Enlargement of Switzerland on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
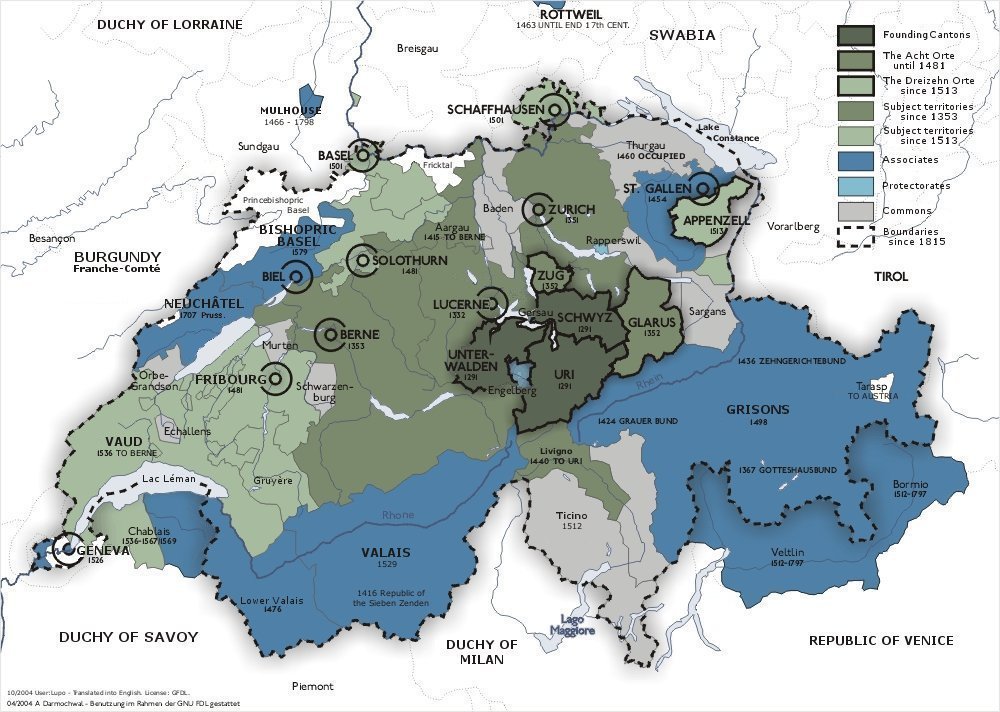 The territorial evolution of Switzerland occurred primarily with the acquisition of territory by the historical cantons of the Old Swiss Confederacy and its close associates. This gradual expansion took place in two phases, the growth from the medieval Founding Cantons to the "
The territorial evolution of Switzerland occurred primarily with the acquisition of territory by the historical cantons of the Old Swiss Confederacy and its close associates. This gradual expansion took place in two phases, the growth from the medieval Founding Cantons to the "


 Switzerland, a multilingual
Switzerland, a multilingual

 New cantons were added only in the
New cantons were added only in the
 After Italian unification in 1861, all land west of Lake Lugano and half of the lake were given to Switzerland so that Swiss trade and transport would not have to pass through Italy. The ''d'Italia'' suffix was added to the name of Campione in the 1930s by Prime Minister Benito Mussolini and an ornamental gate to the city was built, both in an attempt to assert the exclave's Italian-ness.
There remained some territorial disputes after the formation of the Kingdom of Italy, resolved in the ''Convenzione tra l'Italia e la Svizzera per l'accertamento della frontiera fra la Lombardia ed il Cantone dei Grigioni'' of 1863. Since then, the international
After Italian unification in 1861, all land west of Lake Lugano and half of the lake were given to Switzerland so that Swiss trade and transport would not have to pass through Italy. The ''d'Italia'' suffix was added to the name of Campione in the 1930s by Prime Minister Benito Mussolini and an ornamental gate to the city was built, both in an attempt to assert the exclave's Italian-ness.
There remained some territorial disputes after the formation of the Kingdom of Italy, resolved in the ''Convenzione tra l'Italia e la Svizzera per l'accertamento della frontiera fra la Lombardia ed il Cantone dei Grigioni'' of 1863. Since then, the international
Erleichterte Integration grenznaher Regionen als neue Schweizer Kantone
', motion 10.3215 of 18 March 2010 by Dominique Baettig. The motion was widely seen as anti-EU rhetoric rather than a serious proposal. In a statement of 19 May 2010, the Swiss Federal Council recommended its rejection, describing the motion as a "provocation". It argued that its adoption would be considered an unfriendly act by the countries surrounding Switzerland, and that it would also be at odds with international law, which in the government's view does not provide for a right to secession except in exceptional circumstances. The topic attracted the attention of the European media. The media went on to report a high level of apparent popular support for joining Switzerland in the territories in question (as reflected in Internet polls and comments): * In Como, an online poll in June 2010 by the ''La Provincia di Como'' newspaper found 74% of 2,500 respondents in favor of accession to Switzerland, which the local regionalist party ''Lega Lombarda'' has long been advocating. * Another online poll by the South German ''Südkurier'' newspaper found that almost 70% of respondents replied "yes, the Swiss are closer to us in outlook" to a question whether the state ofIpotesi di annessione. Candiani: "Campione resta in Italia"
''TVSvizzera.it'', 21 September 2018
File:Territorial-development-Swiss Confederacy.png, Territorial development of Old Swiss Confederacy, 1291–1797.
File:Historische Karte CH 1315.png, Switzerland in 1315, just before the Battle of Morgarten.
File:Historische Karte CH 1385.png, Switzerland in 1385, just before the Battle of Sempach.
File:Historische Karte CH 1474.png, Switzerland in 1474, just before the Burgundian Wars.
File:Historische Karte CH 1515.png, Switzerland in 1515, just before the Battle of Marignano.
File:Historische Karte CH 1536.png, Switzerland in 1536, during the Reformation, just after the conquest of
 The territorial evolution of Switzerland occurred primarily with the acquisition of territory by the historical cantons of the Old Swiss Confederacy and its close associates. This gradual expansion took place in two phases, the growth from the medieval Founding Cantons to the "
The territorial evolution of Switzerland occurred primarily with the acquisition of territory by the historical cantons of the Old Swiss Confederacy and its close associates. This gradual expansion took place in two phases, the growth from the medieval Founding Cantons to the "Eight Cantons
The Old Swiss Confederacy began as a late medieval alliance between the communities of the valleys in the Central Alps, at the time part of the Holy Roman Empire, to facilitate the management of common interests such as free trade and to ensure ...
" during 1332–1353, and the expansion to the "Thirteen Cantons
The early modern history of the Old Swiss Confederacy ('' Eidgenossenschaft'', also known as the "Swiss Republic" or ''Republica Helvetiorum'') and its constituent Thirteen Cantons encompasses the time of the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648 ...
" of the Reformation period during 1481–1513.
The Helvetic Republic (formed 1798) as revised in the Act of Mediation
The Act of Mediation () was issued by Napoleon Bonaparte, First Consul of the French Republic on 19 February 1803 establishing the Swiss Confederation. The act also abolished the previous Helvetic Republic, which had existed since the invasi ...
(1803) added further territories of former Associates of the Swiss Confederacy, notably those of the Abbey of St. Gall
The Abbey of Saint Gall (german: Abtei St. Gallen) is a dissolved abbey (747–1805) in a Catholic religious complex in the city of St. Gallen in Switzerland. The Carolingian-era monastery existed from 719, founded by Saint Othmar on the spot ...
and the Three Leagues
The Three Leagues, sometimes referred to as Raetia, was the alliance of 1471 of the League of God's House, the League of the Ten Jurisdictions, and the Grey League, leading eventually to the formation of the Swiss canton of Graubünden (Grison ...
. The territories of the Valais
Valais ( , , ; frp, Valês; german: Wallis ), more formally the Canton of Valais,; german: Kanton Wallis; in other official Swiss languages outside Valais: it, (Canton) Vallese ; rm, (Chantun) Vallais. is one of the 26 cantons forming the S ...
, the Swiss Jura
Swiss may refer to:
* the adjectival form of Switzerland
* Swiss people
Places
* Swiss, Missouri
* Swiss, North Carolina
*Swiss, West Virginia
* Swiss, Wisconsin
Other uses
*Swiss-system tournament, in various games and sports
*Swiss Internatio ...
and Geneva
, neighboring_municipalities= Carouge, Chêne-Bougeries, Cologny, Lancy, Grand-Saconnex, Pregny-Chambésy, Vernier, Veyrier
, website = https://www.geneve.ch/
Geneva ( ; french: Genève ) frp, Genèva ; german: link=no, Genf ; it, Ginevr ...
were added to the "restored" Confederacy following the Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna (, ) of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon B ...
in 1815.
The restored Confederacy remained a union of nominally independent states until the formation of Switzerland as a federal state in 1848. Some territorial disputes remained, and were resolved in the 1850s and 1860s. Since then, the territory of Switzerland has remained fixed (with the exception of minor border corrections) by 1863.
There have since been a number of unsuccessful suggestions for further enlargement. The most realistic of these was the possible accession of Vorarlberg
Vorarlberg ( , ; gsw, label= Vorarlbergisch, Vorarlbearg, , or ) is the westernmost state () of Austria. It has the second-smallest geographical area after Vienna and, although it also has the second-smallest population, it is the state with the ...
following a referendum held there in 1919, in which 81% of the people of Vorarlberg voted to join Switzerland; but Vorarlberg was instead incorporated into the First Austrian Republic. There was a brief and unsuccessful revival of Alemannic separatism
Alemannic Separatism is a historical movement of separatism of the Alemannic-German-speaking areas of Austria, France, and Germany (viz., South Baden, Swabia (viz. most of Württemberg and Bavarian Swabia), Alsace and Vorarlberg), aiming ...
after World War II, and in the later half of the 20th century, there were no serious political scenarios of any further enlargement of Switzerland. Since 2008, similar proposals have once again been discussed, at least as hypotheticals, as expressions of Euroscepticism
Euroscepticism, also spelled as Euroskepticism or EU-scepticism, is a political position involving criticism of the European Union (EU) and European integration. It ranges from those who oppose some EU institutions and policies, and seek refor ...
, reflecting the wish of territories within European Union member states to leave the European Union.
Since there is currently no legal framework governing the admission of new cantons, any enlargement would, as a matter of Swiss law, require an amendment of the Swiss federal constitution and therefore a national popular referendum. A corresponding proposal was submitted by Jurassian representative Dominique Baettig
Dominique Baettig (born 22 September 1953, in Delémont) is a Swiss politician and member of the Swiss People's Party. A psychiatrist by profession, he represented the canton of Jura in the National Council in the 2007–2011 legislature.
Po ...
in 2010, but was dropped after Baettig was not re-elected in 2011.
Old Swiss Confederacy


 Switzerland, a multilingual
Switzerland, a multilingual federation
A federation (also known as a federal state) is a political entity characterized by a union of partially self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a central federal government ( federalism). In a federation, the self-govern ...
of 26 cantons whose origins lie in a defensive alliance of alpine valleys around the end of the 13th century, grew through the accession of new states and territories during the 14th to 16th centuries. The accession of Appenzell in 1513 completed the growth of the Confederacy into the Thirteen Cantons
The early modern history of the Old Swiss Confederacy ('' Eidgenossenschaft'', also known as the "Swiss Republic" or ''Republica Helvetiorum'') and its constituent Thirteen Cantons encompasses the time of the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648 ...
of the early modern period. The Valais
Valais ( , , ; frp, Valês; german: Wallis ), more formally the Canton of Valais,; german: Kanton Wallis; in other official Swiss languages outside Valais: it, (Canton) Vallese ; rm, (Chantun) Vallais. is one of the 26 cantons forming the S ...
became an "eternal associate" of the Confederacy in 1529. In 1536 the Swiss canton of Berne
Bern () or Berne; in other Swiss languages, gsw, Bärn ; frp, Bèrna ; it, Berna ; rm, Berna is the ''de facto'' Capital city, capital of Switzerland, referred to as the "federal city" (in german: Bundesstadt, link=no, french: ville fédérale ...
annexed the Vaud
Vaud ( ; french: (Canton de) Vaud, ; german: (Kanton) Waadt, or ), more formally the canton of Vaud, is one of the 26 cantons forming the Swiss Confederation. It is composed of ten districts and its capital city is Lausanne. Its coat of arms b ...
from Savoy.
Geneva
, neighboring_municipalities= Carouge, Chêne-Bougeries, Cologny, Lancy, Grand-Saconnex, Pregny-Chambésy, Vernier, Veyrier
, website = https://www.geneve.ch/
Geneva ( ; french: Genève ) frp, Genèva ; german: link=no, Genf ; it, Ginevr ...
had sought alliances with the Swiss Confederacy (in order to defend itself against Savoy) since the early 16th century. The conclusion of an eternal treaty with the Protestant cantons Berne and Zürich in 1584 tied Geneva closely to Switzerland, but the Catholic cantons, which had allied themselves with the dukes of Savoy
The titles of count, then of duke of Savoy are titles of nobility attached to the historical territory of Savoy. Since its creation, in the 11th century, the county was held by the House of Savoy. The County of Savoy was elevated to a duchy at th ...
since 1560, opposed the full accession of Geneva as a member of the Confederacy.
In addition to the cantons, the Old Swiss Confederacy had several associated states
An associated state is the minor partner in a formal, free relationship between a political territory (some dependent, most fully sovereign states) and a major party—usually a larger nation.
The details of such free association are contai ...
(''Zugewandte Orte''), which included the Sieben Zenden (Valais), the Three Leagues
The Three Leagues, sometimes referred to as Raetia, was the alliance of 1471 of the League of God's House, the League of the Ten Jurisdictions, and the Grey League, leading eventually to the formation of the Swiss canton of Graubünden (Grison ...
(principally present-day Graubünden), and the Imperial Abbey of St. Gall
The Abbey of Saint Gall (german: Abtei St. Gallen) is a dissolved abbey (747–1805) in a Catholic religious complex in the city of St. Gallen in Switzerland. The Carolingian-era monastery existed from 719, founded by Saint Othmar on the spot ...
.
Napoleonic era, Restoration and Regeneration

 New cantons were added only in the
New cantons were added only in the modern period
The term modern period or modern era (sometimes also called modern history or modern times) is the period of history that succeeds the Middle Ages (which ended approximately 1500 AD). This terminology is a historical periodization that is applie ...
, during 1803–1815; this mostly concerned former subject territories now recognized as full cantons (such as Vaud
Vaud ( ; french: (Canton de) Vaud, ; german: (Kanton) Waadt, or ), more formally the canton of Vaud, is one of the 26 cantons forming the Swiss Confederation. It is composed of ten districts and its capital city is Lausanne. Its coat of arms b ...
, Ticino
Ticino (), sometimes Tessin (), officially the Republic and Canton of Ticino or less formally the Canton of Ticino,, informally ''Canton Ticino'' ; lmo, Canton Tesin ; german: Kanton Tessin ; french: Canton du Tessin ; rm, Chantun dal Tessin . ...
and Aargau), and the full integration of territories that had been more loosely allied to the Confederacy (such as Geneva
, neighboring_municipalities= Carouge, Chêne-Bougeries, Cologny, Lancy, Grand-Saconnex, Pregny-Chambésy, Vernier, Veyrier
, website = https://www.geneve.ch/
Geneva ( ; french: Genève ) frp, Genèva ; german: link=no, Genf ; it, Ginevr ...
, Valais
Valais ( , , ; frp, Valês; german: Wallis ), more formally the Canton of Valais,; german: Kanton Wallis; in other official Swiss languages outside Valais: it, (Canton) Vallese ; rm, (Chantun) Vallais. is one of the 26 cantons forming the S ...
and Grisons).
Grisons acceded with the Act of Mediation
The Act of Mediation () was issued by Napoleon Bonaparte, First Consul of the French Republic on 19 February 1803 establishing the Swiss Confederation. The act also abolished the previous Helvetic Republic, which had existed since the invasi ...
in 1803. At that time, the territory of Tarasp
Tarasp is a former municipality in the district of Inn in the Swiss canton of Graubünden. Its eleven settlements are situated within the Lower Engadin valley along the Inn River, at the foot of the Sesvenna Range. On 1 January 2015 the former ...
, formerly an exclave within the territory of the League of God's House
The League of God's House (German: ''Gotteshausbund'', Italian: ''Lega Caddea'', rm, ) was formed in what is now Switzerland on 29 January 1367, to resist the rising power of the Bishopric of Chur and the House of Habsburg. The League allied wi ...
, was ceded by Austria. Similarly, the newly created canton of Aargau included the territory of Fricktal
The Fricktal ("Frick Valley") is a region on Northwestern Switzerland, comprising the Laufenburg and Rheinfelden districts of the Swiss canton of Aargau.
The region was known as ''Frickgau'' in the medieval period, ultimately from a Late L ...
, which had previously remained as the only territory left of the Rhine under direct Habsburg control.
The Canton of St. Gallen
The canton of St. Gallen, also canton of St Gall (german: link=no, Kanton St. Gallen ; rm, Chantun Son Gagl; french: Canton de Saint-Gall; it, Canton San Gallo), is a canton of Switzerland. The capital is St. Gallen.
Located in northeastern ...
was created at the same time, out of a number of disparate territories, which had however all been previously either allied with or subject to Swiss cantons.
The territory of Geneva was fragmented, with various enclaves or exclaves of Savoyard and French territory, and it was not connected to Swiss territory. Due to the efforts of Charles Pictet de Rochemont
Charles Pictet de Rochemont (21 September 1755 – 28 December 1824) was a statesman and diplomat who prepared the declaration of Switzerland's permanent neutrality ratified by the great powers in 1815.
Early life
Charles Pictet was born on 2 ...
, the Congress of Vienna decided to incorporate seven communes of the French Pays de Gex in order to create a land bridge between Geneva and Switzerland.
The Valtellina
Valtellina or the Valtelline (occasionally spelled as two words in English: Val Telline; rm, Vuclina (); lmo, Valtelina or ; german: Veltlin; it, Valtellina) is a valley in the Lombardy region of northern Italy, bordering Switzerland. Toda ...
had been a territory of the Three Leagues
The Three Leagues, sometimes referred to as Raetia, was the alliance of 1471 of the League of God's House, the League of the Ten Jurisdictions, and the Grey League, leading eventually to the formation of the Swiss canton of Graubünden (Grison ...
from the 15th century until 1797, when it was annexed by the Cisalpine Republic
The Cisalpine Republic ( it, Repubblica Cisalpina) was a sister republic of France in Northern Italy that existed from 1797 to 1799, with a second version until 1802.
Creation
After the Battle of Lodi in May 1796, Napoleon Bonaparte organiz ...
. The Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna (, ) of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon B ...
considered restoring the Valtellina to Grisons, and thus to Switzerland, but the strategic importance of the territory was deemed as too high by Austria, and it became part of the Kingdom of Lombardy–Venetia
The Kingdom of Lombardy–Venetia ( la, links=no, Regnum Langobardiae et Venetiae), commonly called the "Lombardo-Venetian Kingdom" ( it, links=no, Regno Lombardo-Veneto, german: links=no, Königreich Lombardo-Venetien), was a constituent land ...
instead. The loss of the Valtellina remained an irredentist
Irredentism is usually understood as a desire that one state annexes a territory of a neighboring state. This desire is motivated by ethnic reasons (because the population of the territory is ethnically similar to the population of the parent st ...
issue in Grisons well into the 20th century.
Along with the Valtellina, Chiavenna was lost to the Cisalpine Republic in 1797, and the Congress of Vienna likewise declined its restoration to Switzerland. While Switzerland accepted the loss of Chiavenna itself, the Valle di Lei north of Chiavenna was indicated as Swiss territory on the Dufour map
Dufour or ''variant'', may refer to:
*Dufour (surname)
Places
*Dufourspitze or Dufour's peak, in the Swiss Alps
*Julia Dufour, a village and municipality in Santa Cruz Province, Argentina
Other uses
*1961 Dufour, main-belt asteroid
*Dufour Audit ...
of 1858. It was only in 1863 that Switzerland reached an understanding with the Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy ( it, Regno d'Italia) was a state that existed from 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Sardinia was proclaimed King of Italy, until 1946, when civil discontent led to an institutional referendum to abandon the monarchy and f ...
on the exact definition of the Swiss-Italian border
The Swiss people (german: die Schweizer, french: les Suisses, it, gli Svizzeri, rm, ils Svizzers) are the citizens of Switzerland or people of Swiss ancestry.
The number of Swiss nationals has grown from 1.7 million in 1815 to 8.7 million ...
.
The Congress of Vienna distributed the remaining territory of the Prince-Bishopric of Basel
The Prince-Bishopric of Basel (german: Hochstift Basel, Fürstbistum Basel, Bistum Basel) was an ecclesiastical principality within the Holy Roman Empire, ruled from 1032 by prince-bishops with their seat at Basel, and from 1528 until 1792 at ...
(intermittently annexed by France) to Berne
Bern () or Berne; in other Swiss languages, gsw, Bärn ; frp, Bèrna ; it, Berna ; rm, Berna is the ''de facto'' Capital city, capital of Switzerland, referred to as the "federal city" (in german: Bundesstadt, link=no, french: ville fédérale ...
and Basel
, french: link=no, Bâlois(e), it, Basilese
, neighboring_municipalities= Allschwil (BL), Hégenheim (FR-68), Binningen (BL), Birsfelden (BL), Bottmingen (BL), Huningue (FR-68), Münchenstein (BL), Muttenz (BL), Reinach (BL), Riehen (BS ...
.
The commune of Le Cerneux-Péquignot had been part the Franche-Comté and as such of the kingdom of France since 1678. It was to be ceded to Neuchâtel according to the treaty of Paris of 30 May 1814, but the necessary border correction did not become official until 1 February 1819.
Similarly, Rhäzüns
Rhäzüns is a municipality in the Imboden Region in the Swiss canton of Grisons.
History
Rhäzüns is first mentioned about 840 as ''Raezunne''.
It formed a single parish with Bonaduz until the Reformation.
It was part of the Grey League f ...
was restored from Austria to Switzerland on 19 January 1819.
Switzerland in 1815 was still a confederacy, not a fully integrated federation. The canton of Neuchâtel joined in 1815 as a member of the confederacy but was at the same time a monarchy, its sovereign being Frederick William IV of Prussia. Although Neuchâtel became a republic in a peaceful revolution in 1848, the same year Switzerland became a federation, Frederick William renounced his claims in the area in 1857, after several attempts at counterrevolution culminating in the Neuchâtel Crisis The Neuchâtel Crisis (1856–1857) was the result of a diplomatic question between the Swiss Confederation and the King of Prussia regarding the rights of the Royal House of Prussia to the Principality of Neuchâtel. The Principality of Neuch� ...
.
A number of territorial disputes remained along the German-Swiss border
The German-speaking part of Switzerland (german: Deutschschweiz, french: Suisse alémanique, it, Svizzera tedesca, rm, Svizra tudestga) comprises about 65 percent of Switzerland (North Western Switzerland, Eastern Switzerland, Central Switz ...
, especially concerning the territories of Thurgau
Thurgau (; french: Thurgovie; it, Turgovia), anglicized as Thurgovia, more formally the Canton of Thurgau, is one of the 26 cantons forming the Swiss Confederation. It is composed of five districts and its capital is Frauenfeld.
Thurgau is par ...
and Schaffhausen
Schaffhausen (; gsw, Schafuuse; french: Schaffhouse; it, Sciaffusa; rm, Schaffusa; en, Shaffhouse) is a town with historic roots, a municipality in northern Switzerland, and the capital of the canton of the same name; it has an estimate ...
. The status of Tägermoos was settled in 1831, the precise borders of Schaffhausen in 1839, and the final remaining questions by 1854.
When Ticino
Ticino (), sometimes Tessin (), officially the Republic and Canton of Ticino or less formally the Canton of Ticino,, informally ''Canton Ticino'' ; lmo, Canton Tesin ; german: Kanton Tessin ; french: Canton du Tessin ; rm, Chantun dal Tessin . ...
chose to become part of the Swiss Confederation in 1798, the people of the Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
exclave Campione d'Italia
Campione d'Italia ( Comasco: , ) is a ''comune'' of the Province of Como in the Lombardy region of Italy and an enclave surrounded by the Swiss canton of Ticino (it is also an exclave). At its closest, the enclave is less than from the rest ...
chose to remain part of Lombardy. In 1800, Ticino proposed exchanging Indemini
Indemini () is a former municipality in the district of Locarno in the canton of Ticino in Switzerland.
On 25 April 2010, the former municipalities of Caviano, Contone, Gerra Gambarogno, Indemini, Magadino, Piazzogna, San Nazzaro, Sant'A ...
for Campione. In 1814 a referendum was held, but the residents of Campione were against it. In 1848, during the wars of Italian unification, Campione petitioned Switzerland for annexation, but this was rejected due to the Swiss desire to maintain neutrality.
Modern Switzerland (1848–present)
 After Italian unification in 1861, all land west of Lake Lugano and half of the lake were given to Switzerland so that Swiss trade and transport would not have to pass through Italy. The ''d'Italia'' suffix was added to the name of Campione in the 1930s by Prime Minister Benito Mussolini and an ornamental gate to the city was built, both in an attempt to assert the exclave's Italian-ness.
There remained some territorial disputes after the formation of the Kingdom of Italy, resolved in the ''Convenzione tra l'Italia e la Svizzera per l'accertamento della frontiera fra la Lombardia ed il Cantone dei Grigioni'' of 1863. Since then, the international
After Italian unification in 1861, all land west of Lake Lugano and half of the lake were given to Switzerland so that Swiss trade and transport would not have to pass through Italy. The ''d'Italia'' suffix was added to the name of Campione in the 1930s by Prime Minister Benito Mussolini and an ornamental gate to the city was built, both in an attempt to assert the exclave's Italian-ness.
There remained some territorial disputes after the formation of the Kingdom of Italy, resolved in the ''Convenzione tra l'Italia e la Svizzera per l'accertamento della frontiera fra la Lombardia ed il Cantone dei Grigioni'' of 1863. Since then, the international borders of Switzerland
The geography of Switzerland encompasses the geographical features of Switzerland, a mountainous and landlocked country located in Western and Central Europe. Switzerland's natural landscape is marked by its numerous lakes and mountains. It ...
have been undisputed and, except for minor corrections, unchanged (the internal borders of the cantons of Switzerland
The 26 cantons of Switzerland (german: Kanton; french: canton ; it, cantone; Sursilvan and Surmiran: ; Vallader and Puter: ; Sutsilvan: ; Rumantsch Grischun: ) are the member states of the Swiss Confederation. The nucleus of the Swiss Co ...
have been subject to revision, mostly in the context of the Jura question). Further Swiss-Italian treaties regarding the course of the border date to 1873/4, 1936/7 and 1941.
The part of the Chablais
Chablais () was a province of the Duchy of Savoy. Its capital was Thonon-les-Bains.
Chablais was elevated to a duchy in 1311 by Henry VII, Holy Roman Emperor.
This region is currently divided into three territories, the ''Chablais savoyard'', the ...
region south of Lake Geneva
, image = Lake Geneva by Sentinel-2.jpg
, caption = Satellite image
, image_bathymetry =
, caption_bathymetry =
, location = Switzerland, France
, coords =
, lake_type = Glacial la ...
was ceded to the Kingdom of Sardinia
The Kingdom of Sardinia,The name of the state was originally Latin: , or when the kingdom was still considered to include Corsica. In Italian it is , in French , in Sardinian , and in Piedmontese . also referred to as the Kingdom of Savoy-S ...
by the Congress of Vienna, but declared a demilitarized zone, and Switzerland was granted the right to occupy both Chablais and Faucigny
Faucigny ( it, Fossigni) is a commune in the Haute-Savoie department in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region in south-eastern France.
Historically, Faucigny was a region in Savoy which included the area of the modern ''département'' of Haute Sav ...
for its own protection in the case of war. In 1860, when France annexed Savoy from the Kingdom of Piedmont-Sardinia
The Kingdom of Sardinia,The name of the state was originally Latin: , or when the kingdom was still considered to include Corsica. In Italian it is , in French , in Sardinian , and in Piedmontese . also referred to as the Kingdom of Savoy-S ...
, Napoleon III
Napoleon III (Charles Louis Napoléon Bonaparte; 20 April 18089 January 1873) was the first President of France (as Louis-Napoléon Bonaparte) from 1848 to 1852 and the last monarch of France as Emperor of the French from 1852 to 1870. A nephew ...
declared his intention to cede Chablais and Faucigny to Switzerland, but later reneged on the promise. The Swiss authorities were themselves ambivalent on the matter, as they feared the destabilising effect the annexation of two Catholic provinces might have on interfaith relations within the country. But popular opinion in Switzerland was outraged at Napoleon's breach of promise. Switzerland increased its military presence at the southern border to prevent clashes between Savoyard and Swiss irregulars. The crisis subsided gradually as it became clear that Napoleon adhered to the promise of neutrality for Haute-Savoie renewed in the Treaty of Turin of 24 March 1860. But Switzerland did not recognize the annexation of Savoy, and the status of Chablais was brought before the Permanent Court of International Justice
The Permanent Court of International Justice, often called the World Court, existed from 1922 to 1946. It was an international court attached to the League of Nations. Created in 1920 (although the idea of an international court was several cent ...
several times between 1922 and 1932.
In 1918 after the First World War, a referendum
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a direct vote by the electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a representative. This may result in the adoption of a ...
was held in the small exclave Büsingen am Hochrhein in Baden-Württemberg in which 96% of voters chose to become part of Switzerland. However the change of country never took place as Switzerland could not offer anything suitable in exchange and consequently, Büsingen has remained an exclave of Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
ever since. Later attempts to transfer Büsingen to Switzerland were also unsuccessful. The status of the municipality of Büsingen was however formally defined in 1967 through negotiations between what was then West Germany
West Germany is the colloquial term used to indicate the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG; german: Bundesrepublik Deutschland , BRD) between its formation on 23 May 1949 and the German reunification through the accession of East Germany on 3 O ...
and Switzerland. Büsingen am Hochrhein officially became part of the Swiss customs area. It had been in a ''de facto'' customs union with Switzerland since 1947. At the same time, the West German exclave of Verenahof, consisting of just three houses and eleven West German citizens, did become part of Switzerland.
In a 1919 referendum, 81% of the people of Vorarlberg
Vorarlberg ( , ; gsw, label= Vorarlbergisch, Vorarlbearg, , or ) is the westernmost state () of Austria. It has the second-smallest geographical area after Vienna and, although it also has the second-smallest population, it is the state with the ...
voted to join Switzerland, but the effort failed because of the ambivalent position of the Swiss government and the opposition of the Allied powers.
The Swiss government expressed willingness to consider the accession of Vorarlberg to Switzerland, mostly in order to prevent its incorporation into Germany. "As far as Switzerland was concerned, she only considered Vorarlberg's Anschluss with herself, because the alternative, an Anschluss with Germany, seemed to constitute a clear threat to her."
Changes to the Swiss border made after 1945 include the addition of the Lago di Lei
Lago di Lei is a reservoir in the Valle di Lei, powering the Hinterrhein storage power stations. The reservoir is almost entirely in Italy, but the barrage was built on territory ceded by Italy to Switzerland (municipality of Ferrera, Grisons ...
barrage to Switzerland in the 1950s,
and the exchange of an area of 1,578 square meters with France in 2002.
Proposals for expansion
Since the formation ofBaden-Württemberg
Baden-Württemberg (; ), commonly shortened to BW or BaWü, is a German state () in Southwest Germany, east of the Rhine, which forms the southern part of Germany's western border with France. With more than 11.07 million inhabitants across a ...
in 1952, there had been no longer any serious political scenarios of South German territories seceding to Switzerland.
The idea was revived, at least in popular discourse, in the context of growing Euroscepticism
Euroscepticism, also spelled as Euroskepticism or EU-scepticism, is a political position involving criticism of the European Union (EU) and European integration. It ranges from those who oppose some EU institutions and policies, and seek refor ...
since the late 2000s.
A poll by ORF
ORF or Orf may refer to:
* Norfolk International Airport, IATA airport code ORF
* Observer Research Foundation, an Indian research institute
* One Race Films, a film production company founded by Vin Diesel
* Open reading frame, a portion of the ...
radio in October 2008 reported that about half of the population of Vorarlberg
Vorarlberg ( , ; gsw, label= Vorarlbergisch, Vorarlbearg, , or ) is the westernmost state () of Austria. It has the second-smallest geographical area after Vienna and, although it also has the second-smallest population, it is the state with the ...
would be in favour of joining Switzerland.
In the Swiss parliament
The Federal Assembly (german: Bundesversammlung, french: Assemblée fédérale, it, Assemblea federale, rm, Assamblea federala), also known as the Swiss parliament (''Parlament'', ''Parlement'', ''Parlamento''), is Switzerland's federal legi ...
, a 2010 motion was submitted by Jurassian representative Dominique Baettig
Dominique Baettig (born 22 September 1953, in Delémont) is a Swiss politician and member of the Swiss People's Party. A psychiatrist by profession, he represented the canton of Jura in the National Council in the 2007–2011 legislature.
Po ...
and co-signed by Swiss People's Party (SVP) party chairman Toni Brunner
Toni, Toñi or Tóni is a unisex given name.
In Spanish, Italian, Croatian and Finnish, it is a masculine given name used as a short form of the names derived from Antonius like Antonio, Ante or Anttoni.
In Danish, English, Finnish, Norwegia ...
. The motion proposed to offer territories adjacent to Switzerland the "Swiss model of sovereignty" as an alternative to a Switzerland–European Union relations, "creeping accession" of Switzerland to the "centralist" European Union (EU). As possible candidates for accession, the motion named Alsace (FR), Aosta Valley, Aosta (IT), South Tyrol (IT), Jura (department), Jura (FR), Vorarlberg
Vorarlberg ( , ; gsw, label= Vorarlbergisch, Vorarlbearg, , or ) is the westernmost state () of Austria. It has the second-smallest geographical area after Vienna and, although it also has the second-smallest population, it is the state with the ...
(AT), Ain (FR), Savoy (FR), Baden-Württemberg
Baden-Württemberg (; ), commonly shortened to BW or BaWü, is a German state () in Southwest Germany, east of the Rhine, which forms the southern part of Germany's western border with France. With more than 11.07 million inhabitants across a ...
(DE), Province of Varese, Varese (IT), Province of Como, Como (IT) "and others".Erleichterte Integration grenznaher Regionen als neue Schweizer Kantone
', motion 10.3215 of 18 March 2010 by Dominique Baettig. The motion was widely seen as anti-EU rhetoric rather than a serious proposal. In a statement of 19 May 2010, the Swiss Federal Council recommended its rejection, describing the motion as a "provocation". It argued that its adoption would be considered an unfriendly act by the countries surrounding Switzerland, and that it would also be at odds with international law, which in the government's view does not provide for a right to secession except in exceptional circumstances. The topic attracted the attention of the European media. The media went on to report a high level of apparent popular support for joining Switzerland in the territories in question (as reflected in Internet polls and comments): * In Como, an online poll in June 2010 by the ''La Provincia di Como'' newspaper found 74% of 2,500 respondents in favor of accession to Switzerland, which the local regionalist party ''Lega Lombarda'' has long been advocating. * Another online poll by the South German ''Südkurier'' newspaper found that almost 70% of respondents replied "yes, the Swiss are closer to us in outlook" to a question whether the state of
Baden-Württemberg
Baden-Württemberg (; ), commonly shortened to BW or BaWü, is a German state () in Southwest Germany, east of the Rhine, which forms the southern part of Germany's western border with France. With more than 11.07 million inhabitants across a ...
should join Switzerland. The paper noted that seldom had a topic generated so much activity by its readership.
* The Lombard Eco-nationalism, eco-nationalist party Domà Nunch replied to Baettig's motion proposing an integration between Switzerland and the Italian border-area of Insubria in order to join into a new Confederation.
In Sardinia, the ''Associazione no-profit Sardegna Canton Marittimo'' was formed in April 2014 with the aim of advocating Sardinia's secession from Italy and becoming a "maritime canton" of Switzerland.
''Die Welt'' in June 2014 based on an OECD study published an article arguing that Southern Germany is more similar to Switzerland than to Northern or Eastern Germany. In the wake of the article, there were once again reports on high levels of support for accession to Switzerland in Southern Germany. ''Schwäbische Zeitung'' reported 86% of participants in an online survey expressing approval.
Also in 2014, there were reports of a movement in South Tyrol (headed by a South Tyrolean living in Switzerland) proposing annexation by the Alpine country.
The 6th "Global Forum Südtirol" held in Bolzano was dedicated to the question.
In 2018 the Swiss Head of the Federal Department of Foreign Affairs, Department of Foreign Affairs Ignazio Cassis, answering to a parliamentary question by the national councillor Marco Romano, declared as "imaginable" the transfer of the Italian exclave Campione d'Italia
Campione d'Italia ( Comasco: , ) is a ''comune'' of the Province of Como in the Lombardy region of Italy and an enclave surrounded by the Swiss canton of Ticino (it is also an exclave). At its closest, the enclave is less than from the rest ...
to the Canton of Ticino. The declaration was made a short time after the bankruptcy of the Casinò di Campione. The undersecretary of the Italian Minister of the Interior Stefano Candiani replied that Campione d'Italia is Italian territory without any doubt.''TVSvizzera.it'', 21 September 2018
Maps showing the territorial evolution of Switzerland
Vaud
Vaud ( ; french: (Canton de) Vaud, ; german: (Kanton) Waadt, or ), more formally the canton of Vaud, is one of the 26 cantons forming the Swiss Confederation. It is composed of ten districts and its capital city is Lausanne. Its coat of arms b ...
by Bern (canton), Bern and Fribourg (canton), Fribourg.
File:Historische Karte CH 18 Jh.png, Switzerland in the 18th century.
File:Old Confederacy 18th centur.png, Another map of Switzerland in the 18th century.
File:Karte Helvetik 1.png, Provisional constitution of the Helvetic Republic, 15 January 1798.
File:Karte Helvetik 3.png, Constitution of the Helvetic Republic, 12 April 1798.
File:Karte Helvetik 4.png, Helvetic Republic, with borders as at the Second Helvetic constitution of 25 May 1802.
File:Karte Mediation.png, Switzerland after Act of Mediation
The Act of Mediation () was issued by Napoleon Bonaparte, First Consul of the French Republic on 19 February 1803 establishing the Swiss Confederation. The act also abolished the previous Helvetic Republic, which had existed since the invasi ...
, during Napoleonic Era, until 1815.
File:Schweiz Wiener Kongress.png, Re-organization and enlargement of Switzerland during the Congress of Vienna in 1814.
File:Karte Schweiz 1815.png, Switzerland during the Restoration, 1815–1847.
See also
* Jurassic separatism *Alemannic separatism
Alemannic Separatism is a historical movement of separatism of the Alemannic-German-speaking areas of Austria, France, and Germany (viz., South Baden, Swabia (viz. most of Württemberg and Bavarian Swabia), Alsace and Vorarlberg), aiming ...
* Euroscepticism
Euroscepticism, also spelled as Euroskepticism or EU-scepticism, is a political position involving criticism of the European Union (EU) and European integration. It ranges from those who oppose some EU institutions and policies, and seek refor ...
* Switzerland as a federal state
Notes and references
{{DEFAULTSORT:Enlargement Of Switzerland Political history of Switzerland Territorial evolution by country, Switzerland Foreign relations of Switzerland Switzerland–European Union relations