Eastern India on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
East India is a region of India consisting of the Indian states of
 During the Neolithic period, agriculture started in South Asia. Neolithic settlements have been found in Chirand. In the Kabra-Kala mound at the confluence of the
During the Neolithic period, agriculture started in South Asia. Neolithic settlements have been found in Chirand. In the Kabra-Kala mound at the confluence of the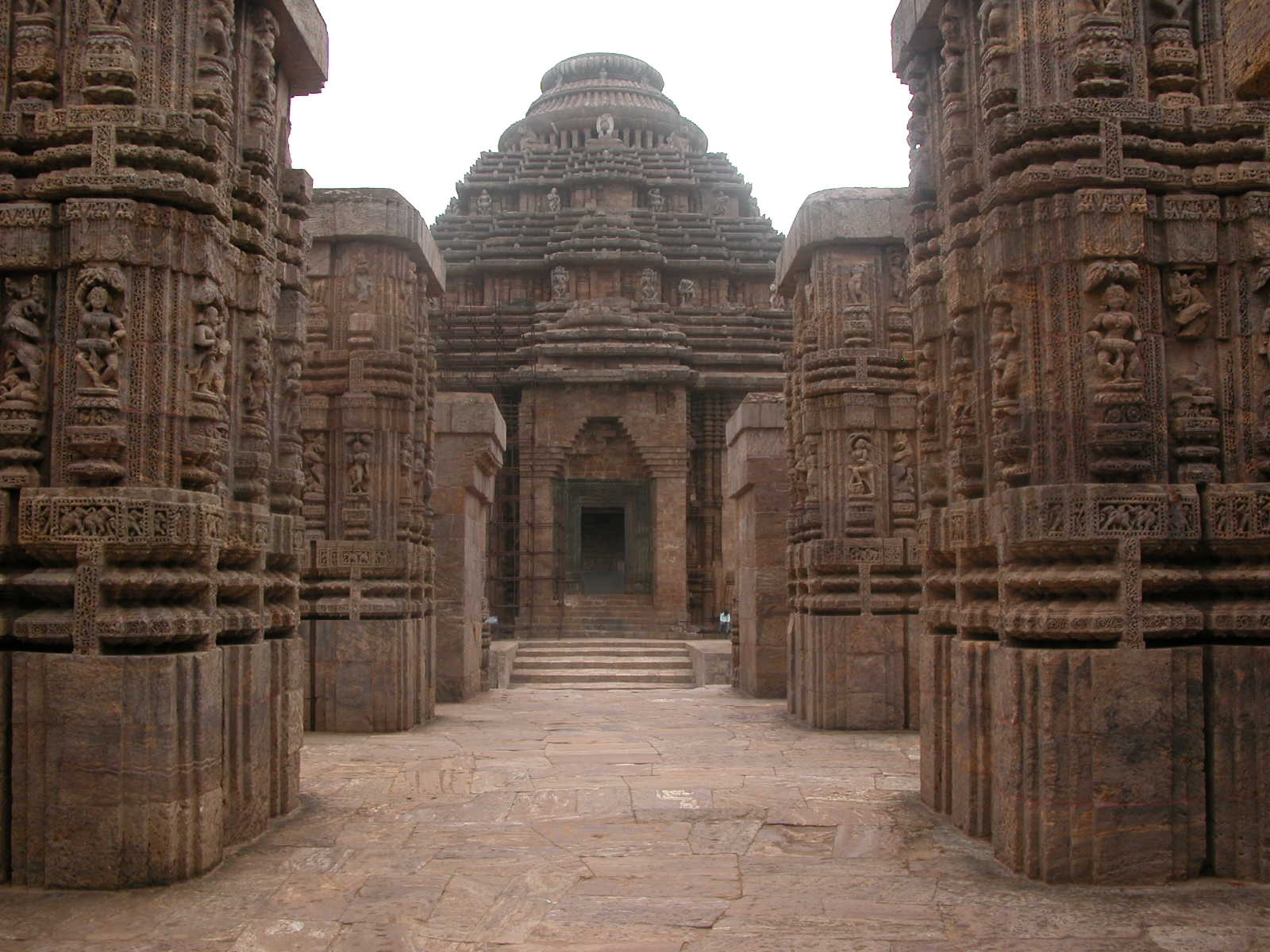  Islamic invasions in the 13th century resulted in the collapse of Hindu kings and most Buddhists, especially in
Islamic invasions in the 13th century resulted in the collapse of Hindu kings and most Buddhists, especially in



 * All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Patna
*
* All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Patna
*
 *
*

 *
*
 There were many ancient cities established in Eastern India. Prominent among them were
There were many ancient cities established in Eastern India. Prominent among them were
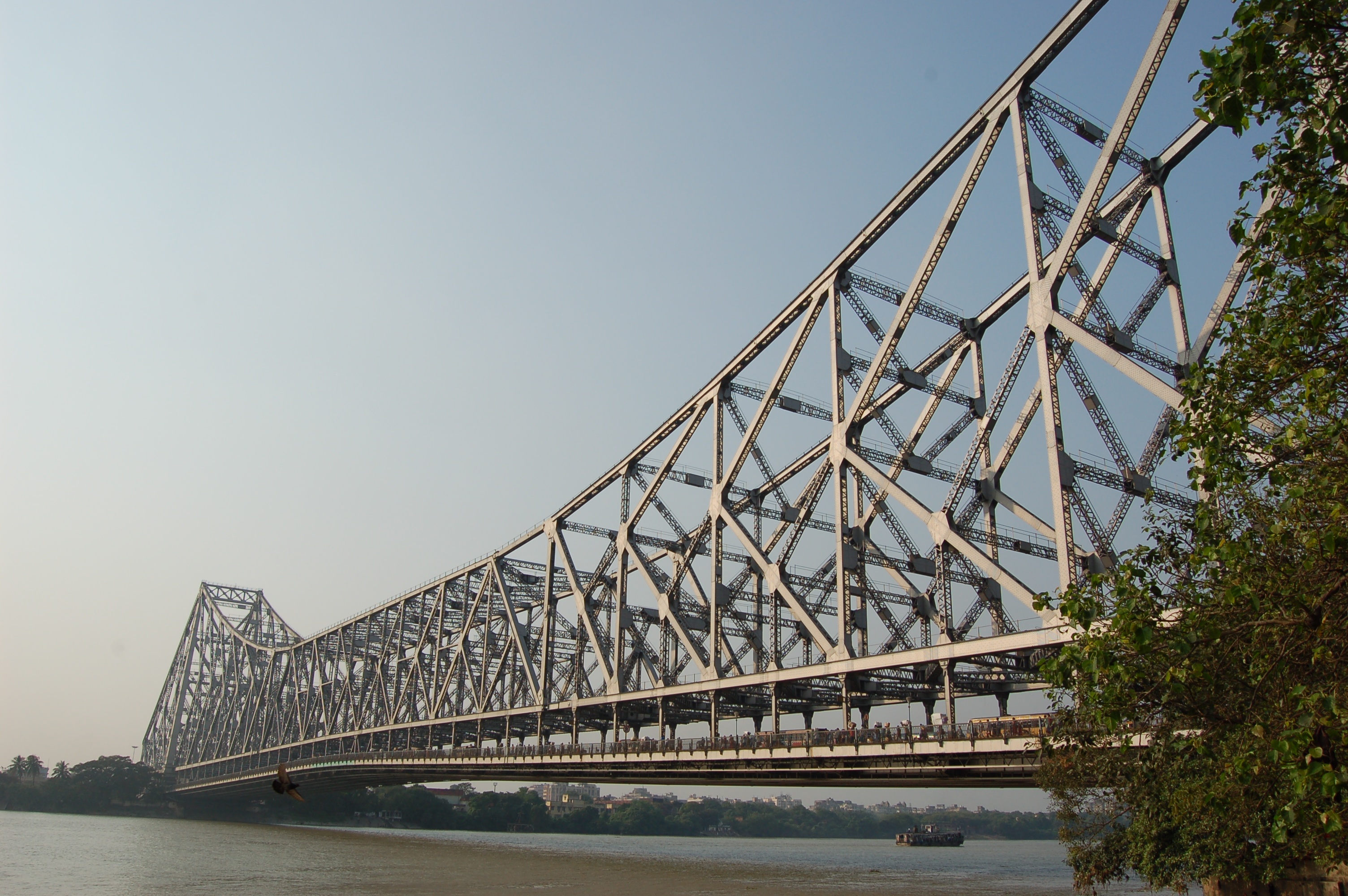

 The
The 
 North Kolkata is the oldest part of the city. Characterised by 19th-century architecture and narrow alleyways, it includes areas such as
North Kolkata is the oldest part of the city. Characterised by 19th-century architecture and narrow alleyways, it includes areas such as 




 The Government has fostered growth in this sphere by the development of IT Parks such as Infocity 1 and the new Infocity 2. The Info City was conceived as a five star park, under the Export Promotion Industrial Parks (EPIP) Scheme to create high quality infrastructure facilities for setting up Information Technology related industries.
The Government has fostered growth in this sphere by the development of IT Parks such as Infocity 1 and the new Infocity 2. The Info City was conceived as a five star park, under the Export Promotion Industrial Parks (EPIP) Scheme to create high quality infrastructure facilities for setting up Information Technology related industries.
Bihar
Bihar (; ) is a state in eastern India. It is the 2nd largest state by population in 2019, 12th largest by area of , and 14th largest by GDP in 2021. Bihar borders Uttar Pradesh to its west, Nepal to the north, the northern part of West ...
, Jharkhand
Jharkhand (; ; ) is a state in eastern India. The state shares its border with the states of West Bengal to the east, Chhattisgarh to the west, Uttar Pradesh to the northwest, Bihar to the north and Odisha to the south. It has an area of . I ...
, Odisha
Odisha (English: , ), formerly Orissa ( the official name until 2011), is an Indian state located in Eastern India. It is the 8th largest state by area, and the 11th largest by population. The state has the third largest population of ...
and West Bengal
West Bengal (, Bengali: ''Poshchim Bongo'', , abbr. WB) is a state in the eastern portion of India. It is situated along the Bay of Bengal, along with a population of over 91 million inhabitants within an area of . West Bengal is the fou ...
and also the union territory of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands
The Andaman and Nicobar Islands is a union territory of India consisting of 572 islands, of which 37 are inhabited, at the junction of the Bay of Bengal and the Andaman Sea. The territory is about north of Aceh in Indonesia and separated f ...
. The region roughly corresponds to the historical region of Magadha
Magadha was a region and one of the sixteen sa, script=Latn, Mahajanapadas, label=none, lit=Great Kingdoms of the Second Urbanization (600–200 BCE) in what is now south Bihar (before expansion) at the eastern Ganges Plain. Magadha was rul ...
from which it inherits its various Eastern Indo-Aryan languages
The Eastern Indo-Aryan languages, also known as Māgadhan languages, are spoken throughout the eastern Indian subcontinent (East India and Assam, Bangladesh), including Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Jharkhand, Bengal, Tripura, Assam, and Odisha; alongs ...
.
The states of Bihar
Bihar (; ) is a state in eastern India. It is the 2nd largest state by population in 2019, 12th largest by area of , and 14th largest by GDP in 2021. Bihar borders Uttar Pradesh to its west, Nepal to the north, the northern part of West ...
and West Bengal
West Bengal (, Bengali: ''Poshchim Bongo'', , abbr. WB) is a state in the eastern portion of India. It is situated along the Bay of Bengal, along with a population of over 91 million inhabitants within an area of . West Bengal is the fou ...
lie on the Indo-Gangetic plain
The Indo-Gangetic Plain, also known as the North Indian River Plain, is a fertile plain encompassing northern regions of the Indian subcontinent, including most of northern and eastern India, around half of Pakistan, virtually all of Bangla ...
. Jharkhand
Jharkhand (; ; ) is a state in eastern India. The state shares its border with the states of West Bengal to the east, Chhattisgarh to the west, Uttar Pradesh to the northwest, Bihar to the north and Odisha to the south. It has an area of . I ...
is situated on the Chota Nagpur Plateau
The Chota Nagpur Plateau is a plateau in eastern India, which covers much of Jharkhand state as well as adjacent parts of Chhattisgarh, Odisha, West Bengal and Bihar. The Indo-Gangetic plain lies to the north and east of the plateau, and the ...
. Odisha
Odisha (English: , ), formerly Orissa ( the official name until 2011), is an Indian state located in Eastern India. It is the 8th largest state by area, and the 11th largest by population. The state has the third largest population of ...
lies on the Eastern Ghats
The Eastern Ghats are a discontinuous range of mountains along India's eastern coast. The Eastern Ghats pass through Odisha, Andhra Pradesh to Tamil Nadu in the south passing some parts of Karnataka as well as Telangana. They are eroded and ...
and the Deccan Plateau
The large Deccan Plateau in southern India is located between the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats, and is loosely defined as the peninsular region between these ranges that is south of the Narmada river. To the north, it is bounded by th ...
. West Bengal's capital Kolkata
Kolkata (, or , ; also known as Calcutta , the official name until 2001) is the capital of the Indian state of West Bengal, on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River west of the border with Bangladesh. It is the primary business, comme ...
is the largest city of this region. The Kolkata Metropolitan Area is the country's third largest. The region is bounded by Bhutan
Bhutan (; dz, འབྲུག་ཡུལ་, Druk Yul ), officially the Kingdom of Bhutan,), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is situated in the Eastern Himalayas, between China in the north and India in the south. A mountainou ...
, Nepal
Nepal (; ne, नेपाल ), formerly the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal ( ne,
सङ्घीय लोकतान्त्रिक गणतन्त्र नेपाल ), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is ma ...
and the state of Sikkim
Sikkim (; ) is a state in Northeastern India. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China in the north and northeast, Bhutan in the east, Province No. 1 of Nepal in the west and West Bengal in the south. Sikkim is also close to the Sil ...
in the north, the states of Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh (; , 'Northern Province') is a state in northern India. With over 200 million inhabitants, it is the most populated state in India as well as the most populous country subdivision in the world. It was established in 195 ...
and Chhattisgarh
Chhattisgarh (, ) is a landlocked state in Central India. It is the ninth largest state by area, and with a population of roughly 30 million, the seventeenth most populous. It borders seven states – Uttar Pradesh to the north, Madhya Prad ...
on the west, the state of Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh (, abbr. AP) is a state in the south-eastern coastal region of India. It is the seventh-largest state by area covering an area of and tenth-most populous state with 49,386,799 inhabitants. It is bordered by Telangana to the ...
in the south and the country of Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the mo ...
in the east. It is also bounded by the Bay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean, bounded on the west and northwest by India, on the north by Bangladesh, and on the east by Myanmar and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands of India. Its southern limit is a line bet ...
in the south-east. It is connected to the Seven Sister States of Northeast India
, native_name_lang = mni
, settlement_type =
, image_skyline =
, image_alt =
, image_caption =
, motto =
, image_map = Northeast india.png
, ...
by the narrow Siliguri Corridor
The Siliguri Corridor, also known as the Chicken's Neck, is a stretch of land around the city of Siliguri in West Bengal, India. at the narrowest section, this geo-political and geo-economical corridor connects the eight states of northeast I ...
in the north east of West Bengal. East India has the fourth-largest gross domestic product than any other region in India.
The region was ruled by several empires, including Gangaridai
Gangaridai ( gr, Γανγαρίδαι; Latin: ''Gangaridae'') is a term used by the ancient Greco-Roman writers (1st century BCE-2nd century AD) to describe a people or a geographical region of the ancient Indian subcontinent. Some of these wri ...
, Nandas, Mauryans
The Maurya Empire, or the Mauryan Empire, was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in the Indian subcontinent based in Magadha, having been founded by Chandragupta Maurya in 322 BCE, and existing in loose-knit fashion until 1 ...
, Guptas
The Gupta Empire was an ancient Indian empire which existed from the early 4th century CE to late 6th century CE. At its zenith, from approximately 319 to 467 CE, it covered much of the Indian subcontinent. This period is considered as the Gold ...
, Palas
A ''palas'' () is a German term for the imposing or prestigious building of a medieval '' Pfalz'' or castle that contained the great hall. Such buildings appeared during the Romanesque period (11th to 13th century) and, according to Thompson ...
, Senas, Eastern Gangas, Gajapatis, Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate was an Islamic empire based in Delhi that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent for 320 years (1206–1526).
, Bengal Sultanate
The Sultanate of Bengal ( Middle Bengali: শাহী বাঙ্গালা ''Shahī Baṅgala'', Classical Persian: ''Saltanat-e-Bangālah'') was an empire based in Bengal for much of the 14th, 15th and 16th centuries. It was the domina ...
, Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
and the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts e ...
.
History

Son
A son is a male offspring; a boy or a man in relation to his parents. The female counterpart is a daughter. From a biological perspective, a son constitutes a first degree relative.
Social issues
In pre-industrial societies and some curren ...
and North Koel rivers in Palamu district
Palamu district is one of the twenty-four districts of Jharkhand state, India. It was formed in 1892. The administrative headquarter of the district is Medininagar (formerly DaltonGanj), situated on the Koel River.
History
The Palamu district ...
, various antiquities and art objects from the Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several pa ...
to medieval periods have been found; the pot-sherds of redware
Redware as a single word is a term for at least two types of pottery of the last few centuries, in Europe and North America. Red ware as two words is a term used for pottery, mostly by archaeologists, found in a very wide range of places. Howeve ...
, black and red ware
Black and red ware (BRW) is a South Asian earthenware, associated with the neolithic phase, Harappa, Bronze Age India, Iron Age India, the megalithic and the early historical period. Although it is sometimes called an archaeological culture, the ...
, black ware, black slipped ware, and NBP ware are from the Chalcolithic
The Copper Age, also called the Chalcolithic (; from grc-gre, χαλκός ''khalkós'', "copper" and ''líthos'', "Rock (geology), stone") or (A)eneolithic (from Latin ''wikt:aeneus, aeneus'' "of copper"), is an list of archaeologi ...
to late medieval periods. There are ancient cave paintings in Isko, Hazaribagh district
Hazaribagh district is one of the twenty-four districts of Jharkhand state, India and the district headquarter located in Hazaribagh town. It is currently a part of the Red Corridor.
Etymology
The district is named after its headquarters, the t ...
, from the Meso-chalcolithic period (9,000–5,000 BC). From Kuchai, near Baripada
Baripada () is a city and a municipality in Mayurbhanj district in the state of Odisha, India. Located along the east bank of the Budhabalanga river, Baripada is the cultural centre of north Odisha. In recent years, it has emerged as an educ ...
, various Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several pa ...
tools like hoe
Hoe or HOE may refer to:
* Hoe (food), a Korean dish of raw fish
* Hoe (letter), a Georgian letter
* Hoe (tool), a hand tool used in gardening and farming
** Hoe-farming, a term for primitive forms of agriculture
* Backhoe, a piece of excavating ...
s, chisel
A chisel is a tool with a characteristically shaped cutting edge (such that wood chisels have lent part of their name to a particular grind) of blade on its end, for carving or cutting a hard material such as wood, stone, or metal by hand, s ...
s, pounders, mace heads, grinding stones and also pieces of pottery. Prehistoric paintings and inscriptions have also been found in Garjan Dongar in Sundergarh district, and Ushakothi in Sambalpur district and Vimkramkhol in Jharsuguda district
Jharsuguda is a district in Odisha, India with Jharsuguda town as its headquarters. This region is rich in coal and other mineral reserves. Of late, many small and medium scale iron and steel units have been set up in the vicinity of Jharsugu ...
. There has been an uncertainty about the inscriptions at Ushakothi and Vimkramkhol regarding whether they are in a proto-Brahmi script
Brahmi (; ; ISO: ''Brāhmī'') is a writing system of ancient South Asia. "Until the late nineteenth century, the script of the Aśokan (non-Kharosthi) inscriptions and its immediate derivatives was referred to by various names such as 'lath' ...
. Yogimath near Khariar
Khariar (also called Khadial, Rajkhariar and Rajakhariar) is a city and a Notified Area Council in Nuapada District of the Indian state of Odisha.
History
The region of Khariar was under the rule of the Chauhan dynasty of Patna State which w ...
has cave paintings from the Neolithic. There is Chalcolithic sites in Pandu Rajar Dhibi in the lower Ajay valley in West Bengal. Iron slag, microlith
A microlith is a small stone tool usually made of flint or chert and typically a centimetre or so in length and half a centimetre wide. They were made by humans from around 35,000 to 3,000 years ago, across Europe, Africa, Asia and Australia. Th ...
s, and potsherds from 1400 BCE, according to carbon dating, were discovered in Singhbhum district
Singhbhum was a district of India during the British Raj, part of the Chota Nagpur Division of the Bengal Presidency. It was located in the present-day Indian state of Jharkhand. Chaibasa was the district headquarters. Located in the southern li ...
. During the late Vedic period, several janapada
The Janapadas () (c. 1500–600 BCE) were the realms, republics (ganapada) and kingdoms (saamarajya) of the Vedic period on the Indian subcontinent. The Vedic period reaches from the late Bronze Age into the Iron Age: from about 1500 BCE to ...
s emerged in India. In the 6th century BCE, the mahajanapadas
The Mahājanapadas ( sa, great realm, from ''maha'', "great", and ''janapada'' "foothold of a people") were sixteen kingdoms or oligarchic republics that existed in ancient India from the sixth to fourth centuries BCE during the second urba ...
emerged in several parts of the Indian subcontinent.
The region was the historical centre of the Nanda
Nanda may refer to:
Indian history and religion
* Nanda Empire, ruled by the Nanda dynasty, an Indian royal dynasty ruling Magadha in the 4th century BCE
** Mahapadma Nanda, first Emperor of the Nanda Empire
** Dhana Nanda (died c. 321 BCE), last ...
, Maurya
The Maurya Empire, or the Mauryan Empire, was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in the Indian subcontinent based in Magadha, having been founded by Chandragupta Maurya in 322 BCE, and existing in loose-knit fashion until 1 ...
, Shunga
is a type of Japanese erotic art typically executed as a kind of ukiyo-e, often in woodblock print format. While rare, there are also extant erotic painted handscrolls which predate ukiyo-e. Translated literally, the Japanese word ''shunga' ...
, Gupta
Gupta () is a common surname or last name of Indian origin. It is based on the Sanskrit word गोप्तृ ''goptṛ'', which means 'guardian' or 'protector'. According to historian R. C. Majumdar, the surname ''Gupta'' was adopted by sev ...
and Pala Pala may refer to:
Places
Chad
*Pala, Chad, the capital of the region of Mayo-Kebbi Ouest
Estonia
*Pala, Kose Parish, village in Kose Parish, Harju County
*Pala, Kuusalu Parish, village in Kuusalu Parish, Harju County
* Pala, Järva County, vil ...
empires that ruled much of the Indian sub-continent at their prime. In medieval India, it was incorporated into the Mughal, Maratha
The Marathi people ( Marathi: मराठी लोक) or Marathis are an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group who are indigenous to Maharashtra in western India. They natively speak Marathi, an Indo-Aryan language. Maharashtra was formed a ...
and then the British empire. After independence in 1947, the states joined the Indian Union and took their current form after the States Reorganisation Act
The States Reorganisation act, 1956 was a major reform of the boundaries of India's states and territories, organising them along linguistic lines.
Although additional changes to India's state boundaries have been made since 1956, the States ...
of 1956. Today, they continue to face problems of overpopulation, environmental degradation and pervasive corruption despite significant economic and social progress.
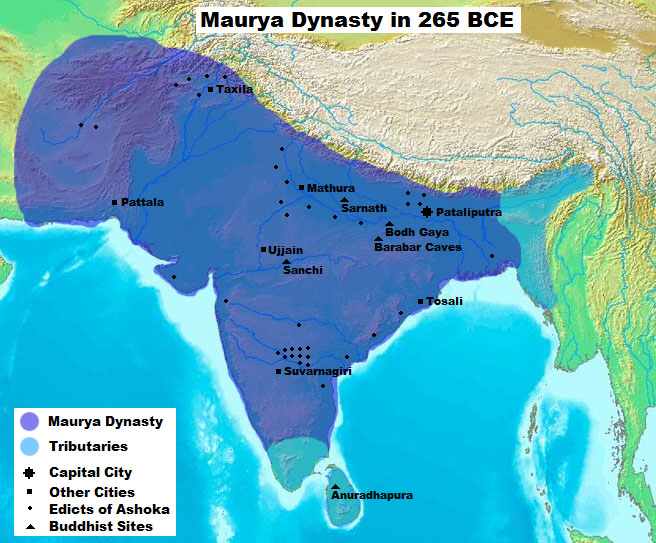
After the Kalinga War
The Kalinga War (ended )Le Huu Phuoc, Buddhist Architecture, Grafikol 2009, p.30 was fought in ancient India between the Maurya Empire under Ashoka and the state of Kalinga, an independent feudal kingdom located on the east coast, in the pr ...
the Maurya king Ashoka
Ashoka (, ; also ''Asoka''; 304 – 232 BCE), popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was the third emperor of the Maurya Empire of Indian subcontinent during to 232 BCE. His empire covered a large part of the Indian subcontinent, s ...
sent emissaries to spread Buddhism across Asia. The university of Nalanda was in Bihar
Bihar (; ) is a state in eastern India. It is the 2nd largest state by population in 2019, 12th largest by area of , and 14th largest by GDP in 2021. Bihar borders Uttar Pradesh to its west, Nepal to the north, the northern part of West ...
. Chinese travellers visited Buddhist and Hindu temples and libraries in the universities of Magadha Empire. The Emperor of Kalinga Mahameghavahana Aira Kharavela was one of the most powerful monarchs of ancient India. The Jain
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religion. Jainism traces its spiritual ideas and history through the succession of twenty-four tirthankaras (supreme preachers of ''Dharma''), with the first in the current time cycle being ...
thirkhankar Mahaveer
Mahavira (Sanskrit: महावीर) also known as Vardhaman, was the 24th ''tirthankara'' (supreme preacher) of Jainism. He was the spiritual successor of the 23rd ''tirthankara'' Parshvanatha. Mahavira was born in the early part of the 6t ...
was born here and founded Jainism
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religion. Jainism traces its spiritual ideas and history through the succession of twenty-four tirthankaras (supreme preachers of ''Dharma''), with the first in the current time cycle bein ...
.
 Islamic invasions in the 13th century resulted in the collapse of Hindu kings and most Buddhists, especially in
Islamic invasions in the 13th century resulted in the collapse of Hindu kings and most Buddhists, especially in East Bengal
ur,
, common_name = East Bengal
, status = Province of the Dominion of Pakistan
, p1 = Bengal Presidency
, flag_p1 = Flag of British Bengal.svg
, s1 = Ea ...
, converted to Islam. East India including Bihar and West Bengal was part of the Mughal Empire in the 16th and 17th centuries. Odisha remained a powerful Hindu dynasty under the rule of Soma/Keshari Dynasty, Eastern Ganga Dynasty, Surya Dynasty till the end of the 16th century. The mighty Nalanda University existed at Nalanda
Nalanda (, ) was a renowned ''mahavihara'' (Buddhist monastic university) in ancient Magadha (modern-day Bihar), India.Bakhtiar Khilji
Ikhtiyār al-Dīn Muḥammad Bakhtiyār Khaljī, (Pashto :اختيار الدين محمد بختيار غلزۍ, fa, اختیارالدین محمد بختیار خلجی, bn, ইখতিয়ারউদ্দীন মুহম্মদ � ...
during the 12th century and also defeated Sena Dynasty
The Sena dynasty was a Hindu dynasty during the early medieval period on the Indian subcontinent, that ruled from Bengal through the 11th and 12th centuries. The empire at its peak covered much of the north-eastern region of the Indian subcont ...
. Sher Shah Suri
Sher Shah Suri ( ps, شیرشاه سوری)
(1472, or 1486 – 22 May 1545), born Farīd Khān ( ps, فرید خان)
, was the founder of the Sur Empire in India, with its capital in Sasaram in modern-day Bihar. He standardized the silver coin ...
, who became king of India after defeating Humayun
Nasir-ud-Din Muhammad ( fa, ) (; 6 March 1508 – 27 January 1556), better known by his regnal name, Humāyūn; (), was the second emperor of the Mughal Empire, who ruled over territory in what is now Eastern Afghanistan, Pakistan, Northe ...
, founded the city of Patna
Patna (
), historically known as Pataliputra, is the capital and largest city of the state of Bihar in India. According to the United Nations, as of 2018, Patna had a population of 2.35 million, making it the 19th largest city in India. ...
on the ruins of ancient Pataliputra
Pataliputra (IAST: ), adjacent to modern-day Patna, was a city in ancient India, originally built by Magadha ruler Ajatashatru in 490 BCE as a small fort () near the Ganges river.. Udayin laid the foundation of the city of Pataliputra at t ...
.
Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the ...
arrived during the 7th century AD and became dominant gradually since the early 13th century with the advent of Muslim rulers as well as Sunni
Sunni Islam () is the largest branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word '' Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia Muslims arose from a dis ...
missionaries such as Shah Jalal
Jalāl Mujarrad Kunyāʾī (), popularly known as Shah Jalal, was a celebrated Sufi figure of Bengal. His name is often associated with the Conquest of Sylhet and the spread of Islam into the region, part of a long history of interactions betw ...
in the region. Later, Muslim rulers, starting from the Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate was an Islamic empire based in Delhi that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent for 320 years (1206–1526).
initiated the preaching of Islam by building mosques. From the 14th century onward, it was ruled by the Bengal Sultanate
The Sultanate of Bengal ( Middle Bengali: শাহী বাঙ্গালা ''Shahī Baṅgala'', Classical Persian: ''Saltanat-e-Bangālah'') was an empire based in Bengal for much of the 14th, 15th and 16th centuries. It was the domina ...
, founded by king Shamsuddin Ilyas Shah
Haji Ilyas, better known as Shamsuddin Ilyas Shah ( bn, শামসুদ্দীন ইলিয়াস শাহ, fa, ), was the founder of the Sultanate of Bengal and its inaugural Ilyas Shahi dynasty which ruled the region for 150 ye ...
, beginning a period of the country's economic prosperity and military dominance over the regional empires, which was referred by the Europeans to as the richest country to trade with. Afterwards, the entire East India came under the Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
, becoming as the most advanced parts in the world. Bengal Subah
The Bengal Subah ( bn, সুবাহ বাংলা; fa, ), also referred to as Mughal Bengal ( bn, মোগল বাংলা), was the largest subdivision of the Mughal Empire (and later an independent state under the Nawabs of Be ...
generated almost half of the empire's GDP and 12% of the world's GDP, larger than the entirety of western Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
.
With the arrival of the Europeans in the 17th century, outposts were established in Odisha Coast and Bengal. The European traders established their trade centres in the ports of Balasore
Balasore or Baleswara is a city in the state of Odisha, about north of the state capital Bhubaneswar and from Kolkata, in eastern India. It is the largest town of northern Odisha and the administrative headquarters of Balasore district. It ...
, Pipili
Pipili is a town and a NAC under jurisdiction of Puri district in the Indian state of Odisha. It is famous for designing beautiful Applique handicrafts. It is a town of artisans famous for their colourful fabrics.
Geography
Pipili is located a ...
, Palur
Palur is a small village in Chengalpattu district in India. Suburban trains running between Chennai Beach - Chengalpattu - Tirumalpur section and Chengalpattu - Arakkonam
Arakkonam () is a railway town and suburb of Chennai within Chennai ...
in the Odisha Coast during the rule of the last independent Hindu king Gajapati Prataprudra Dev. The Portuguese were in Chittagong, Dutch in Chinsura, French in Pondicherry and the English founded Calcutta
Kolkata (, or , ; also known as Calcutta , the official name until 2001) is the capital of the Indian state of West Bengal, on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River west of the border with Bangladesh. It is the primary business, commer ...
. The Maratha Invasion of Bengal badly affected the economy of Bengal and it is estimated that 400,000 people were butchered by the Hindu Maratha bargis and many women and children gang raped, and the genocide has been considered to be among the deadliest massacres in Indian history. In 1756, the British East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and South ...
defeated the local Indian Muslim rulers in Plassey
Palashi or Plassey ( bn, পলাশী, Palāśī, translit-std=ISO, , ) is a village on the east bank of Bhagirathi River, located approximately 50 kilometres north of the city of Krishnanagar in Kaliganj CD Block in the Nadia Distr ...
and established British Rule in the subcontinent. Its capital Calcutta grew into one of the world's greatest ports. Tea from Calcutta was off-loaded by American separatists in the American War of Independence
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
in the 1770s. In the 19th century, Calcutta's traders and merchants traded with the rest of the British Empire, continental Europe, the United States and China. Indentured Indian labourers from Bihar, sailed to new homes in Fiji
Fiji ( , ,; fj, Viti, ; Fiji Hindi: फ़िजी, ''Fijī''), officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consis ...
, Mauritius
Mauritius ( ; french: Maurice, link=no ; mfe, label= Mauritian Creole, Moris ), officially the Republic of Mauritius, is an island nation in the Indian Ocean about off the southeast coast of the African continent, east of Madagascar. It ...
, Guyana
Guyana ( or ), officially the Cooperative Republic of Guyana, is a country on the northern mainland of South America. Guyana is an indigenous word which means "Land of Many Waters". The capital city is Georgetown. Guyana is bordered by the ...
, Surinam and South Africa.
India's independence movement had strong roots in East India. The feudal land system, established through the Permanent Settlement of Bengal, was unpopular among the peasant cultivators and the numerous agricultural labourers found all over Bihar and Bengal (Khetmazdoors). The Indian Rebellion of 1857 started in Bengal
Bengal ( ; bn, বাংলা/বঙ্গ, translit=Bānglā/Bôngô, ) is a geopolitical, cultural and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal, predom ...
. British war propaganda asserted there were atrocities by the mutinous soldiers in the Black Hole of Calcutta
The Black Hole of Calcutta was a dungeon in Fort William, Calcutta, measuring , in which troops of Siraj-ud-Daulah, the Nawab of Bengal, held British prisoners of war on the night of 20 June 1756. John Zephaniah Holwell, one of the Britis ...
. Eventually the British prevailed, and Calcutta remained capital of Britain's Asian dominions until 1911. During Gandhi
Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi (; ; 2 October 1869 – 30 January 1948), popularly known as Mahatma Gandhi, was an Indian lawyer, anti-colonial nationalist Quote: "... marks Gandhi as a hybrid cosmopolitan figure who transformed ... anti- ...
's independence movement, the Bihari village of Champaran was an important supporter of non-violent resistance. Great poets of the stature of Rabindranath Tagore
Rabindranath Tagore (; bn, রবীন্দ্রনাথ ঠাকুর; 7 May 1861 – 7 August 1941) was a Bengali polymath who worked as a poet, writer, playwright, composer, philosopher, social reformer and painter. He resh ...
championed the movement for self-rule.
The Partition also had its roots in undivided Eastern India. The Muslim League Muslim League may refer to:
Political parties Subcontinent
; British India
*All-India Muslim League, Mohammed Ali Jinah, led the demand for the partition of India resulting in the creation of Pakistan.
**Punjab Muslim League, a branch of the organ ...
was founded in Dhaka
Dhaka ( or ; bn, ঢাকা, Ḍhākā, ), List of renamed places in Bangladesh, formerly known as Dacca, is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Bangladesh, largest city of Bangladesh, as well as the world's largest ...
in 1906. In the 1937 provincial elections, it came to power in Bengal in alliance with the Krishak Praja Party
The Krishak Sramik Party ( bn, কৃষক শ্রমিক পার্টি, ''Farmer Labourer Party'') was a major anti-feudal political party in the British Indian province of Bengal and later in the Dominion of Pakistan's East Bengal and ...
. in 1944, it gained an absolute majority in the Bengal Assembly, and Hussein Suhrawardy became the Chief Minister. After widespread communal violence during the Direct Action Day
Direct Action Day (16 August 1946), also known as the 1946 Calcutta Killings, was a day of nationwide communal riots. It led to large-scale violence between Muslims and Hindus in the city of Calcutta (now known as Kolkata) in the Bengal pro ...
protests in Calcutta
Kolkata (, or , ; also known as Calcutta , the official name until 2001) is the capital of the Indian state of West Bengal, on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River west of the border with Bangladesh. It is the primary business, commer ...
, leading to further communal violence across British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one ...
, the creation of Pakistan became inevitable. In 1947, further communal violence displaced millions as independence and partition of British India occurred. Some Bihari and Bengali Muslims fled to the newly created East Pakistan
East Pakistan was a Pakistani province established in 1955 by the One Unit Policy, renaming the province as such from East Bengal, which, in modern times, is split between India and Bangladesh. Its land borders were with India and Myanmar, wit ...
. Most East Bengal Hindus fled to India.
The 1950s saw industrial progress in East India. These were cut short with the conflict in neighbouring East Pakistan
East Pakistan was a Pakistani province established in 1955 by the One Unit Policy, renaming the province as such from East Bengal, which, in modern times, is split between India and Bangladesh. Its land borders were with India and Myanmar, wit ...
and by the Communist
Communism (from Latin la, communis, lit=common, universal, label=none) is a far-left sociopolitical, philosophical, and economic ideology and current within the socialist movement whose goal is the establishment of a communist society, ...
movement at home. In 1971, in the course of Bangladesh's independence struggle, millions of refugees poured into East India.
Bihar
Bihar (; ) is a state in eastern India. It is the 2nd largest state by population in 2019, 12th largest by area of , and 14th largest by GDP in 2021. Bihar borders Uttar Pradesh to its west, Nepal to the north, the northern part of West ...
and Odisha
Odisha (English: , ), formerly Orissa ( the official name until 2011), is an Indian state located in Eastern India. It is the 8th largest state by area, and the 11th largest by population. The state has the third largest population of ...
struggled with economic issues during the British rule
The British Raj (; from Hindi ''rāj'': kingdom, realm, state, or empire) was the rule of the British Crown on the Indian subcontinent;
*
* it is also called Crown rule in India,
*
*
*
*
or Direct rule in India,
* Quote: "Mill, who was hims ...
and in the beginning of post independent India. But in recent years, these two states have shown impressive growth record and developed steadily. The economic boom since 2005 started to spread new malls, highways, airports and IT office complexes, but not evenly across the region. Jharkhand became a separate state on 15 November 2000. In the modern times, these states have seen rapid transformation and home to several mineral and metal based industries, coal based thermal powers units, oil refineries
An oil refinery or petroleum refinery is an industrial process plant where petroleum (crude oil) is transformed and refined into useful products such as gasoline (petrol), diesel fuel, asphalt base, fuel oils, heating oil, kerosene, li ...
, ports
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as H ...
, textile industries and well established public and private educational institutes. Bihar, Odisha and Jharkhand rank 14th, 16th and 18th in the List of Indian states by GDP
These are lists of Indian states and union territories by their nominal gross state domestic product (GSDP). GSDP is the sum of all value added by industries within each state or union territory and serves as a counterpart to the national ...
. Odisha
Odisha (English: , ), formerly Orissa ( the official name until 2011), is an Indian state located in Eastern India. It is the 8th largest state by area, and the 11th largest by population. The state has the third largest population of ...
has shown consistent growth in the state GDP and received the recognition of the fastest-growing economy among the states in India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
.
Education
Nalanda
Nalanda (, ) was a renowned ''mahavihara'' (Buddhist monastic university) in ancient Magadha (modern-day Bihar), India.Puspagiri
Pushpagiri ( Odia: ପୁଷ୍ପଗିରି) was an ancient Indian mahavihara or monastic complex located atop Langudi Hill (or Hills) in Jajpur district of Odisha, India. Pushpagiri was mentioned in the writings of the Chinese traveller ...
and Vikramshila universities were the famed institutions of higher learning in ancient India located in Eastern India. One of the first great universities in recorded history was the ancient Nalanda University located in Bihar and another institute of higher learning was the ancient Puspagiri University recently discovered in Odisha. Education in the eastern part of India has seen rapid transformation. Several new educational institutes have been established to cater the needs of students. East India is now the home to some of the great Indian universities and Institutions of National Importance. Some prominent institutions of higher learning located in the states of Eastern India are listed below.

Bihar
 * All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Patna
*
* All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Patna
*Aryabhatta Knowledge University
Aryabhatta Knowledge University (AKU Patna) is a collegiate public state university located in Mithapur, Patna, Bihar, India. It was named after the Indian astronomer Aryabhatta.
Apart from a few notable exceptions, AKU has authority over tec ...
, Patna
* Birla Institute of Technology, Patna
*Central Institute of Plastics Engineering & Technology, Hajipur
The Central Institute of Petrochemicals Engineering and Technology formerly Central Institute of Plastics and Technology (or CIPET) is an autonomous institution under the Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers (India).
Overview
CIPET was establi ...
* Chanakya National Law University, Patna
Patna (
), historically known as Pataliputra, is the capital and largest city of the state of Bihar in India. According to the United Nations, as of 2018, Patna had a population of 2.35 million, making it the 19th largest city in India. ...
* Chandragupt Institute of Management, Patna
Patna (
), historically known as Pataliputra, is the capital and largest city of the state of Bihar in India. According to the United Nations, as of 2018, Patna had a population of 2.35 million, making it the 19th largest city in India. ...
*Indian Institute of Management Bodh Gaya
The Indian Institute of Management Bodh Gaya (IIM-BG) is an autonomous public business school in Bodh Gaya, Bihar in India. It is the 16th Indian Institute of Management (IIM). The institution was mentored by Indian Institute of Management Calc ...
* Indian Institute of Technology Patna
*Institute of Hotel Management, Hajipur
Institute of Hotel Management, Catering Technology and Applied Nutrition, Hajipur (IHMCT&AN), generally known as IHM Hajipur, is a hospitality management school located in Hajipur, Bihar.
* Muzaffarpur Institute of Technology
* Nalanda University
*National Institute of Fashion Technology
National Institute of Fashion Technology (NIFT) is an autonomous institute that offers courses in fashion, designing, technology, and management. Its head office is located in New Delhi, India.
History
NIFT was established in 1986 under the ...
, Patna
* National Institute of Pharmaceutical Education and Research, Hajipur
*National Institute of Technology, Patna
National Institute of Technology Patna (NIT Patna), formerly Bihar School of Engineering and Bihar College of Engineering, is a public engineering institution located in Patna in the Indian state of Bihar. It was renamed as NIT Patna, by the G ...
*Patna Medical College and Hospital
Patna Medical College and Hospital (abbreviated as PMCH) was established in 1925 and originally known as Prince of Wales Medical College, is a medical college located in Patna, the state capital of Bihar, India.
It is located on the southern b ...
*Patna University
Patna University is a public state university in Patna, Bihar, India. It was established on 1 October 1917 during the British Raj. It is the first university in Bihar and the seventh oldest university in the Indian subcontinent in the modern ...
* Purnea University
*Vidya Vihar Institute of Technology
Vidya Vihar Institute of Technology is an engineering college established in 2009 by Vidya Vihar educational trust at Purnea, Bihar. It is affiliated to Aryabhatta Knowledge University, Patna and has approval of AICTE
The All India Council ...
, Purnia
Purnia ()(also romanized as Purnea) is a city that serves as the administrative headquarters of both Purnia district and Purnia division in the Indian state of Bihar.
Total geographical area of Purnia Urban Agglomeration is which is nex ...
Jharkhand
*Al Kabir Polytechnic
Al-Kabir Polytechnic is one of the first private technical institute of Jharkhand, India established on 1990 (then Bihar). It is recognised by Jharkhand University of Technology, Jharkhand and Approved by AICTE Government of India. The insti ...
, Jamshedpur
Jamshedpur (, ) or Tatanagar is the largest and most populous city in Jharkhand and the first planned industrial city in India. It is a Notified Area Council and Municipal corporation, Municipal Corporation and also the headquarter of the East ...
* All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS), Deoghar
*Binod Bihari Mahto Koyalanchal University
Binod Bihari Mahto Koyalanchal University is a state university located in Dhanbad, Jharkhand, India.
History
Binod Bihari Mahto Koyalanchal University, Dhanbad came into existence by the Jharkhand Government notification of 23 March 2017, pu ...
, Dhanbad
*Birla Institute of Technology, Mesra
Birla Institute of Technology, Mesra (BIT Mesra) is a public deemed institute in Jharkhand, India. It was established in 1955 at Mesra, Ranchi, by the industrialist B. M. Birla. The institute was later headed by G. P. Birla, and the present ...
, Deoghar
Deoghar (pronounced ''Devaghar'') is a major city in Jharkhand, India. It is a holy sacred place of Hinduism. It is one of the 12 ''Jyotirlinga''s sites of Hinduism (Baidyanath Temple). The sacred temples of the city make this a place for p ...
* Birsa Agricultural University, Ranchi
Ranchi (, ) is the capital of the Indian state of Jharkhand. Ranchi was the centre of the Jharkhand movement, which called for a separate state for the tribal regions of South Bihar, northern Odisha, western West Bengal and the eastern area o ...
*Birsa Institute of Technology Sindri
Birsa Institute of Technology Sindri (BIT Sindri), formerly Bihar Institute of Technology Sindri, is an affiliated engineering college in Sindri, Jharkhand, India. Established in 1949, BIT Sindri is one of the oldest engineering and technologica ...
, Dhanbad, AKA BIT Sindri
*Central University of Jharkhand
The Central University of Jharkhand (CUJ) is a central university located in Ranchi, Jharkhand, India. It was established in 2009.
History
CUJ was established in 2009 under the first schedule of the ''Central Universities Act, 2009''. The f ...
, Ranchi
Ranchi (, ) is the capital of the Indian state of Jharkhand. Ranchi was the centre of the Jharkhand movement, which called for a separate state for the tribal regions of South Bihar, northern Odisha, western West Bengal and the eastern area o ...
* Indian Institute of Management Ranchi, AKA IIM Ranchi
*Indian Institute of Technology
The Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs) are central government owned public technical institutes located across India. They are under the ownership of the Ministry of Education of the Government of India. They are governed by the Insti ...
, AKA IIT Dhanbad, formerly Indian School of Mines University
Indian Institute of Technology (Indian School of Mines), Dhanbad (abbreviated IIT (ISM), Dhanbad) is a prestigious public technical university located in Dhanbad, India. It has main campus of 218 acres in Sardar Patel Nagar area of Dhanbad an ...
* Karim City College, Jamshedpur
Jamshedpur (, ) or Tatanagar is the largest and most populous city in Jharkhand and the first planned industrial city in India. It is a Notified Area Council and Municipal corporation, Municipal Corporation and also the headquarter of the East ...
*Mahatma Gandhi Memorial Medical College, Jamshedpur
Mahatma Gandhi Memorial Medical College, also known as MGM Medical College, is an Indian medical college established at Jamshedpur in 1961. It is one of the six medical colleges in Jharkhand which are completely run by the government , it is se ...
*National Institute of Technology, Jamshedpur
National Institute of Technology Jamshedpur (NIT Jamshedpur or NITJSR), is an Institute of National Importance for Technical Education located at Jamshedpur, Jharkhand, India. Established as a Regional Institute of Technology on 15 August 1960, ...
* National Institute of Foundry and Forge Technology, Ranchi
* Patliputra Medical College and Hospital, Dhanbad
* Phulo Jhano Murmu Medical College and Hospital, Dumka
*Rajendra Institute of Medical Sciences
The Rajendra Institute of Medical Sciences (RIMS), established on 15 August 2002 by upgrading the then Rajendra Medical College and Hospital (RMCH) originally setup in 1960, is a medical institute of in Ranchi, the capital of Jharkhand, India ...
Ranchi
Ranchi (, ) is the capital of the Indian state of Jharkhand. Ranchi was the centre of the Jharkhand movement, which called for a separate state for the tribal regions of South Bihar, northern Odisha, western West Bengal and the eastern area o ...
* Sido Kanhu Murmu University Dumka
Dumka ( Santali: ᱫᱩᱢᱠᱟᱹ), the headquarters of the Dumka district and Santhal Pargana region, is a city in the state of Jharkhand, India. It was made the headquarters of the Santhal Pargana region, which was carved out of the Bh ...
*Vinoba Bhave University
Vinoba Bhave University is a state university located at Hazaribagh, Jharkhand, India, about 100 km from Ranchi, the state capital. The university offers courses at the undergraduate and post-graduate levels, manages and maintains 12 cons ...
Hazaribagh
Hazaribagh is a city and a municipal corporation in Hazaribagh district in the Indian state of Jharkhand. It is the divisional headquarters of North Chotanagpur division. It is considered as a health resort and is also popular for Hazaribag ...
* Xavier Institute of Social Service (XISS), Ranchi
Ranchi (, ) is the capital of the Indian state of Jharkhand. Ranchi was the centre of the Jharkhand movement, which called for a separate state for the tribal regions of South Bihar, northern Odisha, western West Bengal and the eastern area o ...
* XLRI - Xavier School of Management, Jamshedpur
Jamshedpur (, ) or Tatanagar is the largest and most populous city in Jharkhand and the first planned industrial city in India. It is a Notified Area Council and Municipal corporation, Municipal Corporation and also the headquarter of the East ...
Odisha
 *
*All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Bhubaneswar
All India Institute of Medical Sciences Bhubaneswar (AIIMS Bhubaneswar), formerly Netaji Subhas Chandra Bose All India Institute of Medical Sciences, is a medical college and medical research public university located in Bhubaneswar, Odisha, ...
* Army Air Defence College, Gopalpur, Brahmapur
* Berhampur University, Berhampur
Brahmapur (; also known as Berhampur) is a city on the eastern coastline of Ganjam district of the Indian state of Odisha. Bramhapur is most famous for its street food, silk sarees or pato sarees, temples and many historical places. Bramhapur al ...
* Biju Patnaik University of Technology, Rourkela
Rourkela is a planned city located in the northern district Sundargarh of Odisha, India. It is the third-largest Urban Agglomeration in Odisha after Bhubaneswar and Cuttack. It is situated about west of state capital Bhubaneswar and is surrou ...
* Central University of Odisha, Koraput
Koraput is a town and a Municipality in Koraput district in the Indian state of Odisha. Koraput town is the district headquarter of Koraput district.
History
The district of Koraput derives its name from its headquarters the present town of ...
*Centurion University of Technology and Management
Centurion University of Technology and Management is a multi-sector, private state university from Odisha, India. With its main campus at Paralakhemundi in the Gajapati district and another constituent campus located at Jatni, on the fringes ...
, Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar (; ) is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Odisha. The region, especially the old town, was historically often depicted as ''Ekamra Kshetra'' (area (''kshetra'') adorned with mango trees (''ekamra'')). Bhubaneswar i ...
* College of Engineering and Technology, Bhubaneswar
* Hi-Tech Medical College & Hospital, Bhubaneswar
* Indian Institute for Production Management, Rourkela
Rourkela is a planned city located in the northern district Sundargarh of Odisha, India. It is the third-largest Urban Agglomeration in Odisha after Bhubaneswar and Cuttack. It is situated about west of state capital Bhubaneswar and is surrou ...
* Indian Institute of Mass Communication, Dhenkanal
Dhenkanal is a town and a municipality in Dhenkanal district in the state of Odisha, India.
Geography
Dhenkanal is at . It has an average elevation of 80 metres (262 feet).
Demographics
As per the 2011 India census, Dhenkanal had a ...
* Indian Institute of Technology Bhubaneswar
*Indian Institutes of Management
The Indian Institutes of Management (IIMs) are central government-owned-public business schools for management offering undergraduate, postgraduate, doctoral and executive programmes along with some additional courses in the field of busines ...
, Sambalpur
Sambalpur () is the fifth largest city in the Indian State of Odisha. It is located on the banks of river Mahanadi, with a population of 335,761 (as per 2011 census). Prehistoric settlements have been recorded there. It is the home of the Sam ...
*Indian Institutes of Science Education and Research
Indian Institutes of Science Education and Research (IISERs) are a group of premier public research institutions in India. The institutes were established by the Government of India through the Ministry of Human Resource Development (MHR ...
, Berhampur
Brahmapur (; also known as Berhampur) is a city on the eastern coastline of Ganjam district of the Indian state of Odisha. Bramhapur is most famous for its street food, silk sarees or pato sarees, temples and many historical places. Bramhapur al ...
*Institute of Medical Sciences and Sum Hospital
The Institute of Medical Sciences and Sum Hospital (IMS and SUM Hospital) is the medical school of the Siksha 'O' Anusandhan in Bhubaneswar, Odisha, India. This institute gained permission in 2007 from Medical Council of India
The Medica ...
, Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar (; ) is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Odisha. The region, especially the old town, was historically often depicted as ''Ekamra Kshetra'' (area (''kshetra'') adorned with mango trees (''ekamra'')). Bhubaneswar i ...
*Institute of Physics, Bhubaneswar
Institute of Physics, Bhubaneswar ( or, ପଦାର୍ଥ ବିଜ୍ଞାନ ଅନୁଷ୍ଠାନ) is an autonomous research institution of the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE), Government of India. The institute was founded by Profes ...
* International Institute of Information Technology, Bhubaneswar
* Kalinga Institute of Industrial Technology, AKA KIIT University, Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar (; ) is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Odisha. The region, especially the old town, was historically often depicted as ''Ekamra Kshetra'' (area (''kshetra'') adorned with mango trees (''ekamra'')). Bhubaneswar i ...
*Kalinga Institute of Medical Sciences
Kalinga Institute of Medical Sciences (KIMS) is the medical school of the Kalinga Institute of Industrial Technology situated in Bhubaneswar, Odisha, India. This institute began offering MBBS courses in medical stream courses in 2007.
Its si ...
, Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar (; ) is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Odisha. The region, especially the old town, was historically often depicted as ''Ekamra Kshetra'' (area (''kshetra'') adorned with mango trees (''ekamra'')). Bhubaneswar i ...
*National Institute of Fashion Technology
National Institute of Fashion Technology (NIFT) is an autonomous institute that offers courses in fashion, designing, technology, and management. Its head office is located in New Delhi, India.
History
NIFT was established in 1986 under the ...
, Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar (; ) is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Odisha. The region, especially the old town, was historically often depicted as ''Ekamra Kshetra'' (area (''kshetra'') adorned with mango trees (''ekamra'')). Bhubaneswar i ...
* National Institute of Science and Technology, Berhampur
Brahmapur (; also known as Berhampur) is a city on the eastern coastline of Ganjam district of the Indian state of Odisha. Bramhapur is most famous for its street food, silk sarees or pato sarees, temples and many historical places. Bramhapur al ...
*National Institute of Science Education and Research
The National Institute of Science Education and Research (NISER) is an autonomous premier public research institute in Jatani, Odisha, India under the umbrella of Department of Atomic Energy, Govt. of India. The institute is a constituent ...
, Bhubaneswar
*National Institutes of Technology
The National Institutes of Technology (NITs) are the central government-owned-public technical institutes under the ownership of Ministry of Education, Government of India. They are governed by the National Institutes of Technology, Scienc ...
, Rourkela
*National Law University Odisha
National Law University Odisha (NLUO) is a public law school and a National law University in India located at Cuttack, Odisha. It was established in 2008 (Act 4 of 2008) under the National Law University Odisha Act, commencing its first batch ...
*North Orissa University
Maharaja Sriram Chandra Bhanja Deo University (MSCB University), formerly North Orissa University (NOU), is a public university in the regional city of Baripada in the state of Odisha, India.
This university mainly provides higher education ...
, Baripada
Baripada () is a city and a municipality in Mayurbhanj district in the state of Odisha, India. Located along the east bank of the Budhabalanga river, Baripada is the cultural centre of north Odisha. In recent years, it has emerged as an educ ...
* Odisha University of Agriculture and Technology, Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar (; ) is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Odisha. The region, especially the old town, was historically often depicted as ''Ekamra Kshetra'' (area (''kshetra'') adorned with mango trees (''ekamra'')). Bhubaneswar i ...
* Pandit Raghunath Murmu Medical College and Hospital Baripada
Baripada () is a city and a municipality in Mayurbhanj district in the state of Odisha, India. Located along the east bank of the Budhabalanga river, Baripada is the cultural centre of north Odisha. In recent years, it has emerged as an educ ...
*Ravenshaw University
Ravenshaw University, formerly known as Ravenshaw college, is a co-educational state university situated in Cuttack, Odisha on the eastern coast of India. Founded as Ravenshaw College in 1868, the institution became a university in 2006. The un ...
, Cuttack
Cuttack (, or officially Kataka ) in Odia is the former capital and the second largest city in the Indian state of Odisha. It is the headquarters of the Cuttack district. The name of the city is an anglicised form of ''Kataka'' which literally ...
* Regional Institute of Education, Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar (; ) is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Odisha. The region, especially the old town, was historically often depicted as ''Ekamra Kshetra'' (area (''kshetra'') adorned with mango trees (''ekamra'')). Bhubaneswar i ...
*Sambalpur University
Sambalpur University is located in Burla town, of district Sambalpur, India, in the state of Odisha. Popularly known as Jyoti Vihar, it offers courses at the undergraduate and post-graduate levels. The governor of Odisha is the chancellor o ...
, Sambalpur
Sambalpur () is the fifth largest city in the Indian State of Odisha. It is located on the banks of river Mahanadi, with a population of 335,761 (as per 2011 census). Prehistoric settlements have been recorded there. It is the home of the Sam ...
*Siksha 'O' Anusandhan
Shiksha 'O' Anusandhan (SOA), formerly Siksha 'O' Anusandhan University (SOA University), is a private deemed university located at Bhubaneswar, Odisha, India. The university is composed of nine degree-granting schools and colleges and has ...
, Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar (; ) is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Odisha. The region, especially the old town, was historically often depicted as ''Ekamra Kshetra'' (area (''kshetra'') adorned with mango trees (''ekamra'')). Bhubaneswar i ...
* Sri Sri University, Cuttack
Cuttack (, or officially Kataka ) in Odia is the former capital and the second largest city in the Indian state of Odisha. It is the headquarters of the Cuttack district. The name of the city is an anglicised form of ''Kataka'' which literally ...
*Srirama Chandra Bhanja Medical College and Hospital
Srirama Chandra Bhanja Medical College and Hospital is a public medical college in Cuttack in the Indian state of Odisha, named after Srirama Chandra Bhanja.
It is one of the oldest centers of medical teaching and training in India. It is lo ...
, Cuttack
Cuttack (, or officially Kataka ) in Odia is the former capital and the second largest city in the Indian state of Odisha. It is the headquarters of the Cuttack district. The name of the city is an anglicised form of ''Kataka'' which literally ...
*Utkal University
Utkal University (UU) is a Public university in Bhubaneswar, Khordha district, Khordha, Odisha, and is the oldest university in Odisha, the state, and the 17th-oldest university in India. It is a teaching-cum-affiliating university. The pre ...
, Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar (; ) is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Odisha. The region, especially the old town, was historically often depicted as ''Ekamra Kshetra'' (area (''kshetra'') adorned with mango trees (''ekamra'')). Bhubaneswar i ...
* Veer Surendra Sai Institute of Medical Sciences and Research, Burla
* Veer Surendra Sai University of Technology, Burla
*Xavier Institute of Management, Bhubaneswar
Xavier Institute of Management, Bhubaneswar (XIMB) is a premier Business School located in Bhubaneswar, the capital of the eastern Indian state of Odisha featuring regularly among the top 20 bschools in India. Established in the year 1987, XIMB ...
West Bengal
 *
*Adamas University
Adamas University is a private university located on Barrackpore-Barasat road in Barasat
Barasat () is a city and a municipality of North 24 Parganas district in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is the headquarters of Barasat Sadar subd ...
, Kolkata
Kolkata (, or , ; also known as Calcutta , the official name until 2001) is the capital of the Indian state of West Bengal, on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River west of the border with Bangladesh. It is the primary business, comme ...
*Aliah University
Aliah University (AU; ur, جامعہ عالیہ) is a state government controlled autonomous university in New Town, West Bengal, India. Previously known as Mohammedan College of Calcutta, it was elevated to university in 2008. It offers ...
, Kolkata
Kolkata (, or , ; also known as Calcutta , the official name until 2001) is the capital of the Indian state of West Bengal, on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River west of the border with Bangladesh. It is the primary business, comme ...
*Amity University, Kolkata
Amity University, Kolkata is a private university in Kolkata in the state of West Bengal, India. It was founded in 2015 and is the eighth university to be established by the Amity Education Group.
History
The Amity Group's was established in ...
* Asansol Engineering College, Asansol
Asansol is a (Tier-II) metropolitan city in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is the second largest and most populated city of West Bengal and the 33rd largest urban agglomeration in India. Asansol is the district headquarters of Paschim B ...
* Calcutta National Medical College
* Government College of Engineering & Textile Technology Serampore
* Government College of Engineering & Textile Technology, Berhampore
*Haldia Institute of Technology
Haldia Institute of Technology, better known as HIT Haldia is an autonomous engineering institute in West Bengal, India, approved by All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE), New Delhi, and affiliated to Maulana Abul Kalam Azad Unive ...
, Haldia
Haldia is an industrial port city in Purba Medinipur in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is a major river port and industrial belt located approximately southwest of Kolkata near the mouth of the Hooghly River, one of the distributarie ...
*Heritage Institute of Technology, Kolkata
Heritage Institute of Technology, popularly known as HITK or HIT is a self-financed institute in the state of the West Bengal. Heritage Institute of Technology is ranked one of the best amongst engineering colleges in Eastern India.The campus i ...
*Indian Institute of Foreign Trade
The Indian Institute of Foreign Trade (IIFT) is a leading business school of India. Established in 1963, it works as an autonomous body under the Ministry of Commerce & Industry, Government of India. It also functions as a civil services tr ...
* Indian Association for the Cultivation of Science
*Indian Institute of Chemical Biology
Indian Institute of Chemical Biology (IICB) is a biomedical research centre in Kolkata, West Bengal, India.
Established in 1935 as Indian Institute of Experimental Medicine (IIEM), it was inducted under the aegis of Council of Scientific & ...
*Indian Institute of Engineering Science and Technology, Shibpur
Indian Institute of Engineering Science and Technology, Shibpur (IIEST Shibpur), erstwhile Bengal Engineering College (also known as B.E. College), formerly Bengal Engineering and Science University (also known as BESU), is a public research u ...
, formerly Bengal Engineering and Science University
*Indian Institute of Management Calcutta
Indian Institute of Management Calcutta (IIM Calcutta or IIM-C) is a public business school located in Joka, Kolkata, West Bengal, India. It was the first Indian Institute of Management to be established, and has been recognized as an Institu ...
* Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur
*Indian Institutes of Science Education and Research
Indian Institutes of Science Education and Research (IISERs) are a group of premier public research institutions in India. The institutes were established by the Government of India through the Ministry of Human Resource Development (MHR ...
, Kolkata
Kolkata (, or , ; also known as Calcutta , the official name until 2001) is the capital of the Indian state of West Bengal, on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River west of the border with Bangladesh. It is the primary business, comme ...
*Indian Statistical Institute
Indian Statistical Institute (ISI) is a higher education and research institute which is recognized as an Institute of National Importance by the 1959 act of the Indian parliament. It grew out of the Statistical Laboratory set up by Prasanta C ...
, Kolkata
Kolkata (, or , ; also known as Calcutta , the official name until 2001) is the capital of the Indian state of West Bengal, on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River west of the border with Bangladesh. It is the primary business, comme ...
*Jadavpur University
Jadavpur University is a public state university located in Jadavpur, Kolkata, West Bengal, India. It was established in 1905 as ''Bengal Technical Institute'' and was converted into Jadavpur University in 1955. In 2022, it was ranked fourth am ...
*Jalpaiguri Government Engineering College
The Jalpaiguri Government Engineering College, abbreviated as JGEC, is an autonomous college, owned fully by Government of West Bengal, and affiliated to Maulana Abul Kalam Azad University of Technology. The courses conducted by JGEC have the ...
*JIS University
JIS University is a private university located near Agarpara, West Bengal, India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous count ...
, Kolkata
Kolkata (, or , ; also known as Calcutta , the official name until 2001) is the capital of the Indian state of West Bengal, on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River west of the border with Bangladesh. It is the primary business, comme ...
*Kalyani Government Engineering College
Kalyani Government Engineering College (KGEC), Kalyani, West Bengal, India offers undergraduate (B.Tech.) and postgraduate (M.Tech., M.C.A.) engineering degree courses affiliated to the Maulana Abul Kalam Azad University of Technology(MAKAUT) ...
* Kazi Nazrul University, Asansol
Asansol is a (Tier-II) metropolitan city in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is the second largest and most populated city of West Bengal and the 33rd largest urban agglomeration in India. Asansol is the district headquarters of Paschim B ...
*Maulana Abul Kalam Azad University of Technology
Maulana Abul Kalam Azad University of Technology (MAKAUT), formerly known as West Bengal University of Technology (WBUT), is a public state university located in Kalyani, West Bengal, India. It is funded completely by the Government of West B ...
*Medical College and Hospital, Kolkata
, mottoeng = Humanity and Science
, type = Public medical school
, established =
, founder = Lord William Bentinck
, principal = Raghunath Mishra
, faculty = ...
*Narula Institute of Technology
Narula Institute of Technology (better known as NiT, Kolkata) is an autonomous private engineering college in West Bengal, India, situated in Agarpara, Kolkata. The college is affiliated with the Maulana Abul Kalam Azad University of Technolog ...
, Kolkata
Kolkata (, or , ; also known as Calcutta , the official name until 2001) is the capital of the Indian state of West Bengal, on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River west of the border with Bangladesh. It is the primary business, comme ...
*National Institute of Technology, Durgapur
National Institute of Technology Durgapur (also known as NIT Durgapur or NITDGP), formerly known as Regional Engineering College, Durgapur (also known as REC Durgapur or RECDGP), is a public technical university in the city of Durgapur in ...
*Presidency University, Kolkata
Presidency University, Kolkata (formerly known as Presidency College, Kolkata) is a second major public state aided research university located in College Street, Kolkata. Considered as one of best colleges when Presidency College was affili ...
*Rabindra Bharati University
Rabindra Bharati University is a public research university in Kolkata, India. It was founded on May 8, 1962, under the Rabindra Bharati Act of the Government of West Bengal in 1961, to mark the birth centenary of the poet Rabindranath Tagore. ...
, Kolkata
Kolkata (, or , ; also known as Calcutta , the official name until 2001) is the capital of the Indian state of West Bengal, on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River west of the border with Bangladesh. It is the primary business, comme ...
*S. N. Bose National Centre for Basic Sciences
S. N. Bose National Centre for Basic Sciences (SNBNCBS) is an autonomous research institute dedicated to basic research in mathematics sciences under the Department of Science and Technology of Government of India. It is located in West Beng ...
*Saha Institute of Nuclear Physics
The Saha Institute of Nuclear Physics (SINP) is an institution of basic research and training in physical and biophysical sciences located in Bidhannagar, Kolkata, India. The institute is named after the famous Indian physicist Meghnad Saha.
...
*Satyajit Ray Film and Television Institute
Satyajit Ray Film and Television Institute (SRFTI) is a film and television institute located in Kolkata, West Bengal, India. Named after Indian filmmaker Satyajit Ray, the institute provides higher and professional education and technical ...
, Kolkata
Kolkata (, or , ; also known as Calcutta , the official name until 2001) is the capital of the Indian state of West Bengal, on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River west of the border with Bangladesh. It is the primary business, comme ...
*Sidho Kanho Birsha University
Sidho Kanho Birsha University (SKBU) is a public state university located in Purulia district of West Bengal, India. It was established under an Act of the West Bengal Legislature on April, 2010. It offers different undergraduate and postgraduat ...
Purulia
Purulia is a city and a municipality in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is the headquarters of the Purulia district. It is located on the north of the Kangsabati River.
Geography
Location
Purulia is located at . It has an average elev ...
*University of Burdwan
The University of Burdwan (also known as Burdwan University or B. U.) is a public university in Purba Bardhaman, West Bengal, India. It was established by the West Bengal Government as a teaching and affiliating university on 15 June 1960 with ...
*University of Calcutta
The University of Calcutta (informally known as Calcutta University; CU) is a public collegiate state university in India, located in Kolkata, West Bengal, India. Considered one of best state research university all over India every yea ...
* University of Engineering & Management (UEM), Kolkata
* University of Gour Banga, Malda
*University of Kalyani
The University of Kalyani, established in 1960, is a Government of West Bengal administered, UGC affiliated, NAAC accredited, collegiate Public Research university in Kalyani, West Bengal, India. It offers courses at the Undergraduate, Post ...
*University of North Bengal
University of North Bengal (abbreviated as NBU) is a public state collegiate major research university in North Bengal region of West Bengal, which is located in Raja Rammohanpur, Siliguri, Darjeeling district, in the Indian state of West Be ...
, Siliguri
Siliguri, ) is a major tier-II city in West Bengal. It forms "Twin Cities" with the neighboring district capital of Jalpaiguri. The city spans areas of the Darjeeling and Jalpaiguri districts in the Indian state of West Bengal. Known as the ...
*Vidyasagar University
Vidyasagar University was established by an Act of the West Bengal legislature which was notified in the '' Calcutta Gazette'' on 24 June 1981. It is an affiliating university in Paschim Medinipur district of southern West Bengal, India. It ...
*Visva-Bharati University
Visva-Bharati () is a public central university and an Institution of National Importance located in Shantiniketan, West Bengal, India. It was founded by Rabindranath Tagore who called it ''Visva-Bharati'', which means the communion of the ...
, Bolpur
Bolpur is a city and a municipality in Birbhum district in the state of West Bengal, India. It is the headquarters of the Bolpur subdivision. Bolpur municipal area includes Santiniketan, Sriniketan and Prantik. The city is known as a Cultu ...
*West Bengal National University of Juridical Sciences
The West Bengal National University of Juridical Sciences (WBNUJS or NUJS) is a premier public law school in India, also known as Columbia of East, and is an elite National Law University located in Bidhannagar, Kolkata, West Bengal, India. I ...
, Kolkata
Kolkata (, or , ; also known as Calcutta , the official name until 2001) is the capital of the Indian state of West Bengal, on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River west of the border with Bangladesh. It is the primary business, comme ...
Urban areas
 There were many ancient cities established in Eastern India. Prominent among them were
There were many ancient cities established in Eastern India. Prominent among them were Pataliputra
Pataliputra (IAST: ), adjacent to modern-day Patna, was a city in ancient India, originally built by Magadha ruler Ajatashatru in 490 BCE as a small fort () near the Ganges river.. Udayin laid the foundation of the city of Pataliputra at t ...
, Bangarh
Bangarh is an ancient city situated in Gangarampur, West Bengal, India. Bangarh was the ancient city which was the administrative centre of Kotivarsha Vishaya (territorial division), itself part of the wider administrative unit of Pundravardh ...
, Tamralipta, Champapuri, Chandraketugarh
Chandraketugarh is a 2,500 years old archaeological site located near the Bidyadhari river, about north-east of Kolkata, India, in the district of North 24 parganas, near the township of Berachampa and the Harua Road railhead. Once it was ...
, Dantapura, Gauda, Katak, Sisupalgarh
Sisupalgarh or Sisupalagada is situated in Khurda District in Odisha, India and houses ruined fortifications. It used to be the capital of ancient Kalinga. It is identified with Kalinganagara of Kharavela and Tosali of Ashoka. It is one of ...
, Tosali, Gaya, Jaugada, Pandua, Rajapura, Asurgarh and Vaishali.
West Bengal

West Bengal
West Bengal (, Bengali: ''Poshchim Bongo'', , abbr. WB) is a state in the eastern portion of India. It is situated along the Bay of Bengal, along with a population of over 91 million inhabitants within an area of . West Bengal is the fou ...
's capital Kolkata
Kolkata (, or , ; also known as Calcutta , the official name until 2001) is the capital of the Indian state of West Bengal, on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River west of the border with Bangladesh. It is the primary business, comme ...
, the capital of British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one ...
until 1911, is the biggest metropolis and economically dominant city of the region and third largest in India and one of the fastest-growing cities in the world. It is also the main centre of commerce or the commercial capital of Eastern and north Eastern India. Kolkata is very fast transforming itself to become city equipped with every facilities for IT and ITES and also financial outsourcing hub and its satellites Salt Lake
A salt lake or saline lake is a landlocked body of water that has a concentration of salts (typically sodium chloride) and other dissolved minerals significantly higher than most lakes (often defined as at least three grams of salt per litre) ...
and Rajarhat-New Town are taken the burdens of India's IT and financial boom. There are many Satellite town
Satellite cities or satellite towns are smaller municipalities that are adjacent to a principal city which is the core of a metropolitan area. They differ from mere suburbs, subdivisions and especially bedroom communities in that they have m ...
also situated in Kolkata, some of them are Salt Lake
A salt lake or saline lake is a landlocked body of water that has a concentration of salts (typically sodium chloride) and other dissolved minerals significantly higher than most lakes (often defined as at least three grams of salt per litre) ...
, Rajarhat-New Town, Kolkata West International City
Kolkata West International City is a satellite township development of Kolkata, located at Salap in Howrah district. The project is under construction in the form of a joint-venture between KMDA and Singapore-based congomolarate Universal Succes ...
, Kalyani, Calcutta Riverside
Calcutta Riverside is a satellite township development across being developed by Riverbank Developers Pvt. Ltd. in joint venture with Bata India Limited planned on the banks of the Hooghly River in Greater Kolkata. The planned township falls i ...
. It is also known as City Of Joy. However, the mid-sized cities of Asansol
Asansol is a (Tier-II) metropolitan city in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is the second largest and most populated city of West Bengal and the 33rd largest urban agglomeration in India. Asansol is the district headquarters of Paschim B ...
, Durgapur
Durgapur () is a planned tier-II urban agglomeration and a major industrial city in Paschim Bardhaman district in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is the fourth largest urban agglomeration after Kolkata, Asansol and Siliguri in West Be ...
, Siliguri
Siliguri, ) is a major tier-II city in West Bengal. It forms "Twin Cities" with the neighboring district capital of Jalpaiguri. The city spans areas of the Darjeeling and Jalpaiguri districts in the Indian state of West Bengal. Known as the ...
in West Bengal
West Bengal (, Bengali: ''Poshchim Bongo'', , abbr. WB) is a state in the eastern portion of India. It is situated along the Bay of Bengal, along with a population of over 91 million inhabitants within an area of . West Bengal is the fou ...
are rapidly growing urban areas. West Bengal
West Bengal (, Bengali: ''Poshchim Bongo'', , abbr. WB) is a state in the eastern portion of India. It is situated along the Bay of Bengal, along with a population of over 91 million inhabitants within an area of . West Bengal is the fou ...
is the highest contributor of GDP among all other eastern state for India and it is also one of the Fastest-growing states in India.
West Bengal is the hub of industry and economic activities in Eastern India and it is also the home to the tallest skylines located in this region and are also one of the tallest buildings in the country. It is also the home of history of rising India.
 The
The Kolkata metropolitan area
Kolkata Metropolitan Area (abbreviated KMA; formerly Calcutta Metropolitan Area), also known as Greater Kolkata, is the urban agglomeration of the city of Kolkata in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is the third most populous metropolitan ...
is spread over and comprises 3 municipal corporations (including Kolkata Municipal Corporation), 39 local municipalities and 24 panchayat samiti
Panchayat samiti is a rural local government (panchayat) body at the intermediate tehsil (taluka/mandal) level in India. It works for the villages of the tehsil that together are called a development block. It has been said to be the "panchayat ...
s, . The urban agglomeration encompassed 72 cities and 527 towns and villages, . Suburban areas in the Kolkata metropolitan area incorporate parts of the following districts: North 24 Parganas
North 24 Parganas (abv. 24 PGS (N)) or sometimes North Twenty Four Parganas is a district in southern West Bengal, of eastern India. North 24 Parganas extends in the tropical zone from latitude 22° 11′ 6″ north to 23° 15′ 2″ north and ...
, South 24 Parganas
South 24 Parganas (Pron: pɔrɡɔnɔs; abbr. 24 PGS (S)), or sometimes South Twenty Four Parganas and Dakshin 24 Parganas, is a district in the Indian state of West Bengal, headquartered in Alipore. It is the largest district of West Bengal by ...
, Howrah
Howrah (, , alternatively spelled as Haora) is a city in the Indian state of West Bengal. Howrah is located on the western bank of the Hooghly River opposite its twin city of Kolkata. Administratively it lies within Howrah district, and is ...
, Hooghly and Nadia
Nadia is a female name. Variations include Nadja, Nadya, Nadine, Nadiya, and Nadiia. Most variations of the name are derived from Arabic, Slavic languages, or both.
In Slavic, names similar to ''Nadia'' mean "hope" in many Slavic languages: ...
. Kolkata, which is under the jurisdiction of the Kolkata Municipal Corporation
Kolkata Municipal Corporation (abbreviated KMC; also Calcutta Municipal Corporation) is the local government of the Indian city of Kolkata, the state capital of West Bengal. This civic administrative body administers an area of . Its motto, ' ...
( KMC), has an area of . The east–west dimension of the city is comparatively narrow, stretching from the Hooghly River in the west to roughly the Eastern Metropolitan Bypass
The Eastern Metropolitan Bypass (known simply as both ''E.M. Bypass'' and ''EM Bypass'') is a (Including Kamalgazi to Baruipur extension) major road on the east side of Kolkata. It connects Ultadanga (North Kolkata) to Baruipur Puratan Bazar ...
in the east—a span of . The north–south distance is greater, and its axis is used to section the city into North, Central and South Kolkata.

Jorasanko
Jorasanko is a neighbourhood of North Kolkata, in Kolkata district, West Bengal, India. It is so called because of the two (''jora'') wooden or bamboo bridges (''sanko'') that spanned a small stream at this point.
History
Apart from the disti ...
, Maniktala, Ultadanga
Ultadanga is one of the most crowded junctions in Kolkata. The place is located at the north-eastern fringe of the city and marks the limit of Kolkata district. Prominent places in Ultadanga are Telenga Bagan and Muchi Bazar.
Etymology
Ultad ...
, Shyambazar
Shyambazar is a neighbourhood of North Kolkata, in Kolkata district in the Indian state of West Bengal. The area, under Shyampukur police station of Kolkata Police, has been, along with neighbouring Bagbazar, the citadel of the Bengali ari ...
, Shobhabazar
Shobhabazar (also spelt Sovabazar; bn, শোভাবাজার) is a neighbourhood of North Kolkata, in Kolkata district, in the Indian state of West Bengal.
History
Sheths and Basaks, well-to-do traders at Saptagram, were among the first ...
, Bagbazar, Cossipore, Sinthee etc. The north suburban areas like Dum Dum, Baranagar
("City of hogs")
, settlement_type =
City
, image_seal =
, image_skyline =
, image_alt =
, image_caption =
, pushpin_map = India West Bengal#India3#Asia
, pushpin_label_ ...
, Belgharia
Belgharia is a locality in Kamarhati Municipality of North 24 Parganas district in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is a part of the area covered by Kolkata Metropolitan Development Authority (KMDA) and a vital locality in Kolkata metropol ...
, Sodepur
Sodepur or Sodpur is a locality in Panihati Municipality of North 24 Parganas district in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is close to Kolkata and also a part of the area covered by Kolkata Metropolitan Development Authority (KMDA). Barrac ...
, Khardaha
Khardaha is a city and a municipality of North 24 Parganas district in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is near Kolkata and also a part of the area covered by Kolkata Metropolitan Development Authority (KMDA).
History
Initially Khardah was ...
, New Barrackpore
New Barrackpore is a city and a municipality of North 24 Parganas district in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is close to Kolkata & a part of the area covered by Kolkata Metropolitan Development Authority. It is the capital of Kolkata.
Geo ...
, Madhyamgram, Barrackpore
Barrackpore (also known as Barrackpur) is a city and a municipality of urban Kolkata of North 24 Parganas district in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is also a part of the area covered by Kolkata Metropolitan Development Authority (K ...
, Barasat
Barasat () is a city and a municipality of North 24 Parganas district in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is the headquarters of Barasat Sadar subdivision. It is a part of the area covered by Kolkata Metropolitan Development Authority (KMDA) ...
etc. are also within the city of Kolkata (as a metropolitan structure).
Central Kolkata hosts the central business district. It contains B.B.D. Bagh, formerly known as Dalhousie Square and the Esplanade
An esplanade or promenade is a long, open, level area, usually next to a river or large body of water, where people may walk. The historical definition of ''esplanade'' was a large, open, level area outside fortress or city walls to provide cl ...
on its east; Strand Road is on its west. The West Bengal Secretariat, General Post Office
The General Post Office (GPO) was the state postal system and telecommunications carrier of the United Kingdom until 1969. Before the Acts of Union 1707, it was the postal system of the Kingdom of England, established by Charles II in 1660. ...
, Reserve Bank of India
The Reserve Bank of India, chiefly known as RBI, is India's central bank and regulatory body responsible for regulation of the Indian banking system. It is under the ownership of Ministry of Finance, Government of India. It is responsible f ...
, Calcutta High Court
The Calcutta High Court is the oldest High Court in India. It is located in B.B.D. Bagh, Kolkata, West Bengal. It has jurisdiction over the state of West Bengal and the Union Territory of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. The High Court b ...
, Lalbazar Police Headquarters and several other government and private offices are located there. Another business hub is the area south of Park Street, which comprises thoroughfares such as Chowringhee Road
Chowringhee Road (also spelt ''Chourangi Road''), located in the Chowringhee neighbourhood of Kolkata, is the arterial road running from the eastern fringes of Esplanade southwards up to the crossing with Lower Circular Road (AJC Bose Roa ...
, Camac Street, Wood Street, Loudon Street, Shakespeare Sarani, AJC Bose Road etc. The Maidan is a large open field in the heart of the city that has been called the "lungs of Kolkata" and accommodates sporting events and public meetings. The Victoria Memorial and Kolkata Race Course
Kolkata Race Course in Hastings, Kolkata, India is the largest horse race venue in India. The race course was built in 1820 and is maintained by the Royal Calcutta Turf Club
The Royal Calcutta Turf Club (RCTC) is a horse racing organisation w ...
are located at the southern end of the Maidan. Among the other parks are Central Park
Central Park is an urban park in New York City located between the Upper West and Upper East Sides of Manhattan. It is the fifth-largest park in the city, covering . It is the most visited urban park in the United States, with an estimated ...
in Bidhannagar and Millennium Park
Millennium Park is a public park located in the Loop community area of Chicago, operated by the Chicago Department of Cultural Affairs. The park, opened in 2004 and intended to celebrate the third millennium, is a prominent civic center ne ...
on Strand Road, along the Hooghly River.
South Kolkata includes many posh neighbourhoods such as Bhawanipore
Bhowanipore (also Bhowanipur; bn, ভবানীপুর) is a neighbourhood of South Kolkata in Kolkata district of West Bengal, India.
History
In 1717, the East India Company obtained the right to rent from 38 villages surrounding their s ...
, Alipore
Alipore (Pron:ˌɑ:lɪˈpɔ:) is a neighbourhood in south Kolkata, in Kolkata district, in the Indian state of West Bengal.
It is flanked by the Tolly Nullah to the north, Bhowanipore to the east, the Diamond Harbour Road to the west and ...
, Ballygunge
Ballygunge is a locality of South Kolkata, in Kolkata district, West Bengal, India.
History
The East India Company obtained from the Mughal emperor Farrukhsiyar, in 1717, the right to rent from 38 villages surrounding their settlement. Of the ...
, Kasba, Dhakuria
Dhakuria is a locality in the city of Kolkata, (previously Calcutta), in West Bengal, India.
It is located in the southern part of the city and is surrounded by Ballygunge and Kasba in the north, Haltu in the east, Jadavpur/ Garia in the sout ...
, Santoshpur, Garia
Garia ( Bengali:গড়িয়া) is a neighborhood in southern Kolkata, West Bengal, India. It is bordered by the neighborhoods of Jadavpur in the north, Bansdroni/Tollygunge in the north-west, Santoshpur/ Mukundapur in the north-east a ...
, Tollygunge
Tollygunge (Bengali: টালিগঞ্জ; nicknamed 'Mini Mumbai' or 'Mini Bombay') is a locality of South Kolkata, in West Bengal, India. It is famed as the centre of the Indian film industry, known as Tollywood, Marathi Cinema, South In ...
, Behala
Behala is a locality of South West Kolkata, in the Indian state of West Bengal. Behala is a part of Kolkata Municipal Corporation area. It is broadly spread across Ward Nos. 118, 119, 120, 121, 122, 123, 124, 125, 126, 127, 128, 129, ...
etc. The south suburban areas like Maheshtala, Budge Budge
Budge Budge () is a town and a municipality of the South 24 Parganas district in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is situated on the eastern banks of the Hooghly River. It is a part of the area covered by the Kolkata Metropolitan Developme ...
, Rajpur Sonarpur
Rajpur Sonarpur () is a city and a municipality of the South 24 Parganas district in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is a part of the area covered by the Kolkata Metropolitan Development Authority (KMDA). Rajpur and Sonarpur are two separat ...
, Baruipur
Baruipur () is a town and a municipality of the South 24 Parganas district in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is a part of the area covered by the Kolkata Metropolitan Development Authority (KMDA). It is the headquarters of the Baruipur su ...
etc. are also within the city of Kolkata (as a metropolitan structure).
Asansol
Asansol is a (Tier-II) metropolitan city in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is the second largest and most populated city of West Bengal and the 33rd largest urban agglomeration in India. Asansol is the district headquarters of Paschim B ...
is the district headquarters of Paschim Bardhaman District in West Bengal. It is the second largest city in West Bengal after Kolkata and the 39th largest urban agglomeration in India. According to a 2010 report prepared by the International Institute for Environment and Development, a UK-based policy research non-governmental think tank, Asansol is ranked 11th among Indian cities. and 42nd in the world in its list of 100 fastest-growing cities. As per the recommendations of the Sixth Central Pay Commission, Asansol has been listed as a Y-category city for calculation of HRA (House Rent Allowance) for public servants. It is one of the three non-Z category cities in West Bengal apart from Kolkata, which belong to the X category making it a tier-II city.

Durgapur
Durgapur () is a planned tier-II urban agglomeration and a major industrial city in Paschim Bardhaman district in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is the fourth largest urban agglomeration after Kolkata, Asansol and Siliguri in West Be ...
is by far the most industrialised city in Eastern India and the second planned city in India. It started with the first prime minister of independent India, Jawaharlal Nehru
Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru (; ; ; 14 November 1889 – 27 May 1964) was an Indian Anti-colonial nationalism, anti-colonial nationalist, secular humanist, social democrat—
*
*
*
* and author who was a central figure in India du ...
. His dream of transforming the backward agricultural country into an industrially advanced nation was picked up in West Bengal by Dr. B.C. Roy. At the earlier stages for the selection of a proper site for a new industrial township. Modernist American architect Joseph Allen Stein
Joseph Stein (10 April 1912 – 6 October 2001) was an American architect and a major figure in the establishment of a regional modern architecture in the San Francisco Bay area in the 1940s and 1950s during the early days of the environmental ...
, invited to head the newly formed Department of Architecture and Planning at the Bengal Engineering College in Calcutta, plunged into a major project as soon as he reached India in 1952 – the designing of Durgapur city with Benjamin Polk, another American architect already living in Calcutta. Thereafter it was the task of local leaders such as Ananda Gopal Mukherjee and bureaucrats such as K.K. Sen to get Durgapur going.
Bihar & Jharkhand
Bihar hasPatna
Patna (
), historically known as Pataliputra, is the capital and largest city of the state of Bihar in India. According to the United Nations, as of 2018, Patna had a population of 2.35 million, making it the 19th largest city in India. ...
, Bhagalpur
Bhagalpur is a city in the Indian state of Bihar, situated on the southern banks of the river Ganges. It is the 2nd largest city of Bihar by population and also the headquarters of Bhagalpur district and Bhagalpur division. Known as the Si ...
, Darbhanga
Darbhanga is the fifth-largest city and municipal corporation in the Indian state of Bihar situated centrally in Mithila region.
Darbhanga is the headquarters of the Darbhanga district and the Darbhanga division. It was the seat of the erst ...
, Muzaffarpur
Muzaffarpur () is a city located in Muzaffarpur district in the Tirhut region of the Indian state of Bihar. It serves as the headquarters of the Tirhut division, the Muzaffarpur district and the Muzaffarpur Railway District. It is the fourth ...
, Gaya, Hajipur
Hajipur (, ) is the headquarters and largest city of Vaishali district of the state of Bihar in India. Hajipur is the 16th most populous city of Bihar, besides being the second-fastest developing city, next to Patna. It had a total population ...
and Purnia
Purnia ()(also romanized as Purnea) is a city that serves as the administrative headquarters of both Purnia district and Purnia division in the Indian state of Bihar.
Total geographical area of Purnia Urban Agglomeration is which is nex ...
as important urban areas. In Jharkhand
Jharkhand (; ; ) is a state in eastern India. The state shares its border with the states of West Bengal to the east, Chhattisgarh to the west, Uttar Pradesh to the northwest, Bihar to the north and Odisha to the south. It has an area of . I ...
the major urban areas are mainly dominated by industrial cities such as Ranchi
Ranchi (, ) is the capital of the Indian state of Jharkhand. Ranchi was the centre of the Jharkhand movement, which called for a separate state for the tribal regions of South Bihar, northern Odisha, western West Bengal and the eastern area o ...
, Jamshedpur
Jamshedpur (, ) or Tatanagar is the largest and most populous city in Jharkhand and the first planned industrial city in India. It is a Notified Area Council and Municipal corporation, Municipal Corporation and also the headquarter of the East ...
, Bokaro Steel City
Bokaro, officially known as Bokaro Steel City () is a planned city in Jharkhand, India. It is fourth largest and most populous city in the state. It is one of the planned cities of India. Bokaro is the administrative headquarters of Bokaro distri ...
, Deoghar
Deoghar (pronounced ''Devaghar'') is a major city in Jharkhand, India. It is a holy sacred place of Hinduism. It is one of the 12 ''Jyotirlinga''s sites of Hinduism (Baidyanath Temple). The sacred temples of the city make this a place for p ...
, Hazaribagh
Hazaribagh is a city and a municipal corporation in Hazaribagh district in the Indian state of Jharkhand. It is the divisional headquarters of North Chotanagpur division. It is considered as a health resort and is also popular for Hazaribag ...
and Dhanbad.
Patna
Patna (
), historically known as Pataliputra, is the capital and largest city of the state of Bihar in India. According to the United Nations, as of 2018, Patna had a population of 2.35 million, making it the 19th largest city in India. ...
is the capital of the Bihar
Bihar (; ) is a state in eastern India. It is the 2nd largest state by population in 2019, 12th largest by area of , and 14th largest by GDP in 2021. Bihar borders Uttar Pradesh to its west, Nepal to the north, the northern part of West ...
, its most populous city and the second most populous city in Eastern India. It is the administrative, industrial and educational centre of the state. Patna is one of the oldest continuously inhabited places in the world. Ancient Patna, known as Pataliputra, was the capital of the Magadha Empire under the Haryanka, Nanda, Mauryan, Shunga, Gupta and Pala.
Pataliputra
Pataliputra (IAST: ), adjacent to modern-day Patna, was a city in ancient India, originally built by Magadha ruler Ajatashatru in 490 BCE as a small fort () near the Ganges river.. Udayin laid the foundation of the city of Pataliputra at t ...
was a seat of learning and fine arts.
The modern city of Patna is situated on the southern bank of the Ganges. The city also straddles the rivers Sone, Gandak and Punpun. The city is approximately 35 km long and 16 km to 18 km wide. It is the second largest city of Eastern India.
In June 2009, the World Bank ranked Patna second in India (after Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, primarily its western or right bank, Delhi shares borders w ...
) for ease of starting a business. As of 2004–2005, Patna had the highest per capita gross district domestic product in Bihar, at 63,063. Using fi gures for assumed average annual growth, Patna is the 21st fastest-growing city in the world and 5th fastest-growing city in India by the City Mayors' Foundation. Patna registered an average annual growth of 3.72% during 2006–2010. The city is also home to many tutorials and coaching institutes who prepare students for various entrance exams. IIT NIT NIFT AIIMS and other leading educational institutions are running successfully in Patna. City is also developing excellent road infrastructure to boom its economy. Ganga expressway
Ganga Expressway is an under-construction 594 km long, 6-lane wide (expandable to 8) greenfield expressway in the state of Uttar Pradesh, India. Phase-1 will connect Bijauli village on NH-334 in Meerut district with Judapur Dandu village on ...
and elevated corridors are under some of the ongoing projects in the city. A world class museum is also on its way to completion. The old museum of the city will be replaced by one of the biggest mall in east India.
Patna Metro rail corporations is also going to start soon by 2021. It would be the second metro railway in Eastern India after Kolkata and the third in North India after Delhi and Lucknow.
IT parks are also developing in and around the city.
Patna recorded a per capita of Rs 63,063. The per capita level for 2007 was higher than Bangalore
Bangalore (), officially Bengaluru (), is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Karnataka. It has a population of more than and a metropolitan population of around , making it the third most populous city and fifth most ...
or Hyderabad
Hyderabad ( ; , ) is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Telangana and the ''de jure'' capital of Andhra Pradesh. It occupies on the Deccan Plateau along the banks of the Musi River, in the northern part of Southern Indi ...
, which are both leading centres for global software development.
The Buddhist, Hindu, and Jain pilgrim centres of Vaishali, Rajgir, Nalanda, Gaya, Bodhgaya, and Pawapuri are nearby and Patna is also a sacred city for Sikhs as the last Sikh Guru, Guru Gobind Singh, was born here.
Odisha

Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar (; ) is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Odisha. The region, especially the old town, was historically often depicted as ''Ekamra Kshetra'' (area (''kshetra'') adorned with mango trees (''ekamra'')). Bhubaneswar i ...
is the capital of the Odisha
Odisha (English: , ), formerly Orissa ( the official name until 2011), is an Indian state located in Eastern India. It is the 8th largest state by area, and the 11th largest by population. The state has the third largest population of ...
. Other Important Cities are Cuttack
Cuttack (, or officially Kataka ) in Odia is the former capital and the second largest city in the Indian state of Odisha. It is the headquarters of the Cuttack district. The name of the city is an anglicised form of ''Kataka'' which literally ...
, Brahmapur, Rourkela
Rourkela is a planned city located in the northern district Sundargarh of Odisha, India. It is the third-largest Urban Agglomeration in Odisha after Bhubaneswar and Cuttack. It is situated about west of state capital Bhubaneswar and is surrou ...
, Paradeep
Paradeep, also spelt Paradip (originally Paradweep, also spelt Paradwip), is a major seaport city and municipality, from Jagatsinghpur city in Jagatsinghpur district of Odisha, India. Paradeep Municipality was constituted as an NAC on 27 Sep ...
, Jajpur
Jajpur (also known as Jajapur) is a town and a municipality in Jajpur district in the Indian state of Odisha. It was the capital of the Kesari dynasty, later supplanted by Cuttack. Now, it is the headquarter of Jajpur district.
Etymology an ...
, Bhadrak
Bhadrak is a city of Odisha state in eastern India. The city is the district headquarters of Bhadrak district. According to legend, the city derives its name from the Goddess Bhadrakali, whose temple is on the banks of the Salandi River.
Hi ...
, Balasore
Balasore or Baleswara is a city in the state of Odisha, about north of the state capital Bhubaneswar and from Kolkata, in eastern India. It is the largest town of northern Odisha and the administrative headquarters of Balasore district. It ...
, Sambalpur
Sambalpur () is the fifth largest city in the Indian State of Odisha. It is located on the banks of river Mahanadi, with a population of 335,761 (as per 2011 census). Prehistoric settlements have been recorded there. It is the home of the Sam ...
and Puri
Puri () is a coastal city and a municipality in the state of Odisha in eastern India. It is the district headquarters of Puri district and is situated on the Bay of Bengal, south of the state capital of Bhubaneswar. It is also known as '' ...
. The Capital city has a long history of over 2000 years starting with Chedi dynasty (around the 2nd century BCE) who had Sisupalgarh
Sisupalgarh or Sisupalagada is situated in Khurda District in Odisha, India and houses ruined fortifications. It used to be the capital of ancient Kalinga. It is identified with Kalinganagara of Kharavela and Tosali of Ashoka. It is one of ...
near present-day Bhubaneswar as their capital. Historically, Bhubaneswar has been known by different names such as Toshali, Kalinga Nagari, Nagar Kalinga, Ekamra Kanan
Ekamra Kanan or Ekamra Kanan Botanical Gardens is a botanical garden and a park located in Bhubaneswar, Odisha, India. This is the biggest park and one of the most popular tourist attractions in the city. The park was established in 1985 and is sp ...
, Ekamra Kshetra and Mandira Malini Nagari (city of temples) or the temple city of India. The largest city of Odisha, Bhubaneswar today is a center of economic and religious importance in the region.
With the economic liberalisation policy adopted by the Government of India
The Government of India ( ISO: ; often abbreviated as GoI), known as the Union Government or Central Government but often simply as the Centre, is the national government of the Republic of India, a federal democracy located in South Asia, ...
in the '90s, Bhubaneswar received large investments in the fields of telecommunications
Telecommunication is the transmission of information by various types of technologies over wire, radio, optical, or other electromagnetic systems. It has its origin in the desire of humans for communication over a distance greater than that ...
, IT and higher education, particularly in science and engineering. The city is home to around 60 engineering colleges (as of 2009) and the number is growing every year. The city is also home to many tutorials and coaching institutes who prepare students for various entrance exams.

Retail
Retail is the sale of goods and Service (economics), services to consumers, in contrast to wholesaling, which is sale to business or institutional customers. A retailer purchases goods in large quantities from manufacturing, manufacturers, dire ...
and Real Estate
Real estate is property consisting of land and the buildings on it, along with its natural resources such as crops, minerals or water; immovable property of this nature; an interest vested in this (also) an item of real property, (more genera ...
have also emerged as big players. Recent times have seen large scale retail chains such as Reliance, Vishal MegaMart, Big Bazaar, Pantaloon, Pal Heights, Indulge, New Leaf, Habib's, had opened outlets in Bhubaneswar. Large corporations like DLF Universal
Delhi Land & Finance (DLF Limited) is a commercial real estate developer. It was founded by Chaudhary Raghvendra Singh in 1946 and it is based in New Delhi, India. DLF developed residential colonies in Delhi such as, Model Town, Rajouri Garde ...
and Reliance Industries have entered the real estate market in the city. DLF Limited is developing an Infopark spread over an area of in the city. Expanding its business portfolio, the Kolkata
Kolkata (, or , ; also known as Calcutta , the official name until 2001) is the capital of the Indian state of West Bengal, on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River west of the border with Bangladesh. It is the primary business, comme ...
-based Saraf Group, promoters of Forum Mart shopping malls is constructing another Shopping mall named Forum Lifestyle mall a lifestyle mall in Bhubaneswar with 1,200 car parks. The rich minerals resources of Odisha have been the backbone of the economy dominated by Government. Steel Authority of India Limited (SAIL) and private organisations like Jindal, Vedanta and TATAS. Despite this rapid growth, an ample number of the populace live in slums. Migration from rural areas, especially from the northern districts of Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh (, abbr. AP) is a state in the south-eastern coastal region of India. It is the seventh-largest state by area covering an area of and tenth-most populous state with 49,386,799 inhabitants. It is bordered by Telangana to the ...
, has led to the growth of slums which are a major challenge to the city's growth.
 The Government has fostered growth in this sphere by the development of IT Parks such as Infocity 1 and the new Infocity 2. The Info City was conceived as a five star park, under the Export Promotion Industrial Parks (EPIP) Scheme to create high quality infrastructure facilities for setting up Information Technology related industries.
The Government has fostered growth in this sphere by the development of IT Parks such as Infocity 1 and the new Infocity 2. The Info City was conceived as a five star park, under the Export Promotion Industrial Parks (EPIP) Scheme to create high quality infrastructure facilities for setting up Information Technology related industries. Infosys
Infosys Limited is an Indian multinational information technology company that provides business consulting, information technology and outsourcing services. The company was founded in Pune and is headquartered in Bangalore. Infosys is ...
and Satyam Computer Services Ltd. have been present in Bhubaneswar since 1996–97. Its current head count stands at around 5000. The first part of the TCS centre is ready and has a capacity to accommodate nearly 1,200 professionals but the software major has only 250 employees at present. The Finland telecommunication company, Nethawk, has its India R&D center at Bhubaneswar. The Canadian giant, Gennum Corporation has its India development centre at Bhubaneswar. The auditors Price water house Coopers Pvt. Ltd. also has a center in Bhubaneswar. The private STP is located at Infocity in Chandaka, Bhubaneswar with a view to provide incubation and infrastructure facilities to new and young entrepreneurs in the MSME sector, The intelligent building of the JSS STP is spread in a sprawling campus and houses state-of-art technology to fulfil the growing demands of highly competent IT professionals.
The Eastern India, particularly Odisha and Jharkhand, have rich mineral resources which resulted in economic boom
An economic expansion is an increase in the level of economic activity, and of the goods and services available. It is a period of economic growth as measured by a rise in real GDP. The explanation of fluctuations in aggregate economic activi ...
in these two states. Several mineral based industries have been established in many cities of Odisha and Jharkhand namely Kalinganagar
Kalinganagar is a planned industrial and modern town in Jajpur district of coastal Odisha, India. It is rich in iron ore. Because of high global demand for steel, Kalinganagar is becoming a major global hub in steel, power and ancillary prod ...
, Angul
Angul (also known as Anugul) is a town and a municipality and the headquarters of Angul district in the state of Odisha, India. Angul has an average elevation of above sea level.
The total geographical area of the district is 6232 km2. ...
, Paradeep
Paradeep, also spelt Paradip (originally Paradweep, also spelt Paradwip), is a major seaport city and municipality, from Jagatsinghpur city in Jagatsinghpur district of Odisha, India. Paradeep Municipality was constituted as an NAC on 27 Sep ...
, Talcher, Rourkela
Rourkela is a planned city located in the northern district Sundargarh of Odisha, India. It is the third-largest Urban Agglomeration in Odisha after Bhubaneswar and Cuttack. It is situated about west of state capital Bhubaneswar and is surrou ...
, Damanjodi, Joda
Joda is a planned industrial and modern city and municipality in the Kendujhar district of the state of Odisha, India. The area has rich iron and manganese ore deposits and the economy centers on the large-scale production of iron ore and man ...
, Barbil
Barbil is a city and a Municipal Council in the Kendujhar district (also known as Iron City) of the state of Odisha, India. The region around Barbil has one of the largest deposits of iron ore and manganese ore in the world. It is a major sour ...
, Choudwar
Choudwar is a town and a municipality in Cuttack district in the Indian state of Odisha. It comes under Bhubaneswar-Cuttack commissionerate.
Geography
Choudwar is located on the banks of Mahanadi and Birupa river near 16 and 55 National Highw ...
, Jharsuguda Jamshedpur
Jamshedpur (, ) or Tatanagar is the largest and most populous city in Jharkhand and the first planned industrial city in India. It is a Notified Area Council and Municipal corporation, Municipal Corporation and also the headquarter of the East ...
, Bokaro, Dhanbad and Ranchi
Ranchi (, ) is the capital of the Indian state of Jharkhand. Ranchi was the centre of the Jharkhand movement, which called for a separate state for the tribal regions of South Bihar, northern Odisha, western West Bengal and the eastern area o ...
.
Languages
Bengali
Bengali or Bengalee, or Bengalese may refer to:
*something of, from, or related to Bengal, a large region in South Asia
* Bengalis, an ethnic and linguistic group of the region
* Bengali language, the language they speak
** Bengali alphabet, the w ...
is the dominant language of West Bengal. Hindi
Hindi (Devanāgarī: or , ), or more precisely Modern Standard Hindi (Devanagari: ), is an Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in the Hindi Belt region encompassing parts of northern, central, eastern, and western India. Hindi has been ...
, , Maithili, Magahi
The Magahi language (), also known as Magadhi (), is a language spoken in Bihar, Jharkhand and West Bengal states of eastern India, and in the Terai of Nepal. Magadhi Prakrit was the ancestor of Magahi, from which the latter's name deriv ...
and Urdu
Urdu (;"Urdu"
''
''
Hindi
Hindi (Devanāgarī: or , ), or more precisely Modern Standard Hindi (Devanagari: ), is an Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in the Hindi Belt region encompassing parts of northern, central, eastern, and western India. Hindi has been ...
, Santali, Khortha and Nagpuri are the dominant language of Jharkhand; however, some tribals speak their own tribal languages. Jharkhand has accorded second language status to Angika, Bengali
Bengali or Bengalee, or Bengalese may refer to:
*something of, from, or related to Bengal, a large region in South Asia
* Bengalis, an ethnic and linguistic group of the region
* Bengali language, the language they speak
** Bengali alphabet, the w ...
, , Ho, Kharia, Kurukh, Khortha, Kurmali
Kurmali or Kudmali (ISO: Kuṛmāli) is an Indo-Aryan language classified as belonging to the Bihari group of languages spoken in eastern India. As a trade dialect, it is also known as Panchpargania (Bengali: পঞ্চপরগনিয়� ...
, Magahi
The Magahi language (), also known as Magadhi (), is a language spoken in Bihar, Jharkhand and West Bengal states of eastern India, and in the Terai of Nepal. Magadhi Prakrit was the ancestor of Magahi, from which the latter's name deriv ...
, Maithili, Mundari, Nagpuri, Odia
Odia, also spelled Oriya or Odiya, may refer to:
* Odia people in Odisha, India
* Odia language, an Indian language, belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European language family
* Odia alphabet, a writing system used for the Odia languag ...
, Santali and Urdu
Urdu (;"Urdu"
''

 The region lies in the humid-subtropical zone, and experiences hot summers from March to June, the monsoon from July to October and mild winters from November to February. The interior states have a drier climate and slightly more extreme climate, especially during the winters and summers, but the whole region receives heavy, sustained rainfall during the monsoon months. Snowfall occurs in the extreme northern regions of West Bengal and
The region lies in the humid-subtropical zone, and experiences hot summers from March to June, the monsoon from July to October and mild winters from November to February. The interior states have a drier climate and slightly more extreme climate, especially during the winters and summers, but the whole region receives heavy, sustained rainfall during the monsoon months. Snowfall occurs in the extreme northern regions of West Bengal and
Macher Jhol.JPG, A traditional Bengali fish meal – Rice with Macher Jhol (Literally translated to "Fish's gravy")
Green Jackfruit & Potato Curry - Kolkata 2011-02-11 1000.JPG, Green jackfruit and potato curry,
Bihar



 Rabindra Sangeet, also known as Tagore Songs, are songs written and composed by
Rabindra Sangeet, also known as Tagore Songs, are songs written and composed by
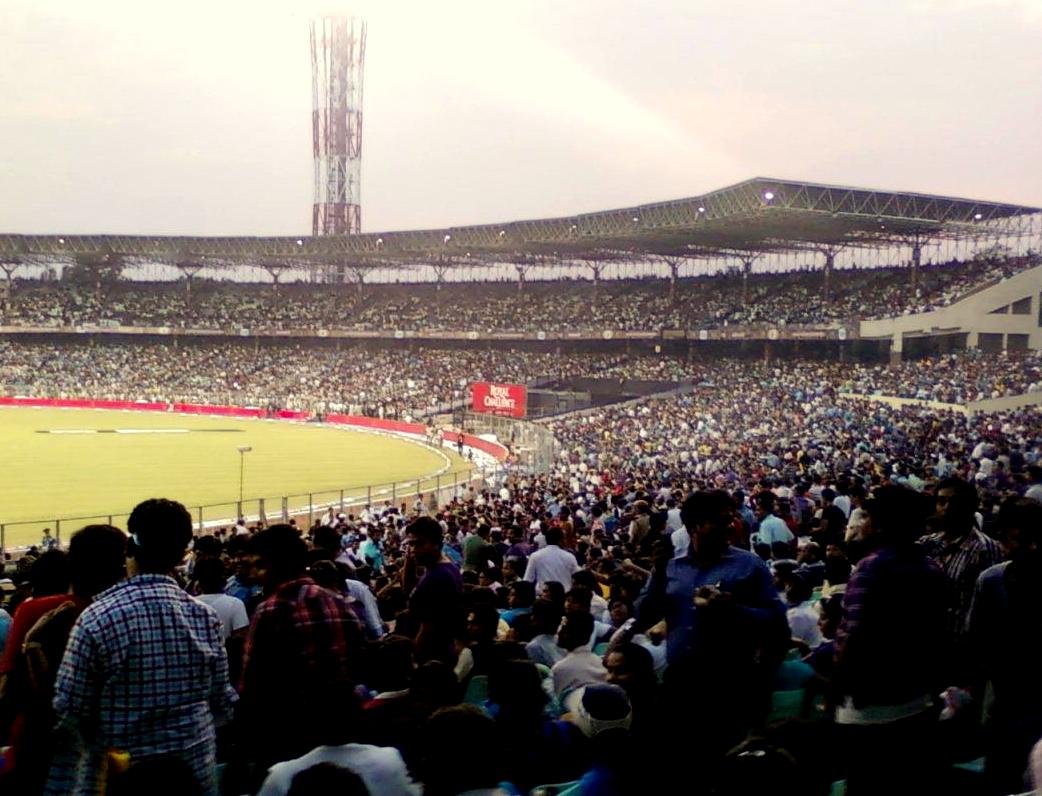 The most popular sports in Kolkata are
The most popular sports in Kolkata are  The
The

 The most popular sports in Odisha are
The most popular sports in Odisha are


''
Odia
Odia, also spelled Oriya or Odiya, may refer to:
* Odia people in Odisha, India
* Odia language, an Indian language, belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European language family
* Odia alphabet, a writing system used for the Odia languag ...
is the dominant language of Odisha
Odisha (English: , ), formerly Orissa ( the official name until 2011), is an Indian state located in Eastern India. It is the 8th largest state by area, and the 11th largest by population. The state has the third largest population of ...
. Odia is the only major classical language in east India and sixth Indian language to be considered as a classical language in the basis of being old and not borrowed from other languages.
According to Indian National Mission for Manuscripts, after Sanskrit, Odia has the second-highest number of manuscripts. As per records there are around 2.13 lakhs ancient manuscript in Odia. In the list Bengali is in 9th position with 15412 ancient manuscripts.
The Indo-Aryan languages
The Indo-Aryan languages (or sometimes Indic languages) are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European language family. As of the early 21st century, they have more than 800 million speakers, primarily concentrated in India, P ...
spoken in this region descend from the Magadhi Prakrit
Magadhi Prakrit (''Māgadhī'') is of one of the three Dramatic Prakrits, the written languages of Ancient India following the decline of Pali and Sanskrit. It was a vernacular Middle Indo-Aryan language, replacing earlier Vedic Sanskrit.
H ...
, which was spoken in the ancient kingdom of Magadha. Odia emerged as a distinct language from Odra Magadhi Prakrit
Magadhi Prakrit (''Māgadhī'') is of one of the three Dramatic Prakrits, the written languages of Ancient India following the decline of Pali and Sanskrit. It was a vernacular Middle Indo-Aryan language, replacing earlier Vedic Sanskrit.
H ...
and Maithili emerged around the 9th century CE.
Many of the minority Tribal languages of East India belong to the Munda branch of the Austroasiatic language family
The Austroasiatic languages , , are a large language family in Mainland Southeast Asia and South Asia. These languages are scattered throughout parts of Thailand, Laos, India, Myanmar, Malaysia, Bangladesh, Nepal, and southern China and are th ...
and Dravidian language family. Major representatives of Autro-Asiatic language include the Mundari, Santali, and Ho. Dravidian languages include Kurukh, Kui and Pengo.
Climate

 The region lies in the humid-subtropical zone, and experiences hot summers from March to June, the monsoon from July to October and mild winters from November to February. The interior states have a drier climate and slightly more extreme climate, especially during the winters and summers, but the whole region receives heavy, sustained rainfall during the monsoon months. Snowfall occurs in the extreme northern regions of West Bengal and
The region lies in the humid-subtropical zone, and experiences hot summers from March to June, the monsoon from July to October and mild winters from November to February. The interior states have a drier climate and slightly more extreme climate, especially during the winters and summers, but the whole region receives heavy, sustained rainfall during the monsoon months. Snowfall occurs in the extreme northern regions of West Bengal and Daringbadi
Daringbadi is a hill station in Kandhmal district of Odisha state in eastern India. Widely known as "Kashmir of Odisha", (for its climatic similarity), it is situated at a height of 915 metres and is a popular tourist destination.
Back in t ...
in Odisha.
Religion and cuisine
About 80% of the population of East India isHindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
with significant Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
and small Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι� ...
, Buddhist
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
and tribal minorities. The Muslims constitute a very large minority in West Bengal with 27% of the population and 17% in Bihar. Hindus form 94% of total population of Odisha. Christians are the largest minority in Odisha with 3% of the state population
Durga
Durga ( sa, दुर्गा, ) is a major Hindu goddess, worshipped as a principal aspect of the mother goddess Mahadevi. She is associated with protection, strength, motherhood, destruction, and wars.
Durga's legend centres around c ...
, Krishna
Krishna (; sa, कृष्ण ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the eighth avatar of Vishnu and also as the Supreme god in his own right. He is the god of protection, compassion, tenderness, and love; and is on ...
, Jagannath
Jagannath ( or, ଜଗନ୍ନାଥ, lit=Lord of the Universe, Jagannātha; formerly en, Juggernaut) is a deity worshipped in regional Hindu traditions in India and Bangladesh as part of a triad along with his brother Balabhadra, and sister ...
and Shiva
Shiva (; sa, शिव, lit=The Auspicious One, Śiva ), also known as Mahadeva (; Help:IPA/Sanskrit, ɐɦaːd̪eːʋɐ, or Hara, is one of the Hindu deities, principal deities of Hinduism. He is the Supreme Being in Shaivism, one o ...
are particularly popular Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
deities in this region.
Durga
Durga ( sa, दुर्गा, ) is a major Hindu goddess, worshipped as a principal aspect of the mother goddess Mahadevi. She is associated with protection, strength, motherhood, destruction, and wars.
Durga's legend centres around c ...
and Kali
Kali (; sa, काली, ), also referred to as Mahakali, Bhadrakali, and Kalika ( sa, कालिका), is a Hindu goddess who is considered to be the goddess of ultimate power, time, destruction and change in Shaktism. In this tra ...
are patron deities of Bengal and Mithila whereas Jagannath
Jagannath ( or, ଜଗନ୍ନାଥ, lit=Lord of the Universe, Jagannātha; formerly en, Juggernaut) is a deity worshipped in regional Hindu traditions in India and Bangladesh as part of a triad along with his brother Balabhadra, and sister ...
or Vishnu
Vishnu ( ; , ), also known as Narayana and Hari, is one of the principal deities of Hinduism. He is the supreme being within Vaishnavism, one of the major traditions within contemporary Hinduism.
Vishnu is known as "The Preserver" withi ...
is patron god
In monotheistic thought, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. Swinburne, R.G. "God" in Honderich, Ted. (ed)''The Oxford Companion to Philosophy'', Oxford University Press, 1995. God is typically ...
among Odia people
The Odia (), formerly spelled Oriya, is an Indo-Aryan ethnic group native to the Indian state of Odisha who speak Odia language. They constitute a majority in the eastern coastal state, with significant minority populations in neighboring An ...
. Rama
Rama (; ), Ram, Raman or Ramar, also known as Ramachandra (; , ), is a major deity in Hinduism. He is the seventh and one of the most popular '' avatars'' of Vishnu. In Rama-centric traditions of Hinduism, he is considered the Supreme Bei ...
and Hanuman
Hanuman (; sa, हनुमान, ), also called Anjaneya (), is a Hindu god and a divine '' vanara'' companion of the god Rama. Hanuman is one of the central characters of the Hindu epic ''Ramayana''. He is an ardent devotee of Rama and on ...
are most revered in Bihar. Shiva
Shiva (; sa, शिव, lit=The Auspicious One, Śiva ), also known as Mahadeva (; Help:IPA/Sanskrit, ɐɦaːd̪eːʋɐ, or Hara, is one of the Hindu deities, principal deities of Hinduism. He is the Supreme Being in Shaivism, one o ...
is popular in all areas of eastern states.
Among tribals of the region Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
is the dominant religion. Some tribals also follow their indigenous religions (Sarana).
There are several places of pilgrimage for Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
. Puri
Puri () is a coastal city and a municipality in the state of Odisha in eastern India. It is the district headquarters of Puri district and is situated on the Bay of Bengal, south of the state capital of Bhubaneswar. It is also known as '' ...
in Odisha is one of the four holy City/Dham of Hindu religion and particularly known for Rath Yatra
Ratha Yatra (), or Chariot festival, is any public procession in a chariot. The term particularly refers to the annual Ratha Yatra in Odisha, Jharkhand, West Bengal and other East Indian states, particularly the Odia festival that involve a ...
festival. Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar (; ) is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Odisha. The region, especially the old town, was historically often depicted as ''Ekamra Kshetra'' (area (''kshetra'') adorned with mango trees (''ekamra'')). Bhubaneswar i ...
is considered to be the "City of Temples". Konark
Konark is a medium town in the Puri district in the state of Odisha, India. It lies on the coast by the Bay of Bengal, 65 kilometres from the capital of the state, Bhubaneswar. It is the site of the 13th-century Sun Temple, also known as the ...
houses an old sun temple
A sun temple (or solar temple) is a building used for religious or spiritual activities, such as prayer and sacrifice, dedicated to the sun or a solar deity. Such temples were built by a number different cultures and are distributed around the ...
.
Bihar Sharif
Bihar Sharif is the headquarters of Nalanda district and the fifth-largest sub-metropolitan area in the eastern Indian state of Bihar. Its name is a combination of two words: ''Bihar'', derived from '' vihara'' (meaning monastery), also the nam ...
is an important pilgrimage centre for some Muslims nearby and from other places.
In Bihar Village Harinagar Bajrang Bali temple is famous for Hindu people.
Dakshineswar Kali Temple
Dakshineswar Kali Temple is a Hindu navaratna temple in Dakshineswar, Kolkata, West Bengal, India. Situated on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River, the presiding deity of the temple is Bhavatarini, a form of Parashakti Adya Kali, otherw ...
is a historical Kali
Kali (; sa, काली, ), also referred to as Mahakali, Bhadrakali, and Kalika ( sa, कालिका), is a Hindu goddess who is considered to be the goddess of ultimate power, time, destruction and change in Shaktism. In this tra ...
temple in West Bengal
West Bengal (, Bengali: ''Poshchim Bongo'', , abbr. WB) is a state in the eastern portion of India. It is situated along the Bay of Bengal, along with a population of over 91 million inhabitants within an area of . West Bengal is the fou ...
. Kalighat Kali Temple
Kalighat Kali Temple is a Hindu temple in Kalighat, Kolkata, West Bengal, India dedicated to the Hindu goddess Kali. It is one of the Shakti Peethas.
Kalighat was a Ghat (landing stage) sacred to Kali on the old course (Adi Ganga) of the Hoo ...
in Kolkata
Kolkata (, or , ; also known as Calcutta , the official name until 2001) is the capital of the Indian state of West Bengal, on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River west of the border with Bangladesh. It is the primary business, comme ...
is the most important of all Shakti Peethas
The Shakti Pitha or the Shakti Peethas ( sa, शक्ति पीठ, , ''seat of Shakti'') are significant shrines and pilgrimage destinations in Shaktism, the goddess-centric denomination in Hinduism. The shrines are dedicated to various fo ...
in India. Belur Math
Belur Math () is the headquarters of the Ramakrishna Math and Ramakrishna Mission, founded by Swami Vivekananda, the chief disciple of Ramakrishna Paramahamsa. It is located on the west bank of Hooghly River, Belur, West Bengal, India. The ...
in Kolkata
Kolkata (, or , ; also known as Calcutta , the official name until 2001) is the capital of the Indian state of West Bengal, on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River west of the border with Bangladesh. It is the primary business, comme ...
is the headquarters of the Ramkrishna Mission founded by Swami Vivekananda
Swami Vivekananda (; ; 12 January 1863 – 4 July 1902), born Narendranath Datta (), was an Indian Hindu monk, philosopher, author, religious teacher, and the chief disciple of the Indian mystic Ramakrishna. He was a key figure in the intr ...
.
In Bihar, Gaya is known for temple for salvation of ancestors. Other places are Sultanganj in Bhagalpur
Bhagalpur is a city in the Indian state of Bihar, situated on the southern banks of the river Ganges. It is the 2nd largest city of Bihar by population and also the headquarters of Bhagalpur district and Bhagalpur division. Known as the Si ...
and Vaidyanath Jyotirlinga
Vaidyanath Jyotirlinga temple, also known as ''Baba dham'' and ''Baidyanath dham'' is one of the twelve Jyotirlingas, the most sacred abodes of Shiva. The location of Vaidyanath Jyotirlinga is disputed. The claimed locations are:
*Vaidyanath Jyot ...
in Deoghar
Deoghar (pronounced ''Devaghar'') is a major city in Jharkhand, India. It is a holy sacred place of Hinduism. It is one of the 12 ''Jyotirlinga''s sites of Hinduism (Baidyanath Temple). The sacred temples of the city make this a place for p ...
, Jharkhand. Bodh Gaya
Bodh Gaya is a religious site and place of pilgrimage associated with the Mahabodhi Temple Complex in Gaya district in the Indian state of Bihar. It is famous as it is the place where Gautama Buddha is said to have attained Enlightenment ( ...
is the city sacred to Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
. There are also other cities sacred to Jains
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religion. Jainism traces its spiritual ideas and history through the succession of twenty-four tirthankaras (supreme preachers of ''Dharma''), with the first in the current time cycle being ...
in Bihar
Bihar (; ) is a state in eastern India. It is the 2nd largest state by population in 2019, 12th largest by area of , and 14th largest by GDP in 2021. Bihar borders Uttar Pradesh to its west, Nepal to the north, the northern part of West ...
and Jharkhand.
Cuisine
West BengalBengali cuisine
Bengali cuisine ( bn, বাঙ্গালী রন্ধনপ্রণালী) is the culinary style of Bengal, a region in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent encompassing Bangladesh and the Indian states of West Bengal, Tripura ...
is a culinary style originating in Bengal
Bengal ( ; bn, বাংলা/বঙ্গ, translit=Bānglā/Bôngô, ) is a geopolitical, cultural and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal, predom ...
which is now divided between the Indian state of West Bengal
West Bengal (, Bengali: ''Poshchim Bongo'', , abbr. WB) is a state in the eastern portion of India. It is situated along the Bay of Bengal, along with a population of over 91 million inhabitants within an area of . West Bengal is the fou ...
and today's Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the mo ...
. Other regions, such as Tripura
Tripura (, Bengali: ) is a state in Northeast India. The third-smallest state in the country, it covers ; and the seventh-least populous state with a population of 36.71 lakh ( 3.67 million). It is bordered by Assam and Mizoram to the ea ...
, and the Barak Valley
The Barak Valley is located in the southern region of the Indian state of Assam. The region is named after the Barak river. The Barak valley consists of three administrative districts of Assam - namely Cachar, Karimganj, and Hailakandi. The ...
region of Assam
Assam (; ) is a state in northeastern India, south of the eastern Himalayas along the Brahmaputra and Barak River valleys. Assam covers an area of . The state is bordered by Bhutan and Arunachal Pradesh to the north; Nagaland and Manipur ...
(in India) including some parts of Jharkhand
Jharkhand (; ; ) is a state in eastern India. The state shares its border with the states of West Bengal to the east, Chhattisgarh to the west, Uttar Pradesh to the northwest, Bihar to the north and Odisha to the south. It has an area of . I ...
and Bihar
Bihar (; ) is a state in eastern India. It is the 2nd largest state by population in 2019, 12th largest by area of , and 14th largest by GDP in 2021. Bihar borders Uttar Pradesh to its west, Nepal to the north, the northern part of West ...
also have large native Bengali
Bengali or Bengalee, or Bengalese may refer to:
*something of, from, or related to Bengal, a large region in South Asia
* Bengalis, an ethnic and linguistic group of the region
* Bengali language, the language they speak
** Bengali alphabet, the w ...
populations and share this cuisine. With an emphasis on fish, vegetables and lentils served with rice as a staple diet, Bengali cuisine is known for its subtle (yet sometimes fiery) flavours, and its huge spread of confectioneries and desserts. It also has the only traditionally developed multi-course tradition from the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographical region in Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, In ...
that is analogous in structure to the modern '' service à la russe'' style of French cuisine
French cuisine () is the cooking traditions and practices from France. It has been influenced over the centuries by the many surrounding cultures of Spain, Italy, Switzerland, Germany and Belgium, in addition to the food traditions of the re ...
, with food served course-wise rather than all at once.
Bengali food has inherited a large number of influences, both foreign and pan-Indian, arising from a historical and strong trade links with many parts of the world. Bengal fell under the sway of various Turkic rulers from the early thirteenth century onwards, and was then governed by the British for two centuries (1757–1947).
Odisha
Odia cuisine
Odia cuisine is the cuisine of the Indian state of Odisha. Compared to other regional Indian cuisines, Odia cuisine uses less oil and is less spicy while nonetheless remaining flavourful. Rice is the staple food of this region. Mustard oil is ...
refers to the cooking of the eastern India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
n state of Odisha
Odisha (English: , ), formerly Orissa ( the official name until 2011), is an Indian state located in Eastern India. It is the 8th largest state by area, and the 11th largest by population. The state has the third largest population of ...
. Foods from this area are rich and varied, while relying heavily on local ingredients. The flavours are usually subtle and delicately spiced, quite unlike the fiery curries typically associated with Indian cuisine. Fish and other seafood such as crab and shrimp are popular. Chicken and mutton are also consumed, but somewhat occasionally. Only 6% of the population of Odisha is vegetarian
Vegetarianism is the practice of abstaining from the consumption of meat (red meat, poultry, seafood, insects, and the flesh of any other animal). It may also include abstaining from eating all by-products of animal slaughter.
Vegetariani ...
, and this is reflected in its cuisine. The oil base used is mostly mustard oil
Mustard oil can mean either the pressed oil used for cooking, or a pungent essential oil also known as volatile oil of mustard. The essential oil results from grinding mustard seed, mixing the grounds with water, and extracting the resulting vola ...
, but in festivals ghee
Ghee is a type of clarified butter, originating from India. It is commonly used in India for cooking, as a traditional medicine, and for religious rituals.
Description
Ghee is typically prepared by simmering butter, which is churned from ...
is used. '' Panch phutana'', a mix of cumin, mustard, fennel, fenugreek and kalonji (nigella) is widely used for tempering vegetables and dals, while ''garam masala
Garam masala Hindustani_language.html"_;"title="rom_Hindustani_language">Hindustani_/_(''garm_masala'',_"hot_spices")is_a_Spice_mix.html" ;"title="Hindustani language">Hindustani / (''garm masala'', "hot spices")">Hindustani_language.html" ;"tit ...
'' (curry powder) and ''haladi'' (turmeric) are commonly used for non-vegetarian curries. Pakhala
Pakhaḷa ( ''Pakhāḷa,'' ) is an Odia cuisine, consisting of cooked rice washed or lightly fermented in water. The liquid part of the dish is known as Toraṇi ( ''ṭorāṇi''). It is popular in the state of Odisha and its similar var ...
, a dish made of rice, water, and yogurt, that is fermented overnight, is very popular in summer, particularly in the rural areas. Oriyas are very fond of sweets and no Oriya repast is considered complete without some dessert at the end. Festivals and fasts witness a cuisine without onion and garlic, whereas other days witness an aroma of garlic and onion paste in curries. One can find restaurants serving food without onion and garlic in major places like Puri
Puri () is a coastal city and a municipality in the state of Odisha in eastern India. It is the district headquarters of Puri district and is situated on the Bay of Bengal, south of the state capital of Bhubaneswar. It is also known as '' ...
and other coastal area, which is run by Brahmin owners.
Odisha has a culinary tradition spanning centuries if not millennia. The kitchen of the Jagannath temple
The Jagannath Temple is an important Hindu temple dedicated to Jagannath, a form of Vishnu - one of the trinity of supreme divinity in Hinduism. Puri is in the state of Odisha, on the eastern coast of India. The present temple was rebuilt f ...
in Puri is reputed to be the largest in the world, with a thousand cooks, working around 752 wood-burning clay hearths called ''chulas'', to feed over 10,000 people every day.
Kolkata
Kolkata (, or , ; also known as Calcutta , the official name until 2001) is the capital of the Indian state of West Bengal, on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River west of the border with Bangladesh. It is the primary business, comme ...
File:Bengali orange rasgulla.jpg, '' Kamalabhog'' Roshogolla from West Bengal
File:Bikalkar rasagola.gif, Bikali Kar Rasagola from Odisha
Chenapoda.jpg, Chhena Poda from Odisha
Rasmalai Secretlondon 09.jpg, Rasmalai
Ras malai, rasamalai, or rossomalai is a dessert originating from the eastern regions of the Indian subcontinent. The dessert is called ''rossomalai'' in Bengali, ''ras malai'' in Hindi, and ''rasa malei'' in Odia. It is popular in India, Bangl ...
, a sweet dish popular in Odisha and West Bengal
Chenagaja.jpg, Chhena Gaja
Chhena gaja () is a sweet dish from Odisha, India. Unlike some other popular chhena-based Odia desserts, such as rasagola, which have spread throughout India, the chhena gaja remains largely popular within the state itself.
Although the ingredi ...
from Odisha
Baleswari khaja pheni Oriya cuisine.jpg, Khaja
Khaja is an Indian deep-fried pastry, commonly filled with fruit or soaked with sugar syrup.
History
Khajjaka, plain or sweet mentioned in Manasollasa, was a wheat flour preparation fried in ghee. Khaja is believed to have originated from the ...
, a sweet dish popular in Bihar, Odisha and West Bengal
Chandrakanti.jpg, Chandrakanti sweet from Odisha
Bihari cuisine
Bihari cuisine is eaten mainly in the eastern Indian state of Bihar, as well as in the places where people originating from the state of Bihar have settled: Jharkhand, Eastern Uttar Pradesh, Bangladesh, Nepal, Mauritius, South Africa, Fiji ...
is eaten mainly in Bihar
Bihar (; ) is a state in eastern India. It is the 2nd largest state by population in 2019, 12th largest by area of , and 14th largest by GDP in 2021. Bihar borders Uttar Pradesh to its west, Nepal to the north, the northern part of West ...
, as well as regions where Bihari people have settled namely, Jharkhand
Jharkhand (; ; ) is a state in eastern India. The state shares its border with the states of West Bengal to the east, Chhattisgarh to the west, Uttar Pradesh to the northwest, Bihar to the north and Odisha to the south. It has an area of . I ...
, eastern Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh (; , 'Northern Province') is a state in northern India. With over 200 million inhabitants, it is the most populated state in India as well as the most populous country subdivision in the world. It was established in 195 ...
, Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the mo ...
, Nepal
Nepal (; ne, नेपाल ), formerly the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal ( ne,
सङ्घीय लोकतान्त्रिक गणतन्त्र नेपाल ), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is ma ...
, Mauritius
Mauritius ( ; french: Maurice, link=no ; mfe, label= Mauritian Creole, Moris ), officially the Republic of Mauritius, is an island nation in the Indian Ocean about off the southeast coast of the African continent, east of Madagascar. It ...
, South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring coun ...
, Fiji
Fiji ( , ,; fj, Viti, ; Fiji Hindi: फ़िजी, ''Fijī''), officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consis ...
, some cities of Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
, Guyana
Guyana ( or ), officially the Cooperative Republic of Guyana, is a country on the northern mainland of South America. Guyana is an indigenous word which means "Land of Many Waters". The capital city is Georgetown. Guyana is bordered by the ...
, Trinidad and Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago (, ), officially the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago, is the southernmost island country in the Caribbean. Consisting of the main islands Trinidad and Tobago, and numerous much smaller islands, it is situated south of ...
, Suriname
Suriname (; srn, Sranankondre or ), officially the Republic of Suriname ( nl, Republiek Suriname , srn, Ripolik fu Sranan), is a country on the northeastern Atlantic coast of South America. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the nor ...
, Jamaica
Jamaica (; ) is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea. Spanning in area, it is the third-largest island of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean (after Cuba and Hispaniola). Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, and west of Hispa ...
and the Caribbean. Bihari cuisine includes Bhojpuri cuisine, Maithil cuisine
Maithil cuisine, also known as Mithila cuisine, is a part of Indian and Nepalese cuisine. It is the traditional cooking style of Maithils residing in the Mithila region of India and Nepal.
Maithil cuisine comprises a broad repertoire of rice, ...
and Magahi cuisine.
Dance

Odissi
Odissi (), also referred to as Orissi in old literature, is a major ancient Indian classical dance that originated in the temples of Odisha – an eastern coastal state of India.Odisha
Odisha (English: , ), formerly Orissa ( the official name until 2011), is an Indian state located in Eastern India. It is the 8th largest state by area, and the 11th largest by population. The state has the third largest population of ...
, in Eastern India. It is the oldest surviving dance form of India on the basis of archaeological evidences. Odissi has a long, unbroken tradition of 2,000 years and finds mention in the ''Natyashastra
The ''Nāṭya Śāstra'' (, ''Nāṭyaśāstra'') is a Sanskrit treatise on the performing arts. The text is attributed to sage Bharata Muni, and its first complete compilation is dated to between 200 BCE and 200 CE, but estimates var ...
'' of Bharatamuni, possibly written circa 200 BCE.
Mahari Dance is one of the important dance forms of Odisha and originated in the temples of Odisha. History of Odisha provides evidence of the 'Devadasi' cult in Odisha. Devadasis were dancing girls who were dedicated to the temples of Odisha. The Devadasis in Odisha were known as 'Maharis' and the dance performed by them came to be known as Mahari Dance.
Gotipua
Gotipua is a traditional dance form in the state of Odisha, India, and the precursor of Odissi classical dance. It has been performed in Orissa for centuries by young boys, who dress as women to praise Jagannath and Krishna. The dance is execu ...
dance is another form of dance in Odisha. In Oriya colloquial language Gotipua means single boy. The dance performance done by a single boy is known as Gotipua dance.
There are many folk dances in east India, with the best-known being Jhijhiya, Jhumair
Jhumair or Jhumar is an Indian folk dance from the Indian states of Jharkhand, Odisha, Chhattisgarh, Bihar and West Bengal. It is folk dance of Sadan, the Indo-Aryan ethnic groups of Chotanagpur. It is mainly performed during harvest season.
T ...
, Domkach
Domkach or Damkach is a folk dance of Indian states of Bihar and Jharkhand. In Bihar, Domkach dance is performed in Mithila and Bhojpur regions. In Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh (; , 'Northern Province') is a state in northern India. Wi ...
, Ghumura Dance
Ghumura dance is a folk dance of Kalahandi district of the Indian state Odisha. It is classified as folk dance as the dress code of Ghumura resembles more like a tribal dance, but there are arguments about mudra and dance forms of Ghumura bearing ...
, Sambalpuri and Chhau dance
Chhau dance, also spelled Chhou dance, is a semi classical Indian dance with martial and folk traditions. It is found in three styles named after the location where they are performed, i.e. the ''Purulia Chhau'' of West Bengal, the ''Seraikell ...
.
Jhijhiya is a cultural dance from the Mithila region.
Jhijhiya is mostly performed at time of Dusshera
Vijayadashami ( sa, विजयदशमी, Vijayadaśamī, translit-std=IAST), also known as Dussehra, Dasara or Dashain, is a major Hindu festival celebrated at the end of Navaratri every year. It is observed on the tenth day in the Hindu ...
, in dedication to Durga Bhairavi
Bhairavi ( sa, भैरवी) is a Hindu goddess, described as one of the Mahāvidyas, the ten avatars of the mother goddess. She is the consort of Bhairava.
Etymology
The name ''Bhairavi'' means "terror" or "awe-inspiring". She is th ...
, the goddess of victory. While performing jhijhiya, women put lanterns made of clay on their head and they balance it while they dance.
Jhumair
Jhumair or Jhumar is an Indian folk dance from the Indian states of Jharkhand, Odisha, Chhattisgarh, Bihar and West Bengal. It is folk dance of Sadan, the Indo-Aryan ethnic groups of Chotanagpur. It is mainly performed during harvest season.
T ...
is a folk dance in Chota Nagpur Plateau
The Chota Nagpur Plateau is a plateau in eastern India, which covers much of Jharkhand state as well as adjacent parts of Chhattisgarh, Odisha, West Bengal and Bihar. The Indo-Gangetic plain lies to the north and east of the plateau, and the ...
region of Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Odisha and West Bengal. It is performed during harvest season and festivals accompanied by musical instrument such as Madal
The madal ( ne, मादल) or maadal is a Nepalese folk musical instrument. The madal is used mainly for rhythm-keeping in Nepalese folk music. It is very popular and widely used as a hand drum in Nepal. The madal has a cylindrical body with a s ...
, Dhol
Dhol (IPA: ) can refer to any one of a number of similar types of double-headed drum widely used, with regional variations, throughout the Indian subcontinent. Its range of distribution in India, Bangladesh and Pakistan primarily includes nort ...
, Bansuri
A bansuri is an ancient side blown flute originating from the Indian subcontinent. It is an aerophone produced from bamboo and metal like material used in Hindustani classical music. It is referred to as ''nadi'' and ''tunava'' in the ''Ri ...
, Nagara, Dhak and Shehnai
The ''shehnai'' is a musical instrument, originating from the Indian subcontinent. It is made of wood, with a double reed at one end and a metal or wooden flared bell at the other end.Domkach
Domkach or Damkach is a folk dance of Indian states of Bihar and Jharkhand. In Bihar, Domkach dance is performed in Mithila and Bhojpur regions. In Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh (; , 'Northern Province') is a state in northern India. Wi ...
is folk dance in the state of Bihar, Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh and Odisha. It performed during marriage in the house of Bride and groom.
Chhau is a form of tribal martial dance popular in the Indian states of West Bengal, Jharkhand and Odisha. There are three regional variations of the dance. Seraikella Chau was developed in Seraikella
Saraikela (also spelled Seraikella) is the district headquarters and a nagar panchayat in the Seraikela Sadar subdivision of the Seraikela Kharsawan district in the Indian state of Jharkhand. It was formerly the capital of the Odia Saraikela Sta ...
, the administrative head of the Seraikela Kharsawan district of Jharkhand
Jharkhand (; ; ) is a state in eastern India. The state shares its border with the states of West Bengal to the east, Chhattisgarh to the west, Uttar Pradesh to the northwest, Bihar to the north and Odisha to the south. It has an area of . I ...
; Purulia Chau in Purulia district
Purulia district (Pron: puruliːaː) is one of the twenty-three districts of West Bengal state in Eastern India. Purulia is the administrative headquarters of the district. Some of the other important towns of Purulia district are Raghunathpur- ...
of West Bengal; and Mayurbhanj Chau in Mayurbhanj district
Mayurbhanj district is one of the 30 districts in Odisha state in eastern India. It is the largest district of Odisha by area. Its headquarters are at Baripada. Other major towns are Rairangpur, Karanjia and Udala. , it is the third-most-popu ...
of Odisha.
Ghumura Dance
Ghumura dance is a folk dance of Kalahandi district of the Indian state Odisha. It is classified as folk dance as the dress code of Ghumura resembles more like a tribal dance, but there are arguments about mudra and dance forms of Ghumura bearing ...
Archaeological evidence showsThe Heroic Dance Ghumura, Edited by Sanjay Kumar, Mahabir Sanskrutika, 2002 cave paintings from the pre-historic period discovered by Gudahandi of Kalahandi
Kalahandi (locally pronounced ''Kalahani'') is a district of Odisha in India. Archaeological evidence of Stone Age and Iron Age human settlement has been recovered from the region. Asurgarh offered an advanced, well civilised, cultured and u ...
and Yogi Matha of Nuapada district that represent the Ghumura and Damru, among other instruments. These paintings date to as early as 8000 BCE and from such painting the antiquity of musical instrument Ghumura and Damru can be imagined. The origin of Ghumura goes back to ancient times. There is a waterfall in the river valley of Indravati which was initially recognised by Chindak Naagas of Chakrakot. Many believe that Ghumura dance originated from this river valley and gradually spread into the areas between Indravati and Mahanadi, indicating this dance form belongs to the 10th century CE.
Bengali dance forms draw from folk traditions, especially those of the tribal groups, as well as from the broader Indian dance tradition. Dance forms of Bihar are another expression of rich traditions and ethnic identity. There are several folk dance forms that can keep one enthralled, such as dhobi nach, jhumarnach, manjhi, gondnach, jitiyanach, more morni, dom-domin, bhuiababa, rah baba, kathghorwa nach, jat jatin, launda nach, bamar nach, jharni, jhijhia, natua nach, bidapad nach, sohrai nach and gond nach.
Music
 Rabindra Sangeet, also known as Tagore Songs, are songs written and composed by
Rabindra Sangeet, also known as Tagore Songs, are songs written and composed by Rabindranath Tagore
Rabindranath Tagore (; bn, রবীন্দ্রনাথ ঠাকুর; 7 May 1861 – 7 August 1941) was a Bengali polymath who worked as a poet, writer, playwright, composer, philosopher, social reformer and painter. He resh ...
. They have distinctive characteristics in the music of Bengal
Bengali music ( bn, বাংলা সংগীত) comprises a long tradition of religious and secular song-writing over a period of almost a millennium. Composed with lyrics in the Bengali language, Bengali music spans a wide variety ...
, popular in India and Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the mo ...
. "Sangeet" means music, "Rabindra Sangeet" means Songs of Rabindra.
Rabindra Sangeet used Indian classical music
Indian classical music is the classical music of the Indian subcontinent. It has two major traditions: the North Indian classical music known as '' Hindustani'' and the South Indian expression known as '' Carnatic''. These traditions were not ...
and traditional folk music
Folk music is a music genre that includes traditional folk music and the contemporary genre that evolved from the former during the 20th-century folk revival. Some types of folk music may be called world music. Traditional folk music has ...
as sources. Tagore wrote some 2,230 songs.
Rabindranath Tagore
Rabindranath Tagore (; bn, রবীন্দ্রনাথ ঠাকুর; 7 May 1861 – 7 August 1941) was a Bengali polymath who worked as a poet, writer, playwright, composer, philosopher, social reformer and painter. He resh ...
was a towering figure in Indian music. Writing in Bengali
Bengali or Bengalee, or Bengalese may refer to:
*something of, from, or related to Bengal, a large region in South Asia
* Bengalis, an ethnic and linguistic group of the region
* Bengali language, the language they speak
** Bengali alphabet, the w ...
, he created a library of over 2,000 songs now known by Bengalis as ''rabindra sangeet'' whose form is primarily influenced by Hindustani classical, sub-classicals, Karnatic, western, bauls, bhatiyali and different folk songs of India. Many singers in West Bengal
West Bengal (, Bengali: ''Poshchim Bongo'', , abbr. WB) is a state in the eastern portion of India. It is situated along the Bay of Bengal, along with a population of over 91 million inhabitants within an area of . West Bengal is the fou ...
and Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the mo ...
base their entire careers on the singing of Tagore musical masterpieces. The national anthem of India and national anthem of Bangladesh are Rabindra Sangeets.
West Bengal's capital Kolkata
Kolkata (, or , ; also known as Calcutta , the official name until 2001) is the capital of the Indian state of West Bengal, on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River west of the border with Bangladesh. It is the primary business, comme ...
is also the cultural capital of India.
''Panchali'' is a form of narrative folk songs of the Indian state of West Bengal
West Bengal (, Bengali: ''Poshchim Bongo'', , abbr. WB) is a state in the eastern portion of India. It is situated along the Bay of Bengal, along with a population of over 91 million inhabitants within an area of . West Bengal is the fou ...
. The word ''Panchali'' probably originates from ''panchal'' or ''panchalika'', meaning ''puppet''. According to another school of that, ''Panchali'' originates from the word ''panch'', which means five in Bengali language
Bengali ( ), generally known by its endonym Bangla (, ), is an Indo-Aryan language native to the Bengal region of South Asia. It is the official, national, and most widely spoken language of Bangladesh and the second most widely spoken ...
, referring to the five elements of this genre: song, music, extempore versifying, poetic contests, and dance.
Music of Odisha
Odissi music
music () is a genre of classical music in India, originated from the eastern state of Odisha. The traditional ritual music for the service of Lord Jagannatha, Odissi music has a history spanning over two thousand years, authentic ''sangita-shas ...
is a classical music in India originated from the eastern state of Odisha. Indian Classical music has five significant branches: Avanti, Panchali, Udramagadhi, Hindustani and carnatic. Of these, Udramagadhi exists in the form of Odissi music. Generally, Odissi is one of the classical dances of India performed with Odissi music. Odissi music got shaped during the time of famous Oriya poet, Jayadeva, who composed lyrics meant to be sung. By the 11th century CE folk music
Folk music is a music genre that includes traditional folk music and the contemporary genre that evolved from the former during the 20th-century folk revival. Some types of folk music may be called world music. Traditional folk music has ...
of Odisha existing in the form of Triswari, Chatuhswari, and Panchaswari was modified into the classical style. However, Odissi songs were written even before the Odia language developed. Odissi music has a rich legacy dating back to the 2nd century BCE, when king Kharvela
Kharavela (also transliterated Khārabēḷa) was a monarch of Kalinga Kalinga may refer to:
Geography, linguistics and/or ethnology
* Kalinga (historical region), a historical region of India
** Kalinga (Mahabharata), an apocryphal kingdom m ...
, the ruler of Odisha (Kalinga Kalinga may refer to:
Geography, linguistics and/or ethnology
* Kalinga (historical region), a historical region of India
** Kalinga (Mahabharata), an apocryphal kingdom mentioned in classical Indian literature
** Kalinga script, an ancient writin ...
) patronised this music and dance.
Like Hindustani and Carnatic systems, Odissi music is a separate system of Indian classical music and is having all the essential as well as potential ingredients of Indian Classical form. But it has not come to limelight due to apathy from the time of British rule in Odisha, want of its proper study, revival, propagation, etc. Despite the fact, the traditional music form could be saved and maintained in its pristine form. Thanks to the musicians particularly of Jaga Akhadas of Puri district, who could develop and maintain the music. The music movement of Odisha, however, took a different turn after independence.
Like other aspects of her culture, music of the sacred land (Odisha) is charming, colourful, variegated encompassing various types. The existing musical tradition of Odisha, the cumulative experience of the last two thousand five hundred years if not more, can broadly be grouped under five categories such as: (1) Tribal Music, (2) Folk Music, (3) Light Music, (4) Light-Classical Music, (5) Classical Music, which need a short elucidations for better understanding the subject in all India context.
The tribal music as the title signifies is confined to the tribals living mainly in the hilly and jungle regions and sparsely in the coastal belt of Odisha. Odisha has the third largest concentration of tribes constituting about one fourth of the total population. They are distributed over 62 tribal communities.
Odisha is the treasure house of Folk Songs which are sung on different festivals and specific occasions in their own enjoyment. Folk music in general is the expression of the ethos and mores of the folk communities. Of the bewildering variety of folk music of Odisha, mention may be made of Geeta, Balipuja Geeta, Kela Keluni Geeta, Dalkhai Geeta, Kendra Geeta, Jaiphula Geeta, Ghumura Geeta, Ghoda Nacha and Danda Nacha Geeta, Gopal Ugala and Osa-Parva-Geeta etc.
Bhajan, Janan, Oriya songs based on ragas, Rangila Chaupadi etc. are grouped under Light classical music, which forms an important segment of Oriya music. Sri Geetagovinda, Anirjukta Pravadha, Divya Manusi Prabandha, Chautisa, Chhanda, Chaupadi (now known as Odissi), Champu, Malasri, Sariman, nVyanjani, Chaturang, Tribhang, Kuduka Geeta, Laxana and Swaramalika are the various sub-forms, which individually or collectively constitute the traditional Odissi music
music () is a genre of classical music in India, originated from the eastern state of Odisha. The traditional ritual music for the service of Lord Jagannatha, Odissi music has a history spanning over two thousand years, authentic ''sangita-shas ...
. These sub-forms of the traditional Odissi music, can be categorised under the classical music of Odisha.
Sports
TheEast Zone cricket team
The East Zone cricket team is a first-class cricket team that represents eastern India in the Duleep Trophy and Syed Mushtaq Ali Trophy Inter Zonal. It is a composite team of five first-class Indian teams from eastern India competing in the Ranj ...
is a first-class cricket
Cricket is a bat-and-ball game played between two teams of eleven players on a field at the centre of which is a pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two bails balanced on three stumps. The batting side scores runs by st ...
team that represents Eastern India in the Duleep Trophy
The Duleep Trophy, also known as Mastercard Duleep trophy due to sponsorship reasons, is a domestic first-class cricket competition played in India. Named after Kumar Shri Duleepsinhji of Nawanagar (also known as 'Duleep'), the competition wa ...
and Deodhar Trophy. It is a composite team of five first-class Indian teams from Eastern India competing in the Ranji Trophy
The Ranji Trophy (also known as Mastercard Ranji Trophy for sponsorship reasons) is a domestic first-class cricket championship played in India between multiple teams representing regional and state cricket associations. Board of Control for Cr ...
, containing notably the Bengal
Bengal ( ; bn, বাংলা/বঙ্গ, translit=Bānglā/Bôngô, ) is a geopolitical, cultural and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal, predom ...
, Jharkhand
Jharkhand (; ; ) is a state in eastern India. The state shares its border with the states of West Bengal to the east, Chhattisgarh to the west, Uttar Pradesh to the northwest, Bihar to the north and Odisha to the south. It has an area of . I ...
and Odisha
Odisha (English: , ), formerly Orissa ( the official name until 2011), is an Indian state located in Eastern India. It is the 8th largest state by area, and the 11th largest by population. The state has the third largest population of ...
from East India amongst the bunch.
In West Bengal
 The most popular sports in Kolkata are
The most popular sports in Kolkata are football
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kicking a ball to score a goal. Unqualified, the word ''football'' normally means the form of football that is the most popular where the word is used. Sports commonly ...
and cricket
Cricket is a bat-and-ball game played between two teams of eleven players on a field at the centre of which is a pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two bails balanced on three stumps. The batting side scores runs by st ...
. The city is a centre of football activity in India and is home to top national clubs such as Mohun Bagan A.C.
Mohun Bagan Athletic Club is an Indian professional sports club based in Kolkata, West Bengal. Founded in 1889, its football section is one of the oldest in India and Asia. The club is most notable for its victory over East Yorkshire Regiment ...
, Kingfisher East Bengal F.C., Prayag United S.C. and the Mohammedan Sporting Club. Calcutta Football League, which was started in 1898, is the oldest football league in Asia. Mohun Bagan A.C., one of the oldest football clubs in Asia, is the only organisation to be dubbed a "National Club of India". As in the rest of India, cricket is popular in Kolkata and is played on grounds and in streets throughout the city. Kolkata has an Indian Premier League
The Indian Premier League (IPL), also known as TATA IPL for sponsorship reasons, is a men's T20 franchise cricket league of India. It is annually contested by ten teams based out of seven Indian cities and three Indian states. The leagu ...
franchise known as the Kolkata Knight Riders
Kolkata Knight Riders (KKR) are a franchise cricket team representing the city of Kolkata in the Indian Premier League. The franchise is owned by Bollywood actor Shah Rukh Khan, actress Juhi Chawla and her spouse Jay Mehta. The Knight Riders ...
; the Cricket Association of Bengal
Cricket Association of Bengal (CAB) is the governing body for cricket in the Indian state of West Bengal. Its headquarters are located in the Eden Gardens stadium, Kolkata. It is a full member of Board of Control for Cricket in India.
It gov ...
, which regulates cricket in West Bengal, is also based in the city. Tournaments, especially those involving cricket, football, badminton
Badminton is a racquet sport played using racquets to hit a shuttlecock across a net. Although it may be played with larger teams, the most common forms of the game are "singles" (with one player per side) and "doubles" (with two players p ...
, and carrom
Carrom is a tabletop game of Indian origin in which players flick discs, attempting to knock them to the corners of the board. The game is very popular in the Indian subcontinent, and is known by various names in different languages. In Sou ...
, are regularly organised on an inter-locality or inter-club basis. The Maidan, a vast field that serves as the city's largest park, hosts several minor football and cricket clubs and coaching institutes.
Eden Gardens
The Eden Gardens is a cricket ground in Kolkata, India. Established in 1864, it is the oldest and second-largest cricket stadium in India and third-largest in the world. The stadium currently has a capacity of 66,000.
Eden Gardens is often re ...
, which has a capacity of 90,000 as of 2011, hosted the final match of the 1987 Cricket World Cup
The 1987 Cricket World Cup (officially known as the Reliance Cup 1987 for sponsorship reasons) was the fourth Cricket World Cup. It was held from 8 October to 8 November 1987 in India and Pakistan – the first such tournament to be held outside ...
. It is home to the Bengal cricket team
The Bengal cricket team represents the Indian state of West Bengal in domestic first-class cricket. It is considered Eastern India's strongest cricket team. The team plays its home matches at the historic Eden Gardens in Kolkata. Bengal has wo ...
and the Kolkata Knight Riders. The multi-use Salt Lake Stadium
The Vivekananda Yuba Bharati Krirangan (VYBK; ), commonly known as the Salt Lake Stadium, is an all-seater multi-purpose stadium located in Bidhannagar, with current capacity of 85,000 spectators. Named after Swami Vivekananda, the stadium f ...
, also known as Yuva Bharati Krirangan, is the world's second-largest football facility by seating capacity
Seating capacity is the number of people who can be seated in a specific space, in terms of both the physical space available, and limitations set by law. Seating capacity can be used in the description of anything ranging from an automobile tha ...
as of 2010. The Calcutta Cricket and Football Club is the second-oldest cricket club in the world. Kolkata has three 18-hole golf courses. The oldest is at the Royal Calcutta Golf Club
Royal Calcutta Golf Club (RCGC) in Kolkata, India was established in 1829 and is the oldest golf club in India and the first outside Great Britain.
RCGC has an 18-hole golf course with the following detail:
*Yardage: 7195/6871
*Par: 72
*Ratin ...
, and was the first golf club to be built outside the United Kingdom. The other two are located at the Tollygunge Club
The Tollygunge Club (Bengali: টালিগঞ্জ ক্লাব), popularly called Tolly, is a country club in India, located in Tollygunge in south Kolkata.
Sir William Cruikshank established the club as an equestrian sports facility i ...
and at Fort William. The Royal Calcutta Turf Club
The Royal Calcutta Turf Club (RCTC) is a horse racing organisation which was founded in 1847 in Calcutta, British India (now Kolkata). Horse events and sports were initially organised for the British cavalry at Akra before they were moved to the ...
hosts horse racing and polo matches. The Calcutta Polo Club
Calcutta Polo Club is a polo club located in Kolkata, West Bengal, India. It was established in 1862 and is considered as the oldest polo club of the world in existence.
History
The modern game of polo, though formalised and popularised by ...
is considered the oldest extant polo club in the world. The Calcutta South Club is a venue for national and international tennis tournaments; it held the first grass-court national championship in 1946. In the period 2005–2007, Sunfeast Open
The Sunfeast Open was an annual Women's Tennis Association, WTA Tour tennis tournament that was started in Kolkata in 2005. The event was a Tier III-tournament with a prize money of USD 175,000 and was played on indoors greenset. The fourth ed ...
, a tier-III tournament on the Women's Tennis Association
The Women's Tennis Association (WTA) is the principal organizing body of women's professional tennis. It governs the WTA Tour which is the worldwide professional tennis tour for women and was founded to create a better future for women's tenn ...
circuit, was held in the Netaji Indoor Stadium
The Netaji Subhash Chandra Bose Indoor Stadium is an indoor sports arena in Kolkata, West Bengal, India. The facility seats 12,000 people. This indoor stadium is located just beside the Eden Gardens. It used to host the Sunfeast Open, a WTA To ...
; it has since been discontinued.
 The
The Calcutta Rowing Club
The Calcutta Rowing Club (CRC), located in Kolkata, India, was founded in 1858 and is one of the oldest rowing clubs of its kind outside the United Kingdom.
History
The club's early history was lost in the great cyclone which hit Calcutta in ...
hosts rowing
Rowing is the act of propelling a human-powered watercraft using the sweeping motions of oars to displace water and generate reactional propulsion. Rowing is functionally similar to paddling, but rowing requires oars to be mechanically ...
heats and training events. Kolkata, considered the leading centre of rugby union in India
Rugby union in India is a minor sport. However, it is a fast-growing sport as some Indian sporting clubs are beginning to embrace the game. Rugby union is the second most popular winter sport after association football in India, which itself trail ...
, gives its name to the oldest international tournament in rugby union, the Calcutta Cup
The Calcutta Cup is the trophy awarded to the winner of the rugby match between England and Scotland played annually in the Six Nations Championship. Like the match itself (England–Scotland), the Calcutta Cup is the oldest trophy contested be ...
. The Automobile Association of Eastern India, established in 1904, and the Bengal Motor Sports Club are involved in promoting motor sports and car rallies in Kolkata and West Bengal. The Beighton Cup
Beighton Cup is a field hockey tournament organized by Hockey Bengal (formerly the Bengal Hockey Association). Instituted in 1895, it is one of the oldest field hockey tournaments in the world and is held every year at Kolkata.
History Aristocr ...
, an event organised by the Bengal Hockey Association and first played in 1895, is India's oldest field hockey
Field hockey is a team sport structured in standard hockey format, in which each team plays with ten outfield players and a goalkeeper. Teams must drive a round hockey ball by hitting it with a hockey stick towards the rival team's shooting ...
tournament; it is usually held on the Mohun Bagan Ground
Mohun Bagan Ground, also known as Mohun Bagan–Calcutta FC Ground, is a football stadium located in the maidan region of central Kolkata, just opposite the Eden Gardens. The stadium is leased to Mohun Bagan AC and is mostly used as training gro ...
of the Maidan. Athletes from Kolkata include Sourav Ganguly
Sourav Chandidas Ganguly (; natively spelled as Gangopadhyay; born 8 July 1972), affectionately known as Dada (meaning ''"elder brother"'' in Bengali), is an Indian cricket administrator, commentator and former national cricket team captain w ...
and Pankaj Roy, who are former captains
Captain is a title, an appellative for the commanding officer of a military unit; the supreme leader of a navy ship, merchant ship, aeroplane, spacecraft, or other vessel; or the commander of a port, fire or police department, election precinct, e ...
of the Indian national cricket team
The India men's national cricket team, also known as Team India or the Men in Blue, represents India in men's international cricket. It is governed by the Board of Control for Cricket in India (BCCI), and is a Full Member of the Internationa ...
; Olympic
Olympic or Olympics may refer to
Sports
Competitions
* Olympic Games, international multi-sport event held since 1896
** Summer Olympic Games
** Winter Olympic Games
* Ancient Olympic Games, ancient multi-sport event held in Olympia, Greece bet ...
tennis bronze medallist Leander Paes
Leander Adrian Paes ( ; born 17 June 1973) is an Indian former professional tennis player. He is regarded as one of the greatest doubles tennis players ever. He holds the record for the most doubles wins in the Davis Cup. Paes won eight men's ...
, golfer Arjun Atwal
Arjun Singh Atwal (born 20 March 1973) is an Indian professional golfer who has played on the Asian Tour and the European Tour and is the first player born in India to become a member of, and later win a tournament on the U.S.-based PGA Tour.
...
, and former footballers Sailen Manna
Sailendra Nath Manna ( bn, শৈলেন মান্না; 1 September 1924 – 27 February 2012), known popularly as Sailen Manna, was an Indian football player who represented the India national team between 1948 and 1956. Predominantly p ...
, Chuni Goswami, P. K. Banerjee and Subrata Bhattacharya.
The Cricket Association of Bengal (CAB) is the governing body for cricket
Cricket is a bat-and-ball game played between two teams of eleven players on a field at the centre of which is a pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two bails balanced on three stumps. The batting side scores runs by st ...
in West Bengal
West Bengal (, Bengali: ''Poshchim Bongo'', , abbr. WB) is a state in the eastern portion of India. It is situated along the Bay of Bengal, along with a population of over 91 million inhabitants within an area of . West Bengal is the fou ...
. Its headquarters is in the Eden Gardens
The Eden Gardens is a cricket ground in Kolkata, India. Established in 1864, it is the oldest and second-largest cricket stadium in India and third-largest in the world. The stadium currently has a capacity of 66,000.
Eden Gardens is often re ...
stadium. It organises different types of cricket tournaments in West Bengal.Cricket Association of Bengal
Cricket Association of Bengal (CAB) is the governing body for cricket in the Indian state of West Bengal. Its headquarters are located in the Eden Gardens stadium, Kolkata. It is a full member of Board of Control for Cricket in India.
It gov ...
is affiliated to the Board of control for cricket in India is the parent body or governing the game of Cricket in Bengal, and involved in conducting the game of cricket in Bengal. The Cricket Association of Bengal promotes and develops Cricket by conducting various League Tournaments, tournaments for the age group Under-13, Under-16, and Under-19 and Under-21 categories. CAB also conducts National and International Tournaments.
In Odisha

 The most popular sports in Odisha are
The most popular sports in Odisha are hockey
Hockey is a term used to denote a family of various types of both summer and winter team sports which originated on either an outdoor field, sheet of ice, or dry floor such as in a gymnasium. While these sports vary in specific rules, numbers o ...
and cricket
Cricket is a bat-and-ball game played between two teams of eleven players on a field at the centre of which is a pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two bails balanced on three stumps. The batting side scores runs by st ...
. The Odisha Cricket Association (OCA) is the governing body of the cricket
Cricket is a bat-and-ball game played between two teams of eleven players on a field at the centre of which is a pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two bails balanced on three stumps. The batting side scores runs by st ...
activities in the Odisha
Odisha (English: , ), formerly Orissa ( the official name until 2011), is an Indian state located in Eastern India. It is the 8th largest state by area, and the 11th largest by population. The state has the third largest population of ...
state of India and the Odisha cricket team
The Odisha cricket team (known as Orissa until 2011) is a domestic cricket team based in the Indian state of Odisha. It is in the elite group of the Ranji Trophy.
Its main home ground is Barabati Stadium in Cuttack. Home matches are also playe ...
. It is affiliated to the Board of Control for Cricket in India
The Board of Control for Cricket in India (BCCI) is the national governing body for cricket in India. Its headquarters are situated at Cricket centre, Wankhede Stadium in Mumbai. The BCCI is the richest governing body of cricket in the worl ...
. The Barabati Stadium
The Barabati Stadium is an Indian sports stadium used mostly for cricket and association football, and also sometimes for concerts and field hockey, located in Cuttack, Odisha. It is a regular venue for international cricket and is the home gro ...
in Cuttack
Cuttack (, or officially Kataka ) in Odia is the former capital and the second largest city in the Indian state of Odisha. It is the headquarters of the Cuttack district. The name of the city is an anglicised form of ''Kataka'' which literally ...
hosts international cricket matches. The Odisha Cricket Association promotes and develops Cricket by conducting various League Tournaments, Tournaments for the age group Under-13, Under-15, Under-17, and Under-19, Under-22 and Under-25 categories besides organising and conducting National Tournaments. The OCA started a local Twenty-20 tournament, Odisha Premier League (OPL) in the lines of Indian Premier League
The Indian Premier League (IPL), also known as TATA IPL for sponsorship reasons, is a men's T20 franchise cricket league of India. It is annually contested by ten teams based out of seven Indian cities and three Indian states. The leagu ...
in 2011. OCA manages the Barabati Stadium
The Barabati Stadium is an Indian sports stadium used mostly for cricket and association football, and also sometimes for concerts and field hockey, located in Cuttack, Odisha. It is a regular venue for international cricket and is the home gro ...
and has got infrastructures and facilities like Odisha cricket academy, newly built Sachin Tendulkar Indoor cricket hall and many grounds like DRIEMS cricket stadium, Ravenshaw university ground, SCB medical ground, Nimpur ground, Basundhara (Bidanasi) ground, Sunshine Ground etc. The Odisha Premier League (OPL) was initiated by Odisha Cricket Association (OCA), Cuttack
Cuttack (, or officially Kataka ) in Odia is the former capital and the second largest city in the Indian state of Odisha. It is the headquarters of the Cuttack district. The name of the city is an anglicised form of ''Kataka'' which literally ...
, India in line of Indian Premier League
The Indian Premier League (IPL), also known as TATA IPL for sponsorship reasons, is a men's T20 franchise cricket league of India. It is annually contested by ten teams based out of seven Indian cities and three Indian states. The leagu ...
(IPL). The popularity of hockey in Odisha
Odisha (English: , ), formerly Orissa ( the official name until 2011), is an Indian state located in Eastern India. It is the 8th largest state by area, and the 11th largest by population. The state has the third largest population of ...
is also very high. Many national players in hockey are from Odisha. Lazarus Barla, Prabodh Tirkey
Prabodh Tirkey (born 6 October 1984) is an Indian hockey midfielder. He is a former captain of the Indian hockey team.
Personal life
Prabodh is the younger brother of the Indian hockey player Ignace Tirkey, who also has captained the Indian S ...
, Dilip Tirkey
Dilip Tirkey (born 25 November 1977), is a former Indian field hockey player, Politician and Sports Administrator. His former playing position was of full back. He was best known for his penalty corner hit. Dilip was one of the most ...
, Ignace Tirkey, Jyoti Sunita Kullu
Jyoti Sunita Kullu (born 9 September 1978 in Sundargarh, Odisha) is a female field hockey player from India, who made her international debut for her native country in 1996 in Delhi at the Indira Gandhi Gold Cup. In 2002, she became the topsc ...
, Subhadra Pradhan
Subhadra Pradhan (born 5 June 1986) is an Indian field hockey player.
Early life
Subhadra Pradhan was born on 5 June 1986 in Saunamara, a small town in Odisha to an Adivasi family. She did schooling in Birsa Munda school and pre-university edu ...
, Birendra Lakra
Birendra Lakra (born 3 February 1990) is an Indian professional field hockey player. He represents India in men's field hockey and recently came out of retirement alongside Rupinderpal Singh and will be the Captain of Indian team in the Asia Cu ...
and Anupa Barla
Anupa Barla (born 6 May 1994) is an Indian female field hockey player.
References
1994 births
Living people
People from Sundergarh district
Indian female field hockey players
Field hockey players from Odisha
Sportswomen from Odisha
...
are the few names who brought the fame to Indian hockey in International level. Premier Hockey League
Premier Hockey League (PHL) was a professional field hockey league competition for clubs in the top division of the Indian hockey system. There were seven teams in the PHL. The competition was held every year from 2005 until 2008.
History
The ...
(PHL) was the league competition for field hockey
Field hockey is a team sport structured in standard hockey format, in which each team plays with ten outfield players and a goalkeeper. Teams must drive a round hockey ball by hitting it with a hockey stick towards the rival team's shooting ...
clubs in the top divisions of the Indian hockey system. There were seven teams in the PHL and in East India the only team was the Orissa Steelers
The Orissa Steelers are the winners of the Premier Hockey League 2007, India's only national league level Field Hockey tournament. The originally proposed name for the team was Rourkela Steelers after the city which is said to be the Hockey Capit ...
who won Premier Hockey League 2007. Odisha has a franchise in Hockey India League HIL named Kalinga Lancers
Kalinga Lancers (abbreviated as KAL) is a field hockey team based in Bhubaneswar, Odisha that plays in the Hockey India League. It is jointly owned by Odisha Industrial Infrastructure Development Corporation (IDCO) and Mahanadi Coalfield Limi ...
owned by Odisha Industrial Infrastructure Development Corporation and MCL. Odisha got its first ISL club Odisha FC, based in Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar (; ) is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Odisha. The region, especially the old town, was historically often depicted as ''Ekamra Kshetra'' (area (''kshetra'') adorned with mango trees (''ekamra'')). Bhubaneswar i ...
, which was formed in 2019 after being shifted from Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, primarily its western or right bank, Delhi shares borders w ...
. Its home ground is the 15,000 seater Kalinga Stadium
The Kalinga Stadium is a multi-purpose International stadium in Bhubaneswar, Odisha, India. Its foundation stone was laid by former chief minister of Odisha Late Biju Patnaik in 1978. It is the home ground of the I League Club Indian Arrows ...
. Bhubaneswar is referred to as the "Sports Capital of India".
Ports


Kolkata Port
Port of Kolkata or Kolkata Port, officially known as Syama Prasad Mookerjee Port Trust (formerly Kolkata Port Trust), is the only riverine major port of India, located in the city of Kolkata, West Bengal, around from the sea. It is the olde ...
, Paradip Port
Paradip Port is a natural, deep-water port on the East coast of India in Paradip, just from Jagatsinghpur city in Jagatsinghpur district of Odisha, India. It is at the confluence of the Mahanadi river and the Bay of Bengal, south of Kolkata a ...
, Dhamra Port
The Dhamra Port is a port in Bhadrak district, Odisha, India, on the shore of the Bay of Bengal about seven kilometres from the old port of Dhamra. The agreement to develop the port was signed in April 1998. The Dhamra Port Company Limited ( ...
and Haldia
Haldia is an industrial port city in Purba Medinipur in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is a major river port and industrial belt located approximately southwest of Kolkata near the mouth of the Hooghly River, one of the distributarie ...
are 4 major ports in East India. Subarnarekha Port
Subarnarekha port formerly known as Kirtania port is a deep-water, all-weather port proposed to be constructed at the mouth of Subarnarekha River in Balasore district in the Indian state of Odisha. The foundation stone for the port was laid in ...
, Kulpi Port, Gopalpur Port
Gopalpur port is a deep sea port of Gopalpur in Ganjam District, Odisha, India. The port has been developed on the banks of the Bay of Bengal. The seaport will increase the sea trade of Odisha, as well as industry and employment.
The Odisha gov ...
are minor ports in East India.
See also
* Eastern States Agency, colonial office of the Bengal Presidency of British India, created by merging the Chhattisgarh States – and Orissa States agencies in 1933, to which the Bengal States Agency was added in 1936; included part of Burma *North India
North India is a loosely defined region consisting of the northern part of India. The dominant geographical features of North India are the Indo-Gangetic Plain and the Himalayas, which demarcate the region from the Tibetan Plateau and Cen ...
* Northeast India
, native_name_lang = mni
, settlement_type =
, image_skyline =
, image_alt =
, image_caption =
, motto =
, image_map = Northeast india.png
, ...
* South India
South India, also known as Dakshina Bharata or Peninsular India, consists of the peninsular southern part of India. It encompasses the Indian states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and Telangana, as well as the union terr ...
* West India
Western India is a loosely defined region of India consisting of its western part. The Ministry of Home Affairs in its Western Zonal Council Administrative division includes the states of Goa, Gujarat, and Maharashtra along with the Unio ...
References and footnotes
External links
* * {{Geography of India Regions of India