European Free Trade Area on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
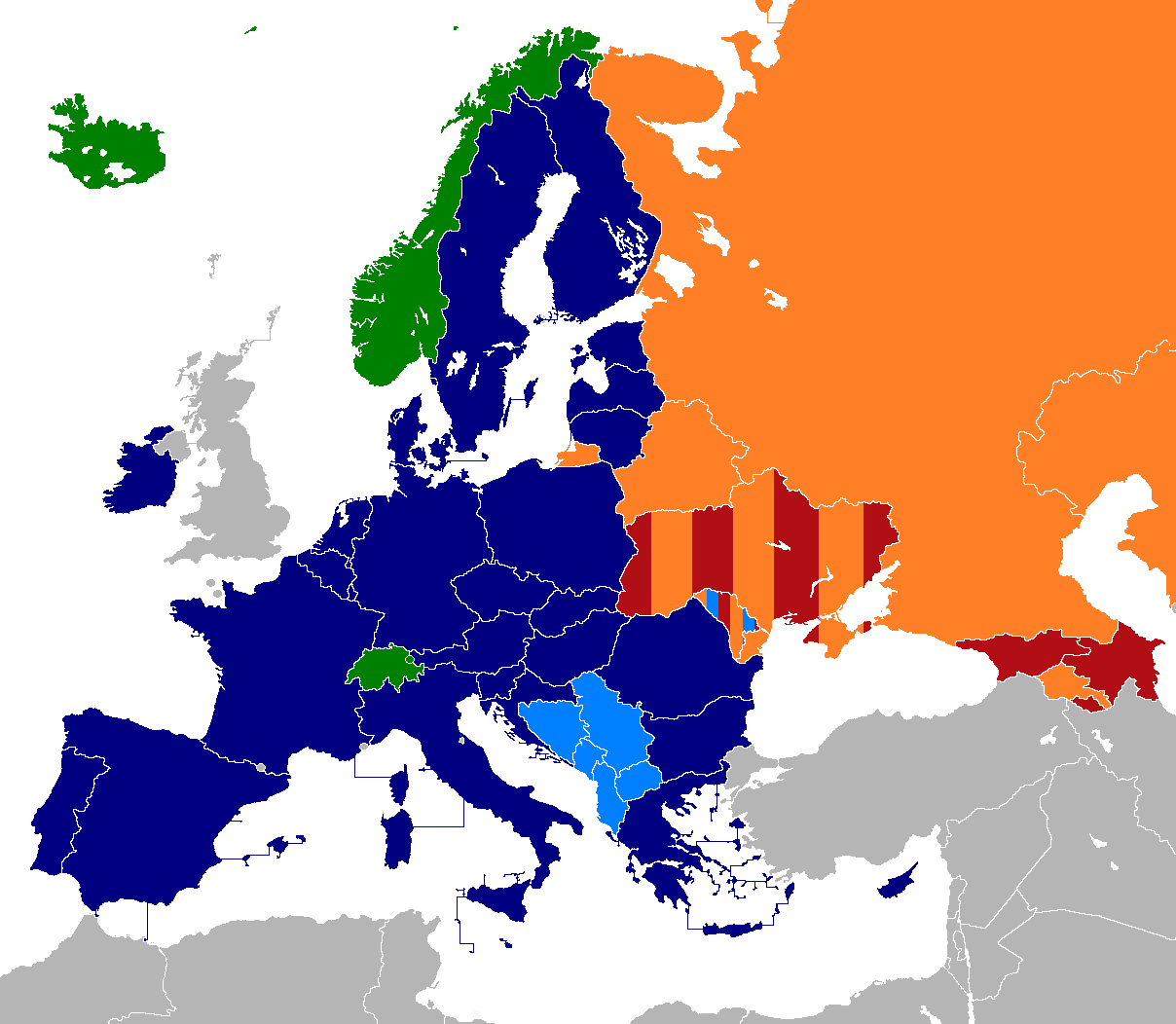
 At present, there are four multi-lateral
At present, there are four multi-lateral
 The
The
 The
The
 The GUAM Organization for Democracy and Economic Development is a
The GUAM Organization for Democracy and Economic Development is a
 The Baltic Free Trade Area was a
The Baltic Free Trade Area was a Baltic regional co-operation, Iivi Zájedová
, Slovenská politologická revue

 At present, there are four multi-lateral
At present, there are four multi-lateral free trade area
A free-trade area is the region encompassing a trade bloc whose member countries have signed a free trade agreement (FTA). Such agreements involve cooperation between at least two countries to reduce trade barriers, import quotas and tariffs, and ...
s in Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
, and one former free trade area in recent history. Note that there are also a number of bilateral free trade agreements
A free-trade agreement (FTA) or treaty is an agreement according to international law to form a free-trade area between the cooperating states. There are two types of trade agreements: bilateral and multilateral. Bilateral trade agreements occu ...
between states and between trade blocks; and that some states participate in more than one free trade area.
EU
The European Union (EU) has always operated as more than a free trade area with its predecessor, theEuropean Economic Community
The European Economic Community (EEC) was a regional organization created by the Treaty of Rome of 1957,Today the largely rewritten treaty continues in force as the ''Treaty on the functioning of the European Union'', as renamed by the Lis ...
(EEC) being founded as a customs union
A customs union is generally defined as a type of trade bloc which is composed of a free trade area with a common external tariff.GATTArticle 24 s. 8 (a)
Customs unions are established through trade pacts where the participant countries set up ...
. The EU has free trade agreements to varying levels with most other European countries.
;EU Single Market
The EU shares its single market with three EFTA members via the European Economic Area
The European Economic Area (EEA) was established via the ''Agreement on the European Economic Area'', an international agreement which enables the extension of the European Union's single market to member states of the European Free Trade As ...
agreement, and the remaining EFTA member—Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel ...
—via bilateral agreements.
;EU Customs Union
The European Union Customs Union
The European Union Customs Union (EUCU), formally known as the Community Customs Union, is a customs union which consists of all the member states of the European Union (EU), Monaco, and the British Overseas Territory of Akrotiri and Dhekel ...
is a customs union
A customs union is generally defined as a type of trade bloc which is composed of a free trade area with a common external tariff.GATTArticle 24 s. 8 (a)
Customs unions are established through trade pacts where the participant countries set up ...
which consists of all the member states of the European Union and Turkey, San Marino, Monaco, Andorra and the UK territory of Akrotiri and Dhekelia
Akrotiri and Dhekelia, officially the Sovereign Base Areas of Akrotiri and Dhekelia (SBA),, ''Periochés Kyríarchon Váseon Akrotiríou ke Dekélias''; tr, Ağrotur ve Dikelya İngiliz Egemen Üs Bölgeleri is a British Overseas Territory o ...
which are outside of the EU. In addition to allowing for free trade between states, the customs union imposes a common external tariff on all goods entering the area.
EFTA
European Free Trade Association
The European Free Trade Association (EFTA) is a regional trade organization and free trade area consisting of four European states: Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway and Switzerland. The organization operates in parallel with the European U ...
(EFTA) was created in 1960 by the outer seven (as a looser alternative to the then-European Communities
The European Communities (EC) were three international organizations that were governed by the same set of institutions. These were the European Coal and Steel Community (ECSC), the European Atomic Energy Community (EAEC or Euratom), and the ...
) but most of its membership has since joined the Communities/EU leaving only four countries (Iceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its ...
, Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of ...
, Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel ...
and Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein (), officially the Principality of Liechtenstein (german: link=no, Fürstentum Liechtenstein), is a German language, German-speaking microstate located in the Alps between Austria and Switzerland. Liechtenstein is a semi-constit ...
) still party to the treaty. The United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and ...
is the only former EFTA member which is not currently part of the EU, following its withdrawal in 2020.
CEFTA
Following the fall of the Iron Curtain, two free trade areas were created inCentral Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern Europe, based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. The Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) between Catholicism and Protestantism significantly shaped the a ...
, the Baltic Free Trade Area (BAFTA) and the Central European Free Trade Agreement
The Central European Free Trade Agreement (CEFTA) is an international trade agreement between countries mostly located in Southeastern Europe. Founded by representatives of Poland, Hungary and Czechoslovakia, CEFTA expanded to Albania, Bosnia ...
(CEFTA), in order to stabilise these countries for membership of the EU. With the 2004 EU enlargement, the original members of both of these have left these agreements and joined the EU.
CEFTA has expanded into southern Europe with members from the Western Balkans and Moldova
Moldova ( , ; ), officially the Republic of Moldova ( ro, Republica Moldova), is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Romania to the west and Ukraine to the north, east, and south. The unrecognised state of Transnistri ...
. All of the new CEFTA countries, except for Moldova, are prospective members of the EU and hence EFTA is the only free trade area with a long-term future, as there are no immediate plans for these countries to change their present status. However, CEFTA may gain new members in the form of countries neighbouring the present EU.
CISFTA
Commonwealth of Independent States
The Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) is a regional intergovernmental organization in Eurasia. It was formed following the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. It covers an area of and has an estimated population of 239,796,010 ...
had been negotiating a CIS free trade area since 1994 and in 2011 eight countries agreed to create a free trade area. These are; Russia, Ukraine, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Armenia and Moldova. In addition, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Russia, Armenia, and Kyrgyzstan form the Eurasian Economic Union, including a customs union and a single market.
GUAM
 The GUAM Organization for Democracy and Economic Development is a
The GUAM Organization for Democracy and Economic Development is a regional organization
Regional organizations (ROs) are, in a sense, international organizations (IOs), as they incorporate international membership and encompass geopolitical entities that operationally transcend a single nation state. However, their membership is c ...
and free-trade area in Eastern Europe composed of Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
, Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of th ...
, Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inva ...
, and Moldova
Moldova ( , ; ), officially the Republic of Moldova ( ro, Republica Moldova), is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Romania to the west and Ukraine to the north, east, and south. The unrecognised state of Transnistri ...
.
Historical
BAFTA
free trade agreement
A free-trade agreement (FTA) or treaty is an agreement according to international law to form a free-trade area between the cooperating states. There are two types of trade agreements: bilateral and multilateral. Bilateral trade agreements occ ...
between Estonia
Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, an ...
, Latvia
Latvia ( or ; lv, Latvija ; ltg, Latveja; liv, Leţmō), officially the Republic of Latvia ( lv, Latvijas Republika, links=no, ltg, Latvejas Republika, links=no, liv, Leţmō Vabāmō, links=no), is a country in the Baltic region of ...
and Lithuania
Lithuania (; lt, Lietuva ), officially the Republic of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Respublika, links=no ), is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania ...
that existed between 1994 and 2004.
BAFTA was created to help prepare the countries for their accession to the EU. Hence, BAFTA was created more as an initiative of the EU than out of a desire for Baltic states
The Baltic states, et, Balti riigid or the Baltic countries is a geopolitical term, which currently is used to group three countries: Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. All three countries are members of NATO, the European Union, the Eurozone ...
to trade between themselves: they were more interested in gaining access to the rest of the Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
an markets.
BAFTA's agreement was signed by the three states on 13 September 1993 and came into force on 1 April 1994. On 1 January 1997 the agreement was extended to cover trade in agricultural
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled peopl ...
produce
Produce is a generalized term for many farm-produced crops, including fruits and vegetables ( grains, oats, etc. are also sometimes considered ''produce''). More specifically, the term ''produce'' often implies that the products are fres ...
. On 1 May 2004, all three states joined the European Union, and BAFTA ceased to exist.
BAFTA was part of general co-operation between the three countries under the Baltic Assembly—modelled on Nordic co-operation (see Nordic Council
The Nordic Council is the official body for formal inter-parliamentary Nordic cooperation among the Nordic countries. Formed in 1952, it has 87 representatives from Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden as well as from the autonomou ...
). As well as the free trade area, they formed a common visa area. Leaders continue to meet regularly, however the assembly now focuses on international issues, including economic development, and military co-operation due to the proximity of Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
., Slovenská politologická revue
See also
* List of free trade agreements *List of bilateral free trade agreements
A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to:
People
* List (surname)
Organizations
* List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America
* SC Germania List, German rugby unio ...
** European Union free trade agreements
The European Union has concluded free trade agreements (FTAs) and other agreements with a trade component with many countries worldwide and is negotiating with many others.
The European Union negotiates free trade deals on behalf of all of its ...
* Inner Six/Outer Seven
* Eurasian Economic Union
* European integration
European integration is the process of industrial, economic, political, legal, social, and cultural integration of states wholly or partially in Europe or nearby. European integration has primarily come about through the European Union and its ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Free Trade Areas In Europe Trade blocs History of the European UnionEurope
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...