Exploration of the Pacific on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Early Polynesian explorers reached nearly all Pacific islands by 1200 CE, followed by Asian navigation in
 Humans reached Australia by at least 40,000 BC which implies some degree of water crossing. People were in the Americas before 10,000 BC. One theory holds that they travelled along the coast by canoe.
Humans reached Australia by at least 40,000 BC which implies some degree of water crossing. People were in the Americas before 10,000 BC. One theory holds that they travelled along the coast by canoe.





Website devoted to the exploration of the Pacific Ocean Online
* Dodge, Ernest Stanley. ''Beyond the Capes; Pacific Exploration from Captain Cook to the Challenger, 1776–1877'' (Little, Brown, 1971). * Engstrand, Iris HW. "Seekers of the 'Northern Mystery': European Exploration of California and the Pacific." ''California History'' 76.2-3 (1997): 78-11
online
*
excerpt
* Heawood, Edward. ''A History Of Geographical Discovery in the Seventeenth And Eighteenth Centuries'' (1912
online
* Howse, Derek, ed. ''Background to Discovery: Pacific Exploration from Dampier to Cook'' (U of California Press, 1990). * Irwin, Geoffrey. ''The prehistoric exploration and colonisation of the Pacific'' (Cambridge UP, 1994). * Lincoln, Margarette, ed. ''Science and exploration in the Pacific: European voyages to the southern oceans in the eighteenth century'' (Boydell & Brewer, 2001). * Lloyd, Christopher. ''Pacific Horizons: The Exploration of the Pacific Before Captain Cook'' (Allen and Unwin, 1946)
online
popular history * Lloyd, Christopher. ''Atlas of maritime history'' (1975
online
popular * Parry, J.H. ''The Age of Reconnaissance'' (1963
online
* Williams, Glyn. "‘To Make Discoveries of Countries Hitherto Unknown’ The Admiralty and Pacific Exploration in the Eighteenth Century." ''The Mariner's Mirror'' 82.1 (1996): 14-27. * Withey, Lynne. ''Voyages of discovery: Captain Cook and the exploration of the Pacific'' (U of California Press, 1989).
online
* * Munro, Doug. ''The Ivory Tower and Beyond: Participant Historians of the Pacific'' (Cambridge Scholars Publishing, 2009). * Routledge, David. "Pacific history as seen from the Pacific Islands." ''Pacific Studies'' 8#2 (1985): 81
online
* Samson, Jane. "Pacific/Oceanic History" in {{cite book, editor=Kelly Boyd , title=Encyclopedia of Historians and Historical Writing vol 2, url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0121vD9STIMC&pg=PA901, year=1999, publisher=Taylor & Francis, pages=901–02, isbn=978-1-884964-33-6
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainland ...
and the West Pacific. During the Middle Ages, Muslim traders linked the Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabian Peninsula, Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Anatolia, Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Pro ...
and East Africa
East Africa, Eastern Africa, or East of Africa, is the eastern subregion of the African continent. In the United Nations Statistics Division scheme of geographic regions, 10-11-(16*) territories make up Eastern Africa:
Due to the historica ...
to the Asian Pacific
Asia-Pacific (APAC) is the part of the Earth, world near the western Pacific Ocean. The Asia-Pacific region varies in area depending on context, but it generally includes East Asia, Russian Far East, South Asia, Southeast Asia, Australia and List ...
coasts, reaching southern China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
and much of the Malay Archipelago
The Malay Archipelago ( Indonesian/ Malay: , tgl, Kapuluang Malay) is the archipelago between mainland Indochina and Australia. It has also been called the " Malay world," " Nusantara", "East Indies", Indo-Australian Archipelago, Spices Arc ...
. Direct European contact with the Pacific began in 1512, with the Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
encountering its western edges, soon followed by the Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
arriving from the American coast.
In 1513, Spanish explorer Vasco Núñez de Balboa
Vasco Núñez de Balboa (; c. 1475around January 12–21, 1519) was a Spanish explorer, governor, and conquistador. He is best known for having crossed the Isthmus of Panama to the Pacific Ocean in 1513, becoming the first European to lead an ...
crossed the Isthmus of Panama and encountered the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the conti ...
, calling it the South Sea. In 1521, a Spanish expedition led by the Portuguese navigator Ferdinand Magellan
Ferdinand Magellan ( or ; pt, Fernão de Magalhães, ; es, link=no, Fernando de Magallanes, ; 4 February 1480 – 27 April 1521) was a Portuguese explorer. He is best known for having planned and led the 1519 Spanish expedition to the Eas ...
was the first recorded crossing of the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the conti ...
, Magellan then naming it the “peaceful sea.” Starting in 1565 with the voyage of Andres de Urdaneta
Andres or Andrés may refer to:
*Andres, Illinois, an unincorporated community in Will County, Illinois, US
*Andres, Pas-de-Calais, a commune in Pas-de-Calais, France
*Andres (name)
*Hurricane Andres
* "Andres" (song), a 1994 song by L7
See also ...
, the Spanish controlled transpacific trade for 250 years; Manila galleons
fil, Galyon ng Maynila
, english_name = Manila Galleon
, duration = From 1565 to 1815 (250 years)
, venue = Between Manila and Acapulco
, location = New Spain (Spanish Empire) ...
would cross from Mexico
Mexico (Spanish language, Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a List of sovereign states, country in the southern portion of North America. It is borders of Mexico, bordered to the north by the United States; to the so ...
to the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
, and vice versa, until 1815. Additional expeditions from Mexico and Peru encountered various archipelagos in the North
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography.
Etymology
The word ''north ...
and South Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continen ...
. In the 17th and 18th centuries, other European powers sent expeditions to the Pacific, namely the Dutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, also known as the (Seven) United Provinces, officially as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands ( Dutch: ''Republiek der Zeven Verenigde Nederlanden''), and commonly referred to in historiograph ...
, England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe ...
, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
, and Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
.
Pre-European exploration
Austronesians
About 3000 BC speakers of the Austronesian languages, probably on the island of Taiwan, mastered the art of long-distance canoe travel and spread themselves, or their languages, south to the Philippines and Indonesia and east to the islands ofMicronesia
Micronesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, consisting of about 2,000 small islands in the western Pacific Ocean. It has a close shared cultural history with three other island regions: the Philippines to the west, Polynesia to the east, ...
and Melanesia
Melanesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It extends from Indonesia's New Guinea in the west to Fiji in the east, and includes the Arafura Sea.
The region includes the four independent countries of Fiji, V ...
. The Polynesians branched off and occupied Polynesia
Polynesia () "many" and νῆσος () "island"), to, Polinisia; mi, Porinihia; haw, Polenekia; fj, Polinisia; sm, Polenisia; rar, Porinetia; ty, Pōrīnetia; tvl, Polenisia; tkl, Polenihia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of ...
to the east. Dates and routes are uncertain, but they seem to have started from the Bismarck Archipelago
The Bismarck Archipelago (, ) is a group of islands off the northeastern coast of New Guinea in the western Pacific Ocean and is part of the Islands Region of Papua New Guinea. Its area is about 50,000 square km.
History
The first inhabitants o ...
, went east past Fiji
Fiji ( , ,; fj, Viti, ; Fiji Hindi: फ़िजी, ''Fijī''), officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consis ...
to Samoa
Samoa, officially the Independent State of Samoa; sm, Sāmoa, and until 1997 known as Western Samoa, is a Polynesian island country consisting of two main islands ( Savai'i and Upolu); two smaller, inhabited islands ( Manono and Apolima); ...
and Tonga
Tonga (, ; ), officially the Kingdom of Tonga ( to, Puleʻanga Fakatuʻi ʻo Tonga), is a Polynesian country and archipelago. The country has 171 islands – of which 45 are inhabited. Its total surface area is about , scattered over in ...
about 1500 BC. By 100 AD they were in the Marquesas Islands
The Marquesas Islands (; french: Îles Marquises or ' or '; Marquesan: ' (North Marquesan) and ' ( South Marquesan), both meaning "the land of men") are a group of volcanic islands in French Polynesia, an overseas collectivity of France in ...
and 300-800 AD in Tahiti
Tahiti (; Tahitian ; ; previously also known as Otaheite) is the largest island of the Windward group of the Society Islands in French Polynesia. It is located in the central part of the Pacific Ocean and the nearest major landmass is Austra ...
(Tahiti is west of the Marquesas.) 300-800 AD is also given for their arrival at Easter Island
Easter Island ( rap, Rapa Nui; es, Isla de Pascua) is an island and special territory of Chile in the southeastern Pacific Ocean, at the southeasternmost point of the Polynesian Triangle in Oceania. The island is most famous for its nearl ...
, their easternmost point and the same date range for Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only stat ...
, which is far to the north and distant from other islands. Far to the southwest, New Zealand was reached about 1250 AD. The Chatham Islands
The Chatham Islands ( ) (Moriori: ''Rēkohu'', 'Misty Sun'; mi, Wharekauri) are an archipelago in the Pacific Ocean about east of New Zealand's South Island. They are administered as part of New Zealand. The archipelago consists of about t ...
, about 500 miles east of New Zealand were reached about 1500. The fact that some Polynesians possessed the South American Sweet potato
The sweet potato or sweetpotato ('' Ipomoea batatas'') is a dicotyledonous plant that belongs to the bindweed or morning glory family, Convolvulaceae. Its large, starchy, sweet-tasting tuberous roots are used as a root vegetable. The young ...
implies that they may have reached the Americas or, conversely, that people from the Americas may have reached Polynesia. Thor Heyerdahl
Thor Heyerdahl KStJ (; 6 October 1914 – 18 April 2002) was a Norwegian adventurer and ethnographer with a background in zoology, botany and geography.
Heyerdahl is notable for his ''Kon-Tiki'' expedition in 1947, in which he sailed 8,000& ...
's ''Kon-Tiki
The ''Kon-Tiki'' expedition was a 1947 journey by raft across the Pacific Ocean from South America to the Polynesian islands, led by Norwegian explorer and writer Thor Heyerdahl. The raft was named ''Kon-Tiki'' after the Inca god Viracocha, fo ...
'' expedition successfully demonstrated that the trip from the Americas to Polynesia using only materials and technology available at the time was at least possible.
Asians
On the Asian side long-distance trade developed all along the coast from Mozambique to Japan. Trade, and therefore knowledge, extended to Indonesia but apparently not Australia. By at the latest 878 when there was a significant Islamic settlement inCanton
Canton may refer to:
Administrative division terminology
* Canton (administrative division), territorial/administrative division in some countries, notably Switzerland
* Township (Canada), known as ''canton'' in Canadian French
Arts and ente ...
much of this trade was controlled by Arabs or Muslims. In 219 BC Xu Fu sailed out into the Pacific searching for the elixir of immortality. Zheng He
Zheng He (; 1371–1433 or 1435) was a Chinese mariner, explorer, diplomat, fleet admiral, and court eunuch during China's early Ming dynasty. He was originally born as Ma He in a Muslim family and later adopted the surname Zheng conferr ...
(1371–1433) was China's greatest explorer, mariner, and navigator.
Japanese fishing boats, if blown out to sea, could be carried by the current all the way to North America. Japanese boats reached Acapulco in 1617, the Aleutians in 1782, Alaska in 1805, the mouth of the Columbia River in 1820, and Cape Flattery in 1833. Such trips may have taken place before Europeans were present in those areas to make detailed records of them.
European exploration
Iberian pioneers
The first contact of European navigators with the western edge of the Pacific Ocean was made by the Portuguese expeditions ofAntónio de Abreu
António de Abreu () was a 16th-century Portuguese navigator and naval officer. He participated under the command of Afonso de Albuquerque in the conquest of Ormus in 1507 and Malacca in 1511, where he got injured. Departing from Malacca in Nov ...
and Francisco Serrão
Francisco Serrão (died 1521) was a Portuguese explorer and a possible cousin of Ferdinand Magellan. His 1512 voyage was the first known European sailing east past Malacca through modern Indonesia and the East Indies. He became a confidant o ...
, via the Lesser Sunda Islands
The Lesser Sunda Islands or nowadays known as Nusa Tenggara Islands ( id, Kepulauan Nusa Tenggara, formerly ) are an archipelago in Maritime Southeast Asia, north of Australia. Together with the Greater Sunda Islands to the west they make up ...
, to the Maluku Islands
The Maluku Islands (; Indonesian: ''Kepulauan Maluku'') or the Moluccas () are an archipelago in the east of Indonesia. Tectonically they are located on the Halmahera Plate within the Molucca Sea Collision Zone. Geographically they are located ...
, in 1512, and with Jorge Álvares
Jorge Álvares (died 8 July 1521) was a Portuguese explorer. He is credited as the first European to have reached China by sea during the Age of Discovery. His starting of settlements on an island in what is now Hong Kong is still considered a sign ...
's expedition to southern China in 1513,Porter, Jonathan. 996
Year 996 ( CMXCVI) was a leap year starting on Wednesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar.
Events
By place
Japan
* February - Chotoku Incident: Fujiwara no Korechika and Takaie shoot an arrow at Retired Emp ...
(1996). ''Macau, the Imaginary City: Culture and Society, 1557 to the Present''. Westview Press. both ordered by Afonso de Albuquerque
Afonso de Albuquerque, 1st Duke of Goa (; – 16 December 1515) was a Portuguese general, admiral, and statesman. He served as viceroy of Portuguese India from 1509 to 1515, during which he expanded Portuguese influence across the Indian Ocean ...
from Malacca
Malacca ( ms, Melaka) is a States and federal territories of Malaysia, state in Malaysia located in the southern region of the Malay Peninsula, next to the Strait of Malacca. Its capital is Malacca City, dubbed the Historic City, which has bee ...
.
Spanish explorer Balboa was the first European to sight the Pacific from America in 1513 after his expedition crossed the Isthmus of Panama
The Isthmus of Panama ( es, Istmo de Panamá), also historically known as the Isthmus of Darien (), is the narrow strip of land that lies between the Caribbean Sea and the Pacific Ocean, linking North and South America. It contains the country ...
and reached a new ocean. He named it ''Mar del Sur'' (literally, "Sea of the South" or "South Sea") because the ocean was to the south of the coast of the isthmus where he first observed the Pacific. Later, Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan
Ferdinand Magellan ( or ; pt, Fernão de Magalhães, ; es, link=no, Fernando de Magallanes, ; 4 February 1480 – 27 April 1521) was a Portuguese explorer. He is best known for having planned and led the 1519 Spanish expedition to the Eas ...
sailed the Pacific East to West on a Castilian (''Spanish'') expedition of world circumnavigation
Circumnavigation is the complete navigation around an entire island, continent, or astronomical body (e.g. a planet or moon). This article focuses on the circumnavigation of Earth.
The first recorded circumnavigation of the Earth was the ...
starting in 1519. Magellan called the ocean ''Pacífico'' (or "Pacific" meaning, "peaceful") because, after sailing through the stormy seas off Cape Horn
Cape Horn ( es, Cabo de Hornos, ) is the southernmost headland of the Tierra del Fuego archipelago of southern Chile, and is located on the small Hornos Island. Although not the most southerly point of South America (which are the Diego Ramí ...
, the expedition found calm waters. The ocean was often called the ''Sea of Magellan'' in his honor until the eighteenth century.
From 1565 to 1815, a Spanish transpacific route known as the Manila galleons
fil, Galyon ng Maynila
, english_name = Manila Galleon
, duration = From 1565 to 1815 (250 years)
, venue = Between Manila and Acapulco
, location = New Spain (Spanish Empire) ...
regularly crossed from Mexico to the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
and back. On the Asian side the Portuguese and later the Dutch built a regular trade from the East Indies to Japan. On the American side Spanish power stretched thousands of miles from Mexico to Chile. The vast central Pacific was visited only by the Manila galleons and an occasional explorer. The south Pacific was first crossed by Spanish expeditions in the 16th century who discovered many islands including Tuvalu
Tuvalu ( or ; formerly known as the Ellice Islands) is an island country and microstate in the Polynesian subregion of Oceania in the Pacific Ocean. Its islands are situated about midway between Hawaii and Australia. They lie east-northea ...
, the Marquesas
The Marquesas Islands (; french: Îles Marquises or ' or '; Marquesan: ' (North Marquesan) and ' (South Marquesan), both meaning "the land of men") are a group of volcanic islands in French Polynesia, an overseas collectivity of France in t ...
, the Cook Islands
)
, image_map = Cook Islands on the globe (small islands magnified) (Polynesia centered).svg
, capital = Avarua
, coordinates =
, largest_city = Avarua
, official_languages =
, lan ...
, the Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands is an island country consisting of six major islands and over 900 smaller islands in Oceania, to the east of Papua New Guinea and north-west of Vanuatu. It has a land area of , and a population of approx. 700,000. Its capit ...
, and the Admiralty Islands
The Admiralty Islands are an archipelago group of 18 islands in the Bismarck Archipelago, to the north of New Guinea in the South Pacific Ocean. These are also sometimes called the Manus Islands, after the largest island.
These rainforest-co ...
, and later the Pitcairn
The Pitcairn Islands (; Pitkern: '), officially the Pitcairn, Henderson, Ducie and Oeno Islands, is a group of four volcanic islands in the southern Pacific Ocean that form the sole British Overseas Territory in the Pacific Ocean. The four i ...
and Vanuatu
Vanuatu ( or ; ), officially the Republic of Vanuatu (french: link=no, République de Vanuatu; bi, Ripablik blong Vanuatu), is an island country located in the South Pacific Ocean. The archipelago, which is of volcanic origin, is east of ...
archipelagos.
The Pacific recognized
Europeans knew that there was a vast ocean to the west, and the Chinese knew that there was one to the east. Learned Europeans thought that the world was round and that the two oceans were one. In 1492, Columbus sailed west to what he thought was Asia. WhenPedro Álvares Cabral
Pedro Álvares Cabral ( or ; born Pedro Álvares de Gouveia; c. 1467 or 1468 – c. 1520) was a Portuguese nobleman, military commander, navigator and explorer regarded as the European discoverer of Brazil. He was the first human ...
, en route to Asia via the Atlantic and the Indian oceans, reached Brazil, in 1500, the true extent of the Americas began to become known. The Martin Waldseemüller
Martin Waldseemüller (c. 1470 – 16 March 1520) was a German cartographer and humanist scholar. Sometimes known by the Latinized form of his name, Hylacomylus, his work was influential among contemporary cartographers. He and his collaborator ...
map of 1507 was the first to show the Americas separating two distinct oceans. This guess was confirmed in 1513, when Balboa crossed Panama and found salt water. The Magellan expedition of 1519-22 proved that there was one continuous ocean from the Americas to Asia. The Diogo Ribeiro map of 1529 was the first to show the Pacific at about its proper size.
The coast of Asia
The Portuguese reached India in 1498, conquered Malacca in 1511 and in 1512António de Abreu
António de Abreu () was a 16th-century Portuguese navigator and naval officer. He participated under the command of Afonso de Albuquerque in the conquest of Ormus in 1507 and Malacca in 1511, where he got injured. Departing from Malacca in Nov ...
and Francisco Serrão
Francisco Serrão (died 1521) was a Portuguese explorer and a possible cousin of Ferdinand Magellan. His 1512 voyage was the first known European sailing east past Malacca through modern Indonesia and the East Indies. He became a confidant o ...
reached the Spice Islands
A spice is a seed, fruit, root, bark, or other plant substance primarily used for flavoring or coloring food. Spices are distinguished from herbs, which are the leaves, flowers, or stems of plants used for flavoring or as a garnish. Spices are ...
. In May 1513 Jorge Álvares
Jorge Álvares (died 8 July 1521) was a Portuguese explorer. He is credited as the first European to have reached China by sea during the Age of Discovery. His starting of settlements on an island in what is now Hong Kong is still considered a sign ...
reached southern China and in the same year Balboa crossed Panama. In 1525 Diogo da Rocha Diogo da Rocha was a captain who sailed for the Portuguese in 1525. He is credited as being the first to encounter the islands "to the Eastwards of Mindanao, and the islands of St. Lazarus" ( possibly Ulithi in the Caroline Islands
The Caro ...
and Gomes de Sequeira reached the Caroline Islands
The Caroline Islands (or the Carolines) are a widely scattered archipelago of tiny islands in the western Pacific Ocean, to the north of New Guinea. Politically, they are divided between the Federated States of Micronesia (FSM) in the ce ...
, and Jorge de Menezes in 1526-27 landed on the ''Islands of Don Jorge de Menezes'', in the northwest coast of New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; id, Papua, or , historically ) is the world's second-largest island with an area of . Located in Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Australia by the wide Torres ...
(now part of Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Gui ...
), and named the region ''Ilhas dos Papuas'' and is thus credited with the European ''discovery'' of Papua. In 1542 Fernão Mendes Pinto
Fernão Mendes Pinto (; c.1509 – 8 July 1583) was a Portuguese explorer and writer. His voyages are recorded in ''Pilgrimage'' ( pt, Peregrinação) (1614), his autobiographical memoir. The historical accuracy of the work is debatable due t ...
reached Japan. From about 1543 until 1614, the Portuguese monopolize the trade between China and Japan, through the nanban trade
or the , was a period in the history of Japan from the arrival of Europeans in 1543 to the first '' Sakoku'' Seclusion Edicts of isolationism in 1614. Nanban (南蛮 Lit. "Southern barbarian") is a Japanese word which had been used to desig ...
. In 1589, João da Gama reached Hokkaido
is Japan, Japan's Japanese archipelago, second largest island and comprises the largest and northernmost Prefectures of Japan, prefecture, making up its own List of regions of Japan, region. The Tsugaru Strait separates Hokkaidō from Honshu; th ...
and possibly sighted the Kuril islands
The Kuril Islands or Kurile Islands (; rus, Кури́льские острова́, r=Kuril'skiye ostrova, p=kʊˈrʲilʲskʲɪjə ɐstrɐˈva; Japanese language, Japanese: or ) are a volcanic archipelago currently administered as part of Sakh ...
, crossing the Pacific further north of the routes usually taken until then. The land that he eventually discovered northeast of Japan, has since become a matter of legend and controversy.
One hundred years after the Spanish and Portuguese the Dutch Republic began its remarkable expansion. The Dutch reached the East Indies in 1596, the Spice Islands in 1602 and in 1619 founded Batavia. In 1600 a Dutch fleet reached Japan from the Strait of Magellan. The Dutch had little success in China but established themselves at Hirado, Nagasaki
is a city located in Nagasaki Prefecture, Japan. The part historically named Hirado is located on Hirado Island. With recent mergers, the city's boundaries have expanded, and Hirado now occupies parts of the main island of Kyushu. The components ...
in 1609 and monopolized the Japan trade from 1639. In 1639 Matthijs Quast
Matthijs Quast (died 6 October 1641) was a Dutch explorer in the seventeenth century. He had made several voyages for the Dutch East India Company to Japan, China and Siam.
Pacific Expedition
Matthijs Quast has become known for an unsuccessful ex ...
and Abel Tasman
Abel Janszoon Tasman (; 160310 October 1659) was a Dutch seafarer, explorer, and merchant, best known for his voyages of 1642 and 1644 in the service of the Dutch East India Company (VOC). He was the first known European explorer to reach New ...
searched the empty ocean east of Japan looking for two islands called ' Rica de Oro' and ' Rica de Plata'. In 1643 Maarten Gerritsz Vries
Maarten Gerritszoon Vries, or Fries, also referred to as de Vries, (18 February 1589, Harlingen, Netherlands – late 1647, at sea near Manila) was a 17th-century Dutch cartographer and explorer, the first Western European to leave an account of ...
reached and charted Sakhalin
Sakhalin ( rus, Сахали́н, r=Sakhalín, p=səxɐˈlʲin; ja, 樺太 ''Karafuto''; zh, c=, p=Kùyèdǎo, s=库页岛, t=庫頁島; Manchu: ᠰᠠᡥᠠᠯᡳᠶᠠᠨ, ''Sahaliyan''; Orok: Бугата на̄, ''Bugata nā''; Nivkh ...
and the Kuril Islands
The Kuril Islands or Kurile Islands (; rus, Кури́льские острова́, r=Kuril'skiye ostrova, p=kʊˈrʲilʲskʲɪjə ɐstrɐˈva; Japanese language, Japanese: or ) are a volcanic archipelago currently administered as part of Sakh ...
. In 1653 Hendrick Hamel
Hendrick Hamel (1630 – 1692) was a Westerner to provide a first hand account of Joseon Korea. After spending thirteen years there, he wrote "Hamel's Journal and a Description of the Kingdom of Korea, 1653-1666," which was subsequently publis ...
was shipwrecked in Korea. At about this time the Russians reached the Pacific overland via Siberia (see below). It is significant that the Russian and Dutch trades were never linked since Siberian furs might easily have been exported to China at great profit.

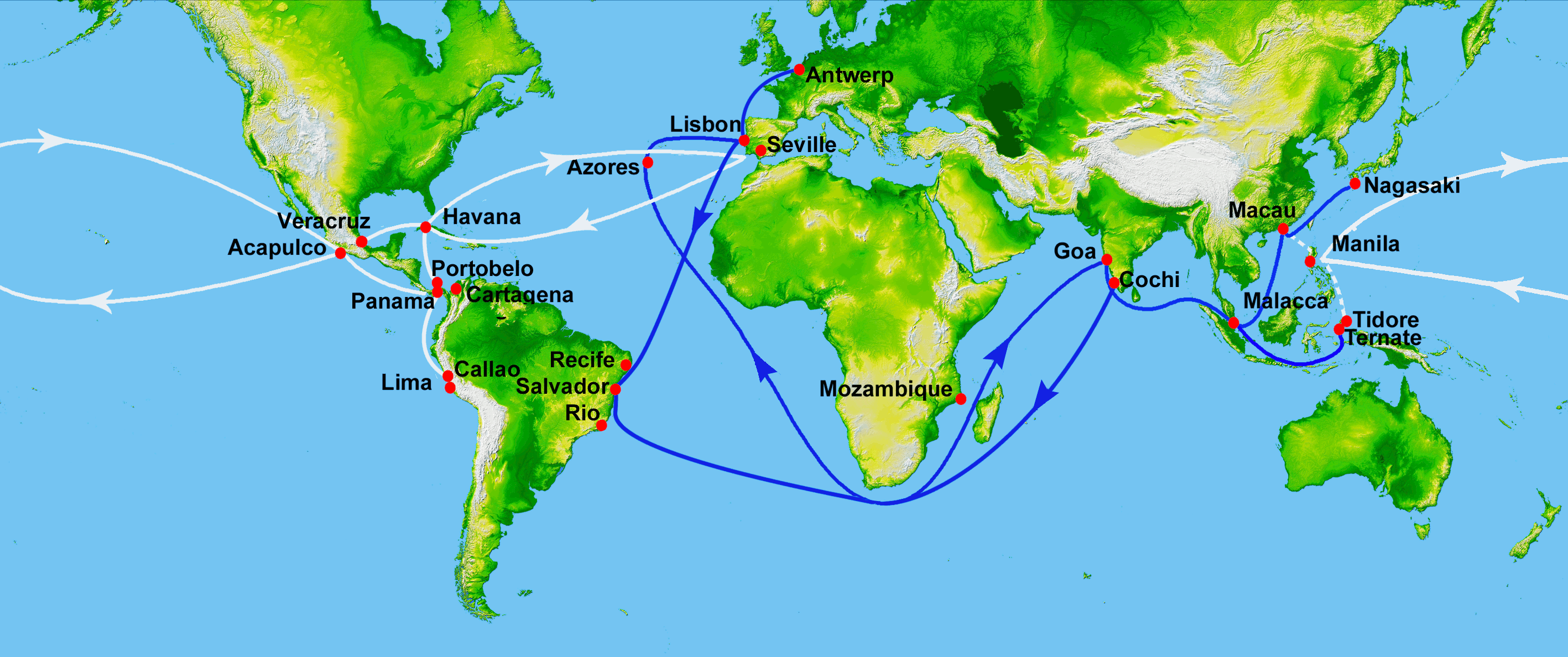
Magellan and the Manila Galleons
In 1519,Ferdinand Magellan
Ferdinand Magellan ( or ; pt, Fernão de Magalhães, ; es, link=no, Fernando de Magallanes, ; 4 February 1480 – 27 April 1521) was a Portuguese explorer. He is best known for having planned and led the 1519 Spanish expedition to the Eas ...
sailed down the east coast of South America, found and sailed through the strait that bears his name. On 28 November 1520, he entered the Pacific. Magellan then sailed north and caught the trade winds
The trade winds or easterlies are the permanent east-to-west prevailing winds that flow in the Earth's equatorial region. The trade winds blow mainly from the northeast in the Northern Hemisphere and from the southeast in the Southern Hemisp ...
which carried him across the Pacific to the Philippines where he was killed. One surviving ship returned west across the Indian Ocean and the other
In Phenomenology (philosophy), phenomenology, the terms the Other and the Constitutive Other identify the other human being, in their differences from the Self, as being a cumulative, constituting factor in the self-image of a person; as acknow ...
went north in the hope of finding the westerlies
The westerlies, anti-trades, or prevailing westerlies, are prevailing winds from the west toward the east in the middle latitudes between 30 and 60 degrees latitude. They originate from the high-pressure areas in the horse latitudes and tren ...
and reaching Mexico. Unable to find the right winds, it was forced to return to the East Indies. In 1565 (44 years later), Andrés de Urdaneta
Andrés de Urdaneta (1508 – June 3, 1568) was a maritime explorer for the Spanish Empire of Basque heritage, who became an Augustinian friar. At the age of seventeen, he accompanied the Loaísa expedition to the Spice Islands where he sp ...
found a wind system that would reliably blow a ship eastward back to the Americas. From then until 1815 the annual Manila Galleons
fil, Galyon ng Maynila
, english_name = Manila Galleon
, duration = From 1565 to 1815 (250 years)
, venue = Between Manila and Acapulco
, location = New Spain (Spanish Empire) ...
crossed the Pacific from Mexico to the Philippines and back, exchanging Mexican silver for spices and porcelain. Until the time of Captain James Cook
James Cook (7 November 1728 Old Style date: 27 October – 14 February 1779) was a British explorer, navigator, cartographer, and captain in the British Royal Navy, famous for his three voyages between 1768 and 1779 in the Pacific Ocean and ...
these were the only large ships to regularly cross the Pacific. The route was purely commercial and there was no exploration of the areas to the north and south. In 1668, the Spanish founded a colony on Guam
Guam (; ch, Guåhan ) is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. It is the westernmost point and territory of the United States (reckoned from the geographic cent ...
as a resting place for west-bound galleons. For a long time this was the only non-coastal European settlement in the Pacific.
South America
In 1513, six years before Magellan, Spanish explorerVasco Núñez de Balboa
Vasco Núñez de Balboa (; c. 1475around January 12–21, 1519) was a Spanish explorer, governor, and conquistador. He is best known for having crossed the Isthmus of Panama to the Pacific Ocean in 1513, becoming the first European to lead an ...
crossed the Isthmus of Panama and saw the Pacific Ocean. In 1517-18, two ships were built on the Pacific coast. In 1522, Pascual de Andagoya
Pascual de Andagoya (1495–1548) was a Spanish Basque conquistador. He was born in the village of Andagoya, in the valley of Cuartango (Álava), in Spain.
As often happened at the time, Andagoya left as an explorer of the New World at a very ...
sailed the coast as far as Ecuador. In 1532, Francisco Pizarro
Francisco Pizarro González, Marquess of the Atabillos (; ; – 26 June 1541) was a Spanish conquistador, best known for his expeditions that led to the Spanish conquest of Peru.
Born in Trujillo, Spain to a poor family, Pizarro chose ...
conquered Peru. A regular trade developed that carried Peruvian silver up the coast to Panama where it was carried overland to the Caribbean and part to Spain. Spanish settlement extended as far south as central Chile. In 1557-8, Juan Fernández Ladrillero discovered the Juan Fernandez islands
''Juan'' is a given name, the Spanish and Manx versions of ''John''. It is very common in Spain and in other Spanish-speaking communities around the world and in the Philippines, and also (pronounced differently) in the Isle of Man. In Spanish, ...
and explored the Chilean coast down to the Strait of Magellan.


The South Pacific
Several Spanish expeditions were sent from South America across the Pacific Ocean in the 16th and early 17th centuries. They all used the southerntrade winds
The trade winds or easterlies are the permanent east-to-west prevailing winds that flow in the Earth's equatorial region. The trade winds blow mainly from the northeast in the Northern Hemisphere and from the southeast in the Southern Hemisp ...
. In 1567/68, Álvaro de Mendaña de Neira
Álvaro de Mendaña y Neira (or Neyra) (1 October 1542 – 18 October 1595) was a Spanish navigator and discoverer, best known for two of the earliest recorded expeditions across the Pacific in 1567 and 1595. His voyages led to the discovery of ...
sailed from Peru to the Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands is an island country consisting of six major islands and over 900 smaller islands in Oceania, to the east of Papua New Guinea and north-west of Vanuatu. It has a land area of , and a population of approx. 700,000. Its capit ...
. In 1595, he tried again and reached the Santa Cruz Islands
The Santa Cruz Islands are a group of islands in the Pacific Ocean, part of Temotu Province of the nation of Solomon Islands discovered by the Spaniards. They lie approximately 250 miles (400 km) to the southeast of the Solomon Islands ...
(eastern Solomons toward Fiji). He died there and the survivors reached the Philippines. In 1606, Pedro Fernandes de Queirós
Pedro Fernandes de Queirós ( es, Pedro Fernández de Quirós) (1563–1614) was a Portuguese navigator in the service of Spain. He is best known for his involvement with Spanish voyages of discovery in the Pacific Ocean, in particular the 1595–1 ...
reached Vanuatu
Vanuatu ( or ; ), officially the Republic of Vanuatu (french: link=no, République de Vanuatu; bi, Ripablik blong Vanuatu), is an island country located in the South Pacific Ocean. The archipelago, which is of volcanic origin, is east of ...
south of the Solomons. He continued exploring and eventually sailed back to Mexico. One of his separated ships under Luis Vaz de Torres sailed west and discovered the strait that bears his name sighting the northern tip of Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by ...
. Other Spanish expeditions discovered Tuvalu
Tuvalu ( or ; formerly known as the Ellice Islands) is an island country and microstate in the Polynesian subregion of Oceania in the Pacific Ocean. Its islands are situated about midway between Hawaii and Australia. They lie east-northea ...
, the Marquesas
The Marquesas Islands (; french: Îles Marquises or ' or '; Marquesan: ' (North Marquesan) and ' (South Marquesan), both meaning "the land of men") are a group of volcanic islands in French Polynesia, an overseas collectivity of France in t ...
, the Cook Islands
)
, image_map = Cook Islands on the globe (small islands magnified) (Polynesia centered).svg
, capital = Avarua
, coordinates =
, largest_city = Avarua
, official_languages =
, lan ...
, the Admiralty Islands
The Admiralty Islands are an archipelago group of 18 islands in the Bismarck Archipelago, to the north of New Guinea in the South Pacific Ocean. These are also sometimes called the Manus Islands, after the largest island.
These rainforest-co ...
and the Pitcairn
The Pitcairn Islands (; Pitkern: '), officially the Pitcairn, Henderson, Ducie and Oeno Islands, is a group of four volcanic islands in the southern Pacific Ocean that form the sole British Overseas Territory in the Pacific Ocean. The four i ...
. In 1722, the Dutchman Jacob Roggeveen
Jacob Roggeveen (1 February 1659 – 31 January 1729) was a Dutch explorer who was sent to find Terra Australis and Davis Land, but instead found Easter Island (called so because he landed there on Easter Sunday). Jacob Roggeveen also found Bora ...
sailed from Cape Horn to Batavia and discovered Easter Island and Samoa.
Cape Horn
Six years after Magellan, in 1526, one of the ships of the Loaísa expedition sailed through the Strait of Magellan and followed the coast north to Mexico. In 1578,Francis Drake
Sir Francis Drake ( – 28 January 1596) was an English explorer, sea captain, privateer, slave trader, naval officer, and politician. Drake is best known for his circumnavigation of the world in a single expedition, from 1577 to 1580 ...
passed through the Strait, sailed north raiding Spanish ships during his successful circumnavigation. On 5 June 1579, the ship briefly made first landfall at South Cove, Cape Arago, just south of Coos Bay, Oregon, and then sailed south while searching for a suitable harbour to repair his ailing ship. On 17 June, Drake and his crew found a protected cove when they landed on the Pacific coast of what is now Northern California. While ashore, he claimed the area for Queen Elizabeth I as Nova Albion or New Albion
New Albion, also known as ''Nova Albion'' (in reference to an archaic name for Britain), was the name of the continental area north of Mexico claimed by Sir Francis Drake for England when he landed on the North American west coast in 1579. Thi ...
. In 1580, Pedro Sarmiento de Gamboa
Pedro Sarmiento de Gamboa (1532–1592) was a Spanish explorer, author, historian, mathematician, and astronomer. His birthplace is not certain and may have been Pontevedra, in Galicia, where his paternal family originated, or Alcalá de Henare ...
, who was hunting for Drake, was the first to sail from the Strait to Europe. In 1587, Thomas Cavendish
Sir Thomas Cavendish (1560 – May 1592) was an English explorer and a privateer known as "The Navigator" because he was the first who deliberately tried to emulate Sir Francis Drake and raid the Spanish towns and ships in the Pacific and retu ...
followed Drake, captured a Manila galleon and returned via the Pacific and the Indian Ocean. In 1599, the first Dutch ships passed through the Strait of Magellan (Will Adams, the first Englishman to reach Japan, was on board). Olivier van Noort
Olivier van Noort (1558 – 22 February 1627) was a Dutch merchant captain and pirate and the first Dutchman to circumnavigate the world.Quanchi, ''Historical Dictionary of the Discovery and Exploration of the Pacific Islands'', page 246
Olivier ...
followed and became the first Dutch circumnavigator.
In 1525, Francisco de Hoces
Francisco de Hoces (died 1526) was a Spanish sailor who in 1525 joined the Loaísa Expedition to the Spice Islands as commander of the vessel ''San Lesmes''.
In January 1526, the ''San Lesmes'' was blown by a gale southwards from the eastern mo ...
, while trying to enter the Strait as part of the Loaisa expedition, was blown south by a storm and saw what he thought was land's end. In 1578, Drake was blown south on the west side and saw what he thought was open water. In 1616, Willem Schouten
Willem Cornelisz Schouten ( – 1625) was a Dutch navigator for the Dutch East India Company. He was the first to sail the Cape Horn route to the Pacific Ocean.
Biography
Willem Cornelisz Schouten was born in c. 1567 in Hoorn, Holland, S ...
sought a more southerly passage and rounded Cape Horn
Cape Horn ( es, Cabo de Hornos, ) is the southernmost headland of the Tierra del Fuego archipelago of southern Chile, and is located on the small Hornos Island. Although not the most southerly point of South America (which are the Diego Ramí ...
. In 1619, the Garcia de Nodal expedition followed the Dutch and proved that Tierra del Fuego was an island by circumnavigating it. Since the Strait of Magellan is narrow and hard to navigate Cape Horn became the standard route until the opening of the Panama Canal. It is a measure of the difficulty of these seas that it was not until 1820 that anyone went as far south as Antarctica.
North America
When the Spanish conquered Mexico in 1521, they gained a stretch of Pacific coast. In 1533,Fortún Ximénez
Fortún Ximénez Bertandoña (; died 1533) was a Spanish sailor of Basque origin who led a mutiny during an early expedition along the coast of Mexico and is the first European known to have landed in Baja California.
Ximénez was the pilot of a ...
reached Baja California
Baja California (; 'Lower California'), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Baja California ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Baja California), is a state in Mexico. It is the northernmost and westernmost of the 32 federal entities of Mex ...
and in 1539 Francisco de Ulloa
Francisco de Ulloa () (died 1540) was a Spanish explorer who explored the west coast of present-day Mexico and the Baja California Peninsula under the commission of Hernán Cortés. Ulloa's voyage was among the first to disprove the cartograph ...
showed that it was a peninsula, but the myth of an Island of California
The Island of California ( es, Isla de California) refers to a long-held European misconception, dating from the 16th century, that the Baja California Peninsula was not part of mainland North America but rather a large island (spelled on ea ...
continued for many years. In 1542 Juan Rodriguez Cabrillo
''Juan'' is a given name, the Spanish and Manx versions of '' John''. It is very common in Spain and in other Spanish-speaking communities around the world and in the Philippines, and also (pronounced differently) in the Isle of Man. In Spanis ...
reached a point north of San Francisco. In 1578 Drake landed somewhere on the coast. In 1587 Pedro de Unamuno, coming from the Philippines, stopped at Morro Bay, California
Morro Bay (''Morro'', Spanish for "Hill") is a seaside city in San Luis Obispo County, California. Located on the Central Coast of California, the city population was 10,757 as of the 2020 census, up from 10,234 at the 2010 census. The town ...
. In 1592, Juan de Fuca
Juan de Fuca (10 June 1536, Cefalonia 23 July 1602, Cefalonia)Greek Consulate of Vancouver,Greek Pioneers: Juan de Fuca. was a Greek pilot who served PhilipII of Spain. He is best known for his claim to have explored the Strait of Aniánnow k ...
may have reached Puget Sound
Puget Sound ( ) is a sound of the Pacific Northwest, an inlet of the Pacific Ocean, and part of the Salish Sea. It is located along the northwestern coast of the U.S. state of Washington. It is a complex estuarine system of interconnected m ...
.
In 1595, Sebastian Rodriguez Cermeño (Sebastião Rodrigues Soromenho), commander of the Manila galleon ''San Agustín'', attempted an exploration of the California coast. He reached the continent between Point St. George and Trinidad Head in California, but the galleon was later wrecked in a storm off Drake's Bay
Drakes Bay (Coast Miwok: ''Tamál-Húye'') is a wide bay named so by U.S. surveyor George Davidson in 1875 along the Point Reyes National Seashore on the coast of northern California in the United States, approximately northwest of San Fra ...
and the survivors had to sail the rest of the way back to Mexico in a small launch. The smaller vessel, however, allowed Cermeño to sail closer to the coast and to make useful observations of coastal features. In 1602, Sebastián Vizcaíno
Sebastián Vizcaíno (1548–1624) was a Spanish soldier, entrepreneur, explorer, and diplomat whose varied roles took him to New Spain, the Baja California peninsula, the California coast and Asia.
Early career
Vizcaíno was born in 154 ...
re-explored the California coast, one of his ships reaching Oregon. His was the last northward exploration for the next 150 years.
The Portolà expedition of 1769 began the land exploration of Alta California
Alta California ('Upper California'), also known as ('New California') among other names, was a province of New Spain, formally established in 1804. Along with the Baja California peninsula, it had previously comprised the province of , but ...
, following the coast as far north as San Francisco Bay
San Francisco Bay is a large tidal estuary in the U.S. state of California, and gives its name to the San Francisco Bay Area. It is dominated by the big cities of San Francisco, San Jose, and Oakland.
San Francisco Bay drains water f ...
and using the reports of Cermeño and Vizcaíno for guidance.
After conquering Mexico the Spanish occupied the southern two thirds of Mexico, all of Central America and the South American coast down to Chile. North of this the land was too dry to support a dense population that could be ruled and taxed. The only exception was the Pueblo
In the Southwestern United States, Pueblo (capitalized) refers to the Native tribes of Puebloans having fixed-location communities with permanent buildings which also are called pueblos (lowercased). The Spanish explorers of northern New Spain ...
peoples far to the north in New Mexico. People like Francisco Vásquez de Coronado
Francisco is the Spanish and Portuguese form of the masculine given name '' Franciscus''.
Nicknames
In Spanish, people with the name Francisco are sometimes nicknamed " Paco". San Francisco de Asís was known as ''Pater Comunitatis'' (father o ...
penetrated far into the interior and found nothing that the Spanish valued. The Chichimeca
Chichimeca () is the name that the Nahua peoples of Mexico generically applied to nomadic and semi-nomadic peoples who were established in present-day Bajio region of Mexico. Chichimeca carried the meaning as the Roman term "barbarian" that d ...
country of northern Mexico was slowly absorbed and Baja California began to be settled in 1687. The returning Manila galleons followed the westerlies
The westerlies, anti-trades, or prevailing westerlies, are prevailing winds from the west toward the east in the middle latitudes between 30 and 60 degrees latitude. They originate from the high-pressure areas in the horse latitudes and tren ...
to the coast of California, but immediately turned south, making only a few attempts to explore the coast. For more see History of the West Coast of North America
The human history of the west coast of North America is believed to stretch back to the arrival of the earliest people over the Bering Strait, or alternately along a now-submerged coastal plain, through the development of significant pre-Columbi ...
and Early knowledge of the Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest coast of North America was one of the last coastlines reached by European explorers. In terms of sailing time from Europe, it was one of the most distant places on earth. This article covers what Europeans knew or thought ...
.
Australia and the southwest
Australia is remarkable for the number of explorers who missed it. Some think that the Portuguese reached Australia before 1600 but these theories are difficult to prove. The 1567–1606 Spanish voyages from South America stopped at islands to the east before reaching Australia. The first European to definitely see Australia wasWillem Janszoon
Willem Janszoon (; ), sometimes abbreviated to Willem Jansz., was a Dutch navigator and colonial governor. Janszoon served in the Dutch East Indies in the periods 16031611 and 16121616, including as governor of Fort Henricus on the island of S ...
who in February 1606 reached the Cape York Peninsula and thought it was part of New Guinea. Also in 1606 (June to October) Luis Váez de Torres
Luis is a given name. It is the Spanish form of the originally Germanic name or . Other Iberian Romance languages have comparable forms: (with an accent mark on the i) in Portuguese and Galician, in Aragonese and Catalan, while is archa ...
of the Quiros expedition from South America followed the south coast of New Guinea and passed through the Torres Strait
The Torres Strait (), also known as Zenadh Kes, is a strait between Australia and the Melanesian island of New Guinea. It is wide at its narrowest extent. To the south is Cape York Peninsula, the northernmost extremity of the Australian mai ...
without recognizing Australia. His voyage, and therefore the separation between Australia and New Guinea, was not generally known until 1765. From about 1611, the standard Dutch route to the East Indies was to follow the roaring forties
The Roaring Forties are strong westerly winds found in the Southern Hemisphere, generally between the latitudes of 40°S and 50°S. The strong west-to-east air currents are caused by the combination of air being displaced from the Equator ...
as far east as possible and then turn sharply north to Batavia. Since it was difficult to know longitude some ships would reach the west coast or be wrecked on it. In 1616, Dirk Hartog
Dirk Hartog (; baptised 30 October 1580 – buried 11 October 1621) was a 17th-century Dutch sailor and explorer. Dirk Hartog's expedition was the second European group to land in Australia and the first to leave behind an artefact to record his ...
bumped into the west coast and did some exploring. Frederick de Houtman
Frederick de Houtman ( – 21 October 1627) was a Dutch explorer, navigator, and colonial governor who sailed on the first Dutch expedition to the East Indies from 1595 until 1597, during which time he made observations of the southern ce ...
did the same in 1619. In 1623 Jan Carstenszoon
Jan Carstenszoon or more commonly Jan Carstensz In Dutch patronyms ending in -szoon were almost universally abbreviated to -sz was a 17th-century Dutch explorer. In 1623, Carstenszoon was commissioned by the Dutch East India Company to lead an ...
followed the south coast of New Guinea, missed Torres Strait and went along the north coast of Australia. In 1643, Abel Tasman
Abel Janszoon Tasman (; 160310 October 1659) was a Dutch seafarer, explorer, and merchant, best known for his voyages of 1642 and 1644 in the service of the Dutch East India Company (VOC). He was the first known European explorer to reach New ...
left Mauritius
Mauritius ( ; french: Maurice, link=no ; mfe, label= Mauritian Creole, Moris ), officially the Republic of Mauritius, is an island nation in the Indian Ocean about off the southeast coast of the African continent, east of Madagascar. It ...
, missed Australia, found Tasmania
)
, nickname =
, image_map = Tasmania in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of Tasmania in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdi ...
, continued east and found New Zealand, missed the strait between the north and south islands, turned northwest, missed Australia again and sailed along the north coast of New Guinea. In 1644, he followed the south coast of New Guinea, missed the Torres Strait, turned south and mapped the north coast of Australia. In 1688, the English buccaneer William Dampier
William Dampier (baptised 5 September 1651; died March 1715) was an English explorer, pirate, privateer, navigator, and naturalist who became the first Englishman to explore parts of what is today Australia, and the first person to circumnav ...
beached a ship on the northwest coast. In 1696, Willem de Vlamingh
Willem Hesselsz de Vlamingh (November 1640 – ) was a Dutch sea captain who explored the central west coast of New Holland ( Australia) in the late 17th century, where he landed in what is now Perth on the Swan River. The mission proved fruit ...
explored the southwest coast. In 1699, Dampier was sent to find the east coast of Australia. He sailed along the west coast, went north to Timor, followed the north coast of New Guinea to the Bismarck Archipelago
The Bismarck Archipelago (, ) is a group of islands off the northeastern coast of New Guinea in the western Pacific Ocean and is part of the Islands Region of Papua New Guinea. Its area is about 50,000 square km.
History
The first inhabitants o ...
and abandoned his search because his ship had become rotten. Until Captain Cook the east coast was completely unknown and New Zealand had only been seen once.

Pacific Islands
See also:History of the Pacific Islands
History of the Pacific Islands covers the history of the islands in the Pacific Ocean.
Histories
Easter Island – Rapanui
Easter Island is one of the youngest inhabited territories on earth, and for most of the history of Easter Island it w ...
* 1521: by Ferdinand Magellan, two atolls
* 1521: Thieves' Islands (Mariana Islands) also by the Portuguese Ferdinand Magellan, from Spain.
* 1525: Caroline Islands
The Caroline Islands (or the Carolines) are a widely scattered archipelago of tiny islands in the western Pacific Ocean, to the north of New Guinea. Politically, they are divided between the Federated States of Micronesia (FSM) in the ce ...
by Diogo da Rocha Diogo da Rocha was a captain who sailed for the Portuguese in 1525. He is credited as being the first to encounter the islands "to the Eastwards of Mindanao, and the islands of St. Lazarus" ( possibly Ulithi in the Caroline Islands
The Caro ...
and Gomes de Sequeira, from the Portuguese East Indies (Moluccas).
* 1526: Islands of the Painted People (Marshall Islands) by Alonso de Salazar of the Loaísa expedition
* 1543: Bonin Islands
The Bonin Islands, also known as the , are an archipelago of over 30 subtropical and tropical islands, some directly south of Tokyo, Japan and northwest of Guam. The name "Bonin Islands" comes from the Japanese word ''bunin'' (an archaic rea ...
by Bernardo de la Torre Bernardo de la Torre was a Spanish sailor, primarily noted for having explored parts of the Western Pacific Ocean south of Japan in the 16th century.
Bernardo de la Torre sailed under the instructions of Ruy López de Villalobos, who sent him in ...
from Mexico
* 1568: Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands is an island country consisting of six major islands and over 900 smaller islands in Oceania, to the east of Papua New Guinea and north-west of Vanuatu. It has a land area of , and a population of approx. 700,000. Its capit ...
, the Ellice Islands
Tuvalu ( or ; formerly known as the Ellice Islands) is an island country and microstate in the Polynesian subregion of Oceania in the Pacific Ocean. Its islands are situated about midway between Hawaii and Australia. They lie east-nor ...
(Tuvalu) and Wake Island
Wake Island ( mh, Ānen Kio, translation=island of the kio flower; also known as Wake Atoll) is a coral atoll in the western Pacific Ocean in the northeastern area of the Micronesia subregion, east of Guam, west of Honolulu, southeast of T ...
by Álvaro de Mendaña de Neira
Álvaro de Mendaña y Neira (or Neyra) (1 October 1542 – 18 October 1595) was a Spanish navigator and discoverer, best known for two of the earliest recorded expeditions across the Pacific in 1567 and 1595. His voyages led to the discovery of ...
from South America
* 1574: Juan Fernández Islands
The Juan Fernández Islands ( es, Archipiélago Juan Fernández) are a sparsely inhabited series of islands in the South Pacific Ocean reliant on tourism and fishing. Situated off the coast of Chile, they are composed of three main volcanic ...
by Juan Fernández.
* 1595: Marquesas Islands
The Marquesas Islands (; french: Îles Marquises or ' or '; Marquesan: ' (North Marquesan) and ' ( South Marquesan), both meaning "the land of men") are a group of volcanic islands in French Polynesia, an overseas collectivity of France in ...
and the Santa Cruz Islands
The Santa Cruz Islands are a group of islands in the Pacific Ocean, part of Temotu Province of the nation of Solomon Islands discovered by the Spaniards. They lie approximately 250 miles (400 km) to the southeast of the Solomon Islands ...
by Álvaro de Mendaña de Neira
Álvaro de Mendaña y Neira (or Neyra) (1 October 1542 – 18 October 1595) was a Spanish navigator and discoverer, best known for two of the earliest recorded expeditions across the Pacific in 1567 and 1595. His voyages led to the discovery of ...
from South America
* 1606: Tuamotu Archipelago
The Tuamotu Archipelago or the Tuamotu Islands (french: Îles Tuamotu, officially ) are a French Polynesian chain of just under 80 islands and atolls in the southern Pacific Ocean. They constitute the largest chain of atolls in the world, extendin ...
, Butaritari
Butaritari is an atoll in the Pacific Ocean island nation of Kiribati. The atoll is roughly four-sided. The south and southeast portion of the atoll comprises a nearly continuous islet. The atoll reef is continuous but almost without islets al ...
and Makin (Gilbert Islands
The Gilbert Islands ( gil, Tungaru;Reilly Ridgell. ''Pacific Nations and Territories: The Islands of Micronesia, Melanesia, and Polynesia.'' 3rd. Ed. Honolulu: Bess Press, 1995. p. 95. formerly Kingsmill or King's-Mill IslandsVery often, this n ...
), the New Hebrides
New Hebrides, officially the New Hebrides Condominium (french: link=no, Condominium des Nouvelles-Hébrides, "Condominium of the New Hebrides") and named after the Hebrides, Hebrides Scottish archipelago, was the colonial name for the isla ...
(Vanuatu) by Pedro Fernandes de Queirós
Pedro Fernandes de Queirós ( es, Pedro Fernández de Quirós) (1563–1614) was a Portuguese navigator in the service of Spain. He is best known for his involvement with Spanish voyages of discovery in the Pacific Ocean, in particular the 1595–1 ...
from South America
* 1616: Friendly Islands
Tonga (, ; ), officially the Kingdom of Tonga ( to, Puleʻanga Fakatuʻi ʻo Tonga), is a Polynesian country and archipelago. The country has 171 islands – of which 45 are inhabited. Its total surface area is about , scattered over in ...
(Tonga) and the Bismarck Archipelago
The Bismarck Archipelago (, ) is a group of islands off the northeastern coast of New Guinea in the western Pacific Ocean and is part of the Islands Region of Papua New Guinea. Its area is about 50,000 square km.
History
The first inhabitants o ...
by Willem Schouten
Willem Cornelisz Schouten ( – 1625) was a Dutch navigator for the Dutch East India Company. He was the first to sail the Cape Horn route to the Pacific Ocean.
Biography
Willem Cornelisz Schouten was born in c. 1567 in Hoorn, Holland, S ...
from Cape Horn.
* 1642: Van Diemen's Land
Van Diemen's Land was the colonial name of the island of Tasmania used by the British during the European exploration of Australia in the 19th century. A British settlement was established in Van Diemen's Land in 1803 before it became a sep ...
(Tasmania), New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island coun ...
and the Cannibal Isles (Fiji) by Abel Tasman
Abel Janszoon Tasman (; 160310 October 1659) was a Dutch seafarer, explorer, and merchant, best known for his voyages of 1642 and 1644 in the service of the Dutch East India Company (VOC). He was the first known European explorer to reach New ...
* 1722: Easter Island
Easter Island ( rap, Rapa Nui; es, Isla de Pascua) is an island and special territory of Chile in the southeastern Pacific Ocean, at the southeasternmost point of the Polynesian Triangle in Oceania. The island is most famous for its nearl ...
and the Navigator Islands
The Samoan Islands ( sm, Motu o Sāmoa) are an archipelago covering in the central South Pacific, forming part of Polynesia and of the wider region of Oceania. Administratively, the archipelago comprises all of the Independent State of Samoa an ...
(Samoa) by Jacob Roggeveen
Jacob Roggeveen (1 February 1659 – 31 January 1729) was a Dutch explorer who was sent to find Terra Australis and Davis Land, but instead found Easter Island (called so because he landed there on Easter Sunday). Jacob Roggeveen also found Bora ...
from Cape Horn
* 1741: Aleutian Islands
The Aleutian Islands (; ; ale, Unangam Tanangin,”Land of the Aleuts", possibly from Chukchi ''aliat'', "island"), also called the Aleut Islands or Aleutic Islands and known before 1867 as the Catherine Archipelago, are a chain of 14 large v ...
by Vitus Bering
Vitus Jonassen Bering (baptised 5 August 1681 – 19 December 1741),All dates are here given in the Julian calendar, which was in use throughout Russia at the time. also known as Ivan Ivanovich Bering, was a Danish cartographer and explorer in ...
and Alexei Chirikov
Aleksei Ilyich Chirikov (russian: Алексе́й Ильи́ч Чи́риков; 1703 – November 14, 1748) was a Russian navigator and captain who, along with Vitus Bering, was the first Russian to reach the northwest coast of North America. H ...
from Russia
* 1765: Tokelau
Tokelau (; ; known previously as the Union Islands, and, until 1976, known officially as the Tokelau Islands) is a dependent territory of New Zealand in the southern Pacific Ocean. It consists of three tropical coral atolls: Atafu, Nukunonu, a ...
and Nikunau
Nikunau is a low coral atoll in the Gilbert Islands that forms a council district of the Republic of Kiribati. It consists of two parts, with the larger in the northwest, joined by an isthmus about wide.
There are several landlocked hypersaline ...
by John Byron
Vice-Admiral John Byron (8 November 1723 – 1 April 1786) was a British Royal Navy officer and explorer. He earned the nickname "Foul-Weather Jack" in the press because of his frequent encounters with bad weather at sea. As a midshipman, he sa ...
* 1767: Tahiti
Tahiti (; Tahitian ; ; previously also known as Otaheite) is the largest island of the Windward group of the Society Islands in French Polynesia. It is located in the central part of the Pacific Ocean and the nearest major landmass is Austra ...
by Samuel Wallis
Samuel Wallis (23 April 1728 – 21 January 1795 in London) was a British naval officer and explorer of the Pacific Ocean. He made the first recorded visit by a European navigator to Tahiti.
Biography
Wallis was born at Fenteroon Farm, n ...
* 1774: New Caledonia
)
, anthem = ""
, image_map = New Caledonia on the globe (small islands magnified) (Polynesia centered).svg
, map_alt = Location of New Caledonia
, map_caption = Location of New Caledonia
, mapsize = 290px
, subdivision_type = Sovereign st ...
and Norfolk Island
Norfolk Island (, ; Norfuk: ''Norf'k Ailen'') is an external territory of Australia located in the Pacific Ocean between New Zealand and New Caledonia, directly east of Australia's Evans Head and about from Lord Howe Island. Together wit ...
by James Cook
James Cook (7 November 1728 Old Style date: 27 October – 14 February 1779) was a British explorer, navigator, cartographer, and captain in the British Royal Navy, famous for his three voyages between 1768 and 1779 in the Pacific Ocean and ...
* 1777: Christmas Island
Christmas Island, officially the Territory of Christmas Island, is an Australian external territory comprising the island of the same name. It is located in the Indian Ocean, around south of Java and Sumatra and around north-west of the ...
(now Kiribati) by James Cook
James Cook (7 November 1728 Old Style date: 27 October – 14 February 1779) was a British explorer, navigator, cartographer, and captain in the British Royal Navy, famous for his three voyages between 1768 and 1779 in the Pacific Ocean and ...
* 1778: Sandwich Islands
The Hawaiian Islands ( haw, Nā Mokupuni o Hawai‘i) are an archipelago of eight major islands, several atolls, and numerous smaller islets in the North Pacific Ocean, extending some from the island of Hawaii in the south to northernmost Ku ...
(Hawaii) by James Cook
James Cook (7 November 1728 Old Style date: 27 October – 14 February 1779) was a British explorer, navigator, cartographer, and captain in the British Royal Navy, famous for his three voyages between 1768 and 1779 in the Pacific Ocean and ...
* 1788: Gilbert Islands
The Gilbert Islands ( gil, Tungaru;Reilly Ridgell. ''Pacific Nations and Territories: The Islands of Micronesia, Melanesia, and Polynesia.'' 3rd. Ed. Honolulu: Bess Press, 1995. p. 95. formerly Kingsmill or King's-Mill IslandsVery often, this n ...
(now Kiribati) by Thomas Gilbert and John Marshall
John Marshall (September 24, 1755July 6, 1835) was an American politician and lawyer who served as the fourth Chief Justice of the United States from 1801 until his death in 1835. He remains the longest-serving chief justice and fourth-longes ...
.
* 1791: Chatham Islands
The Chatham Islands ( ) (Moriori: ''Rēkohu'', 'Misty Sun'; mi, Wharekauri) are an archipelago in the Pacific Ocean about east of New Zealand's South Island. They are administered as part of New Zealand. The archipelago consists of about t ...
by William R. Broughton
William Robert Broughton (22 March 176214 March 1821) was a British naval officer in the late 18th century. As a lieutenant in the Royal Navy, he commanded HMS ''Chatham'' as part of the Vancouver Expedition, a voyage of exploration through t ...
Mythical lands
Europeans had long believed in aStrait of Anian
A strait is an Ocean, oceanic landform connecting two Sea, seas or two other large areas of water. The surface water generally flows at the same elevation on both sides and through the strait in either direction. Most commonly, it is a narrow ...
somewhere near Bering Strait. A large and distorted Hokkaido
is Japan, Japan's Japanese archipelago, second largest island and comprises the largest and northernmost Prefectures of Japan, prefecture, making up its own List of regions of Japan, region. The Tsugaru Strait separates Hokkaidō from Honshu; th ...
was called 'Ezo
(also spelled Yezo or Yeso) is the Japanese term historically used to refer to the lands to the north of the Japanese island of Honshu. It included the northern Japanese island of Hokkaido, which changed its name from "Ezo" to "Hokkaidō" in 18 ...
', 'Jesso' and many other spellings. One of the Kuril Islands
The Kuril Islands or Kurile Islands (; rus, Кури́льские острова́, r=Kuril'skiye ostrova, p=kʊˈrʲilʲskʲɪjə ɐstrɐˈva; Japanese language, Japanese: or ) are a volcanic archipelago currently administered as part of Sakh ...
named "Companies Landt" by Vries grew into a large mass attached to North America. Joao-da-Gama-Land was thought to be east of Japan. There was an overgrown Puget Sound called "Grande Mer de l'Ouest" possibly connected to Hudson Bay
Hudson Bay ( crj, text=ᐐᓂᐯᒄ, translit=Wînipekw; crl, text=ᐐᓂᐹᒄ, translit=Wînipâkw; iu, text=ᑲᖏᖅᓱᐊᓗᒃ ᐃᓗᐊ, translit=Kangiqsualuk ilua or iu, text=ᑕᓯᐅᔭᕐᔪᐊᖅ, translit=Tasiujarjuaq; french: b ...
. In the far south was a Terra Australis
(Latin: '"Southern Land'") was a hypothetical continent first posited in antiquity and which appeared on maps between the 15th and 18th centuries. Its existence was not based on any survey or direct observation, but rather on the idea that ...
. The map published in Diderot
Denis Diderot (; ; 5 October 171331 July 1784) was a French philosopher, art critic, and writer, best known for serving as co-founder, chief editor, and contributor to the '' Encyclopédie'' along with Jean le Rond d'Alembert. He was a promi ...
's ''Encyclopédie
''Encyclopédie, ou dictionnaire raisonné des sciences, des arts et des métiers'' (English: ''Encyclopedia, or a Systematic Dictionary of the Sciences, Arts, and Crafts''), better known as ''Encyclopédie'', was a general encyclopedia publis ...
'' in 1755 is filled with nonsense. In 1875 no less than 123 mythical islands were removed from the Royal Navy chart of the North Pacific.
Further expeditions

Alaska and the Russians
The modern period begins with Russian expeditions. They crossed Siberia and reached the Pacific in 1639 (Ivan Moskvitin
Ivan Yuryevich Moskvitin (russian: Иван Юрьевич Москвитин) (? - after 1647) was a Russian explorer, presumably a native of Moscow, who led a Russian reconnaissance party to the Sea of Okhotsk, becoming the first Russian to reac ...
). In 1644 Vassili Poyarkov
Vassili Danilovich Poyarkov (Василий Данилович Поярков in Russian, ? - after 1668) was the first Russian explorer of the Amur region.
The Russian expansion into Siberia began with the conquest of the Khanate of Sibir in 15 ...
found the Amur River
The Amur (russian: река́ Аму́р, ), or Heilong Jiang (, "Black Dragon River", ), is the world's tenth longest river, forming the border between the Russian Far East and Northeastern China (Inner Manchuria). The Amur proper is long ...
. In 1648 Semyon Dezhnyov
Semyon Ivanovich Dezhnyov ( rus, Семён Ива́нович Дежнёв, p=sʲɪˈmʲɵn ɪˈvanəvʲɪtɕ dʲɪˈʐnʲɵf; sometimes spelled Dezhnyov; c. 1605 – 1673) was a Russian explorer of Siberia and the first European to sail through t ...
(probably) entered the Pacific from the Arctic Ocean. In 1652 Mikhail Stadukhin followed the coast of the Sea of Okhotsk
The Sea of Okhotsk ( rus, Охо́тское мо́ре, Ohótskoye móre ; ja, オホーツク海, Ohōtsuku-kai) is a marginal sea of the western Pacific Ocean. It is located between Russia's Kamchatka Peninsula on the east, the Kuril Islands ...
. In 1697 Vladimir Atlasov entered the Kamchatka Peninsula
The Kamchatka Peninsula (russian: полуостров Камчатка, Poluostrov Kamchatka, ) is a peninsula in the Russian Far East, with an area of about . The Pacific Ocean and the Sea of Okhotsk make up the peninsula's eastern and w ...
overland from the north. In 1716 the first seagoing boats were built to reach Kamchatka from the mainland. In 1728 Vitus Bering
Vitus Jonassen Bering (baptised 5 August 1681 – 19 December 1741),All dates are here given in the Julian calendar, which was in use throughout Russia at the time. also known as Ivan Ivanovich Bering, was a Danish cartographer and explorer in ...
sailed from Kamchatka through the strait that bears his name without seeing America. In 1732 Mikhail Gvozdev
Mikhail Spiridonovich Gvozdev (russian: Михаи́л Спиридо́нович Гво́здев; – after 1759) was a Russian military geodesist and a commander of the expedition to northern Alaska in 1732, when the Alaskan shore was sight ...
and Ivan Fedorov (navigator)
Ivan Fyodorov (russian: Ива́н Фёдоров; died ) was a Russian navigator and commanding officer of the expedition to northern Alaska in 1732.
After the First Kamchatka expedition of Vitus Bering, Russian exploration efforts were contin ...
saw the tip of Alaska from the Bering Strait. In 1741 Vitus Bering
Vitus Jonassen Bering (baptised 5 August 1681 – 19 December 1741),All dates are here given in the Julian calendar, which was in use throughout Russia at the time. also known as Ivan Ivanovich Bering, was a Danish cartographer and explorer in ...
and Alexei Chirikov
Aleksei Ilyich Chirikov (russian: Алексе́й Ильи́ч Чи́риков; 1703 – November 14, 1748) was a Russian navigator and captain who, along with Vitus Bering, was the first Russian to reach the northwest coast of North America. H ...
sailed just south of the Aleutian Islands and reached the Alaska panhandle. Peter Kuzmich Krenitzin
Pyotr Kuzmich Krenitsyn (russian: Пётр Кузьмич Креницын) (1728 – July 4, 1770), spelt "Krenitzin" in the United States, was a Russian explorer and Captain/Lieutenant of the Imperial Russian Navy. Following Vitus Bering's 1741 ...
mapped the Aleutians before 1769. The myth of a land mass north of the Aleutians took a long time to dispel. Russians fur hunters island-hopped along the Aleutians and then along the south coast of Alaska looking mainly for sea otter
The sea otter (''Enhydra lutris'') is a marine mammal native to the coasts of the northern and eastern North Pacific Ocean. Adult sea otters typically weigh between , making them the heaviest members of the weasel family, but among the smal ...
( Attu at the west end of the Aleutians in 1745, Unalaska Island
Unalaska ( ale, Nawan-Alaxsxa, russian: Уналашка) is a volcanic island in the Fox Islands group of the Aleutian Islands in the US state of Alaska located at . The island has a land area of . It measures long and wide. The city of Unala ...
at the east end in 1759, Kodiak Island
Kodiak Island ( Alutiiq: ''Qikertaq''), is a large island on the south coast of the U.S. state of Alaska, separated from the Alaska mainland by the Shelikof Strait. The largest island in the Kodiak Archipelago, Kodiak Island is the second la ...
1784, Kenai Peninsula
The Kenai Peninsula ( Dena'ina: ''Yaghenen'') is a large peninsula jutting from the coast of Southcentral Alaska. The name Kenai (, ) is derived from the word "Kenaitze" or "Kenaitze Indian Tribe", the name of the Native Athabascan Alaskan tribe ...
1785, Yakutat, 1795, Sitka
russian: Ситка
, native_name_lang = tli
, settlement_type = Consolidated city-borough
, image_skyline = File:Sitka 84 Elev 135.jpg
, image_caption = Downtown Sitka in 1984
, image_size ...
1799, Fort Ross
Fort Ross ( Russian: Форт-Росс, Kashaya ''mé·ṭiʔni''), originally Fortress Ross ( pre-reformed Russian: Крѣпость Россъ, tr. ''Krepostʹ Ross''), is a former Russian establishment on the west coast of North America i ...
1812). North of the Aleutians posts appeared on the west coast after 1819. Spaniards from Mexico met the Russians in 1788. (see below). Russian America
Russian America (russian: Русская Америка, Russkaya Amerika) was the name for the Russian Empire's colonial possessions in North America from 1799 to 1867. It consisted mostly of present-day Alaska in the United States, but a ...
was sold to the United States in 1867.

Captain Cook
On his first voyage (1768–1771)James Cook
James Cook (7 November 1728 Old Style date: 27 October – 14 February 1779) was a British explorer, navigator, cartographer, and captain in the British Royal Navy, famous for his three voyages between 1768 and 1779 in the Pacific Ocean and ...
went to Tahiti from Cape Horn, circumnavigated New Zealand, followed the east coast of Australia for the first time and returned via the Torres Strait and the Cape of Good Hope. On his second voyage (1772–1775) he sailed from west to east keeping as far south as possible and showed that there was probably no Terra Australis
(Latin: '"Southern Land'") was a hypothetical continent first posited in antiquity and which appeared on maps between the 15th and 18th centuries. Its existence was not based on any survey or direct observation, but rather on the idea that ...
. On his third voyage (1776–1780), he found the Hawaiian Islands
The Hawaiian Islands ( haw, Nā Mokupuni o Hawai‘i) are an archipelago of eight major islands, several atolls, and numerous smaller islets in the North Pacific Ocean, extending some from the island of Hawaii in the south to northernmost ...
(first seen by Spanish captain Ruy López de Villalobos in 1542. The Spanish named these islands "Isla de Mesa, de los Monjes y Desgraciada") and followed the North American coast from Oregon to the Bering Strait, mapping this coast for the first time and showing that there was probably no Northwest Passage
The Northwest Passage (NWP) is the sea route between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans through the Arctic Ocean, along the northern coast of North America via waterways through the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. The eastern route along the ...
. Cook was killed in Hawaii in 1779. The expedition made a second attempt at the Bering Strait, stopped at Kamchatka and China and reached England in 1780. Cook set a high standard of scientific exploration, showed that there was no large land mass in the southern ocean, mapped the two largest island groups in the Pacific, and by following the east coast of Australia and the west coast of North America closed the last gaps in European knowledge of the Pacific coasts. On his second voyage, Cook was accompanied by Johann Reinhold Forster
Johann Reinhold Forster (22 October 1729 – 9 December 1798) was a German Reformed (Calvinist) pastor and naturalist of partially Scottish descent who made contributions to the early ornithology of Europe and North America. He is best known ...
and Forster's son Georg
Georg may refer to:
* Georg (film), ''Georg'' (film), 1997
*Georg (musical), Estonian musical
* Georg (given name)
* Georg (surname)
* , a Kriegsmarine coastal tanker
See also
* George (disambiguation)
{{disambiguation ...
, who influenced significantly Alexander von Humboldt
Friedrich Wilhelm Heinrich Alexander von Humboldt (14 September 17696 May 1859) was a German polymath, geographer, naturalist, explorer, and proponent of Romantic philosophy and science. He was the younger brother of the Prussian minister ...
and his understanding of the Pacific, which Humboldt encountered in 1802–3. Several German-speaking navigators and explorers followed, most of them in the service of expeditions launched by Imperial Russia. After Cook everything was detail.
Cook's rivals and successors
Several governments sponsored Pacific expeditions, often in rivalry or emulation of Captain Cook. At the time of Cook's first voyage, in 1766-1769Louis Antoine de Bougainville
Louis-Antoine, Comte de Bougainville (, , ; 12 November 1729 – August 1811) was a French admiral and explorer. A contemporary of the British explorer James Cook, he took part in the Seven Years' War in North America and the American Revolutio ...
crossed the Pacific and publicized Tahiti, in 1767 Samuel Wallis
Samuel Wallis (23 April 1728 – 21 January 1795 in London) was a British naval officer and explorer of the Pacific Ocean. He made the first recorded visit by a European navigator to Tahiti.
Biography
Wallis was born at Fenteroon Farm, n ...
and Philip Carteret
Rear-Admiral Philip Carteret, Seigneur of Trinity (22 January 1733, Trinity Manor, Jersey – 21 July 1796, Southampton) was a British naval officer and explorer who participated in two of the Royal Navy's circumnavigation expeditions in 176 ...
separately crossed the Pacific, and in 1769 Jean-François-Marie de Surville visited the Solomon Islands and New Zealand. In 1785-1788 Jean-François de Galaup, comte de Lapérouse
Jean François de Galaup, comte de Lapérouse (; variant spelling: ''La Pérouse''; 23 August 17411788?), often called simply Lapérouse, was a French naval officer and explorer. Having enlisted at the age of 15, he had a successful naval caree ...
followed the American coast from Chile to Alaska, crossed to China, explored northern Japan and Kamchatka, went south to Australia and lost his life in the Santa Cruz Islands
The Santa Cruz Islands are a group of islands in the Pacific Ocean, part of Temotu Province of the nation of Solomon Islands discovered by the Spaniards. They lie approximately 250 miles (400 km) to the southeast of the Solomon Islands ...
. The Malaspina Expedition (1789–1794) visited the American coast, Manila, New Zealand and Australia. In 1792-93 George Vancouver
Captain George Vancouver (22 June 1757 – 10 May 1798) was a British Royal Navy officer best known for his 1791–1795 expedition, which explored and charted North America's northwestern Pacific Coast regions, including the coasts of what are ...
more thoroughly mapped the west coast of Canada. In 1803/6 Adam Johann von Krusenstern
Adam Johann von Krusenstern (also Krusenstjerna in Swedish; russian: Ива́н Фёдорович Крузенште́рн, tr. ; 10 October 177012 August 1846) was a Russian admiral and explorer, who led the first Russian circumnavigatio ...
led the first Russian circumnavigation and investigated both sides of the North Pacific. In 1820 Fabian Gottlieb von Bellingshausen
Fabian Gottlieb Thaddeus von Bellingshausen (russian: Фадде́й Фадде́евич Беллинсга́узен, translit=Faddéy Faddéevich Bellinsgáuzen; – ) was a Russian naval officer, cartographer and explorer, who ultimatel ...
saw Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest cont ...
. A number of other voyages are listed in "European and American voyages of scientific exploration
The era of European and American voyages of scientific exploration followed the Age of Discovery and were inspired by a new confidence in science and reason that arose in the Age of Enlightenment. Maritime expeditions in the Age of Discovery were ...
."
Spain on the west coast of North America
For Europeans in theAge of Exploration
The Age of Discovery (or the Age of Exploration), also known as the early modern period, was a period largely overlapping with the Age of Sail, approximately from the 15th century to the 17th century in European history, during which seafaring ...
western North America was one of the most distant places on Earth (9 to 12 months of sailing). Spain had long claimed the entire west coast of the Americas. The area north of Mexico however was given little attention in the early years. This changed when the Russians appeared in Alaska. The Spanish moved north to California and built a series of missions along the Pacific coast including: San Diego
San Diego ( , ; ) is a city on the Pacific Ocean coast of Southern California located immediately adjacent to the Mexico–United States border. With a 2020 population of 1,386,932, it is the eighth most populous city in the United States ...
in 1767, Monterey, California
Monterey (; es, Monterrey; Ohlone: ) is a city located in Monterey County on the southern edge of Monterey Bay on the U.S. state of California's Central Coast. Founded on June 3, 1770, it functioned as the capital of Alta California under b ...
in 1770 and San Francisco in 1776. San Francisco Bay was discovered in 1769 by Gaspar de Portolà
Gaspar is a given and/or surname of French, German, Portuguese, and Spanish origin, cognate to Casper (given name) or Casper (surname).
It is a name of biblical origin, per Saint Gaspar, one of the wise men mentioned in the Bible.
Notable peo ...
from the landward side because its mouth is not obvious from the sea. The Spanish settlement of San Francisco remained the northern limit of land occupation. By sea, from 1774 to 1793 the Spanish expeditions to the Pacific Northwest
During the Age of Exploration, the Spanish Empire undertook several expeditions to the Pacific Northwest of North America. Spanish claims to the region date to the papal bull of 1493, and the Treaty of Tordesillas signed in 1494. In 1513, th ...
tried to assert Spanish claims against the Russians and British. In 1774 Juan José Pérez Hernández
Juan José Pérez Hernández (born Joan Perés c. 1725 – November 3, 1775), often simply Juan Pérez, was an 18th-century Spanish explorer. He was the first known European to sight, examine, name, and record the islands near present-day Br ...
reached what is now the south end of the Alaska panhandle. In 1778 Captain Cook sailed the west coast and spent a month at Nootka Sound on Vancouver Island. An expedition led by Juan Francisco de la Bodega y Quadra sailed north to Nootka and reached Prince William Sound. In 1788 Esteban José Martínez Esteban () is a Spanish male given name, derived from Greek Στέφανος (Stéphanos) and related to the English names Steven and Stephen. Although in its original pronunciation the accent is on the penultimate syllable, English-speakers tend t ...
went north and met the Russians for the first time (Unalaska and Kodiak Island) and heard that the Russians were planning to occupy Nootka Sound. In 1789 Martinez went north to build a fort at Nootka and found British and American merchant ships already there. He seized a British ship which led to the Nootka Crisis
The Nootka Crisis, also known as the Spanish Armament, was an international incident and political dispute between the Nuu-chah-nulth Nation, the Spanish Empire, the Kingdom of Great Britain, and the fledgling United States of America triggered b ...
and Spanish recognition of non-Spanish trade on the northwest coast. In 1791 the Malaspina expedition mapped the Alaska coast. In 1792 Dionisio Alcalá Galiano
Dionisio Alcalá Galiano (8 October 1760 – 21 October 1805) was a Spanish naval officer, cartographer, and explorer. He mapped various coastlines in Europe and the Americas with unprecedented accuracy using new technology such as chronomete ...
circumnavigated Vancouver Island. In 1792-93 George Vancouver
Captain George Vancouver (22 June 1757 – 10 May 1798) was a British Royal Navy officer best known for his 1791–1795 expedition, which explored and charted North America's northwestern Pacific Coast regions, including the coasts of what are ...
also mapped the complex coast of British Columbia. Vancouver Island
Vancouver Island is an island in the northeastern Pacific Ocean and part of the Canadian province of British Columbia. The island is in length, in width at its widest point, and in total area, while are of land. The island is the largest by ...
was originally named Quadra's and Vancouver's Island in commemoration of the friendly negotiations held by the Spanish commander of the Nootka Sound settlement, Juan Francisco de la Bodega y Quadra and British naval captain George Vancouver
Captain George Vancouver (22 June 1757 – 10 May 1798) was a British Royal Navy officer best known for his 1791–1795 expedition, which explored and charted North America's northwestern Pacific Coast regions, including the coasts of what are ...
in Nootka Sound in 1792. In 1793 Alexander Mackenzie reached the Pacific overland from Canada. By this time Spain was becoming involved in the French wars and increasingly unable to assert its claims on the Pacific coast. In 1804 the Lewis and Clark Expedition
The Lewis and Clark Expedition, also known as the Corps of Discovery Expedition, was the United States expedition to cross the newly acquired western portion of the country after the Louisiana Purchase. The Corps of Discovery was a select gr ...
reached the Pacific overland from the Mississippi River. By the Adams–Onís Treaty
The Adams–Onís Treaty () of 1819, also known as the Transcontinental Treaty, the Florida Purchase Treaty, or the Florida Treaty,Weeks, p.168. was a treaty between the United States and Spain in 1819 that ceded Florida to the U.S. and define ...
of 1819 Spain gave up its claims north of California. Canadian fur traders, and later a smaller number of Americans, crossed the mountains and built posts on the coast. In 1846 the Oregon Treaty
The Oregon Treaty is a treaty between the United Kingdom and the United States that was signed on June 15, 1846, in Washington, D.C. The treaty brought an end to the Oregon boundary dispute by settling competing American and British claims to ...
divided the Oregon country
Oregon Country was a large region of the Pacific Northwest of North America that was subject to a long dispute between the United Kingdom and the United States in the early 19th century. The area, which had been created by the Treaty of 1818, co ...
between Britain and the United States. The United States conquered California in 1848 and purchased Alaska in 1867.
Northeast
The Russians moved south and the Japanese moved north and explored theKuril Islands
The Kuril Islands or Kurile Islands (; rus, Кури́льские острова́, r=Kuril'skiye ostrova, p=kʊˈrʲilʲskʲɪjə ɐstrɐˈva; Japanese language, Japanese: or ) are a volcanic archipelago currently administered as part of Sakh ...
and Sakhalin
Sakhalin ( rus, Сахали́н, r=Sakhalín, p=səxɐˈlʲin; ja, 樺太 ''Karafuto''; zh, c=, p=Kùyèdǎo, s=库页岛, t=庫頁島; Manchu: ᠰᠠᡥᠠᠯᡳᠶᠠᠨ, ''Sahaliyan''; Orok: Бугата на̄, ''Bugata nā''; Nivkh ...
. About 1805 Adam Johann von Krusenstern
Adam Johann von Krusenstern (also Krusenstjerna in Swedish; russian: Ива́н Фёдорович Крузенште́рн, tr. ; 10 October 177012 August 1846) was a Russian admiral and explorer, who led the first Russian circumnavigatio ...
was apparently the first Russian to reach eastern Siberia by sea from European Russia. In 1808 Mamiya Rinzo explored the coast of Sakhalin. During the Crimean War a British fleet failed to capture Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky
Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky ( rus, Петропавловск-Камчатский, a=Петропавловск-Камчатский.ogg, p=pʲɪtrɐˈpavləfsk kɐmˈtɕatskʲɪj) is a city and the administrative, industrial, scientific, and cultu ...
. In 1860 Russia annexed the southeast corner of Siberia from China.
The Pacific opened to trade and imperialism
After Captain Cook large numbers of European merchant vessels began to enter the Pacific. The reasons for this are not completely clear. On Cook's third voyage furs bought at Nootka were sold in China at a 1,800 percent profit - enough to pay for a trading voyage. The first to do this was James Hanna from Macao in 1785. Robert Gray in 1787 was the first American. ThisMaritime fur trade
The maritime fur trade was a ship-based fur trade system that focused on acquiring furs of sea otters and other animals from the indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast and natives of Alaska. The furs were mostly sold in China in exc ...
reached its peak about 1810, drew many ships into the Pacific and drew Canadians and Americans to the coast. The first Pacific whaling
Whaling is the process of hunting of whales for their usable products such as meat and blubber, which can be turned into a type of oil that became increasingly important in the Industrial Revolution.
It was practiced as an organized industr ...
ship left London in 1788 and by the nineteenth century there were hundreds of whaleships in the Pacific each year. Clipper ships
A clipper was a type of mid-19th-century merchant sailing vessel, designed for speed. Clippers were generally narrow for their length, small by later 19th century standards, could carry limited bulk freight, and had a large total sail area. "Cl ...
cut the sailing time from Europe to the Pacific. England founded a colony in Australia in 1788 and New Zealand in 1840. After about 1800 England began to replace the Dutch Republic along the Asian coast. Hong Kong
Hong Kong ( (US) or (UK); , ), officially the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China (abbr. Hong Kong SAR or HKSAR), is a List of cities in China, city and Special administrative regions of China, special ...
became a colony in 1839 during the First Opium War
The First Opium War (), also known as the Opium War or the Anglo-Sino War was a series of military engagements fought between Britain and the Qing dynasty of China between 1839 and 1842. The immediate issue was the Chinese enforcement of the ...
, which was also the first time that a large European military and naval force appeared in the Pacific. European ships and sailors disrupted life on the Pacific islands. Most of the Pacific islands were soon claimed by one European power or another.
See also
* Colonisation of Oceania *Europeans in Oceania
European exploration and settlement of Oceania began in the 16th century, starting with the Spanish ( Castilian) landings and shipwrecks in the Mariana Islands, east of the Philippines. This was followed by the Portuguese landing and settling tem ...
References
Bibliography
* Camino, Mercedes Maroto. ''Producing the Pacific: Maps and narratives of Spanish exploration (1567-1606)'' (Rodopi, 2005). * Daum, Andreas. "German Naturalists in the Pacific around 1800: Entanglement, Autonomy, and a Transnational Culture of Expertise". In ''Explorations and Entanglements: Germans in Pacific Worlds from the Early Modern Period to World War I'', ed. Hartmut Berghoff, Frank Biess, and Ulrike Strasser. New York: Berghahn Books, 2019, 79-102. * Delaney, John. ''Strait Through: Magellan to Cook & the Pacific'', (Princeton University Library, 2010)Website devoted to the exploration of the Pacific Ocean Online
* Dodge, Ernest Stanley. ''Beyond the Capes; Pacific Exploration from Captain Cook to the Challenger, 1776–1877'' (Little, Brown, 1971). * Engstrand, Iris HW. "Seekers of the 'Northern Mystery': European Exploration of California and the Pacific." ''California History'' 76.2-3 (1997): 78-11
online
*
Felipe Fernández-Armesto
Felipe Fernández-Armesto (born 1950) is a British professor of history and author of several popular works, notably on cultural and environmental history.
Life and career
He was born in London; his father was the Spanish journalist Felipe Ferná ...
, ''Pathfinders - A Global History of Exploration'', (2006).
* Guest, Harriet. ''Empire, Barbarism, and Civilisation: Captain Cook, William Hodges and the Return to the Pacific'' (Cambridge UP, 2007).
* Hayes, Derek. ''Historical Atlas of the North Pacific Ocean: Maps of Discovery and Scientific Exploration, 1500–2000'', (2001)
* Haycox, Stephen, et al. eds. ''Enlightenment and Exploration in the North Pacific, 1741–1805.'' (U of Washington Press, 1997excerpt
* Heawood, Edward. ''A History Of Geographical Discovery in the Seventeenth And Eighteenth Centuries'' (1912
online
* Howse, Derek, ed. ''Background to Discovery: Pacific Exploration from Dampier to Cook'' (U of California Press, 1990). * Irwin, Geoffrey. ''The prehistoric exploration and colonisation of the Pacific'' (Cambridge UP, 1994). * Lincoln, Margarette, ed. ''Science and exploration in the Pacific: European voyages to the southern oceans in the eighteenth century'' (Boydell & Brewer, 2001). * Lloyd, Christopher. ''Pacific Horizons: The Exploration of the Pacific Before Captain Cook'' (Allen and Unwin, 1946)
online
popular history * Lloyd, Christopher. ''Atlas of maritime history'' (1975
online
popular * Parry, J.H. ''The Age of Reconnaissance'' (1963
online
* Williams, Glyn. "‘To Make Discoveries of Countries Hitherto Unknown’ The Admiralty and Pacific Exploration in the Eighteenth Century." ''The Mariner's Mirror'' 82.1 (1996): 14-27. * Withey, Lynne. ''Voyages of discovery: Captain Cook and the exploration of the Pacific'' (U of California Press, 1989).
Historiography
* Davidson, James Wightman. "Problems of Pacific history." ''Journal of Pacific History'' 1#1 (1966): 5–21. * Gulliver, Katrina. "Finding the Pacific world." ''Journal of World History'' 22#1 (2011): 83–100online
* * Munro, Doug. ''The Ivory Tower and Beyond: Participant Historians of the Pacific'' (Cambridge Scholars Publishing, 2009). * Routledge, David. "Pacific history as seen from the Pacific Islands." ''Pacific Studies'' 8#2 (1985): 81
online
* Samson, Jane. "Pacific/Oceanic History" in {{cite book, editor=Kelly Boyd , title=Encyclopedia of Historians and Historical Writing vol 2, url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0121vD9STIMC&pg=PA901, year=1999, publisher=Taylor & Francis, pages=901–02, isbn=978-1-884964-33-6
Primary sources
* Lamb, Jonathan, Vanessa Smith, and Nicholas Thomas, eds. ''Exploration and exchange: A South Seas anthology, 1680-1900'' (U of Chicago Press, 2000).Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the contine ...
History of the Pacific Ocean