Exhaust pipe on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 An exhaust system is used to guide reaction
An exhaust system is used to guide reaction
 An exhaust pipe must be carefully designed to carry toxic and/or noxious gases away from the users of the machine. Indoor generators and furnaces can quickly fill an enclosed space with poisonous exhaust gases such as
An exhaust pipe must be carefully designed to carry toxic and/or noxious gases away from the users of the machine. Indoor generators and furnaces can quickly fill an enclosed space with poisonous exhaust gases such as
 In most
In most
 In most production engines, the
In most production engines, the
 With trucks, sometimes the silencer is crossways under the front of the cab and its tailpipe blows sideways to the offside (right side if
With trucks, sometimes the silencer is crossways under the front of the cab and its tailpipe blows sideways to the offside (right side if
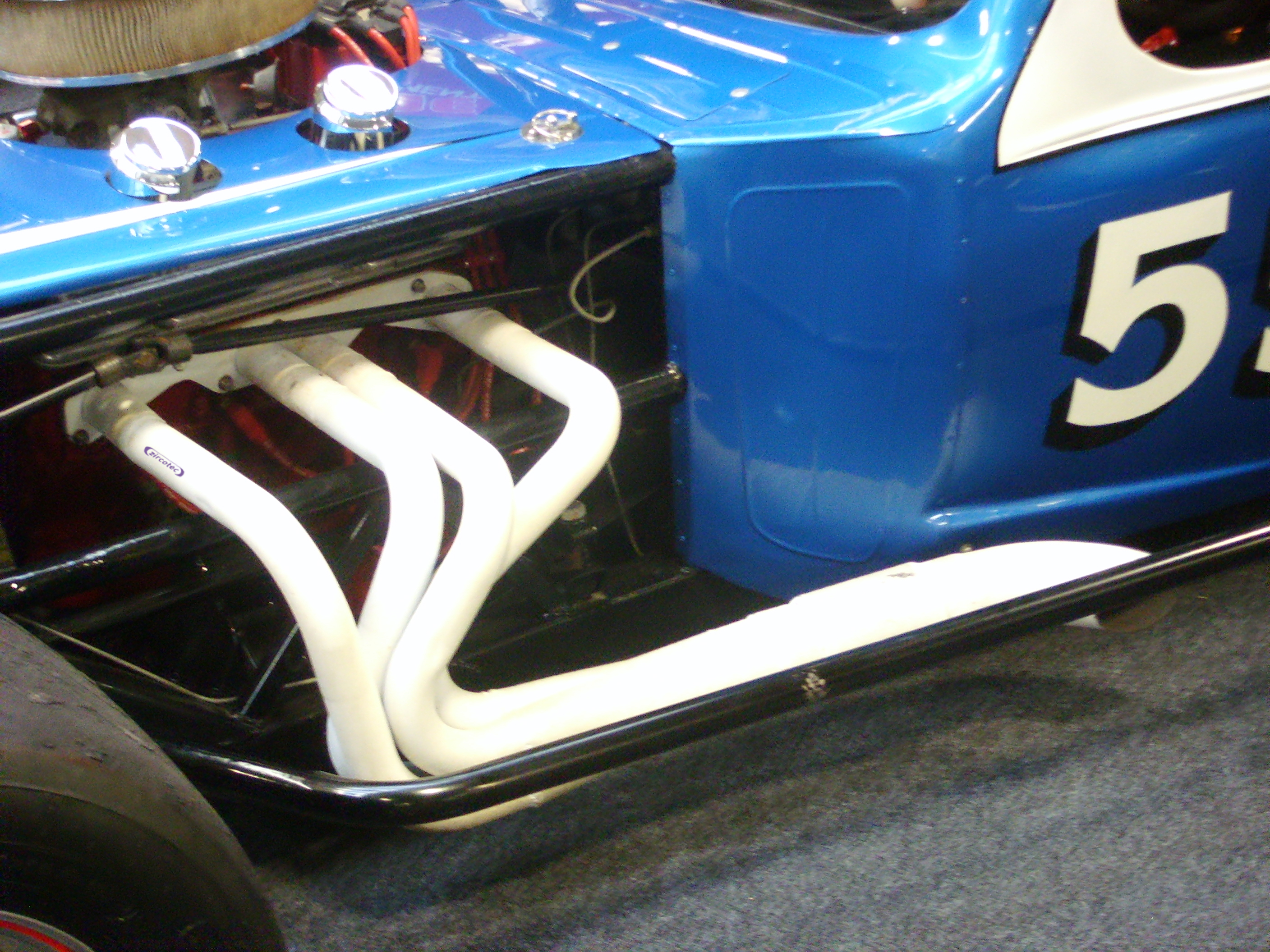 Aftermarket exhaust parts can increase peak power by reducing the back pressure of the exhaust system. These parts sometimes can void factory warranties, however the European Union ''Block Exemption Regulations 1400/2002'' prevents manufacturers from rejecting warranty claims if the aftermarket parts are of matching quality and specifications to the original parts.
Many automotive companies offer aftermarket exhaust system upgrades as a subcategory of
Aftermarket exhaust parts can increase peak power by reducing the back pressure of the exhaust system. These parts sometimes can void factory warranties, however the European Union ''Block Exemption Regulations 1400/2002'' prevents manufacturers from rejecting warranty claims if the aftermarket parts are of matching quality and specifications to the original parts.
Many automotive companies offer aftermarket exhaust system upgrades as a subcategory of
Image:Aa brrrmpipe2.jpg, Large truck's diesel exhaust pipe
Image:Aa brrrmpipe.jpg, Waste collection vehicle's diesel exhaust pipe
Image:Exhaust pipe muffler.JPG, Dual exhaust pipes attached to a car's muffler
File:Aa longreachforklist exhpipe.jpg, Exhaust system of diesel telescopic-arm vehicle
File:2010 FPV GT (FG) Boss 335 sedan (2010-10-16) 05.jpg, Underbody of a car showing the exhaust system

 An exhaust system is used to guide reaction
An exhaust system is used to guide reaction exhaust gas
Exhaust gas or flue gas is emitted as a result of the combustion of fuels such as natural gas, gasoline (petrol), diesel fuel, fuel oil, biodiesel blends, or coal. According to the type of engine, it is discharged into the atmosphere through an ...
es away from a controlled combustion
Combustion, or burning, is a high-temperature exothermic redox chemical reaction between a fuel (the reductant) and an oxidant, usually atmospheric oxygen, that produces oxidized, often gaseous products, in a mixture termed as smoke. Combus ...
inside an engine
An engine or motor is a machine designed to convert one or more forms of energy into mechanical energy.
Available energy sources include potential energy (e.g. energy of the Earth's gravitational field as exploited in hydroelectric power ...
or stove
A stove or range is a device that burns fuel or uses electricity to generate heat inside or on top of the apparatus, to be used for general warming or cooking. It has evolved highly over time, with cast-iron and induction versions being develope ...
. The entire system conveys burnt gases from the engine and includes one or more exhaust pipes. Depending on the overall system design, the exhaust gas may flow through one or more of:
*Cylinder head
In an internal combustion engine, the cylinder head (often abbreviated to simply "head") sits above the cylinders and forms the roof of the combustion chamber.
In sidevalve engines, the head is a simple sheet of metal; whereas in more modern o ...
and exhaust manifold
In automotive engineering, an exhaust manifold collects the exhaust gases from multiple cylinders into one pipe. The word '' manifold'' comes from the Old English word ''manigfeald'' (from the Anglo-Saxon ''manig'' anyand ''feald'' old and ref ...
*A turbocharger
In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger (often called a turbo) is a forced induction device that is powered by the flow of exhaust gases. It uses this energy to compress the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to pro ...
to increase engine power.
*A catalytic converter
A catalytic converter is an exhaust emission control device that converts toxic gases and pollutants in exhaust gas from an internal combustion engine into less-toxic pollutants by catalyzing a redox reaction. Catalytic converters are usual ...
to reduce air pollution
Air pollution is the contamination of air due to the presence of substances in the atmosphere that are harmful to the health of humans and other living beings, or cause damage to the climate or to materials. There are many different type ...
.
*A muffler (North America) / silencer (UK/India), to reduce noise
Noise is unwanted sound considered unpleasant, loud or disruptive to hearing. From a physics standpoint, there is no distinction between noise and desired sound, as both are vibrations through a medium, such as air or water. The difference aris ...
.
Design criteria
 An exhaust pipe must be carefully designed to carry toxic and/or noxious gases away from the users of the machine. Indoor generators and furnaces can quickly fill an enclosed space with poisonous exhaust gases such as
An exhaust pipe must be carefully designed to carry toxic and/or noxious gases away from the users of the machine. Indoor generators and furnaces can quickly fill an enclosed space with poisonous exhaust gases such as hydrocarbons
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and hydrophobic, and their odors are usually weak or ...
, carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide ( chemical formula CO) is a colorless, poisonous, odorless, tasteless, flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the simpl ...
and nitrogen oxides Nitrogen oxide may refer to a binary compound of oxygen and nitrogen, or a mixture of such compounds:
Charge-neutral
*Nitric oxide (NO), nitrogen(II) oxide, or nitrogen monoxide
*Nitrogen dioxide (), nitrogen(IV) oxide
* Nitrogen trioxide (), or ...
, if they are not properly vented to the outdoors. Also, the gases from most types of machines are very hot; the pipe must be heat-resistant, and it must not pass through or near anything that can burn or can be damaged by heat. A chimney
A chimney is an architectural ventilation structure made of masonry, clay or metal that isolates hot toxic exhaust gases or smoke produced by a boiler, stove, furnace, incinerator, or fireplace from human living areas. Chimneys are typ ...
serves as an exhaust pipe in a stationary structure. For the internal combustion engine
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal co ...
it is important to have the exhaust system "tuned" (refer to tuned exhaust
In an internal combustion engine, the geometry of the exhaust system can be optimised ("tuned") to maximise the power output of the engine. Tuned exhausts are designed so that reflected pressure waves arrive at the exhaust port at a particular t ...
) for optimal efficiency. Also, this should meet the regulation norms maintained in each country. In China, China 5; In European countries, EURO 5; In India, BS-4, etc.,
Motorcycles
 In most
In most motorcycle
A motorcycle (motorbike, bike, or trike (if three-wheeled)) is a two or three-wheeled motor vehicle Steering, steered by a Motorcycle handlebar, handlebar. Motorcycle design varies greatly to suit a range of different purposes: Long-distance ...
s all or most of the exhaust system is visible and may be chrome plate
Chrome plating (less commonly chromium plating) is a technique of electroplating a thin layer of chromium onto a metal object. A chrome-plated item is called ''chrome''. The chromed layer can be decorative, provide corrosion resistance, ease ...
d as a display feature. Aftermarket exhausts may be made from steel, aluminium, titanium, or carbon fiber.
Motorcycle exhausts come in many varieties depending on the type of engine and its intended use. A twin-cylinder bike may have independent exhaust sections, as seen in the Kawasaki EX250 (also known as the Ninja 250
The Kawasaki Ninja 250R (codenamed EX250; previous generations had market-specific names) is a motorcycle in the Ninja sport bike series from the Japanese manufacturer Kawasaki originally introduced in 1986. As the marque's entry-level sport b ...
in the US, or the GPX 250), or a single exhaust section known as a two-into-one (2-1). 4 cylinder machines, super-sport bikes like Kawasaki's ZX series, Honda
is a Japanese public multinational conglomerate manufacturer of automobiles, motorcycles, and power equipment, headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan.
Honda has been the world's largest motorcycle manufacturer since 1959, reaching a producti ...
's CBR series, Yamaha's YZF series, latterly titled R6 and R1, and Suzuki
is a Japanese multinational corporation headquartered in Minami-ku, Hamamatsu, Japan. Suzuki manufactures automobiles, motorcycles, all-terrain vehicles (ATVs), outboard marine engines, wheelchairs and a variety of other small internal co ...
's GSX-R, often have a twin exhaust system. A "full system" may be bought as an aftermarket accessory, also called a 4-2-1 or 4–1, depending on its layout. In the past, these bikes would come as standard with a single exhaust muffler, a practice that lasted until the early 2000s, when EU noise and pollution regulations mostly stopped this practice, forcing companies to use other methods to increase the performance of the motorcycle.
Trucks
In manytruck
A truck or lorry is a motor vehicle designed to transport cargo, carry specialized payloads, or perform other utilitarian work. Trucks vary greatly in size, power, and configuration, but the vast majority feature body-on-frame constructi ...
s / lorries all or most of the exhaust system is visible, often with a vertical exhaust pipe. Often in such trucks, the silencer is surrounded by a perforated metal sheath to avoid people getting burnt from touching the hot silencer. This sheath may be chrome plate
Chrome plating (less commonly chromium plating) is a technique of electroplating a thin layer of chromium onto a metal object. A chrome-plated item is called ''chrome''. The chromed layer can be decorative, provide corrosion resistance, ease ...
d as a display feature.
Part of the pipe between the engine and the silencer is often flexible metal industrial ducting, which helps to avoid vibration from the engine being transferred into the exhaust system. Sometimes a large diesel exhaust
Diesel exhaust is the gaseous exhaust produced by a diesel type of internal combustion engine, plus any contained particulates. Its composition may vary with the fuel type or rate of consumption, or speed of engine operation (e.g., idling or at ...
pipe is vertical, to blow the hot noxious gas well away from people; in such cases, the end of the exhaust pipe often has a hinged metal flap to stop debris, birds, and rainwater from falling inside.
In former times, exhaust systems of truck
A truck or lorry is a motor vehicle designed to transport cargo, carry specialized payloads, or perform other utilitarian work. Trucks vary greatly in size, power, and configuration, but the vast majority feature body-on-frame constructi ...
s / lorries in Britain were usually out of sight underneath the chassis.
Two-stroke engines
In atwo-stroke engine
A two-stroke (or two-stroke cycle) engine is a type of internal combustion engine that completes a power cycle with two strokes (up and down movements) of the piston during one power cycle, this power cycle being completed in one revolution of ...
, such as that used on dirt bike
The six main types of motorcycles are generally recognized as ''standard'', ''cruiser'', ''touring'', ''sports'', ''off-road'', and ''dual-purpose''. ''Sport touring'' is sometimes recognized as a seventh category or integrated with the ''touring' ...
s, a bulge in the exhaust pipe known as an expansion chamber
On a two-stroke engine, an expansion chamber or tuned pipe is a tuned exhaust system used to enhance its power output by improving its volumetric efficiency.
History
Expansion chambers were invented and successfully manufactured by Limbach ...
uses the pressure of the exhaust to create a pump
A pump is a device that moves fluids (liquids or gases), or sometimes slurries, by mechanical action, typically converted from electrical energy into hydraulic energy. Pumps can be classified into three major groups according to the method they ...
that squeezes more air and fuel into the cylinder during the intake stroke. This provides greater power and fuel efficiency. See Kadenacy effect.
Marine engines
With an onboard diesel or petrol (gasoline) engine below-decks on marine vessels:- * Lagging the exhaust pipe stops it from overheating the engine room where people must work to service the engine. *Feeding water into the exhaust pipe cools the exhaust gas and thus lessens the back-pressure at the engine's cylinders. Often in marine service, the exhaust manifold is integral with a heat exchanger which allows seawater to cool a closed system of freshwater circulating within the engine.Outboard motors
Inoutboard motor
An outboard motor is a propulsion system for boats, consisting of a self-contained unit that includes engine, gearbox and propeller or jet drive, designed to be affixed to the outside of the transom. They are the most common motorised method ...
s the exhaust system is usually a vertical passage through the engine structure and to reduce out-of-water noise blows out underwater, sometimes through the middle of the propeller.
Terminology
Manifold or header
 In most production engines, the
In most production engines, the manifold
In mathematics, a manifold is a topological space that locally resembles Euclidean space near each point. More precisely, an n-dimensional manifold, or ''n-manifold'' for short, is a topological space with the property that each point has a n ...
is an assembly designed to collect the exhaust gas from two or more cylinders into one pipe. Manifolds are often made of cast iron
Cast iron is a class of iron– carbon alloys with a carbon content more than 2%. Its usefulness derives from its relatively low melting temperature. The alloy constituents affect its color when fractured: white cast iron has carbide impuri ...
in stock production cars and may have material-saving design features such as using the least metal, to occupy the least space necessary, or have the lowest production cost. These design restrictions often result in a design that is cost-effective but that does not do the most efficient job of venting the gases from the engine. Inefficiencies generally occur due to the nature of the combustion engine and its cylinders. Since cylinders fire at different times, exhaust leaves them at different times, and pressure waves from gas emerging from one cylinder might not be completely vacated through the exhaust system when another comes. This creates back pressure and restriction in the engine's exhaust system that can restrict the engine's true performance possibilities.
Regardless of the negative attributes of steel tube exhaust outlet configurations, engineers who design engine components choose conventional cast iron exhaust manifolds list positive attributes, such as an array of heat management properties and superior longevity to any other type of exhaust outlet design.
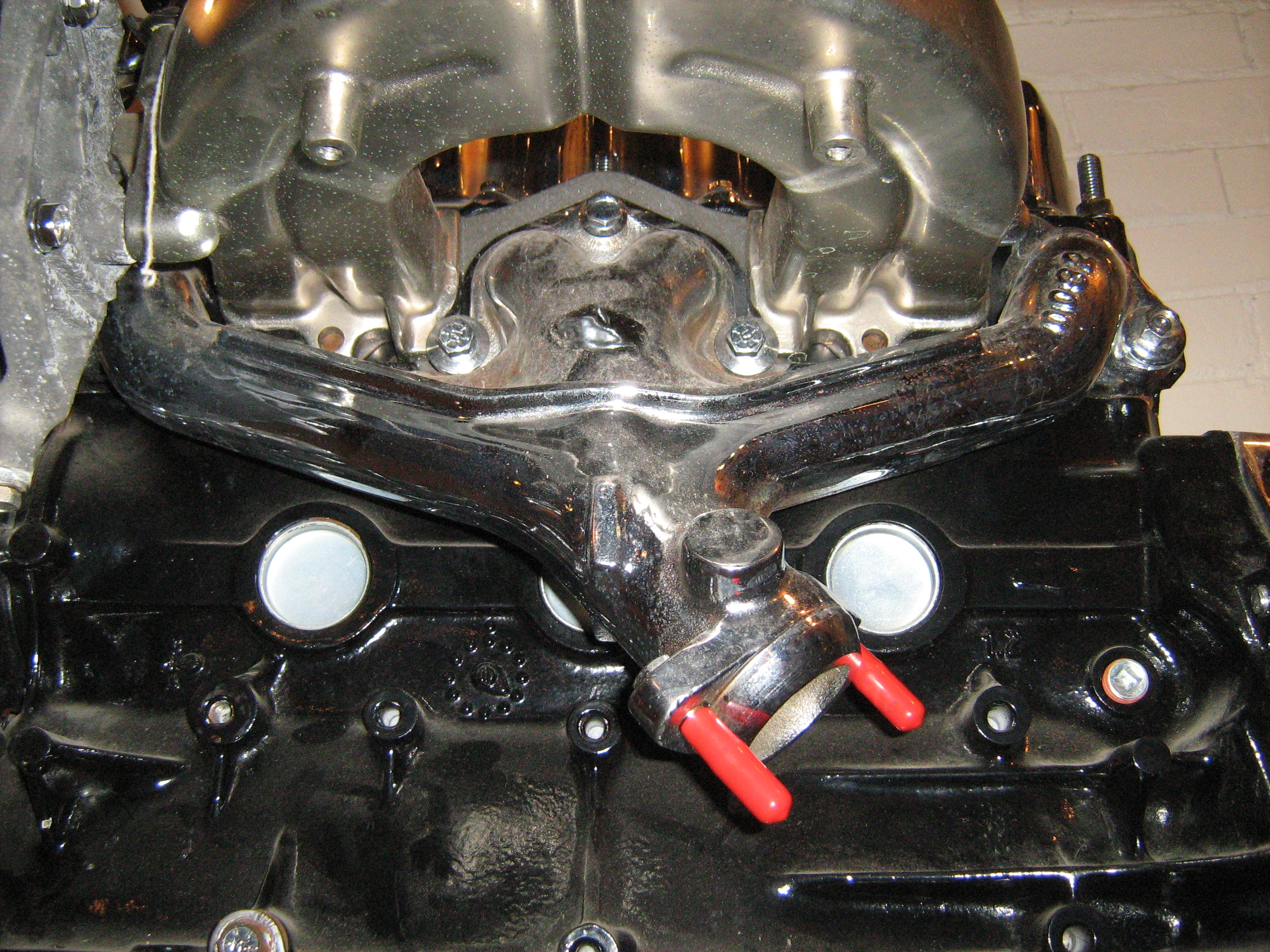
A header is a manifold specifically designed for performance. During design, engineers create a manifold without regard to weight or cost but instead for optimal flow of the exhaust gases. This design results in a header that is more efficient at scavenging the exhaust from the cylinders. Headers are generally circular steel tubing with bends and folds calculated to make the paths from each cylinder's exhaust port to the common outlet all equal length and joined at narrow angles to encourage pressure waves to flow through the outlet, not back towards other cylinders. In a set of tuned headers the pipe lengths are carefully calculated to enhance exhaust flow in a particular engine revolutions per minute
Revolutions per minute (abbreviated rpm, RPM, rev/min, r/min, or with the notation min−1) is a unit of rotational speed or rotational frequency for rotating machines.
Standards
ISO 80000-3:2019 defines a unit of rotation as the dimensio ...
range.
A common method of increasing the power output of an engine is the use of upgraded headers. The increased power output is often due to a result of a larger cross-section area of the pipes (reducing the resistance on the exhaust gasses) and/or designing the pipe lengths so that the pressure wave assists in exhaust scavenging. For inline-four engine
A straight-four engine (also called an inline-four) is a four-cylinder piston engine where cylinders are arranged in a line along a common crankshaft.
The vast majority of automotive four-cylinder engines use a straight-four layout (with the ...
s and V8 engine
A V8 engine is an eight-cylinder piston engine in which two banks of four cylinders share a common crankshaft and are arranged in a V configuration.
The first V8 engine was produced by the French Antoinette company in 1904, developed and u ...
s, exhaust manifolds are usually either a 4-2-1 design (where the four pipes merge into two, followed by a separate merge of these two pipes into one) or a 4-1 design (where the four pipes directly merge into one).
Headers are generally made by aftermarket automotive companies, but sometimes can be bought from the high-performance parts department at car dealerships
A car dealership, or car dealer, is a business that sells new or used cars, at the retail level, based on a dealership contract with an automaker or its sales subsidiary. Car dealerships also often sell spare parts and automotive mainte ...
. Generally, most car performance enthusiasts buy aftermarket headers made by companies solely focused on producing reliable, cost-effective well-designed headers specifically for their cars. Headers can also be custom designed by a custom shop. Due to the advanced materials that some aftermarket headers are made of, this can be expensive. Luckily, an exhaust system can be custom-built for any car, and generally is not specific to the car's motor or design except for needing to properly connect solidly to the engine. This is usually accomplished by correct sizing in the design stage, and selecting a proper gasket type and size for the engine.
Catalytic converter
Some systems (referred to as catless or de-cat systems) eliminate the catalytic converter. It is a U.S. legal requirement to have a catalytic converter. Converters may not be removed from a vehicle that is used only for "off-road" driving in the United States. The main purpose of a catalytic converter on an automobile is to reduce harmful emissions of hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen oxides into the atmosphere. They work by transforming the polluted exhaust components into water and carbon dioxide. There is a light-off temperature from which catalytic converters start to be efficient and work properly. Catalytic converters can cause back pressure if they are not designed for the required flow rate or if they are clogged. In these situations, upgrading or removal of the catalytic converter can increase power at high revs. However, the catalytic converter is a key component of the vehicle's emission control systems, therefore a non-standard product can cause a vehicle to be unroadworthy.Piping
The piping that connects all of the individual components of the exhaust system is called the exhaust pipe. If the diameter is too small, power at high RPM will be reduced. Too large a diameter can reduce torque at low RPM and can cause the exhaust to sit lower to the ground, increasing the risk of it being hit and damaged while the car is moving. On cars with two sets of exhaust pipes, a crossover pipe is often used to connect the two pipes. Common designs of crossover pipes are a perpendicular pipe ('H-pipe', due to their shape) or angled pipes that slowly merge and separate ('X-pipe').Muffler
Original equipment mufflers typically reduces the noise level from the tailpipe by bouncing sound waves off of the back, front, and sides of the muffler. They are designed to meet the maximum allowable noise level required by government regulations, however, some original equipment mufflers are a significant source of backpressure. Glasspack mufflers (also called 'cannons' or 'hotdogs') are straight-through design mufflers that consist of an inner perforated tube, an outer solid tube, and fibreglass sound insulation between the two tubes. They often have less back pressure than original equipment mufflers, but are relatively ineffective at reducing sound levels. Another common type of muffler is the chambered muffler, which consists of a series of concentric or eccentric pipes inside the expansion chamber cavity. These pipes allow sound to travel into them and cause the sound waves to bounce off the closed, flat, ends of the pipe. These reflections partially cancel each other out, reducing the sound level. Resonators are sections of pipe that expand to a larger diameter and allow the sound waves to reflect off the walls and cancel out, therefore reducing the noise level. Resonators can be used inside mufflers, or also as separate components in an exhaust system.Tailpipe and exhaust
 With trucks, sometimes the silencer is crossways under the front of the cab and its tailpipe blows sideways to the offside (right side if
With trucks, sometimes the silencer is crossways under the front of the cab and its tailpipe blows sideways to the offside (right side if driving on the left
Left-hand traffic (LHT) and right-hand traffic (RHT) are the practices, in bidirectional traffic, of keeping to the left side or to the right side of the road, respectively. They are fundamental to traffic flow, and are sometimes referred to ...
, left side if driving on the right
Left-hand traffic (LHT) and right-hand traffic (RHT) are the practices, in bidirectional traffic, of keeping to the left side or to the right side of the road, respectively. They are fundamental to traffic flow, and are sometimes referred to ...
). The side of a passenger car on which the exhaust exits beneath the rear bumper usually indicates the market for which the vehicle was designed, i.e. Japanese (and some older British) vehicles have exhausts on the right so they are furthest from the curb in countries which drive on the left, while European vehicles have exhausts on the left.
The end of the final length of exhaust pipe where it vents to open air, generally the only visible part of the exhaust system part on a vehicle, often ends with just a straight or angled cut, but may include a fancy tip. The tip is sometimes chromed. It is often of larger pipe than the rest of the exhaust system. This produces a final reduction in pressure and is sometimes used to enhance the appearance of the car.
In the late 1950s in the United States manufacturers had a fashion in car styling to form the rear bumper with a hole at each end through which the exhaust would pass. Two outlets symbolized V-8 power, and only the most expensive cars (Cadillac, Lincoln, Imperial, Packard) were fitted with this design. One justification for this was that luxury cars in those days had such a long rear overhang that the exhaust pipe scraped the ground when the car traversed ramps. The fashion disappeared after customers noted that the rear end of the car is a low-pressure area that collected soot from the exhaust and its acidic content ate into the chrome-plated rear bumper.
When a bus, truck
A truck or lorry is a motor vehicle designed to transport cargo, carry specialized payloads, or perform other utilitarian work. Trucks vary greatly in size, power, and configuration, but the vast majority feature body-on-frame constructi ...
or tractor
A tractor is an engineering vehicle specifically designed to deliver a high tractive effort (or torque) at slow speeds, for the purposes of hauling a trailer or machinery such as that used in agriculture, mining or construction. Most commo ...
or excavator
Excavators are heavy construction equipment consisting of a boom, dipper (or stick), bucket and cab on a rotating platform known as the "house". The house sits atop an undercarriage with tracks or wheels. They are a natural progression fr ...
has a vertical exhaust pipe (called stacks or pipes behind the cab), sometimes the end is curved, or has a hinged cover flap which the gas flow blows out of the way, to try to prevent foreign objects (including turds from a bird perching on the exhaust pipe when the vehicle is not being used) getting inside the exhaust pipe.
In some trucks, when the silencer (muffler) is front-to-back under the chassis, the end of the tailpipe turns 90° and blows downwards. That protects anyone near a stationary truck from getting a direct blast of the exhaust gas, but often raises dust when the truck is driving on a dry dusty unmade surface such as on a building site
Construction is a general term meaning the art and science to form objects, systems, or organizations,"Construction" def. 1.a. 1.b. and 1.c. ''Oxford English Dictionary'' Second Edition on CD-ROM (v. 4.0) Oxford University Press 2009 and co ...
.
Lake pipes
A consequence of the problematic nature in the adaptation of large-diameter exhaust tubing to the undercarriage of ladder-frame orbody-on-frame
Body-on-frame, also known as ladder frame construction, is a common motor vehicle construction method, whereby a separate body or coach is mounted on a strong and relatively rigid vehicle frame or chassis that carries the powertrain (the en ...
chassis
A chassis (, ; plural ''chassis'' from French châssis ) is the load-bearing framework of an artificial object, which structurally supports the object in its construction and function. An example of a chassis is a vehicle frame, the underpar ...
architecture vehicles with altered geometry suspensions, lake pipes evolved to become a front-engined vehicle exhaust archetype crafted by specialty motorsport engine specialists of the 1930s, 1940s, and 1950s, whose focus was the optimization of the acoustic effect associated with high-output internal combustion engines. The name is derived from their use on the vast, empty dry lake beds
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much larger ...
northeast of Los Angeles County
Los Angeles County, officially the County of Los Angeles, and sometimes abbreviated as L.A. County, is the List of the most populous counties in the United States, most populous county in the United States and in the U.S. state of California, ...
, where engine specialists custom-crafted, interchanged, and evaluated one-piece header manifolds of various mil thicknesses, a function of temperature, humidity, elevation and climate they anticipated.
No intrinsic performance gain to be derived, ''per se'', lake pipes evolved a function of practicality. In common instances, their manifolds routed straight out the front wheel wells posing an asphyxiation risk to the race driver, "lake pipes" were fashioned, extending from the header flange along the rocker panels, bottom side of the vehicle, beneath the doors, thus allowing (1) suspension tuners a lower ride height sufficient for land speed record attempts, and (2) engine tuners ease and flexibility of interchanging different exhaust manifolds without hoisting the vehicle, thus precluding having to wrench undercarriage of the vehicle.
Body-on-frame chassis architecture ceding to superleggera
Superleggera (Italian for ''Superlight'') is a custom tube and alloy panel automobile coachwork construction technology developed by Felice Bianchi Anderloni of Italian coachbuilder Carrozzeria Touring Superleggera. A separate chassis was st ...
, unit-body and monocoque
Monocoque ( ), also called structural skin, is a structural system in which loads are supported by an object's external skin, in a manner similar to an egg shell. The word ''monocoque'' is a French term for "single shell".
First used for boats, ...
archetypes, in tandem with smog abatement legislation rendered lake pipes obsolete as a performance option. No meaningful performance gain to be had for contemporary vehicles, lake pipes are aesthetic accessories that are usually chrome-plated. Some allow the driver to control whether the exhaust gas is routed to the standard exhaust system, or through the lake pipes. Some are equipped with laker caps which, affixed by fasteners at the terminal end of exhaust tips, serve to (1) "cap" the exhaust system when not in use, and/or (2) indicate that the presence of lake pipes is merely cosmetic.
Header-back
The Header-back (or header back) is the part of the exhaust system from the outlet of the header to the final vent to open air — everything from the header back. Header-back systems are generally produced as aftermarket performance systems for cars withoutturbocharger
In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger (often called a turbo) is a forced induction device that is powered by the flow of exhaust gases. It uses this energy to compress the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to pro ...
s.
Turbo-back
The Turbo-back (or turbo back) is the part of the exhaust system from the outlet of a turbocharger to the final vent to open air. Turbo-back systems are generally produced as aftermarket performance systems for cars with turbochargers. Some turbo-back (and header-back) systems replace stock catalytic converters with others having less flow restriction.Cat-back
Cat-back (also cat back and catback) refers to the portion of the exhaust system from the outlet of thecatalytic converter
A catalytic converter is an exhaust emission control device that converts toxic gases and pollutants in exhaust gas from an internal combustion engine into less-toxic pollutants by catalyzing a redox reaction. Catalytic converters are usual ...
to the final vent to open air. This generally includes the pipe from the converter to the muffler, the muffler, and the final length of pipe to open air.
Cat-back exhaust systems generally use larger diameter pipes than the stock system. The mufflers included in these kits are often glasspack
A glasspack is a type of automobile muffler in which the exhaust gas passes straight through the center of the muffler. The basic design consists of one smaller tube centered inside of a larger outer tube that is enlarged or swollen in the middle ...
s, to reduce backpressure. If the system is engineered more for show than functionality, it may be tuned to enhance the lower sounds that are lacking from high-RPM low- displacement engines.
Exhaust system tuning
 Aftermarket exhaust parts can increase peak power by reducing the back pressure of the exhaust system. These parts sometimes can void factory warranties, however the European Union ''Block Exemption Regulations 1400/2002'' prevents manufacturers from rejecting warranty claims if the aftermarket parts are of matching quality and specifications to the original parts.
Many automotive companies offer aftermarket exhaust system upgrades as a subcategory of
Aftermarket exhaust parts can increase peak power by reducing the back pressure of the exhaust system. These parts sometimes can void factory warranties, however the European Union ''Block Exemption Regulations 1400/2002'' prevents manufacturers from rejecting warranty claims if the aftermarket parts are of matching quality and specifications to the original parts.
Many automotive companies offer aftermarket exhaust system upgrades as a subcategory of engine tuning
Engine tuning is the adjustment or modification of the internal combustion engine or Engine Control Unit (ECU) to yield optimal performance and increase the engine's power output, economy, or durability. These goals may be mutually exclusive; ...
. This is often fairly expensive as it usually includes replacing the entire exhaust manifold
In automotive engineering, an exhaust manifold collects the exhaust gases from multiple cylinders into one pipe. The word '' manifold'' comes from the Old English word ''manigfeald'' (from the Anglo-Saxon ''manig'' anyand ''feald'' old and ref ...
or other large components. These upgrades however can significantly improve engine performance by reducing the exhaust back pressure and by reducing the amount of heat from the exhaust being lost into the underbonnet area. This reduces the underbonnet temperature and consequently lowers the intake manifold temperature, increasing power. This also has a positive side effect of preventing heat-sensitive components from being damaged.
Backpressure is most commonly reduced by replacing exhaust manifolds with headers, which have smoother bends and normally wider pipe diameters.
Exhaust heat management helps in reducing the amount of exhaust heat radiated out from the exhaust pipe and components. One dominant solution to aftermarket upgrades is the use of a ceramic coating applied via thermal spraying. This not only reduces heat loss and lessens back pressure, but also provides an effective way to protect the exhaust system from wear and tear, thermal degradation, and corrosion.
Images
See also
*Automobile emissions control
Vehicle emissions control is the study of reducing the emissions produced by motor vehicles, especially internal combustion engines.
Types of emissions
Emissions of many air pollutants have been shown to have variety of negative effects on pub ...
*Expansion chamber
On a two-stroke engine, an expansion chamber or tuned pipe is a tuned exhaust system used to enhance its power output by improving its volumetric efficiency.
History
Expansion chambers were invented and successfully manufactured by Limbach ...
* Exhaust note
* Motor vehicle emissions
* Nitrogen oxide sensor
*British Leyland Motor Corp v Armstrong Patents Co
''British Leyland Motor Corp. v Armstrong Patents Co.'' is a 1986 decision of the House of Lords concerning the doctrine of non-derogation from grants. This doctrine is comparable to, but somewhat broader than, the doctrine of legal estoppel, a ...
- litigation involving right to supply aftermarket exhaust systems
* Exhaust Heat Management
* Zircotec
References
External links
* {{Automotive engine , collapsed Engine components