Emperor Kōmei on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
was the 121st
Emperor of Japan
The Emperor of Japan is the monarch and the head of the Imperial Family of Japan. Under the Constitution of Japan, he is defined as the symbol of the Japanese state and the unity of the Japanese people, and his position is derived from "the ...
, according to the traditional order of succession
An order of succession or right of succession is the line of individuals necessitated to hold a high office when it becomes vacated such as head of state or an honour such as a title of nobility.
孝明天皇 (121)
/ref> Kōmei's reign spanned the years from 1846 through 1867, corresponding to the final years of the
''Japans Kaiserhof in der Edo-Zeit'', p. 186.
/ref> During his reign there was much internal turmoil as a result of
 Before Kōmei's accession to the Chrysanthemum Throne, his personal name ('' imina'') was and his title was . Osahito was born on 22 July 1831 and was the fourth son of Emperor Ninkō and his consort Ōgimachi Naoko (正親町雅子). Osahito's Imperial Family lived with him in the Dairi of the
Before Kōmei's accession to the Chrysanthemum Throne, his personal name ('' imina'') was and his title was . Osahito was born on 22 July 1831 and was the fourth son of Emperor Ninkō and his consort Ōgimachi Naoko (正親町雅子). Osahito's Imperial Family lived with him in the Dairi of the
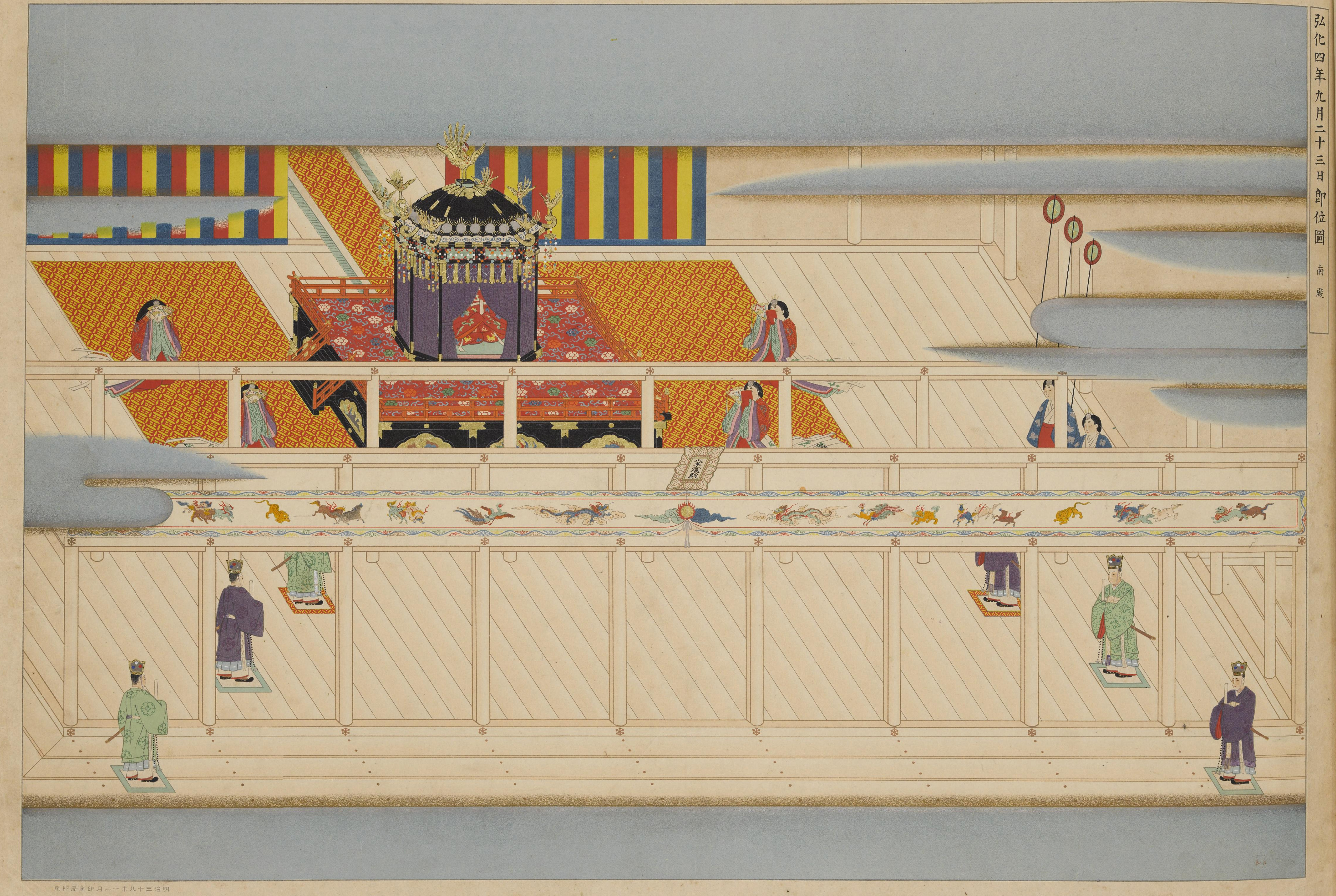 Prince Osahito was enthroned as Emperor on 10 March 1846 upon the death of his father. The succession was considered to have been received by the new monarch; and shortly thereafter, Emperor Kōmei is said to have acceded the throne. The years of Kōmei's reign correspond with a period in which Tokugawa Ieyoshi, Tokugawa Iesada,
Prince Osahito was enthroned as Emperor on 10 March 1846 upon the death of his father. The succession was considered to have been received by the new monarch; and shortly thereafter, Emperor Kōmei is said to have acceded the throne. The years of Kōmei's reign correspond with a period in which Tokugawa Ieyoshi, Tokugawa Iesada,

he Emperor Kōmei's/nowiki> disappearance from the political scene, leaving as his successor a boy of fifteen or sixteen ctually fourteen/nowiki>, was most opportune". However, there is no evidence of this and it is generally believed that he was simply one more victim of what was a worldwide pandemic at the time. Nevertheless, by the time of Emperor Kōmei's death the government was faced with bankruptcy and near collapse. Japan was also surrounded by colonial powers, who stood poised to gain considerable influence with substantial investments in Japanese trade. Kōmei's son, Imperial Prince Mutsuhito, was crowned as
 Emperor Kōmei was the last Japanese Emperor who had more than one era name (''nengō'') during a single ruling term. Beginning with his successor,
Emperor Kōmei was the last Japanese Emperor who had more than one era name (''nengō'') during a single ruling term. Beginning with his successor,
''Emperor of Japan: Meiji and His World, 1852–1912'', p. 531
''A History of Japan, 1582–1941: Internal and External Worlds.''
Cambridge:
OCLC 50694793
* Jansen, Marius B. (2002)
''The Making of Modern Japan.''
Cambridge:
OCLC 52086912
* Keene, Donald. (2002)
''Emperor of Japan: Meiji and His World, 1852–1912.''
New York:
OCLC 46731178
* Meyer, Eva-Maria. (1999)
''Japans Kaiserhof in der Edo-Zeit: unter besonderer Berücksichtigung der Jahre 1846 bis 1867.''
Münster: LIT Verlag.
OCLC 42041594
* Nussbaum, Louis Frédéric and Käthe Roth. (2005). ''Japan Encyclopedia.'' Cambridge:
OCLC 48943301
* Ponsonby-Fane, Richard Arthur Brabazon. (1959)
''The Imperial House of Japan.''
Kyoto: Ponsonby Memorial Society
OCLC 194887
* __________. (1956)
''Kyoto: the Old Capital, 794–1869.''
Kyoto: Ponsonby Memorial Society
OCLC 36644
Imperial Household Agency
The (IHA) is an agency of the government of Japan in charge of state matters concerning the Imperial Family, and also the keeping of the Privy Seal and State Seal of Japan. From around the 8th century AD, up until the Second World War, it ...
(''Kunaichō'')孝明天皇 (121)
/ref> Kōmei's reign spanned the years from 1846 through 1867, corresponding to the final years of the
Edo period
The or is the period between 1603 and 1867 in the history of Japan, when Japan was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and the country's 300 regional '' daimyo''. Emerging from the chaos of the Sengoku period, the Edo period was character ...
.Meyer, Eva-Maria. (1999)''Japans Kaiserhof in der Edo-Zeit'', p. 186.
/ref> During his reign there was much internal turmoil as a result of
Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the n ...
's first major contact with the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
, which occurred under Commodore Perry in 1853 and 1854, and the subsequent forced re-opening of Japan to western nations, ending a 220-year period of national seclusion. Emperor Kōmei did not care much for anything foreign, and he opposed opening Japan to Western powers. His reign would continue to be dominated by insurrection and partisan conflicts eventually culminating in the collapse
Collapse or its variants may refer to:
Concepts
* Collapse (structural)
* Collapse (topology), a mathematical concept
* Collapsing manifold
* Collapse, the action of collapsing or telescoping objects
* Collapsing user interface elements
** ...
of the Tokugawa shogunate
The Tokugawa shogunate (, Japanese 徳川幕府 ''Tokugawa bakufu''), also known as the , was the military government of Japan during the Edo period from 1603 to 1868. Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005)"''Tokugawa-jidai''"in ''Japan Encyclopedia ...
shortly after his death and the Meiji Restoration
The , referred to at the time as the , and also known as the Meiji Renovation, Revolution, Regeneration, Reform, or Renewal, was a political event that restored practical imperial rule to Japan in 1868 under Emperor Meiji. Although there were ...
in the beginning of the reign
A reign is the period of a person's or dynasty's occupation of the office of monarch of a nation (e.g., Saudi Arabia, Belgium, Andorra), of a people (e.g., the Franks, the Zulus) or of a spiritual community (e.g., Catholicism, Tibetan Buddhism ...
of his son and successor Emperor Meiji
, also called or , was the 122nd emperor of Japan according to the traditional order of succession. Reigning from 13 February 1867 to his death, he was the first monarch of the Empire of Japan and presided over the Meiji era. He was the figur ...
.
Early life
 Before Kōmei's accession to the Chrysanthemum Throne, his personal name ('' imina'') was and his title was . Osahito was born on 22 July 1831 and was the fourth son of Emperor Ninkō and his consort Ōgimachi Naoko (正親町雅子). Osahito's Imperial Family lived with him in the Dairi of the
Before Kōmei's accession to the Chrysanthemum Throne, his personal name ('' imina'') was and his title was . Osahito was born on 22 July 1831 and was the fourth son of Emperor Ninkō and his consort Ōgimachi Naoko (正親町雅子). Osahito's Imperial Family lived with him in the Dairi of the Heian Palace
The was the original imperial palace of (present-day Kyoto), the capital of Japan, from 794 to 1227. The palace, which served as the imperial residence and the administrative centre for most of the Heian period (from 794 to 1185), was located ...
.
Reign
 Prince Osahito was enthroned as Emperor on 10 March 1846 upon the death of his father. The succession was considered to have been received by the new monarch; and shortly thereafter, Emperor Kōmei is said to have acceded the throne. The years of Kōmei's reign correspond with a period in which Tokugawa Ieyoshi, Tokugawa Iesada,
Prince Osahito was enthroned as Emperor on 10 March 1846 upon the death of his father. The succession was considered to have been received by the new monarch; and shortly thereafter, Emperor Kōmei is said to have acceded the throne. The years of Kōmei's reign correspond with a period in which Tokugawa Ieyoshi, Tokugawa Iesada, Tokugawa Iemochi
(July 17, 1846 – August 29, 1866) was the 14th ''shōgun'' of the Tokugawa shogunate of Japan, who held office from 1858 to 1866.
During his reign there was much internal turmoil as a result of the "re-opening" of Japan to western nations. ...
, and Tokugawa Yoshinobu
Prince was the 15th and last ''shōgun'' of the Tokugawa shogunate of Japan. He was part of a movement which aimed to reform the aging shogunate, but was ultimately unsuccessful. He resigned of his position as shogun in late 1867, while aiming ...
were leaders at the pinnacle of the Tokugawa shogunate
The Tokugawa shogunate (, Japanese 徳川幕府 ''Tokugawa bakufu''), also known as the , was the military government of Japan during the Edo period from 1603 to 1868. Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005)"''Tokugawa-jidai''"in ''Japan Encyclopedia ...
. On 8 July 1853 US Commodore Matthew Perry
Matthew Langford Perry (born August 19, 1969) is an American-Canadian actor. He is best known for his role as Chandler Bing on the NBC television sitcom ''Friends'' (1994–2004).
As well as starring in the short-lived television series '' St ...
arrived with his "Black Ships
The Black Ships (in ja, 黒船, translit=kurofune, Edo period term) was the name given to Western vessels arriving in Japan in the 16th and 19th centuries.
In 1543 Portuguese initiated the first contacts, establishing a trade route linking ...
" to force trade with Japan. The Tokugawa shogunate, which had controlled military and civil affairs in Japan's feudal provinces for some three centuries, proved unable to meet the new challenge of open trade with the West. At the time, Emperor Kōmei still retained only symbolic power at his court in Kyoto. As the shogunate, divided by internal disputes, gradually surrendered sovereignty to the foreign powers under threat of military force, Emperor Kōmei began to assert himself and regain many of the powers his ancestors had conceded to the Tokugawa clan at the close of the Sengoku ("warring states") period. The Emperor's younger sister, Imperial princess , was married to the Tokugawa ''shōgun
, officially , was the title of the military dictators of Japan during most of the period spanning from 1185 to 1868. Nominally appointed by the Emperor, shoguns were usually the de facto rulers of the country, though during part of the Kamaku ...
'' Tokugawa Iemochi
(July 17, 1846 – August 29, 1866) was the 14th ''shōgun'' of the Tokugawa shogunate of Japan, who held office from 1858 to 1866.
During his reign there was much internal turmoil as a result of the "re-opening" of Japan to western nations. ...
as part of the Movement to Unite Court and Bakufu. Both the Emperor and his sister were against the marriage, even though he realized the gains to be had from such familial connections with the true ruler of Japan. Emperor Kōmei did not care much for anything foreign, and he opposed opening Japan to Western powers, even as the shogun continued to accept foreign demands.
Consultation with the shogunate
On 22 January 1858, ''Daigaku-no-kami
was a Japanese Imperial court position and the title of the chief education expert in the rigid court hierarchy. The Imperial ''Daigaku-no-kami'' predates the Heian period; and the court position continued up through the early Meiji period. The ...
'' Hayashi Akira headed the bakufu delegation which sought advice from Emperor Kōmei in deciding how to deal with newly assertive foreign powers. This would have been the first time the Emperor's counsel was actively sought since the establishment of the Tokugawa shogunate. The most easily identified consequence of this transitional overture would be the increased numbers of messengers streaming back and forth between Edo and Kyoto during the next decade. Concerning these difficult Imperial audiences in Kyoto, there is no small irony in the fact that the shogun and his bakufu were represented by a 19th-century neo-Confucian scholar/bureaucrat who would have been somewhat surprised to find himself at a crucial nexus of managing political change—moving arguably "by the book" through uncharted waters with well-settled theories and history as the only reliable guide. Hayashi Akira was dispatched from Edo to Kyoto in October 1858 to explain the terms of the , also known as the ''Harris Treaty''. Hayashi's twofold task was to both explain the terms to a sceptical Emperor and gain the sovereign's assent to it. Kōmei did ultimately acquiesce in February 1859 when he came to understand that there was no alternative.
The pilgrimage of the 14th shogun Tokugawa Iemochi to Kyoto in 1863 was a defining moment not only in 19th century relations between the military bakufu and the Imperial Court, but also in what history would come to call the Meiji Restoration
The , referred to at the time as the , and also known as the Meiji Renovation, Revolution, Regeneration, Reform, or Renewal, was a political event that restored practical imperial rule to Japan in 1868 under Emperor Meiji. Although there were ...
. The reception by Emperor Kōmei of the shogun in the Kyoto palace can be seen as a moment at which the political realm was thoroughly redefined, becoming a transitional imperial realm. This impression was enforced by the ensuing pilgrimage by Emperor Kōmei to the Kamo shrine, with the shogun in tow. This public demonstration showed that a new order had now emerged in the realm.
After reluctantly accepting the Harris Treaty, Japan quickly signed similar treaties, called the Ansei Treaties
The Ansei Treaties (Japanese:安政条約) or the Ansei Five-Power Treaties (Japanese:安政五カ国条約) are a series of treaties signed in 1858, during the Japanese Ansei era, between Japan on the one side, and the United States, Great Bri ...
(also known as the Ansei Five-Power Treaties, with Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
, Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It ...
, and the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
). The treaties stipulated that the citizens of those foreign nations would be allowed to reside and trade at will in the cities of Edo
Edo ( ja, , , "bay-entrance" or "estuary"), also romanized as Jedo, Yedo or Yeddo, is the former name of Tokyo.
Edo, formerly a ''jōkamachi'' (castle town) centered on Edo Castle located in Musashi Province, became the ''de facto'' capital of ...
, Nagasaki
is the capital and the largest city of Nagasaki Prefecture on the island of Kyushu in Japan.
It became the sole port used for trade with the Portuguese and Dutch during the 16th through 19th centuries. The Hidden Christian Sites in the ...
, Niigata, Kobe
Kobe ( , ; officially , ) is the capital city of Hyōgo Prefecture Japan. With a population around 1.5 million, Kobe is Japan's seventh-largest city and the third-largest port city after Tokyo and Yokohama. It is located in Kansai region, whi ...
and Yokohama
is the second-largest city in Japan by population and the most populous municipality of Japan. It is the capital city and the most populous city in Kanagawa Prefecture, with a 2020 population of 3.8 million. It lies on Tokyo Bay, south of T ...
. Those five cities were to be opened to foreign trade with the four Western nations in the treaties. In addition, the treaties stipulated that a system of extraterritoriality
In international law, extraterritoriality is the state of being exempted from the jurisdiction of local law, usually as the result of diplomatic negotiations.
Historically, this primarily applied to individuals, as jurisdiction was usually cl ...
would provide for the subjugation of foreign residents to the laws of their own consular courts instead of the Japanese legal system.

The "Order to Expel Barbarians"
Emperor Kōmei was infuriated with nearly every development during his reign as Emperor, and during his lifetime he never saw any foreigners nor did he know much about them. Unequal trade treaties with the Western powers, such as the Treaty of Kanagawa and the Harris Treaty were signed without Imperial sanction and in spite of the Emperor's refusal to approve them. He twice expressed his will to resign from his position in protest. During his reign he started to gain more power as theTokugawa shogunate
The Tokugawa shogunate (, Japanese 徳川幕府 ''Tokugawa bakufu''), also known as the , was the military government of Japan during the Edo period from 1603 to 1868. Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005)"''Tokugawa-jidai''"in ''Japan Encyclopedia ...
declined, though this was limited to consultation and other forms of deference according to protocol. Emperor Kōmei generally agreed with anti-Western sentiments, and, breaking with centuries of imperial tradition, began to take an active role in matters of state. As opportunities arose, he fulminated against the treaties and attempted to interfere in the shogunal succession. His efforts culminated in 1863 with his "Order to expel barbarians
The was an edict issued by the Japanese Emperor Kōmei in 1863 against the Westernization of Japan following the opening of the country by Commodore Perry in 1854.
The order
The edict was based on widespread anti-foreign and legitimist sentim ...
". Although the Shogunate had no intention of enforcing the order, it nevertheless inspired attacks against the Shogunate itself and against foreigners in Japan: the most famous incident was the killing of British trader Charles Lennox Richardson
Charles Lennox Richardson (16 April 1834 – 14 September 1862) was a British merchant based in Shanghai who was killed in Japan during the Namamugi Incident. His middle name is spelled ''Lenox'' in census and family documents.
Merchant
Richards ...
, for which the Tokugawa government paid an indemnity of 100,000 pound sterling
Sterling (abbreviation: stg; Other spelling styles, such as STG and Stg, are also seen. ISO code: GBP) is the currency of the United Kingdom and nine of its associated territories. The pound ( sign: £) is the main unit of sterling, and ...
. Other incidents included the bombardments of Shimonoseki and Kagoshima, and the destruction of Japanese warships, coastal guns, and assorted military infrastructure throughout the country. These incidents showed that Japan could not match the military might of the Western powers at the time, and that military confrontation could not prove to be a diplomatic solution.
Illness and death
In January 1867 the Emperor was diagnosed withsmallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by variola virus (often called smallpox virus) which belongs to the genus Orthopoxvirus. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (WHO) c ...
, which caused surprise because Kōmei had allegedly never been ill before. On 30 January 1867 he suffered a fatal violent bout of vomiting and diarrhea, and had purple spots on his face. Emperor Kōmei's death was distinctly convenient for the anti-bakufu forces whom Kōmei had consistently opposed. It was rumored at the time that he was assassinated either by radicals from Choshu, or radical officials in the court. British diplomat Sir Ernest Satow wrote, "it is impossible to deny that Emperor Meiji
, also called or , was the 122nd emperor of Japan according to the traditional order of succession. Reigning from 13 February 1867 to his death, he was the first monarch of the Empire of Japan and presided over the Meiji era. He was the figur ...
on 12 September 1868 and these issues were put to rest under the Meiji Restoration
The , referred to at the time as the , and also known as the Meiji Renovation, Revolution, Regeneration, Reform, or Renewal, was a political event that restored practical imperial rule to Japan in 1868 under Emperor Meiji. Although there were ...
.
After Kōmei's death in 1867, his ''kami'' was enshrined in the Imperial mausoleum, , which is at Sennyū-ji in Higashiyama-ku, Kyoto. Also enshrined in this mausoleum complex are Kōmei's immediate predecessors since Emperor Go-Mizunoo: Meishō, Go-Kōmyō, Go-Sai
, also known as , was the 111th emperor of Japan,Imperial Household Agency (''Kunaichō'') 後西天皇 (111)/ref> according to the traditional order of succession.Ponsonby-Fane, Richard. (1959). ''The Imperial House of Japan'', pp. 116.
Go-Sai' ...
, Reigen, Higashiyama, Nakamikado, Sakuramachi, Momozono, Go-Sakuramachi, Go-Momozono, Kōkaku and Ninkō. Empress Dowager
Empress dowager (also dowager empress or empress mother) () is the English language translation of the title given to the mother or widow of a Chinese, Japanese, Korean, or Vietnamese emperor in the Chinese cultural sphere.
The title was a ...
Eishō is also entombed at this Imperial mausoleum complex.
Emperor Kōmei was the last Emperor to be given a posthumous name
A posthumous name is an honorary name given mostly to the notable dead in East Asian culture. It is predominantly practiced in East Asian countries such as China, Korea, Vietnam, Japan, and Thailand. Reflecting on the person's accomplishm ...
chosen after his death. Beginning with the reign of his son, Emperor Meiji
, also called or , was the 122nd emperor of Japan according to the traditional order of succession. Reigning from 13 February 1867 to his death, he was the first monarch of the Empire of Japan and presided over the Meiji era. He was the figur ...
, posthumous names were chosen in advance, being the same as their reign names.
Kugyō
is a collective term for the very few most powerful men attached to the court of the Emperor of Japan in pre- Meiji eras. Even during those years in which the court's actual influence outside the palace walls was minimal, the hierarchic organization persisted. In general, this elite group included only three to four men at a time. These were hereditary courtiers whose experience and background would have brought them to the pinnacle of a life's career. During Kōmei's reign, this apex of the ''Daijō-kan
The , also known as the Great Council of State, was (i) (''Daijō-kan'') the highest organ of Japan's premodern Imperial government under the Ritsuryō legal system during and after the Nara period or (ii) (''Dajō-kan'') the highest organ of J ...
'' included:
* '' Kampaku'', Takatsukasa Masamichi
was a Japanese court noble of the late Edo period. He held the regent position of kampaku from 1823–1856.
Biography
Masamichi was born the son of regent Takatsukasa Masahiro.
He served as kampaku from 1823–1856. In 1856, at the Ansei P ...
, 1823–1856
* ''Kampaku'', Kujō Hisatada, 1856–1862
* ''Kampaku'', Konoe Tadahiro, 1862–1863
* ''Kampaku'', Takatsukasa Sukehiro
, son of regent Masamichi, was a ''kugyō'' or Japanese court noble of the late Tokugawa shogunate and early Meiji periods. He held a regent position kampaku in 1863. After his biological son Sukemasa died young, he adopted a son of Kujō Hisata ...
, 1863
* ''Kampaku'', Nijō Nariyuki
was a Japanese ''kugyō'' (court noble) of the late Edo period and the early Meiji period. He was the last '' kampaku'' regent in Japanese history and the last ''sesshō'' as a subject. He was the 26th head of the Nijō family.
Life
Nijō Nar ...
, 1863–1866
* ''Sadaijin
The ''Kenkyusha's New Japanese-English Dictionary'', Kenkyusha Limited, was a government position in Japan in the late Nara and Heian periods. The position was consolidated in the Taihō Code of 702.
The Asuka Kiyomihara Code of 689 marks the in ...
''
* '' Udaijin''
* ''Naidaijin
The , literally meaning "Inner Minister", was an ancient office in the Japanese Imperial Court. Its role, rank and authority varied throughout the pre- Meiji period of Japanese history, but in general remained as a significant post under the Ta ...
''
* '' Dainagon''
Eras of Kōmei's reign
Emperor Meiji
, also called or , was the 122nd emperor of Japan according to the traditional order of succession. Reigning from 13 February 1867 to his death, he was the first monarch of the Empire of Japan and presided over the Meiji era. He was the figur ...
, a single era name (identical to the Emperor’s eventual posthumous name
A posthumous name is an honorary name given mostly to the notable dead in East Asian culture. It is predominantly practiced in East Asian countries such as China, Korea, Vietnam, Japan, and Thailand. Reflecting on the person's accomplishm ...
) was selected and did not change until his death. There were seven ''nengō'' during Kōmei's reign.
* '' Kōka'' (1844–1848)
* '' Kaei'' (1848–1854)
* '' Ansei'' (1854–1860)
* '' Man'en'' (1860–1861)
* ''Bunkyū
was a after ''Man'en'' and before '' Genji''. This period spanned the years from March 1861 through March 1864. The reigning emperor was .
Change of era
* March 29, 1861 (''Man'en 2/Bunkyū 1, 19th day of the 2nd month'') : The new era name of ...
'' (1861–1864)
* '' Genji'' (1864–1865)
* '' Keiō'' (1865–1868)
Genealogy
The family included six children, four daughters and two sons; but the futureEmperor Meiji
, also called or , was the 122nd emperor of Japan according to the traditional order of succession. Reigning from 13 February 1867 to his death, he was the first monarch of the Empire of Japan and presided over the Meiji era. He was the figur ...
was the only one to survive to adulthood. The Kōmei principal consort was . After Kōmei's death in 1867, Asako was given the title by Emperor Meiji
, also called or , was the 122nd emperor of Japan according to the traditional order of succession. Reigning from 13 February 1867 to his death, he was the first monarch of the Empire of Japan and presided over the Meiji era. He was the figur ...
.Keene, Donald. (2002)''Emperor of Japan: Meiji and His World, 1852–1912'', p. 531
Spouse
Concubines
Issue
Notes
References
* Cullen, Louis M. (2003)''A History of Japan, 1582–1941: Internal and External Worlds.''
Cambridge:
Cambridge University Press
Cambridge University Press is the university press of the University of Cambridge. Granted letters patent by King Henry VIII in 1534, it is the oldest university press in the world. It is also the King's Printer.
Cambridge University Pr ...
. OCLC 50694793
* Jansen, Marius B. (2002)
''The Making of Modern Japan.''
Cambridge:
Harvard University Press
Harvard University Press (HUP) is a publishing house established on January 13, 1913, as a division of Harvard University, and focused on academic publishing. It is a member of the Association of American University Presses. After the retir ...
. OCLC 52086912
* Keene, Donald. (2002)
''Emperor of Japan: Meiji and His World, 1852–1912.''
New York:
Columbia University Press
Columbia University Press is a university press based in New York City, and affiliated with Columbia University. It is currently directed by Jennifer Crewe (2014–present) and publishes titles in the humanities and sciences, including the fie ...
. OCLC 46731178
* Meyer, Eva-Maria. (1999)
''Japans Kaiserhof in der Edo-Zeit: unter besonderer Berücksichtigung der Jahre 1846 bis 1867.''
Münster: LIT Verlag.
OCLC 42041594
* Nussbaum, Louis Frédéric and Käthe Roth. (2005). ''Japan Encyclopedia.'' Cambridge:
Harvard University Press
Harvard University Press (HUP) is a publishing house established on January 13, 1913, as a division of Harvard University, and focused on academic publishing. It is a member of the Association of American University Presses. After the retir ...
. OCLC 48943301
* Ponsonby-Fane, Richard Arthur Brabazon. (1959)
''The Imperial House of Japan.''
Kyoto: Ponsonby Memorial Society
OCLC 194887
* __________. (1956)
''Kyoto: the Old Capital, 794–1869.''
Kyoto: Ponsonby Memorial Society
OCLC 36644
See also
*Emperor of Japan
The Emperor of Japan is the monarch and the head of the Imperial Family of Japan. Under the Constitution of Japan, he is defined as the symbol of the Japanese state and the unity of the Japanese people, and his position is derived from "the ...
* List of Emperors of Japan
* Imperial cult
* Heian Shrine
* Tsuki no wa no misasagi
{{DEFAULTSORT:Komei, Emperor
Japanese emperors
Komei of Japan, Emperor
Komei of Japan, Emperor
Emperor Komei
Emperor Komei
Emperor Komei
Emperor Komei
Emperor Komei
Deaths from smallpox
Infectious disease deaths in Japan
19th-century Japanese monarchs
Sons of emperors
People from Kyoto