Endomembrane system on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The endomembrane system is composed of the different membranes (endomembranes) that are suspended in the
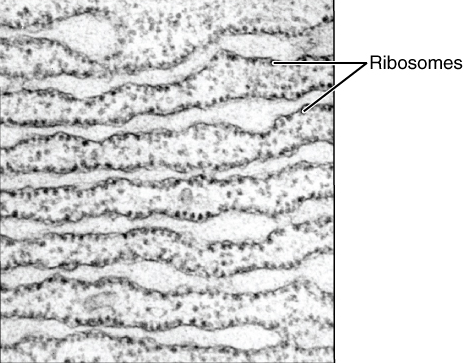 There are two distinct, though connected, regions of ER that differ in structure and function: smooth ER and rough ER. The rough endoplasmic reticulum is so named because the cytoplasmic surface is covered with ribosomes, giving it a bumpy appearance when viewed through an
There are two distinct, though connected, regions of ER that differ in structure and function: smooth ER and rough ER. The rough endoplasmic reticulum is so named because the cytoplasmic surface is covered with ribosomes, giving it a bumpy appearance when viewed through an
cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. ...
within a eukaryotic cell
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacter ...
. These membranes divide the cell into functional and structural compartments, or organelle
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit, usually within a cell, that has a specific function. The name ''organelle'' comes from the idea that these structures are parts of cells, as organs are to the body, hence ''organelle,'' th ...
s. In eukaryote
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacter ...
s the organelles of the endomembrane system include: the nuclear membrane
The nuclear envelope, also known as the nuclear membrane, is made up of two lipid bilayer membranes that in eukaryotic cells surround the nucleus, which encloses the genetic material.
The nuclear envelope consists of two lipid bilayer membra ...
, the endoplasmic reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is, in essence, the transportation system of the eukaryotic cell, and has many other important functions such as protein folding. It is a type of organelle made up of two subunits – rough endoplasmic reticulum ...
, the Golgi apparatus
The Golgi apparatus (), also known as the Golgi complex, Golgi body, or simply the Golgi, is an organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. Part of the endomembrane system in the cytoplasm, it packages proteins into membrane-bound vesicles i ...
, lysosome
A lysosome () is a membrane-bound organelle found in many animal cells. They are spherical vesicles that contain hydrolytic enzymes that can break down many kinds of biomolecules. A lysosome has a specific composition, of both its membrane p ...
s, vesicles
Vesicle may refer to:
; In cellular biology or chemistry
* Vesicle (biology and chemistry), a supramolecular assembly of lipid molecules, like a cell membrane
* Synaptic vesicle
; In human embryology
* Vesicle (embryology), bulge-like features o ...
, endosome
Endosomes are a collection of intracellular sorting organelles in eukaryotic cells. They are parts of endocytic membrane transport pathway originating from the trans Golgi network. Molecules or ligands internalized from the plasma membrane can ...
s, and plasma (cell) membrane among others. The system is defined more accurately as the set of membranes that forms a single functional and developmental unit, either being connected directly, or exchanging material through vesicle transport
In cell biology, a vesicle is a structure within or outside a cell, consisting of liquid or cytoplasm enclosed by a lipid bilayer. Vesicles form naturally during the processes of secretion (exocytosis), uptake (endocytosis) and transport of mater ...
. Importantly, the endomembrane system does not include the membranes of plastid
The plastid (Greek: πλαστός; plastós: formed, molded – plural plastids) is a membrane-bound organelle found in the cells of plants, algae, and some other eukaryotic organisms. They are considered to be intracellular endosymbiotic cyan ...
s or mitochondria
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used ...
, but might have evolved partially from the actions of the latter (see below
Below may refer to:
*Earth
*Ground (disambiguation)
*Soil
*Floor
*Bottom (disambiguation)
*Less than
*Temperatures below freezing
*Hell or underworld
People with the surname
*Ernst von Below (1863–1955), German World War I general
*Fred Below ( ...
).
The nuclear membrane contains a lipid bilayer
The lipid bilayer (or phospholipid bilayer) is a thin polar membrane made of two layers of lipid molecules. These membranes are flat sheets that form a continuous barrier around all cells. The cell membranes of almost all organisms and many vir ...
that encompasses the contents of the nucleus. The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a synthesis and transport organelle that branches into the cytoplasm in plant and animal cells. The Golgi apparatus is a series of multiple compartments where molecules are packaged for delivery to other cell components or for secretion from the cell. Vacuole
A vacuole () is a membrane-bound organelle which is present in plant and fungal cells and some protist, animal, and bacterial cells. Vacuoles are essentially enclosed compartments which are filled with water containing inorganic and organic m ...
s, which are found in both plant and animal cells (though much bigger in plant cells), are responsible for maintaining the shape and structure of the cell as well as storing waste products. A vesicle is a relatively small, membrane-enclosed sac that stores or transports substances. The cell membrane is a protective barrier that regulates what enters and leaves the cell. There is also an organelle known as the Spitzenkörper
The Spitzenkörper (German for pointed body, SPK) is a structure found in fungal hyphae that is the organizing center for hyphal growth and morphogenesis. It consists of many small vesicles and is present in growing hyphal tips, during spore ger ...
that is only found in fungi, and is connected with hyphal tip growth.
In prokaryote
A prokaryote () is a single-celled organism that lacks a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Greek πρό (, 'before') and κάρυον (, 'nut' or 'kernel').Campbell, N. "Biology:Concepts & Con ...
s endomembranes are rare, although in many photosynthetic bacteria the plasma membrane is highly folded and most of the cell cytoplasm is filled with layers of light-gathering membrane. These light-gathering membranes may even form enclosed structures called chlorosomes in green sulfur bacteria
The green sulfur bacteria are a phylum of obligately anaerobic photoautotrophic bacteria that metabolize sulfur.
Green sulfur bacteria are nonmotile (except ''Chloroherpeton thalassium'', which may glide) and capable of anoxygenic photosynthe ...
. Another example is the complex "pepin" system of ''Thiomargarita
''Thiomargarita'' is a genus (family Thiotrichaceae) which includes the vacuolate sulfur bacteria species ''Thiomargarita namibiensis'', ''Candidatus Thiomargarita nelsonii'', and ''Ca. Thiomargarita joergensii''. In 2022, scientists working ...
'' species, especially '' T. magnifica''.
The organelles of the endomembrane system are related through direct contact or by the transfer of membrane segments as vesicles. Despite these relationships, the various membranes are not identical in structure and function. The thickness, molecular composition, and metabolic behavior of a membrane are not fixed, they may be modified several times during the membrane's life. One unifying characteristic the membranes share is a lipid bilayer, with protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
s attached to either side or traversing them.
History of the concept
Most lipids are synthesized in yeast either in the endoplasmic reticulum, lipid particles, or the mitochondrion, with little or no lipid synthesis occurring in the plasma membrane or nuclear membrane.Sphingolipid
Sphingolipids are a class of lipids containing a backbone of sphingoid bases, a set of aliphatic amino alcohols that includes sphingosine. They were discovered in brain extracts in the 1870s and were named after the mythological sphinx because o ...
biosynthesis begins in the endoplasmic reticulum, but is completed in the Golgi apparatus. The situation is similar in mammals, with the exception of the first few steps in ether lipid
In organic chemistry, ethers are a class of compounds that contain an ether group—an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups. They have the general formula , where R and R′ represent the alkyl or aryl groups. Ethers can again be ...
biosynthesis, which occur in peroxisomes. The various membranes that enclose the other subcellular organelles must therefore be constructed by transfer of lipids from these sites of synthesis. However, although it is clear that lipid transport is a central process in organelle biogenesis, the mechanisms by which lipids are transported through cells remain poorly understood.
The first proposal that the membranes within cells form a single system that exchanges material between its components was by Morré and Mollenhauer in 1974. This proposal was made as a way of explaining how the various lipid membranes are assembled in the cell, with these membranes being assembled through ''lipid flow'' from the sites of lipid synthesis. The idea of lipid flow through a continuous system of membranes and vesicles was an alternative to the various membranes being independent entities that are formed from transport of free lipid components, such as fatty acid
In chemistry, particularly in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, f ...
s and sterol
Sterol is an organic compound with formula , whose molecule is derived from that of gonane by replacement of a hydrogen atom in position 3 by a hydroxyl group. It is therefore an alcohol of gonane. More generally, any compounds that contain the go ...
s, through the cytosol. Importantly, the transport of lipids through the cytosol and lipid flow through a continuous endomembrane system are not mutually exclusive processes and both may occur in cells.
Components of the system
Nuclear envelope
Thenuclear envelope
The nuclear envelope, also known as the nuclear membrane, is made up of two lipid bilayer membranes that in eukaryotic cells surround the nucleus, which encloses the genetic material.
The nuclear envelope consists of two lipid bilayer membr ...
surrounds the nucleus
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
* Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
*Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucl ...
, separating its contents from the cytoplasm. It has two membranes, each a lipid bilayer
The lipid bilayer (or phospholipid bilayer) is a thin polar membrane made of two layers of lipid molecules. These membranes are flat sheets that form a continuous barrier around all cells. The cell membranes of almost all organisms and many vir ...
with associated proteins. The outer nuclear membrane is continuous with the rough endoplasmic reticulum membrane, and like that structure, features ribosome
Ribosomes ( ) are macromolecular machines, found within all cells, that perform biological protein synthesis (mRNA translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by the codons of messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules to fo ...
s attached to the surface. The outer membrane is also continuous with the inner nuclear membrane since the two layers are fused together at numerous tiny holes called nuclear pore
A nuclear pore is a part of a large complex of proteins, known as a nuclear pore complex that spans the nuclear envelope, which is the double membrane surrounding the eukaryotic cell nucleus. There are approximately 1,000 nuclear pore comple ...
s that perforate the nuclear envelope. These pores are about 120 nm in diameter and regulate the passage of molecules between the nucleus and cytoplasm, permitting some to pass through the membrane, but not others. Since the nuclear pores are located in an area of high traffic, they play an important role in cell physiology
Cell physiology is the biological study of the activities that take place in a Cell (biology), cell to keep it alive. The term ''physiology'' refers to normal functions in a living organism. Animal cells, plant cells and microorganism cells show si ...
. The space between the outer and inner membranes is called the perinuclear space
The nuclear envelope, also known as the nuclear membrane, is made up of two lipid bilayer membranes that in eukaryotic cells surround the nucleus, which encloses the genetic material.
The nuclear envelope consists of two lipid bilayer membra ...
and is joined with the lumen of the rough ER.
The nuclear envelope's structure is determined by a network of intermediate filaments (protein filaments). This network is organized into lining similar to mesh called the nuclear lamina
The nuclear lamina is a dense (~30 to 100 nm thick) fibrillar network inside the nucleus of eukaryote cells. It is composed of intermediate filaments and membrane associated proteins. Besides providing mechanical support, the nuclear lamina ...
, which binds to chromatin
Chromatin is a complex of DNA and protein found in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells. The primary function is to package long DNA molecules into more compact, denser structures. This prevents the strands from becoming tangled and also plays important ...
, integral membrane proteins, and other nuclear components along the inner surface of the nucleus. The nuclear lamina is thought to help materials inside the nucleus reach the nuclear pores and in the disintegration of the nuclear envelope during mitosis
In cell biology, mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. Cell division by mitosis gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the total number of chromosomes is maintai ...
and its reassembly at the end of the process.
The nuclear pores are highly efficient at selectively allowing the passage of materials to and from the nucleus, because the nuclear envelope has a considerable amount of traffic. RNA and ribosomal subunits must be continually transferred from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. Histone
In biology, histones are highly basic proteins abundant in lysine and arginine residues that are found in eukaryotic cell nuclei. They act as spools around which DNA winds to create structural units called nucleosomes. Nucleosomes in turn a ...
s, gene regulatory proteins, DNA and RNA polymerase
In molecular biology, RNA polymerase (abbreviated RNAP or RNApol), or more specifically DNA-directed/dependent RNA polymerase (DdRP), is an enzyme that synthesizes RNA from a DNA template.
Using the enzyme helicase, RNAP locally opens th ...
s, and other substances essential for nuclear activities must be imported from the cytoplasm. The nuclear envelope of a typical mammalian cell contains 3000–4000 pore complexes. If the cell is synthesizing DNA each pore complex needs to transport about 100 histone molecules per minute. If the cell is growing rapidly, each complex also needs to transport about 6 newly assembled large and small ribosomal subunits per minute from the nucleus to the cytosol, where they are used to synthesize proteins.
Endoplasmic reticulum
Theendoplasmic reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is, in essence, the transportation system of the eukaryotic cell, and has many other important functions such as protein folding. It is a type of organelle made up of two subunits – rough endoplasmic reticulum ...
(ER) is a membranous synthesis and transport organelle that is an extension of the nuclear envelope. More than half the total membrane in eukaryotic cells is accounted for by the ER. The ER is made up of flattened sacs and branching tubules that are thought to interconnect, so that the ER membrane forms a continuous sheet enclosing a single internal space. This highly convoluted space is called the ER lumen and is also referred to as the ER cisterna
A cisterna (plural cisternae) is a flattened membrane vesicle found in the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus. Cisternae are an integral part of the packaging and modification processes of proteins occurring in the Golgi.
Function
Protei ...
l space. The lumen takes up about ten percent of the entire cell volume. The endoplasmic reticulum membrane allows molecules to be selectively transferred between the lumen and the cytoplasm, and since it is connected to the nuclear envelope, it provides a channel between the nucleus and the cytoplasm.
The ER has a central role in producing, processing, and transporting biochemical compounds for use inside and outside of the cell. Its membrane is the site of production of all the transmembrane proteins and lipids for most of the cell's organelles, including the ER itself, the Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, endosome
Endosomes are a collection of intracellular sorting organelles in eukaryotic cells. They are parts of endocytic membrane transport pathway originating from the trans Golgi network. Molecules or ligands internalized from the plasma membrane can ...
s, mitochondria
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used ...
, peroxisome
A peroxisome () is a membrane-bound organelle, a type of microbody, found in the cytoplasm of virtually all eukaryotic cells. Peroxisomes are oxidative organelles. Frequently, molecular oxygen serves as a co-substrate, from which hydrogen pe ...
s, secretory vesicles, and the plasma membrane. Furthermore, almost all of the proteins that will exit the cell, plus those destined for the lumen of the ER, Golgi apparatus, or lysosomes, are originally delivered to the ER lumen. Consequently, many of the proteins found in the cisternal space of the endoplasmic reticulum lumen are there only temporarily as they pass on their way to other locations. Other proteins, however, constantly remain in the lumen and are known as endoplasmic reticulum resident proteins. These special proteins contain a specialized retention signal made up of a specific sequence of amino acids
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha am ...
that enables them to be retained by the organelle. An example of an important endoplasmic reticulum resident protein is the chaperone protein
In molecular biology, molecular chaperones are proteins that assist the conformational folding or unfolding of large proteins or macromolecular protein complexes. There are a number of classes of molecular chaperones, all of which function to as ...
known as BiP which identifies other proteins that have been improperly built or processed and keeps them from being sent to their final destinations.
The ER is involved in cotranslational sorting of proteins. A polypeptide which contains an ER signal sequence is recognised by the signal recognition particle
The signal recognition particle (SRP) is an abundant, cytosolic, universally conserved ribonucleoprotein ( protein- RNA complex) that recognizes and targets specific proteins to the endoplasmic reticulum in eukaryotes and the plasma memb ...
which halts the production of the protein. The SRP transports the nascent protein to the ER membrane where it is released through a membrane channel and translation resumes.
 There are two distinct, though connected, regions of ER that differ in structure and function: smooth ER and rough ER. The rough endoplasmic reticulum is so named because the cytoplasmic surface is covered with ribosomes, giving it a bumpy appearance when viewed through an
There are two distinct, though connected, regions of ER that differ in structure and function: smooth ER and rough ER. The rough endoplasmic reticulum is so named because the cytoplasmic surface is covered with ribosomes, giving it a bumpy appearance when viewed through an electron microscope
An electron microscope is a microscope that uses a beam of accelerated electrons as a source of illumination. As the wavelength of an electron can be up to 100,000 times shorter than that of visible light photons, electron microscopes have a hi ...
. The smooth ER appears smooth since its cytoplasmic surface lacks ribosomes.
Functions of the smooth ER
In the great majority of cells, smooth ER regions are scarce and are often partly smooth and partly rough. They are sometimes called transitional ER because they contain ER exit sites from which transport vesicles carrying newly synthesized proteins and lipids bud off for transport to the Golgi apparatus. In certain specialized cells, however, the smooth ER is abundant and has additional functions. The smooth ER of these specialized cells functions in diverse metabolic processes, including synthesis of lipids, metabolism of carbohydrates, and detoxification of drugs and poisons. Enzymes of the smooth ER are vital to the synthesis of lipids, includingoil
An oil is any nonpolar chemical substance that is composed primarily of hydrocarbons and is hydrophobic (does not mix with water) & lipophilic (mixes with other oils). Oils are usually flammable and surface active. Most oils are unsaturated ...
s, phospholipid
Phospholipids, are a class of lipids whose molecule has a hydrophilic "head" containing a phosphate group and two hydrophobic "tails" derived from fatty acids, joined by an alcohol residue (usually a glycerol molecule). Marine phospholipids typ ...
s, and steroid
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and ...
s. Sex hormones of vertebrates and the steroid hormones secreted by the adrenal gland
The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys. Each gland has an outer cortex ...
s are among the steroids produced by the smooth ER in animal cells. The cells that synthesize these hormones are rich in smooth ER.
Liver
The liver is a major organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it i ...
cells are another example of specialized cells that contain an abundance of smooth ER. These cells provide an example of the role of smooth ER in carbohydrate metabolism. Liver cells store carbohydrates in the form of glycogen
Glycogen is a multibranched polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in animals, fungi, and bacteria. The polysaccharide structure represents the main storage form of glucose in the body.
Glycogen functions as one of ...
. The breakdown of glycogen eventually leads to the release of glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, u ...
from the liver cells, which is important in the regulation of sugar concentration in the blood. However, the primary product of glycogen breakdown is glucose-1-phosphate. This is converted to glucose-6-phosphate and then an enzyme of the liver cell's smooth ER removes the phosphate from the glucose, so that it can then leave the cell.
Enzymes of the smooth ER can also help detoxify drugs and poisons. Detoxification usually involves the addition of a hydroxyl group to a drug, making the drug more soluble and thus easier to purge from the body. One extensively studied detoxification reaction is carried out by the cytochrome P450
Cytochromes P450 (CYPs) are a superfamily of enzymes containing heme as a cofactor that functions as monooxygenases. In mammals, these proteins oxidize steroids, fatty acids, and xenobiotics, and are important for the clearance of various co ...
family of enzymes, which catalyze water-insoluble drugs or metabolites that would otherwise accumulate to toxic levels in cell membrane.
Muscle cells have another specialized function of smooth ER. The ER membrane pumps calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar ...
ions from the cytosol into the cisternal space. When a muscle cell becomes stimulated by a nerve impulse, calcium goes back across the ER membrane into the cytosol and generates the contraction of the muscle cell.
Functions of the rough ER
Many types of cells export proteins produced by ribosomes attached to the rough ER. The ribosomes assembleamino acids
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha am ...
into protein units, which are carried into the rough ER for further adjustments. These proteins may be either transmembrane proteins
A transmembrane protein (TP) is a type of integral membrane protein that spans the entirety of the cell membrane. Many transmembrane proteins function as gateways to permit the transport of specific substances across the membrane. They frequentl ...
, which become embedded in the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum, or water-soluble proteins, which are able to pass through the membrane into the lumen. Those that reach the inside of the endoplasmic reticulum are folded into the correct three-dimensional conformation. Chemicals, such as carbohydrates or sugars, are added, then the endoplasmic reticulum either transports the completed proteins, called secretory proteins, to areas of the cell where they are needed, or they are sent to the Golgi apparatus for further processing and modification.
Once secretory proteins are formed, the ER membrane separates them from the proteins that will remain in the cytosol. Secretory proteins depart from the ER enfolded in the membranes of vesicles that bud like bubbles from the transitional ER. These vesicles in transit to another part of the cell are called transport vesicles. An alternative mechanism for transport of lipids and proteins out of the ER are through lipid transfer proteins at regions called membrane contact sites where the ER becomes closely and stably associated with the membranes of other organelles, such as the plasma membrane, Golgi or lysosomes.
In addition to making secretory proteins, the rough ER makes membranes that grows in place from the addition of proteins and phospholipids. As polypeptides
Peptides (, ) are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Long chains of amino acids are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides.
A p ...
intended to be membrane proteins grow from the ribosomes, they are inserted into the ER membrane itself and are kept there by their hydrophobic
In chemistry, hydrophobicity is the physical property of a molecule that is seemingly repelled from a mass of water (known as a hydrophobe). In contrast, hydrophiles are attracted to water.
Hydrophobic molecules tend to be nonpolar and, ...
portions. The rough ER also produces its own membrane phospholipids; enzymes built into the ER membrane assemble phospholipids. The ER membrane expands and can be transferred by transport vesicles to other components of the endomembrane system.
Golgi apparatus
TheGolgi apparatus
The Golgi apparatus (), also known as the Golgi complex, Golgi body, or simply the Golgi, is an organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. Part of the endomembrane system in the cytoplasm, it packages proteins into membrane-bound vesicles i ...
(also known as the Golgi body and the Golgi complex) is composed of separate sacs called cisternae
A cisterna (plural cisternae) is a flattened membrane vesicle found in the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus. Cisternae are an integral part of the packaging and modification processes of proteins occurring in the Golgi.
Function
Protei ...
. Its shape is similar to a stack of pancakes. The number of these stacks varies with the specific function of the cell. The Golgi apparatus is used by the cell for further protein modification. The section of the Golgi apparatus that receives the vesicles from the ER is known as the cis face, and is usually near the ER. The opposite end of the Golgi apparatus is called the trans face, this is where the modified compounds leave. The trans face is usually facing the plasma membrane, which is where most of the substances the Golgi apparatus modifies are sent.
Vesicles sent off by the ER containing proteins are further altered at the Golgi apparatus and then prepared for secretion from the cell or transport to other parts of the cell. Various things can happen to the proteins on their journey through the enzyme covered space of the Golgi apparatus. The modification and synthesis of the carbohydrate portions of glycoproteins is common in protein processing. The Golgi apparatus removes and substitutes sugar monomers, producing a large variety of oligosaccharides
An oligosaccharide (/ˌɑlɪgoʊˈsækəˌɹaɪd/; from the Greek ὀλίγος ''olígos'', "a few", and σάκχαρ ''sácchar'', "sugar") is a saccharide polymer containing a small number (typically two to ten) of monosaccharides (simple suga ...
. In addition to modifying proteins, the Golgi also manufactures macromolecules itself. In plant cells, the Golgi produces pectins
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic peri ...
and other polysaccharides needed by the plant structure.
Once the modification process is completed, the Golgi apparatus sorts the products of its processing and sends them to various parts of the cell. Molecular identification labels or tags are added by the Golgi enzymes to help with this. After everything is organized, the Golgi apparatus sends off its products by budding vesicles from its trans face.
Vacuoles
Vacuole
A vacuole () is a membrane-bound organelle which is present in plant and fungal cells and some protist, animal, and bacterial cells. Vacuoles are essentially enclosed compartments which are filled with water containing inorganic and organic m ...
s, like vesicles, are membrane-bound sacs within the cell. They are larger than vesicles and their specific function varies. The operations of vacuoles are different for plant and animal vacuoles.
In plant cells, vacuoles cover anywhere from 30% to 90% of the total cell volume. Most mature plant cells contain one large central vacuole encompassed by a membrane called the tonoplast. Vacuoles of plant cells act as storage compartments for the nutrients and waste of a cell. The solution that these molecules are stored in is called the cell sap. Pigments
A pigment is a colored material that is completely or nearly insoluble in water. In contrast, dyes are typically soluble, at least at some stage in their use. Generally dyes are often organic compounds whereas pigments are often inorganic compoun ...
that color the cell are sometime located in the cell sap. Vacuoles can also increase the size of the cell, which elongates as water is added, and they control the turgor pressure
Turgor pressure is the force within the cell that pushes the plasma membrane against the cell wall.
It is also called ''hydrostatic pressure'', and is defined as the pressure in a fluid measured at a certain point within itself when at equilibriu ...
(the osmotic pressure that keeps the cell wall from caving in). Like lysosomes of animal cells, vacuoles have an acidic pH and contain hydrolytic enzymes. The pH of vacuoles enables them to perform homeostatic procedures in the cell. For example, when the pH in the cells environment drops, the H+ ions surging into the cytosol can be transferred to a vacuole in order to keep the cytosol's pH constant.
In animals, vacuoles serve in exocytosis
Exocytosis () is a form of active transport and bulk transport in which a cell transports molecules (e.g., neurotransmitters and proteins) out of the cell ('' exo-'' + ''cytosis''). As an active transport mechanism, exocytosis requires the use ...
and endocytosis
Endocytosis is a cellular process in which substances are brought into the cell. The material to be internalized is surrounded by an area of cell membrane, which then buds off inside the cell to form a vesicle containing the ingested material. ...
processes. Endocytosis refers to when substances are taken into the cell, whereas for exocytosis substances are moved from the cell into the extracellular space. Material to be taken-in is surrounded by the plasma membrane, and then transferred to a vacuole. There are two types of endocytosis, phagocytosis
Phagocytosis () is the process by which a cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle (≥ 0.5 μm), giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome. It is one type of endocytosis. A cell that performs phagocytosis is ...
(cell eating) and pinocytosis
In cellular biology, pinocytosis, otherwise known as fluid endocytosis and bulk-phase pinocytosis, is a mode of endocytosis in which small molecules dissolved in extracellular fluid are brought into the cell through an invagination of the cell ...
(cell drinking). In phagocytosis, cells engulf large particles such as bacteria. Pinocytosis is the same process, except the substances being ingested are in the fluid form.
Vesicles
Vesicles
Vesicle may refer to:
; In cellular biology or chemistry
* Vesicle (biology and chemistry), a supramolecular assembly of lipid molecules, like a cell membrane
* Synaptic vesicle
; In human embryology
* Vesicle (embryology), bulge-like features o ...
are small membrane-enclosed transport units that can transfer molecules between different compartments. Most vesicles transfer the membranes assembled in the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi apparatus, and then from the Golgi apparatus to various locations.
There are various types of vesicles each with a different protein configuration. Most are formed from specific regions of membranes. When a vesicle buds off from a membrane it contains specific proteins on its cytosolic surface. Each membrane a vesicle travels to contains a marker on its cytosolic surface. This marker corresponds with the proteins on the vesicle traveling to the membrane. Once the vesicle finds the membrane, they fuse.
There are three well known types of vesicles. They are clathrin
Clathrin is a protein that plays a major role in the formation of coated vesicles. Clathrin was first isolated and named by Barbara Pearse in 1976. It forms a triskelion shape composed of three clathrin heavy chains and three light chains. When ...
-coated, COPI
COPI is a coatomer, a protein complex that coats vesicles transporting proteins from the ''cis'' end of the Golgi complex back to the rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER), where they were originally synthesized, and between Golgi compartments. Thi ...
-coated, and COPII
The Coat Protein Complex II, or COPII, is a group of proteins that facilitate the formation of vesicles to transport proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi apparatus or endoplasmic-reticulum–Golgi intermediate compartment. This ...
-coated vesicles. Each performs different functions in the cell. For example, clathrin-coated vesicles transport substances between the Golgi apparatus and the plasma membrane. COPI- and COPII-coated vesicles are frequently used for transportation between the ER and the Golgi apparatus.
Lysosomes
Lysosomes
A lysosome () is a membrane-bound organelle found in many animal cells. They are spherical vesicles that contain hydrolytic enzymes that can break down many kinds of biomolecules. A lysosome has a specific composition, of both its membrane prote ...
are organelles that contain hydrolytic enzymes that are used for intracellular digestion. The main functions of a lysosome are to process molecules taken in by the cell and to recycle worn out cell parts. The enzymes inside of lysosomes are acid hydrolases which require an acidic environment for optimal performance. Lysosomes provide such an environment by maintaining a pH of 5.0 inside of the organelle. If a lysosome were to rupture, the enzymes released would not be very active because of the cytosol's neutral pH. However, if numerous lysosomes leaked the cell could be destroyed from autodigestion.
Lysosomes carry out intracellular digestion, in a process called phagocytosis (from the Greek , to eat and , vessel, referring here to the cell), by fusing with a vacuole and releasing their enzymes into the vacuole. Through this process, sugars, amino acids, and other monomers pass into the cytosol and become nutrients for the cell. Lysosomes also use their hydrolytic enzymes to recycle the cell's obsolete organelles in a process called autophagy
Autophagy (or autophagocytosis; from the Ancient Greek , , meaning "self-devouring" and , , meaning "hollow") is the natural, conserved degradation of the cell that removes unnecessary or dysfunctional components through a lysosome-dependent re ...
. The lysosome engulfs another organelle and uses its enzymes to take apart the ingested material. The resulting organic monomers are then returned to the cytosol for reuse. The last function of a lysosome is to digest the cell itself through autolysis.
Spitzenkörper
The spitzenkörper is a component of the endomembrane system found only infungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately fr ...
, and is associated with hyphal tip growth. It is a phase-dark body that is composed of an aggregation of membrane-bound vesicles containing cell wall components, serving as a point of assemblage and release of such components intermediate between the Golgi and the cell membrane. The spitzenkörper is motile and generates new hyphal tip growth as it moves forward.
Plasma membrane
Theplasma membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (t ...
is a phospholipid bilayer membrane that separates the cell from its environment and regulates the transport of molecules and signals into and out of the cell. Embedded in the membrane are proteins that perform the functions of the plasma membrane. The plasma membrane is not a fixed or rigid structure, the molecules that compose the membrane are capable of lateral movement. This movement and the multiple components of the membrane are why it is referred to as a fluid mosaic. Smaller molecules such as carbon dioxide, water, and oxygen can pass through the plasma membrane freely by diffusion
Diffusion is the net movement of anything (for example, atoms, ions, molecules, energy) generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion is driven by a gradient in Gibbs free energy or chemical ...
or osmosis
Osmosis (, ) is the spontaneous net movement or diffusion of solvent molecules through a selectively-permeable membrane from a region of high water potential (region of lower solute concentration) to a region of low water potential (region ...
. Larger molecules needed by the cell are assisted by proteins through active transport
In cellular biology, ''active transport'' is the movement of molecules or ions across a cell membrane from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration—against the concentration gradient. Active transport requires cellul ...
.
The plasma membrane of a cell has multiple functions. These include transporting nutrients into the cell, allowing waste to leave, preventing materials from entering the cell, averting needed materials from leaving the cell, maintaining the pH of the cytosol, and preserving the osmotic pressure
Osmotic pressure is the minimum pressure which needs to be applied to a solution to prevent the inward flow of its pure solvent across a semipermeable membrane.
It is also defined as the measure of the tendency of a solution to take in a pure ...
of the cytosol. Transport proteins which allow some materials to pass through but not others are used for these functions. These proteins use ATP hydrolysis to pump materials against their concentration gradients.
In addition to these universal functions, the plasma membrane has a more specific role in multicellular organisms. Glycoproteins on the membrane assist the cell in recognizing other cells, in order to exchange metabolites and form tissues. Other proteins on the plasma membrane allow attachment to the cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton is a complex, dynamic network of interlinking protein filaments present in the cytoplasm of all cells, including those of bacteria and archaea. In eukaryotes, it extends from the cell nucleus to the cell membrane and is co ...
and extracellular matrix
In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM), also called intercellular matrix, is a three-dimensional network consisting of extracellular macromolecules and minerals, such as collagen, enzymes, glycoproteins and hydroxyapatite that provide s ...
; a function that maintains cell shape and fixes the location of membrane proteins. Enzymes that catalyze reactions are also found on the plasma membrane. Receptor proteins on the membrane have a shape that matches with a chemical messenger, resulting in various cellular responses.
Evolution
The origin of the endomembrane system is linked to the origin of eukaryotes themselves and the origin of eukaryoties to the endosymbiotic origin ofmitochondria
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used ...
. Many models have been put forward to explain the origin of the endomembrane system (reviewed in). The most recent concept suggests that the endomembrane system evolved from outer membrane vesicles the endosymbiotic mitochondrion secreted, and got enclosed within infoldings of the host prokaryote (in turn, a result of the ingestion of the endosymbiont). This OMV (outer membrane vesicles)-based model for the origin of the endomembrane system is currently the one that requires the fewest novel inventions at eukaryote origin and explains the many connections of mitochondria with other compartments of the cell. Currently, this "inside-out" hypothesis (which states that the alphaproteobacteria
Alphaproteobacteria is a class of bacteria in the phylum Pseudomonadota (formerly Proteobacteria). The Magnetococcales and Mariprofundales are considered basal or sister to the Alphaproteobacteria. The Alphaproteobacteria are highly diverse and ...
, the ancestral mitochondria, were engulfed by the blebs of an asgardarchaeon, and later the blebs fused leaving infoldings which would eventually become the endomembrane system) is favored more than the outside-in one (which suggested that the endomembrane system arose due to infoldings within the archaeal membrane).
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Endomembrane System Cell anatomy Membrane biology