Eliot Ness on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Eliot Ness (April 19, 1903 – May 16, 1957) was an American Prohibition agent known for his efforts to bring down Al Capone and enforce
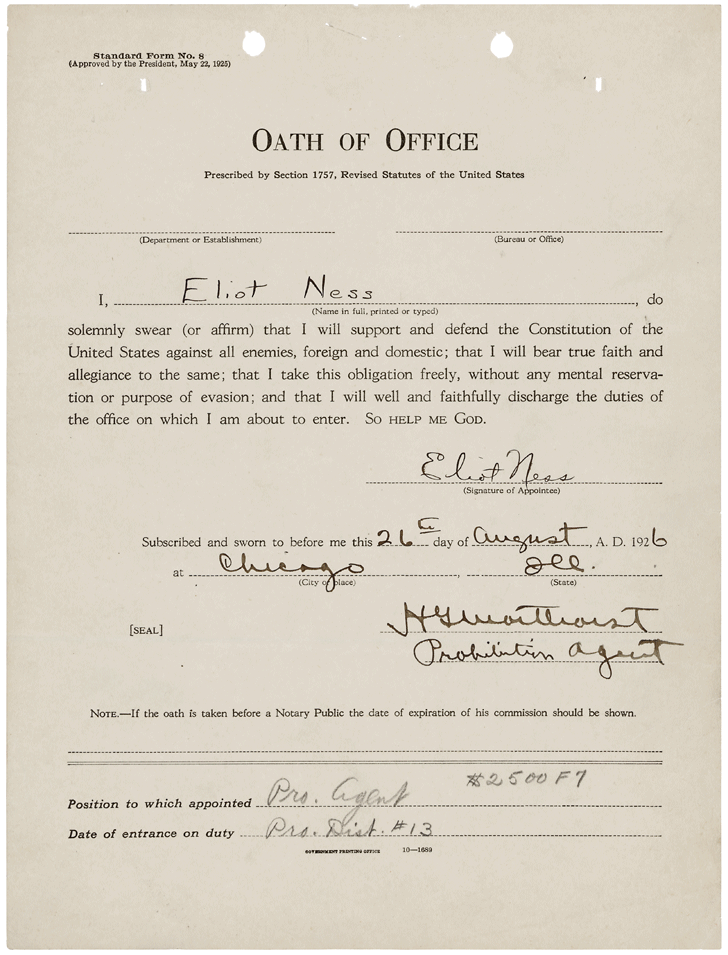 Ness's brother-in-law, Alexander Jamie, an agent of the Bureau of Investigation (which became the
Ness's brother-in-law, Alexander Jamie, an agent of the Bureau of Investigation (which became the  With corruption of Chicago's law enforcement agents endemic, Ness went through the records of all
With corruption of Chicago's law enforcement agents endemic, Ness went through the records of all
 The book was adapted in multiple media and inspired many additional works. The best-known adaptations include the 1959 TV series ''
The book was adapted in multiple media and inspired many additional works. The best-known adaptations include the 1959 TV series ''
 On January 10, 2014, Illinois U.S. Senators
On January 10, 2014, Illinois U.S. Senators  The authors of two separate Ness biographies later disputed the accuracy of Burke's claims, suggesting he mischaracterized Ness's career. "If Hollywood has given Eliot Ness too much credit for getting Capone," Max Allan Collins wrote in an article for ''
The authors of two separate Ness biographies later disputed the accuracy of Burke's claims, suggesting he mischaracterized Ness's career. "If Hollywood has given Eliot Ness too much credit for getting Capone," Max Allan Collins wrote in an article for ''
"Ness, Eliot" ''Encyclopedia Of Cleveland History''
The FBI, Eliot Ness & The Untouchables
(historicalgmen.squarespace.com)
Biography of Eliot Ness
(Free Information Society)
(Pennsylvania Center for the Book)
Eliot Ness FBI file
{{DEFAULTSORT:Ness, Eliot 1903 births 1957 deaths Al Capone American law enforcement officials American people of Norwegian descent Anti-crime activists Burials at Lake View Cemetery, Cleveland Cleveland Division of Police Diebold Illinois Republicans Ohio Republicans People from Chicago People from Cleveland The Untouchables University of Chicago alumni
Prohibition
Prohibition is the act or practice of forbidding something by law; more particularly the term refers to the banning of the manufacture, storage (whether in barrels or in bottles), transportation, sale, possession, and consumption of alcohol ...
in Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name ...
. He was the leader of a team of law enforcement agents, nicknamed The Untouchables
Untouchables or The Untouchables may refer to:
American history
* Untouchables (law enforcement), a 1930s American law enforcement unit led by Eliot Ness
* ''The Untouchables'' (book), an autobiography by Eliot Ness and Oscar Fraley
* ''The U ...
. His co-authorship of an autobiography, ''The Untouchables
Untouchables or The Untouchables may refer to:
American history
* Untouchables (law enforcement), a 1930s American law enforcement unit led by Eliot Ness
* ''The Untouchables'' (book), an autobiography by Eliot Ness and Oscar Fraley
* ''The U ...
'', which was released shortly after his death, launched several television and motion picture portrayals establishing Ness's posthumous fame as an incorruptible crime fighter.
Early life
Eliot Ness was born on April 19, 1903, in the Kensington neighborhood of Chicago, Illinois. He was the youngest of five children born to Peter Ness (1850–1931) and Emma King (1863–1937). His parents, bothNorwegian
Norwegian, Norwayan, or Norsk may refer to:
*Something of, from, or related to Norway, a country in northwestern Europe
* Norwegians, both a nation and an ethnic group native to Norway
* Demographics of Norway
*The Norwegian language, including ...
immigrants, operated a bakery. Ness attended Christian Fenger High School in Chicago. He was educated at the University of Chicago
The University of Chicago (UChicago, Chicago, U of C, or UChi) is a private university, private research university in Chicago, Illinois. Its main campus is located in Chicago's Hyde Park, Chicago, Hyde Park neighborhood. The University of Chic ...
, graduating in 1925 with a degree in political science
Political science is the scientific study of politics. It is a social science dealing with systems of governance and power, and the analysis of political activities, political thought, political behavior, and associated constitutions and la ...
and business administration, and was a member of Sigma Alpha Epsilon
Sigma Alpha Epsilon (), commonly known as SAE, is a North American Greek-letter social college fraternity. It was founded at the University of Alabama on March 9, 1856. Of all existing national social fraternities today, Sigma Alpha Epsilon is t ...
. He began his career as an investigator for the Retail Credit Company of Atlanta
Atlanta ( ) is the capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Georgia. It is the seat of Fulton County, the most populous county in Georgia, but its territory falls in both Fulton and DeKalb counties. With a population of 498,715 ...
assigned to the Chicago territory, where he conducted background investigations for the purpose of credit information. In 1929, he returned to the university to take a graduate course in criminology taught by August Vollmer
August "Gus" Vollmer (March 7, 1876 – November 4, 1955) was the first police chief of Berkeley, California, and a leading figure in the development of the field of criminal justice in the United States in the early 20th century. He has been de ...
, a noted police reformer and chief of the Berkeley Police Department. Vollmer's ideas about professionalizing law enforcement would influence Ness throughout his career.
Career
1926–1931
 Ness's brother-in-law, Alexander Jamie, an agent of the Bureau of Investigation (which became the
Ness's brother-in-law, Alexander Jamie, an agent of the Bureau of Investigation (which became the Federal Bureau of Investigation
The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) is the domestic intelligence and security service of the United States and its principal federal law enforcement agency. Operating under the jurisdiction of the United States Department of Justice, ...
in 1935), influenced Ness to enter law enforcement. Ness joined the U.S. Treasury Department
The Department of the Treasury (USDT) is the national treasury and finance department of the federal government of the United States, where it serves as an executive department. The department oversees the Bureau of Engraving and Printing and ...
in 1926, working with the 1,000-strong Bureau of Prohibition in Chicago.
In March 1930, attorney Frank J. Loesch
Frank Joseph Loesch (April 9, 1852 – July 31, 1944) was a prominent Chicago attorney, reformer and a founder of the Chicago Crime Commission, which attempted to combat widespread corruption and organized crime related violence.
Biography
Loesch ...
of the Chicago Crime Commission asked President
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
* President (education), a leader of a college or university
* President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Automobiles
* Nissan President, a 1966–2010 Japanese ...
Herbert Hoover
Herbert Clark Hoover (August 10, 1874 – October 20, 1964) was an American politician who served as the 31st president of the United States from 1929 to 1933 and a member of the Republican Party, holding office during the onset of the Gr ...
to take down Al Capone. Agents of the Bureau of Internal Revenue, working under Elmer Irey and Special Agent Frank J. Wilson of the Intelligence Unit, were already investigating Capone and his associates for income tax
An income tax is a tax imposed on individuals or entities (taxpayers) in respect of the income or profits earned by them (commonly called taxable income). Income tax generally is computed as the product of a tax rate times the taxable income. Tax ...
evasion. In late 1930, Attorney General William D. Mitchell, seeking a faster end to the case, implemented a plan devised by President Hoover for sending a small team of Prohibition agents, working under a special United States attorney
United States attorneys are officials of the U.S. Department of Justice who serve as the chief federal law enforcement officers in each of the 94 U.S. federal judicial districts. Each U.S. attorney serves as the United States' chief federal ...
, to target the illegal breweries and supply routes of Capone while gathering evidence of conspiracy to violate the National Prohibition Act (informally known as the Volstead Act
The National Prohibition Act, known informally as the Volstead Act, was an act of the 66th United States Congress, designed to carry out the intent of the 18th Amendment (ratified January 1919), which established the prohibition of alcoholic d ...
). U.S. attorney George E.Q. Johnson
George E. Q. Johnson (July 11, 1874 – September 19, 1949) was a United States Attorney in Chicago, Illinois who won tax evasion convictions of Al Capone and several of his associates. He briefly served as a United States district judge of the ...
, the Chicago prosecutor directly in charge of both the Prohibition
Prohibition is the act or practice of forbidding something by law; more particularly the term refers to the banning of the manufacture, storage (whether in barrels or in bottles), transportation, sale, possession, and consumption of alcohol ...
and income tax investigations of Capone, chose the 27-year-old Ness (now assigned to the Justice Department) to lead this small squad.
 With corruption of Chicago's law enforcement agents endemic, Ness went through the records of all
With corruption of Chicago's law enforcement agents endemic, Ness went through the records of all Prohibition
Prohibition is the act or practice of forbidding something by law; more particularly the term refers to the banning of the manufacture, storage (whether in barrels or in bottles), transportation, sale, possession, and consumption of alcohol ...
agents to create a reliable team (initially of six, eventually growing to about ten) later known as "The Untouchables
Untouchables or The Untouchables may refer to:
American history
* Untouchables (law enforcement), a 1930s American law enforcement unit led by Eliot Ness
* ''The Untouchables'' (book), an autobiography by Eliot Ness and Oscar Fraley
* ''The U ...
." Raids against illegal stills and breweries began in March 1931. Within six months, Ness's agents had destroyed bootlegging operations worth an estimated $500,000 and representing an additional $2 million in lost income for Capone; their raids would ultimately cost Capone in excess of $9 million in lost revenue. The main source of information for the raids was an extensive wiretapping
Telephone tapping (also wire tapping or wiretapping in American English) is the monitoring of telephone and Internet-based conversations by a third party, often by covert means. The wire tap received its name because, historically, the monitorin ...
operation.
In 1931, a member of Al Capone's gang promised Ness that two $1,000 notes ($36,684.47 in 2022) would be on his desk every Monday morning if he turned a blind eye to their bootlegging activities. Ness refused the bribe. Failed attempts by members of the Chicago Outfit
The Chicago Outfit (also known as the Outfit, the Chicago Mafia, the Chicago Mob, the Chicago crime family, the South Side Gang or The Organization) is an Italian-American organized crime syndicate or crime family based in Chicago, Illinois, ...
to bribe or intimidate Ness and his agents inspired Charles Schwarz of the ''Chicago Daily News
The ''Chicago Daily News'' was an afternoon daily newspaper in the midwestern United States, published between 1875 and 1978 in Chicago, Illinois.
History
The ''Daily News'' was founded by Melville E. Stone, Percy Meggy, and William Doughert ...
'' to begin calling them "untouchables". George Johnson adopted the nickname and promoted it to the press, establishing it as the squad's unofficial title.
The efforts of Ness and his team inflicted major financial damage on Capone's operations and led to his indictment on 5,000 violations of the Volstead Act in June 1931. Federal judge James H. Wilkerson prevented that indictment from coming to trial, instead pursuing the tax evasion case built by George Johnson and Frank Wilson. On October 17, 1931, Capone was convicted on three of 22 counts of tax evasion. He was sentenced to eleven years in prison and, following a failed appeal, began his sentence in 1932. On May 3, 1932, Ness was among the federal agents who took Capone from the Cook County Jail
The Cook County Jail, located on in South Lawndale, Chicago, Illinois, is operated by the Sheriff of Cook County. A city jail has existed on this site since after the Great Chicago Fire of 1871, but major County prisoners were not generally co ...
to Dearborn Station
Dearborn Station (also referred to as Polk Street Depot) was, beginning in the late 1800s, one of six intercity train stations serving downtown Chicago, Illinois. It remained in operation until May 1, 1971. Built in 1883, it is located at ...
, where he boarded the Dixie Flyer to the Atlanta Federal Penitentiary—the only time the two men are known to have met in person.
1932–1957
In 1932, Ness was promoted to Chief Investigator of the Prohibition Bureau for Chicago. Following the end of Prohibition in 1933, he was assigned as an alcohol tax agent in the "Moonshine Mountains" of southern Ohio, Kentucky, and Tennessee, and in 1934 he was transferred to Cleveland, Ohio. In December 1935, Cleveland mayor Harold H. Burton hired Ness as the city's Safety Director, which put him in charge of both thepolice
The police are a constituted body of persons empowered by a state, with the aim to enforce the law, to ensure the safety, health and possessions of citizens, and to prevent crime and civil disorder. Their lawful powers include arrest and th ...
and fire departments. Ness soon began a reform program inspired by the ideas of August Vollmer, which focused on professionalizing and modernizing the police, stopping juvenile delinquency, and improving traffic safety
Road traffic safety refers to the methods and measures used to prevent road users from being killed or seriously injured. Typical road users include pedestrians, cyclists, motorists, vehicle passengers, horse riders, and passengers of on-road ...
. He declared war on the mob, and his primary targets included "Big" Angelo Lonardo, "Little" Angelo Scirrca, Moe Dalitz, John Angerola, George Angersola, and Charles Pollizi.
Ness was also Safety Director at the time of the murders known as the Cleveland Torso Murders, occurring in the Cleveland area from 1935 to 1938; though he had oversight of the police department, he was only peripherally involved in the investigation. Ness interrogated one of the prime suspects of the murders, Dr. Francis E. Sweeney, using a polygraph test
A polygraph, often incorrectly referred to as a lie detector test, is a device or procedure that measures and records several physiological indicators such as blood pressure, pulse, respiration, and skin conductivity while a person is asked an ...
. At one point in time, two bodies of the victims of the serial killer were placed within view of his office window.
In 1938, Ness and his wife Edna divorced. His otherwise successful career in Cleveland withered gradually. He especially fell out of favor after he had the city's large shantytowns evacuated and burned during the Cleveland Torso Murders. Cleveland critics targeted his divorce, his high-profile social drinking, and his conduct in a car accident one night when he was driving drunk. Although there were no victims in the accident, Ness, fearful that he might lose his job, tried to get the accident covered up. Later, his involvement in the accident was revealed by a local newspaper and calls for his resignation increased; however, Burton's successor as mayor, Frank Lausche, kept Ness on.
In 1939, Ness married illustrator Evaline Michelow. In 1942, the Nesses moved to Washington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...
, where he worked for the federal government. He directed the battle against prostitution in communities surrounding military bases, where venereal disease
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs), also referred to as sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) and the older term venereal diseases, are infections that are Transmission (medicine), spread by Human sexual activity, sexual activity, especi ...
was a serious medical issue. Later he made a number of forays into the corporate world, all of which failed owing to his lack of business acumen. In 1944, he left to become chairman of the Diebold Corporation, a security company based in Ohio.
After his second divorce and third marriage, he ran unsuccessfully for Mayor of Cleveland in 1947, after which he left Diebold in 1951. In the aftermath, Ness was forced into taking odd jobs to earn a living, including bookstore clerk and wholesaler of electronics parts and frozen hamburger patties. By 1956, he came to work for a startup company called Guaranty Paper Corporation, which claimed to have a new method of watermarking legal and official documents to prevent counterfeiting. Ness was offered the job because of his expertise in law enforcement and moved from Cleveland to Coudersport, Pennsylvania
Coudersport is a borough in and the county seat of Potter County, Pennsylvania. It is located approximately east by south of Erie on the Allegheny River. The population was 2,371 at the 2020 census.
History
The Coudersport and Port Allegany Ra ...
, where much of the investment capital for the company was located. Now drinking more heavily, Ness spent his free time in a local bar, telling stories of his law enforcement career. Guaranty Paper began to fall apart when it became clear that one of Ness's business partners had misrepresented the nature of their supposedly proprietary watermarking process, leaving Ness in serious financial jeopardy.
In later years, Ness struggled financially; he was nearly penniless at the time of his death, with his role in bringing down Al Capone having been largely forgotten.
Personal life
Ness was married to Edna Stahle (1900–1988) from 1929 to 1938, illustrator Evaline Michelow (1911–1986) from 1939 to 1945, and artist Elisabeth Andersen Seaver (1906–1977) from 1946 until his death in 1957. He also had an adopted son, Robert (1946–1976).Death
Shortly after his approval of the final galleys for ''The Untouchables
Untouchables or The Untouchables may refer to:
American history
* Untouchables (law enforcement), a 1930s American law enforcement unit led by Eliot Ness
* ''The Untouchables'' (book), an autobiography by Eliot Ness and Oscar Fraley
* ''The U ...
'', on whose writing he and Oscar Fraley
Oscar Fraley (August 2, 1914 – January 6, 1994) was an American sports writer and author, perhaps best known, with Eliot Ness, as the co-author of the American memoir ''The Untouchables''.
Early life
Born in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, Fraley ...
had been collaborating as a means, on Ness' part, of earning money in his later years, Ness collapsed and died of a heart attack
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow decreases or stops to the coronary artery of the heart, causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which ma ...
at his home in Coudersport, Pennsylvania
Coudersport is a borough in and the county seat of Potter County, Pennsylvania. It is located approximately east by south of Erie on the Allegheny River. The population was 2,371 at the 2020 census.
History
The Coudersport and Port Allegany Ra ...
, on May 16, 1957. He was 54 years of age. His body was cremated, and his ashes were scattered in one of the small ponds on the grounds of Lake View Cemetery
Lake View Cemetery is a privately owned, nonprofit garden cemetery located in the cities of Cleveland, Cleveland Heights, and East Cleveland in the U.S. state of Ohio. Founded in 1869, the cemetery was favored by wealthy families during the Gil ...
in Cleveland. An admirer later donated a plot near the pond and erected a cenotaph
A cenotaph is an empty tomb or a monument erected in honour of a person or group of people whose remains are elsewhere. It can also be the initial tomb for a person who has since been reinterred elsewhere. Although the vast majority of cenot ...
in his honor there.
Ness was survived by his widow, Elisabeth Andersen Seaver, and adopted son, Robert.
Legacy
Archive
The Western Reserve Historical Society houses additional Ness papers, including a scrapbook (1928–1936), copies of newspaper clippings (1935–1950), a typewritten manuscript detailing Ness's career in Chicago, and miscellaneous papers, including a report on the Fidelity Check Corporation and Guaranty Paper, of which Ness was president.Art, entertainment, and media
Numerous media works have been developed based on Eliot Ness's life and the legend surrounding his work in Chicago. The first of these resulted in Ness's last years in collaboration withOscar Fraley
Oscar Fraley (August 2, 1914 – January 6, 1994) was an American sports writer and author, perhaps best known, with Eliot Ness, as the co-author of the American memoir ''The Untouchables''.
Early life
Born in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, Fraley ...
in writing the book ''The Untouchables
Untouchables or The Untouchables may refer to:
American history
* Untouchables (law enforcement), a 1930s American law enforcement unit led by Eliot Ness
* ''The Untouchables'' (book), an autobiography by Eliot Ness and Oscar Fraley
* ''The U ...
'' (1957), which was published after Ness's death and went on to sell 1.5 million copies. Although the historical veracity of this book has been questioned, later research suggests that it is broadly accurate. A 21-page manuscript that Ness wrote for the book is housed in the archives of the Western Reserve Historical Society in Cleveland, Ohio.
The Untouchables
Untouchables or The Untouchables may refer to:
American history
* Untouchables (law enforcement), a 1930s American law enforcement unit led by Eliot Ness
* ''The Untouchables'' (book), an autobiography by Eliot Ness and Oscar Fraley
* ''The U ...
'', which starred Robert Stack
Robert Stack (born Charles Langford Modini Stack; January 13, 1919 – May 14, 2003) was an American actor. Known for his deep voice and commanding presence, he appeared in over forty feature films. He starred in the highly successful ABC tele ...
as Ness and was narrated by Walter Winchell
Walter Winchell (April 7, 1897 – February 20, 1972) was a syndicated American newspaper gossip columnist and radio news commentator. Originally a vaudeville performer, Winchell began his newspaper career as a Broadway reporter, critic and co ...
, and the 1987 film ''The Untouchables
Untouchables or The Untouchables may refer to:
American history
* Untouchables (law enforcement), a 1930s American law enforcement unit led by Eliot Ness
* ''The Untouchables'' (book), an autobiography by Eliot Ness and Oscar Fraley
* ''The U ...
'', directed by Brian De Palma
Brian Russell De Palma (born September 11, 1940) is an American film director and screenwriter. With a career spanning over 50 years, he is best known for his work in the suspense, crime and psychological thriller genres. De Palma was a leading ...
, which starred Kevin Costner
Kevin Michael Costner (born January 18, 1955) is an American actor, producer, film director and musician. He has received various accolades, including two Academy Awards, two Golden Globe Awards, a Primetime Emmy Award, and two Screen Actor ...
as Ness and featured Sean Connery and Robert De Niro as Al Capone. These two fictionalized portrayals, more than actual history, have inspired numerous novels; a TV-movie
A television film, alternatively known as a television movie, made-for-TV film/movie or TV film/movie, is a feature-length film that is produced and originally distributed by or to a television network, in contrast to theatrical films made for ...
, ''The Return of Eliot Ness'', in which Stack returned to the role; a second, short-lived 1993 TV series titled ''The Untouchables
Untouchables or The Untouchables may refer to:
American history
* Untouchables (law enforcement), a 1930s American law enforcement unit led by Eliot Ness
* ''The Untouchables'' (book), an autobiography by Eliot Ness and Oscar Fraley
* ''The U ...
'', which starred Tom Amandes
Tom Amandes (born March 9, 1959) is an American actor. His best-known role to date is that of Eliot Ness in the 1990s television series ''The Untouchables''; he also played Geena Davis' boyfriend in '' The Long Kiss Goodnight'', and Abraham Lin ...
as Ness and William Forsythe as Capone; stage plays such as Peter Ullian's ''In the Shadow of the Terminal Tower''; and comic books such as ''Torso
The torso or trunk is an anatomical term for the central part, or the core, of the body of many animals (including humans), from which the head, neck, limbs, tail and other appendages extend. The tetrapod torso — including that of a huma ...
''. Ness was portrayed by actor Jim True-Frost
Jim True-Frost (''né'' True; July 31, 1966) is an American stage, television and screen actor. He is most known for his portrayal of Roland "Prez" Pryzbylewski on all five seasons of the HBO program ''The Wire'', as James Woodrow in '' Tre ...
in the fifth-season episode "The Good Listener" of the HBO television series '' Boardwalk Empire''.
Max Allan Collins
Max Allan Collins (born March 3, 1948) is an American mystery writer, noted for his graphic novels. His work has been published in several formats and his '' Road to Perdition'' series was the basis for a film of the same name. He wrote the ''Di ...
used Ness as the "police contact/best friend" character in his series of historical private eye novels featuring Chicago detective Nate Heller. Later he spun Ness off into his own series, set during his tenure as Cleveland's Public Safety Director. The first book, ''The Dark City'' (1987), depicted Ness's getting hired and undertaking a cleanup of the graft-ridden police force; the second, ''Butcher's Dozen'' (1988), his pursuit of the serial killer known as the Mad Butcher of Kingsbury Run
The Cleveland Torso Murderer, also known as the Mad Butcher of Kingsbury Run, was an unidentified serial killer who was active in Cleveland, Ohio, United States, in the 1930s. The killings were characterized by the dismemberment of twelve know ...
. ''Bullet Proof'' (1989) pitted Ness against labor racketeers intent on taking over Cleveland's food service industry. Ness is mentioned in many hip hop and rap tracks ("California Love
"California Love" is a song by American rapper 2Pac featuring fellow American rapper-producer Dr. Dre and American singer Roger Troutman. The song was released as 2Pac's comeback single after his release from prison in 1995 and was his first sing ...
", for example). ''Murder by the Numbers'' (1993) depicted Ness's investigation of the numbers racket in Cleveland. All of these novels, while fictionalized, were closely based on actual cases investigated by Ness and the Cleveland Police. Collins also wrote a one-man stage play, ''Eliot Ness – An Untouchable Life'', which was nominated for an Edgar Award. Collins wrote Ness into his graphic novel ''Road to Perdition
''Road to Perdition'' is a 2002 American crime drama film directed by Sam Mendes. The screenplay was adapted by David Self from the graphic novel of the same name written by Max Allan Collins and illustrated by Richard Piers Rayner. The film ...
''.
In 2018, Collins collaborated with historian A. Brad Schwartz
A is the first letter of the Latin and English alphabet.
A may also refer to:
Science and technology Quantities and units
* ''a'', a measure for the attraction between particles in the Van der Waals equation
* ''A'' value, a measure of ...
on a nonfiction dual biography of Ness and Capone entitled ''Scarface and the Untouchable: Al Capone, Eliot Ness, and the Battle for Chicago.'' Collins and Schwartz are currently writing a second volume about Ness's years in Cleveland, entitled ''The Untouchable and the Butcher.''
Beer
Cleveland-based Great Lakes Brewing Company, which claims several connections to Ness (including the brewery owners' mother having worked as his stenographer), named an amber lager "Eliot Ness" and included several subtle nods to his career in the beer description and label art.Proposed building naming
 On January 10, 2014, Illinois U.S. Senators
On January 10, 2014, Illinois U.S. Senators Dick Durbin
Richard Joseph Durbin (born November 21, 1944) is an American lawyer and politician serving as the senior United States senator from Illinois, a seat he has held since 1997. A member of the Democratic Party, Durbin has served as the Senate De ...
and Mark Kirk
Mark Steven Kirk (born September 15, 1959) is a retired American politician and attorney who served as a United States senator from Illinois from 2010 to 2017, and as the United States representative for Illinois's 10th congressional district fr ...
and Ohio Senator Sherrod Brown
Sherrod Campbell Brown (; born November 9, 1952) is an American politician serving as the senior United States senator from Ohio, a seat which he has held since 2007. A member of the Democratic Party, he was the U.S. representative for Ohio's ...
proposed naming the headquarters of the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives in Washington, D.C., after Ness. If approved, it would have been called the Eliot Ness ATF Building. Brown said in a statement: "Eliot Ness is perhaps best known as the man who helped to bring Al Capone to justice. But Eliot Ness was more than just a Chicago U.S. prohibition agent. He fought for law and justice in Ohio, and fought for peace and freedom in World War II. He was a public servant and an American hero who deserves to be remembered."
Chicago Aldermen Edward M. Burke (14th Ward) and James Balcer (11th Ward) introduced a resolution in the Chicago City Council to oppose the renaming. In a news release, Burke said: "Eliot Ness had a checkered career after leaving the federal government. I simply do not think his image matches the actual reality of his legacy."
 The authors of two separate Ness biographies later disputed the accuracy of Burke's claims, suggesting he mischaracterized Ness's career. "If Hollywood has given Eliot Ness too much credit for getting Capone," Max Allan Collins wrote in an article for ''
The authors of two separate Ness biographies later disputed the accuracy of Burke's claims, suggesting he mischaracterized Ness's career. "If Hollywood has given Eliot Ness too much credit for getting Capone," Max Allan Collins wrote in an article for ''HuffPost
''HuffPost'' (formerly ''The Huffington Post'' until 2017 and sometimes abbreviated ''HuffPo'') is an American progressive news website, with localized and international editions. The site offers news, satire, blogs, and original content, and ...
'', "he has received too little credit anywhere else for helping professionalize law enforcement in the mid-20th Century."
Although the Senate resolution was never adopted, the main atrium in the ATF headquarters building was later renamed for Eliot Ness and features a historical exhibit about the Untouchables.
Festival and museum
Coudersport, Pennsylvania
Coudersport is a borough in and the county seat of Potter County, Pennsylvania. It is located approximately east by south of Erie on the Allegheny River. The population was 2,371 at the 2020 census.
History
The Coudersport and Port Allegany Ra ...
, the town where Ness spent his final months and died, has held an annual "Eliot Ness Festival" every third weekend in July since 2018. Past events have included a public reunion of people descended from the original Untouchables, a dramatization of Al Capone's trial, film screenings, author talks, and antique car shows.
In 2019, an "Eliot Ness Museum" inspired by the annual festival opened in downtown Coudersport, featuring several antique cars and exhibits describing Ness's life and career.
References
Further reading
* * * * * *"Ness, Eliot" ''Encyclopedia Of Cleveland History''
External links
The FBI, Eliot Ness & The Untouchables
(historicalgmen.squarespace.com)
Biography of Eliot Ness
(Free Information Society)
(Pennsylvania Center for the Book)
Eliot Ness FBI file
{{DEFAULTSORT:Ness, Eliot 1903 births 1957 deaths Al Capone American law enforcement officials American people of Norwegian descent Anti-crime activists Burials at Lake View Cemetery, Cleveland Cleveland Division of Police Diebold Illinois Republicans Ohio Republicans People from Chicago People from Cleveland The Untouchables University of Chicago alumni