Environmental destruction on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Environmental degradation is the deterioration of the
Environmental degradation is one of the ten threats officially cautioned by the High-level Panel on Threats, Challenges and Change, high-level PaneI on Threats, Challenges and Change of the
 Scientists assert that human activity has pushed the earth into a sixth mass extinction event. The
Scientists assert that human activity has pushed the earth into a sixth mass extinction event. The
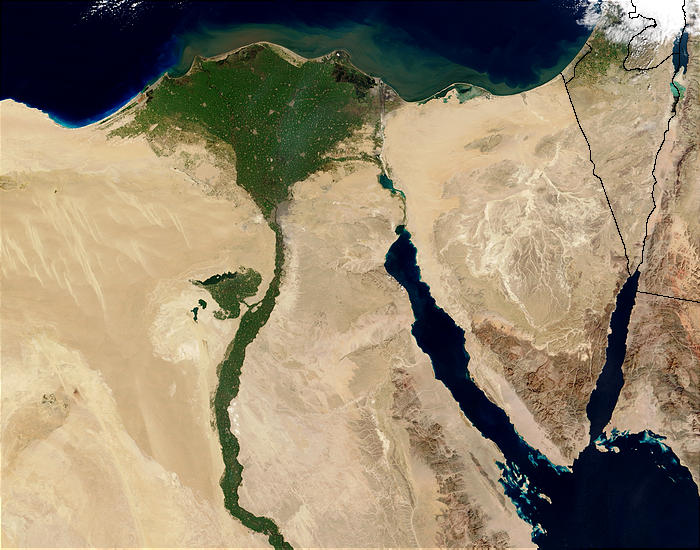 One major component of environmental degradation is the depletion of the resource of fresh water on Earth. Approximately only 2.5% of all of the water on Earth is
One major component of environmental degradation is the depletion of the resource of fresh water on Earth. Approximately only 2.5% of all of the water on Earth is
Climate Institute. Web. Retrieved 2011-11-03. Fresh water is an exceptionally important resource, since life on Earth is ultimately dependent on it. Water transports nutrients, minerals and chemicals within the
 The human population on Earth is expanding rapidly, which together with even more rapid
The human population on Earth is expanding rapidly, which together with even more rapid
. Powell, Fannetta. "Environmental Degradation and Human Disease". Lecture. SlideBoom. 2009. Web. Retrieved 2011-11-14.

 Agriculture is dependent on available
Agriculture is dependent on available
Web. Retrieved 2011-11-14. The transfer of water from agricultural to urban and suburban use raises concerns about agricultural sustainability, rural socioeconomic decline, food security, an increased
 Water management is the process of planning, developing, and managing water resources across all water applications, in terms of both quantity and quality." Water management is supported and guided by institutions, infrastructure, incentives, and information systems
The issue of the depletion of fresh water has stimulated increased efforts in water management. While water management systems are often flexible, adaptation to new hydrologic conditions may be very costly. Preventative approaches are necessary to avoid high costs of inefficiency and the need for rehabilitation of
Water management is the process of planning, developing, and managing water resources across all water applications, in terms of both quantity and quality." Water management is supported and guided by institutions, infrastructure, incentives, and information systems
The issue of the depletion of fresh water has stimulated increased efforts in water management. While water management systems are often flexible, adaptation to new hydrologic conditions may be very costly. Preventative approaches are necessary to avoid high costs of inefficiency and the need for rehabilitation of
Ecology of Increasing Disease ''Population growth and environmental degradation''
Environmental Change in the Kalahari: Integrated Land Degradation Studies for Nonequilibrium Dryland Environments in the Annals of the Association of American Geographers
Public Daily Brief Threat: Environmental Degradation
* ttp://www.tms.org/Meetings/Specialty/ED2005/home.html Environmental Degradation of Materials in Nuclear Systems-Water Reactorsbr>Herndon and Gibbon Lieutenants United States Navy
The First North American Explorers of the Amazon Valley, by Historian Normand E. Klare. Actual Reports from the explorers are compared with present Amazon Basin conditions.
Environmental Degradation Index by Jha & Murthy (for 174 countries)
{{Authority control Environmental issues
environment
Environment most often refers to:
__NOTOC__
* Natural environment, all living and non-living things occurring naturally
* Biophysical environment, the physical and biological factors along with their chemical interactions that affect an organism or ...
through depletion of resources such as quality of air
The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, known collectively as air, retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphere. The atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing f ...
, water
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as ...
and soil
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth or dirt, is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, liquids, and organisms that together support life. Some scientific definitions distinguish ''dirt'' from ''soil'' by restricting the former ...
; the destruction of ecosystems
An ecosystem (or ecological system) consists of all the organisms and the physical environment with which they interact. These biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Energy enters the syst ...
; habitat destruction
Habitat destruction (also termed habitat loss and habitat reduction) is the process by which a natural habitat becomes incapable of supporting its native species. The organisms that previously inhabited the site are displaced or dead, thereby ...
; the extinction
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds (taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the Endling, last individual of the species, although the Functional ext ...
of wildlife
Wildlife refers to undomesticated animal species, but has come to include all organisms that grow or live wild in an area without being introduced by humans. Wildlife was also synonymous to game: those birds and mammals that were hunted ...
; and pollution
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into the natural environment that cause adverse change. Pollution can take the form of any substance (solid, liquid, or gas) or energy (such as radioactivity, heat, sound, or light). Pollutants, th ...
. It is defined as any change or disturbance to the environment perceived to be deleterious or undesirable.
Environmental concerns can be defined as the negative effects of any human activity on the environment. The biological as well as the physical features of the environment are included. Some of the primary environmental challenges that are causing great worry are air pollution, water pollution, natural environment pollution, rubbish pollution, and so oEnvironmental degradation is one of the ten threats officially cautioned by the High-level Panel on Threats, Challenges and Change, high-level PaneI on Threats, Challenges and Change of the
United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoni ...
. The United Nations International Strategy for Disaster Reduction
The United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction (UNDRR) was created in December 1999 to ensure the implementation of the International Strategy for Disaster Reduction (General Assembly (GA) resolution 54/219).
defines environmental degradation as "the reduction of the capacity of the environment to meet social and ecological objectives, and needs". Environmental degradation comes in many types. When natural habitats are destroyed or natural resources are depleted, the environment is degraded. Efforts to counteract this problem include environmental protection
Environmental protection is the practice of protecting the natural environment by individuals, organizations and governments. Its objectives are to conserve natural resources and the existing natural environment and, where possible, to repair dam ...
and environmental resources management
Environmental resource management is the management of the interaction and impact of human societies on the environment. It is not, as the phrase might suggest, the management of the environment itself. Environmental resources management aims ...
. Mismanagement that leads to degradation can also lead to environmental conflict
Environmental conflicts or ecological distribution conflicts (EDCs) are social conflicts caused by environmental degradation or by unequal distribution of environmental resources.Libiszewski, Stephan.What is an Environmental Conflict." ''Journal ...
where communities organize in opposition to the forces that mismanaged the environment.
Biodiversity loss
 Scientists assert that human activity has pushed the earth into a sixth mass extinction event. The
Scientists assert that human activity has pushed the earth into a sixth mass extinction event. The loss of biodiversity
Biodiversity loss includes the worldwide extinction of different species, as well as the local reduction or loss of species in a certain habitat, resulting in a loss of biological diversity. The latter phenomenon can be temporary or permanent, de ...
has been attributed in particular to human overpopulation
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, cultu ...
, continued human population growth
Population growth is the increase in the number of people in a population or dispersed group. Actual global human population growth amounts to around 83 million annually, or 1.1% per year. The global population has grown from 1 billion in 1800 to ...
and overconsumption
Overconsumption describes a situation where a consumer overuses their available goods and services to where they can't, or don't want to, replenish or reuse them. In microeconomics, this may be described as the point where the marginal cost of ...
of natural resources by the world's wealthy. A 2020 report by the World Wildlife Fund
The World Wide Fund for Nature Inc. (WWF) is an international non-governmental organization founded in 1961 that works in the field of wilderness preservation and the reduction of human impact on the environment. It was formerly named the W ...
found that human activity – specifically overconsumption, population growth and intensive farming
Intensive agriculture, also known as intensive farming (as opposed to extensive farming), conventional, or industrial agriculture, is a type of agriculture, both of crop plants and of animals, with higher levels of input and output per unit of ...
– has destroyed 68% of vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () ( chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, with ...
wildlife
Wildlife refers to undomesticated animal species, but has come to include all organisms that grow or live wild in an area without being introduced by humans. Wildlife was also synonymous to game: those birds and mammals that were hunted ...
since 1970. The ''Global Assessment Report on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services
Global means of or referring to a globe and may also refer to:
Entertainment
* ''Global'' (Paul van Dyk album), 2003
* ''Global'' (Bunji Garlin album), 2007
* ''Global'' (Humanoid album), 1989
* ''Global'' (Todd Rundgren album), 2015
* Bruno ...
'', published by the United Nation's IPBES
The Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES) is an intergovernmental organization established to improve the interface between science and policy on issues of biodiversity and ecosystem services. It ...
in 2019, posits that roughly one million species of plants and animals face extinction from anthropogenic causes, such as expanding human land use for industrial agriculture
Industrial agriculture is a form of modern farming that refers to the industrialized production of crops and animals and animal products like eggs or milk. The methods of industrial agriculture include innovation in agricultural machinery and fa ...
and livestock
Livestock are the domesticated animals raised in an agricultural setting to provide labor and produce diversified products for consumption such as meat, eggs, milk, fur, leather, and wool. The term is sometimes used to refer solely to ani ...
rearing, along with overfishing
Overfishing is the removal of a species of fish (i.e. fishing) from a body of water at a rate greater than that the species can replenish its population naturally (i.e. the overexploitation of the fishery's existing fish stock), resulting in t ...
.
Since the establishment of agriculture over 11,000 years ago, humans have altered roughly 70% of the earth's land surface, with the global biomass
Biomass is plant-based material used as a fuel for heat or electricity production. It can be in the form of wood, wood residues, energy crops, agricultural residues, and waste from industry, farms, and households. Some people use the terms bio ...
of vegetation being reduced by half, and terrestrial animal communities seeing a decline in biodiversity greater than 20% on average. A 2021 study says that just 3% of the planet's terrestrial surface is ecologically and fauna
Fauna is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding term for plants is '' flora'', and for fungi, it is '' funga''. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively referred to as '' biota''. ...
lly intact, meaning areas with healthy populations of native animal species and little to no human footprint. Many of these intact ecosystems were in areas inhabited by indigenous peoples.
The implications of these losses for human livelihoods and wellbeing have raised serious concerns. With regard to the agriculture sector for example, ''The State of the World’s Biodiversity for Food and Agriculture'', published by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations in 2019, states that “countries report that many species that contribute to vital ecosystem services, including pollinators, the natural enemies of pests, soil organisms and wild food species, are in decline as a consequence of the destruction and degradation of habitats, overexploitation, pollution and other threats” and that “key ecosystems that deliver numerous services essential to food and agriculture, including supply of freshwater, protection against hazards and provision of habitat for species such as fish and pollinators, are declining.”
Impacts of environmental degradation on women’s livelihoods
On the way biodiversity loss and ecosystem degradation impact livelihoods, theFood and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO)french: link=no, Organisation des Nations unies pour l'alimentation et l'agriculture; it, Organizzazione delle Nazioni Unite per l'Alimentazione e l'Agricoltura is an intern ...
finds also that in contexts of degraded lands and ecosystems in rural areas, both girls and women bear heavier workloads.
Women's livelihoods, health, food and nutrition security, access to water and energy, and coping abilities are all disproportionately affected by environmental degradation. Environmental pressures and shocks, particularly in rural areas, force women to deal with the aftermath, greatly increasing their load of unpaid care work.
This implies, for example, longer journeys to get primary necessities and greater exposure to the risks of human trafficking, rape, and sexual violence.
Water degradation
 One major component of environmental degradation is the depletion of the resource of fresh water on Earth. Approximately only 2.5% of all of the water on Earth is
One major component of environmental degradation is the depletion of the resource of fresh water on Earth. Approximately only 2.5% of all of the water on Earth is fresh water
Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salts and other total dissolved solids. Although the term specifically excludes seawater and brackish water, it does incl ...
, with the rest being salt water
Saline water (more commonly known as salt water) is water that contains a high concentration of dissolved salts (mainly sodium chloride). On the United States Geological Survey (USGS) salinity scale, saline water is saltier than brackish w ...
. 69% of fresh water is frozen in ice caps
In glaciology, an ice cap is a mass of ice that covers less than of land area (usually covering a highland area). Larger ice masses covering more than are termed ice sheets.
Description
Ice caps are not constrained by topographical features ...
located on Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest cont ...
and Greenland
Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland ...
, so only 30% of the 2.5% of fresh water
is available for consumption.”Water.”Climate Institute. Web. Retrieved 2011-11-03. Fresh water is an exceptionally important resource, since life on Earth is ultimately dependent on it. Water transports nutrients, minerals and chemicals within the
biosphere
The biosphere (from Greek βίος ''bíos'' "life" and σφαῖρα ''sphaira'' "sphere"), also known as the ecosphere (from Greek οἶκος ''oîkos'' "environment" and σφαῖρα), is the worldwide sum of all ecosystems. It can also ...
to all forms of life, sustains both plants and animals, and moulds the surface of the Earth with transportation and deposition of materials.Young, Gordon J., James Dooge, and John C. Rodda. Global Water Resource Issues. Cambridge UP, 2004.
The current top three uses of fresh water account for 95% of its consumption; approximately 85% is used for irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has been devel ...
of farmland, golf courses, and parks, 6% is used for domestic purposes such as indoor bathing uses and outdoor garden and lawn use, and 4% is used for industrial purposes such as processing, washing, and cooling in manufacturing centres.Frederick, Kenneth D., and David C. Major. “Climate Change and Water Resources.” Climatic Change 37.1 (1997): p 7-23. It is estimated that one in three people over the entire globe are already facing water shortages, almost one-fifth of the world population
In demographics, the world population is the total number of humans currently living. It was estimated by the United Nations to have exceeded 8 billion in November 2022. It took over 200,000 years of human prehistory and history for th ...
live in areas of physical water scarcity, and almost one quarter of the world's population live in a developing country
A developing country is a sovereign state with a lesser developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreeme ...
that lacks the necessary infrastructure to use water from available rivers and aquifers. Water scarcity is an increasing problem due to many foreseen issues in the future including population growth, increased urbanization
Urbanization (or urbanisation) refers to the population shift from rural to urban areas, the corresponding decrease in the proportion of people living in rural areas, and the ways in which societies adapt to this change. It is predominantly th ...
, higher standards of living
Standard of living is the level of income, comforts and services available, generally applied to a society or location, rather than to an individual. Standard of living is relevant because it is considered to contribute to an individual's qualit ...
, and climate change.
Industrial and domestic sewage, pesticides, fertilizers, plankton blooms, silt, oils, chemical residues, radioactive material, and other pollutants are some of the most frequent water pollutants. These have a huge negative impact on the water and can cause degradation in various levels.
Climate change and temperature
Climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
affects the Earth's water supply in a large number of ways. It is predicted that the mean global temperature will rise in the coming years due to a number of forces affecting the climate. The amount of atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) will rise, and both of these will influence water resources; evaporation
Evaporation is a type of vaporization that occurs on the surface of a liquid as it changes into the gas phase. High concentration of the evaporating substance in the surrounding gas significantly slows down evaporation, such as when h ...
depends strongly on temperature and moisture availability which can ultimately affect the amount of water available to replenish groundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and Pore space in soil, soil pore spaces and in the fractures of stratum, rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available freshwater in the world is groundwater. A unit ...
supplies.
Transpiration
Transpiration is the process of water movement through a plant and its evaporation from aerial parts, such as leaves, stems and flowers. Water is necessary for plants but only a small amount of water taken up by the roots is used for growth ...
from plants can be affected by a rise in atmospheric CO2, which can decrease their use of water, but can also raise their use of water from possible increases of leaf area. Temperature rise can reduce the snow season in the winter and increase the intensity of the melting snow leading to peak runoff of this, affecting soil moisture, flood and drought risks, and storage capacities depending on the area.Ragab, Ragab, and Christel Prudhomme. "Soil and Water: Climate Change and Water Resources Management in Arid and Semi-Arid Regions: Prospective Challenges for the 21st Century". Biosystems Engineering 81.1 (2002): p 3-34.
Warmer winter temperatures cause a decrease in snowpack
Snowpack forms from layers of snow that accumulate in geographic regions and high elevations where the climate includes cold weather for extended periods during the year. Snowpacks are an important water resource that feed streams and rivers as t ...
, which can result in diminished water resources during summer. This is especially important at mid-latitudes and in mountain regions that depend on glacial runoff to replenish their river systems and groundwater supplies, making these areas increasingly vulnerable to water shortages over time; an increase in temperature will initially result in a rapid rise in water melting from glaciers
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such as ...
in the summer, followed by a retreat in glaciers and a decrease in the melt and consequently the water supply every year as the size of these glaciers get smaller and smaller.
Thermal expansion
Thermal expansion is the tendency of matter to change its shape, area, volume, and density in response to a change in temperature, usually not including phase transitions.
Temperature is a monotonic function of the average molecular kin ...
of water and increased melting of oceanic glaciers from an increase in temperature gives way to a rise in sea level. This can affect the freshwater supply to coastal areas as well. As river mouths and deltas with higher salinity
Salinity () is the saltiness or amount of salt (chemistry), salt dissolved in a body of water, called saline water (see also soil salinity). It is usually measured in g/L or g/kg (grams of salt per liter/kilogram of water; the latter is dimensio ...
get pushed further inland, an intrusion of saltwater results in an increase of salinity in reservoirs and aquifers. Sea-level rise may also consequently be caused by a depletion of groundwater,Konikow, Leonard F. "Contribution of Global Groundwater Depletion since 1990 to Sea-level Rise". ''Geophysical Research Letters'' 38.17 (2011). as climate change can affect the hydrologic cycle
The water cycle, also known as the hydrologic cycle or the hydrological cycle, is a biogeochemical cycle that describes the continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the Earth. The mass of water on Earth remains fairly const ...
in a number of ways. Uneven distributions of increased temperatures and increased precipitation around the globe results in water surpluses and deficits, but a global decrease in groundwater suggests a rise in sea level, even after meltwater
Meltwater is water released by the melting of snow or ice, including glacial ice, tabular icebergs and ice shelves over oceans. Meltwater is often found in the ablation zone of glaciers, where the rate of snow cover is reducing. Meltwater ca ...
and thermal expansion were accounted for, which can provide a positive feedback
Positive feedback (exacerbating feedback, self-reinforcing feedback) is a process that occurs in a feedback loop which exacerbates the effects of a small disturbance. That is, the effects of a perturbation on a system include an increase in th ...
to the problems sea-level rise causes to fresh-water supply.
A rise in air temperature results in a rise in water temperature, which is also very significant in water degradation as the water would become more susceptible to bacterial growth
250px, Growth is shown as ''L'' = log(numbers) where numbers is the number of colony forming units per ml, versus ''T'' (time.)
Bacterial growth is proliferation of bacterium into two daughter cells, in a process called binary fission. Providing ...
. An increase in water temperature can also affect ecosystems
An ecosystem (or ecological system) consists of all the organisms and the physical environment with which they interact. These biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Energy enters the syst ...
greatly because of a species' sensitivity to temperature, and also by inducing changes in a body of water's self-purification system from decreased amounts of dissolved oxygen in the water due to rises in temperature.
Climate change and precipitation
A rise in global temperatures is also predicted to correlate with an increase in global precipitation but because of increased runoff, floods, increased rates ofsoil erosion
Soil erosion is the denudation or wearing away of the upper layer of soil. It is a form of soil degradation. This natural process is caused by the dynamic activity of erosive agents, that is, water, ice (glaciers), snow, air (wind), plants, a ...
, and mass movement of land, a decline in water quality
Water quality refers to the chemical, physical, and biological characteristics of water based on the standards of its usage. It is most frequently used by reference to a set of standards against which compliance, generally achieved through tr ...
is probable, because while water will carry more nutrients it will also carry more contaminants. While most of the attention about climate change is directed towards global warming and greenhouse effect
The greenhouse effect is a process that occurs when energy from a planet's host star goes through the planet's atmosphere and heats the planet's surface, but greenhouse gases in the atmosphere prevent some of the heat from returning directly ...
, some of the most severe effects of climate change
The effects of climate change impact the physical environment, ecosystems and human societies. The environmental effects of climate change are broad and far-reaching. They affect the water cycle, oceans, sea and land ice ( glaciers), sea le ...
are likely to be from changes in precipitation, evapotranspiration
Evapotranspiration (ET) is the combined processes by which water moves from the earth’s surface into the atmosphere. It covers both water evaporation (movement of water to the air directly from soil, canopies, and water bodies) and transp ...
, runoff, and soil moisture. It is generally expected that, on average, global precipitation will increase, with some areas receiving increases and some decreases.
Climate model
Numerical climate models use quantitative methods to simulate the interactions of the important drivers of climate, including atmosphere, oceans, land surface and ice. They are used for a variety of purposes from study of the dynamics of the c ...
s show that while some regions should expect an increase in precipitation, such as in the tropics and higher latitudes, other areas are expected to see a decrease, such as in the subtropics. This will ultimately cause a latitudinal variation in water distribution. The areas receiving more precipitation are also expected to receive this increase during their winter and actually become drier during their summer, creating even more of a variation of precipitation distribution. Naturally, the distribution of precipitation across the planet is very uneven, causing constant variations in water availability in respective locations.
Changes in precipitation affect the timing and magnitude of floods and droughts, shift runoff processes, and alter groundwater recharge
Groundwater recharge or deep drainage or deep percolation is a hydrologic process, where water moves downward from surface water to groundwater. Recharge is the primary method through which water enters an aquifer. This process usually occurs ...
rates. Vegetation patterns and growth rates will be directly affected by shifts in precipitation amount and distribution, which will in turn affect agriculture as well as natural ecosystems. Decreased precipitation will deprive areas of water causing water tables to fall and reservoirs of wetlands, rivers, and lakes to empty. In addition, a possible increase in evaporation and evapotranspiration will result, depending on the accompanied rise in temperature. Groundwater reserves will be depleted, and the remaining water has a greater chance of being of poor quality from saline or contaminants on the land surface.
Climate change is resulting into a very high rate of land degradation causing enhanced desertification and nutrient deficient soils. The menace of land degradation is increasing by the day and has been characterized as a major global threat. According to Global Assessment of Land Degradation and Improvement (GLADA) a quarter of land area around the globe can now be marked as degraded. Land degradation is supposed to influence lives of 1.5 billion people and 15 billion tons of fertile soil is lost every year due to anthropogenic activities and climate change.
Population growth
economic growth
Economic growth can be defined as the increase or improvement in the inflation-adjusted market value of the goods and services produced by an economy in a financial year. Statisticians conventionally measure such growth as the percent rate o ...
is the main cause of the degradation of the environment. Humanity's appetite for resources is disrupting the environment's natural equilibrium. Production industries are venting smoke into the atmosphere and discharging chemicals that are polluting water resources. The smoke includes detrimental gases such as carbon monoxide and sulphur dioxide. The high levels of pollution in the atmosphere form layers that are eventually absorbed into the atmosphere. Organic compounds such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) have generated an opening in the ozone layer, which admits higher levels of ultraviolet radiation, putting the globe at risk.
The available fresh water being affected by the climate is also being stretched across an ever-increasing global population. It is estimated that almost a quarter of the global population is living in an area that is using more than 20% of their renewable water supply; water use will rise with population while the water supply is also being aggravated by decreases in streamflow and groundwater caused by climate change. Even though some areas may see an increase in freshwater supply from an uneven distribution of precipitation increase, an increased use of water supply is expected.Raleigh, Clionadh, and Henrik Urdal
Henrik Urdal (born 19 October 1972) is a Norwegian political scientist and the current director of the Peace Research Institute Oslo (PRIO). Before his appointment as director in 2017 he was a research professor and research director at the insti ...
. “Climate Change, Environmental Degradation, and Armed Conflict.” Political Geography 26.6 (2007): 674–94.
An increased population means increased withdrawals from the water supply for domestic, agricultural, and industrial uses, the largest of these being agriculture,MacDonald, Glen M. "Water, Climate Change, and Sustainability in the Southwest". PNAS 107.50 (2010): p 56-62. believed to be the major non-climate driver of environmental change and water deterioration. The next 50 years will likely be the last period of rapid agricultural expansion
Agricultural expansion describes the growth of agricultural land (arable land, pastures, etc.) especially in the 20th and 21st centuries.
The agricultural expansion is often explained as a direct consequence of the global increase in food and en ...
, but the larger and wealthier population over this time will demand more agriculture.Tilman, David, Joseph Fargione, Brian Wolff, Carla D'Antonio, Andrew Dobson, Robert Howarth, David Scindler, William Schlesinger, Danielle Simberloff, and Deborah Swackhamer. "Forecasting Agriculturally Driven Global Environmental Change". ''Science'' 292.5515 (2011): p 281-84.
Population increase over the last two decades, at least in the United States, has also been accompanied by a shift to an increase in urban areas from rural areas,Wallach, Bret. ''Understanding the Cultural Landscape''. New York; Guilford, 2005. which concentrates the demand for water into certain areas, and puts stress on the fresh water supply from industrial and human contaminants. Urbanization
Urbanization (or urbanisation) refers to the population shift from rural to urban areas, the corresponding decrease in the proportion of people living in rural areas, and the ways in which societies adapt to this change. It is predominantly th ...
causes overcrowding and increasingly unsanitary living conditions, especially in developing countries, which in turn exposes an increasingly number of people to disease. About 79% of the world's population is in developing countries, which lack access to sanitary water and sewer systems, giving rises to disease and deaths from contaminated water and increased numbers of disease-carrying insects.. Powell, Fannetta. "Environmental Degradation and Human Disease". Lecture. SlideBoom. 2009. Web. Retrieved 2011-11-14.
Agriculture
soil moisture
Soil moisture is the water content of the soil. It can be expressed in terms of volume or weight. Soil moisture measurement can be based on ''in situ'' probes (e.g., capacitance probes, neutron probes) or remote sensing methods.
Water that enter ...
, which is directly affected by climate dynamics, with precipitation being the input in this system and various processes being the output, such as evapotranspiration
Evapotranspiration (ET) is the combined processes by which water moves from the earth’s surface into the atmosphere. It covers both water evaporation (movement of water to the air directly from soil, canopies, and water bodies) and transp ...
, surface runoff
Surface runoff (also known as overland flow) is the flow of water occurring on the ground surface when excess rainwater, stormwater, meltwater, or other sources, can no longer sufficiently rapidly infiltrate in the soil. This can occur when t ...
, drainage, and percolation into groundwater. Changes in climate, especially the changes in precipitation and evapotranspiration predicted by climate models, will directly affect soil moisture, surface runoff, and groundwater recharge
Groundwater recharge or deep drainage or deep percolation is a hydrologic process, where water moves downward from surface water to groundwater. Recharge is the primary method through which water enters an aquifer. This process usually occurs ...
.
In areas with decreasing precipitation as predicted by the climate models, soil moisture may be substantially reduced. With this in mind, agriculture in most areas already needs irrigation, which depletes fresh water supplies both by the physical use of the water and the degradation agriculture causes to the water. Irrigation increases salt and nutrient content in areas that would not normally be affected, and damages streams and rivers from damming and removal of water. Fertilizer enters both human and livestock waste streams that eventually enter groundwater, while nitrogen, phosphorus, and other chemicals from fertilizer can acidify both soils and water.
Certain agricultural demands may increase more than others with an increasingly wealthier global population, and meat
Meat is animal flesh that is eaten as food. Humans have hunted, farmed, and scavenged animals for meat since prehistoric times. The establishment of settlements in the Neolithic Revolution allowed the domestication of animals such as chic ...
is one commodity expected to double global food demand by 2050, which directly affects the global supply of fresh water. Cows need water to drink, more if the temperature is high and humidity is low, and more if the production system the cow is in is extensive, since finding food takes more effort. Water is needed in the processing of the meat, and also in the production of feed for the livestock. Manure can contaminate bodies of freshwater, and slaughterhouses, depending on how well they are managed, contribute waste such as blood, fat, hair, and other bodily contents to supplies of fresh water."Environmental Implications of the Global Demand for Red Meat"Web. Retrieved 2011-11-14. The transfer of water from agricultural to urban and suburban use raises concerns about agricultural sustainability, rural socioeconomic decline, food security, an increased
carbon footprint
A carbon footprint is the total greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions caused by an individual, event, organization, service, place or product, expressed as carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2e). Greenhouse gases, including the carbon-containing gases carbo ...
from imported food, and decreased foreign trade balance. The depletion of fresh water, as applied to more specific and populated areas, increases fresh water scarcity among the population and also makes populations susceptible to economic, social, and political conflict in a number of ways; rising sea levels forces migration
Migration, migratory, or migrate may refer to: Human migration
* Human migration, physical movement by humans from one region to another
** International migration, when peoples cross state boundaries and stay in the host state for some minimum le ...
from coastal areas to other areas farther inland, pushing populations closer together breaching borders and other geographical patterns, and agricultural surpluses and deficits from the availability of water induce trade problems and economies of certain areas. Climate change is an important cause of involuntary migration and forced displacement According to the Food and Agriculture Organization
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO)french: link=no, Organisation des Nations unies pour l'alimentation et l'agriculture; it, Organizzazione delle Nazioni Unite per l'Alimentazione e l'Agricoltura is an intern ...
of the United Nations, global greenhouse gas emissions from animal agriculture exceeds that of transportation.
Water management
 Water management is the process of planning, developing, and managing water resources across all water applications, in terms of both quantity and quality." Water management is supported and guided by institutions, infrastructure, incentives, and information systems
The issue of the depletion of fresh water has stimulated increased efforts in water management. While water management systems are often flexible, adaptation to new hydrologic conditions may be very costly. Preventative approaches are necessary to avoid high costs of inefficiency and the need for rehabilitation of
Water management is the process of planning, developing, and managing water resources across all water applications, in terms of both quantity and quality." Water management is supported and guided by institutions, infrastructure, incentives, and information systems
The issue of the depletion of fresh water has stimulated increased efforts in water management. While water management systems are often flexible, adaptation to new hydrologic conditions may be very costly. Preventative approaches are necessary to avoid high costs of inefficiency and the need for rehabilitation of water supplies
Water supply is the provision of water by public utilities, commercial organisations, community endeavors or by individuals, usually via a system of pumps and pipes. Public water supply systems are crucial to properly functioning societies. Thes ...
, and innovations to decrease overall demand may be important in planning water sustainability.
Water supply systems, as they exist now, were based on the assumptions of the current climate, and built to accommodate existing river flows and flood frequencies. Reservoirs are operated based on past hydrologic records, and irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has been devel ...
systems on historical temperature, water availability, and crop water requirements; these may not be a reliable guide to the future. Re-examining engineering designs, operations, optimizations, and planning, as well as re-evaluating legal, technical, and economic approaches to manage water resources are very important for the future of water management in response to water degradation. Another approach is water privatization
Water privatization is short for private sector participations in the provision of water services and sanitation. Water privatization has a variable history in which its popularity and favorability has fluctuated in the market and politics. One o ...
; despite its economic and cultural effects, service quality and overall quality of the water can be more easily controlled and distributed. Rationality and sustainability
Specific definitions of sustainability are difficult to agree on and have varied in the literature and over time. The concept of sustainability can be used to guide decisions at the global, national, and individual levels (e.g. sustainable livi ...
is appropriate, and requires limits to overexploitation
Overexploitation, also called overharvesting, refers to harvesting a renewable resource to the point of diminishing returns. Continued overexploitation can lead to the destruction of the resource, as it will be unable to replenish. The term ap ...
and pollution and efforts in conservation.
See also
*Anthropocene
The Anthropocene ( ) is a proposed geological epoch dating from the commencement of significant human impact on Earth's geology and ecosystems, including, but not limited to, anthropogenic climate change.
, neither the International Commissio ...
* Environmental change Environmental change is a change or disturbance of the environment most often caused by human influences and natural ecological processes. Environmental changes include various factors, such as natural disasters, human interferences, or animal in ...
* Environmental issues
Environmental issues are effects of human activity on the biophysical environment, most often of which are harmful effects that cause environmental degradation. Environmental protection is the practice of protecting the natural environment on t ...
* Ecological collapse
Ecological collapse refers to a situation where an ecosystem suffers a drastic, possibly permanent, reduction in carrying capacity for all organisms, often resulting in mass extinction. Usually, an ecological collapse is precipitated by a disastr ...
* Ecologically sustainable development Ecologically sustainable development is the environmental component of sustainable development. It can be achieved partially through the use of the precautionary principle; if there are threats of serious or irreversible environmental damage, lack ...
* Eco-socialism
Eco-socialism (also known as green socialism or socialist ecology) is an ideology merging aspects of socialism with that of green politics, ecology and alter-globalization or anti-globalization. Eco-socialists generally believe that the expansi ...
* Exploitation of natural resources
The exploitation of natural resources is the use of natural resources for economic growth, sometimes with a negative connotation of accompanying environmental degradation. It started to emerge on an industrial scale in the 19th century as the e ...
* I=PAT
* Restoration ecology
Restoration ecology is the scientific study supporting the practice of ecological restoration, which is the practice of renewing and restoring degraded, damaged, or destroyed ecosystems and habitats in the environment by active human interrupt ...
* United Nations Decade on Biodiversity
* United Nations Development Programme
The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP)french: Programme des Nations unies pour le développement, PNUD is a United Nations agency tasked with helping countries eliminate poverty and achieve sustainable economic growth and human dev ...
(UNDP)
* United Nations Environment Programme
The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) is responsible for coordinating responses to environmental issues within the United Nations system. It was established by Maurice Strong, its first director, after the United Nations Conference on ...
(UNEP)
* World Resources Institute
The World Resources Institute (WRI) is a global research non-profit organization established in 1982 with funding from the MacArthur Foundation under the leadership of James Gustave Speth. WRI's activities are focused on seven areas: food, for ...
(WRI)
Sources
References
External links
Ecology of Increasing Disease ''Population growth and environmental degradation''
Environmental Change in the Kalahari: Integrated Land Degradation Studies for Nonequilibrium Dryland Environments in the Annals of the Association of American Geographers
Public Daily Brief Threat: Environmental Degradation
* ttp://www.tms.org/Meetings/Specialty/ED2005/home.html Environmental Degradation of Materials in Nuclear Systems-Water Reactorsbr>Herndon and Gibbon Lieutenants United States Navy
The First North American Explorers of the Amazon Valley, by Historian Normand E. Klare. Actual Reports from the explorers are compared with present Amazon Basin conditions.
Environmental Degradation Index by Jha & Murthy (for 174 countries)
{{Authority control Environmental issues