Earth's location in the Universe on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Knowledge of the location of Earth has been shaped by 400 years of telescopic observations, and has expanded radically since the start of the 20th century. Initially, Earth was believed to be the Geocentric model, center of the Universe,
which consisted only of those planets visible with the classical planet, naked eye and an outlying sphere of fixed stars. After the acceptance of the heliocentric model in the 17th century, observations by William Herschel and others showed that the Sun lay within a vast, disc-shaped galaxy of stars. By the 20th century, observations of spiral nebulae revealed that the Milky Way galaxy was one of billions in an expanding universe, grouped into clusters and superclusters. By the end of the 20th century, the large-scale structure of the cosmos, overall structure of the visible universe was becoming clearer, with superclusters forming into a vast web of galactic filament, filaments and Void (astronomy), voids. Superclusters, filaments and voids are the largest coherent structures in the Universe that we can observe. At still larger scales (over 1000 megaparsecs) the Universe becomes homogeneous, meaning that all its parts have on average the same density, composition and structure.
Since there is believed to be no "center" or "edge" of the Universe, there is no particular reference point with which to plot the overall location of the Earth in the universe. Because the observable universe is defined as that region of the Universe visible to terrestrial observers, Earth is, because of the constancy of the speed of light, the center of Earth's observable universe. Reference can be made to the Earth's position with respect to specific structures, which exist at various scales. It is still undetermined whether the Universe is Infinity, infinite. There have been numerous hypotheses that the known universe may be only one such example within a higher multiverse; however, no direct evidence of any sort of multiverse has been observed, and some have argued that the hypothesis is not falsifiable.
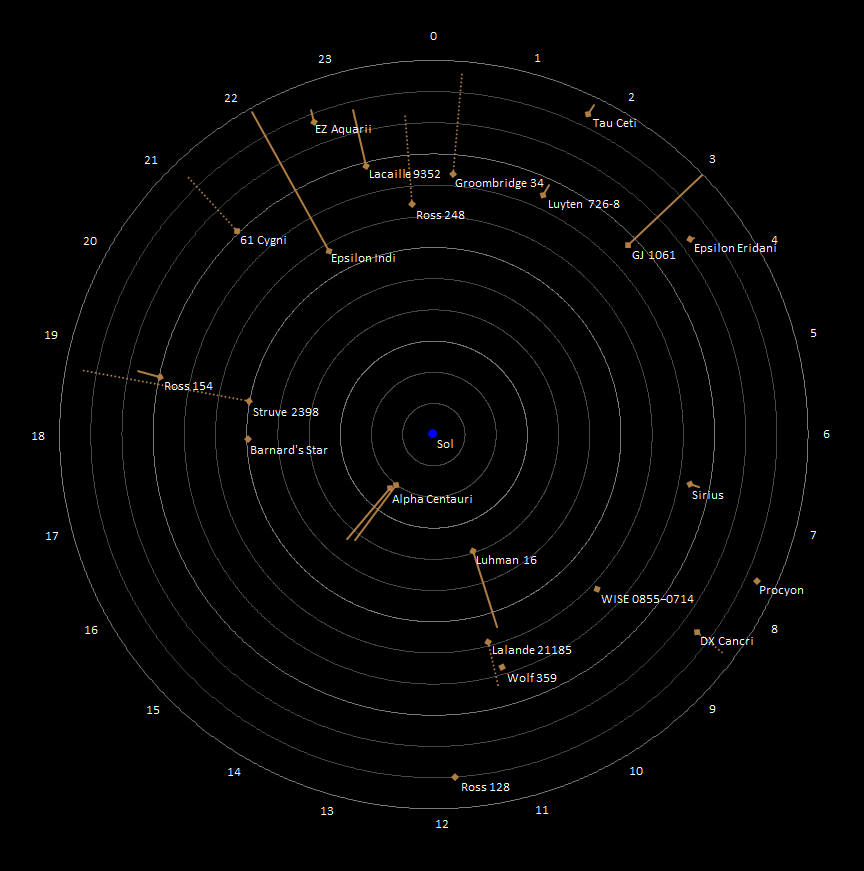
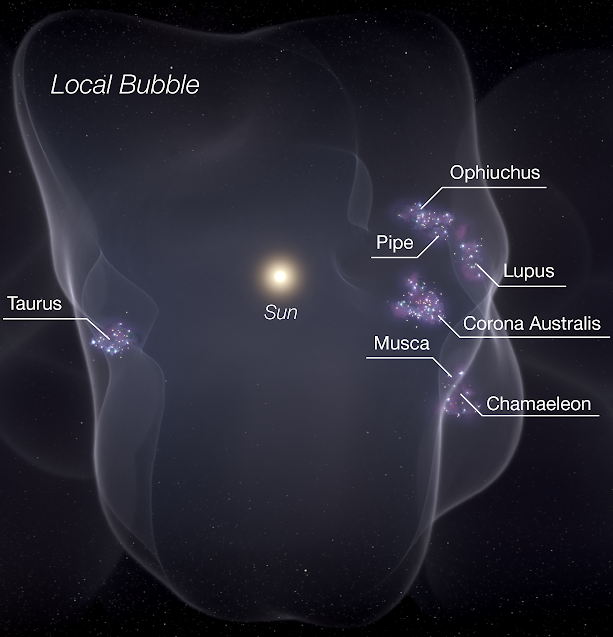 Earth is the third planet from the Sun with an approximate distance of , and is traveling nearly through outer space.
Earth is the third planet from the Sun with an approximate distance of , and is traveling nearly through outer space.
NOTE: Estimated velocity of the Earth traveling through outer space may be between – see discussion at "Wikipedia:Reference desk/Archives/Science/2019 July 20#How fast are we moving through space?"
Details

 Earth is the third planet from the Sun with an approximate distance of , and is traveling nearly through outer space.
Earth is the third planet from the Sun with an approximate distance of , and is traveling nearly through outer space.NOTE: Estimated velocity of the Earth traveling through outer space may be between – see discussion at "Wikipedia:Reference desk/Archives/Science/2019 July 20#How fast are we moving through space?"
Table
Gallery
See also
* ''Cosmic View'' * ''Cosmic Zoom'' * ''Galaxy Song'' * History of the center of the Universe * Orders of magnitude (length) * ''Pale Blue Dot'' * Powers of Ten (film), ''Powers of Ten'' (film) * List of nearest starsNotes
References
{{Portal bar, Stars, Spaceflight, Physics, Science, Weather Earth, Location in the Universe Physical cosmology