The Eastern Front or Eastern Theater of
World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
(german: Ostfront; ro, Frontul de răsărit; russian: Восточный фронт, Vostochny front) was a
theater of operations that encompassed at its greatest extent the entire frontier between
Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
and
Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and ...
on one side and
Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
,
Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedo ...
, the
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
, and
Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
on the other. It stretched from the
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and ...
in the north to the
Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
in the south, involved most of
Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, whic ...
, and stretched deep into
Central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern Europe, based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. The Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) between Catholicism and Protestantism significantly shaped the a ...
as well. The term contrasts with "
Western Front", which was being fought in
Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to th ...
and
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
.
During 1910, Russian General
Yuri Danilov
Yuri Nikiforovich Danilov ; – 3 February 1937) served as General of the Infantry in the Russian Army during World War I.
From 1907 to 1914, Danilov was in charge of the Intelligence Section of Russian Main Staff of the Imperial Russian Army.' ...
developed "Plan 19" under which four armies would invade
East Prussia. This plan was criticised as Austria-Hungary could be a greater threat than the German Empire. So instead of four armies invading East Prussia, the Russians planned to send two armies to East Prussia, and two armies to defend against Austro-Hungarian forces invading from
Galicia. In the opening months of the war, the
Imperial Russian Army attempted an
invasion of eastern Prussia in the
Northwestern theater, only to be
beaten back by Germany after some
initial success. At the same time, in the south, they successfully
invaded Galicia, defeating the Austro-Hungarian forces there. In
Russian Poland
Congress Poland, Congress Kingdom of Poland, or Russian Poland, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland, was a polity created in 1815 by the Congress of Vienna as a semi-autonomous Polish state, a successor to Napoleon's Duchy of Warsaw. It w ...
, the Germans failed to
take Warsaw. But by 1915, the German and Austro-Hungarian forces were on the advance, dealing the Russians heavy casualties
in Galicia and
in Poland, forcing them to
retreat.
Grand Duke Nicholas was
sacked from his position as the commander-in-chief and replaced by Tsar Nicholas himself. Several offensives against the Germans in 1916 failed, including
Lake Naroch Offensive
The Lake Naroch offensive in 1916 was an unsuccessful Russian offensive on the Eastern Front in World War I. It was launched at the request of Marshal Joseph Joffre and intended to relieve the German pressure on French forces. Due to lack of reco ...
and the
Baranovichi Offensive
The Baranovichi offensive was a battle fought on the Eastern Front during World War I between an army of Russia and the forces of Germany and Austria-Hungary in July 1916.
Background
Concurrent to an attack by Russian Southwestern Front, the ...
. However, General
Aleksei Brusilov oversaw a highly successful operation against Austria-Hungary that became known as the
Brusilov offensive, which saw the Russian Army make large gains.
Being the largest and most lethal offensive of WW1, the effects of the Brusilov offensive were far reaching. It helped to relieve the German pressure on
Battle of Verdun
The Battle of Verdun (french: Bataille de Verdun ; german: Schlacht um Verdun ) was fought from 21 February to 18 December 1916 on the Western Front in France. The battle was the longest of the First World War and took place on the hills north ...
, while also helping to relieve the Austro-Hungarian pressure on the Italians. As a result, the Austro-Hungarian Armed forces were fatally weakened, and finally Romania decided to enter the war on the side of the Allied Forces. However, the Russian human and material losses also greatly contributed to the
Russian revolutions.
The Kingdom of Romania
entered the war in August 1916. The Allied Powers promised the region of
Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the Ap ...
(which was part of Austria-Hungary) in return for Romanian support. The Romanian Army
invaded Transylvania and had initial successes, but was forced to stop and was pushed back by the Germans and Austro-Hungarians when Bulgaria attacked them from the south. Meanwhile, a
revolution
In political science, a revolution (Latin: ''revolutio'', "a turn around") is a fundamental and relatively sudden change in political power and political organization which occurs when the population revolts against the government, typically due ...
occurred in Russia in March 1917 (one of the causes being the hardships of the war). Tsar Nicholas II was forced to abdicate and a
Russian Provisional Government was founded, with
Georgy Lvov as its first leader, who was eventually replaced by
Alexander Kerensky.
The newly formed
Russian Republic continued to fight the war alongside Romania and the rest of the Entente in desultory fashion. It was
overthrown by the
Bolsheviks
The Bolsheviks (russian: Большевики́, from большинство́ ''bol'shinstvó'', 'majority'),; derived from ''bol'shinstvó'' (большинство́), "majority", literally meaning "one of the majority". also known in English ...
in November 1917. Following the
Armistice of Focșani
The Armistice of Focșani ( ro, Armistițiul de la Focșani, also called the Truce of Focșani) was an agreement that ended the hostilities between Romania (member of the Allied Powers) and the Central Powers in World War I. It was signed on 9 ...
between Romania and the Central Powers, Romania also signed a
peace treaty
A peace treaty is an agreement between two or more hostile parties, usually countries or governments, which formally ends a state of war between the parties. It is different from an armistice
An armistice is a formal agreement of warring ...
with the Central Powers on 7 May 1918, however it was canceled by Romania on 10 November 1918. The
new government established by the Bolsheviks signed the
Treaty of Brest-Litovsk with the Central Powers in March 1918, taking it out of the war; leading to Central Powers victory in the Eastern Front and Russian defeat in World War I.
Geography
The front in the east was much longer than that in the west. The theater of war was roughly delimited by the
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and ...
in the west and
Minsk
Minsk ( be, Мінск ; russian: Минск) is the capital and the largest city of Belarus, located on the Svislach and the now subterranean Niamiha rivers. As the capital, Minsk has a special administrative status in Belarus and is the admi ...
in the east, and
Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
in the north and the
Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
in the south, a distance of more than . This had a drastic effect on the nature of the warfare.

While the war on the
Western Front developed into
trench warfare
Trench warfare is a type of land warfare using occupied lines largely comprising military trenches, in which troops are well-protected from the enemy's small arms fire and are substantially sheltered from artillery. Trench warfare became ar ...
, the battle lines on the Eastern Front were much more fluid and trenches never truly developed. This was because the greater length of the front ensured that the density of soldiers in the line was lower so the line was easier to break. Once broken, the sparse communication networks made it difficult for the defender to rush reinforcements to the rupture in the line, mounting rapid counteroffensives to seal off any breakthrough.
Propaganda
Propaganda was a key component of the culture of World War I. It was often shown through state-controlled media, and helped to bolster
nationalism
Nationalism is an idea and movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the state. As a movement, nationalism tends to promote the interests of a particular nation (as in a group of people), Smith, Anthony. ''Nationalism: The ...
and
patriotism within countries. On the Eastern Front, propaganda took many forms such as opera, film, spy fiction, theater, spectacle, war novels and graphic art. Across the Eastern Front the amount of propaganda used in each country varied from state to state. Propaganda took many forms within each country and was distributed by many different groups. Most commonly the state produced propaganda, but other groups, such as anti-war organizations, also generated propaganda.
Initial situation in belligerent countries
Germany
Prior to the outbreak of war, German strategy was based almost entirely on the so-called
Schlieffen Plan
The Schlieffen Plan (german: Schlieffen-Plan, ) is a name given after the First World War to German war plans, due to the influence of Field Marshal Alfred von Schlieffen and his thinking on an invasion of France and Belgium, which began on ...
. With the
Franco-Russian Agreement in place, Germany knew that war with either of these combatants would result in war with the other, which meant that there would be war in both the west and the east (
two-front war
According to military terminology, a two-front war occurs when opposing forces encounter on two geographically separate fronts. The forces of two or more allied parties usually simultaneously engage an opponent in order to increase their chance ...
). Therefore, the German General Staff, under Alfred von Schlieffen and then
Helmuth von Moltke the Younger
Graf Helmuth Johannes Ludwig von Moltke (; 25 May 1848 – 18 June 1916), also known as Moltke the Younger, was a German general and Chief of the Great German General Staff. He was also the nephew of '' Generalfeldmarschall'' ''Graf'' Helmuth ...
, planned a quick, all-out ground war on the Western Front to take France and, upon victory, Germany would turn its attention to Russia in the east.
Schlieffen believed Russia would not be ready or willing to move against and attack Germany due to the huge losses of military equipment that Russia had suffered in the
Russo-Japanese War
The Russo-Japanese War ( ja, 日露戦争, Nichiro sensō, Japanese-Russian War; russian: Ру́сско-япóнская войнá, Rússko-yapónskaya voyná) was fought between the Empire of Japan and the Russian Empire during 1904 and 1 ...
of 1904–1905, its low population density and
lack of railroads.
Conversely, the
Imperial German Navy believed it could be victorious over Britain with Russian neutrality, something which Moltke knew would not be possible.
Romania

In the immediate years preceding the
First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, the Kingdom of Romania was involved in the
Second Balkan War on the side of Serbia, Montenegro, Greece and the Ottoman Empire against Bulgaria. The
Treaty of Bucharest, signed on 10 August 1913, ended the Balkan conflict and added 6,960 square kilometers to Romania's territory. Although militarized, Romania decided upon a policy of neutrality at the start of the First World War, mainly due to having territorial interests in both Austria-Hungary (
Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the Ap ...
and
Bukovina) and in Russia (
Bessarabia). Strong cultural influences also affected Romanian leanings, however. King
Carol I, as a
Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen
( en, Nothing without God)
, national_anthem =
, common_languages = German
, religion = Roman Catholic
, currency =
, title_leader = Prince
, leader1 ...
, favoured his Germanic roots, while the Romanian people, influenced by their Orthodox church and Latin-based language, were inclined to join France. Perhaps King Carol's attempts at joining the war on the side of the Central powers would have been fruitful had he not died in 1914, but Romanian disenchantment with Austria-Hungary had already influenced public and political opinion. French endorsement of Romanian action against Bulgaria, and support of the terms of the Treaty of Bucharest was particularly effective at inclining Romania towards the Entente. Furthermore, Russian courting of Romanian sympathies, exemplified by the visit of the Tsar to
Constanța on 14 June 1914, signaled in a new era of positive relations between the two countries. Nevertheless, King
Ferdinand I of Romania maintained a policy of neutrality, intending to gain the most for Romania by negotiating between competing powers. The result of the negotiations with the Entente was the
Treaty of Bucharest (1916), which stipulated the conditions under which Romania agreed to join the war on the side of the Entente, particularly territorial promises in
Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
: Transylvania,
Crișana
Crișana ( hu, Körösvidék, german: Kreischgebiet) is a geographical and historical region in north-western Romania, named after the Criș (Körös) River and its three tributaries: the Crișul Alb, Crișul Negru, and Crișul Repede. In Rom ...
and
Maramureș
or Marmaroshchyna ( ro, Maramureș ; uk, Мармарощина, Marmaroshchyna; hu, Máramaros) is a geographical, historical and cultural region in northern Romania and western Ukraine. It is situated in the northeastern Carpathians, alon ...
, the whole
Banat and most of Bukovina. According to historian John Keegan, these enticements offered by the Allies were never concrete, for in secret, Russia and France agreed not to honor any conventions when the end of the war came.
Russia
The immediate reason for Russia's involvement in the First World War was a direct result of the decisions made by the statesmen and generals during July 1914. The
July crisis was the culmination of a series of diplomatic conflicts that took place in the decades prior to 1914, and this is fundamental to an understanding of Russia's position immediately prior to the War. According to
D. C. Lieven, Russia was formidable and was able to back up her diplomatic policies with force. One of the most significant factors in bringing Russia to the brink of war was the downfall of her economy. The 20 percent jump in defense expenditure during 1866–77 and in 1871-5 forced them to change their position within Europe and shift the balance of power out of her favour. At the time, Russian infrastructure was backward and the Russian government had to invest far more than its European rivals in structural changes. In addition there were overwhelming burdens of defense, which would ultimately result in an economic downfall for the Russians. This was a major strain on the Russian population, but also served as a direct threat to military expenditure. Thus the only way the Russians could sustain the strains of European war would be to place more emphasis on foreign investment from the French who essentially came to Russia's aid for industrial change. The
Franco-Russian Alliance
The Franco-Russian Alliance (french: Alliance Franco-Russe, russian: Франко-Русский Альянс, translit=Franko-Russkiy Al'yans), or Russo-French Rapprochement (''Rapprochement Russo-Français'', Русско-Французско� ...
allowed for the Russian defense to grow and aid the European balance of power during the growth of the German Empire's might. Nevertheless, one of the key factors was that of the Russian foreign policy between 1890 and 1914. The Russian army was large, but had poor leadership and poor equipment, and increasingly poor morale until by 1917 it turned against the government.
Russian propaganda

In order for the Russians to legitimize their war efforts, the government constructed an image of the enemy through state-instituted
propaganda. Their main aim was to help overcome the legend of the "invincible" German war machine, in order to boost the morale of civilians and soldiers. Russian propaganda often took the form of showing the Germans as a civilized nation, with barbaric "inhuman" traits. Russian propaganda also exploited the image of the Russian
POWs who were in the German camps, again in order to boost the morale of their troops, serving as encouragement to defeat the enemy and to get their fellow soldiers out of German POW camps that were perceived as inhumane.
An element of the Russian propaganda was the Investigate Commission formed in April 1915. It was led by Aleksei Krivtsov, and the study was tasked with the job of studying the legal violations committed by of the
Central Powers and then getting this information to the Russian public. This commission published photographs of letters that were allegedly found on fallen German soldiers. These letters document the German correspondents saying to "take no prisoners." A museum was also set up in Petrograd, which displayed pictures that showed how "inhumanly" the Germans were treating prisoners of war.
Also, the Russians chose to discard the name
Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
to remove the German-sounding "Saint" and "-burg", favouring the more Russian-sounding Petrograd.
Austria-Hungary

Austria-Hungary's participation in the outbreak of World War I has been neglected by historians, as emphasis has traditionally been placed on Germany's role as the prime instigator.
However, the "spark" that ignited the First World War is attributed to the
assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand
Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria, heir presumptive to the Austro-Hungarian throne, and his wife, Sophie, Duchess of Hohenberg, were assassinated on 28 June 1914 by Bosnian Serb student Gavrilo Princip. They were shot at close range whil ...
by Gavrilo Princip, which took place on 28 June 1914. Approximately a month later, on 28 July 1914, Austria-Hungary declared war on Serbia. This act led to a series of events that would quickly expand into the First World War; thus, the Habsburg government in Vienna initiated the pivotal decision that would begin the conflict.
The causes of the Great War have generally been defined in diplomatic terms, but certain deep-seated issues in Austria-Hungary undoubtedly contributed to the beginnings of the First World War. The Austro-Hungarian situation in the Balkans pre-1914 is a primary factor in its involvement in the war. The
movement towards South Slav unity was a major problem for the Habsburg Empire, which was facing increasing nationalist pressure from its multinational populace. As Europe's third largest state, the Austro-Hungarian monarchy was hardly homogeneous; comprising over fifty million people and eleven nationalities, the Empire was a conglomeration of a number of diverse cultures, languages, and peoples.
Specifically, the South Slavic people of Austria-Hungary desired to amalgamate with Serbia in an effort to officially solidify their shared cultural heritage. Over seven million South Slavs lived inside the Empire, while three million lived outside it. With the growing emergence of nationalism in the twentieth century, unity of all South Slavs looked promising. This tension is exemplified by
Conrad von Hötzendorf
Conrad may refer to:
People
* Conrad (name)
Places
United States
* Conrad, Illinois, an unincorporated community
* Conrad, Indiana, an unincorporated community
* Conrad, Iowa, a city
* Conrad, Montana, a city
* Conrad Glacier, Washingt ...
's letter to Franz Ferdinand:
The unification of the South Slav race is one of the powerful national movements which can neither be ignored nor kept down. The question can only be, whether unification will take place within the boundaries of the Monarchy – that is at the expense of Serbia's independence – or under Serbia's leadership at the expense of the Monarchy. The cost to the Monarchy would be the loss of its South Slav provinces and thus of almost its entire coastline. The loss of territory and prestige would relegate the Monarchy to the status of a small power.
The
annexation of Bosnia-Herzegovina in 1908 by Austrian foreign minister Baron von Aehrenthal in an effort to assert domination over the Balkans inflamed Slavic nationalism and angered Serbia. Bosnia-Herzegovina became a "rallying cry" for South Slavs, with hostilities between Austria-Hungary and Serbia steadily increasing. The situation was ripe for conflict, and when the Serbian nationalist Gavrilo Princip assassinated Austrian imperial heir, Franz Ferdinand, these longstanding hostilities culminated into an all-out war.
The Allied Powers wholeheartedly supported the Slavs' nationalistic fight.
George Macaulay Trevelyan
George Macaulay Trevelyan (16 February 1876 – 21 July 1962) was a British historian and academic. He was a Fellow of Trinity College, Cambridge, from 1898 to 1903. He then spent more than twenty years as a full-time author. He returned to the ...
, a British historian, saw Serbia's war against Austria-Hungary as a "war of liberation" that would "free South Slavs from tyranny." In his own words: "If ever there was a battle for freedom, there is such a battle now going on in Southeastern Europe against Austrian and Magyar. If this war ends in the overthrow of the Magyar tyranny, an immense step forward will have been taken toward racial liberty and European peace."
1914
Prior to 1914, the Russian's lack of success in war and diplomacy in the six decades before 1914 sapped the country's moral strength. The triumphs of Britain and Germany in the martial, diplomatic and economic spheres put these countries in the front rank of the world's leading nations. This was a source of national pride, self-confidence and unity. It helped reconcile the worker to the state and the Bavarian or Scotsman to rule from Berlin or London.
In the years prior to 1914, Austro-Russian co-operation was both crucial for European peace and difficult to maintain. Old suspicions exacerbated by the
Bosnian crisis stood in the way of agreement between the two empires, as did ethnic sensitivities. Russia's historical role as liberator of the Balkans was difficult to square with Austria's determination to control adjacent territories. In 1913–1914 Saint Petersburg was too concerned with its own weakness and what it saw as threats to vital Russian interests, to spare much thought for Vienna's feelings. The Russians were, with some justice, indignant that the concessions they had made after the First
Balkan War
The Balkan Wars refers to a series of two conflicts that took place in the Balkan States in 1912 and 1913. In the First Balkan War, the four Balkan States of Greece, Serbia, Montenegro and Bulgaria declared war upon the Ottoman Empire and defea ...
in the interest of European peace had not been reciprocated by the Central Powers.
This was doubly dangerous given the growing evidence flowing into Petersburg about Germany's aggressive intentions. Both Bazarov and the agents of the Russian secret political police in Germany reported the concern aroused in public opinion by the press war against Russia, which raged in the spring of 1914.
The Russian military was the largest in the world consisting of 1.4 million men on duty just prior to the war. They could also mobilize up to 5 million men, but only had 4.6 million rifles to give them. It also had poor leadership.
The Empires Clash


The war in the east began with the
Russian invasion of East Prussia on 17 August 1914 and the Austro-Hungarian province of
Galicia. The Russian offensive in the
Battle of Stallupönen, which was the opening battle of the Eastern Front, quickly turned to a disastrous defeat followed by the
Battle of Tannenberg
The Battle of Tannenberg, also known as the Second Battle of Tannenberg, was fought between Russia and Germany between 26 and 30 August 1914, the first month of World War I. The battle resulted in the almost complete destruction of the Russ ...
in August 1914. Later, the German troops under the command of Hindenburg inflicted a crushing defeat on the numerically superior Russian army in the
First Battle of the Masurian Lakes. A second Russian incursion into Galicia was completely successful, with the
Russians
, native_name_lang = ru
, image =
, caption =
, population =
, popplace =
118 million Russians in the Russian Federation (2002 '' Winkler Prins'' estimate)
, region1 =
, pop1 ...
controlling almost all of that region by the end of 1914, routing four Austrian armies in the process. Under the command of
Nikolai Ivanov,
Nikolai Ruzsky
Nikolai Vladimirovich Ruzsky (russian: Никола́й Влади́мирович Ру́зский; – October 18, 1918) was a Russian general, member of the state and military councils, best known for his role in World War I and the abdi ...
and
Aleksei Brusilov, the Russians won the
Battle of Galicia in September and began the
Siege of Przemyśl, the next fortress on the road towards
Kraków
Kraków (), or Cracow, is the second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city dates back to the seventh century. Kraków was the official capital of Poland until 1596 ...
.
This early Russian success in 1914 on the Austro-Russian border was a reason for concern to the Central Powers and caused considerable
German forces to be transferred to the East to take pressure off the Austrians, leading to the creation of the new
German Ninth Army
The 9th Army (german: 9. Armee) was a World War II field army. It was activated on 15 May 1940 with General Johannes Blaskowitz in command.
History
1940
The 9th Army first saw service along the Siegfried Line during its involvement in the invas ...
. The Austro-Hungarian government accepted the Polish proposal of establishing the
Supreme National Committee as the Polish central authority within the Empire, responsible for the formation of the
Polish Legions, an auxiliary military formation within the Austro-Hungarian army. At the end of 1914, the main focus of the fighting shifted to central part of
Russian Poland
Congress Poland, Congress Kingdom of Poland, or Russian Poland, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland, was a polity created in 1815 by the Congress of Vienna as a semi-autonomous Polish state, a successor to Napoleon's Duchy of Warsaw. It w ...
, west of the river
Vistula. The October
Battle of the Vistula River
The Battle of the Vistula River, also known as the Battle of Warsaw, was a Russian victory against the German Empire and Austria-Hungary on the Eastern Front during the First World War.
Background
By mid-September 1914 the Russians were dri ...
and the November
Battle of Łódź brought little advancement for the Germans, but at least kept the Russians at a safe distance.
The Russian and Austro-Hungarian armies continued to clash along the
Carpathian Front throughout the winter of 1914–1915. Przemysl fortress managed to hold out deep behind enemy lines throughout this period, with the Russians bypassing it in order to attack the Austro-Hungarian troops further to the west. They made some progress, crossing the
Carpathian Mountains in February and March 1915, but then the German relief helped the Austrians stop further Russian advances. In the meantime, Przemysl was almost entirely destroyed and the
Siege of Przemysl
A siege is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition, or a well-prepared assault. This derives from la, sedere, lit=to sit. Siege warfare is a form of constant, low-intensity conflict characterize ...
ended in a defeat for the Austrians.
1915
Central Powers victories. Great retreat of the Russian Imperial Army
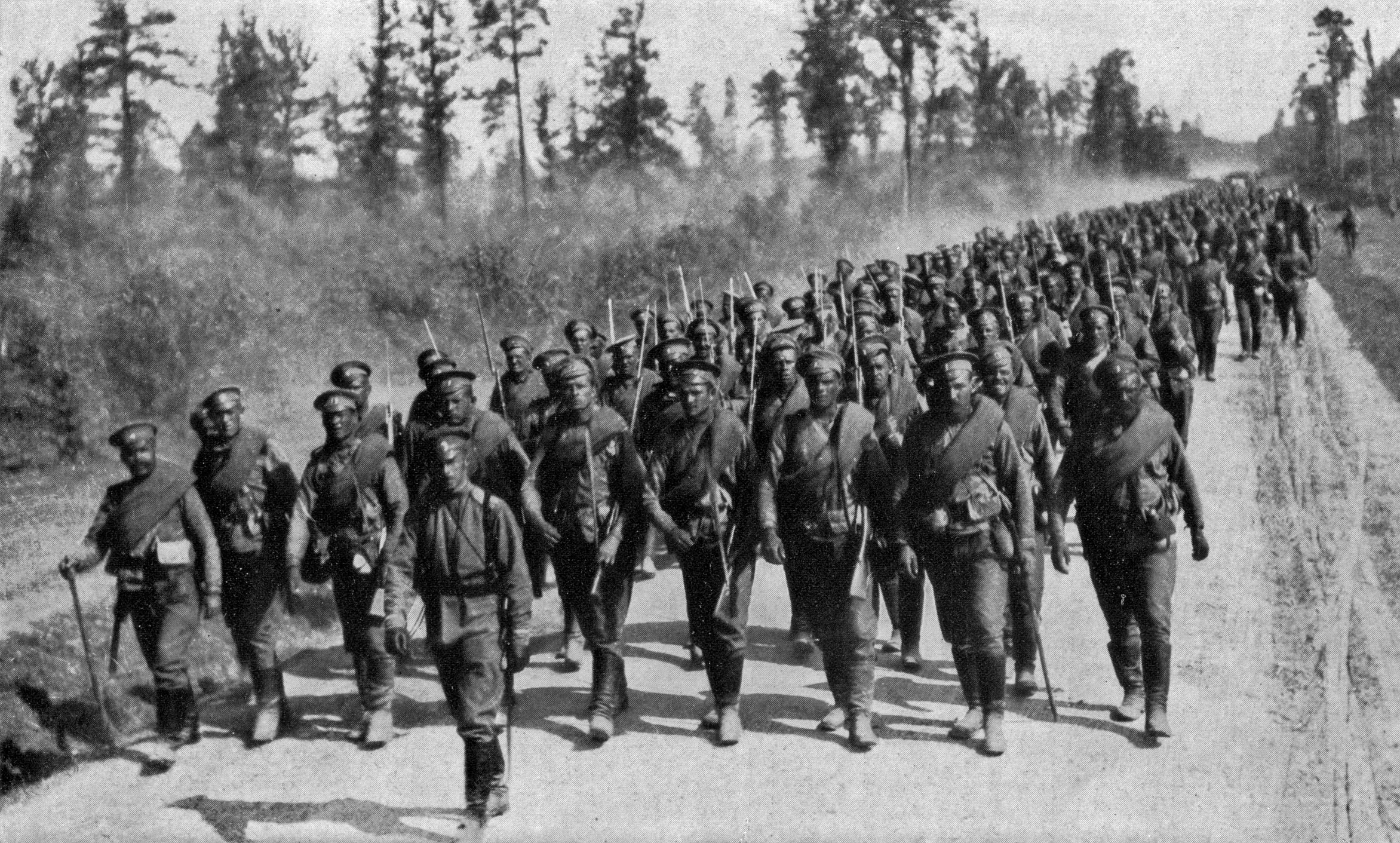

In 1915 the Chief of
German Great General Staff, General of Infantry
Erich von Falkenhayn decided to make its main effort on the Eastern Front, and accordingly transferred considerable forces there. The year began with a successful German offensive in the area of the
Masurian lakes. At the same time, a large battle for the city of
Przasnysz
Przasnysz (; yi, פראשניץ, russian: Прасныш) is a town in north-central Poland. Located in the Masovian Voivodship, about 110 km north of Warsaw and about 115 km south of Olsztyn, it is the capital of Przasnysz County. It ...
took place on the Polish front. The city changed hands several times but eventually remained in Russian hands. As a result of the battle, the Germans lost 38 000 soldiers and Russian losses amounted to about 70 000 men. In May 1915, to eliminate the Russian threat the
Central Powers began the successful
Gorlice–Tarnów Offensive
The Gorlice–Tarnów offensive during World War I was initially conceived as a minor German offensive to relieve Russian pressure on the Austro-Hungarians to their south on the Eastern Front, but resulted in the Central Powers' chief offensi ...
in Galicia.
After the
Second Battle of the Masurian Lakes
The Second Battle of the Masurian Lakes, also known as the Winter Battle of the Masurian Lakes, was the northern part of the Central Powers' offensive on the Eastern Front in the winter of 1915. The offensive was intended to advance beyond the V ...
, the German and Austro-Hungarian troops on the Eastern Front functioned under a unified command. The offensive soon turned into a general advance and a
corresponding strategic retreat by the Russian Army. The cause of the reverses suffered by the Russian Army, despite a significant numerical superiority over the German enemy, was not so many errors in the tactical sphere, as the deficiency in technical equipment, particularly in artillery and ammunition as well as the corruption and incompetence of the Russian officers. Only by 1916 did the buildup of Russian war industries increase the production of war material and improve the supply situation.
By mid-1915, the Russians had been expelled from
Russian Poland
Congress Poland, Congress Kingdom of Poland, or Russian Poland, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland, was a polity created in 1815 by the Congress of Vienna as a semi-autonomous Polish state, a successor to Napoleon's Duchy of Warsaw. It w ...
and hence pushed
hundreds of kilometers away from the borders of the Central Powers, removing the threat of Russian invasion of Germany, although there was still slight Russian penetration into Austria-Hungary. At the end of 1915 the German-Austrian advance was stopped on the line
Riga–
Jakobstadt–
Dünaburg
Daugavpils (; russian: Двинск; ltg, Daugpiļs ; german: Dünaburg, ; pl, Dyneburg; see other names) is a state city in south-eastern Latvia, located on the banks of the Daugava River, from which the city gets its name. The parts of the ...
–
Baranovichi–
Pinsk
Pinsk ( be, Пі́нск; russian: Пи́нск ; Polish: Pińsk; ) is a city located in the Brest Region of Belarus, in the Polesia region, at the confluence of the Pina River and the Pripyat River. The region was known as the Marsh of Pinsk ...
–
Dubno
Dubno ( uk, Ду́бно) is a city and municipality located on the Ikva River in Rivne Oblast (province) of western Ukraine. It serves as the administrative center of Dubno Raion (district). The city is located on intersection of two major ...
–
Tarnopol. The general outline of this front line did not change until the Russian collapse in 1917.
During the campaign of 1915, the Russian Empire lost the entire line of western fortresses, and more than 4,000 guns. The causes of heavy defeats and losses of personnel, weapons, and as a result - vast territories (the entire Kingdom of Poland, part of the Baltic states,
Grodno, partly
Volhynia and
Podolia provinces - up to 300,000 square kilometers) were to a large extent systemic shortcomings in the management of the armed forces and the defense industry. The multi-stage placement of military orders, their slow passage in the depths of the War Ministry, the disunity of the front and rear played a negative role. Thus, until the autumn of 1915, the Russian Supreme Commander-in-Chief only coordinated the actions of the commanders-in-chief of the armies of the fronts, distributed reinforcements, requesting them from the War Ministry. The Minister of War was responsible for organizing the production of weapons and ammunition, the implementation of the replenishment of troop personnel, military transportation outside the provinces declared a theater of military operations. The military districts in the theater of operations were subordinate to the commanders-in-chief of the armies of the fronts, but not to the Headquarters. Military production also lagged behind: until the end of autumn, the active army suffered from a shortage of rifles and ammunition, the consumption of which turned out to be incommensurable with the volume of production.
Contemporaries also noted the isolation of the Russian commanding staff from the soldiers, the lack of practical warfare skills among the top-level commanders. “We did have courage to send people to mass slaughter, hiding behind the difficulty of tactical responsibility, to slaughter often without purpose. We sent them, being ourselves far away, not seeing either our own or the enemy, and therefore not conforming to reality. Instead of punishment, we reward such leaders, because as far as the leaders were far away, the same, but still more, the higher leaders kept even more distant. People ceased to be people, but turned into pawns. We went to the fight in a state of some kind of oblivion and stunnedness, ”wrote the representative of the Supreme Commander-in-Chief, Infantry General
Fyodor Palitzin
Fyodor Fyodorovich Palitzin (russian: Фёдор Фёдорович Палицын; – 19 February 1923) (also known as Palitsyn) was a Russian General who commanded the Russian Expeditionary Force in France.
Palitzin attended the Pavel Militar ...
, in his diary.
Failures in the Russian system of command and control of troops and the organization of hostilities occurred at other levels. Thus, serious shortcomings in reconnaissance led to the absence of any analysis of the enemy's plans and actions. With a general superiority in forces, almost every Central Powers's operation in 1915 was "unexpected" for the command from the front to the regimental level. Passion for undercover intelligence in the highest headquarters did not justify itself, and tactical intelligence was still based on little reliable testimony of prisoners, in the absence of which the command up to the army, inclusive, was simply “blind”. The separation of artillery from infantry with subordination to the inspectors of the corps and ammunition supply units (park brigades and divisions) created difficulties in the operational replenishment of ammunition and shells in the combat units. At the same time, huge stockpiles of ammunition were created in the fortresses, which were then delivered to the enemy during the retreat or destroyed due to the impossibility of evacuation. Special units were not created for the construction of fortifications in the rear of the troops. Most often, such work was hastily carried out by militia squads and the mobilized local population, sometimes including women, and then brought to the necessary defensive state by the combat units retreating on them, already exhausted by battles and night marches.
The country’s geographic expanses and a large population again became the salvation of the Russia from complete military defeat, however, by the end of the 1915 campaign, it became obvious that without a radical restructuring of the war strategy, methods of managing military potential, victory becomes unattainable, and new defeats can cause another collapse of transport ( as in the case of mass exodus and the hasty "evacuation" of the western provinces), supplies, public administration and, as a result, the aggravation of the struggle for power in the country. Nevertheless, as before, for the military leadership of the Russian Empire, there was only one way to victory - the creation of multiple numerical superiority over the Germans. To some extent, the Russian side in the autumn played along with E. von Falkenhayn, who, not considering the Russian direction to have at least some strategic prospect for achieving victory in the war, made it impossible to develop the offensive of the Eastern Front.
Russo-Turkish offensive, winter 1915–1916
After the
Battle of Sarikamish, the Russo-Turkish front quickly turned in favor of Russian forces. The Turks were concerned with reorganizing their army and also fighting the massive Allied armada that landed in
Galipoli. Meanwhile, Russia was preoccupied with other armies on the Eastern Front. However, the appointment of
Grand Duke Nicholas Nikolaevich as Viceroy and Commander in the Caucasus in September 1915 revived the situation of the Russo-Turkish front.
When the Allies withdrew from Gallipoli in December, the Caucasus Army's Chief of Staff General
Nikolai Yudenich believed Turkish forces would take action against his army. This concern was legitimate: Bulgaria's entry into the war as Germany's ally in October caused serious alarm, as a land route from Germany to Turkey was now open and would allow for an unrestricted flow of German weapons to the Turks.
A "window of opportunity" appeared that would allow the Russians to destroy the Turkish Third Army, as the British required assistance in Mesopotamia (now modern day Iraq). Britain's efforts to besiege Baghdad had been halted at Ctesiphon, and they were forced to retreat. This led to an increasing number of attacks by Turkish forces. The British requested the Russians to attack in an attempt to distract the Turks, and Yudenich agreed.
The resulting offensive began on 10 January 1916.
This offensive was unanticipated by the Turks, as it was in the middle of winter. The Turkish situation was exacerbated by the absences of Third Army's commander Kamil Pasha and Chief of Staff Major Guse. Coupled with an imbalance of forces – the Russians had 325 000 troops, while the Turks only 78 000 – the situation appeared grim for the Central Powers.
After three months of fighting, the Russians captured the city of
Trabzon
Trabzon (; Ancient Greek: Tραπεζοῦς (''Trapezous''), Ophitic Pontic Greek: Τραπεζούντα (''Trapezounta''); Georgian: ტრაპიზონი (''Trapizoni'')), historically known as Trebizond in English, is a city on the B ...
on 18 April 1916.
1916
Allied operations in 1916 were dictated by an urgent need to force Germany to transfer forces from its Western to Eastern fronts, to relieve the pressure on the French at the
Battle of Verdun
The Battle of Verdun (french: Bataille de Verdun ; german: Schlacht um Verdun ) was fought from 21 February to 18 December 1916 on the Western Front in France. The battle was the longest of the First World War and took place on the hills north ...
. This was to be accomplished by a series of Russian offensives which would force the Germans to deploy additional forces to counter them. The first such operation was the
Lake Naroch Offensive
The Lake Naroch offensive in 1916 was an unsuccessful Russian offensive on the Eastern Front in World War I. It was launched at the request of Marshal Joseph Joffre and intended to relieve the German pressure on French forces. Due to lack of reco ...
in March–April 1916, which ended in failure.
Brusilov offensive

The Italian operations during 1916 had one extraordinary result: Austrian divisions were pulled away from the Russian southern front. This allowed the Russian forces to organize a counter-offensive. The Brusilov offensive was a large tactical assault carried out by Russian forces against Austro-Hungarian forces in Galicia. General
Aleksei Brusilov believed victory against the Central Powers was possible if close attention was paid to preparation. Brusilov suggested that the Russians should attack on a wide front, and to position their trenches a mere away from Austrian trenches.
Brusilov's plan worked impeccably. The Russians outnumbered the Austrians 200,000 to 150,000, and held a considerable advantage in guns, with 904 large guns to 600. Most importantly innovative new tactics similar to those independently invented by
Erwin Rommel were used to perform quick and effective close-range surprise attacks that allowed a steady advance.
The Russian Eighth Army overwhelmed the Austrian Fourth and pushed on to Lutsk, advancing beyond the starting position. Over a million Austrians were lost, with over 500,000 men killed or taken prisoner by mid-June.
Although the Brusilov offensive was initially successful, it slowed down considerably. An inadequate number of troops and poorly maintained supply lines hindered Brusilov's ability to follow up on the initial victories in June. The Brusilov offensive is considered to be the greatest Russian victory of the First World War.
Although it cost the Russians half a million casualties only during the first two months offensive, the offensive successfully diverted substantial forces of the Central Powers from the Western front, and persuaded Romania to join the war, diverting even more Central Powers forces to the East.
Russian Ammunition Crisis
The development of the Russian armament industry was mainly supported by French investors before the war. The Russian High Command saw the reason for the losses of the war in the lack of munitions. Most of these supplies were lost when advancing German troops occupied the fortifications. The production of munitions in the Tsarist empire was difficult, confidence in private enterprise among army personnel was low, and little capital was invested in the industry until 1916. About fifty percent of Russian ammunition requirements were supplied by Britain and the USA. As the Western companies were also responsible for supplying the needs of the Western Front, only a small proportion of the required quantity could be transported to Russia. In the following year, the Russian armaments industry was able to increase its production figures by a factor of two and a half and, despite the insufficient help of the Allies to cover the needs of the Russian army.
Romania enters the war

Up until 1916, the Romanians followed the tides of war with interest, while attempting to situate themselves in the most advantageous position. French and Russian diplomats had begun courting the Romanians early on, but persuasion tactics gradually intensified. For King Ferdinand to commit his force of half a million men, he expected the Allies to offer a substantial incentive. Playing on Romanian anti-Hungarian sentiment the Allies promised the Austria-Hungarian territory of Ardeal (Transylvania) to Romania. Transylvanian
demographics
Demography () is the statistical study of populations, especially human beings.
Demographic analysis examines and measures the dimensions and dynamics of populations; it can cover whole societies or groups defined by criteria such as ed ...
strongly favoured the Romanians. Romania succumbed to Allied enticement on 18 August 1916. Nine days later, on 27 August, Romanian troops marched into Transylvania.
Romania's entry into the war provoked major strategic changes for the Germans. In September 1916, German troops were mobilized to the Eastern Front. Additionally, the German Chief of the General Staff, General
Erich Von Falkenhayn was forced to resign from office though his successor appointed him to command the combined Central Powers forces against Romania, along with General
August von Mackensen.
Kaiser Wilhelm II
, house = Hohenzollern
, father = Frederick III, German Emperor
, mother = Victoria, Princess Royal
, religion = Lutheranism (Prussian United)
, signature = Wilhelm II, German Emperor Signature-.svg
Wilhelm II (Friedrich Wilhelm Viktor ...
immediately replaced Falkenhayn with
Paul von Hindenburg
Paul Ludwig Hans Anton von Beneckendorff und von Hindenburg (; abbreviated ; 2 October 1847 – 2 August 1934) was a German field marshal and statesman who led the Imperial German Army during World War I and later became President of Germany fr ...
. Von Hindenburg's deputy, the more adept
Erich Ludendorff, was given effective control of the army and ordered to advance on Romania. On 3 September, the first troops of the Central Powers marched into Romanian territory. Simultaneously, the
Bulgarian Air Force commenced an incessant bombing of
Bucharest
Bucharest ( , ; ro, București ) is the capital and largest city of Romania, as well as its cultural, industrial, and financial centre. It is located in the southeast of the country, on the banks of the Dâmbovița River, less than north of ...
. In an attempt to relieve some pressure, French and British forces launched a new offensive known as the
Battle of the Somme, while the Brusilov offensive continued in the East.
The entrance of Romania into the war was disconcerting for von Hindenburg. On 15 September,
Paul von Hindenburg
Paul Ludwig Hans Anton von Beneckendorff und von Hindenburg (; abbreviated ; 2 October 1847 – 2 August 1934) was a German field marshal and statesman who led the Imperial German Army during World War I and later became President of Germany fr ...
issued the following order, stating that: "The main task of the Armies is now to hold fast all positions on the Western, Eastern, Italian and Macedonian Fronts, and to employ all other available forces against Rumania." Fortunately for the Central Powers, the quantity and quality of the Romanian Army was overestimated. Although numbering half a million men, the Romanian Army suffered from poor training and a lack of appropriate equipment.
The initial success of the Romanian Army in Austria-Hungarian territory was quickly undermined by the Central Powers. German and Austro-Hungarian troops advanced from the north, while Bulgarian-Turkish-German forces marched into Romania from the south. Although thought to be a tactical blunder by contemporaries, the Romanians opted to mount operations in both directions. By the middle of November the German force passed through the Carpathians, suffering significant casualties due to determined Romanian resistance. By 5 December, Bulgarian troops had crossed the Danube and were approaching the capital,
Bucharest
Bucharest ( , ; ro, București ) is the capital and largest city of Romania, as well as its cultural, industrial, and financial centre. It is located in the southeast of the country, on the banks of the Dâmbovița River, less than north of ...
. At the same time as the Austro-Hungarian troops moved east, and as the Bulgarians marched north, the Turks had sent in two army divisions by sea to the
Dobruja
Dobruja or Dobrudja (; bg, Добруджа, Dobrudzha or ''Dobrudža''; ro, Dobrogea, or ; tr, Dobruca) is a historical region in the Balkans that has been divided since the 19th century between the territories of Bulgaria and Romania. I ...
from the east. Eventually, the Romanian forces were pushed back behind the
Siret
Siret (; german: Sereth; hu, Szeretvásár; uk, Серет, Seret; yi, סערעט, Seret) is a town, municipality and former Latin bishopric in Suceava County, northeastern Romania. It is situated in the historical region of Bukovina. Siret is ...
in northern
Moldavia
Moldavia ( ro, Moldova, or , literally "The Country of Moldavia"; in Romanian Cyrillic alphabet, Romanian Cyrillic: or ; chu, Землѧ Молдавскаѧ; el, Ἡγεμονία τῆς Μολδαβίας) is a historical region and for ...
. They received help from the Allies, notably from France which sent a
military mission
A military operation is the coordinated military actions of a state, or a non-state actor, in response to a developing situation. These actions are designed as a military plan to resolve the situation in the state or actor's favor. Operations ma ...
of more than a thousand officers, health and support staff.
Proclamation to win over the Poles
The
Act of 5 November 1916 was proclaimed then to the
Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, who share a common history, culture, the Polish language and are identified with the country of Poland in C ...
jointly by the Emperors
Wilhelm II of
Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
and
Franz Joseph
Franz Joseph I or Francis Joseph I (german: Franz Joseph Karl, hu, Ferenc József Károly, 18 August 1830 – 21 November 1916) was Emperor of Austria, King of Hungary, and the other states of the Habsburg monarchy from 2 December 1848 until his ...
of Austria-Hungary. This act promised the creation of the
Kingdom of Poland
The Kingdom of Poland ( pl, Królestwo Polskie; Latin: ''Regnum Poloniae'') was a state in Central Europe. It may refer to:
Historical political entities
* Kingdom of Poland, a kingdom existing from 1025 to 1031
* Kingdom of Poland, a kingdom exi ...
out of territory of
Congress Poland, envisioned by its authors as a
puppet state
A puppet state, puppet régime, puppet government or dummy government, is a state that is ''de jure'' independent but ''de facto'' completely dependent upon an outside power and subject to its orders.Compare: Puppet states have nominal sove ...
controlled by the
Central Powers. The origin of that document was the dire need to draft new recruits from German-occupied Poland for the
war with Russia. Following the
Armistice of 11 November 1918 ending the World War I, in spite of the previous initial total dependence of the kingdom on its sponsors, it ultimately served against their intentions as the cornerstone
proto state of the nascent
Second Polish Republic, the latter conposed also of territories never intended by the Central Powers to be ceded to Poland.
Aftermath of 1916
By January 1917, the ranks of the Romanian army had been significantly thinned. Roughly 150,000 Romanian soldiers had been taken prisoner, 200,000 men were dead or wounded, and lost two thirds of their country, including the capital. Importantly, the
Ploiești oilfields, the only significant source of oil in Europe west of the Black Sea, had been destroyed before they were abandoned to the Central Powers.
1917
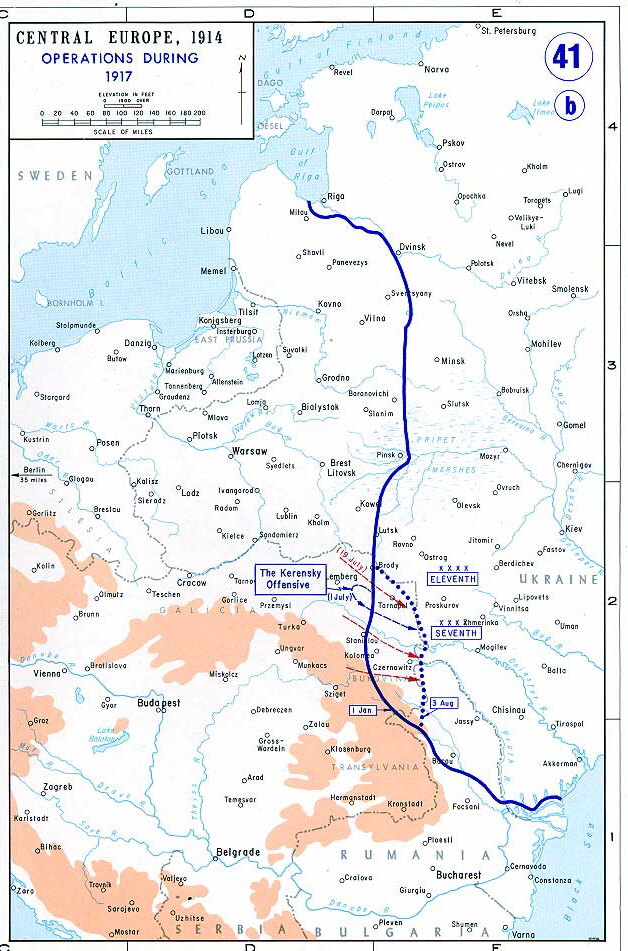
Russia – the February Revolution
The Russian
February Revolution aimed to topple the Russian monarchy and resulted in the creation of the Provisional Government. The revolution was a turning point in Russian history, and its significance and influence can still be felt in many countries today. Although many Russians wanted a revolution, no one had expected it to happen when it did – let alone how it did.
On International Women's Day, Thursday, 23 February 1917/8 March 1917, as many as 90,000 female workers in the city of Petrograd left their factory jobs and marched through the streets, shouting "Bread", "Down with the autocracy!" and "Stop the War!" These women were tired, hungry, and angry, after working long hours in miserable conditions to feed their families because their menfolk were fighting at the front. They were not alone in demanding change; more than 150,000 men and women took to the streets to protest the next day.
By Saturday, 25 February, the city of Petrograd was essentially shut down. No one was allowed to work or wanted to work. Even though there were a few incidents of police and soldiers firing into the crowds, those groups soon mutinied and joined the protesters. Tsar Nicholas II, who was not in Petrograd during the revolution, heard reports of the protests but chose not to take them seriously. By 1 March, it was obvious to everyone except the czar himself, that his rule was over. On 2 March it was made official.From this point onwards Russia was administrated by the
Russian Provisional Government until the
October Revolution
The October Revolution,. officially known as the Great October Socialist Revolution. in the Soviet Union, also known as the Bolshevik Revolution, was a revolution in Russia led by the Bolshevik Party of Vladimir Lenin that was a key mome ...
.
Romania – the Summer Campaign and aftermath
In early July 1917, on the
Romanian front
The Romanian Front ( ro, Frontul Românesc, FR) was a moderate fascist party created in Romania in 1935. Led by former Prime Minister Alexandru Vaida-Voevod, it originated as a right-wing splinter group from the mainstream National Peasants' Part ...
, a relatively small area, there was one of the largest concentrations of combat forces and means known during the conflagration: nine armies, 80 infantry divisions with 974 battalions, 19 cavalry divisions with 550 squadrons and 923 artillery batteries, whose effectives numbered some 800,000 men, with about one million in their immediate
reserve. The three great battles, decisive for the Romanian nation's destiny, delivered at
Mărăști,
Mărășești
Mărășești () is a small town in Vrancea County, Western Moldavia, Romania. It administers six villages: Călimănești, Haret, Modruzeni, Pădureni, Siretu and Tișița.
Geography
The town is located in the eastern part of the county, on th ...
and
Oituz
Oituz (formerly ''Grozești''; hu, Gorzafalva) is a commune in Bacău County, Western Moldavia, Romania. It is composed of six villages: Călcâi (''Zöldlonka''), Ferestrău-Oituz (''Fűrészfalva''), Hârja (''Herzsa''), Marginea, Oituz and Poi ...
represented a turning point in the
world war
A world war is an international conflict which involves all or most of the world's major powers. Conventionally, the term is reserved for two major international conflicts that occurred during the first half of the 20th century, World WarI (1914 ...
on the Eastern front. These battles, named by the localities and zones where they took place, were fought approximately on the front alignment stabilized in early 1917, which the conflicting sides had thoroughly consolidated for half a year.
[România în anii primului război mondial, vol. 2, p. 834]
Between late July and early September, the Romanian Army fought the battles of
Mărăști,
Mărășești
Mărășești () is a small town in Vrancea County, Western Moldavia, Romania. It administers six villages: Călimănești, Haret, Modruzeni, Pădureni, Siretu and Tișița.
Geography
The town is located in the eastern part of the county, on th ...
and
Oituz
Oituz (formerly ''Grozești''; hu, Gorzafalva) is a commune in Bacău County, Western Moldavia, Romania. It is composed of six villages: Călcâi (''Zöldlonka''), Ferestrău-Oituz (''Fűrészfalva''), Hârja (''Herzsa''), Marginea, Oituz and Poi ...
, managing to stop the German-Austro-Hungarian advance, inflicting heavy losses in the process and winning the most important Allied victories on the Eastern Front in 1917.
As a result of these operations, the remaining Romanian territories remained unoccupied, tying down nearly 1,000,000 Central Powers troops and prompting ''
The Times
''The Times'' is a British daily national newspaper based in London. It began in 1785 under the title ''The Daily Universal Register'', adopting its current name on 1 January 1788. ''The Times'' and its sister paper '' The Sunday Times'' (f ...
'' to describe the Romanian front as "The only point of light in the East".
On 7 May 1918, in light of the existing politico-military situation, Romania was forced to conclude the
Treaty of Bucharest with the Central Powers, imposing harsh conditions on the country but recognizing its
union with Bessarabia.
Alexandru Marghiloman
Alexandru Marghiloman (4 July 1854 – 10 May 1925) was a Romanian conservative statesman who served for a short time in 1918 (March–October) as Prime Minister of Romania, and had a decisive role during World War I.
Early career
Born in Buz ...
became the new German-sponsored Prime Minister. King Ferdinand, however, refused to sign the treaty.
The Germans were able to repair the oil fields around
Ploiești and by the end of the war had pumped a million tons of oil. They also requisitioned two million tons of grain from Romanian farmers. These materials were vital in keeping Germany in the war to the end of 1918.
Kerensky Offensive
On 29 June,
Alexander Kerensky, the Minister of War in the
Russian Provisional Government, launched the Kerensky offensive to end Austria-Hungary once and for all. The Russians made only 6 miles (9.7 km) of progress but the Austrians counterattacked and drove them almost entirely out of Austria-Hungary, and they retreated 150 miles (240 km), losing
Tarnopol,
Stanislau and
Czernowitz
Chernivtsi ( uk, Чернівці́}, ; ro, Cernăuți, ; see also other names) is a city in the historical region of Bukovina, which is now divided along the borders of Romania and Ukraine, including this city, which is situated on the up ...
. This defeat was accompanied by 60,000 casualties and contributed greatly to the collapse of the Russian Army during the
October Revolution
The October Revolution,. officially known as the Great October Socialist Revolution. in the Soviet Union, also known as the Bolshevik Revolution, was a revolution in Russia led by the Bolshevik Party of Vladimir Lenin that was a key mome ...
.
Russia – the October Revolution
By September 1917, just months after the February Revolution, Lenin believed the Russian people were ready for another revolution, this time on Marxist principles. On 10 October, at a secret meeting of the Bolshevik party leaders, Lenin used all his power to convince the others that it was time for armed insurrection. Troops who were loyal to the Bolsheviks took control of the telegraph stations, power stations, strategic bridges, post offices, train stations, and state banks.
Petrograd was officially in the hands of the Bolsheviks, who greatly increased their organization in factory groups and in many barracks throughout Petrograd. They concentrated on devising a plan for overturning the Provisional Government, with a coup d'état. On 24 October, Lenin emerged from hiding in a suburb, entered the city, set up his headquarters at the Smolny Institute and worked to complete his three-phase plan. With the main bridges and the main railways secured, only the Winter Palace, and with it the Provisional Government, remained to be taken. On the evening of 7 November, the troops that were loyal to the Bolsheviks infiltrated the Winter Palace. After an almost bloodless coup, the Bolsheviks were the new leaders of Russia. Lenin announced that the new regime would end the war, abolish all private land ownership, and create a system for workers' control over the factories.
1918
On 7 November 1917, the Communist
Bolsheviks
The Bolsheviks (russian: Большевики́, from большинство́ ''bol'shinstvó'', 'majority'),; derived from ''bol'shinstvó'' (большинство́), "majority", literally meaning "one of the majority". also known in English ...
took power under their leader
Vladimir Lenin
Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov. ( 1870 – 21 January 1924), better known as Vladimir Lenin,. was a Russian revolutionary, politician, and political theorist. He served as the first and founding head of government of Soviet Russia from 1917 to 1 ...
. Lenin's new Bolshevik government tried to end the war, with a
ceasefire being declared on 15 December 1917 along lines agreed in November. At the same time, the Bolsheviks launched a full-scale military offensive against its opponents:
Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
and separatist governments in the Don region. During the peace negotiations between the Soviets and the Central Powers, the Germans demanded enormous concessions, eventually resulting in the failure of the long-drawn-out peace negotiations on 17 February 1918. At the same time, the Central Powers concluded a military treaty with Ukraine which was losing ground in the fight with invading Bolshevik forces. The
Russian Civil War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Russian Civil War
, partof = the Russian Revolution and the aftermath of World War I
, image =
, caption = Clockwise from top left:
{{flatlist,
*Soldiers ...
, which started just after November 1917, would tear apart Russia for three years. As a result of the events in 1917, many groups opposed to Lenin's Bolsheviks had formed. With the fall of Nicholas II, many parts of the Russian Empire took the opportunity to declare their independence, one of which was Finland, which did so in December 1917; however, Finland too collapsed into a
civil war
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
. Finland declared itself independent on 6 December 1917, and this was accepted by Lenin a month later.
The Finnish Parliament elected a German prince as King of Finland. However, the Socialists (The Reds) and the Whites in Finland fell into war with each other in January 1918. The Reds wanted Finland to be a Soviet republic and were aided by Russian forces still in Finland.
The Whites of Finland were led by General
C.G.E.Mannerheim, a Finnish baron who had been in the Tsar's service since he was 15 years old.
The Whites were also offered help by a German Expeditionary Corps led by German General Goltz. Though Mannerheim never accepted the offer, the German corps landed in Finland in April 1918.
Formation of the Red Army
After the disintegration of the Russian imperial army and navy in 1917, the Council of People's Commissars headed by Leon Trotsky set about creating a new army. By a decree on 28 January 1918, the council created the Workers' and Peoples' Red Army; it began recruitment on a voluntary basis, but on 22 April, the Soviet government made serving in the army compulsory for anyone who did not employ hired labor. While the majority of the army was made up of workers and peasants, many of the Red Army's officers had served a similar function in the imperial army before its collapse.
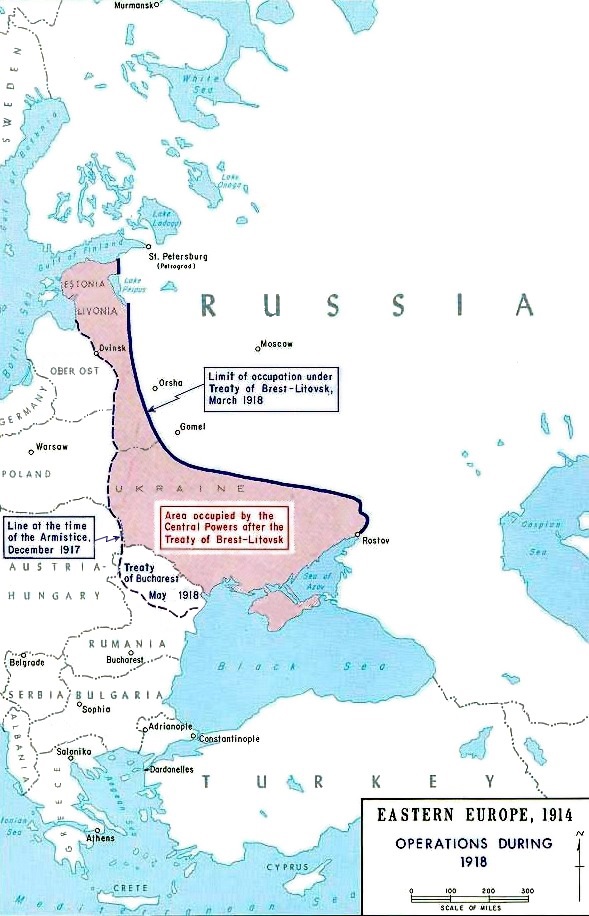
Treaty of Brest-Litovsk (March 1918)
With the German Army just from the Russian capital
Petrograd (St. Petersburg) on 3 March 1918, the
Treaty of Brest-Litovsk was signed and the Eastern Front ceased to be a war zone. While the treaty was practically obsolete before the end of the year, it did provide some relief to the Bolsheviks, who were embroiled in a civil war, and affirmed the independence of
Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
. However,
Estonia
Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, a ...
and
Latvia were intended to become a
United Baltic Duchy to be ruled by German princes and German nobility as fiefdoms under the German Kaiser. A
rump Polish state was also foreseen on the formerly Russian territories.
Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of B ...
's sovereignty had already been declared in December 1917, and accepted by most nations, including France and Russia, but not by the United Kingdom and the United States. In October it also turned into a German puppet state.
Armistice
With the end of major combat on the Eastern Front, the Germans were able to transfer substantial forces to the west in order to mount an
offensive in France in the spring of 1918.
This offensive on the Western Front failed to achieve a decisive breakthrough, and the arrival of more and more
American units in Europe was sufficient to offset the German advantage. Even after the Russian collapse, about a million German soldiers remained tied up in the east until the end of the war, attempting to run a short-lived addition to the German Empire in Europe. In the end, the Central Powers had to relinquish all of their captured lands on the eastern front, with Germany even being forced to cede territory they held before the war, under various treaties (such as the
Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles (french: Traité de Versailles; german: Versailler Vertrag, ) was the most important of the peace treaties of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June ...
) signed after the armistice in 1918. Although the Allied Powers' victory led to the Central Powers being forced to cancel the treaty signed with Russia, the victors were at the time intervening in the Russian Civil War, causing bad relations between Russia and the Allied Powers.
Role of women on the Eastern Front

In comparison to the attention directed to the role played by women on the Western Front during the First World War, the role of women in the east has garnered limited scholarly focus. It is estimated that 20 percent of the Russian industrial working class was conscripted into the army; therefore, women's share of industrial jobs increased dramatically. There were percentage increases in every industry, but the most noticeable increase happened in industrial labour, which increased from 31.4 percent in 1913 to 45 percent in 1918.
Women also fought on the Eastern Front. In the later stages of Russia's participation in the war, Russia began forming all-woman combat units, the
Women's Battalion
Women's Battalions (Russia) were all-female combat units formed after the February Revolution by the Russian Provisional Government, in a last-ditch effort to inspire the mass of war-weary soldiers to continue fighting in World War I.
In the spri ...
s, in part to fight plummeting morale among male soldiers by demonstrating Russian women's willingness to fight. In Romania,
Ecaterina Teodoroiu actively fought in the Romanian Army and is remembered today as a national hero.
British nursing efforts were not limited to the Western Front. Nicknamed the "Gray partridges" in reference to their dark gray overcoats, Scottish volunteer nurses arrived in Romania in 1916 under the leadership of
Elsie Inglis. In addition to nursing injured personnel, Scottish nurses manned transport vehicles and acted as regimental cooks. The "Gray Partridges" were well respected by Romanian, Serbian and Russian troops and as a result, the Romanian press went as far as to characterize them as "healthy, masculine, and tanned women." As a testament to her abilities, Elsie Inglis and her volunteers were entrusted to turn an abandoned building in the city of
Galați into an operational hospital, which they did in a little more than a day. Yvonne Fitzroy's published journal, "With the Scottish Nurses in Roumania," provides an excellent first hand account of Scottish nursing activities in the Eastern Front.
Prisoners of war in Russia
During World War I, approximately 200,000 German soldiers and 2.5 million soldiers from the Austro-Hungarian army entered Russian captivity. During the 1914 Russian campaign the Russians began taking thousands of Austrian prisoners. As a result, the Russian authorities made emergency facilities in Kyiv, Penza, Kazan, and later Turkestan to hold the Austrian prisoners of war. As the war continued Russia began to detain soldiers from Germany as well as a growing number from the Austro-Hungarian army. The Tsarist state saw the large population of POWs as a workforce that could benefit the war economy in Russia. Many
POWs were employed as farm laborers and miners in Donbas and Krivoi Rog. However, the majority of POWs were employed as laborers constructing canals and building railroads. The living and working environments for these POWs was bleak. There was a shortage of food, clean drinking water and proper medical care. During the summer months malaria was a major problem, and the malnutrition among the POWs led to many cases of scurvy. While working on the Murmansk rail building project over 25,000 POWs died. Information about the bleak conditions of the labor camps reached the German and Austro-Hungarian governments. They began to complain about the treatment of POWs. The Tsarist authorities initially refused to acknowledge the German and Habsburg governments. They rejected their claims because Russian POWs were working on railway construction in Serbia. However, they slowly agreed to stop using prison labor.
Life in the camps was extremely rough for the men who resided in them. The Tsarist government could not provide adequate supplies for the men living in their POW camps. The Russian government's inability to supply the POWs in their camps with supplies was due to inadequate resources and bureaucratic rivalries. However, the conditions in the POW camps varied; some were more bearable than others.
Disease on the Eastern Front
Disease played a critical role in the loss of life on the Eastern Front. In the East, disease accounted for approximately four times the number of deaths caused by direct combat, in contrast to the three to one ratio in the West. Malaria, cholera, and dysentery contributed to the epidemiological crisis on the Eastern Front; however, typhus fever, transmitted by pathogenic lice and previously unknown to German medical officers before the outbreak of the war, was the most deadly. There was a direct correlation between the environmental conditions of the East and the prevalence of disease. With cities excessively crowded by refugees fleeing their native countries, unsanitary medical conditions created a suitable environment for diseases to spread. Primitive hygienic conditions, along with general lack of knowledge about proper medical care was evident in the German-occupied
Ober Ost
, short for ( "Supreme Commander of All German Forces in the East"), was both a high-ranking position in the armed forces of the German Empire as well as the name given to the occupied territories on the German section of the Eastern Front of Wo ...
.
Ultimately, a large scale sanitation program was put into effect. This program, named ''Sanititätswesen'' (Medical Affairs), was responsible for ensuring proper hygienic procedures were being carried out in Latvia, Lithuania, and Poland. Quarantine centers were built, and diseased neighbourhoods were isolated from the rest of the population. Delousing stations were prevalent in the countryside and in cities to prevent the spread of typhus fever, with mass numbers of natives being forced to take part in this process at military bathhouses. A "sanitary police" was also introduced to confirm the cleanliness of homes, and any home deemed unfit would be boarded up with a warning sign. Dogs and cats were also killed for fear of possible infection.
To avoid the spread of disease, prostitution became regulated. Prostitutes were required to register for a permit, and authorities demanded mandatory medical examinations for all prostitutes, estimating that seventy percent of prostitutes carried a venereal disease. Military brothels were introduced to combat disease; the city of
Kowno emphasized proper educational use of contraceptives such as condoms, encouraged proper cleansing of the genital area after intercourse, and gave instructions on treatment in the case of infection.
Casualties
The Russian casualties in the First World War are difficult to estimate, due to the poor quality of available statistics.
Cornish gives a total of 2,006,000 military dead (700,000 killed in action, 970,000 died of wounds, 155,000 died of disease and 181,000 died while POWs). This measure of Russian losses is similar to that of the British Empire, 5% of the male population in the 15 to 49 age group. He says civilian casualties were five to six hundred thousand in the first two years, and were then not kept, so a total of ''over 1,500,000'' is not unlikely. He has over five million men ''passing into captivity'', the majority during 1915.
When Russia withdrew from the war, 2,500,000 Russian POWs were in German and Austrian hands. This by far exceeded the total number of prisoners of war (1,880,000) lost by the armies of
Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* The United Kingdom, a sovereign state in Europe comprising the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland and many smaller islands
* Great Britain, the largest island in the United King ...
, France and Germany combined. Only the
Austro-Hungarian Army
The Austro-Hungarian Army (, literally "Ground Forces of the Austro-Hungarians"; , literally "Imperial and Royal Army") was the ground force of the Austro-Hungarian Dual Monarchy from 1867 to 1918. It was composed of three parts: the joint arm ...
, with 2,200,000 POWs, came even close.
Territorial changes
Austria
The empire of Austria lost approximately 60% of its territory as a result of the war, and evolved into a smaller state with a small homogeneous population of 6.5 million people. With the loss, Vienna was now an imperial capital without an empire to support it. The states that were formed around Austria feared the return of the Austro-Hungarian Empire and put measures into place to prevent it from re-forming.
Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia
, rue, Чеськословеньско, , yi, טשעכאסלאוואקיי,
, common_name = Czechoslovakia
, life_span = 1918–19391945–1992
, p1 = Austria-Hungary
, image_p1 ...
was created through the merging of the Czech provinces of Bohemia and Moravia, previously under Austrian rule, united with Slovakia and Ruthenia, which were part of Hungary. Although these groups had many differences between them, they believed that together they would create a stronger state.
The new country was a multi-ethnic state. The population consisted of Czechs (51%), Slovaks (16%), Germans (22%), Hungarians (5%) and
Rusyns (4%), with other ethnic groups making up 2%.
["The War of the World", Niall Ferguson Allen Lane 2006.] Many of the Germans, Hungarians, Ruthenians and Poles
[, '' Prague Post'', 6 July 2005] and some Slovaks, felt oppressed because the political elite did not generally allow political autonomy for minority ethnic groups.
The state proclaimed the official ideology that there are no Czechs and Slovaks, but only one nation of Czechoslovaks (see
Czechoslovakism), to the disagreement of Slovaks and other ethnic groups. Once a unified Czechoslovakia was restored after World War II the conflict between the
Czechs
The Czechs ( cs, Češi, ; singular Czech, masculine: ''Čech'' , singular feminine: ''Češka'' ), or the Czech people (), are a West Slavic ethnic group and a nation native to the Czech Republic in Central Europe, who share a common ancestry, ...
and the
Slovaks surfaced again.
Hungary
After the war Hungary was severely disrupted by the loss of 72% of its territory, 64% of its population and most of its natural resources. The loss of territory was similar to that of Austria after the breaking up the Austria-Hungary territory. They lost the territories of Transylvania, Slovakia, Croatia, Slavonia,
Syrmia, and
Banat.
Italy
Italy incorporated the regions of Trieste and South Tyrol from Austria.
Poland
The creation of a free and Independent Poland was one of
Wilson's fourteen points. At the end of the 18th century the state of Poland was broken apart by Prussia, Russia, and Austria. During the
Paris Peace Conference, 1919
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), ma ...
, the
Commission on Polish Affairs
Commission or commissioning may refer to:
Business and contracting
* Commission (remuneration), a form of payment to an agent for services rendered
** Commission (art), the purchase or the creation of a piece of art most often on behalf of another ...
was created which recommended there be a passageway across West Prussia and Posen, in order to give Poland access to the Baltic through the port of Danzig at the mouth of the Vistula River. The creation of the state of Poland would separate East Prussia from the rest of Germany, as it was before the
Partitions of Poland. Poland also received Upper Silesia. British
Foreign Secretary Lord Curzon
George Nathaniel Curzon, 1st Marquess Curzon of Kedleston, (11 January 1859 – 20 March 1925), styled Lord Curzon of Kedleston between 1898 and 1911 and then Earl Curzon of Kedleston between 1911 and 1921, was a British Conservative statesman ...
proposed
Poland's eastern border with Russia. Neither the Soviet Russians nor the Polish were happy with the demarcation of the border.
Romania
The state of Romania was enlarged greatly after the war. As a result of the Paris peace conference Romania kept the
Dobrudja
Dobruja or Dobrudja (; bg, Добруджа, Dobrudzha or ''Dobrudža''; ro, Dobrogea, or ; tr, Dobruca) is a historical region in the Balkans that has been divided since the 19th century between the territories of Bulgaria and Romania. I ...
and Transylvania. Between the states of Yugoslavia, Czechoslovakia, and Romania an alliance named the
Little Entente was formed. They worked together on matters of foreign policy in order to prevent a Habsburg restoration.
Yugoslavia
Initially
Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label=Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavija ...
began as the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes. The name was changed to Yugoslavia in 1929. The State secured its territory at the Paris peace talks after the end of the war. The state suffered from many internal problems because of the many diverse cultures and languages within the state. Yugoslavia was divided on national, linguistic, economic, and religious lines.
See also
*
Belgian Expeditionary Corps in Russia, a Belgian armoured car unit that fought within the Russian military.
*
Diplomatic history of World War I
The diplomatic history of World War I covers the non-military interactions among the major players during World War I. For the domestic histories of participants see home front during World War I. For a longer-term perspective see international re ...
*
Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
Notes
References
* Sanborn, Josh. "The mobilization of 1914 and the question of the Russian nation: A reexamination." ''Slavic Review'' 59.2 (2000): 267-289
online* Wildman, Allan K. ''End of the Russian Imperial Army: The Old Army & the Soldiers' Revolt (March–April 1917)'' (1980).
* Trevelyan, George Macaulay (June 1915). "Austria-Hungary and Serbia". The North American Review 201 (715): 860–868.
* Mamatey, Albert (Oct. 1915). "The Situation in Austria-Hungary". The Journal of Race Development 6 (2): 203–217.
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Roshwald, Aviel; Stites, Richard, eds. (1999). European Culture in the Great War:The Arts, Entertainment and Propaganda 1914–1918. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 6,349–358.
* Oxana Nagornaja, Jeffrey Mankoff (2009). "United by Barbed Wire: Russian POWs in Germany, National Stereotypes, and International Relations". Explorations in Russian and Eurasian History 10 (3): 475–498. Retrieved 14 February 2014.
* Vinogradov, V.N (1992). "Romania in the First World War: The Years of Neutrality, 1914–16." The International History Review 14 (3): 452–461.
* Gatrell, Peter (2005). "Prisoners of War on the Eastern Front during World War I". Kritika 6 (3): 557–566. Retrieved 18 March 2014.
* Tucker, Spencer C. (1998). The Great War 1914–18. Bloomington: Indiana University Press. pp. 220–223.
*
External links
* Dowling, Timothy C.
Eastern Front in
* Sanborn, Joshua A.
Russian Empire in
* Steinberg, John W.
Warfare 1914–1918 (Russian Empire) in
* Szlanta, Piotr, Richter, Klaus
Warfare 1914–1918 (East Central Europe) in
* Zhvanko, Liubov
Ukraine in
* Sergeev, Evgenii Iur'evich
Pre-war Military Planning (Russian Empire) in
* Nachtigal, Reinhard, Radauer, Lena
Prisoners of War (Russian Empire) in
* Szlanta, Piotr, Richter, Klaus
Prisoners of War (East Central Europe) in
* Shcherbinin, Pavel Petrovich
Women's Mobilization for War (Russian Empire) in
*
*
With the Russian army, 1914–1917by
Alfred Knox
Major-General Sir Alfred William Fortescue Knox (30 October 1870 – 9 March 1964) was a career British military officer and later a Conservative Party politician.
Military career
Born in Ulster, Knox joined the British Army when he attended th ...
War And Revolution In Russia 1914–1917by General Basil Gourko.
modern photos by Andrey Dybowski (rus).
Der Vormarsch der Flieger Abteilung 27 in der Ukraine(The advance of Flight Squadron 27 in the Ukraine). Thi
portfolio comprising 263 photographs mounted on 48 pages, is a photo-documentary of the German occupation and military advances through the southern Ukraine in the spring and summer of 1918.
{{Authority control
Campaigns and theatres of World War I
Eastern Front
Austria-Hungary in World War I
Bulgaria in World War I
German Empire in World War I
Ottoman Empire in World War I
Romania in World War I
Russian Empire in World War I
Ukraine in World War I
Invasions of Russia
 While the war on the Western Front developed into
While the war on the Western Front developed into  In the immediate years preceding the
In the immediate years preceding the  In order for the Russians to legitimize their war efforts, the government constructed an image of the enemy through state-instituted propaganda. Their main aim was to help overcome the legend of the "invincible" German war machine, in order to boost the morale of civilians and soldiers. Russian propaganda often took the form of showing the Germans as a civilized nation, with barbaric "inhuman" traits. Russian propaganda also exploited the image of the Russian POWs who were in the German camps, again in order to boost the morale of their troops, serving as encouragement to defeat the enemy and to get their fellow soldiers out of German POW camps that were perceived as inhumane.
An element of the Russian propaganda was the Investigate Commission formed in April 1915. It was led by Aleksei Krivtsov, and the study was tasked with the job of studying the legal violations committed by of the Central Powers and then getting this information to the Russian public. This commission published photographs of letters that were allegedly found on fallen German soldiers. These letters document the German correspondents saying to "take no prisoners." A museum was also set up in Petrograd, which displayed pictures that showed how "inhumanly" the Germans were treating prisoners of war.
Also, the Russians chose to discard the name
In order for the Russians to legitimize their war efforts, the government constructed an image of the enemy through state-instituted propaganda. Their main aim was to help overcome the legend of the "invincible" German war machine, in order to boost the morale of civilians and soldiers. Russian propaganda often took the form of showing the Germans as a civilized nation, with barbaric "inhuman" traits. Russian propaganda also exploited the image of the Russian POWs who were in the German camps, again in order to boost the morale of their troops, serving as encouragement to defeat the enemy and to get their fellow soldiers out of German POW camps that were perceived as inhumane.
An element of the Russian propaganda was the Investigate Commission formed in April 1915. It was led by Aleksei Krivtsov, and the study was tasked with the job of studying the legal violations committed by of the Central Powers and then getting this information to the Russian public. This commission published photographs of letters that were allegedly found on fallen German soldiers. These letters document the German correspondents saying to "take no prisoners." A museum was also set up in Petrograd, which displayed pictures that showed how "inhumanly" the Germans were treating prisoners of war.
Also, the Russians chose to discard the name  Austria-Hungary's participation in the outbreak of World War I has been neglected by historians, as emphasis has traditionally been placed on Germany's role as the prime instigator. However, the "spark" that ignited the First World War is attributed to the
Austria-Hungary's participation in the outbreak of World War I has been neglected by historians, as emphasis has traditionally been placed on Germany's role as the prime instigator. However, the "spark" that ignited the First World War is attributed to the 
 The war in the east began with the Russian invasion of East Prussia on 17 August 1914 and the Austro-Hungarian province of Galicia. The Russian offensive in the Battle of Stallupönen, which was the opening battle of the Eastern Front, quickly turned to a disastrous defeat followed by the
The war in the east began with the Russian invasion of East Prussia on 17 August 1914 and the Austro-Hungarian province of Galicia. The Russian offensive in the Battle of Stallupönen, which was the opening battle of the Eastern Front, quickly turned to a disastrous defeat followed by the  In 1915 the Chief of German Great General Staff, General of Infantry Erich von Falkenhayn decided to make its main effort on the Eastern Front, and accordingly transferred considerable forces there. The year began with a successful German offensive in the area of the Masurian lakes. At the same time, a large battle for the city of
In 1915 the Chief of German Great General Staff, General of Infantry Erich von Falkenhayn decided to make its main effort on the Eastern Front, and accordingly transferred considerable forces there. The year began with a successful German offensive in the area of the Masurian lakes. At the same time, a large battle for the city of  The Italian operations during 1916 had one extraordinary result: Austrian divisions were pulled away from the Russian southern front. This allowed the Russian forces to organize a counter-offensive. The Brusilov offensive was a large tactical assault carried out by Russian forces against Austro-Hungarian forces in Galicia. General Aleksei Brusilov believed victory against the Central Powers was possible if close attention was paid to preparation. Brusilov suggested that the Russians should attack on a wide front, and to position their trenches a mere away from Austrian trenches.
Brusilov's plan worked impeccably. The Russians outnumbered the Austrians 200,000 to 150,000, and held a considerable advantage in guns, with 904 large guns to 600. Most importantly innovative new tactics similar to those independently invented by Erwin Rommel were used to perform quick and effective close-range surprise attacks that allowed a steady advance. The Russian Eighth Army overwhelmed the Austrian Fourth and pushed on to Lutsk, advancing beyond the starting position. Over a million Austrians were lost, with over 500,000 men killed or taken prisoner by mid-June.
Although the Brusilov offensive was initially successful, it slowed down considerably. An inadequate number of troops and poorly maintained supply lines hindered Brusilov's ability to follow up on the initial victories in June. The Brusilov offensive is considered to be the greatest Russian victory of the First World War. Although it cost the Russians half a million casualties only during the first two months offensive, the offensive successfully diverted substantial forces of the Central Powers from the Western front, and persuaded Romania to join the war, diverting even more Central Powers forces to the East.
The Italian operations during 1916 had one extraordinary result: Austrian divisions were pulled away from the Russian southern front. This allowed the Russian forces to organize a counter-offensive. The Brusilov offensive was a large tactical assault carried out by Russian forces against Austro-Hungarian forces in Galicia. General Aleksei Brusilov believed victory against the Central Powers was possible if close attention was paid to preparation. Brusilov suggested that the Russians should attack on a wide front, and to position their trenches a mere away from Austrian trenches.
Brusilov's plan worked impeccably. The Russians outnumbered the Austrians 200,000 to 150,000, and held a considerable advantage in guns, with 904 large guns to 600. Most importantly innovative new tactics similar to those independently invented by Erwin Rommel were used to perform quick and effective close-range surprise attacks that allowed a steady advance. The Russian Eighth Army overwhelmed the Austrian Fourth and pushed on to Lutsk, advancing beyond the starting position. Over a million Austrians were lost, with over 500,000 men killed or taken prisoner by mid-June.
Although the Brusilov offensive was initially successful, it slowed down considerably. An inadequate number of troops and poorly maintained supply lines hindered Brusilov's ability to follow up on the initial victories in June. The Brusilov offensive is considered to be the greatest Russian victory of the First World War. Although it cost the Russians half a million casualties only during the first two months offensive, the offensive successfully diverted substantial forces of the Central Powers from the Western front, and persuaded Romania to join the war, diverting even more Central Powers forces to the East.
 Up until 1916, the Romanians followed the tides of war with interest, while attempting to situate themselves in the most advantageous position. French and Russian diplomats had begun courting the Romanians early on, but persuasion tactics gradually intensified. For King Ferdinand to commit his force of half a million men, he expected the Allies to offer a substantial incentive. Playing on Romanian anti-Hungarian sentiment the Allies promised the Austria-Hungarian territory of Ardeal (Transylvania) to Romania. Transylvanian
Up until 1916, the Romanians followed the tides of war with interest, while attempting to situate themselves in the most advantageous position. French and Russian diplomats had begun courting the Romanians early on, but persuasion tactics gradually intensified. For King Ferdinand to commit his force of half a million men, he expected the Allies to offer a substantial incentive. Playing on Romanian anti-Hungarian sentiment the Allies promised the Austria-Hungarian territory of Ardeal (Transylvania) to Romania. Transylvanian 
 On 7 November 1917, the Communist
On 7 November 1917, the Communist  In comparison to the attention directed to the role played by women on the Western Front during the First World War, the role of women in the east has garnered limited scholarly focus. It is estimated that 20 percent of the Russian industrial working class was conscripted into the army; therefore, women's share of industrial jobs increased dramatically. There were percentage increases in every industry, but the most noticeable increase happened in industrial labour, which increased from 31.4 percent in 1913 to 45 percent in 1918.
Women also fought on the Eastern Front. In the later stages of Russia's participation in the war, Russia began forming all-woman combat units, the
In comparison to the attention directed to the role played by women on the Western Front during the First World War, the role of women in the east has garnered limited scholarly focus. It is estimated that 20 percent of the Russian industrial working class was conscripted into the army; therefore, women's share of industrial jobs increased dramatically. There were percentage increases in every industry, but the most noticeable increase happened in industrial labour, which increased from 31.4 percent in 1913 to 45 percent in 1918.
Women also fought on the Eastern Front. In the later stages of Russia's participation in the war, Russia began forming all-woman combat units, the