () is a type of fodder made from green foliage crops which have been preserved by fermentation to the point of acidification. It can be fed to cattle, sheep and other such ruminants (cud-chewing animals). The fermentation and storage ...
.
''Permanent crops:'' Approximately 0%
''Other:'' 100% (2012 est.) The total population comprises around 56,000 inhabitants, of whom approximately 18,000 live in the capital,
Nuuk
Nuuk (; da, Nuuk, formerly ) is the capital and largest city of Greenland, a constituent country of the Kingdom of Denmark. Nuuk is the seat of government and the country's largest cultural and economic centre. The major cities from other coun ...
.
Natural hazards
Continuousice sheet
In glaciology, an ice sheet, also known as a continental glacier, is a mass of glacial ice that covers surrounding terrain and is greater than . The only current ice sheets are in Antarctica and Greenland; during the Last Glacial Period at La ...
covers 84% of the country; the rest is permafrost.
Environment – current issues
Protection of the Arctic environment,climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
, pollution of the food chain, excessive hunting of endangered species (walrus, polar bears, narwhal, beluga whale and several sea birds).
Climate


 Greenland's climate is a
Greenland's climate is a tundra climate
The tundra climate is a polar climate sub-type located in high latitudes and high mountains. undra climate https://www.britannica.com/science/tundra-climateThe Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica, 2019 It is classified as ET according to Köppen ...
on and near the coasts and an ice cap climate
An ice cap climate is a polar climate where no mean monthly temperature exceeds . The climate covers areas in or near the high latitudes (65° latitude) to polar regions (70–90° north and south latitude), such as Antarctica, some of the northe ...
in inland areas. It typically has short, cool summers and long, moderately cold winters.
Due to Gulf Stream influences, Greenland's winter temperatures are very mild for its latitude. In Nuuk
Nuuk (; da, Nuuk, formerly ) is the capital and largest city of Greenland, a constituent country of the Kingdom of Denmark. Nuuk is the seat of government and the country's largest cultural and economic centre. The major cities from other coun ...
, the capital, average winter temperatures are only . In comparison, the average winter temperatures for Iqaluit
Iqaluit ( ; , ; ) is the capital of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian territory of Nunavut, its largest community, and its only city. It was known as Frobisher Bay from 1942 to 1987, after the Frobisher Bay, large bay on the c ...
, Nunavut, Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
, are around . Conversely, summer temperatures are very low, with an average high around . This is too low to sustain trees, and the land is treeless tundra
In physical geography, tundra () is a type of biome where tree growth is hindered by frigid temperatures and short growing seasons. The term ''tundra'' comes through Russian (') from the Kildin Sámi word (') meaning "uplands", "treeless mou ...
.
On the Greenland ice sheet, the temperature is far below freezing throughout the year, and record high temperatures have peaked only slightly above freezing. The record high temperature at Summit Camp
Summit Camp, also Summit Station, is a year-round staffed research station near the apex of the Greenland ice sheet. The station is located at above sea level. The population of the station is typically five in wintertime and reaches a maximu ...
is .
In the far south of Greenland, there is a very small forest in the Qinngua Valley, due to summer temperatures being barely high enough to sustain trees. There are mountains over high surrounding the valley, which protect it from cold, fast winds travelling across the ice sheet. It is the only natural forest in Greenland, but is only long.
Climate change
The Greenland ice sheet is thick and broad enough to blanket an area the size ofMexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatema ...
. The ice is so massive that its weight presses the bedrock of Greenland below sea level and is so all-concealing that not until recently did scientists discover Greenland's Grand Canyon or the possibility that Greenland might actually be three islands."Greenland's Ice Sheet Is Slip-Sliding Away"''Los Angeles Times'', June 25, 2006 If the ice melted, the interior bedrock below sea level would be covered by water. It is not clear whether this water would be at sea level or a lake above sea level. If it would be at sea level it could connect to the sea at Ilulissat Icefjord, in Baffin Bay and near
Nordostrundingen
Nordostrundingen (corrupted from da, Nordøstrundingen which means Northeastern rounding, in English Northeast Foreland), is a headland located at the northeastern end of Greenland. Administratively it is part of the Northeast Greenland National ...
, creating three large islands. But it is most likely that it would be a lake with one drain.
It is thought that before the last Ice Age, Greenland had mountainous edges and a lowland (and probably very dry) center which drained to the sea via one big river flowing out westwards, past where Disko Island
Disko Island ( kl, Qeqertarsuaq, da, Diskoøen) is a large island in Baffin Bay, off the west coast of Greenland. It has an area of ,sea level rise
Globally, sea levels are rising due to human-caused climate change. Between 1901 and 2018, the globally averaged sea level rose by , or 1–2 mm per year on average.IPCC, 2019Summary for Policymakers InIPCC Special Report on the Ocean and Cry ...
caused by ice loss (melt and glaciers falling into the sea) on Greenland. Between 1997 and 2003 ice loss was , compared to about for 1993/4-1998/9. Half of the increase was from higher summer melting, with the rest caused by the movements of some glaciers exceeding the speeds needed to balance upstream snow accumulation. A complete loss of ice on Greenland would cause a sea level rise of as much as .
Researchers at NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil List of government space agencies, space program ...
's Jet Propulsion Laboratory
The Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) is a federally funded research and development center and NASA field center in the City of La Cañada Flintridge, California, United States.
Founded in the 1930s by Caltech researchers, JPL is owned by NASA an ...
and the University of Kansas
The University of Kansas (KU) is a public research university with its main campus in Lawrence, Kansas, United States, and several satellite campuses, research and educational centers, medical centers, and classes across the state of Kansas. T ...
reported in February 2006 that the glaciers are melting twice as fast as they were five years ago. By 2005, Greenland was beginning to lose more ice volume than anyone expected – an annual loss of up to per year, according to more recent satellite gravity measurements released by JPL. The increased ice loss may be partially offset by increased snow accumulation due to increased precipitation.
Between 1991 and 2006, monitoring of the weather at one location (Swiss Camp) found that the average winter temperature had risen almost .
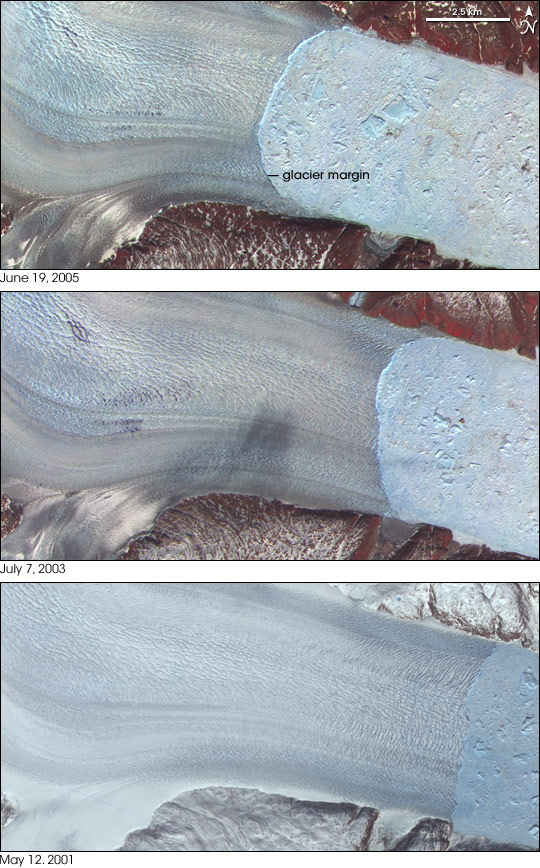
Recently, Greenland's three largest outlet glaciers have started moving faster, satellite data show. These are the Jakobshavn Isbræ at Ilulissat on the western edge of Greenland, and the Kangerdlugssuaq and Helheim
Hel (Old Norse: ) is an afterlife location in Norse mythology and paganism. It is ruled over by a being of the same name, Hel. In late Icelandic sources, varying descriptions of Hel are given and various figures are described as being buried ...
glaciers on the eastern edge of Greenland. The two latter accelerated greatly during the years 2004–2005, but returned to pre-2004 velocities in 2006. The accelerating ice flow has been accompanied by a dramatic increase in seismic activity. In March 2006, researchers at Harvard University
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of high ...
and the Lamont–Doherty Earth Observatory
The Lamont–Doherty Earth Observatory (LDEO) is the scientific research center of the Columbia Climate School, and a unit of The Earth Institute at Columbia University. It focuses on climate and earth sciences and is located on a 189-acre (64 ...
at Columbia University
Columbia University (also known as Columbia, and officially as Columbia University in the City of New York) is a private research university in New York City. Established in 1754 as King's College on the grounds of Trinity Church in Manhatt ...
reported that the glaciers now generate swarms of earthquakes up to magnitude 5.0.
The retreat of Greenland's ice is revealing islands that were thought to be part of the mainland. In September 2005 Dennis Schmitt
Dennis Schmitt (born May 23, 1946) is a veteran explorer, adventurer and composer.
Early life
Schmitt grew up in Berkeley, California, the son of mixed German and American parentage. His father was a plumber. Displaying early aptitude with lang ...
discovered an island north of the Arctic Circle in eastern Greenland which he named Uunartoq Qeqertaq
Uunartoq Qeqertaq ( Greenlandic), ''Warming Island'' in English, is an island off the east central coast of Greenland, north of the Arctic Circle. It became recognised as an island only in September 2005, by US explorer Dennis Schmitt. It was at ...
, Inuit
Inuit (; iu, ᐃᓄᐃᑦ 'the people', singular: Inuk, , dual: Inuuk, ) are a group of culturally similar indigenous peoples inhabiting the Arctic and subarctic regions of Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwest Territories ...
for "warming island".
Future projections
In theArctic
The Arctic ( or ) is a polar region located at the northernmost part of Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean, adjacent seas, and parts of Canada (Yukon, Northwest Territories, Nunavut), Danish Realm (Greenland), Finland, Iceland, N ...
, temperatures are rising faster than anywhere else in the world. Greenland is losing 200 billion tonnes of ice per year. Research suggests that this could increase the sea levels' rise by 30 centimeters by the end of the century. These projections have the possibility of changing as satellite data only dates back to 40 years ago. This means that researchers must view old photographs of glaciers and compare them to ones taken today to determine the future of Greenland's ice.
Temperature extremes
Highest temperatures
Lowest temperatures
Topography
The ice sheet covering Greenland varies significantly in elevation across the landmass, rising dramatically between the coastline at sea level and the East-Central interior, where elevations reach . The coastlines are rocky and predominantly barren with fjords. Numerous small islands spread from the Central to Southern coastlines. Greenland's mountain ranges are partially or completely buried by ice. The highest mountains are in the Watkins Range, which runs along the eastern coast. Greenland's highest mountain is Gunnbjorn Fjeld with a height of . Scientists discovered an asteroidimpact crater
An impact crater is a circular depression in the surface of a solid astronomical object formed by the hypervelocity impact of a smaller object. In contrast to volcanic craters, which result from explosion or internal collapse, impact crater ...
in the northwestern region of Greenland, buried underneath the ice sheet. At a size larger than Washington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...
, it is the first impact crater found beneath one of Earth's ice sheets.
Extreme points
This is a list of the extreme points ofGreenland
Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland i ...
, the points that are farther north, south, east or west than any other location.
Territory of Greenland
* Northernmost point —Kaffeklubben Island
Kaffeklubben Island or Coffee Club Island ( da, Kaffeklubben Ø; kl, Inuit Qeqertaat) is an uninhabited island lying off the northern tip of Greenland. It contains the northernmost undisputed point of land on Earth.
Discovery
The first re ...
(83°40'N) – the northernmost permanent land in the world. There are also some shifting gravel bars that lie north of Kaffeklubben, the most famous being Oodaaq
Oodaaq or Oodap Qeqertaa is a bank of gravel and silt northeast of Greenland that has been considered by some to be the northernmost point of land on Earth, though a number of other places have also been given that title since its discovery. I ...
.
* Southernmost point — unnamed islet 2.3 km south of Cape Farewell, Egger Island
Egger Island ( da, Eggers Ø; kl, Itilleq, old spelling: ''Itivdleq'') is Greenland's southernmost island. It is located in the Kujalleq municipality and is uninhabited.
Geography
Egger Island is an important landmark for a small islet off Ca ...
(59°44'N)
* Westernmost point — Nordvestø, Carey Islands (73°10'W)
* Easternmost point — Nordostrundingen
Nordostrundingen (corrupted from da, Nordøstrundingen which means Northeastern rounding, in English Northeast Foreland), is a headland located at the northeastern end of Greenland. Administratively it is part of the Northeast Greenland National ...
, Greenland
Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland i ...
(11°19'W)
* Highest point — Gunnbjørn Fjeld
Gunnbjørn Fjeld is the tallest mountain in Greenland, the Kingdom of Denmark, and north of the Arctic Circle. It is a nunatak, a rocky peak protruding through glacial ice.
Geography
Gunnbjørn Fjeld is located in the Watkins Range, an area o ...
,
Mainland Greenland
* Northernmost point —Cape Morris Jesup
Cape Morris Jesup ( da, Kap Morris Jesup) is a headland in Peary Land, Greenland.
Geography
Cape Morris Jesup is the northernmost point of mainland Greenland. It is from the geographic North Pole. It is located in Johannes V. Jensen Land, abo ...
(83°39'N)
* Southernmost point — Peninsula near Tasiusaq, Kujalleq
Tasiusaq is a settlement in the Kujalleq municipality in southern Greenland, founded in 1933. It is located at the Tasermiut Fjord ( da, Ketils Fjord), east of Nanortalik. Its population was 53 in 2020. In the Greenlandic language, the name of ...
(59°58'26.4"N)
* Westernmost point — Cape Alexander (73°08'W)
* Easternmost point — Nordostrundingen
Nordostrundingen (corrupted from da, Nordøstrundingen which means Northeastern rounding, in English Northeast Foreland), is a headland located at the northeastern end of Greenland. Administratively it is part of the Northeast Greenland National ...
, Greenland
Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland i ...
(11°19'W)
* Highest point — Gunnbjørn Fjeld, .
Towns
Greenland has 17 towns – settlements with more than 500 inhabitants.Nuuk
Nuuk (; da, Nuuk, formerly ) is the capital and largest city of Greenland, a constituent country of the Kingdom of Denmark. Nuuk is the seat of government and the country's largest cultural and economic centre. The major cities from other coun ...
is the largest town – and the capital – with roughly one third of the country's urban population. Sisimiut
Sisimiut (), formerly known as Holsteinsborg, is the capital and largest city of the Qeqqata municipality, the second-largest city in Greenland, and the largest Arctic city in North America.The term 'city' is loosely used to describe any popula ...
with approximately 5,500 inhabitants is the second largest town, while Ilulissat is number three with around 5,000 inhabitants.
* Aasiaat
Aasiaat () or Ausiait, formerly Egedesminde, is a town in the Qeqertalik municipality in western Greenland, located in the heart of Aasiaat Archipelago at the southern end of Disko Bay. With a population of 3,069 as of 2020, it is Greenland's fo ...
* Ilulissat
* Ittoqqortoormiit
Ittoqqortoormiit (East Greenlandic: ; West Greenlandic: ''Illoqqortoormiut'' ), formerly known as Scoresbysund, is a settlement in the Sermersooq municipality in eastern Greenland. Its population was 345 as of 2020 and has been described as one o ...
* Kangaatsiaq
Kangaatsiaq (, old spelling: ''Kangâtsiaq'') is a town located in the Qeqertalik municipality in western Greenland. The town received town status as recently as 1986, though as a settlement it has existed much longer. It has 520 inhabitants as of ...
* Maniitsoq
Maniitsoq (), formerly Sukkertoppen, is a town in Maniitsoq Island, western Greenland located in the Qeqqata municipality. With 2,534 inhabitants , it is the sixth-largest town in Greenland.
History
Archaeological finds indicate that the are ...
* Nanortalik
Nanortalik (), formerly Nennortalik, is a town in Nanortalik Island, Kujalleq municipality, southern Greenland. With 1,185 inhabitants as of 2020, it is the eleventh-largest town in the country. The name ''Nanortalik'' means "Place of Polar Bear ...
* Narsaq
Narsaq is a town in the Kujalleq municipality in southern Greenland. The name ''Narsaq'' is Kalaallisut for "Plain", referring to the shore of Tunulliarfik Fjord where the town is located.
History
People have lived in the area for thousands o ...
* Nuuk
Nuuk (; da, Nuuk, formerly ) is the capital and largest city of Greenland, a constituent country of the Kingdom of Denmark. Nuuk is the seat of government and the country's largest cultural and economic centre. The major cities from other coun ...
* Paamiut
Paamiut, formerly Frederikshåb, is a town in southwestern Greenland in the Sermersooq municipality.
Geography
Paamiut is located on the coast of Labrador Sea in the southern end of a small estuary called Kuannersooq ("Inlet").
History
Pe ...
* Qaanaaq
Qaanaaq (), formerly known as Thule or New Thule, is the main town in the northern part of the Avannaata municipality in northwestern Greenland. It is one of the northernmost towns in the world. The inhabitants of Qaanaaq speak the local Inukt ...
* Qaqortoq
Qaqortoq, formerly Julianehåb, is a city in the Kujalleq municipality in southern Greenland, located near Cape Thorvaldsen. With a population of 3,050 in 2020, it is the most populous town and the municipal capital in southern Greenland and the ...
* Qasigiannguit
Qasigiannguit (), formerly Christianshåb, is a town located in western Greenland on the southeastern shore of Disko Bay in the Qeqertalik municipality. With 1,081 inhabitants in 2020, it is the thirteenth-largest town in Greenland. The main indu ...
* Qeqertarsuaq
Qeqertarsuaq () is a port and town in Qeqertalik municipality, located on the south coast of Disko Island on the west coast of Greenland. Founded in 1773, the town is now home to a campus of the University of Copenhagen known as Arctic Station. ...
* Sisimiut
Sisimiut (), formerly known as Holsteinsborg, is the capital and largest city of the Qeqqata municipality, the second-largest city in Greenland, and the largest Arctic city in North America.The term 'city' is loosely used to describe any popula ...
* Tasiilaq
Tasiilaq, formerly Ammassalik and Angmagssalik, is a town in the Sermersooq municipality in southeastern Greenland. With 1,985 inhabitants as of 2020, it is the most populous community on the eastern coast, and the seventh-largest town in Green ...
* Upernavik
Upernavik (Kalaallisut: "Springtime Place") is a small town in the Avannaata municipality in northwestern Greenland, located on a small island of the same name. With 1,092 inhabitants as of 2020, it is the twelfth-largest town in Greenland. It c ...
* Uummannaq
Uummannaq is a town in the Avannaata municipality, in central-western Greenland. With 1,407 inhabitants in 2020, it is the eighth-largest town in Greenland, and is home to the country's most northerly ferry terminal. Founded in 1763 as Omenak, t ...
History of exploration
Gallery
See also
*List of mountain peaks of Greenland
This article comprises three sortable tables of major mountain peaksThis article defines a significant summit as a summit with at least of topographic prominence, and a major summit as a summit with at least of topographic prominence. All ...
*List of mountain ranges of Greenland
This is a list of mountain ranges of Greenland.
List by alphabetical order
*Alángup Qáqai, located in SW Disko Island
*Albert Heim Range ''(Albert Heim Bjerge)'', located in northern Hudson Land, north of Promenadedal.
*Alexandrine Range ' ...
* Greenland's Grand Canyon
*Climate change adaptation in Greenland
Climate change in Greenland is affecting the livelihood of the Greenlandic population. Geographically Greenland is situated between the Arctic and the Atlantic Ocean, with two thirds of the island being north of the Arctic Circle. Since the midd ...
References
External links
www.geus.dk
Geological map of Greenland from the Geological Survey of Denmark and Greenland (GEUS).
"Times Atlas reviews Greenland map accuracy after climate change row"
– ''The Guardian'', 22 September 2011 {{DEFAULTSORT:Geography Of Greenland