Emperor Leopold on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Leopold I (Leopold Ignaz Joseph Balthasar Franz Felician; hu, I. Lipót; 9 June 1640 – 5 May 1705) was
 Born on 9 June 1640 in
Born on 9 June 1640 in
 French expansion increasingly threatened the Empire, especially the seizure of the strategic
French expansion increasingly threatened the Empire, especially the seizure of the strategic
 The emperor himself defined the guidelines of the politics.
The emperor himself defined the guidelines of the politics.
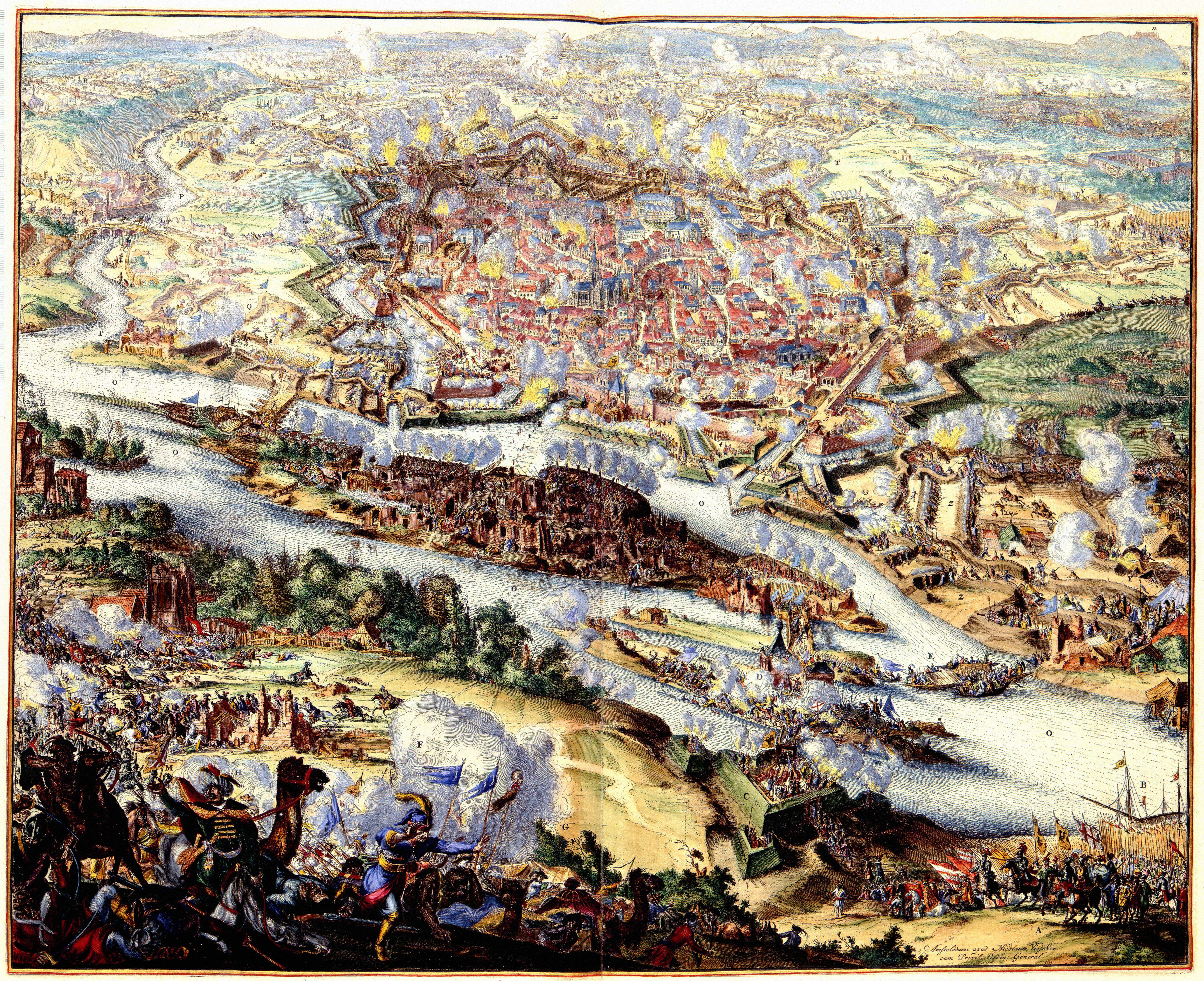 On 12 September 1683, the allied army fell upon the enemy, who was completely routed, and
On 12 September 1683, the allied army fell upon the enemy, who was completely routed, and
 In 1666, he married
In 1666, he married
File:Hungary-thaler-leopold-1692.png, Hungarian
Holy Roman Emperor
The Holy Roman Emperor, originally and officially the Emperor of the Romans ( la, Imperator Romanorum, german: Kaiser der Römer) during the Middle Ages, and also known as the Roman-German Emperor since the early modern period ( la, Imperat ...
, King of Hungary
The King of Hungary ( hu, magyar király) was the ruling head of state of the Kingdom of Hungary from 1000 (or 1001) to 1918. The style of title "Apostolic King of Hungary" (''Apostoli Magyar Király'') was endorsed by Pope Clement XIII in 175 ...
, Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg
, anthem = " Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capi ...
, and Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; cs, Čechy ; ; hsb, Čěska; szl, Czechy) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. Bohemia can also refer to a wider area consisting of the historical Lands of the Bohemian Crown ruled by the Bohem ...
. The second son of Ferdinand III, Holy Roman Emperor
Ferdinand III (Ferdinand Ernest; 13 July 1608, in Graz – 2 April 1657, in Vienna) was from 1621 Archduke of Austria, King of Hungary from 1625, King of Croatia and Bohemia from 1627 and Holy Roman Emperor from 1637 until his death in 1657.
...
, by his first wife, Maria Anna of Spain
, house = Habsburg
, father = Philip III of Spain
, mother = Margaret of Austria
, birth_date =
, birth_place = El Escorial, Spain
, death_date =
, death_place = Linz, Austria
, burial_place = Imperial Crypt
, ...
, Leopold became heir apparent
An heir apparent, often shortened to heir, is a person who is first in an order of succession and cannot be displaced from inheriting by the birth of another person; a person who is first in the order of succession but can be displaced by the b ...
in 1654 by the death of his elder brother Ferdinand IV. Elected in 1658, Leopold ruled the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 unt ...
until his death in 1705, becoming the second longest-ruling Habsburg emperor (46 years and 9 months). He was both a composer and considerable patron
Patronage is the support, encouragement, privilege, or financial aid that an organization or individual bestows on another. In the history of art, arts patronage refers to the support that kings, popes, and the wealthy have provided to artists su ...
of music.
Leopold's reign is known for conflicts with the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
in the Great Turkish War
The Great Turkish War (german: Großer Türkenkrieg), also called the Wars of the Holy League ( tr, Kutsal İttifak Savaşları), was a series of conflicts between the Ottoman Empire and the Holy League consisting of the Holy Roman Empire, Pola ...
(1683-1699) and rivalry with Louis XIV
Louis XIV (Louis Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was List of French monarchs, King of France from 14 May 1643 until his death in 1715. His reign of 72 years and 110 days is the Li ...
, a contemporary and first cousin (on the maternal side; fourth cousin on the paternal side), in the west. After more than a decade of warfare, Leopold emerged victorious in the east thanks to the military talents of Prince Eugene of Savoy
Prince Eugene Francis of Savoy–Carignano, (18 October 1663 – 21 April 1736) better known as Prince Eugene, was a Generalfeldmarschall, field marshal in the army of the Holy Roman Empire and of the Austrian Habsburg dynasty during the 17th a ...
. By the Treaty of Karlowitz
The Treaty of Karlowitz was signed in Karlowitz, Military Frontier of Archduchy of Austria (present-day Sremski Karlovci, Serbia), on 26 January 1699, concluding the Great Turkish War of 1683–1697 in which the Ottoman Empire was defeated by ...
, Leopold recovered almost all of the Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from the Middle Ages into the 20th century. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the Coronation of the Hungarian monarch, c ...
, which had fallen under Turkish power in the years after the 1526 Battle of Mohács
The Battle of Mohács (; hu, mohácsi csata, tr, Mohaç Muharebesi or Mohaç Savaşı) was fought on 29 August 1526 near Mohács, Kingdom of Hungary, between the forces of the Kingdom of Hungary and its allies, led by Louis II, and thos ...
.
Leopold fought three wars against France: the Franco-Dutch War
The Franco-Dutch War, also known as the Dutch War (french: Guerre de Hollande; nl, Hollandse Oorlog), was fought between France and the Dutch Republic, supported by its allies the Holy Roman Empire, Spain, Brandenburg-Prussia and Denmark-Nor ...
, the Nine Years' War
The Nine Years' War (1688–1697), often called the War of the Grand Alliance or the War of the League of Augsburg, was a conflict between Kingdom of France, France and a European coalition which mainly included the Holy Roman Empire (led by t ...
, and the War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict that took place from 1701 to 1714. The death of childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700 led to a struggle for control of the Spanish Empire between his heirs, Phil ...
. In this last, Leopold sought to give his younger son Charles
Charles is a masculine given name predominantly found in English and French speaking countries. It is from the French form ''Charles'' of the Proto-Germanic name (in runic alphabet) or ''*karilaz'' (in Latin alphabet), whose meaning was " ...
the entire Spanish inheritance, disregarding the will of the late Charles II. Leopold started a war that soon engulfed much of Europe. The early years of the war went fairly well for Austria, with victories at Schellenberg
Schellenberg is a municipality in the lowland area of Liechtenstein, on the banks of the Rhine. , it has a population of 1,107 and covers an area of
History Early history
The area was first settled by Celts, then by Rhaetians. Rome conquere ...
and Blenheim Blenheim ( ) is the English name of Blindheim, a village in Bavaria, Germany, which was the site of the Battle of Blenheim in 1704. Almost all places and other things called Blenheim are named directly or indirectly in honour of the battle.
Places ...
, but the war would drag on until 1714, nine years after Leopold's death, which barely had an effect on the warring nations. When peace returned with the Treaty of Rastatt
The Treaty of Rastatt was a peace treaty between France and Austria that was concluded on 7 March 1714 in the Baden city of Rastatt to end the War of the Spanish Succession between both countries. The treaty followed the Treaty of Utrecht of 11 A ...
, Austria could not be said to have emerged as triumphant as it had from the war against the Turks.
Early years
 Born on 9 June 1640 in
Born on 9 June 1640 in Vienna
en, Viennese
, iso_code = AT-9
, registration_plate = W
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code =
, timezone = CET
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST ...
, Leopold received the traditional program of education in the liberal arts
Liberal arts education (from Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as La ...
, history, literature, natural science and astronomy. He was particularly interested in music, as his father emperor Ferdinand III had been. From an early age Leopold showed an inclination toward learning.John P. Spielman; ''Leopold I of Austria'' (1977) He became fluent in Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
, Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
, German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
, French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
, and Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
. In addition to German, Italian would be the most favored language at his court.
Likewise he had received comprehensive ecclesiastical training as he had originally been selected for a career in the higher clergy. This plan, though, was dropped upon the 1654 death of his older brother, Ferdinand IV, when Leopold became heir apparent.Joseph A. Biesinger; "Germany: European nations" in ''Facts on File library of world history''. pg 529. Nonetheless, Leopold's spiritual education had had a manifest impact on him. Leopold remained under the spell of his clerical education and Jesuit
, image = Ihs-logo.svg
, image_size = 175px
, caption = ChristogramOfficial seal of the Jesuits
, abbreviation = SJ
, nickname = Jesuits
, formation =
, founders ...
influence throughout his life. For a monarch he was uncommonly knowledgeable about theology, metaphysics, jurisprudence and the sciences. He also retained his interest in astrology
Astrology is a range of divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that claim to discern information about human affairs and terrestrial events by studying the apparent positions of celestial objects. Di ...
and alchemy
Alchemy (from Arabic: ''al-kīmiyā''; from Ancient Greek: χυμεία, ''khumeía'') is an ancient branch of natural philosophy, a philosophical and protoscientific tradition that was historically practiced in China, India, the Muslim wo ...
which he had developed under Jesuit tutors. A deeply religious and devoted person, Leopold personified the ''pietas Austriaca'', or the loyal Catholic attitude of his house. On the other hand, his piety and education may have caused in him a fatalistic strain which inclined him to reject all compromise on denominational questions, which is not always considered a positive characteristic of a ruler.
Leopold was said to have typical Habsburg physical attributes, such as the prominent '' Habsburg lower jaw''. Short, thin, and of sick constitution, Leopold was cold and reserved in public and socially inept. However, he is also said to have been open with close associates. Coxe Coxe is a surname, and may refer to:
* Alfred Conkling Coxe Sr., American federal judge
* Alfred Conkling Coxe Jr., American federal judge
* Arthur Cleveland Coxe, American bishop, son of Samuel Hanson Cox
*Cameron Coxe, Welsh footballer
*Daniel Co ...
described Leopold in the following manner: "His gait was stately, slow and deliberate; his air pensive, his address awkward, his manner uncouth, his disposition cold and phlegmatic." Spielman argues that his long-expected career in the clergy caused Leopold to have "early adopted the intense Catholic piety expected of him and the gentle manners appropriate to a merely supporting role. He grew to manhood without the military ambition that characterized most of his fellow monarchs. From the beginning, his reign was defensive and profoundly conservative."John P. Spielman; "Europe, 1450 to 1789" in ''Encyclopedia of the Early Modern World''
Elected king of Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Cr ...
in 1655, he followed suit in 1656 and 1657 in Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; cs, Čechy ; ; hsb, Čěska; szl, Czechy) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. Bohemia can also refer to a wider area consisting of the historical Lands of the Bohemian Crown ruled by the Bohem ...
and Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg
, anthem = " Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capi ...
respectively. In July 1658, more than a year after his father's death, Leopold was elected Holy Roman Emperor at Frankfurt
Frankfurt, officially Frankfurt am Main (; Hessian: , " Frank ford on the Main"), is the most populous city in the German state of Hesse. Its 791,000 inhabitants as of 2022 make it the fifth-most populous city in Germany. Located on it ...
in opposition to the French Cardinal Mazarin
Cardinal Jules Mazarin (, also , , ; 14 July 1602 – 9 March 1661), born Giulio Raimondo Mazzarino () or Mazarini, was an Italian cardinal, diplomat and politician who served as the chief minister to the Kings of France Louis XIII and Louis X ...
, who sought to place the Imperial Crown on the head of Prince-elector
The prince-electors (german: Kurfürst pl. , cz, Kurfiřt, la, Princeps Elector), or electors for short, were the members of the electoral college that elected the emperor of the Holy Roman Empire.
From the 13th century onwards, the princ ...
Ferdinand Maria or some other non-Habsburg prince. To conciliate France, which had considerable influence in German affairs thanks to the League of the Rhine
The League of the Rhine (also known as the ''Erster Rheinbund'', First Rhine- Bund; or the ''Rheinische Allianz'' - Rhenish Alliance) was a defensive union of more than 50 German princes and their cities along the River Rhine, formed on 14 Augu ...
, the newly elected Emperor promised not to assist Spain, then at war with France. This marked the beginning of a nearly 47-year reign characterized by a lasting rivalry with France and its king, Louis XIV
Louis XIV (Louis Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was List of French monarchs, King of France from 14 May 1643 until his death in 1715. His reign of 72 years and 110 days is the Li ...
. The latters dominant personality and power completely overshadowed Leopold, even to this day. Although Leopold did not lead his troops in person as Louis XIV did, he was no less a warrior-king given the greater part of his public life was directed towards the arrangement and furtherance of wars.
Second Northern War
Leopold's first war was theSecond Northern War
The Second Northern War (1655–60), (also First or Little Northern War) was fought between Sweden and its adversaries the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (1655–60), the Tsardom of Russia ( 1656–58), Brandenburg-Prussia (1657–60), the ...
(1655–1660), in which King Charles X of Sweden
Charles X Gustav, also Carl Gustav ( sv, Karl X Gustav; 8 November 1622 – 13 February 1660), was King of Sweden from 1654 until his death. He was the son of John Casimir, Count Palatine of Zweibrücken-Kleeburg and Catherine of Sweden. Afte ...
tried to become King of Poland with the aid of allies including György II Rákóczi, Prince of Transylvania
The Prince of Transylvania ( hu, erdélyi fejedelem, german: Fürst von Siebenbürgen, la, princeps Transsylvaniae, ro, principele TransilvanieiFallenbüchl 1988, p. 77.) was the head of state of the Principality of Transylvania from the last d ...
. Leopold's predecessor, Ferdinand III, had allied with King John II Casimir Vasa
John II Casimir ( pl, Jan II Kazimierz Waza; lt, Jonas Kazimieras Vaza; 22 March 1609 – 16 December 1672) was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1648 until his abdication in 1668 as well as titular King of Sweden from 1648 ...
of Poland in 1656. In 1657, Leopold expanded this alliance to include Austrian troops (paid by Poland). These troops helped defeat the Transylvanian army, and campaigned as far as Denmark. The war ended with the Treaty of Oliwa
The Treaty or Peace of Oliva of 23 April (OS)/3 May (NS) 1660Evans (2008), p.55 ( pl, Pokój Oliwski, sv, Freden i Oliva, german: Vertrag von Oliva) was one of the peace treaties ending the Second Northern War (1655-1660).Frost (2000), p.183 ...
in 1660.
Early wars against the Ottoman Empire
TheOttoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
often interfered in the affairs of Transylvania, always an unruly district, and this interference brought on a war with the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 unt ...
, which after some desultory operations really began in 1663. By a personal appeal to the diet at Regensburg
Regensburg or is a city in eastern Bavaria, at the confluence of the Danube, Naab and Regen rivers. It is capital of the Upper Palatinate subregion of the state in the south of Germany. With more than 150,000 inhabitants, Regensburg is the ...
Leopold induced the princes to send assistance for the campaign; troops were also sent by France, and in August 1664, the great Imperial general Raimondo Montecuccoli
Raimondo Montecuccoli (; 21 February 1609 – 16 October 1680) was an Italian-born professional soldier, military theorist, and diplomat, who served the Habsburg monarchy.
Experiencing the Thirty Years' War from scratch as a simple footsoldier ...
gained a notable victory at Saint Gotthard. By the Peace of Vasvár
The Peace of Vasvár was a treaty between the Habsburg monarchy and the Ottoman Empire which followed the Battle of Saint Gotthard of 1 August 1664 (near Mogersdorf, Burgenland), and concluded the Austro-Turkish War (1663–64). It held for abou ...
the Emperor made a twenty years' truce with the Sultan, granting more generous terms than his recent victory seemed to render necessary.
Wars against France
 French expansion increasingly threatened the Empire, especially the seizure of the strategic
French expansion increasingly threatened the Empire, especially the seizure of the strategic Duchy of Lorraine
The Duchy of Lorraine (french: Lorraine ; german: Lothringen ), originally Upper Lorraine, was a duchy now included in the larger present-day region of Lorraine in northeastern France. Its capital was Nancy.
It was founded in 959 following th ...
in 1670, followed by the 1672 Franco-Dutch War
The Franco-Dutch War, also known as the Dutch War (french: Guerre de Hollande; nl, Hollandse Oorlog), was fought between France and the Dutch Republic, supported by its allies the Holy Roman Empire, Spain, Brandenburg-Prussia and Denmark-Nor ...
. By mid June, the Dutch Republic tethered at the brink of destruction, which lead Leopold to agree to an alliance with Brandenburg-Prussia
Brandenburg-Prussia (german: Brandenburg-Preußen; ) is the historiographic denomination for the early modern realm of the Brandenburgian Hohenzollerns between 1618 and 1701. Based in the Electorate of Brandenburg, the main branch of the Hohe ...
and the Republic on June 25. However, he was also pondering a revolt in Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Cr ...
and viewed French conquests in the Rhineland
The Rhineland (german: Rheinland; french: Rhénanie; nl, Rijnland; ksh, Rhingland; Latinised name: ''Rhenania'') is a loosely defined area of Western Germany along the Rhine, chiefly its middle section.
Term
Historically, the Rhinelands ...
a higher priority than helping the Dutch. His commander, Raimondo Montecuccoli
Raimondo Montecuccoli (; 21 February 1609 – 16 October 1680) was an Italian-born professional soldier, military theorist, and diplomat, who served the Habsburg monarchy.
Experiencing the Thirty Years' War from scratch as a simple footsoldier ...
, was ordered to remain on the defensive and avoid a direct conflict. Chaotic logistics made it impossible to maintain the troops and Brandenburg left the war in June 1673 under the Treaty of Vossem.
An anti-French Quadruple Alliance was formed in August, consisting of the Republic, Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
, Emperor Leopold, and the Duke of Lorraine
The rulers of Lorraine have held different posts under different governments over different regions, since its creation as the kingdom of Lotharingia by the Treaty of Prüm, in 855. The first rulers of the newly established region were kings of ...
, while in May 1674, the Imperial Diet declared it an Imperial war
A ''Reichskrieg'' ("Imperial War", pl. ''Reichskriege'') was a war fought by the Holy Roman Empire as a whole against a common enemy. After the Peace of Westphalia in 1648, a ''Reichskrieg'' was a formal state of war that could only be declare ...
. The 1678 Treaty of Nijmegen
The Treaties of Peace of Nijmegen ('; german: Friede von Nimwegen) were a series of treaties signed in the Dutch city of Nijmegen between August 1678 and October 1679. The treaties ended various interconnected wars among France, the Dutch Repub ...
is generally seen as a French victory, although the Alliance succeeded in limiting their gains.
Almost immediately after the conclusion of peace Louis renewed his aggressions on the German frontier through the ''Réunions'' policy. Engaged in a serious struggle with the Ottoman Empire, the emperor was again slow to move, and although he joined the Association League against France in 1682 he was glad to make a truce at Regensburg
Regensburg or is a city in eastern Bavaria, at the confluence of the Danube, Naab and Regen rivers. It is capital of the Upper Palatinate subregion of the state in the south of Germany. With more than 150,000 inhabitants, Regensburg is the ...
two years later. In 1686 the League of Augsburg
The Grand Alliance was the anti-French coalition formed on 20 December 1689 between the Dutch Republic, England and the Holy Roman Empire. It was signed by the two leading opponents of France: William III, Stadtholder of the Dutch Republic and ( ...
was formed by the emperor and the imperial princes, to preserve the terms of the treaties of Westphalia
Westphalia (; german: Westfalen ; nds, Westfalen ) is a region of northwestern Germany and one of the three historic parts of the state of North Rhine-Westphalia. It has an area of and 7.9 million inhabitants.
The territory of the regio ...
and of Nijmegen
Nijmegen (;; Spanish and it, Nimega. Nijmeegs: ''Nimwèège'' ) is the largest city in the Dutch province of Gelderland and tenth largest of the Netherlands as a whole, located on the Waal river close to the German border. It is about 6 ...
. The whole European position was now bound up with events in England, and the tension lasted until 1688, when William III of Orange
William III (William Henry; ; 4 November 16508 March 1702), also widely known as William of Orange, was the sovereign Prince of Orange from birth, Stadtholder of Holland, Zeeland, Utrecht, Guelders, and Overijssel in the Dutch Republic from ...
won the English crown through the Glorious Revolution
The Glorious Revolution; gd, Rèabhlaid Ghlòrmhor; cy, Chwyldro Gogoneddus , also known as the ''Glorieuze Overtocht'' or ''Glorious Crossing'' in the Netherlands, is the sequence of events leading to the deposition of King James II and ...
and Louis invaded Germany. In May 1689, the Grand Alliance was formed, including the emperor, the kings of England, Spain and Denmark, the elector of Brandenburg
Brandenburg (; nds, Brannenborg; dsb, Bramborska ) is a state in the northeast of Germany bordering the states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony, as well as the country of Poland. With an area of 29,480 squ ...
and others, and a fierce struggle against France was waged throughout almost the whole of western Europe. In general the several campaigns were favourable to the allies, and in September 1697, England, Spain and the United Provinces made peace with France at the Treaty of Rijswijk
The Peace of Ryswick, or Rijswijk, was a series of treaties signed in the Dutch city of Rijswijk between 20 September and 30 October 1697. They ended the 1688 to 1697 Nine Years' War between France and the Grand Alliance, which included England, ...
.
Leopold refused to assent to the treaty, as he considered that his allies had somewhat neglected his interests, but in the following month he came to terms and a number of places were transferred from France to Germany. The peace with France lasted for about four years and then Europe was involved in the War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict that took place from 1701 to 1714. The death of childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700 led to a struggle for control of the Spanish Empire between his heirs, Phil ...
. The king of Spain, Charles II, was a Habsburg by descent and was related by marriage to the Austrian branch, while a similar tie bound him to the royal house of France. He was feeble and childless, and attempts had been made by the European powers to arrange for a peaceable division of his extensive kingdom. Leopold refused to consent to any partition, and when in November 1700 Charles died, leaving his crown to Philippe de France, Duke of Anjou, a grandson of Louis XIV, all hopes of a peaceable settlement vanished. Under the guidance of William III a powerful league, a renewed Grand Alliance, was formed against France; of this the emperor was a prominent member, and in 1703 he transferred his claim on the Spanish monarchy to his second son, Charles
Charles is a masculine given name predominantly found in English and French speaking countries. It is from the French form ''Charles'' of the Proto-Germanic name (in runic alphabet) or ''*karilaz'' (in Latin alphabet), whose meaning was " ...
. The early course of the war was not favorable to the Imperialists, but the tide of defeat had been rolled back by the great victory of Blenheim Blenheim ( ) is the English name of Blindheim, a village in Bavaria, Germany, which was the site of the Battle of Blenheim in 1704. Almost all places and other things called Blenheim are named directly or indirectly in honour of the battle.
Places ...
before Leopold died on 5 May 1705.
Internal problems
 The emperor himself defined the guidelines of the politics.
The emperor himself defined the guidelines of the politics. Johann Weikhard of Auersperg
Prince Johann Weikhard of Auersperg (also spelled ''Johann Weichard von Auersperg''; 11 March 1615 at Žužemberk Castle – 11 November 1677 in Ljubljana) was Prime Minister of Austria and Knight of the Order of the Golden Fleece. He was the fi ...
was overthrown in 1669 as the leading minister. He was followed by Wenzel Eusebius, Prince of Lobkowicz
Václav Eusebius František, Prince of Lobkowicz (''German: Fürst Wenzel Eusebius von Lobkowicz'') (30 January 1609 – Roudnice, 22 April 1677) was a Bohemian military leader and diplomat of the Lobkowicz family. After 1646, he was Duke of ...
. Both had arranged some connections to France without the knowledge of the emperor. In 1674 also Lobkowicz lost his appointment.
In governing his own lands Leopold found his chief difficulties in Hungary, where unrest was caused partly by his desire to crush Protestant
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
ism and partly by the so-called Magnate conspiracy
The Magnate conspiracy, also known as the Zrinski- Frankopan Conspiracy ( hr, Zrinsko-frankopanska urota) in Croatia, and Wesselényi conspiracy ( hu, Wesselényi-összeesküvés) in Hungary, was a 17th-century attempt to throw off Habsburg ...
. A rising was suppressed in 1671 and for some years Hungary was treated with great severity. In 1681, after another rising, some grievances were removed and a less repressive policy was adopted, but this did not deter the Hungarians from revolting again. Espousing the cause of the rebels the sultan sent an enormous army into Austria early in 1683; this advanced almost unchecked to Vienna
en, Viennese
, iso_code = AT-9
, registration_plate = W
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code =
, timezone = CET
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST ...
, which was besieged from July to September, while Leopold took refuge at Passau
Passau (; bar, label= Central Bavarian, Båssa) is a city in Lower Bavaria, Germany, also known as the Dreiflüssestadt ("City of Three Rivers") as the river Danube is joined by the Inn from the south and the Ilz from the north.
Passau's po ...
. Realizing the gravity of the situation somewhat tardily, some of the German princes, among them the electors of Saxony
Saxony (german: Sachsen ; Upper Saxon German, Upper Saxon: ''Saggsn''; hsb, Sakska), officially the Free State of Saxony (german: Freistaat Sachsen, links=no ; Upper Saxon: ''Freischdaad Saggsn''; hsb, Swobodny stat Sakska, links=no), is a ...
and Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total l ...
, led their contingents to the Imperial Army, which was commanded by the emperor's brother-in-law, Charles, duke of Lorraine, but the most redoubtable of Leopold's allies was the king of Poland, John III Sobieski
John III Sobieski ( pl, Jan III Sobieski; lt, Jonas III Sobieskis; la, Ioannes III Sobiscius; 17 August 1629 – 17 June 1696) was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1674 until his death in 1696.
Born into Polish nobility, Sobi ...
, who was already dreaded by the Turks. Austrian forces occupied the castle of Trebišov
Trebišov ( hu, Tőketerebes; german: Trebischau; russian: Требишев) is a small industrial town in the easternmost part of Slovakia, with a population of around 25,000. The town is an administrative, economic and cultural center with machi ...
in 1675, but in 1682 Imre Thököly
Imre is a Hungarian masculine first name, which is also in Estonian use, where the corresponding name day is 10 April. It has been suggested that it relates to the name Emeric, Emmerich or Heinrich. Its English equivalents are Emery and Henry ...
captured it and then fled from continuous Austrian attacks, so they blew the castle up, leaving it in ruins. They fled as supposedly Hungarian rebel troops under the command of Imre Thököly, cooperating with the Turks, and sacked the city of Bielsko
Bielsko (german: Bielitz, cs, Bílsko) was until 1950 an independent town situated in Cieszyn Silesia, Poland. In 1951 it was joined with Biała Krakowska to form the new town of Bielsko-Biała. Bielsko constitutes the western part of that to ...
in 1682. In 1692, Leopold gave up his rights to the property, giving his rights by donation to Theresia Keglević.
He also expelled Jewish communities from his realm, for example the Viennese Jewish community, which used to live in an area called "Im Werd" across the Danube Canal. After the expulsion of the Jewish population, with popular support, the area was renamed ''Leopoldstadt
Leopoldstadt (; bar, Leopoidstod, "Leopold-Town") is the 2nd municipal Districts of Vienna, district of Vienna (german: 2. Bezirk) in Austria. there are 103,233 inhabitants over . It is situated in the heart of the city and, together with Bri ...
'' as a thanksgiving. But Frederick William I, Elector of Brandenburg, issued an edict in 1677, in which he announced his special protection for 50 families of these expelled Jews.
Success against the Turks and in Hungary
 On 12 September 1683, the allied army fell upon the enemy, who was completely routed, and
On 12 September 1683, the allied army fell upon the enemy, who was completely routed, and Vienna
en, Viennese
, iso_code = AT-9
, registration_plate = W
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code =
, timezone = CET
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST ...
was saved. The imperial forces, among whom Prince Eugene of Savoy
Prince Eugene Francis of Savoy–Carignano, (18 October 1663 – 21 April 1736) better known as Prince Eugene, was a Generalfeldmarschall, field marshal in the army of the Holy Roman Empire and of the Austrian Habsburg dynasty during the 17th a ...
was rapidly becoming prominent, followed up the victory with others, notably one near Mohács
Mohács (; Croatian and Bunjevac: ''Mohač''; german: Mohatsch; sr, Мохач; tr, Mohaç) is a town in Baranya County, Hungary, on the right bank of the Danube.
Etymology
The name probably comes from the Slavic ''*Mъchačь'',''*Mocháč'': ...
in 1687 and another at Zenta in 1697, and in January 1699, the sultan signed the treaty of Karlowitz
The Treaty of Karlowitz was signed in Karlowitz, Military Frontier of Archduchy of Austria (present-day Sremski Karlovci, Serbia), on 26 January 1699, concluding the Great Turkish War of 1683–1697 in which the Ottoman Empire was defeated by ...
by which he admitted the sovereign rights of the house of Habsburg over nearly the whole of Hungary (including Serbs in Vojvodina
The Serbs of Vojvodina are the largest ethnic group in this northern province of Serbia. For centuries, Vojvodina was ruled by several European powers, but Vojvodina Serbs never assimilated into cultures of those countries. Thus, they have consi ...
). As the Habsburg forces retreated, they withdrew 37,000 Serb
The Serbs ( sr-Cyr, Срби, Srbi, ) are the most numerous South Slavic ethnic group native to the Balkans in Southeastern Europe, who share a common Serbian ancestry, culture, history and language.
The majority of Serbs live in their na ...
families under Patriarch Arsenije III Čarnojević Arsenije ( sr-cyr, Арсеније; ) is a Serbian given name, a variant of the Greek name '' Arsenios''. Diminutives of the name include '' Arsen'', ''Arsa'' and '' Arso''. It may refer to:
* Arsenije Sremac (d. 1266), second Archbishop of the Se ...
of the Serbian Patriarchate of Peć
The Serbian Patriarchate of Peć ( sr, Српска патријаршија у Пећи, ''Srpska patrijaršija u Peći'') or just Patriarchate of Peć ( sr, Пећка патријаршија, ''Pećka patrijaršija''), was an autocephalous ...
. In 1690 and 1691 Emperor Leopold I had conceived through a number of edicts (Privileges) the autonomy of Serbs in his Empire, which would last and develop for more than two centuries until its abolition in 1912. Before the conclusion of the war, however, Leopold had taken measures to strengthen his hold upon this country. In 1687, the Hungarian diet
The Diet of Hungary or originally: Parlamentum Publicum / Parlamentum Generale ( hu, Országgyűlés) became the supreme legislative institution in the medieval kingdom of Hungary from the 1290s, and in its successor states, Royal Hungary and t ...
in Pressburg
Bratislava (, also ; ; german: Preßburg/Pressburg ; hu, Pozsony) is the capital and largest city of Slovakia. Officially, the population of the city is about 475,000; however, it is estimated to be more than 660,000 — approximately 140% of ...
(now Bratislava) changed the constitution, the right of the Habsburgs to succeed to the throne without election was admitted and the emperor's elder son Joseph I Joseph I or Josef I may refer to:
*Joseph I of Constantinople, Ecumenical Patriarch in 1266–1275 and 1282–1283
* Joseph I, Holy Roman Emperor (1678–1711)
*Joseph I (Chaldean Patriarch) (reigned 1681–1696)
*Joseph I of Portugal (1750–1777) ...
was crowned hereditary king of Hungary.
The Holy Roman Empire
ThePeace of Westphalia
The Peace of Westphalia (german: Westfälischer Friede, ) is the collective name for two peace treaties signed in October 1648 in the Westphalian cities of Osnabrück and Münster. They ended the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) and brought pe ...
in 1648 had been a political defeat for the Habsburgs. It ended the idea that Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
was a single Christian empire; governed spiritually by the Pope
The pope ( la, papa, from el, πάππας, translit=pappas, 'father'), also known as supreme pontiff ( or ), Roman pontiff () or sovereign pontiff, is the bishop of Rome (or historically the patriarch of Rome), head of the worldwide Cathol ...
and temporally by the Holy Roman Emperor. Moreover, the treaty was devoted to parceling out land and influence to the "winners", the anti-Habsburg alliance led by France and Sweden. However, the Habsburgs did gain some benefits out of the wars
''The Wars'' is a 1977 novel by Timothy Findley that follows Robert Ross, a nineteen-year-old Canadian who enlists in World War I after the death of his beloved older sister in an attempt to escape both his grief and the social norms of oppressi ...
; the Protestant aristocracy in Habsburg territories had been decimated, and the ties between Vienna and the Habsburg domains in Bohemia and elsewhere were greatly strengthened. These changes would allow Leopold to initiate necessary political and institutional reforms during his reign to develop somewhat of an absolutist state along French lines. The most important consequences of the war was in retrospect to weaken the Habsburgs as emperors but strengthen them in their own lands. Leopold was the first to realize this altered state of affairs and act in accordance with it.Thomas Noble. "Western Civilization: Beyond Boundaries". Cengage Learning. 2008. p. 507-508.
Administrative reform
The reign of Leopold saw some important changes made in the constitution of the Empire. In 1663 the imperial diet entered upon the last stage of its existence, and became a body permanently in session at Regensburg. This perpetual diet would become a vital tool for consolidation of Habsburg power under Leopold.Anton Schindling
Anton Schindling (20 January 1947 in Frankfurt - 4 January 2020 in Tübingen) was a German historian. He held chairs at the Catholic University of Eichstätt-Ingolstadt (1985–1987), the University of Osnabrück (1987–1995) and the University of ...
. "The Development of the Eternal Diet in Regensburg". The Journal of Modern History 58 (December 1986). p. S69.
Political changes
In 1692, the duke ofHanover
Hanover (; german: Hannover ; nds, Hannober) is the capital and largest city of the German state of Lower Saxony. Its 535,932 (2021) inhabitants make it the 13th-largest city in Germany as well as the fourth-largest city in Northern Germany ...
was raised to the rank of an elector, becoming the ninth member of the electoral college. In 1700, Leopold, greatly in need of help for the impending war with France, granted the title of king in Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an e ...
to the elector of Brandenburg
Brandenburg (; nds, Brannenborg; dsb, Bramborska ) is a state in the northeast of Germany bordering the states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony, as well as the country of Poland. With an area of 29,480 squ ...
. The net result of these and similar changes was to weaken the authority of the emperor over the members of the Empire and to compel him to rely more and more upon his position as ruler of the Austrian archduchies and of Hungary and Bohemia.
Character and overall assessment
Leopold was a man of industry and education, and during his later years, he showed some political ability. Regarding himself as an absolute sovereign, he was extremely tenacious of his rights. Greatly influenced by theJesuits
, image = Ihs-logo.svg
, image_size = 175px
, caption = ChristogramOfficial seal of the Jesuits
, abbreviation = SJ
, nickname = Jesuits
, formation =
, founders = ...
, he was a staunch proponent of the Counter-Reformation
The Counter-Reformation (), also called the Catholic Reformation () or the Catholic Revival, was the period of Catholic resurgence that was initiated in response to the Protestant Reformation. It began with the Council of Trent (1545–1563) a ...
. In person, he was short, but strong and healthy. Although he had no inclination for a military life, he loved exercise in the open air, such as hunting and riding; he also had a taste and talent for music and
composed several Oratorios and Suites of Dances.
Perhaps due to inbreeding among his progenitors, the hereditary Habsburg jaw was most prominent in Leopold. Because his jaw was depicted unusually large on a 1670 silver coin, Leopold was nicknamed "the Hogmouth"; however, most collectors do not believe the coin was an accurate depiction.
Marriages and children
 In 1666, he married
In 1666, he married Margaret Theresa of Spain
Margaret Theresa of Spain ( es, link=no, Margarita Teresa, german: link=no, Margarete Theresia; 12 July 1651 – 12 March 1673) was, by marriage to Leopold I, Holy Roman Empress, German Queen, Archduchess of Austria and Queen of Hungary and ...
(1651–1673), daughter of King Philip IV of Spain
Philip IV ( es, Felipe, pt, Filipe; 8 April 160517 September 1665), also called the Planet King (Spanish: ''Rey Planeta''), was King of Spain from 1621 to his death and (as Philip III) King of Portugal from 1621 to 1640. Philip is remembered ...
, who was both his niece and his first cousin. She was depicted in Diego Velázquez
Diego Rodríguez de Silva y Velázquez (baptized June 6, 1599August 6, 1660) was a Spanish painter, the leading artist in the court of King Philip IV of Spain and Portugal, and of the Spanish Golden Age. He was an individualistic artist of th ...
' paintings sent from the court of Madrid to Leopold as he waited in Vienna for his fiancée to grow up. Leopold and Margaret Theresa had four children:
# Archduke Ferdinand Wenzel (1667–1668)
# Archduchess Maria Antonia (1669–1692), who married Maximilian II Emanuel, Elector of Bavaria
Maximilian, Maximillian or Maximiliaan (Maximilien in French) is a male given name.
The name "Max" is considered a shortening of "Maximilian" as well as of several other names.
List of people
Monarchs
*Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor (1459– ...
.
# Archduke Johann Leopold (1670)
# Archduchess Maria Anna Antonia (1672)
His second wife was Claudia Felicitas of Austria, who died in 1676 at the age of 22. Neither of their two daughters survived:
# Archduchess Anna Maria Josepha (1674)
# Archduchess Maria Josepha Clementina (1675–1676)
His third wife was Eleonor Magdalene of Neuburg. They had the following children:
# Joseph I, Holy Roman Emperor
, father = Leopold I, Holy Roman Emperor
, mother = Eleonore Magdalene of Neuburg
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Vienna, Austria
, death_date =
, death_place = Vienna, Austria
, burial_place = Imperial Crypt, Vienna
, r ...
(1678–1711), who married Wilhelmine Amalia of Brunswick-Lüneburg
Wilhelmine Amalie of Brunswick-Lüneburg (21 April 1673 – 10 April 1742) was Holy Roman Empress, Queen of the Germans, Queen of Hungary, Queen of Bohemia, Archduchess consort of Austria etc. as the spouse of Joseph I, Holy Roman Emperor.
...
# Archduchess Maria Christina (1679)
# Archduchess Maria Elisabeth (1680–1741), Governor of the Austrian Netherlands
The Austrian Netherlands nl, Oostenrijkse Nederlanden; french: Pays-Bas Autrichiens; german: Österreichische Niederlande; la, Belgium Austriacum. was the territory of the Burgundian Circle of the Holy Roman Empire between 1714 and 1797. The pe ...
# Archduke Leopold Joseph (1682–1684)
# Archduchess Maria Anna (1683–1754) married John V of Portugal
Dom John V ( pt, João Francisco António José Bento Bernardo; 22 October 1689 – 31 July 1750), known as the Magnanimous (''o Magnânimo'') and the Portuguese Sun King (''o Rei-Sol Português''), was King of Portugal from 9 December 17 ...
# Archduchess Maria Theresa (1684–1696)
# Charles VI, Holy Roman Emperor
, house = Habsburg
, spouse =
, issue =
, issue-link = #Children
, issue-pipe =
, father = Leopold I, Holy Roman Emperor
, mother = Eleonore Magdalene of Neuburg
, birth_date ...
(1685–1740), who married Elisabeth Christine of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel
Elisabeth Christine of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel (28 August 1691 – 21 December 1750) was Princess of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel, Holy Roman Empress, German Queen, Queen of Bohemia and Hungary; and Archduchess of Austria by her marriage to Emp ...
# Archduchess Maria Josepha (1687–1703)
# Archduchess Maria Magdalena (1689–1743)
# Archduchess Maria Margaret (1690–1691)
Music
Like his father, Leopold was a patron of music and a composer. He continued to enrich the court's musical life by employing and providing support for distinguished composers such asAntonio Bertali
Antonio Bertali (March 1605–17 April 1669) was an Italian composer and violinist of the Baroque era.
He was born in Verona and received early music education there from Stefano Bernardi. Probably from 1624, he was employed as court musi ...
, Giovanni Bononcini, Johann Kaspar Kerll
Johann Caspar Kerll (9 April 1627 – 13 February 1693) was a German baroque composer and organist. He is also known as Kerl, Gherl, Giovanni Gasparo Cherll and Gaspard Kerle.
Born in Adorf in the Electorate of Saxony as the son of an organist ...
, Ferdinand Tobias Richter, Alessandro Poglietti, and Johann Fux
Johann Joseph Fux (; – 13 February 1741) was an Austrian composer, music theorist and pedagogue of the late Baroque era. His most enduring work is not a musical composition but his treatise on counterpoint, '' Gradus ad Parnassum'', which has ...
. Leopold's surviving works show the influence of Bertali and Viennese composers in general (in oratorios and other dramatic works), and of Johann Heinrich Schmelzer
Johann Heinrich Schmelzer (c. 1620–1623between 29 February and 20 March 1680) was an Austrian composer and violinist of the middle Baroque era. Almost nothing is known about his early years, but he seems to have arrived in Vienna during the 1630 ...
(in ballets and German comedies). His sacred music is perhaps his most successful, particularly ''Missa angeli custodis'', a Requiem Mass
A Requiem or Requiem Mass, also known as Mass for the dead ( la, Missa pro defunctis) or Mass of the dead ( la, Missa defunctorum), is a Mass of the Catholic Church offered for the repose of the soul or souls of one or more deceased persons, ...
for his first wife, and ''Three Lections'', composed for the burial of his second wife. Much of Leopold's music was published with works by his father, and described as "works of exceeding high merit."
Titles
The full titulature of Leopold after he had become emperor went as follows: "Leopold I, by the grace of God elected Holy Roman Emperor, forever August, King of Germany, King of Hungary, King of Bohemia, Dalmatia, Croatia, Slavonia, Rama, Serbia, Galicia, Lodomeria, Cumania, Bulgaria, Archduke of Austria, Duke of Burgundy, Brabant, Styria, Carinthia, Carniola, Margrave of Moravia, Duke of Luxemburg, of the Upper and Lower Silesia, of Württemberg and Teck, Prince of Swabia, Count of Habsburg, Tyrol, Kyburg and Gorizia, Landgrave of Alsace, Marquess of the Holy Roman Empire, Burgovia, the Enns, the Upper and Lower Lusatia, Lord of the Marquisate of Slavonia, of Port Naon and Salines, etc. etc."Coins
Thaler
A thaler (; also taler, from german: Taler) is one of the large silver coins minted in the states and territories of the Holy Roman Empire and the Habsburg monarchy during the Early Modern period. A ''thaler'' size silver coin has a diameter o ...
of Leopold I minted in 1692. Latin inscription: Obverse, LEOPOLDVS D IG ATIARO ANORVMI PERATORS MPERAVGSTVS
STVS (''Surinaamse Televisie Stichting'') is a television network in Suriname and was founded in 1965 by Prime Minister Johan Adolf Pengel. It broadcasts in the Dutch language and it is owned by the government. It is headquartered in Paramaribo, S ...
GER ANIAEHV GARIAEBO EMIAEREX; Reverse, ARCHIDVX AVS RIAEDVX BVR VNDIAEMAR HIOMOR VIAECO ESTYOLIS
OLiS (Oficjalna Lista Sprzedaży; en, Official Sales Chart) is the official chart of the highest selling music albums in Poland. The chart exists since 23 October 2000 and is provided by ZPAV.
This is a chart of best selling music albums in the ...
1692, "Leopold, by the grace of God, Emperor of the Romans, Ever Augustus, King of Germany, Hungary, and Bohemia; Archduke of Austria, Duke of Burgundy, Margrave of Moravia, Count of Tyrol 1692"
File:Coin of Leopold I 3 Kreuzer 1670.jpg, Silver coin of Leopold I, 3 Kreuzer
The Kreuzer (), in English usually kreutzer ( ), was a coin and unit of currency in the southern German states prior to the introduction of the German gold mark in 1871/73, and in Austria and Switzerland. After 1760 it was made of copper. In s ...
, dated 1670. The Latin inscription reads (obverse): ''LEOPOLDVS D IG ATIAR MANORVMI PERATORS MPERA GVSTVSG RMANIAEH NGARIAEB HEMIAEREX'' (reverse):''ARCHID XAVS RIAEDVX B RGVNDIAECO ESTYR LIS1670.'' In English: "Leopold, by the Grace of God, Emperor of the Romans, always August, King of Germany, Hungary, and Bohemia, Archduke of Austria, Duke of Burgundy, Count of Tyrol, 1670."
Ancestors
See also
*Academy of Sciences Leopoldina
The German National Academy of Sciences Leopoldina (german: Deutsche Akademie der Naturforscher Leopoldina – Nationale Akademie der Wissenschaften), short Leopoldina, is the national academy of Germany, and is located in Halle (Saale). Founded ...
* Family tree of the German monarchs
References
Sources
* * Crankshaw, Edward, ''The Habsburgs: Portrait of a Dynasty'' (New York, The Viking Press, 1971). * * * Frey, Linda and Marsha Frey. ''A Question of Empire: Leopold I and the War of Spanish Succession, 1701–1705'' (1983) * Goloubeva, Maria. ''The Glorification of Emperor Leopold I in Image, Spectacle and Text'' (Mainz, 2000) (Veröffentlichungen des Instituts für Europäische Geschichte. Abteilung für Universalgeschichte, 184). * * *External links
*Regnal titles
{{Authority control 1640 births 1705 deaths 17th-century Holy Roman Emperors 18th-century Holy Roman Emperors 17th-century archdukes of Austria 18th-century archdukes of Austria German monarchs Burials at the Imperial Crypt Burials at St. Stephen's Cathedral, Vienna Austrian Baroque composers Male classical composers Musicians from Vienna Dukes of Teschen Grand Masters of the Order of the Golden Fleece Knights of the Golden Fleece Leopoldstadt People of the Great Turkish War 17th-century classical composers Dukes of Carniola Sons of emperors Austrian patrons of music Children of Ferdinand III, Holy Roman Emperor