Explorer 1 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Explorer 1 was the first
 Explorer 1 was designed and built by the California Institute of Technology's JPL under the direction of Dr. William H. Pickering. It was the second satellite to carry a mission payload (Sputnik 2 was the first).
The total mass of the satellite was , of which were instrumentation. In comparison, the mass of the first Soviet satellite Sputnik 1 was . The instrument section at the front end of the satellite and the empty scaled-down fourth-stage rocket casing orbited as a single unit, spinning around its long axis at 750 revolutions per minute.
Data from the scientific instruments was transmitted to the ground by two antennas. A 60 milliwatt transmitter fed a
Explorer 1 was designed and built by the California Institute of Technology's JPL under the direction of Dr. William H. Pickering. It was the second satellite to carry a mission payload (Sputnik 2 was the first).
The total mass of the satellite was , of which were instrumentation. In comparison, the mass of the first Soviet satellite Sputnik 1 was . The instrument section at the front end of the satellite and the empty scaled-down fourth-stage rocket casing orbited as a single unit, spinning around its long axis at 750 revolutions per minute.
Data from the scientific instruments was transmitted to the ground by two antennas. A 60 milliwatt transmitter fed a 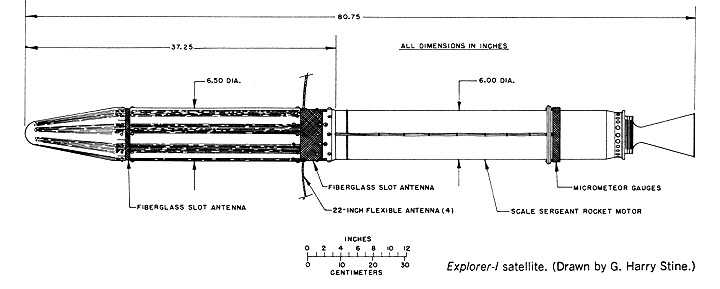
 After a
After a  The original expected lifetime of the satellite before
The original expected lifetime of the satellite before
 Explorer 1 changed
Explorer 1 changed
Explorer I
NASA images and videos of Explorer 1 and other early satellites
Department of Astronautics,
Explorer I Collection, The University of Alabama in Huntsville Archives and Special Collections
* * *
Lecture with detailed evaluation of the Explorer 1 rotation anomaly
{{Orbital launches in 1958 Spacecraft launched in 1958 1958 in the United States Satellites formerly orbiting Earth Explorers Program Individual spacecraft in the collection of the Smithsonian Institution First artificial satellites of a country Spacecraft which reentered in 1970 Articles containing video clips Geospace monitoring satellites ur:ایکسپلورر 1
satellite
A satellite or artificial satellite is an object intentionally placed into orbit in outer space. Except for passive satellites, most satellites have an electricity generation system for equipment on board, such as solar panels or radioiso ...
launched by the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
in 1958 and was part of the U.S. participation in the International Geophysical Year
The International Geophysical Year (IGY; french: Année géophysique internationale) was an international scientific project that lasted from 1 July 1957 to 31 December 1958. It marked the end of a long period during the Cold War when scientific i ...
(IGY). The mission followed the first two satellites the previous year; the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
's Sputnik 1
Sputnik 1 (; see § Etymology) was the first artificial Earth satellite. It was launched into an elliptical low Earth orbit by the Soviet Union on 4 October 1957 as part of the Soviet space program. It sent a radio signal back to Earth for ...
and Sputnik 2, beginning the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because t ...
Space Race
The Space Race was a 20th-century competition between two Cold War rivals, the United States and the Soviet Union, to achieve superior spaceflight capability. It had its origins in the ballistic missile-based nuclear arms race between the t ...
between the two nations.
Explorer 1 was launched on 1 February 1958 at 03:47:56 GMT (or 31 January 1958 at 22:47:56 Eastern Time
The Eastern Time Zone (ET) is a time zone encompassing part or all of 23 states in the eastern part of the United States, parts of eastern Canada, the state of Quintana Roo in Mexico, Panama, Colombia, mainland Ecuador, Peru, and a small ...
) atop the first Juno booster from LC-26A at the Cape Canaveral Missile Test Center of the Atlantic Missile Range
The Eastern Range (ER) is an American rocket range (Spaceport) that supports missile and rocket launches from the two major launch heads located at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station and the Kennedy Space Center (KSC), Florida. The rang ...
(AMR), in Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and ...
. It was the first spacecraft to detect the Van Allen radiation belt, returning data until its batteries were exhausted after nearly four months. It remained in orbit until 1970.
Explorer 1 was given Satellite Catalog Number 00004 and the Harvard designation
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher le ...
1958 Alpha 1, the forerunner to the modern International Designator.
Background
The U.S. Earth satellite program began in 1954 as a joint U.S. Army and U.S. Navy proposal, calledProject Orbiter
Project Orbiter was a proposed United States spacecraft, an early competitor to Project Vanguard. It was jointly run by the United States Army and United States Navy. It was ultimately rejected by the Ad Hoc Committee on Special Capabilities, wh ...
, to put a scientific satellite into orbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an object or position in space such as ...
during the International Geophysical Year
The International Geophysical Year (IGY; french: Année géophysique internationale) was an international scientific project that lasted from 1 July 1957 to 31 December 1958. It marked the end of a long period during the Cold War when scientific i ...
. The proposal, using a military Redstone missile, was rejected in 1955 by the Eisenhower administration
Dwight D. Eisenhower's tenure as the 34th president of the United States began with his first inauguration on January 20, 1953, and ended on January 20, 1961. Eisenhower, a Republican from Kansas, took office following a landslide victory ...
in favor of the Navy's Project Vanguard, using a booster advertised as more civilian in nature. Following the launch of the Soviet satellite Sputnik 1
Sputnik 1 (; see § Etymology) was the first artificial Earth satellite. It was launched into an elliptical low Earth orbit by the Soviet Union on 4 October 1957 as part of the Soviet space program. It sent a radio signal back to Earth for ...
on 4 October 1957, the initial Project Orbiter
Project Orbiter was a proposed United States spacecraft, an early competitor to Project Vanguard. It was jointly run by the United States Army and United States Navy. It was ultimately rejected by the Ad Hoc Committee on Special Capabilities, wh ...
program was revived as the Explorer program to catch up with the Soviet Union.
Explorer 1 was designed and built by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory
The Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) is a Federally funded research and development centers, federally funded research and development center and NASA field center in the City of La Cañada Flintridge, California, La Cañada Flintridge, California ...
(JPL), while a Jupiter-C
The Jupiter-C was an American research and development vehicle developed from the Jupiter-A. Jupiter-C was used for three unmanned sub-orbital spaceflights in 1956 and 1957 to test re-entry nosecones that were later to be deployed on the more ...
rocket was modified by the Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA) to accommodate a satellite payload; the resulting rocket known as the Juno I. The Jupiter-C design used for the launch had already been flight-tested in nose cone reentry tests for the Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but slightly less than one-thousand ...
intermediate-range ballistic missile
An intermediate-range ballistic missile (IRBM) is a ballistic missile with a range of 3,000–5,500 km (1,864–3,418 miles), between a medium-range ballistic missile (MRBM) and an intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM). Classifying ...
(IRBM), and was modified into Juno I. Working closely together, ABMA and JPL completed the job of modifying the Jupiter-C and building Explorer 1 in 84 days. However, before work was completed, the Soviet Union launched a second satellite, Sputnik 2, on 3 November 1957. The U.S. Navy's attempt to put the first U.S. satellite into orbit failed with the launch of the Vanguard TV-3
Vanguard TV-3 (also called Vanguard Test Vehicle-Three), was the first attempt of the United States to launch a satellite into orbit around the Earth, after the successful Soviet launches of Sputnik 1 and Sputnik 2. Vanguard TV-3 was a small s ...
on 6 December 1957.
Spacecraft
 Explorer 1 was designed and built by the California Institute of Technology's JPL under the direction of Dr. William H. Pickering. It was the second satellite to carry a mission payload (Sputnik 2 was the first).
The total mass of the satellite was , of which were instrumentation. In comparison, the mass of the first Soviet satellite Sputnik 1 was . The instrument section at the front end of the satellite and the empty scaled-down fourth-stage rocket casing orbited as a single unit, spinning around its long axis at 750 revolutions per minute.
Data from the scientific instruments was transmitted to the ground by two antennas. A 60 milliwatt transmitter fed a
Explorer 1 was designed and built by the California Institute of Technology's JPL under the direction of Dr. William H. Pickering. It was the second satellite to carry a mission payload (Sputnik 2 was the first).
The total mass of the satellite was , of which were instrumentation. In comparison, the mass of the first Soviet satellite Sputnik 1 was . The instrument section at the front end of the satellite and the empty scaled-down fourth-stage rocket casing orbited as a single unit, spinning around its long axis at 750 revolutions per minute.
Data from the scientific instruments was transmitted to the ground by two antennas. A 60 milliwatt transmitter fed a dipole antenna
In radio and telecommunications a dipole antenna or doublet is the simplest and most widely used class of antenna. The dipole is any one of a class of antennas producing a radiation pattern approximating that of an elementary electric dipole wi ...
consisting of two fiberglass
Fiberglass ( American English) or fibreglass (Commonwealth English) is a common type of fiber-reinforced plastic using glass fiber. The fibers may be randomly arranged, flattened into a sheet called a chopped strand mat, or woven into glass cl ...
slot antenna
A slot antenna consists of a metal surface, usually a flat plate, with one or more holes or slots cut out. When the plate is driven as an antenna by an applied radio frequency current, the slot radiates electromagnetic waves in a way similar to ...
s in the body of the satellite operating on 108.03 MHz, and four flexible whips forming a turnstile antenna were fed by a 10 milliwatt transmitter operating on 108.00 MHz.
Because of the limited space available and the requirements for low weight, the payload instrumentation was designed and built with simplicity and high reliability in mind, using germanium
Germanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ge and atomic number 32. It is lustrous, hard-brittle, grayish-white and similar in appearance to silicon. It is a metalloid in the carbon group that is chemically similar to its group neighbors ...
and silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic ...
transistor
upright=1.4, gate (G), body (B), source (S) and drain (D) terminals. The gate is separated from the body by an insulating layer (pink).
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch ...
s in its electronics
The field of electronics is a branch of physics and electrical engineering that deals with the emission, behaviour and effects of electrons using electronic devices. Electronics uses active devices to control electron flow by amplification ...
. A total of 20 transistors were used in Explorer 1, plus additional ones in the Army's micrometeorite amplifier. Electrical power was provided by mercury chemical batteries that made up approximately 40% of the payload weight.
The external skin of the instrument section was sandblasted stainless steel
Stainless steel is an alloy of iron that is resistant to rusting and corrosion. It contains at least 11% chromium and may contain elements such as carbon, other nonmetals and metals to obtain other desired properties. Stainless steel's r ...
with white stripes. Several other color schemes had been tested, resulting in backup articles, models, and photographs showing different configurations, including alternate white and green striping and blue stripes alternating with copper. The final coloration was determined by studies of shadow–sunlight intervals based on firing time, trajectory
A trajectory or flight path is the path that an object with mass in motion follows through space as a function of time. In classical mechanics, a trajectory is defined by Hamiltonian mechanics via canonical coordinates; hence, a complete tr ...
, orbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an object or position in space such as ...
, and inclination
Orbital inclination measures the tilt of an object's orbit around a celestial body. It is expressed as the angle between a reference plane and the orbital plane or axis of direction of the orbiting object.
For a satellite orbiting the Ea ...
.

Science payload
The Explorer 1 payload consisted of the IowaCosmic Ray
Cosmic rays are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the Solar System in our own ...
Instrument without a tape data recorder which was not modified in time to make it onto the spacecraft. The real-time data received on the ground was therefore very sparse and puzzling showing normal counting rates and no counts at all. The later Explorer 3 mission, which included a tape data recorder in the payload, provided the additional data for confirmation of the earlier Explorer 1 data.
The scientific instrumentation of Explorer 1 was designed and built under the direction of Dr. James Van Allen of the University of Iowa
The University of Iowa (UI, U of I, UIowa, or simply Iowa) is a public research university in Iowa City, Iowa, United States. Founded in 1847, it is the oldest and largest university in the state. The University of Iowa is organized into 12 co ...
containing:
* Anton 314 omnidirectional Geiger–Müller tube
The Geiger–Müller tube or G–M tube is the sensing element of the Geiger counter instrument used for the detection of ionizing radiation. It is named after Hans Geiger, who invented the principle in 1908, and Walther Müller, who collaborated ...
, designed by Dr. George Ludwig of Iowa's Cosmic Ray Laboratory, to detect cosmic ray
Cosmic rays are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the Solar System in our own ...
s. It could detect proton
A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol , H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 ''e'' elementary charge. Its mass is slightly less than that of a neutron and 1,836 times the mass of an electron (the proton–electron mass ...
s with E>30 MeV and electron
The electron ( or ) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family,
and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have n ...
s with E>3 MeV. Most of the time the instrument was saturated.
* Five temperature sensors (one internal, three external and one on the nose cone);
* Acoustic detector (crystal transducer
A transducer is a device that converts energy from one form to another. Usually a transducer converts a signal in one form of energy to a signal in another.
Transducers are often employed at the boundaries of automation, measurement, and con ...
and solid-state amplifier
An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that can increase the magnitude of a signal (a time-varying voltage or current). It may increase the power significantly, or its main effect may be to boost t ...
) to detect micrometeorite (cosmic dust
Cosmic dust, also called extraterrestrial dust, star dust or space dust, is dust which exists in outer space, or has fallen on Earth. Most cosmic dust particles measure between a few molecules and 0.1 mm (100 micrometers). Larger particles are c ...
) impacts. It responded to micrometeorite impacts on the spacecraft skin in such a way that each impact would be a function of mass
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a physical body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different ele ...
and velocity
Velocity is the directional speed of an object in motion as an indication of its rate of change in position as observed from a particular frame of reference and as measured by a particular standard of time (e.g. northbound). Velocity i ...
. Its effective area was 0.075 m2 and the average threshold sensitivity was 2.5 g cm/s;
* Wire grid detector, also to detect micrometeorite impacts. It consisted of 12 parallel connected cards mounted in a fiberglass
Fiberglass ( American English) or fibreglass (Commonwealth English) is a common type of fiber-reinforced plastic using glass fiber. The fibers may be randomly arranged, flattened into a sheet called a chopped strand mat, or woven into glass cl ...
supporting ring. Each card was wound with two layers of enameled nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive but large pieces are slow t ...
alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which at least one is a metal. Unlike chemical compounds with metallic bases, an alloy will retain all the properties of a metal in the resulting material, such as electrical conductivity, ductili ...
wire with a diameter of 17 µm
The micrometre ( international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: μm) or micrometer ( American spelling), also commonly known as a micron, is a unit of length in the International System of Uni ...
(21 µm with the enamel insulation included) in such way that a total area of was completely covered. If a micrometeorite of about 10 µm impacted, it would fracture the wire, destroy the electrical connection, and thus record the event.
Flight
 After a
After a jet stream
Jet streams are fast flowing, narrow, meandering air currents in the atmospheres of some planets, including Earth. On Earth, the main jet streams are located near the altitude of the tropopause and are westerly winds (flowing west to east) ...
-related delay on 28 January 1958, at 03:47:56 GMT on 1 February 1958 the Juno I rocket was launched, putting Explorer 1 into orbit with a perigee
An apsis (; ) is the farthest or nearest point in the orbit of a planetary body about its primary body. For example, the apsides of the Earth are called the aphelion and perihelion.
General description
There are two apsides in any el ...
of and an apogee
An apsis (; ) is the farthest or nearest point in the orbit of a planetary body about its primary body. For example, the apsides of the Earth are called the aphelion and perihelion.
General description
There are two apsides in any el ...
of having a period of 114.80 minutes, and an inclination
Orbital inclination measures the tilt of an object's orbit around a celestial body. It is expressed as the angle between a reference plane and the orbital plane or axis of direction of the orbiting object.
For a satellite orbiting the Ea ...
of 33.24°. Goldstone Tracking Station could not report after 90 minutes as planned whether the launch had succeeded because the orbit was larger than expected. At about 06:30 GMT, after confirming that Explorer 1 was indeed in orbit, a news conference was held in the Great Hall at the National Academy of Sciences
The National Academy of Sciences (NAS) is a United States nonprofit, non-governmental organization. NAS is part of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, along with the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) and the Nat ...
in Washington, D.C. to announce it to the world.
 The original expected lifetime of the satellite before
The original expected lifetime of the satellite before orbital decay
Orbital decay is a gradual decrease of the distance between two orbiting bodies at their closest approach (the periapsis) over many orbital periods. These orbiting bodies can be a planet and its satellite, a star and any object orbiting it, or ...
was three years. Mercury batteries powered the high-power transmitter for 31 days and the low-power transmitter for 105 days. Explorer 1 stopped transmission of data on 23 May 1958, when its batteries died, but remained in orbit for more than 12 years. It reentered the atmosphere over the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the conti ...
on 31 March 1970 after more than 58,400 orbits.
Results
 Explorer 1 changed
Explorer 1 changed rotation axis
Rotation around a fixed axis is a special case of rotational motion. The fixed-axis hypothesis excludes the possibility of an axis changing its orientation and cannot describe such phenomena as wobbling or precession. According to Euler's r ...
after launch. The elongated body of the spacecraft had been designed to spin about its long (least- inertia) axis but refused to do so, and instead started precessing due to energy dissipation from flexible structural elements. Later it was understood that on general grounds, the body ends up in the spin state that minimizes the kinetic
Kinetic (Ancient Greek: κίνησις “kinesis”, movement or to move) may refer to:
* Kinetic theory, describing a gas as particles in random motion
* Kinetic energy, the energy of an object that it possesses due to its motion
Art and ent ...
rotational energy
Rotational energy or angular kinetic energy is kinetic energy due to the rotation of an object and is part of its total kinetic energy. Looking at rotational energy separately around an object's axis of rotation, the following dependence on the ob ...
for a fixed angular momentum (this being the maximal-inertia axis). This motivated the first further development of the Eulerian theory of rigid body dynamics after nearly 200 years – to address this kind of momentum-preserving energy dissipation.
Sometimes the instrumentation reported the expected cosmic ray count (approximately 30 counts per second) but other times it would show a peculiar zero counts per second. The University of Iowa (under James Van Allen) observed that all of the zero counts per second reports were from an altitude of more than over South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the sou ...
, while passes at would show the expected level of cosmic rays. Later, after Explorer 3
Explorer 3 (Harvard designation 1958 Gamma) was an American artificial satellite launched into medium Earth orbit in 1958. It was the second successful launch in the Explorer program, and was nearly identical to the first U.S. satellite Expl ...
, it was concluded that the original Geiger counter had been overwhelmed ("saturated") by strong radiation coming from a belt of charged particles trapped in space by the Earth's magnetic field
Earth's magnetic field, also known as the geomagnetic field, is the magnetic field that extends from Earth's interior out into space, where it interacts with the solar wind, a stream of charged particles emanating from the Sun. The magneti ...
. This belt of charged particles is now known as the Van Allen radiation belt. The discovery was considered to be one of the outstanding discoveries of the International Geophysical Year
The International Geophysical Year (IGY; french: Année géophysique internationale) was an international scientific project that lasted from 1 July 1957 to 31 December 1958. It marked the end of a long period during the Cold War when scientific i ...
.
The acoustic micrometeorite detector detected 145 impacts of cosmic dust in 78,750 seconds. This calculates to an average impact rate of 8.0−3 impacts per second per square meter, or 29 impacts per hour per square meter, over the twelve-day period.
Legacy
Explorer 1 was the first of the long-runningExplorers program
The Explorers program is a NASA exploration program that provides flight opportunities for physics, geophysics, heliophysics, and astrophysics investigations from space. Launched in 1958, Explorer 1 was the first spacecraft of the United Stat ...
. Four follow-up satellites of the Explorer series were launched by the Juno I launch vehicle
A launch vehicle or carrier rocket is a rocket designed to carry a payload ( spacecraft or satellites) from the Earth's surface to outer space. Most launch vehicles operate from a launch pads, supported by a launch control center and sys ...
in 1958, of these, Explorer 3 and 4 were successful, while Explorer 2 and 5 failed to reach orbit. The final flight of the Juno I booster, the satellite Beacon-1, also failed. The Juno I vehicle was replaced by the Juno II
Juno II was an American space launch vehicle used during the late 1950s and early 1960s. It was derived from the Jupiter missile, which was used as the first stage.
Development
Solid rocket motors derived from the MGM-29 Sergeant were use ...
launch vehicle in 1959.
A follow-up to the first mission, Explorer-1 RIME was successfully launched aboard a Delta II
Delta II was an expendable launch system, originally designed and built by McDonnell Douglas. Delta II was part of the Delta rocket family and entered service in 1989. Delta II vehicles included the Delta 6000, and the two later Delta 7000 va ...
launch vehicle in late October 2011. The PRIME was built using modern satellite construction techniques. The orbiting satellite was a backup, because the initial Explorer-1 PRIME, launched on 4 March 2011, did not reach orbit due to a launch vehicle failure.
An identically constructed flight backup of Explorer 1 is on display in the Smithsonian Institution
The Smithsonian Institution ( ), or simply the Smithsonian, is a group of museums and education and research centers, the largest such complex in the world, created by the U.S. government "for the increase and diffusion of knowledge". Found ...
's National Air and Space Museum
The National Air and Space Museum of the Smithsonian Institution, also called the Air and Space Museum, is a museum in Washington, D.C., in the United States.
Established in 1946 as the National Air Museum, it opened its main building on the N ...
, Milestones of Flight Gallery in Washington, D.C. LC-26
Blockhouse of LC-26
Launch Complex 26 (LC-26) is a deactivated launch site at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, Florida. LC-26 consisted of two pads, ''A'' and ''B''. Pad A was used for the Jupiter-C and Juno I rockets, and was the launch site ...
was deactivated in 1963, and was designated for use as a museum in 1964, the Air Force Space and Missile Museum
The Air Force Space and Missile Museum is located at Launch Complex 26 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, Florida. It includes artifacts from the early American space program and includes an outdoor area displaying rockets, missiles, and spa ...
. Here too, a full-scale Explorer 1 is on display, but this one is a mockup.Gallery
See also
* Timeline of artificial satellites and space probes * Explorer programReferences
Bibliography
External links
NASA images and videos of Explorer 1 and other early satellites
Department of Astronautics,
National Air and Space Museum
The National Air and Space Museum of the Smithsonian Institution, also called the Air and Space Museum, is a museum in Washington, D.C., in the United States.
Established in 1946 as the National Air Museum, it opened its main building on the N ...
, Smithsonian Institution
The Smithsonian Institution ( ), or simply the Smithsonian, is a group of museums and education and research centers, the largest such complex in the world, created by the U.S. government "for the increase and diffusion of knowledge". Found ...
Explorer I Collection, The University of Alabama in Huntsville Archives and Special Collections
* * *
Lecture with detailed evaluation of the Explorer 1 rotation anomaly
{{Orbital launches in 1958 Spacecraft launched in 1958 1958 in the United States Satellites formerly orbiting Earth Explorers Program Individual spacecraft in the collection of the Smithsonian Institution First artificial satellites of a country Spacecraft which reentered in 1970 Articles containing video clips Geospace monitoring satellites ur:ایکسپلورر 1