Erythrocyte on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Red blood cells (RBCs), also referred to as red cells, red blood corpuscles (in humans or other animals not having nucleus in red blood cells), haematids, erythroid cells or erythrocytes (from
''Blood Groups and Red Cell Antigens''
/ref> Nearly half of the blood's volume ( 40% to 45%) is red blood cells.
 The vast majority of vertebrates, including mammals and humans, have red blood cells. Red blood cells are cells present in blood to transport oxygen. The only known vertebrates without red blood cells are the crocodile icefish (family
The vast majority of vertebrates, including mammals and humans, have red blood cells. Red blood cells are cells present in blood to transport oxygen. The only known vertebrates without red blood cells are the crocodile icefish (family
 The proteins of the membrane skeleton are responsible for the deformability, flexibility and durability of the red blood cell, enabling it to squeeze through capillaries less than half the diameter of the red blood cell (7–8 μm) and recovering the discoid shape as soon as these cells stop receiving compressive forces, in a similar fashion to an object made of rubber.
There are currently more than 50 known membrane proteins, which can exist in a few hundred up to a million copies per red blood cell. Approximately 25 of these membrane proteins carry the various blood group antigens, such as the A, B and Rh antigens, among many others. These membrane proteins can perform a wide diversity of functions, such as transporting ions and molecules across the red cell membrane, adhesion and interaction with other cells such as endothelial cells, as signaling receptors, as well as other currently unknown functions. The blood types of humans are due to variations in surface glycoproteins of red blood cells. Disorders of the proteins in these membranes are associated with many disorders, such as
The proteins of the membrane skeleton are responsible for the deformability, flexibility and durability of the red blood cell, enabling it to squeeze through capillaries less than half the diameter of the red blood cell (7–8 μm) and recovering the discoid shape as soon as these cells stop receiving compressive forces, in a similar fashion to an object made of rubber.
There are currently more than 50 known membrane proteins, which can exist in a few hundred up to a million copies per red blood cell. Approximately 25 of these membrane proteins carry the various blood group antigens, such as the A, B and Rh antigens, among many others. These membrane proteins can perform a wide diversity of functions, such as transporting ions and molecules across the red cell membrane, adhesion and interaction with other cells such as endothelial cells, as signaling receptors, as well as other currently unknown functions. The blood types of humans are due to variations in surface glycoproteins of red blood cells. Disorders of the proteins in these membranes are associated with many disorders, such as  Transport
*
Transport
*
HCOH + O2 -> CO2 + H2O
Thus, the function of the circulatory system is as much about the transport of carbon dioxide as about the transport of oxygen.
As stated elsewhere in this article, most of the carbon dioxide in the blood is in the form of bicarbonate ion. The bicarbonate provides a critical pH buffer. Thus, unlike hemoglobin for O2 transport, there is a physiological advantage to not having a specific CO2 transporter molecule.
Red blood cells, nevertheless, play a key role in the CO2 transport process, for two reasons.
First, because, besides hemoglobin, they contain a large number of copies of the enzyme carbonic anhydrase on the inside of their cell membrane. Carbonic anhydrase, as its name suggests, acts as a catalyst of the exchange between carbonic acid and carbon dioxide (which is the CO2 + H2O <=>> H2CO3 <=>> HCO3- + H+
The H+ ions released by this rapid reaction within RBC, while still in the capillary, act to reduce the oxygen binding affinity of hemoglobin, the Bohr effect.
The second major contribution of RBC to carbon dioxide transport is that carbon dioxide directly reacts with globin protein components of hemoglobin to form
 * Hemolysis is the general term for excessive breakdown of red blood cells. It can have several causes and can result in
* Hemolysis is the general term for excessive breakdown of red blood cells. It can have several causes and can result in
 Several blood tests involve red blood cells. These include a ''RBC count'' (the number of red blood cells per volume of blood), calculation of the
Several blood tests involve red blood cells. These include a ''RBC count'' (the number of red blood cells per volume of blood), calculation of the
''Blood Groups and Red Cell Antigens''
by Laura Dean. Searchable and downloadable online textbook in the public domain.
Database of vertebrate erythrocyte sizes
Red Gold
Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
''erythros'' for "red" and ''kytos'' for "hollow vessel", with ''-cyte'' translated as "cell" in modern usage), are the most common type of blood cell and the vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () (chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, with c ...
's principal means of delivering oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as ...
(O2) to the body tissues—via blood flow through the circulatory system. RBCs take up oxygen in the lungs, or in fish the gills, and release it into tissues while squeezing through the body's capillaries
A capillary is a small blood vessel from 5 to 10 micrometres (μm) in diameter. Capillaries are composed of only the tunica intima, consisting of a thin wall of simple squamous endothelial cells. They are the smallest blood vessels in the body: ...
.
The cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. ...
of a red blood cell is rich in hemoglobin, an iron
Iron () is a chemical element with Symbol (chemistry), symbol Fe (from la, Wikt:ferrum, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 element, group 8 of the periodic table. It is, Abundanc ...
-containing biomolecule that can bind oxygen and is responsible for the red color of the cells and the blood. Each human red blood cell contains approximately 270 million hemoglobin molecules. The cell membrane is composed of proteins and lipids, and this structure provides properties essential for physiological cell
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery ...
function such as deformability and stability
Stability may refer to:
Mathematics
*Stability theory, the study of the stability of solutions to differential equations and dynamical systems
** Asymptotic stability
** Linear stability
** Lyapunov stability
** Orbital stability
** Structural sta ...
of the blood cell while traversing the circulatory system and specifically the capillary
A capillary is a small blood vessel from 5 to 10 micrometres (μm) in diameter. Capillaries are composed of only the tunica intima, consisting of a thin wall of simple squamous endothelial cells. They are the smallest blood vessels in the bod ...
network.
In humans, mature red blood cells are flexible biconcave disk
A biconcave disc — also referred to as a discocyte — is a geometric shape resembling an oblate spheroid with two concavities on the top and on the bottom.
Biconcave discs appear in the study of cell biology, where it is meta-stable, and ...
s. They lack a cell nucleus and organelles, to accommodate maximum space for hemoglobin; they can be viewed as sacks of hemoglobin, with a plasma membrane as the sack. Approximately 2.4 million new erythrocytes are produced per second in human adults. Erich Sackmann, ''Biological Membranes Architecture and Function.'', Handbook of Biological Physics, (ed. R.Lipowsky and E.Sackmann, vol.1, Elsevier, 1995 The cells develop in the bone marrow and circulate for about 100–120 days in the body before their components are recycled by macrophages. Each circulation takes about 60 seconds (one minute). Approximately 84% of the cells in the human body are 20–30 trillion red blood cells.Laura Dean''Blood Groups and Red Cell Antigens''
/ref> Nearly half of the blood's volume ( 40% to 45%) is red blood cells.
Packed red blood cells
Packed red blood cells, also known as packed cells, are red blood cells that have been separated for blood transfusion. The packed cells are typically used in anemia that is either causing symptoms or when the hemoglobin is less than usually 70� ...
(pRBC) are red blood cells that have been donated, processed, and stored in a blood bank
A blood bank is a center where blood gathered as a result of blood donation is stored and preserved for later use in blood transfusion. The term "blood bank" typically refers to a department of a hospital usually within a Clinical Pathology laborat ...
for blood transfusion.
Structure
Vertebrates
 The vast majority of vertebrates, including mammals and humans, have red blood cells. Red blood cells are cells present in blood to transport oxygen. The only known vertebrates without red blood cells are the crocodile icefish (family
The vast majority of vertebrates, including mammals and humans, have red blood cells. Red blood cells are cells present in blood to transport oxygen. The only known vertebrates without red blood cells are the crocodile icefish (family Channichthyidae
The crocodile icefish or white-blooded fish comprise a family (Channichthyidae) of notothenioid fish found in the Southern Ocean around Antarctica. They are the only known vertebrates to lack hemoglobin in their blood as adults. Icefish populatio ...
); they live in very oxygen-rich cold water and transport oxygen freely dissolved in their blood. While they no longer use hemoglobin, remnants of hemoglobin genes can be found in their genome.
Vertebrate red blood cells consist mainly of hemoglobin, a complex metalloprotein
Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large proportion of all proteins are part of this category. For instance, at least 1000 human proteins (out of ~20,000) contain zinc-binding protein domains al ...
containing heme
Heme, or haem (pronounced / hi:m/ ), is a precursor to hemoglobin, which is necessary to bind oxygen in the bloodstream. Heme is biosynthesized in both the bone marrow and the liver.
In biochemical terms, heme is a coordination complex "consis ...
groups whose iron atoms temporarily bind to oxygen molecules (O2) in the lungs or gills and release them throughout the body. Oxygen can easily diffuse
Diffusion is the net movement of anything (for example, atoms, ions, molecules, energy) generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion is driven by a gradient in Gibbs free energy or chemical p ...
through the red blood cell's cell membrane. Hemoglobin in the red blood cells also carries some of the waste product carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is trans ...
back from the tissues; most waste carbon dioxide, however, is transported back to the pulmonary capillaries
A capillary is a small blood vessel from 5 to 10 micrometres (μm) in diameter. Capillaries are composed of only the tunica intima, consisting of a thin wall of simple squamous endothelial cells. They are the smallest blood vessels in the body: ...
of the lungs as bicarbonate (HCO3−) dissolved in the blood plasma. Myoglobin, a compound related to hemoglobin, acts to store oxygen in muscle cells.
The color of red blood cells is due to the heme group of hemoglobin. The blood plasma alone is straw-colored, but the red blood cells change color depending on the state of the hemoglobin: when combined with oxygen the resulting oxyhemoglobin is scarlet, and when oxygen has been released the resulting deoxyhemoglobin is of a dark red burgundy color. However, blood can appear bluish when seen through the vessel wall and skin. Pulse oximetry
Pulse oximetry is a noninvasive method for monitoring a person's oxygen saturation. Peripheral oxygen saturation (SpO2) readings are typically within 2% accuracy (within 4% accuracy in 95% of cases) of the more accurate (and invasive) reading o ...
takes advantage of the hemoglobin color change to directly measure the arterial
An artery (plural arteries) () is a blood vessel in humans and most animals that takes blood away from the heart to one or more parts of the body (tissues, lungs, brain etc.). Most arteries carry oxygenated blood; the two exceptions are the pu ...
blood oxygen saturation
Oxygen saturation (symbol SO2) is a relative measure of the concentration of oxygen that is dissolved or carried in a given medium as a proportion of the maximal concentration that can be dissolved in that medium at the given temperature. It ca ...
using colorimetric techniques. Hemoglobin also has a very high affinity for carbon monoxide, forming carboxyhemoglobin which is a very bright red in color. Flushed, confused patients with a saturation reading of 100% on pulse oximetry are sometimes found to be suffering from carbon monoxide poisoning.
Having oxygen-carrying proteins inside specialized cells (as opposed to oxygen carriers being dissolved in body fluid) was an important step in the evolution of vertebrates as it allows for less viscous blood, higher concentrations of oxygen, and better diffusion of oxygen from the blood to the tissues. The size of red blood cells varies widely among vertebrate species; red blood cell width is on average about 25% larger than capillary
A capillary is a small blood vessel from 5 to 10 micrometres (μm) in diameter. Capillaries are composed of only the tunica intima, consisting of a thin wall of simple squamous endothelial cells. They are the smallest blood vessels in the bod ...
diameter, and it has been hypothesized that this improves the oxygen transfer from red blood cells to tissues.
Mammals
The red blood cells of mammals are typically shaped as biconcave disks: flattened and depressed in the center, with a dumbbell-shaped cross section, and a torus-shaped rim on the edge of the disk. This shape allows for a high surface-area-to-volume (SA/V) ratio to facilitate diffusion of gases. However, there are some exceptions concerning shape in theartiodactyl
The even-toed ungulates (Artiodactyla , ) are ungulates—hoofed animals—which bear weight equally on two (an even number) of their five toes: the third and fourth. The other three toes are either present, absent, vestigial, or pointing poster ...
order (even-toed ungulates
Ungulates ( ) are members of the diverse clade Ungulata which primarily consists of large mammals with hooves. These include odd-toed ungulates such as horses, rhinoceroses, and tapirs; and even-toed ungulates such as cattle, pigs, giraffes, ca ...
including cattle, deer, and their relatives), which displays a wide variety of bizarre red blood cell morphologies: small and highly ovaloid cells in llama
The llama (; ) (''Lama glama'') is a domesticated South American camelid, widely used as a meat and pack animal by Andean cultures since the Pre-Columbian era.
Llamas are social animals and live with others as a herd. Their wool is soft ...
s and camels (family Camelidae), tiny spherical cells in mouse deer (family Tragulidae
The asterisk ( ), from Late Latin , from Ancient Greek , ''asteriskos'', "little star", is a typographical symbol. It is so called because it resembles a conventional image of a heraldic star.
Computer scientists and mathematicians often v ...
), and cells which assume fusiform, lanceolate, crescentic, and irregularly polygonal and other angular forms in red deer and wapiti (family Cervidae
Deer or true deer are hoofed ruminant mammals forming the family Cervidae. The two main groups of deer are the Cervinae, including the muntjac, the elk (wapiti), the red deer, and the fallow deer; and the Capreolinae, including the reind ...
). Members of this order have clearly evolved a mode of red blood cell development substantially different from the mammalian norm. Overall, mammalian red blood cells are remarkably flexible and deformable so as to squeeze through tiny capillaries
A capillary is a small blood vessel from 5 to 10 micrometres (μm) in diameter. Capillaries are composed of only the tunica intima, consisting of a thin wall of simple squamous endothelial cells. They are the smallest blood vessels in the body: ...
, as well as to maximize their apposing surface by assuming a cigar shape, where they efficiently release their oxygen load.
Red blood cells in mammals are unique amongst vertebrates as they do not have nuclei when mature. They do have nuclei during early phases of erythropoiesis
Erythropoiesis (from Greek 'erythro' meaning "red" and 'poiesis' "to make") is the process which produces red blood cells (erythrocytes), which is the development from erythropoietic stem cell to mature red blood cell.
It is stimulated by decrea ...
, but extrude them during development as they mature; this provides more space for hemoglobin. The red blood cells without nuclei, called reticulocytes, subsequently lose all other cellular organelles such as their mitochondria, Golgi apparatus and endoplasmic reticulum.
The spleen acts as a reservoir of red blood cells, but this effect is somewhat limited in humans. In some other mammals such as dogs and horses, the spleen sequesters large numbers of red blood cells, which are dumped into the blood during times of exertion stress, yielding a higher oxygen transport capacity.
Human
A typical human red blood cell has a disk diameter of approximately 6.2–8.2 µm and a thickness at the thickest point of 2–2.5 µm and a minimum thickness in the centre of 0.8–1 µm, being much smaller than most other human cells. These cells have an average volume of about 90 fL with a surface area of about 136 μm2, and can swell up to a sphere shape containing 150 fL, without membrane distension. Adult humans have roughly 20–30 trillion red blood cells at any given time, constituting approximately 70% of all cells by number. Women have about 4–5 million red blood cells per microliter (cubic millimeter) of blood and men about 5–6 million; people living at high altitudes with low oxygen tension will have more. Red blood cells are thus much more common than the other blood particles: there are about 4,000–11,000 white blood cells and about 150,000–400,000platelet
Platelets, also called thrombocytes (from Greek θρόμβος, "clot" and κύτος, "cell"), are a component of blood whose function (along with the coagulation factors) is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping, thereby i ...
s per microliter.
Human red blood cells take on average 60 seconds to complete one cycle of circulation.
The blood's red color is due to the spectral properties of the hemic iron ions in hemoglobin. Each hemoglobin molecule carries four heme groups; hemoglobin constitutes about a third of the total cell volume. Hemoglobin is responsible for the transport of more than 98% of the oxygen in the body (the remaining oxygen is carried dissolved in the blood plasma). The red blood cells of an average adult human male store collectively about 2.5 grams of iron, representing about 65% of the total iron contained in the body.
Microstructure
Nucleus
Red blood cells in mammals ''anucleate'' when mature, meaning that they lack a cell nucleus. In comparison, the red blood cells of other vertebrates have nuclei; the only known exceptions aresalamander
Salamanders are a group of amphibians typically characterized by their lizard-like appearance, with slender bodies, blunt snouts, short limbs projecting at right angles to the body, and the presence of a tail in both larvae and adults. All t ...
s of the genus ''Batrachoseps
''Batrachoseps'' is a genus of lungless salamanders (plethodontids) often called slender salamanders. They can be distinguished from other lungless salamanders by the four toes they have on each foot.
Their genus name ''Batracho-seps'' means "f ...
'' and fish of the genus '' Maurolicus''.
The elimination of the nucleus in vertebrate red blood cells has been offered as an explanation for the subsequent accumulation of non-coding DNA in the genome. The argument runs as follows: Efficient gas transport requires red blood cells to pass through very narrow capillaries, and this constrains their size. In the absence of nuclear elimination, the accumulation of repeat sequences is constrained by the volume occupied by the nucleus, which increases with genome size.
Nucleated red blood cells in mammals consist of two forms: normoblasts, which are normal erythropoietic precursors to mature red blood cells, and megaloblasts, which are abnormally large precursors that occur in megaloblastic anemia
Megaloblastic anemia is a type of macrocytic anemia. An anemia is a red blood cell defect that can lead to an undersupply of oxygen. Megaloblastic anemia results from inhibition of DNA synthesis during red blood cell production. When DNA synth ...
s.
Membrane composition
Red blood cells are deformable, flexible, are able to adhere to other cells, and are able to interface with immune cells. Theirmembrane
A membrane is a selective barrier; it allows some things to pass through but stops others. Such things may be molecules, ions, or other small particles. Membranes can be generally classified into synthetic membranes and biological membranes. ...
plays many roles in this. These functions are highly dependent on the membrane composition. The red blood cell membrane is composed of 3 layers: the glycocalyx
The glycocalyx, also known as the pericellular matrix, is a glycoprotein and glycolipid covering that surrounds the cell membranes of bacteria, epithelial cells, and other cells. In 1970, Martinez-Palomo discovered the cell coating in animal c ...
on the exterior, which is rich in carbohydrates; the lipid bilayer
The lipid bilayer (or phospholipid bilayer) is a thin polar membrane made of two layers of lipid molecules. These membranes are flat sheets that form a continuous barrier around all cells. The cell membranes of almost all organisms and many vir ...
which contains many transmembrane proteins, besides its lipidic main constituents; and the membrane skeleton, a structural network of proteins located on the inner surface of the lipid bilayer. Half of the membrane mass in human and most mammalian red blood cells are proteins. The other half are lipids, namely phospholipids and cholesterol.
Membrane lipids
The red blood cell membrane comprises a typicallipid bilayer
The lipid bilayer (or phospholipid bilayer) is a thin polar membrane made of two layers of lipid molecules. These membranes are flat sheets that form a continuous barrier around all cells. The cell membranes of almost all organisms and many vir ...
, similar to what can be found in virtually all human cells. Simply put, this lipid bilayer is composed of cholesterol and phospholipids in equal proportions by weight. The lipid composition is important as it defines many physical properties such as membrane permeability and fluidity. Additionally, the activity of many membrane proteins is regulated by interactions with lipids in the bilayer.
Unlike cholesterol, which is evenly distributed between the inner and outer leaflets, the 5 major phospholipids are asymmetrically disposed, as shown below:
Outer monolayer
* Phosphatidylcholine
Phosphatidylcholines (PC) are a class of phospholipids that incorporate choline as a headgroup.
They are a major component of biological membranes and can be easily obtained from a variety of readily available sources, such as egg yolk or soybea ...
(PC);
* Sphingomyelin (SM).
Inner monolayer
* Phosphatidylethanolamine (PE);
* Phosphoinositol
Inositol phosphates are a group of mono- to hexa phosphorylated inositols. They play crucial roles in diverse cellular functions, such as cell growth, apoptosis, cell migration, endocytosis, and cell differentiation.
The group comprises:
* inosit ...
(PI) (small amounts).
* Phosphatidylserine
Phosphatidylserine (abbreviated Ptd-L-Ser or PS) is a phospholipid and is a component of the cell membrane. It plays a key role in cell cycle signaling, specifically in relation to apoptosis. It is a key pathway for viruses to enter cells via ap ...
(PS);
This asymmetric phospholipid distribution among the bilayer is the result of the function of several energy-dependent and energy-independent phospholipid transport proteins. Proteins called " Flippases" move phospholipids from the outer to the inner monolayer, while others called " floppases" do the opposite operation, against a concentration gradient in an energy-dependent manner. Additionally, there are also " scramblase" proteins that move phospholipids in both directions at the same time, down their concentration gradients in an energy-independent manner. There is still considerable debate ongoing regarding the identity of these membrane maintenance proteins in the red cell membrane.
The maintenance of an asymmetric phospholipid distribution in the bilayer (such as an exclusive localization of PS and PIs in the inner monolayer) is critical for the cell integrity and function due to several reasons:
* Macrophages
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer ce ...
recognize and phagocytose
Phagocytosis () is the process by which a cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle (≥ 0.5 μm), giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome. It is one type of endocytosis. A cell that performs phagocytosis is ...
red cells that expose PS at their outer surface. Thus the confinement of PS in the inner monolayer is essential if the cell is to survive its frequent encounters with macrophages of the reticuloendothelial system, especially in the spleen.
* Premature destruction of thallassemic and sickle red cells has been linked to disruptions of lipid asymmetry leading to exposure of PS on the outer monolayer.
* An exposure of PS can potentiate adhesion of red cells to vascular endothelial cells, effectively preventing normal transit through the microvasculature. Thus it is important that PS is maintained only in the inner leaflet of the bilayer to ensure normal blood flow in microcirculation.
* Both PS and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) can regulate membrane mechanical function, due to their interactions with skeletal proteins such as spectrin
Spectrin is a cytoskeletal protein that lines the intracellular side of the plasma membrane in eukaryotic cells. Spectrin forms pentagonal or hexagonal arrangements, forming a scaffold and playing an important role in maintenance of plasma membr ...
and protein 4.1R. Recent studies have shown that binding of spectrin to PS promotes membrane mechanical stability. PIP2 enhances the binding of protein band 4.1R to glycophorin C but decreases its interaction with protein band 3, and thereby may modulate the linkage of the bilayer to the membrane skeleton.
The presence of specialized structures named " lipid rafts" in the red blood cell membrane have been described by recent studies. These are structures enriched in cholesterol and sphingolipids
Sphingolipids are a class of lipids containing a backbone of sphingoid bases, a set of aliphatic amino alcohols that includes sphingosine. They were discovered in brain extracts in the 1870s and were named after the mythological sphinx because ...
associated with specific membrane proteins, namely flotillins, STOMatins (band 7), G-proteins, and β-adrenergic receptors. Lipid rafts that have been implicated in cell signaling events in nonerythroid cells have been shown in erythroid cells to mediate β2-adregenic receptor signaling and increase cAMP levels, and thus regulating entry of malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. S ...
l parasites into normal red cells.
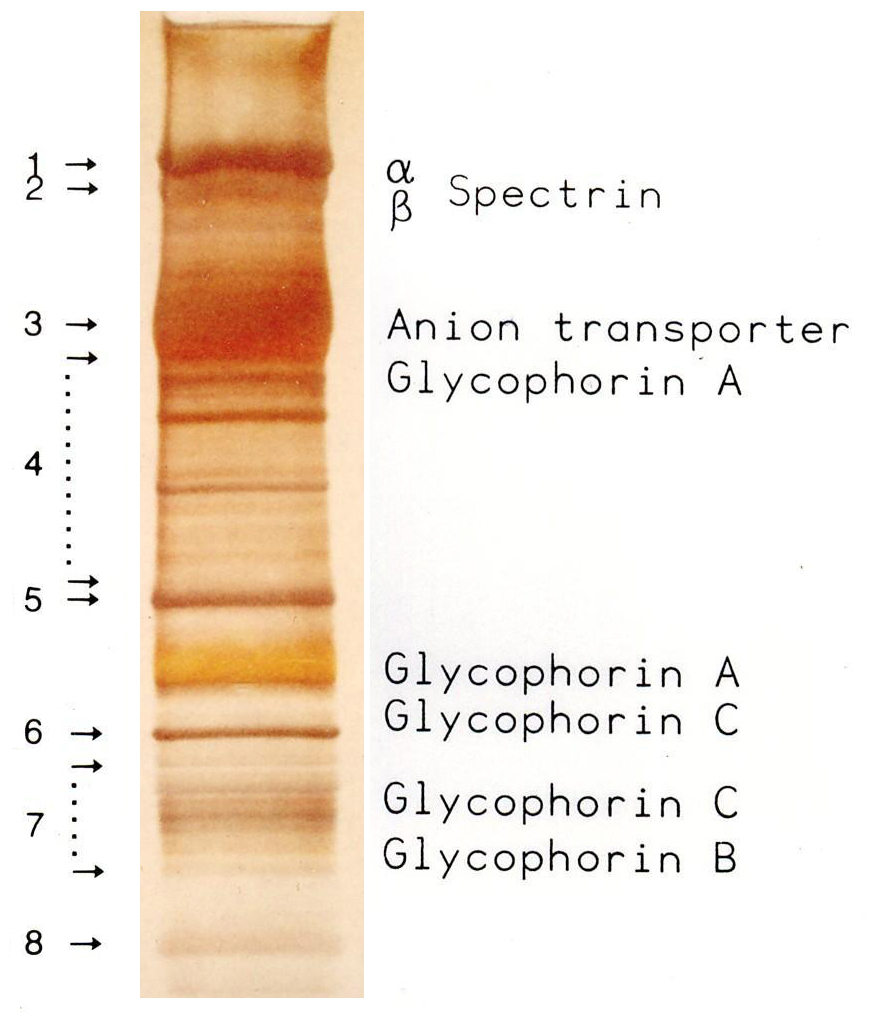
Membrane proteins
 The proteins of the membrane skeleton are responsible for the deformability, flexibility and durability of the red blood cell, enabling it to squeeze through capillaries less than half the diameter of the red blood cell (7–8 μm) and recovering the discoid shape as soon as these cells stop receiving compressive forces, in a similar fashion to an object made of rubber.
There are currently more than 50 known membrane proteins, which can exist in a few hundred up to a million copies per red blood cell. Approximately 25 of these membrane proteins carry the various blood group antigens, such as the A, B and Rh antigens, among many others. These membrane proteins can perform a wide diversity of functions, such as transporting ions and molecules across the red cell membrane, adhesion and interaction with other cells such as endothelial cells, as signaling receptors, as well as other currently unknown functions. The blood types of humans are due to variations in surface glycoproteins of red blood cells. Disorders of the proteins in these membranes are associated with many disorders, such as
The proteins of the membrane skeleton are responsible for the deformability, flexibility and durability of the red blood cell, enabling it to squeeze through capillaries less than half the diameter of the red blood cell (7–8 μm) and recovering the discoid shape as soon as these cells stop receiving compressive forces, in a similar fashion to an object made of rubber.
There are currently more than 50 known membrane proteins, which can exist in a few hundred up to a million copies per red blood cell. Approximately 25 of these membrane proteins carry the various blood group antigens, such as the A, B and Rh antigens, among many others. These membrane proteins can perform a wide diversity of functions, such as transporting ions and molecules across the red cell membrane, adhesion and interaction with other cells such as endothelial cells, as signaling receptors, as well as other currently unknown functions. The blood types of humans are due to variations in surface glycoproteins of red blood cells. Disorders of the proteins in these membranes are associated with many disorders, such as hereditary spherocytosis
Hereditary spherocytosis (HS) is a congenital hemolytic disorder, wherein a genetic mutation coding for a structural membrane protein phenotype leads to a spherical shaping of erythrocytic cellular morphology. As erythrocytes are sphere-shaped (s ...
, hereditary elliptocytosis
Hereditary elliptocytosis, also known as ovalocytosis, is an inherited blood disorder in which an abnormally large number of the person's red blood cells are elliptical rather than the typical biconcave disc shape. Such morphologically distinctive ...
, hereditary stomatocytosis
Hereditary stomatocytosis describes a number of inherited, mostly autosomal dominant human conditions which affect the red blood cell and create the appearance of a slit-like area of central pallor (stomatocyte) among erythrocytes on peripheral b ...
, and paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) is a rare, acquired, life-threatening disease of the blood characterized by destruction of red blood cells by the complement system, a part of the body's innate immune system. This destructive process occu ...
.
The red blood cell membrane proteins organized according to their function:
 Transport
*
Transport
* Band 3
Band 3 anion transport protein, also known as anion exchanger 1 (AE1) or band 3 or solute carrier family 4 member 1 (SLC4A1), is a protein that is encoded by the gene in humans.
Band 3 anion transport protein is a phylogenetically-preserved ...
– Anion transporter, also an important structural component of the red blood cell membrane, makes up to 25% of the cell membrane surface, each red cell contains approximately one million copies. Defines the Diego Blood Group;
* Aquaporin 1 – water transporter, defines the Colton Blood Group;
* Glut1
Glucose transporter 1 (or GLUT1), also known as solute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporter member 1 (SLC2A1), is a uniporter protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SLC2A1'' gene. GLUT1 facilitates the transport of glucose across ...
– glucose and L-dehydroascorbic acid transporter;
* Kidd antigen protein – urea transporter;
* RHAG
Rh-associated glycoprotein (RHAG) is an ammonia transporter protein that in humans is encoded by the ''RHAG'' gene. RHAG has also recently been designated CD241 (cluster of differentiation 241). Mutations in the RHAG gene can cause stomatocytosi ...
– gas transporter, probably of carbon dioxide, defines Rh Blood Group and the associated unusual blood group phenotype Rhnull;
* Na+/K+ – ATPase;
* Ca2+ – ATPase;
* Na+ K+ 2Cl− – cotransporter;
* Na+-Cl− – cotransporter;
* Na-H exchanger;
* K-Cl – cotransporter;
* Gardos Channel.
Cell adhesion
* ICAM-4 – interacts with integrins
Integrins are transmembrane receptors that facilitate cell-cell and cell-extracellular matrix (ECM) adhesion. Upon ligand binding, integrins activate signal transduction pathways that mediate cellular signals such as regulation of the cell cycle, ...
;
* BCAM – a glycoprotein that defines the Lutheran blood group and also known as Lu or laminin
Laminins are a family of glycoproteins of the extracellular matrix of all animals. They are major components of the basal lamina (one of the layers of the basement membrane), the protein network foundation for most cells and organs. The laminins ...
-binding protein.
Structural role – The following membrane proteins establish linkages with skeletal proteins and may play an important role in regulating cohesion between the lipid bilayer and membrane skeleton, likely enabling the red cell to maintain its favorable membrane surface area by preventing the membrane from collapsing (vesiculating).
* Ankyrin
Ankyrins are a family of proteins that mediate the attachment of integral membrane proteins to the spectrin-actin based membrane cytoskeleton. Ankyrins have binding sites for the beta subunit of spectrin and at least 12 families of integral mem ...
-based macromolecular complex – proteins linking the bilayer to the membrane skeleton through the interaction of their cytoplasmic domains with Ankyrin
Ankyrins are a family of proteins that mediate the attachment of integral membrane proteins to the spectrin-actin based membrane cytoskeleton. Ankyrins have binding sites for the beta subunit of spectrin and at least 12 families of integral mem ...
.
** Band 3
Band 3 anion transport protein, also known as anion exchanger 1 (AE1) or band 3 or solute carrier family 4 member 1 (SLC4A1), is a protein that is encoded by the gene in humans.
Band 3 anion transport protein is a phylogenetically-preserved ...
– also assembles various glycolytic enzymes, the presumptive CO2 transporter, and carbonic anhydrase into a macromolecular complex termed a " metabolon," which may play a key role in regulating red cell metabolism and ion and gas transport function
Function or functionality may refer to:
Computing
* Function key, a type of key on computer keyboards
* Function model, a structured representation of processes in a system
* Function object or functor or functionoid, a concept of object-oriente ...
.
** RHAG
Rh-associated glycoprotein (RHAG) is an ammonia transporter protein that in humans is encoded by the ''RHAG'' gene. RHAG has also recently been designated CD241 (cluster of differentiation 241). Mutations in the RHAG gene can cause stomatocytosi ...
– also involved in transport, defines associated unusual blood group phenotype Rhmod.
* Protein 4.1R-based macromolecular complex – proteins interacting with Protein 4.1R.
** Protein 4.1R – weak expression of Gerbich antigens;
** Glycophorin C and D – glycoprotein, defines Gerbich Blood Group;
** XK – defines the Kell Blood Group and the Mcleod unusual phenotype (lack of Kx antigen and greatly reduced expression of Kell antigens);
** RhD/RhCE – defines Rh Blood Group and the associated unusual blood group phenotype Rhnull;
** Duffy protein – has been proposed to be associated with chemokine clearance;
** Adducin – interaction with band 3;
** Dematin- interaction with the Glut1 glucose transporter.
Surface electrostatic potential
Thezeta potential
Zeta potential is the electrical potential at the slipping plane. This plane is the interface which separates mobile fluid from fluid that remains attached to the surface.
Zeta potential is a scientific term for electrokinetic potential in coll ...
is an electrochemical property of cell surfaces that is determined by the net electrical charge of molecules exposed at the surface of cell membranes of the cell. The normal zeta potential of the red blood cell is −15.7 milli volts (mV).Tokumasu F, Ostera GR, Amaratunga C, Fairhurst RM (2012) Modifications in erythrocyte membrane zeta potential by ''Plasmodium falciparum'' infection. Exp Parasitol Much of this potential appears to be contributed by the exposed sialic acid residues in the membrane: their removal results in zeta potential of −6.06 mV.
Function
Role in transport
Recall thatrespiration
Respiration may refer to:
Biology
* Cellular respiration, the process in which nutrients are converted into useful energy in a cell
** Anaerobic respiration, cellular respiration without oxygen
** Maintenance respiration, the amount of cellul ...
, as illustrated schematically here with a unit of carbohydrate, produces about as many molecules of carbon dioxide, CO2, as it consumes of oxygen, O2.
:anhydride
An organic acid anhydride is an acid anhydride that is an organic compound. An acid anhydride is a compound that has two acyl groups bonded to the same oxygen atom. A common type of organic acid anhydride is a carboxylic anhydride, where the pa ...
of carbonic acid). Because it is a catalyst, it can affect many CO2 molecules, so it performs its essential role without needing as many copies as are needed for O2 transport by hemoglobin.
In the presence of this catalyst carbon dioxide and carbonic acid reach an equilibrium very rapidly, while the red cells are still moving through the capillary. Thus it is the RBC that ensures that most of the CO2 is transported as bicarbonate.
At physiological pH the equilibrium strongly favors carbonic acid, which is mostly dissociated into bicarbonate ion.
:carbaminohemoglobin
Carbaminohemoglobin (carbaminohaemoglobin BrE) (CO2Hb, also known as carbhemoglobin and carbohemoglobin) is a compound of hemoglobin and carbon dioxide, and is one of the forms in which carbon dioxide exists in the blood. Twenty-three percent of ...
compounds.
As oxygen is released in the tissues, more CO2 binds to hemoglobin, and as oxygen binds in the lung, it displaces the hemoglobin bound CO2, this is called the Haldane effect. Despite the fact that only a small amount of the CO2 in blood is bound to hemoglobin in venous blood, a greater proportion of the change in CO2 content between venous and arterial blood comes from the change in this bound CO2. That is, there is always an abundance of bicarbonate in blood, both venous and arterial, because of its aforementioned role as a pH buffer.
In summary, carbon dioxide produced by cellular respiration diffuses very rapidly to areas of lower concentration, specifically into nearby capillaries.
When it diffuses into a RBC, CO2 is rapidly converted by the carbonic anhydrase found on the inside of the RBC membrane into bicarbonate ion. The bicarbonate ions in turn leave the RBC in exchange for chloride ions from the plasma, facilitated by the band 3 anion transport protein
Band 3 anion transport protein, also known as anion exchanger 1 (AE1) or band 3 or solute carrier family 4 member 1 (SLC4A1), is a protein that is encoded by the gene in humans.
Band 3 anion transport protein is a phylogenetically-preserved ...
colocated in the RBC membrane. The bicarbonate ion does not diffuse back out of the capillary, but is carried to the lung. In the lung the lower partial pressure of carbon dioxide in the alveoli causes carbon dioxide to diffuse rapidly from the capillary into the alveoli. The carbonic anhydrase in the red cells keeps the bicarbonate ion in equilibrium with carbon dioxide. So as carbon dioxide leaves the capillary, and CO2 is displaced by O2 on hemoglobin, sufficient bicarbonate ion converts rapidly to carbon dioxide to maintain the equilibrium.
Secondary functions
When red blood cells undergo shear stress in constricted vessels, they release ATP, which causes the vessel walls to relax and dilate so as to promote normal blood flow. When their hemoglobin molecules are deoxygenated, red blood cells releaseS-Nitrosothiol
In organic chemistry, ''S''-nitrosothiols, also known as thionitrites, are organic compounds or functional groups containing a nitroso group attached to the sulfur atom of a thiol. ''S''-Nitrosothiols have the general formula , where ''R'' denot ...
s, which also act to dilate blood vessels, thus directing more blood to areas of the body depleted of oxygen.
Red blood cells can also synthesize nitric oxide enzymatically, using L-arginine as substrate, as do endothelial cells. Exposure of red blood cells to physiological levels of shear stress activates nitric oxide synthase and export of nitric oxide, which may contribute to the regulation of vascular tonus.
Red blood cells can also produce hydrogen sulfide, a signalling gas that acts to relax vessel walls. It is believed that the cardioprotective effects of garlic are due to red blood cells converting its sulfur compounds into hydrogen sulfide.
Red blood cells also play a part in the body's immune response: when lysed by pathogens such as bacteria, their hemoglobin releases free radical
A daughter category of ''Ageing'', this category deals only with the biological aspects of ageing.
Ageing
Ailments of unknown cause
Biogerontology
Biological processes
Causes of death
Cellular processes
Gerontology
Life extension
Metabo ...
s, which break down the pathogen's cell wall and membrane, killing it.
Cellular processes
As a result of not containing mitochondria, red blood cells use none of the oxygen they transport; instead they produce the energy carrier ATP by the glycolysis ofglucose
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, u ...
and lactic acid fermentation on the resulting pyruvate. Furthermore, the pentose phosphate pathway
The pentose phosphate pathway (also called the phosphogluconate pathway and the hexose monophosphate shunt and the HMP Shunt) is a metabolic pathway parallel to glycolysis. It generates NADPH and pentoses (5-carbon sugars) as well as ribose 5-pho ...
plays an important role in red blood cells; see glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency (G6PDD), which is the most common enzyme deficiency worldwide, is an inborn error of metabolism that predisposes to red blood cell breakdown. Most of the time, those who are affected have no symptoms. ...
for more information.
As red blood cells contain no nucleus, protein biosynthesis is currently assumed to be absent in these cells.
Because of the lack of nuclei and organelles, mature red blood cells do not contain DNA and cannot synthesize any RNA, and consequently cannot divide and have limited repair capabilities. The inability to carry out protein synthesis means that no virus can evolve to target mammalian red blood cells. However, infection with parvoviruses (such as human parvovirus B19) can affect erythroid precursors while they still have DNA, as recognized by the presence of giant pronormoblasts with viral particles and inclusion bodies, thus temporarily depleting the blood of reticulocytes and causing anemia.
Life cycle
Human red blood cells are produced through a process namederythropoiesis
Erythropoiesis (from Greek 'erythro' meaning "red" and 'poiesis' "to make") is the process which produces red blood cells (erythrocytes), which is the development from erythropoietic stem cell to mature red blood cell.
It is stimulated by decrea ...
, developing from committed stem cells to mature red blood cells in about 7 days. When matured, in a healthy individual these cells live in blood circulation for about 100 to 120 days (and 80 to 90 days in a full term infant). At the end of their lifespan, they are removed from circulation. In many chronic diseases, the lifespan of the red blood cells is reduced.
Creation
Erythropoiesis
Erythropoiesis (from Greek 'erythro' meaning "red" and 'poiesis' "to make") is the process which produces red blood cells (erythrocytes), which is the development from erythropoietic stem cell to mature red blood cell.
It is stimulated by decrea ...
is the process by which new red blood cells are produced; it lasts about 7 days. Through this process red blood cells are continuously produced in the red bone marrow of large bones. (In the embryo, the liver
The liver is a major organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it ...
is the main site of red blood cell production.) The production can be stimulated by the hormone erythropoietin (EPO), synthesised by the kidney. Just before and after leaving the bone marrow, the developing cells are known as reticulocyte
Reticulocytes are immature red blood cells (RBCs). In the process of erythropoiesis (red blood cell formation), reticulocytes develop and mature in the bone marrow and then circulate for about a day in the blood stream before developing into ma ...
s; these constitute about 1% of circulating red blood cells.
Functional lifetime
The functional lifetime of a red blood cell is about 100–120 days, during which time the red blood cells are continually moved by the blood flow push (inarteries
An artery (plural arteries) () is a blood vessel in humans and most animals that takes blood away from the heart to one or more parts of the body (tissues, lungs, brain etc.). Most arteries carry oxygenated blood; the two exceptions are the pu ...
), pull (in veins) and a combination of the two as they squeeze through microvessels such as capillaries. They are also recycled in the bone marrow.
Senescence
The aging red blood cell undergoes changes in its plasma membrane, making it susceptible to selective recognition by macrophages and subsequentphagocytosis
Phagocytosis () is the process by which a cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle (≥ 0.5 μm), giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome. It is one type of endocytosis. A cell that performs phagocytosis is ...
in the mononuclear phagocyte system
In immunology, the mononuclear phagocyte system or mononuclear phagocytic system (MPS) also known as the reticuloendothelial system or macrophage system is a part of the immune system that consists of the phagocytic cells located in reticular co ...
( spleen, liver
The liver is a major organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it ...
and lymph nodes), thus removing old and defective cells and continually purging the blood. This process is termed eryptosis, red blood cell programmed death. This process normally occurs at the same rate of production by erythropoiesis, balancing the total circulating red blood cell count. Eryptosis is increased in a wide variety of diseases including sepsis
Sepsis, formerly known as septicemia (septicaemia in British English) or blood poisoning, is a life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to infection causes injury to its own tissues and organs. This initial stage is follo ...
, haemolytic uremic syndrome
Hemolysis or haemolysis (), also known by several other names, is the rupturing (lysis) of red blood cells (erythrocytes) and the release of their contents (cytoplasm) into surrounding fluid (e.g. blood plasma). Hemolysis may occur in vivo o ...
, malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. S ...
, sickle cell anemia
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a group of blood disorders typically inherited from a person's parents. The most common type is known as sickle cell anaemia. It results in an abnormality in the oxygen-carrying protein haemoglobin found in red bl ...
, beta- thalassemia, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency (G6PDD), which is the most common enzyme deficiency worldwide, is an inborn error of metabolism that predisposes to red blood cell breakdown. Most of the time, those who are affected have no symptoms. ...
, phosphate depletion, iron deficiency and Wilson's disease
Wilson's disease is a genetic disorder in which excess copper builds up in the body. Symptoms are typically related to the brain and liver. Liver-related symptoms include vomiting, weakness, fluid build up in the abdomen, swelling of the legs, ...
. Eryptosis can be elicited by osmotic shock, oxidative stress, and energy depletion, as well as by a wide variety of endogenous mediators and xenobiotics. Excessive eryptosis is observed in red blood cells lacking the cGMP-dependent protein kinase type I or the AMP-activated protein kinase AMPK. Inhibitors of eryptosis include erythropoietin, nitric oxide, catecholamine
A catecholamine (; abbreviated CA) is a monoamine neurotransmitter, an organic compound that has a catechol (benzene with two hydroxyl side groups next to each other) and a side-chain amine.
Catechol can be either a free molecule or a su ...
s and high concentrations of urea.
Much of the resulting breakdown products are recirculated in the body. The heme constituent of hemoglobin are broken down into iron (Fe3+) and biliverdin. The biliverdin is reduced to bilirubin, which is released into the plasma and recirculated to the liver bound to albumin. The iron is released into the plasma to be recirculated by a carrier protein called transferrin. Almost all red blood cells are removed in this manner from the circulation before they are old enough to hemolyze. Hemolyzed hemoglobin is bound to a protein in plasma called haptoglobin, which is not excreted by the kidney.
Clinical significance
Disease
Blood diseases involving the red blood cells include: * Anemias (or anaemias) are diseases characterized by low oxygen transport capacity of the blood, because of low red cell count or some abnormality of the red blood cells or the hemoglobin. :*Iron deficiency anemia
Iron-deficiency anemia is anemia caused by a lack of iron. Anemia is defined as a decrease in the number of red blood cells or the amount of hemoglobin in the blood. When onset is slow, symptoms are often vague such as feeling tired, weak, s ...
is the most common anemia; it occurs when the dietary intake or absorption of iron is insufficient, and hemoglobin, which contains iron, cannot be formed.
:* Pernicious anemia is an autoimmune disease wherein the body lacks intrinsic factor, required to absorb vitamin B12 from food. Vitamin B12 is needed for the production of red blood cells and hemoglobin.
:* Sickle-cell disease is a genetic disease that results in abnormal hemoglobin molecules. When these release their oxygen load in the tissues, they become insoluble, leading to mis-shaped red blood cells. These sickle shaped red cells are less deformable and viscoelastic
In materials science and continuum mechanics, viscoelasticity is the property of materials that exhibit both viscous and elastic characteristics when undergoing deformation. Viscous materials, like water, resist shear flow and strain linearly ...
, meaning that they have become rigid and can cause blood vessel blockage, pain, strokes, and other tissue damage.
:* Thalassemia is a genetic disease that results in the production of an abnormal ratio of hemoglobin subunits.
:*Hereditary spherocytosis
Hereditary spherocytosis (HS) is a congenital hemolytic disorder, wherein a genetic mutation coding for a structural membrane protein phenotype leads to a spherical shaping of erythrocytic cellular morphology. As erythrocytes are sphere-shaped (s ...
syndromes are a group of inherited disorders characterized by defects in the red blood cell's cell membrane, causing the cells to be small, sphere-shaped, and fragile instead of donut-shaped and flexible. These abnormal red blood cells are destroyed by the spleen. Several other hereditary disorders of the red blood cell membrane are known.
:* Aplastic anemia is caused by the inability of the bone marrow to produce blood cells.
:* Pure red cell aplasia
Pure red cell aplasia (PRCA) or erythroblastopenia refers to a type of aplastic anemia affecting the precursors to red blood cells but usually not to white blood cells. In PRCA, the bone marrow ceases to produce red blood cells. There are multiple ...
is caused by the inability of the bone marrow to produce only red blood cells.
hemolytic anemia
Hemolytic anemia or haemolytic anaemia is a form of anemia due to hemolysis, the abnormal breakdown of red blood cells (RBCs), either in the blood vessels (intravascular hemolysis) or elsewhere in the human body (extravascular). This most commonly ...
.
:* The malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. S ...
parasite spends part of its life-cycle in red blood cells, feeds on their hemoglobin and then breaks them apart, causing fever. Both sickle-cell disease and thalassemia are more common in malaria areas, because these mutations convey some protection against the parasite.
* Polycythemias (or erythrocytoses) are diseases characterized by a surplus of red blood cells. The increased viscosity of the blood can cause a number of symptoms.
:* In polycythemia vera
Polycythemia vera is an uncommon myeloproliferative neoplasm (a type of chronic leukemia) in which the bone marrow makes too many red blood cells. It may also result in the overproduction of white blood cells and platelets.
Most of the healt ...
the increased number of red blood cells results from an abnormality in the bone marrow.
* Several microangiopathic diseases, including disseminated intravascular coagulation and thrombotic microangiopathies, present with pathognomonic Pathognomonic (rare synonym ''pathognomic'') is a term, often used in medicine, that means "characteristic for a particular disease". A pathognomonic sign is a particular sign whose presence means that a particular disease is present beyond any doub ...
(diagnostic) red blood cell fragments called schistocyte
A schistocyte or schizocyte (from Greek for "divided" and for "hollow" or "cell") is a fragmented part of a red blood cell. Schistocytes are typically irregularly shaped, jagged, and have two pointed ends.
Several microangiopathic diseases, ...
s. These pathologies generate fibrin strands that sever red blood cells as they try to move past a thrombus.
Transfusion
Red blood cells may be given as part of a blood transfusion. Blood may bedonated
A donation is a gift for charity, humanitarian aid, or to benefit a cause. A donation may take various forms, including money, alms, services, or goods such as clothing, toys, food, or vehicles. A donation may satisfy medical needs such as bl ...
from another person, or stored by the recipient at an earlier date. Donated blood usually requires screening to ensure that donors do not contain risk factors for the presence of blood-borne diseases, or will not suffer themselves by giving blood. Blood is usually collected and tested for common or serious blood-borne disease
A blood-borne disease is a disease that can be spread through contamination by blood and other body fluids. Blood can contain pathogens of various types, chief among which are microorganisms, like bacteria and parasites, and non-living infectious ...
s including Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the '' Hepatitis B virus'' (HBV) that affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. It can cause both acute and chronic infection.
Many people have no symptoms during an initial infection. ...
, Hepatitis C and HIV. The blood type (A, B, AB, or O) or the blood product is identified and matched with the recipient's blood to minimise the likelihood of acute hemolytic transfusion reaction An acute hemolytic transfusion reaction (AHTR), also called immediate hemolytic transfusion reaction, is a life-threatening reaction to receiving a blood transfusion. AHTRs occur within 24 hours of the transfusion and can be triggered by a few milli ...
, a type of transfusion reaction. This relates to the presence of antigens on the cell's surface. After this process, the blood is stored, and within a short duration is used. Blood can be given as a whole product or the red blood cells separated as packed red blood cells
Packed red blood cells, also known as packed cells, are red blood cells that have been separated for blood transfusion. The packed cells are typically used in anemia that is either causing symptoms or when the hemoglobin is less than usually 70� ...
.
Blood is often transfused when there is known anaemia, active bleeding, or when there is an expectation of serious blood loss, such as prior to an operation. Before blood is given, a small sample of the recipient's blood is tested with the transfusion in a process known as cross-matching
Cross-matching or crossmatching is a test performed before a blood transfusion as part of blood compatibility testing. Normally, this involves adding the recipient's blood plasma to a sample of the donor's red blood cells. If the blood is incom ...
.
In 2008 it was reported that human embryonic stem cell
Embryonic stem cells (ESCs) are pluripotent stem cells derived from the inner cell mass of a blastocyst, an early-stage pre- implantation embryo. Human embryos reach the blastocyst stage 4–5 days post fertilization, at which time they consist ...
s had been successfully coaxed into becoming red blood cells in the lab. The difficult step was to induce the cells to eject their nucleus; this was achieved by growing the cells on stromal cell
Stromal cells, or mesenchymal stromal cells, are differentiating cells found in abundance within bone marrow but can also be seen all around the body. Stromal cells can become connective tissue cells of any organ, for example in the uterine mucosa ...
s from the bone marrow. It is hoped that these artificial red blood cells can eventually be used for blood transfusions.
A human trial is conducted in 2022, using blood cultured from stem cells obtained from donor blood.
Tests
 Several blood tests involve red blood cells. These include a ''RBC count'' (the number of red blood cells per volume of blood), calculation of the
Several blood tests involve red blood cells. These include a ''RBC count'' (the number of red blood cells per volume of blood), calculation of the hematocrit
The hematocrit () (Ht or HCT), also known by several other names, is the volume percentage (vol%) of red blood cells (RBCs) in blood, measured as part of a blood test. The measurement depends on the number and size of red blood cells. It is norm ...
(percentage of blood volume occupied by red blood cells), and the erythrocyte sedimentation rate. The blood type needs to be determined to prepare for a blood transfusion or an organ transplantation
Organ transplantation is a medical procedure in which an organ is removed from one body and placed in the body of a recipient, to replace a damaged or missing organ. The donor and recipient may be at the same location, or organs may be transpor ...
.
Many diseases involving red blood cells are diagnosed with a blood film
A blood smear, peripheral blood smear or blood film is a thin layer of blood smeared on a glass microscope slide and then stained in such a way as to allow the various blood cells to be examined microscopically. Blood smears are examined in the ...
(or peripheral blood smear), where a thin layer of blood is smeared on a microscope slide. This may reveal poikilocytosis, which are variations in red blood cell shape. When red blood cells sometimes occur as a stack, flat side next to flat side. This is known as ''rouleaux
Rouleaux (singular is rouleau) are stacks or aggregations of red blood cells (RBCs) that form because of the unique discoid shape of the cells in vertebrates. The flat surface of the discoid RBCs gives them a large surface area to make contact wi ...
formation'', and it occurs more often if the levels of certain serum proteins are elevated, as for instance during inflammation
Inflammation (from la, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molec ...
.
Separation and blood doping
Red blood cells can be obtained fromwhole blood
Whole blood (WB) is human blood from a standard blood donation. It is used in the treatment of massive bleeding, in exchange transfusion, and when people donate blood to themselves. One unit of whole blood (~517 mls) brings up hemoglobin level ...
by centrifugation, which separates the cells from the blood plasma in a process known as blood fractionation. Packed red blood cells
Packed red blood cells, also known as packed cells, are red blood cells that have been separated for blood transfusion. The packed cells are typically used in anemia that is either causing symptoms or when the hemoglobin is less than usually 70� ...
, which are made in this way from whole blood with the plasma removed, are used in transfusion medicine. During plasma donation, the red blood cells are pumped back into the body right away and only the plasma is collected.
Some athletes have tried to improve their performance by blood doping
Blood doping is a form of doping in which the number of red blood cells in the bloodstream is boosted in order to enhance athletic performance. Because such blood cells carry oxygen from the lungs to the muscles, a higher concentration in the blo ...
: first about 1 litre of their blood is extracted, then the red blood cells are isolated, frozen and stored, to be reinjected shortly before the competition. (Red blood cells can be conserved for 5 weeks at , or over 10 years using cryoprotectants) This practice is hard to detect but may endanger the human cardiovascular system which is not equipped to deal with blood of the resulting higher viscosity. Another method of blood doping involves injection with erythropoietin to stimulate production of red blood cells. Both practices are banned by the World Anti-Doping Agency
The World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA; french: Agence mondiale antidopage, AMA) is a foundation initiated by the International Olympic Committee based in Canada to promote, coordinate, and monitor the fight against drugs in sports. The agency's key ...
.
History
The first person to describe red blood cells was the young Dutch biologist Jan Swammerdam, who had used an earlymicroscope
A microscope () is a laboratory instrument used to examine objects that are too small to be seen by the naked eye. Microscopy is the science of investigating small objects and structures using a microscope. Microscopic means being invisi ...
in 1658 to study the blood of a frog. Unaware of this work, Anton van Leeuwenhoek
Antonie Philips van Leeuwenhoek ( ; ; 24 October 1632 – 26 August 1723) was a Dutch microbiologist and microscopist in the Golden Age of Dutch science and technology. A largely self-taught man in science, he is commonly known as " the ...
provided another microscopic description in 1674, this time providing a more precise description of red blood cells, even approximating their size, "25,000 times smaller than a fine grain of sand".
In the 1740s, Vincenzo Menghini Vincenzo Antonio Menghini (15 February 1704-27 January 1759) was an Italian physician and scientist, who was one of the first to report the abundance of iron in red blood cells.
Biography
He was born in Budrio to a family with a small business. H ...
in Bologna was able to demonstrate the presence of iron by passing magnets over the powder or ash remaining from heated red blood cells.
In 1901, Karl Landsteiner published his discovery of the three main blood groups
The term human blood group systems is defined by the International Society of Blood Transfusion (ISBT) as systems in the human species where cell-surface antigens—in particular, those on blood cells—are "controlled at a single gene locus or by ...
—A, B, and C (which he later renamed to O). Landsteiner described the regular patterns in which reactions occurred when serum was mixed with red blood cells, thus identifying compatible and conflicting combinations between these blood groups. A year later Alfred von Decastello and Adriano Sturli, two colleagues of Landsteiner, identified a fourth blood group—AB.
In 1959, by use of X-ray crystallography, Dr. Max Perutz
Max Ferdinand Perutz (19 May 1914 – 6 February 2002) was an Austrian-born British molecular biologist, who shared the 1962 Nobel Prize for Chemistry with John Kendrew, for their studies of the structures of haemoglobin and myoglobin. He went ...
was able to unravel the structure of hemoglobin, the red blood cell protein that carries oxygen.
The oldest intact red blood cells ever discovered were found in Ötzi the Iceman, a natural mummy of a man who died around 3255 BCE. These cells were discovered in May 2012.
See also
*Altitude training
Altitude training is the practice by some endurance athletes of training for several weeks at high altitude, preferably over above sea level, though more commonly at intermediate altitudes due to the shortage of suitable high-altitude locations. A ...
* Blood substitute
* Red blood cell indices
* Serum (blood)
* Er blood group collection
The Er blood group system consists of five human red blood cell surface antigens, Era, Erb, Er3, Er4 and Er5. The incidences of Era and Er3 are each greater than 99% of the human population, while the incidence of Erb is less than 0.01%. Er4 and E ...
References
External links
''Blood Groups and Red Cell Antigens''
by Laura Dean. Searchable and downloadable online textbook in the public domain.
Database of vertebrate erythrocyte sizes
Red Gold
PBS
The Public Broadcasting Service (PBS) is an American public broadcaster and non-commercial, free-to-air television network based in Arlington, Virginia. PBS is a publicly funded nonprofit organization and the most prominent provider of educat ...
site containing facts and history
{{DEFAULTSORT:Red Blood Cell
Human cells
Blood cells
Respiration
1658 in science
Microscopic discoveries by Antonie van Leeuwenhoek