Eastern South Slavic languages on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
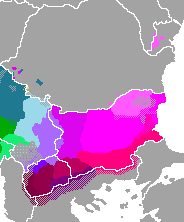


 The Eastern South Slavic dialects form the eastern subgroup of the South Slavic languages. They are spoken mostly in
The Eastern South Slavic dialects form the eastern subgroup of the South Slavic languages. They are spoken mostly in
, UCLA International Institute



 The Eastern South Slavic dialects form the eastern subgroup of the South Slavic languages. They are spoken mostly in
The Eastern South Slavic dialects form the eastern subgroup of the South Slavic languages. They are spoken mostly in Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedo ...
and North Macedonia
North Macedonia, ; sq, Maqedonia e Veriut, (Macedonia before February 2019), officially the Republic of North Macedonia,, is a country in Southeast Europe. It gained independence in 1991 as one of the successor states of Yugoslavia. It ...
, and adjacent areas in the neighbouring countries. They form the so-called Balkan Slavic linguistic area, which encompasses the southeastern part of the dialect continuum
A dialect continuum or dialect chain is a series of language varieties spoken across some geographical area such that neighboring varieties are mutually intelligible, but the differences accumulate over distance so that widely separated varie ...
of South Slavic.
Linguistic features
Languages and dialects
Eastern South Slavic dialects share a number of characteristics that set them apart from the other branch of the South Slavic languages, theWestern South Slavic languages
The South Slavic languages are one of three branches of the Slavic languages. There are approximately 30 million speakers, mainly in the Balkans. These are separated geographically from speakers of the other two Slavic branches ( West and Eas ...
. This area consists of Bulgarian and Macedonian, and according to some authors encompasses the southeastern dialect of Serbian, the so-called Prizren-Timok dialect. The last is part of the broader transitional Torlakian dialectal area. The Balkan Slavic area is also part of the Balkan Sprachbund. The external boundaries of the Balkan Slavic/Eastern South Slavic area can be defined with the help of some linguistic structural features. Among the most important of them are: the loss of the infinitive
Infinitive (abbreviated ) is a linguistics term for certain verb forms existing in many languages, most often used as non-finite verbs. As with many linguistic concepts, there is not a single definition applicable to all languages. The word is deri ...
and case declension, and the use of enclitic definite articles. In the Balkan Slavic languages, clitic doubling also occurs, which is characteristic feature of all the languages of the Balkan Sprachbund. The grammar of Balkan Slavic looks like a hybrid of “Slavic” and “Romance” grammars with some Albanian additions. The Serbo-Croatian vocabulary in both Macedonian and Serbian-Torlakian is very similar, stemming from the border changes of 1878, 1913, and 1918, when these areas came under direct Serbian linguistic influence.
Areal
The external and internal boundaries of the linguistic sub-group between the transitional Torlakian dialect and Serbian and between Macedonian and Bulgarian languages are not clearly defined. For example, standard Serbian, which is based on its Western ( Eastern Herzegovinian dialect), is very different from its Eastern ( Prizren-Timok dialect), especially in its position in the Balkan Sprachbund. During the 19th century, the Balkan Slavic dialects were often described as forming the ''Bulgarian language
Bulgarian (, ; bg, label=none, български, bălgarski, ) is an Eastern South Slavic language spoken in Southeastern Europe, primarily in Bulgaria. It is the language of the Bulgarians.
Along with the closely related Macedonian l ...
''. At the time, the areas east of Niš
Niš (; sr-Cyrl, Ниш, ; names in other languages) is the third largest city in Serbia and the administrative center of the Nišava District. It is located in southern part of Serbia. , the city proper has a population of 183,164, while ...
were considered under direct Bulgarian ethnolinguistic influence and in the middle of the 19th century, that motivated the Serb linguistic reformer Vuk Karadžić
Vuk Stefanović Karadžić ( sr-Cyrl, Вук Стефановић Караџић, ; 6 November 1787 (26 October OS)7 February 1864) was a Serbian philologist, anthropologist and linguist. He was one of the most important reformers of the moder ...
to use the Eastern Herzegovina dialects for his standardisation of Serbian. Bulgarian was standardized afterwards, at the end of the 19th century on the basis of its eastern Central Balkan dialect
The Central Balkan dialect is a Bulgarian dialect that is part of the Balkan group of the Eastern Bulgarian dialects. Its range includes most of north-central Bulgaria (without the regions of Dryanovo and Elena), as well as the regions of Karl ...
, while Macedonian was standardized in the middle of the 20th century using its west-central Prilep-Bitola dialect
The Prilep-Bitola dialect ( mk, Прилепско-битолски дијалект, ''Prilepsko-bitolski dijalekt'') is a member of the central subgroup of the western group of dialects of Macedonian. This dialect is spoken in much of the Pel ...
. Although some researchers still describe the standard Macedonian and Bulgarian languages as varieties
Variety may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Entertainment formats
* Variety (radio)
* Variety show, in theater and television
Films
* ''Variety'' (1925 film), a German silent film directed by Ewald Andre Dupont
* ''Variety'' (1935 film), ...
of a pluricentric language, they have very different and remote dialectal bases. Jouko Lindstedt
Jouko Lindstedt (born in 1955) is a Finnish linguist and a professor at the University of Helsinki. Lindstedt is a member of the Academy of Esperanto and was nominated as the Esperantist of the Year in 2000 (with Hans Bakker and Mauro La Torre ) by ...
has assumed that the dividing line between Macedonian and Bulgarian may be in fact the Yat border
Yat or jat (Ѣ ѣ; italics: ) is the thirty-second letter of the old Cyrillic alphabet and the Rusyn alphabet.
There is also another version of yat, the iotified yat (majuscule: , minuscule: ), which is a Cyrillic character combining a ...
, which goes through the modern region of Macedonia
Macedonia () is a geographical and historical region of the Balkan Peninsula in Southeast Europe. Its boundaries have changed considerably over time; however, it came to be defined as the modern geographical region by the mid 19th century. T ...
along the Velingrad
Velingrad ( bg, Велинград ) is a town in Pazardzhik Province, Southern Bulgaria, located at the western end of Chepino Valley, part of the Rhodope Mountains. It is the administrative center of the homonymous Velingrad Municipality a ...
– Petrich
Petrich ( bg, Петрич ) is a town in Blagoevgrad Province in southwestern Bulgaria, located in Sandanski–Petrich Valley at the foot of the Belasica Mountains in the Strumeshnitsa Valley. According to the 2021 census, the town has 26,778 ...
– Thessaloniki
Thessaloniki (; el, Θεσσαλονίκη, , also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece, with over one million inhabitants in its metropolitan area, and the capital of the geographic region of ...
line. Many older Serbian scholars on the other hand believed that the Yat border divides the Serbian and Bulgarian languages. However, modern Serbian linguists such as Pavle Ivić
Pavle Ivić ( sr-cyr, Павле Ивић, ; 1 December 1924 – 19 September 1999) was a Serbian South Slavic dialectologist and phonologist.
Biography
Both his field work and his synthesizing studies were extensive and authoritative. A few of ...
have accepted that the main isoglosses bundle dividing Eastern and Western South Slavic runs from the mouth of the Timok
The Timok (Serbian and Bulgarian: Тимок; ro, Timoc), sometimes also known as Great Timok ( sr, Велики Тимок, Veliki Timok; ro, Timocul Mare), is a river in eastern Serbia, a right tributary of the Danube. For the last 15 k ...
river alongside Osogovo mountain and Sar Mountain. In Bulgaria this isogloss is considered the eastern most border of the broader set of transitional Torlakian dialects.
History
Some of the phenomena that distinguish ''western and eastern subgroups'' of the South Slavic people and languages can be explained by two separate migratory waves of different Slavic tribal groups of the futureSouth Slavs
South Slavs are Slavic peoples who speak South Slavic languages and inhabit a contiguous region of Southeast Europe comprising the eastern Alps and the Balkan Peninsula. Geographically separated from the West Slavs and East Slavs by Austria, ...
via two routes: the west and east of the Carpathian Mountains.The Slavic Languages, Roland Sussex, Paul Cubberley, Publisher Cambridge University Press, 2006, , p. 42. The western Balkans was settled with ''Sclaveni
The ' (in Latin) or ' (various forms in Greek, see below) were early Slavic tribes that raided, invaded and settled the Balkans in the Early Middle Ages and eventually became the progenitors of modern South Slavs. They were mentioned by early Byz ...
'', the eastern with '' Antes''. The early habitat of the Slavic tribes, that are said to have moved to Bulgaria, was described as being in present Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
and Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by ...
. The mythical homeland of the Serbs and Croats lies in the area of today Bohemia, in the present-day Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, or simply Czechia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Historically known as Bohemia, it is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast. The ...
and in Lesser Poland
Lesser Poland, often known by its Polish name Małopolska ( la, Polonia Minor), is a historical region situated in southern and south-eastern Poland. Its capital and largest city is Kraków. Throughout centuries, Lesser Poland developed a ...
. In this way, the Balkans were settled by different groups of Slavs from different dialect areas. This is evidenced by some isoglosses
An isogloss, also called a heterogloss (see Etymology below), is the geographic boundary of a certain linguistic feature, such as the pronunciation of a vowel, the meaning of a word, or the use of some morphological or syntactic feature. Major d ...
of ancient origin, dividing the western and eastern parts of the South Slavic range.
The extinct Old Church Slavonic, which survives in a relatively small body of manuscripts, most of them written in the First Bulgarian Empire during the 10th century, is also classified as Eastern South Slavic. The language has an Eastern South Slavic basis with small admixture of Western Slavic features, inherited during the mission of Saints Cyril and Methodius
Cyril (born Constantine, 826–869) and Methodius (815–885) were two brothers and Byzantine Christian theologians and missionaries. For their work evangelizing the Slavs, they are known as the "Apostles to the Slavs".
They are credited wi ...
to Great Moravia
Great Moravia ( la, Regnum Marahensium; el, Μεγάλη Μοραβία, ''Meghálī Moravía''; cz, Velká Morava ; sk, Veľká Morava ; pl, Wielkie Morawy), or simply Moravia, was the first major state that was predominantly West Slavic to ...
during the 9th century. New Church Slavonic represents a later stage of the Old Church Slavonic, and is its continuation through the liturgical tradition introduced by its precursor. Ivo Banac
Ivo Banac (; 1 March 1947 – 30 June 2020) was a Croatian-American historian, a professor of European history at Yale University and a politician of the former Liberal Party in Croatia, known as the Great Bard of Croatian historiography. , Banac ...
maintains that during the Middle Ages, Torlak and Eastern Herzegovinian dialects were Eastern South Slavic, but since the 12th century, the Shtokavian dialects
Shtokavian or Štokavian (; sh-Latn, štokavski / sh-Cyrl, italics=no, штокавски, ) is the prestige dialect of the pluricentric Serbo-Croatian language and the basis of its Serbian, Croatian, Bosnian and Montenegrin standards. I ...
, including Eastern Herzegovinian, began to separate themselves from the other neighboring Eastern dialects, counting also Torlakian.
The specific contact mechanism in the Balkan Sprachbund, based on the high number of second Balkan language speakers there, is among the key factors that reduced the number of Slavic morphological categories in that linguistic area. The Primary Chronicle of Kyivan Rus'
Kievan Rusʹ, also known as Kyivan Rusʹ ( orv, , Rusĭ, or , , ; Old Norse: ''Garðaríki''), was a state in Eastern and Northern Europe from the late 9th to the mid-13th century.John Channon & Robert Hudson, ''Penguin Historical Atlas of ...
, written ca. 1100, claims that then the Vlachs
"Vlach" ( or ), also "Wallachian" (and many other variants), is a historical term and exonym used from the Middle Ages until the Modern Era to designate mainly Romanians but also Aromanians, Megleno-Romanians, Istro-Romanians and other E ...
attacked the Slavs on the Danube and settled among them. Nearly at the same time are dated the first historical records about the emerging Albanians, as living in the area to the west of the Lake Ohrid
Lake Ohrid ( mk, Охридско Езеро , al, Liqeni i Ohrit , also referred as ''Liqeni i Pogradecit'';) is a lake which straddles the mountainous border between the southwestern part of North Macedonia and eastern Albania. It is one of E ...
. There are references in some Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
documents from that period to "''Bulgaro-Albano-Vlachs''" and even to "''Serbo-Albano-Bulgaro-Vlachs''". As a consequence, case inflection, and some other characteristics of Slavic languages, were lost in Eastern South Slavic area, approximately between the 11th–16th centuries. Migratory waves were particularly strong in the 16th–19th century, bringing about large-scale linguistic and ethnic changes on the Central and Eastern Balkan South Slavic area. They reduced the number of Slavic-speakers and led to the additional settlement of Albanian and Vlach-speakers there.
Separation between Macedonian and Bulgarian
Therise of nationalism under the Ottoman Empire
The rise of the Western notion of nationalism in the Ottoman Empire eventually caused the breakdown of the Ottoman ''millet'' concept. An understanding of the concept of nationhood prevalent in the Ottoman Empire, which was different from the cu ...
began to degrade its specific social system, and especially the so-called Rum millet
Rūm millet (millet-i Rûm), or "''Roman nation''", was the name of the Eastern Orthodox Christian community in the Ottoman Empire. Despite being subordinated within the Ottoman political system, the community maintained a certain internal aut ...
, through constant identification of the religious creed with ethnicity. The national awakening of each ethnic group was complex and most of the groups interacted with each other.
During the Bulgarian national revival
The Bulgarian National Revival ( bg, Българско национално възраждане, ''Balgarsko natsionalno vazrazhdane'' or simply: Възраждане, ''Vazrazhdane'', and tr, Bulgar ulus canlanması) sometimes called the Bu ...
, which occurred in the 19th century, the Bulgarian and Macedonian Slavs under the supremacy of the Greek Orthodox clergy wanted to create their own Church and schools which would use a common modern "Macedono-Bulgarian" literary standard, called simply ''Bulgarian''. The national elites active in this movement used mainly ethnolinguistic principles to differentiation between "Slavic-Bulgarian" and "Greek" groups. At that time, every ethnographic subgroup in the Macedonian-Bulgarian linguistic area wrote in their own local dialect and choosing a "base dialect" for the new standard was not an issue. Subsequently, during the 1850s and 1860s a long discussion was held in the Bulgarian periodicals about the need for a dialectal group (eastern, western or compromise) upon which to base the new standard and which dialect that should be. During the 1870s this issue became contentious, and sparked fierce debates. The general opposition arose between Western and Eastern dialects in the Eastern South Slavic linguistic area. The fundamental issue then was in which part of the ''Bulgarian lands'' the Bulgarian tongue was preserved in a most true manner and every dialectal community insisted on that. The Eastern dialect was proposed then as a basis by the majority of the Bulgarian elite. It was claiming that around the last medieval capital of Bulgaria Tarnovo
Veliko Tarnovo ( bg, Велико Търново, Veliko Tărnovo, ; "Great Tarnovo") is a town in north central Bulgaria and the administrative centre of Veliko Tarnovo Province.
Often referred as the "''City of the Tsars''", Veliko Tarnovo ...
, the Bulgarian language was preserved in its purest form. It was not a surprise, because the most significant part of the new Bulgarian intelligentsia came from the towns of the Eastern Sub-Balkan valley in Central Bulgaria. This proposal alienated a considerable part of the then Bulgarian population and stimulated regionalist linguistic tendencies in Macedonia. In 1870 Marin Drinov
Marin Stoyanov Drinov ( bg, Марин Стоянов Дринов, russian: Марин Степанович Дринов; 20 October 1838 - 13 March 1906) was a Bulgarian historian and philologist from the National Revival period who lived and ...
, who played a decisive role in the standardization of the Bulgarian language, practiclaly rejected the proposal of Parteniy Zografski
Parteniy Zografski or Parteniy Nishavski ( bg, Партений Зографски/Нишавски; mk, Партенија Зографски; 1818 – February 7, 1876) was a 19th-century Bulgarian cleric, philologist, and folklorist from G ...
and Kuzman Shapkarev
Kuzman Anastasov Shapkarev, ( bg, Кузман Анастасов Шапкарев), (1 January 1834 in Ohrid – 18 March 1909 in Sofia) was a Bulgarian folklorist, ethnographer and scientist from the Ottoman region of Macedonia, author of te ...
for a mixed eastern and western Bulgarian/Macedonian foundation of the standard Bulgarian language, stating in his article in the newspaper '' Makedoniya'': "Such an artificial assembly of written language is something impossible, unattainable and never heard of."
In 1878, a distinct Bulgarian state was established. The new state did not include the region of Macedonia which remained outside its borders in the frame of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
. As a consequence, the idea of a common compromise standard was finally rejected by the Bulgarian codifiers during the 1880s and the eastern Central Balkan dialect
The Central Balkan dialect is a Bulgarian dialect that is part of the Balkan group of the Eastern Bulgarian dialects. Its range includes most of north-central Bulgaria (without the regions of Dryanovo and Elena), as well as the regions of Karl ...
was chosen as a basis for standard Bulgarian. Macedono-Bulgarian writers and organizations who continued to seek greater representation of Macedonian dialects in the Bulgarian standard were deemed separatists. One example is the Young Macedonian Literary Association
The Young Macedonian Literary Association was founded in 1891 in Sofia, Bulgaria together with its magazine ''Loza''. The association was formed as primarily a scholarly and literary organization.
Although the members of the Young Macedonian Li ...
, which the Bulgarian government outlawed in 1892. Though standard Bulgarian was taught in the local schools in Macedonia till 1913, the fact of political separation became crucial for the development of a separate Macedonian language.
With the advent of Macedonian nationalism
Macedonian nationalism (, ) is a general grouping of nationalist ideas and concepts among ethnic Macedonians that were first formed in the late 19th century among separatists seeking the autonomy of the region of Macedonia from the Ottoman Emp ...
, the idea of linguistic separatism emerged in the late 19th century, and the need for a separate Macedonian standard language subsequently appeared in the early 20th century. In the Interwar period, the territory of today's North Macedonia
North Macedonia, ; sq, Maqedonia e Veriut, (Macedonia before February 2019), officially the Republic of North Macedonia,, is a country in Southeast Europe. It gained independence in 1991 as one of the successor states of Yugoslavia. It ...
became part of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia, Bulgarian was banned for use and the local vernacular fell under heavy influence from the official Serbo-Croatian language. However, the political and paramilitary organizations of the Macedonian Slavs in Europe and the Americas, the Internal Macedonian Revolutionary Organization
The Internal Macedonian Revolutionary Organization (IMRO; bg, Вътрешна Македонска Революционна Организация (ВМРО), translit=Vatrešna Makedonska Revoljucionna Organizacija (VMRO); mk, Внатр� ...
(IMRO) and the Macedonian Patriotic Organization
Macedonian Patriotic Organization (MPO) is the oldest organization of Americans and Canadians of Macedonian descent in North America. It was founded in Fort Wayne, Indiana, USA, in 1922, by Macedonian Bulgarian immigrants originating mainly fro ...
(MPO), and even their left-wing offsets, the IMRO (United) and the Macedonian-American People's League continued to use literary Bulgarian in their writings and propaganda in the interbellum. During the World wars Bulgaria's short annexations over Macedonia saw two attempts to bring the Macedonian dialects back towards Bulgarian. This political situation stimulated the necessity of a separate Macedonian language and led gradually to its codification after the Second World War. It followed the establishment of SR Macedonia, as part of Communist Yugoslavia and finalized the progressive split in the common Macedonian–Bulgarian language.
During the first half of the 20th century the national identity of the Macedonian Slavs shifted from predominantly Bulgarian to ethnic Macedonian and their regional identity had become their national one. Although, there was no clear separating line between these two languages on level of dialect then, the Macedonian standard was based on its westernmost dialects. Afterwards, Macedonian became the official language in the new republic, Serbo-Croatian was adopted as a second official language, and Bulgarian was proscribed. Moreover, in 1946–1948 the newly standardized Macedonian language was introduced as a second language even in Southwestern Bulgaria. Subsequently, the sharp and continuous deterioration of the political relationships between the two countries, the influence of both standard languages during the time, but also the strong Serbo-Croatian linguistic influence in Yugoslav era, led to a horizontal cross-border dialectal divergence. Although some researchers have described the standard Macedonian and Bulgarian languages as varieties
Variety may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Entertainment formats
* Variety (radio)
* Variety show, in theater and television
Films
* ''Variety'' (1925 film), a German silent film directed by Ewald Andre Dupont
* ''Variety'' (1935 film), ...
of a pluricentric language, they in fact have separate dialectal bases; the Prilep-Bitola dialect
The Prilep-Bitola dialect ( mk, Прилепско-битолски дијалект, ''Prilepsko-bitolski dijalekt'') is a member of the central subgroup of the western group of dialects of Macedonian. This dialect is spoken in much of the Pel ...
and Central Balkan dialect
The Central Balkan dialect is a Bulgarian dialect that is part of the Balkan group of the Eastern Bulgarian dialects. Its range includes most of north-central Bulgaria (without the regions of Dryanovo and Elena), as well as the regions of Karl ...
, respectively. The prevailing academic consensus (outside of Bulgaria and Greece) is that Macedonian and Bulgarian are two autonomous language
Autonomy and heteronomy are complementary attributes of a language variety describing its functional relationship with related varieties.
The concepts were introduced by William A. Stewart in 1968, and provide a way of distinguishing a ''language ...
s within the eastern subbranch of the South Slavic languages. Macedonian is thus an ''ausbau language
In sociolinguistics, an abstand language is a language variety or cluster of varieties with significant linguistic distance from all others, while an ausbau language is a standard variety, possibly with related dependent varieties. Heinz Kloss in ...
''; i.e. it is delimited from Bulgarian as these two standard languages have separate dialectal bases. The uniqueness of Macedonian in comparison to Bulgarian
Bulgarian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the country of Bulgaria
* Bulgarians, a South Slavic ethnic group
* Bulgarian language, a Slavic language
* Bulgarian alphabet
* A citizen of Bulgaria, see Demographics of Bulgaria
* Bul ...
is a matter of political controversy
In politics, a political scandal is an action or event regarded as morally or legally wrong and causing general public outrage. Politicians, government officials, party officials and lobbyists can be accused of various illegal, corrupt, uneth ...
in Bulgaria.Language profile Macedonian, UCLA International Institute
Differences between the languages
* Theword stress
In linguistics, and particularly phonology, stress or accent is the relative emphasis or prominence given to a certain syllable in a word or to a certain word in a phrase or sentence. That emphasis is typically caused by such properties as i ...
in Macedonian is antepenultimate
In linguistics, the ultima is the last syllable of a word, the penult is the next-to-last syllable, and the antepenult is third-from-last syllable. In a word of three syllables, the names of the syllables are antepenult-penult-ultima.
Etymology
Ul ...
, meaning it falls on the third from last syllable in words with three or more syllables, on the second syllable in words with two syllables and on the first or only syllable in words with one syllable. That means that Macedonian has fixed accent and for the most part automatically determined. The word stress in Bulgarian is free and it can appear on almost any syllable of the word, as well as on various morphological units like prefixes, roots, suffixes and articles.
* losing of the ''х'' sound in Macedonian - The development of the Macedonian dialects since the 16th century has been marked by the gradual disappearance of the ''x'' sound or its replacement by ''в'' or ''ф'' (шетах �etah→ шетав �etav. This sound in the standard Macedonian language today is found in some original Slavic words (храна rana
Rana may refer to:
Astronomy
* Rana (crater), a crater on Mars
* Delta Eridani or Rana, a star
People, groups and titles
* Rana (name), a given name and surname (including a list of people and characters with the name)
* Rana (title), a histori ...
храброст rabrost and in loanword
A loanword (also loan word or loan-word) is a word at least partly assimilated from one language (the donor language) into another language. This is in contrast to cognates, which are words in two or more languages that are similar because t ...
s (хемија emija хигиена igiena, but it has disappeared from the initial and intervocalic positions, as well as from the verb system. In the standard Bulgarian language today the sound х is still found in all of that positions.
* Plural with the suffix -''иња'' njafor neuter nouns - In the standard Macedonian language, some neuter nouns ending in -e form the plural with the suffix -''иња''. In the Bulgarian language, neuter nouns ending in -e usually form the plural with the suffix -е(та) (e)taor -е(на) (e)na and the suffix -''иња'' does not exist at all.
* Past indefinite tense with ''има'' (to have) - The standard Macedonian language is the only standard Slavic language in which there is a past indefinite tense (the so-called perfect), which is formed with the auxiliary verb to have and a verbal adjective in the neuter gender. This grammatical tense in linguistics is called ''have-perfect'' and it can be compared to the present perfect tense in English, Perfekt in German and passé composé in French. This construction of ''има'' with a verbal adjective also exists in some non-standard forms of the Bulgarian language, but it is not part of the standard language and is not as developed and widespread as in Macedonian.
Example: ''Гостите имаат дојдено''. - The guests have arrived.
* Changing the root in some imperfect verb forms is characteristic only for the Bulgarian language. Like all Slavic languages, Macedonian and Bulgarian distinguish perfect and imperfect verb forms. However, in the Macedonian standard language, the derivation of imperfect verbs from their perfect pair takes place only with a suffix, and not with a change of the vowel in the root of the verb, as in the Bulgarian language.
* Clitic doubling - In the standard Macedonian language
Macedonian (; , , ) is an Eastern South Slavic language. It is part of the Indo-European language family, and is one of the Slavic languages, which are part of a larger Balto-Slavic branch. Spoken as a first language by around two million ...
, clitic doubling is obligatory with definite direct and indirect object
In linguistics, an object is any of several types of arguments. In subject-prominent, nominative-accusative languages such as English, a transitive verb typically distinguishes between its subject and any of its objects, which can include but ...
s, which contrasts with standard Bulgarian where clitic doubling is optional. Non-standard dialects of Macedonian and Bulgarian have differing rules regarding clitic doubling.
See also
*Slavic dialects of Greece
The Slavic dialects of Greece are the Eastern South Slavic dialects of Macedonian and Bulgarian spoken by minority groups in the regions of Macedonia and Thrace in northern Greece. Usually, dialects in Thrace are classified as Bulgarian, whi ...
*Pomak language
Pomak language ( el, πομακική γλώσσα, ''pomakiki glosa'' or πομακικά, ''pomakika''; bg, помашки език, ''pomaški ezik''; tr, Pomakça) is a term used in Greece and Turkey to refer to some of the Rup dialects of t ...
*Shopi
Shopi or Šopi ( South Slavic: Шопи) is a regional term, used by a group of people in the Balkans. The areas traditionally inhabited by the ''Shopi'' or ''Šopi'' is called ''Shopluk'' or ''Šopluk'' (Шоплук), a mesoregion, roughly ...
Notes
References
{{reflist Languages of the Balkans South Slavic languages Serbian dialects Dialects of the Macedonian language Dialects of the Bulgarian language