Electronic countermeasures on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 An electronic countermeasure (ECM) is an electrical or electronic device designed to trick or deceive
An electronic countermeasure (ECM) is an electrical or electronic device designed to trick or deceive
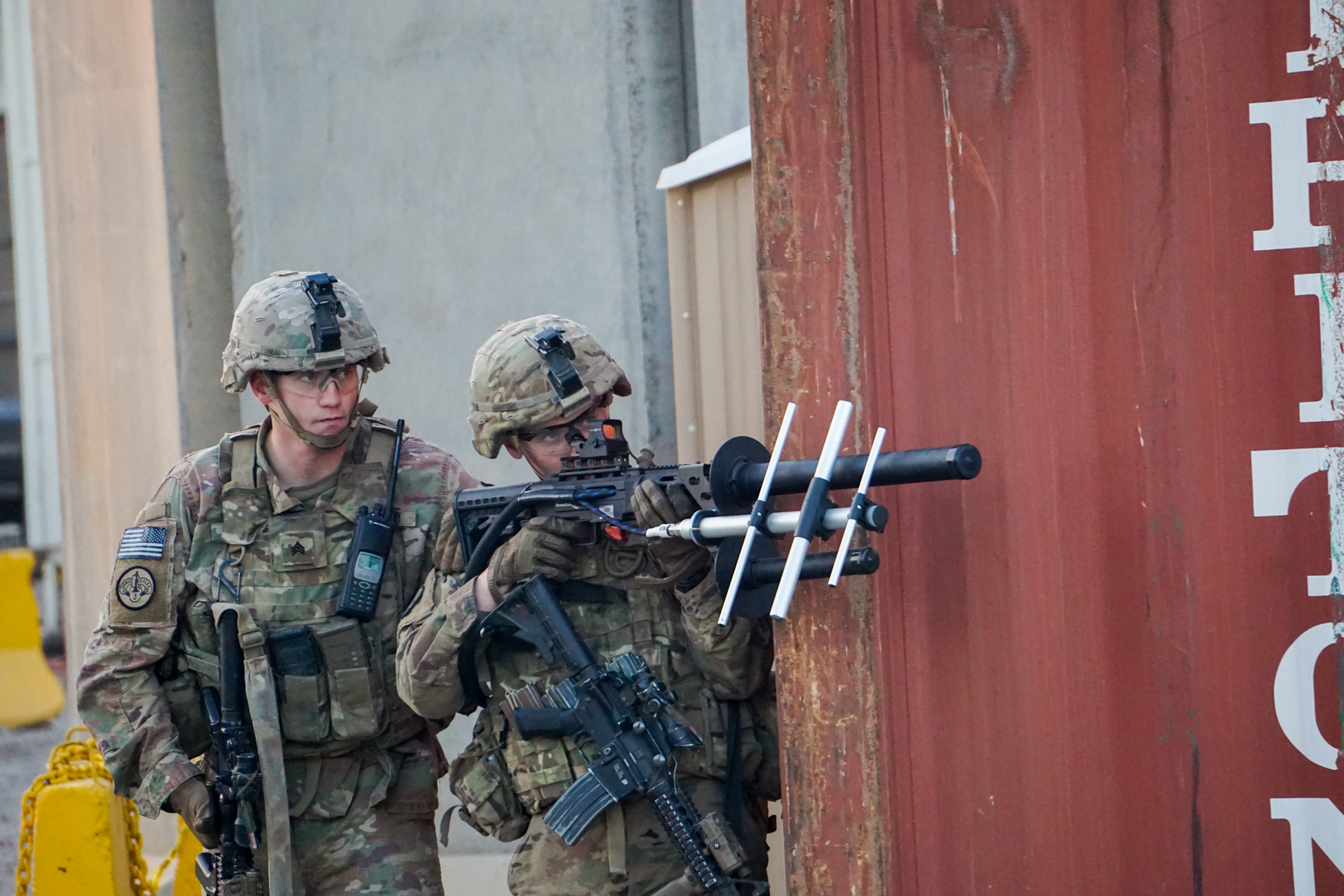 Radio jamming or communications jamming is the deliberate transmission of radio signals that disrupt communications by decreasing the signal-to-noise ratio to the point where the target communications link is either degraded or denied service.
Radio jamming or communications jamming is the deliberate transmission of radio signals that disrupt communications by decreasing the signal-to-noise ratio to the point where the target communications link is either degraded or denied service.
 ECM is practiced by nearly all modern military units—land, sea or air. Aircraft, however, are the primary weapons in the ECM battle because they can "see" a larger patch of earth than a sea or land-based unit. When employed effectively, ECM can keep aircraft from being tracked by search radars, or targeted by surface-to-air missiles or air-to-air missiles. An aircraft ECM can take the form of an attachable underwing pod or could be embedded in the airframe. Fighter planes using a conventional electronically scanned antenna mount dedicated jamming pods instead or, in the case of the US, German, and Italian air forces, may rely on electronic warfare aircraft to carry them. ECM pods vary widely in power and capability; while many fighter aircraft are capable of carrying an ECM pod, these pods are generally less powerful, capable and of shorter range than the equipment carried by dedicated ECM aircraft, thus making them an important part of the inventory.
ECM is practiced by nearly all modern military units—land, sea or air. Aircraft, however, are the primary weapons in the ECM battle because they can "see" a larger patch of earth than a sea or land-based unit. When employed effectively, ECM can keep aircraft from being tracked by search radars, or targeted by surface-to-air missiles or air-to-air missiles. An aircraft ECM can take the form of an attachable underwing pod or could be embedded in the airframe. Fighter planes using a conventional electronically scanned antenna mount dedicated jamming pods instead or, in the case of the US, German, and Italian air forces, may rely on electronic warfare aircraft to carry them. ECM pods vary widely in power and capability; while many fighter aircraft are capable of carrying an ECM pod, these pods are generally less powerful, capable and of shorter range than the equipment carried by dedicated ECM aircraft, thus making them an important part of the inventory.
 Infrared homing systems can be decoyed with flares and other
Infrared homing systems can be decoyed with flares and other
Electronic Counter Measures (PDF)
(Lee Pucker)
A Down of Electronic Counter Measures
in Russian
in Russian {{refend Military communications Weapons countermeasures
 An electronic countermeasure (ECM) is an electrical or electronic device designed to trick or deceive
An electronic countermeasure (ECM) is an electrical or electronic device designed to trick or deceive radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, we ...
, sonar
Sonar (sound navigation and ranging or sonic navigation and ranging) is a technique that uses sound propagation (usually underwater, as in submarine navigation) to navigate, measure distances (ranging), communicate with or detect objects on o ...
, or other detection systems, like infrared (IR) or lasers. It may be used both offensively and defensively to deny targeting information to an enemy. The system may make many separate targets appear to the enemy, or make the real target appear to disappear or move about randomly. It is used effectively to protect aircraft
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to fly by gaining support from the air. It counters the force of gravity by using either static lift or by using the dynamic lift of an airfoil, or in a few cases the downward thrust from jet engine ...
from guided missiles. Most air force
An air force – in the broadest sense – is the national military branch that primarily conducts aerial warfare. More specifically, it is the branch of a nation's armed services that is responsible for aerial warfare as distinct from an ...
s use ECM to protect their aircraft from attack. It has also been deployed by military ships and recently on some advanced tanks to fool laser/IR guided missiles. It is frequently coupled with stealth advances so that the ECM systems have an easier job. Offensive ECM often takes the form of jamming. Self-protecting (defensive) ECM includes using blip enhancement and jamming of missile terminal homers.
History
The first example of electronic countermeasures being applied in a combat situation took place during theRusso-Japanese war
The Russo-Japanese War ( ja, 日露戦争, Nichiro sensō, Japanese-Russian War; russian: Ру́сско-япóнская войнá, Rússko-yapónskaya voyná) was fought between the Empire of Japan and the Russian Empire during 1904 and 1 ...
. On July 13, 1904, Russian wireless telegraphy
Wireless telegraphy or radiotelegraphy is transmission of text messages by radio waves, analogous to electrical telegraphy using cables. Before about 1910, the term ''wireless telegraphy'' was also used for other experimental technologies for ...
stations installed in the Port Arthur fortress and on board Russian light cruisers successfully interrupted wireless communication between a group of Japanese battleships. The spark-gap transmitters in the Russian stations generated senseless noise while the Japanese were making attempts to coordinate their efforts in the bombing of a Russian naval base. Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
and United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
interfered with enemy communications along the western front during World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
while the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against ...
tried to intercept German naval radio transmissions.Polmar (1979), p. 121. There were also efforts at sending false radio signals, having shore stations send transmissions using ships' call signs, and jamming enemy radio signals.
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
ECM expanded to include dropping chaff (originally called Window), jamming and spoofing radar and navigation signals. German bomber aircraft navigated using radio signals transmitted from ground stations, which the British disrupted with spoofed signals in the Battle of the Beams
The Battle of the Beams was a period early in the Second World War when bombers of the German Air Force ('' Luftwaffe'') used a number of increasingly accurate systems of radio navigation for night bombing in the United Kingdom. British scientif ...
. During the RAF's night attacks on Germany the extent of electronic countermeasures was much expanded, and a specialised organisation, No. 100 Group RAF, was formed to counter the increasing German night fighter
A night fighter (also known as all-weather fighter or all-weather interceptor for a period of time after the Second World War) is a fighter aircraft adapted for use at night or in other times of bad visibility. Night fighters began to be used i ...
force and radar defences. Cold War developments included anti-radiation missile
An anti-radiation missile (ARM) is a missile designed to detect and home in on an enemy radio emission source. Typically, these are designed for use against an enemy radar, although jammers and even radios used for communications can also be ...
s designed to home in on enemy radar transmitters.
In the 2007 Operation Orchard Israeli attack on a suspected Syrian nuclear weapons site, the Israel Air Force used electronic warfare to take control of Syrian airspace prior to the attack. Israeli electronic warfare (EW) systems took over Syria's air defense systems, feeding them a false sky-picture while Israel Air Force jets crossed much of Syria, bombed their targets and returned.
Radar ECM
Basic radar ECM strategies are (1) radar interference, (2) target modifications, and (3) changing the electrical properties of air. Interference techniques include jamming and deception. Jamming is accomplished by a friendly platform transmitting signals on the radar frequency to produce a noise level sufficient to hide echos. The jammer's continuous transmissions will provide a clear direction to the enemy radar, but no range information. Deception may use a transponder to mimic the radar echo with a delay to indicate incorrect range. Transponders may alternatively increase return echo strength to make a small decoy appear to be a larger target. Target modifications include radar absorbing coatings and modifications of the surface shape to either "stealth" a high-value target or enhance reflections from a decoy. Dispersal of small aluminium strips called chaff is a common method of changing the electromagnetic properties of air to provide confusing radar echos.Communications ECM
 Radio jamming or communications jamming is the deliberate transmission of radio signals that disrupt communications by decreasing the signal-to-noise ratio to the point where the target communications link is either degraded or denied service.
Radio jamming or communications jamming is the deliberate transmission of radio signals that disrupt communications by decreasing the signal-to-noise ratio to the point where the target communications link is either degraded or denied service.
Aircraft ECM
 ECM is practiced by nearly all modern military units—land, sea or air. Aircraft, however, are the primary weapons in the ECM battle because they can "see" a larger patch of earth than a sea or land-based unit. When employed effectively, ECM can keep aircraft from being tracked by search radars, or targeted by surface-to-air missiles or air-to-air missiles. An aircraft ECM can take the form of an attachable underwing pod or could be embedded in the airframe. Fighter planes using a conventional electronically scanned antenna mount dedicated jamming pods instead or, in the case of the US, German, and Italian air forces, may rely on electronic warfare aircraft to carry them. ECM pods vary widely in power and capability; while many fighter aircraft are capable of carrying an ECM pod, these pods are generally less powerful, capable and of shorter range than the equipment carried by dedicated ECM aircraft, thus making them an important part of the inventory.
ECM is practiced by nearly all modern military units—land, sea or air. Aircraft, however, are the primary weapons in the ECM battle because they can "see" a larger patch of earth than a sea or land-based unit. When employed effectively, ECM can keep aircraft from being tracked by search radars, or targeted by surface-to-air missiles or air-to-air missiles. An aircraft ECM can take the form of an attachable underwing pod or could be embedded in the airframe. Fighter planes using a conventional electronically scanned antenna mount dedicated jamming pods instead or, in the case of the US, German, and Italian air forces, may rely on electronic warfare aircraft to carry them. ECM pods vary widely in power and capability; while many fighter aircraft are capable of carrying an ECM pod, these pods are generally less powerful, capable and of shorter range than the equipment carried by dedicated ECM aircraft, thus making them an important part of the inventory.
Future airborne jammers
The Next Generation Jammer is being developed to replace the current AN/ALQ-99 carried on the E/A-18G electronic warfare plane. Planned for adoption around 2020, it will use a small AESA antenna divided into quadrants for all around coverage and retain the capability of highly directional jamming. DARPA's Precision Electronic Warfare (PREW) project aims to develop a low-cost system capable of synchronizing several simple airborne jamming pods with enough precision to replicate the directionality of an electronically scanned antenna, avoiding collateral jamming of non-targeted receivers. An expendable active decoy that uses DRFM technology to jam RF based threats has already been developed bySelex ES
Selex ES was a subsidiary of Finmeccanica S.p.A., active in the electronics and information technology business, based in Italy and the United Kingdom, UK, and formed in January 2013, following Finmeccanica's decision to combine its existing SE ...
(merged into Leonardo new name of Finmeccanica since 2017). The system, named BriteCloud, is self-contained within a small canister that is similar to a standard flare cartridge. The 55 mm format of the system has undergone flight trials with the Gripen aircraft and the development of a 218 variant is at an advanced stage.
Dedicated ECM aircraft
* EA-3 Skywarrior * EB-66 Destroyer * EC-130H Compass Call * EA-6B Prowler equipped with ALQ-92 communications jammer, ALQ-100 multi-band track breaking system, and five ALQ-99 tactical jammer pods.Polmar (1979), p. 122. *EA-18G Growler
The Boeing EA-18G Growler is an American carrier-based electronic warfare aircraft, a specialized version of the two-seat F/A-18F Super Hornet. The EA-18G replaced the Northrop Grumman EA-6B Prowlers in service with the United States Navy. ...
* EF-111A Raven
* Tornado ECR
* J-16 D
* Su-24MP
* Yak-28PP
* Mi-8PP
* EB-66B Destroyer
Shipboard ECM
The ULQ-6 deception transmitter was one of the earlier shipboard ECM installations. The Raytheon SLQ-32 shipboard ECM package came in three versions providing warning, identification and bearing information about radar-guided cruise missiles. The SLQ-32 V3 included quick reaction electronic countermeasures for cruisers and large amphibious ships and auxiliaries in addition to the RBOC (Rapid Blooming Off-board Chaff) launchers found on most surface ships. The BLR-14 Submarine Acoustic Warfare System (or SAWS) provides an integrated receiver, processor, display, and countermeasures launch system for submarines.Infrared and acoustic analogies
 Infrared homing systems can be decoyed with flares and other
Infrared homing systems can be decoyed with flares and other infrared countermeasure
An infrared countermeasure (IRCM) is a device designed to protect aircraft from infrared homing ("heat seeking") missiles by confusing the missiles' infrared guidance system so that they miss their target (electronic countermeasure). Heat-see ...
s. Acoustic homing and detection systems used for ships are also susceptible to countermeasures. United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
warships use Masker and PRAIRIE (propeller AIR Ingestion and Emission) systems to create small air bubbles around a ship's hull and wake to reduce sound transmission. Surface ships tow noisemakers like the AN/SLQ-25 Nixie
The AN/SLQ-25 Nixie and its variants are towed torpedo decoys used on US and allied warships. It consists of a towed decoy device (TB-14A) and a shipboard signal generator. The decoy emits signals to draw a torpedo away from its intended targe ...
to decoy homing torpedoes. Submarines can deploy similar acoustic device countermeasures (or ADCs) from a 3-inch (75-mm) signal launching tube. United States ballistic missile submarines could deploy the Mark 70 MOSS ( Mobile submarine simulator) decoy from torpedo tubes to simulate a full size submarine. Most navies additionally equip surface ships with decoy launchers.http://www.terma.com/media/118849/skws_022007.pdf
See also
*Electronic warfare
Electronic warfare (EW) is any action involving the use of the electromagnetic spectrum (EM spectrum) or directed energy to control the spectrum, attack an enemy, or impede enemy assaults. The purpose of electronic warfare is to deny the opponen ...
** Electronic warfare support measures
In military telecommunications, electronic support (ES) or electronic support measures (ESM) gather intelligence through passive "listening" to electromagnetic radiations of military interest. They are an aspect of electronic warfare involving ac ...
** Electronic counter-countermeasure
Electronic counter-countermeasures (ECCM) is a part of electronic warfare which includes a variety of practices which attempt to reduce or eliminate the effect of electronic countermeasures (ECM) on electronic sensors aboard vehicles, ships and ai ...
* No. 100 Group RAF
* Starshel rounds
* Krasukha (electronic warfare system)
* Khibiny (electronic countermeasures system)
* Samyukta electronic warfare system
References
Sources
* Polmar, Norman: "The U. S. Navy Electronic Warfare (Part 2)", ''United States Naval Institute Proceedings'', November 1979.Electronic Counter Measures (PDF)
(Lee Pucker)
A Down of Electronic Counter Measures
in Russian
in Russian {{refend Military communications Weapons countermeasures