Dyfnwal ab Owain on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Dyfnwal ab Owain (died 975) was a tenth-century King of Strathclyde. He was a son of Owain ap Dyfnwal, King of Strathclyde, and seems to have been a member of the royal dynasty of Strathclyde. At some point in the ninth- or tenth century, the
 For hundreds of years until the late ninth century, the power centre of the
For hundreds of years until the late ninth century, the power centre of the  At some point after the loss of Al Clud, the
At some point after the loss of Al Clud, the  Dyfnwal was a son of Owain ap Dyfnwal, King of Strathclyde. The names of the latter and of his apparent descendants suggest that they were indeed members of the royal kindred of Strathclyde. Sons of Dyfnwal seem to include Rhydderch, Máel Coluim, and Owain. The name of Dyfnwal's son Máel Coluim is
Dyfnwal was a son of Owain ap Dyfnwal, King of Strathclyde. The names of the latter and of his apparent descendants suggest that they were indeed members of the royal kindred of Strathclyde. Sons of Dyfnwal seem to include Rhydderch, Máel Coluim, and Owain. The name of Dyfnwal's son Máel Coluim is
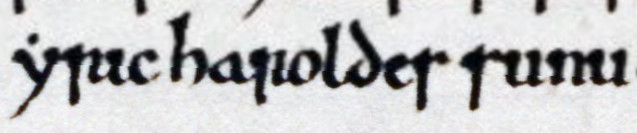 Dyfnwal is attested by the tenth-century ''Life of St Cathróe'', which appears to indicate that he was established as king by at least the 940s. According to this source, when Cathróe left the realm of Custantín mac Áeda, King of Alba at about this time, he was granted safe passage through the lands of the Cumbrians by Dyfnwal because the two men were related. Dyfnwal thereupon had Cathróe escorted through his kingdom to the frontier of the Scandinavian-controlled Northumbrian territory. The ''Life of St Cathróe'' locates this southern frontier to the of . One possibility is that this refers to
Dyfnwal is attested by the tenth-century ''Life of St Cathróe'', which appears to indicate that he was established as king by at least the 940s. According to this source, when Cathróe left the realm of Custantín mac Áeda, King of Alba at about this time, he was granted safe passage through the lands of the Cumbrians by Dyfnwal because the two men were related. Dyfnwal thereupon had Cathróe escorted through his kingdom to the frontier of the Scandinavian-controlled Northumbrian territory. The ''Life of St Cathróe'' locates this southern frontier to the of . One possibility is that this refers to  The ''Life of St Cathróe'' identifies Cathróe's parents as Fochereach and Bania. Whilst the former's name is Gaelic, the latter's name could be either Gaelic or
The ''Life of St Cathróe'' identifies Cathróe's parents as Fochereach and Bania. Whilst the former's name is Gaelic, the latter's name could be either Gaelic or
 In 945, the "A" version of the eleventh- to thirteenth-century ''
In 945, the "A" version of the eleventh- to thirteenth-century '' Although the Wendover version of ''Flores historiarum'' alleges that Máel Coluim mac Domnaill was given Cumbrian territory to hold as a fief from the English, the terminology employed by the more reliable ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' seems to suggest that Edmund merely surrendered or granted the region to him, or that he merely recognised certain rights of the Scots in the region (such as the right to tribute). Edmund, therefore, may have allowed his Scottish counterpart to collect tribute from the Cumbrians in return for keeping them in check and for lending Edmund military assistance. It is possible that the territory in question corresponds to the region around
Although the Wendover version of ''Flores historiarum'' alleges that Máel Coluim mac Domnaill was given Cumbrian territory to hold as a fief from the English, the terminology employed by the more reliable ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' seems to suggest that Edmund merely surrendered or granted the region to him, or that he merely recognised certain rights of the Scots in the region (such as the right to tribute). Edmund, therefore, may have allowed his Scottish counterpart to collect tribute from the Cumbrians in return for keeping them in check and for lending Edmund military assistance. It is possible that the territory in question corresponds to the region around  Edmund was assassinated in 946, and succeeded by his brother
Edmund was assassinated in 946, and succeeded by his brother  There is also reason to suspect that a man other than Dyfnwal ruled as king in the wake of Edmund's 945 campaign. For instance, a certain Cadmon is recorded to have witnessed two royal charters of Edmund's successor, Eadred—one in 946 and another in 949—which could be evidence that Cadmon was then the ruling Cumbrian monarch. There may be evidence indicating that, from about the time of the campaign until at least 958, the English regarded the land of the Cumbrians as part of the English realm. For instance, a charter apparently issued upon Eadred's coronation—the first of the two witnessed by Cadmon—accords Eadred the title "king of the Anglo-Saxons, Northumbrians, pagans, and Britons", whilst a 958 charter of Eadred's royal successor
There is also reason to suspect that a man other than Dyfnwal ruled as king in the wake of Edmund's 945 campaign. For instance, a certain Cadmon is recorded to have witnessed two royal charters of Edmund's successor, Eadred—one in 946 and another in 949—which could be evidence that Cadmon was then the ruling Cumbrian monarch. There may be evidence indicating that, from about the time of the campaign until at least 958, the English regarded the land of the Cumbrians as part of the English realm. For instance, a charter apparently issued upon Eadred's coronation—the first of the two witnessed by Cadmon—accords Eadred the title "king of the Anglo-Saxons, Northumbrians, pagans, and Britons", whilst a 958 charter of Eadred's royal successor
 Máel Coluim mac Domnaill was slain in 954, and succeeded by Illulb mac Custantín. At some point during the latter's reign, the Scots permanently acquired
Máel Coluim mac Domnaill was slain in 954, and succeeded by Illulb mac Custantín. At some point during the latter's reign, the Scots permanently acquired
 After Illulb's death in 962, the Scottish kingship appears to have been taken up by Dub mac Maíl Choluim, a man who was in turn replaced by Illulb's son,
After Illulb's death in 962, the Scottish kingship appears to have been taken up by Dub mac Maíl Choluim, a man who was in turn replaced by Illulb's son,  Although there is no specific evidence that Rhydderch was himself a king, the fact that Cuilén was involved with his daughter, coupled with the fact that his warband was evidently strong enough to overcome that of Cuilén, suggests that Rhydderch must have been a man of eminent standing. According to the ''Prophecy of Berchán'', Cuilén met his end whilst "seeking a foreign land", which could indicate that he was attempting to lift taxes from the Cumbrians. Another way in which Cuilén may have met his end concerns the record of his father's seizure of Edinburgh. The fact that this conquest would have likely included at least part of Lothian, coupled with the evidence placing Cuilén's demise in the same area, could indicate that Cuilén was slain in the midst of exercising overlordship of this contested territory. If so, the records that link Rhydderch with the
Although there is no specific evidence that Rhydderch was himself a king, the fact that Cuilén was involved with his daughter, coupled with the fact that his warband was evidently strong enough to overcome that of Cuilén, suggests that Rhydderch must have been a man of eminent standing. According to the ''Prophecy of Berchán'', Cuilén met his end whilst "seeking a foreign land", which could indicate that he was attempting to lift taxes from the Cumbrians. Another way in which Cuilén may have met his end concerns the record of his father's seizure of Edinburgh. The fact that this conquest would have likely included at least part of Lothian, coupled with the evidence placing Cuilén's demise in the same area, could indicate that Cuilén was slain in the midst of exercising overlordship of this contested territory. If so, the records that link Rhydderch with the  Cuilén seems to have been succeeded by his kinsman
Cuilén seems to have been succeeded by his kinsman
 There is evidence to suggest that Dyfnwal was amongst the assembled kings who are recorded to have met with Edgar at
There is evidence to suggest that Dyfnwal was amongst the assembled kings who are recorded to have met with Edgar at  Whilst the symbolic tale of the men rowing Edgar down the river may be an unhistorical embellishment, most of the names accorded to the eight kings can be associated with contemporary rulers, suggesting that some of these men may have taken part in a concord with him. Although the latter accounts allege that the kings submitted to Edgar, the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' merely states that they came to an agreement of cooperation with him, and thus became his ("co-workers", "even-workers", "fellow-workers"). One possibility is that the assembly somehow relates to Edmund's attested incursion into Cumbria in 945. According to the same source, when Edmund Cumbria to Máel Coluim mac Domnaill, he had done so on the condition that the latter would be his ("co-worker", "even-worker", "fellow-worker", "together-wright"). Less reliable non-contemporary sources such as ''De primo Saxonum adventu'', both the Wendover and Paris versions of ''Flores historiarum'', and ''Chronica majora'' allege that Edgar granted
Whilst the symbolic tale of the men rowing Edgar down the river may be an unhistorical embellishment, most of the names accorded to the eight kings can be associated with contemporary rulers, suggesting that some of these men may have taken part in a concord with him. Although the latter accounts allege that the kings submitted to Edgar, the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' merely states that they came to an agreement of cooperation with him, and thus became his ("co-workers", "even-workers", "fellow-workers"). One possibility is that the assembly somehow relates to Edmund's attested incursion into Cumbria in 945. According to the same source, when Edmund Cumbria to Máel Coluim mac Domnaill, he had done so on the condition that the latter would be his ("co-worker", "even-worker", "fellow-worker", "together-wright"). Less reliable non-contemporary sources such as ''De primo Saxonum adventu'', both the Wendover and Paris versions of ''Flores historiarum'', and ''Chronica majora'' allege that Edgar granted  One of the other named kings was Cináed. Considering the fact that the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' numbers the kings at six, if Cináed was indeed present, it is unlikely that his rival, Cuilén's brother Amlaíb mac Illuilb, was also in attendance. Woolf (2007) p. 208. Although the chronology concerning the reigns of Cináed and Amlaíb mac Illuilb is uncertain—with Amlaíb mac Illuilb perhaps reigning from 971/976–977 and Cináed from 971/977–995—the part played by the King of Alba at the assembly could well have concerned the frontier of his realm. Matthews (2007) p. 25. One of the other named kings seems to have been Maccus mac Arailt, whilst another could have been this man's brother,
One of the other named kings was Cináed. Considering the fact that the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' numbers the kings at six, if Cináed was indeed present, it is unlikely that his rival, Cuilén's brother Amlaíb mac Illuilb, was also in attendance. Woolf (2007) p. 208. Although the chronology concerning the reigns of Cináed and Amlaíb mac Illuilb is uncertain—with Amlaíb mac Illuilb perhaps reigning from 971/976–977 and Cináed from 971/977–995—the part played by the King of Alba at the assembly could well have concerned the frontier of his realm. Matthews (2007) p. 25. One of the other named kings seems to have been Maccus mac Arailt, whilst another could have been this man's brother,  Another aspect of the assembly may have concerned the remarkable rising power of Amlaíb Cúarán in Ireland. Edgar may have wished to not only rein in men such as Maccus and Gofraid, but prevent them—and the Scots and Cumbrians—from affiliating themselves with Amlaíb Cúarán, and recognising the latter's authority in the Irish Sea region. Another factor concerning Edgar, and his Scottish and Cumbrian counterparts, may have been the stability of the northern English frontier. For example, a certain Thored Gunnerson is recorded to have ravaged
Another aspect of the assembly may have concerned the remarkable rising power of Amlaíb Cúarán in Ireland. Edgar may have wished to not only rein in men such as Maccus and Gofraid, but prevent them—and the Scots and Cumbrians—from affiliating themselves with Amlaíb Cúarán, and recognising the latter's authority in the Irish Sea region. Another factor concerning Edgar, and his Scottish and Cumbrian counterparts, may have been the stability of the northern English frontier. For example, a certain Thored Gunnerson is recorded to have ravaged
 Both Dyfnwal and his English counterpart died in 975. According to various
Both Dyfnwal and his English counterpart died in 975. According to various  It is conceivable that Dyfnwal was still reigning in 973, and that it was Edgar's death two years later that precipitated the transfer of the kingship to Dyfnwal's son Máel Coluim, and contributed to Dyfnwal's pilgrimage to Rome. In fact, the upheaval caused by the absence of the English and Cumbrian kings could well have contributed to Cináed's final elimination of Amlaíb mac Illuilb in 997. Another possibility is that Máel Coluim's part in the 973 assembly may have partly concerned his father's impending pilgrimage, and that he sought surety for Dyfnwal's safe passage through Edgar's realm. The fact that Máel Coluim is identified as one of the assembled kings could indicate that Dyfnwal had relinquished control to him at some point before the convention. Evidence that he had indeed assumed the kingship may exist in the record of a certain ''Malcolm dux'' who witnessed an English royal charter in 970. Although the authenticity of this document is questionable, the attested Malcolm could well be identical to Máel Coluim himself. If Máel Coluim was indeed king in 973, Dyfnwal's role at the assembly may have been that of an ' elder statesman' of sorts—possibly serving as an adviser or mentor—especially considering his decades of experience in international affairs. The fact that he left his realm for Rome could be evidence that he did not regard his realm or dynasty to be threatened during his absence.
It is conceivable that Dyfnwal was still reigning in 973, and that it was Edgar's death two years later that precipitated the transfer of the kingship to Dyfnwal's son Máel Coluim, and contributed to Dyfnwal's pilgrimage to Rome. In fact, the upheaval caused by the absence of the English and Cumbrian kings could well have contributed to Cináed's final elimination of Amlaíb mac Illuilb in 997. Another possibility is that Máel Coluim's part in the 973 assembly may have partly concerned his father's impending pilgrimage, and that he sought surety for Dyfnwal's safe passage through Edgar's realm. The fact that Máel Coluim is identified as one of the assembled kings could indicate that Dyfnwal had relinquished control to him at some point before the convention. Evidence that he had indeed assumed the kingship may exist in the record of a certain ''Malcolm dux'' who witnessed an English royal charter in 970. Although the authenticity of this document is questionable, the attested Malcolm could well be identical to Máel Coluim himself. If Máel Coluim was indeed king in 973, Dyfnwal's role at the assembly may have been that of an ' elder statesman' of sorts—possibly serving as an adviser or mentor—especially considering his decades of experience in international affairs. The fact that he left his realm for Rome could be evidence that he did not regard his realm or dynasty to be threatened during his absence.
 Surviving sources fail to note the Cumbrian kingdom between the obituaries of Dyfnwal in 975 and his son, Máel Coluim, in 997. There is reason to suspect that Dyfnwal had another son, Owain, who reigned after Máel Coluim. Clarkson (2014) ch. 7 ¶ 17; Clarkson (2010) ch. 9 ¶ 41; Woolf (2007) pp. 222, 233, 236. For instance, according to the "B" version of ''Annales Cambriæ'', a certain Owain—identified as the son of a man named Dyfnwal—was slain in 1015. This obituary is corroborated by ''Brut y Tywysogyon'', and ''Brenhinedd y Saesson''. Although it may be possible that the record of this man's death refers to
Surviving sources fail to note the Cumbrian kingdom between the obituaries of Dyfnwal in 975 and his son, Máel Coluim, in 997. There is reason to suspect that Dyfnwal had another son, Owain, who reigned after Máel Coluim. Clarkson (2014) ch. 7 ¶ 17; Clarkson (2010) ch. 9 ¶ 41; Woolf (2007) pp. 222, 233, 236. For instance, according to the "B" version of ''Annales Cambriæ'', a certain Owain—identified as the son of a man named Dyfnwal—was slain in 1015. This obituary is corroborated by ''Brut y Tywysogyon'', and ''Brenhinedd y Saesson''. Although it may be possible that the record of this man's death refers to  Dyfnwal may be the man immortalised in the name of a
Dyfnwal may be the man immortalised in the name of a
Kingdom of Strathclyde
Strathclyde (lit. " Strath of the River Clyde", and Strað-Clota in Old English), was a Brittonic successor state of the Roman Empire and one of the early medieval kingdoms of the Britons, located in the region the Welsh tribes referred to as ...
expanded substantially southwards. As a result of this extension far beyond the valley of the River Clyde
The River Clyde ( gd, Abhainn Chluaidh, , sco, Clyde Watter, or ) is a river that flows into the Firth of Clyde in Scotland. It is the ninth-longest river in the United Kingdom, and the third-longest in Scotland. It runs through the major cit ...
, the realm became known as the Kingdom of Cumbria. By 927, the kingdom seems to have reached as far south as the River Eamont
The River Eamont is a river in Cumbria, England and one of the major tributaries of the River Eden. The name of the river is from Old English (ēa-gemōt) and is a back formation from Eamont Bridge which means the ''junction of streams.''
T ...
.
Dyfnwal appears to have reigned between the 930s and the 970s. He is first attested in the 940s, when he is recorded associated with the ecclesiast Cathróe on the latter's journey to Continental Europe
Continental Europe or mainland Europe is the contiguous continent of Europe, excluding its surrounding islands. It can also be referred to ambiguously as the European continent, – which can conversely mean the whole of Europe – and, by ...
. At the midpoint of the decade, the Cumbrian kingdom was ravaged by the forces of Edmund, King of the English. Two of Dyfnwal's sons are said to have been blinded by the English, which could indicate that Dyfnwal had broken a pledge to his southern counterpart. One possibility is that he had harboured insular Scandinavian opponents of Edmund. The latter is recorded to have handed over control of the Cumbrian realm to Máel Coluim mac Domnaill, King of Alba
Máel Coluim mac Domnaill (anglicised Malcolm I; died 954) was king of Alba (before 943 – 954), becoming king when his cousin Constantine II abdicated to become a monk. He was the son of Donald II.
Biography
Malcolm was born in 897 in Au ...
. How much authority the Scots enjoyed over the Cumbrian realm is uncertain.
In 971, the reigning Cuilén mac Illuilb, King of Alba was slain by Rhydderch ap Dyfnwal. At some point after this act, Cuilén's eventual successor, Cináed mac Maíl Choluim, King of Alba, is recorded to have penetrated deep into Cumbrian territory, possibly as a retaliatory act. The following year, the reigning Edgar, King of the English
Edgar ( ang, Ēadgār ; 8 July 975), known as the Peaceful or the Peaceable, was King of the English from 959 until his death in 975. The younger son of King Edmund I and Ælfgifu of Shaftesbury, he came to the throne as a teenager following ...
held a remarkable assembly at Chester
Chester is a cathedral city and the county town of Cheshire, England. It is located on the River Dee, close to the English–Welsh border. With a population of 79,645 in 2011,"2011 Census results: People and Population Profile: Chester Loca ...
which numerous northern kings seem to have attended. Both Dyfnwal and his son, Máel Coluim, appear to have attended this assembly. The latter is styled King of the Cumbrians in the context of this meeting, which might indicate that Dyfnwal had previously abdicated the throne.
Dyfnwal is recorded to have died in 975 whilst undertaking a pilgrimage to Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus ( legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
. Quite when he gave up the throne is unknown. One possibility is that Rhydderch had succeeded him before the killing of Cuilén. Another possibility is that the apparent retaliatory raid by Cináed marked the end of Dyfnwal's kingship. It is also possible that he held on to power until 973 or 975. In any event, Máel Coluim appears to have been succeeded by another son of Dyfnwal named Owain, who is recorded to have died in 1015. The later Owain Foel, King of Strathclyde Owain () is a name of Welsh origin, variously written in Old Welsh as Ougein, Eugein, Euguen, Iguein, Ou(u)ein, Eug(u)ein, Yuein, and in Middle Welsh as Ewein, Owein, and Ywein. Other variants of the name Owain include Ewein, Iguein, Owein, Ouein, Y ...
, who is attested in 1018, may well be a grandson of Dyfnwal. Dyfnwal is likely the eponym
An eponym is a person, a place, or a thing after whom or which someone or something is, or is believed to be, named. The adjectives which are derived from the word eponym include ''eponymous'' and ''eponymic''.
Usage of the word
The term ''epon ...
of Dunmail Raise in England, and possibly Cardonald
Cardonald ( sco, Cardonal, gd, Cair Dhòmhnaill
) is ...
and Dundonald/) is ...
Dundonald Castle
Dundonald Castle is situated on a hill overlooking the village of Dundonald, between Kilmarnock and Troon in South Ayrshire, Scotland. Dundonald Castle is a fortified tower house built for Robert II on his accession to the throne of Scotl ...
in Scotland.
Background: the tenth century Cumbrian realm
 For hundreds of years until the late ninth century, the power centre of the
For hundreds of years until the late ninth century, the power centre of the Kingdom of Al Clud
Strathclyde (lit. "Strath of the River Clyde", and Strað-Clota in Old English), was a Brittonic successor state of the Roman Empire and one of the early medieval kingdoms of the Britons, located in the region the Welsh tribes referred to as Yr ...
was the fortress of Al Clud ("Rock of the Clyde"). In 870, this British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
stronghold was seized by Irish-based Scandinavians
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and ...
, after which the centre of the realm seems to have relocated further up the River Clyde
The River Clyde ( gd, Abhainn Chluaidh, , sco, Clyde Watter, or ) is a river that flows into the Firth of Clyde in Scotland. It is the ninth-longest river in the United Kingdom, and the third-longest in Scotland. It runs through the major cit ...
, and the kingdom itself began to bear the name of the valley of the River Clyde, Ystrad Clud (Strathclyde). The kingdom's new capital may have been situated in the vicinity of Partick
Partick ( sco, Pairtick, Scottish Gaelic: ''Partaig'') is an area of Glasgow on the north bank of the River Clyde, just across from Govan. To the west lies Whiteinch, to the east Yorkhill and Kelvingrove Park (across the River Kelvin), and ...
. and Govan
Govan ( ; Cumbric?: ''Gwovan'?''; Scots: ''Gouan''; Scottish Gaelic: ''Baile a' Ghobhainn'') is a district, parish, and former burgh now part of south-west City of Glasgow, Scotland. It is situated west of Glasgow city centre, on the south b ...
which straddle the River Clyde, The realm's new hinterland
Hinterland is a German word meaning "the land behind" (a city, a port, or similar). Its use in English was first documented by the geographer George Chisholm in his ''Handbook of Commercial Geography'' (1888). Originally the term was associate ...
appears to have encompassed the valley and the region of modern Renfrewshire
Renfrewshire () ( sco, Renfrewshire; gd, Siorrachd Rinn Friù) is one of the 32 council areas of Scotland.
Located in the west central Lowlands, it is one of three council areas contained within the boundaries of the historic county of Re ...
, which may explain this change in terminology.
 At some point after the loss of Al Clud, the
At some point after the loss of Al Clud, the Kingdom of Strathclyde
Strathclyde (lit. " Strath of the River Clyde", and Strað-Clota in Old English), was a Brittonic successor state of the Roman Empire and one of the early medieval kingdoms of the Britons, located in the region the Welsh tribes referred to as ...
appears to have undergone a period of expansion. Although the precise chronology is uncertain, by 927 the southern frontier appears to have reached the River Eamont
The River Eamont is a river in Cumbria, England and one of the major tributaries of the River Eden. The name of the river is from Old English (ēa-gemōt) and is a back formation from Eamont Bridge which means the ''junction of streams.''
T ...
, close to Penrith. The catalyst for this southern extension may have been the dramatic decline of the Kingdom of Northumbria
la, Regnum Northanhymbrorum
, conventional_long_name = Kingdom of Northumbria
, common_name = Northumbria
, status = State
, status_text = Unified Anglian kingdom (before 876)North: Anglian kingdom (af ...
at the hands of conquering Scandinavians, and the expansion may have been facilitated by cooperation between the Britons and the insular Scandinavians in the late ninth- or early tenth century. Over time, the Kingdom of Strathclyde increasingly came to be known as the Kingdom of Cumbria reflecting its expansion far beyond the Clyde valley.
 Dyfnwal was a son of Owain ap Dyfnwal, King of Strathclyde. The names of the latter and of his apparent descendants suggest that they were indeed members of the royal kindred of Strathclyde. Sons of Dyfnwal seem to include Rhydderch, Máel Coluim, and Owain. The name of Dyfnwal's son Máel Coluim is
Dyfnwal was a son of Owain ap Dyfnwal, King of Strathclyde. The names of the latter and of his apparent descendants suggest that they were indeed members of the royal kindred of Strathclyde. Sons of Dyfnwal seem to include Rhydderch, Máel Coluim, and Owain. The name of Dyfnwal's son Máel Coluim is Gaelic
Gaelic is an adjective that means "pertaining to the Gaels". As a noun it refers to the group of languages spoken by the Gaels, or to any one of the languages individually. Gaelic languages are spoken in Ireland, Scotland, the Isle of Man, an ...
, and may be evidence of a marriage alliance between his family and the neighbouring royal Alpínid dynasty
The House of Alpin, also known as the Alpínid dynasty, Clann Chináeda, and Clann Chinaeda meic Ailpín, was the kin-group which ruled in Pictland, possibly Dál Riata, and then the kingdom of Alba from the advent of Kenneth MacAlpin (Cináe ...
of the Scottish Kingdom of Alba
The Kingdom of Alba ( la, Scotia; sga, Alba) was the Kingdom of Scotland between the deaths of Donald II in 900 and of Alexander III in 1286. The latter's death led indirectly to an invasion of Scotland by Edward I of England in 1296 and the ...
. Dyfnwal's father is attested in 934. Although Dyfnwal's father may well be identical to the Cumbrian monarch recorded to have fought at the Battle of Brunanburh
The Battle of Brunanburh was fought in 937 between Æthelstan, King of England, and an alliance of Olaf Guthfrithson, King of Dublin, Constantine II, King of Scotland, and Owain, King of Strathclyde. The battle is often cited as the poin ...
in 937, the sources that note this king fail to identify him by name. Dyfnwal's own reign, therefore, may have stretched from about the 930s to the 970s. Thornton (2001) p. 67.
Cathróe amongst the Cumbrians
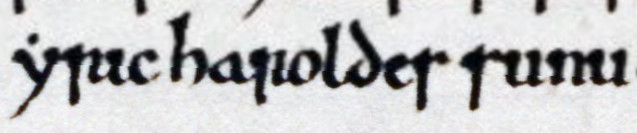 Dyfnwal is attested by the tenth-century ''Life of St Cathróe'', which appears to indicate that he was established as king by at least the 940s. According to this source, when Cathróe left the realm of Custantín mac Áeda, King of Alba at about this time, he was granted safe passage through the lands of the Cumbrians by Dyfnwal because the two men were related. Dyfnwal thereupon had Cathróe escorted through his kingdom to the frontier of the Scandinavian-controlled Northumbrian territory. The ''Life of St Cathróe'' locates this southern frontier to the of . One possibility is that this refers to
Dyfnwal is attested by the tenth-century ''Life of St Cathróe'', which appears to indicate that he was established as king by at least the 940s. According to this source, when Cathróe left the realm of Custantín mac Áeda, King of Alba at about this time, he was granted safe passage through the lands of the Cumbrians by Dyfnwal because the two men were related. Dyfnwal thereupon had Cathróe escorted through his kingdom to the frontier of the Scandinavian-controlled Northumbrian territory. The ''Life of St Cathróe'' locates this southern frontier to the of . One possibility is that this refers to Leeds
Leeds () is a city and the administrative centre of the City of Leeds district in West Yorkshire, England. It is built around the River Aire and is in the eastern foothills of the Pennines. It is also the third-largest settlement (by popul ...
. If correct, this could indicate that the Cumbrian realm stretched towards this settlement, and would further evince the general southward expansion of the kingdom. Another possibility is that refers to Leath Ward in Cumberland, or to a settlement in the Lowther Lowther may refer to: Places
*River Lowther, Cumbria, England
*Lowther, Cumbria, civil parish in Cumbria, England
*Lowther, New Zealand, township in Southland, New Zealand
*Lowther, New South Wales, locality in Australia
*CFS Lowther, military in ...
valley, not terribly far from where the River Eamont flows.
 The ''Life of St Cathróe'' identifies Cathróe's parents as Fochereach and Bania. Whilst the former's name is Gaelic, the latter's name could be either Gaelic or
The ''Life of St Cathróe'' identifies Cathróe's parents as Fochereach and Bania. Whilst the former's name is Gaelic, the latter's name could be either Gaelic or British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
, Clarkson (2010) ch. 9 ¶ 24. and Cathróe's own name could be either Pictish
Pictish is the extinct Brittonic language spoken by the Picts, the people of eastern and northern Scotland from Late Antiquity to the Early Middle Ages. Virtually no direct attestations of Pictish remain, short of a limited number of geographica ...
or British. The fact that Cathróe is stated to have been related to Dyfnwal could indicate that the former's ancestors included a Briton who possessed a genealogical connection with the royal Cumbrian dynasty, or that Dyfnwal possessed Scottish ancestry, or else that the families of Cathróe and Dyfnwal were merely connected by way of a marriage. Cathróe is also said by the source to have been related to the wife of a certain King of York named Erich. Although the latter may be identical to Eiríkr Haraldsson—a man who is generally thought to be identical to the Norwegian dynast Eiríkr blóðøx—this man is not otherwise attested by insular sources until 947, and Northumbria itself appears to have been ruled by the Uí Ímair
The Uí Ímair (; meaning ‘''scions of Ivar’''), also known as the Ivar Dynasty or Ivarids was a royal Norse-Gael dynasty which ruled much of the Irish Sea region, the Kingdom of Dublin, the western coast of Scotland, including the Hebrides ...
dynasts Amlaíb mac Gofraid and Amlaíb Cúarán during the time of Cathróe's journey. Whilst it is possible that Erich actually refers to Amlaíb mac Gofraid, if he instead refers to Eiríkr Haraldsson, it could be evidence that the latter had been based in the Solway region whilst the Uí Ímair
The Uí Ímair (; meaning ‘''scions of Ivar’''), also known as the Ivar Dynasty or Ivarids was a royal Norse-Gael dynasty which ruled much of the Irish Sea region, the Kingdom of Dublin, the western coast of Scotland, including the Hebrides ...
held power in Northumbria, or that the latter indeed held power in Northumbria as early as about 946.
English aggression and Scottish overlordship
 In 945, the "A" version of the eleventh- to thirteenth-century ''
In 945, the "A" version of the eleventh- to thirteenth-century ''Annales Cambriæ
The (Latin for ''Annals of Wales'') is the title given to a complex of Latin chronicles compiled or derived from diverse sources at St David's in Dyfed, Wales. The earliest is a 12th-century presumed copy of a mid-10th-century original; later ed ...
'', and the thirteenth- and fourteenth-century ''Brut y Tywysogyon
''Brut y Tywysogion'' ( en, Chronicle of the Princes) is one of the most important primary sources for Welsh history. It is an annalistic chronicle that serves as a continuation of Geoffrey of Monmouth’s ''Historia Regum Britanniae''. ''Br ...
'' reveal that the Cumbrian realm was wasted by the English. The ninth- to twelfth-century ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle
The ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' is a collection of annals in Old English, chronicling the history of the Anglo-Saxons. The original manuscript of the ''Chronicle'' was created late in the 9th century, probably in Wessex, during the reign of A ...
'' offers more information, and relates that Edmund I, King of the English harried across the land of the Cumbrians, and the region to Máel Coluim mac Domnaill, King of Alba
Máel Coluim mac Domnaill (anglicised Malcolm I; died 954) was king of Alba (before 943 – 954), becoming king when his cousin Constantine II abdicated to become a monk. He was the son of Donald II.
Biography
Malcolm was born in 897 in Au ...
. Similarly, the twelfth-century '' Historia Anglorum'' records that the English ravaged the realm, and that Edmund commended the lands to Máel Coluim mac Domnaill who had agreed to assist him by land and sea. According to the version of events preserved by the thirteenth-century Wendover
Wendover is a market town and civil parish at the foot of the Chiltern Hills in Buckinghamshire, England. It is situated at the point where the main road across the Chilterns between London and Aylesbury intersects with the once important road a ...
and Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Si ...
versions of ''Flores historiarum'', Edmund was assisted in the campaign by Hywel Dda, King of Dyfed, and had two of Dyfnwal's sons blinded. If the latter claim is to be believed, it could reveal that the two princes had been English hostages before hostilities broke out, or perhaps prisoners captured in the midst of the campaign. The gruesome fate inflicted upon these sons could reveal that their father was regarded to have broken certain pledges rendered to the English. One possibility is that Dyfnwal was punished for harbouring insular Scandinavian potentates such as Amlaíb Cúarán. The latter is certainly recorded to have been driven from Northumbria by the English the year before. He could well have taken refuge amongst the Cumbrians, or may have been attempting to construct a power base in the Cumbrian periphery. The close working relationship between Edmund and Máel Coluim mac Domnaill suggests that Amlaíb Cúarán was unlikely to have been harboured by the Scots during this period. Edmund's strike upon Dyfnwal's realm, therefore, seems to have been undertaken as a means to break a Cumbrian-Scandinavian alliance, and to limit the threat of an insular Scandinavian counter offensive from the Forth
Forth or FORTH may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''forth'' magazine, an Internet magazine
* ''Forth'' (album), by The Verve, 2008
* ''Forth'', a 2011 album by Proto-Kaw
* Radio Forth, a group of independent local radio stations in Scotla ...
-Clyde Clyde may refer to:
People
* Clyde (given name)
* Clyde (surname)
Places
For townships see also Clyde Township
Australia
* Clyde, New South Wales
* Clyde, Victoria
* Clyde River, New South Wales
Canada
* Clyde, Alberta
* Clyde, Ontario, a tow ...
region. The southward expansion of the Cumbrian realm—an extension possibly enabled by the insular Scandinavian power—may have also factored into the invasion, with the English clawing back lost territories. Whatever lay behind the campaign, it is possible that it was utilised by the English Cerdicing dynasty as a way to overawe and intimidate neighbouring potentates.
 Although the Wendover version of ''Flores historiarum'' alleges that Máel Coluim mac Domnaill was given Cumbrian territory to hold as a fief from the English, the terminology employed by the more reliable ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' seems to suggest that Edmund merely surrendered or granted the region to him, or that he merely recognised certain rights of the Scots in the region (such as the right to tribute). Edmund, therefore, may have allowed his Scottish counterpart to collect tribute from the Cumbrians in return for keeping them in check and for lending Edmund military assistance. It is possible that the territory in question corresponds to the region around
Although the Wendover version of ''Flores historiarum'' alleges that Máel Coluim mac Domnaill was given Cumbrian territory to hold as a fief from the English, the terminology employed by the more reliable ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' seems to suggest that Edmund merely surrendered or granted the region to him, or that he merely recognised certain rights of the Scots in the region (such as the right to tribute). Edmund, therefore, may have allowed his Scottish counterpart to collect tribute from the Cumbrians in return for keeping them in check and for lending Edmund military assistance. It is possible that the territory in question corresponds to the region around Carlisle
Carlisle ( , ; from xcb, Caer Luel) is a city that lies within the Northern English county of Cumbria, south of the Scottish border at the confluence of the rivers Eden, Caldew and Petteril. It is the administrative centre of the City ...
—roughly modern-day Cumberland
Cumberland ( ) is a historic counties of England, historic county in the far North West England. It covers part of the Lake District as well as the north Pennines and Solway Firth coast. Cumberland had an administrative function from the 12th c ...
—which in turn could reveal that the Scots were already in possession of the kingdom's more northerly lands. It is conceivable that the Scots were allowed authority over Cumbrian territory because it was too far to be overseen effectively by the English themselves. As such, it may have been recognised that the Cumbrian territories were situated within the Alpínid sphere of influence rather than that of the Cerdicings. In any event, it is uncertain what authority Máel Coluim mac Domnaill enjoyed over the Cumbrians. Although it is possible that there was a temporary Scottish takeover of the realm, Dyfnwal lived on for decades, and there were certainly later kings. In fact, the Wendover version of the ''Flores historiarum'' reveals that the Cumbrians were ruled by a king the year after Edmund's invasion. The concord between the English and the Scots could have been precipitated by the former as a way of further securing their northern frontier from the threat of insular Scandinavians. Similarly, the English campaign against the Cumbrians may have been undertaken in order to isolate the Scots from an alliance with the Scandinavians. In this way, Edmund's conquest and grant of Cumbrian territories to his Scottish counterpart may have been a way of winning the latter's obeisance.
 Edmund was assassinated in 946, and succeeded by his brother
Edmund was assassinated in 946, and succeeded by his brother Eadred
Eadred (c. 923 – 23 November 955) was King of the English from 26 May 946 until his death. He was the younger son of Edward the Elder and his third wife Eadgifu, and a grandson of Alfred the Great. His elder brother, Edmund, was killed try ...
, a monarch who soon after made a show of force against opposition in Northumbria, and received a renewal of oaths from his Scottish counterpart. In about 949/950, Máel Coluim mac Domnaill is recorded to have raided into Northumbria, perhaps against the retrenched forces of Eadred's Scandinavian opponents. Whilst it is possible that this event was undertaken in the context of compensation for the English campaigning against the Cumbrians in 946, an alternate possibility is that this Scottish invasion was instead an opportunistic attempt to extract tribute from the Northumbrian ruler Osulf (fl.
''Floruit'' (; abbreviated fl. or occasionally flor.; from Latin for "they flourished") denotes a date or period during which a person was known to have been alive or active. In English, the unabbreviated word may also be used as a noun indicatin ...
946–950), rather than the York-based Scandinavians.
In 952, the seventeenth-century ''Annals of the Four Masters
The ''Annals of the Kingdom of Ireland'' ( ga, Annála Ríoghachta Éireann) or the ''Annals of the Four Masters'' (''Annála na gCeithre Máistrí'') are chronicles of medieval Irish history. The entries span from the Deluge, dated as 2,24 ...
'' and the fifteenth- to sixteenth-century ''Annals of Ulster
The ''Annals of Ulster'' ( ga, Annála Uladh) are annals of medieval Ireland. The entries span the years from 431 AD to 1540 AD. The entries up to 1489 AD were compiled in the late 15th century by the scribe Ruaidhrí Ó Luinín, ...
'' appear to report an attack upon the Scandinavians of Northumbria by an alliance of English, Scots, and Cumbrians. If these two annal-entries indeed refer to Cumbrians rather than Welshmen, it would appear to indicate that the former—presumably led by Dyfnwal himself—were supporting the cause of the English with the Scots. One possibility is that the annal-entries record the clash of this coalition against the forces of Eiríkr, a man who was finally overwhelmed and slain two years later.
 There is also reason to suspect that a man other than Dyfnwal ruled as king in the wake of Edmund's 945 campaign. For instance, a certain Cadmon is recorded to have witnessed two royal charters of Edmund's successor, Eadred—one in 946 and another in 949—which could be evidence that Cadmon was then the ruling Cumbrian monarch. There may be evidence indicating that, from about the time of the campaign until at least 958, the English regarded the land of the Cumbrians as part of the English realm. For instance, a charter apparently issued upon Eadred's coronation—the first of the two witnessed by Cadmon—accords Eadred the title "king of the Anglo-Saxons, Northumbrians, pagans, and Britons", whilst a 958 charter of Eadred's royal successor
There is also reason to suspect that a man other than Dyfnwal ruled as king in the wake of Edmund's 945 campaign. For instance, a certain Cadmon is recorded to have witnessed two royal charters of Edmund's successor, Eadred—one in 946 and another in 949—which could be evidence that Cadmon was then the ruling Cumbrian monarch. There may be evidence indicating that, from about the time of the campaign until at least 958, the English regarded the land of the Cumbrians as part of the English realm. For instance, a charter apparently issued upon Eadred's coronation—the first of the two witnessed by Cadmon—accords Eadred the title "king of the Anglo-Saxons, Northumbrians, pagans, and Britons", whilst a 958 charter of Eadred's royal successor Edgar
Edgar is a commonly used English given name, from an Anglo-Saxon name ''Eadgar'' (composed of '' ead'' "rich, prosperous" and '' gar'' "spear").
Like most Anglo-Saxon names, it fell out of use by the later medieval period; it was, however, r ...
accords the latter kingship over "the Mercians, Northumbrians and Britons". The fact that the ''acta'' of Edmund, Eadred, and Edgar fail to record the presence of Dyfnwal could be evidence of English rule over the Cumbrians, who may have been in turn administered by English-aligned agents.
Cumbrian and Scottish contention
 Máel Coluim mac Domnaill was slain in 954, and succeeded by Illulb mac Custantín. At some point during the latter's reign, the Scots permanently acquired
Máel Coluim mac Domnaill was slain in 954, and succeeded by Illulb mac Custantín. At some point during the latter's reign, the Scots permanently acquired Edinburgh
Edinburgh ( ; gd, Dùn Èideann ) is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 Council areas of Scotland, council areas. Historically part of the county of Midlothian (interchangeably Edinburghshire before 1921), it is located in Lothian ...
from the English, as partly evidenced by the ninth- to twelfth-century ''Chronicle of the Kings of Alba
The ''Chronicle of the Kings of Alba'', or ''Scottish Chronicle'', is a short written chronicle of the Kings of Alba, covering the period from the time of Kenneth MacAlpin (Cináed mac Ailpín) (d. 858) until the reign of Kenneth II (Cináed mac ...
''. Confirmation of this conquest seems to be preserved by the twelfth-century '' Historia regum Anglorum'', a source which states that, during the reign of Edgar, King of the English
Edgar ( ang, Ēadgār ; 8 July 975), known as the Peaceful or the Peaceable, was King of the English from 959 until his death in 975. The younger son of King Edmund I and Ælfgifu of Shaftesbury, he came to the throne as a teenager following ...
, the Northumbrian frontier extended as far as the , a waterway which seems to refer to the River Tyne
The River Tyne is a river in North East England. Its length (excluding tributaries) is . It is formed by the North Tyne and the South Tyne, which converge at Warden Rock near Hexham in Northumberland at a place dubbed 'The Meeting of the Wat ...
in Lothian. The acquisition of Edinburgh, and extension into Lothian itself, may well have taken place during the reign of the embattled and unpopular Eadwig, King of the English. Illulb's attack may be evidenced by passages preserved by the twelfth-century ''Prophecy of Berchán
In religion, a prophecy is a message that has been communicated to a person (typically called a '' prophet'') by a supernatural entity. Prophecies are a feature of many cultures and belief systems and usually contain divine will or law, or p ...
'' which not only note "woe" inflicted upon the Britons and English, but also the conquest of foreign territories by way of Scottish military might. The notice of Britons in this text could be evidence that Illulb campaigned against Cumbrian-controlled territories. Such conflict may have meant that the apparent Cumbrian extension southwards was mirrored by movement eastwards. One possibility is that the Scots seized Edinburgh not from the English but from Cumbrians who had temporarily taken possession of it. Certainly, the fortress of Edinburgh had anciently been a British stronghold.
Rhydderch, son of Dyfnwal
 After Illulb's death in 962, the Scottish kingship appears to have been taken up by Dub mac Maíl Choluim, a man who was in turn replaced by Illulb's son,
After Illulb's death in 962, the Scottish kingship appears to have been taken up by Dub mac Maíl Choluim, a man who was in turn replaced by Illulb's son, Cuilén
Cuilén (also ''Culén, Cuilean'', anglicized Colin; died 971) was an early King of Alba ( Scotland).
He was a son of Illulb mac Custantín, King of Alba, after whom he is known by the patronymic mac Illuilb (also ''mac Iduilb'', ''mac Ilduil ...
. The latter's death at the hands of Britons in 971 is recorded by several sources. Some of these sources place his death in locations that could refer to either Abington in South Lanarkshire, Lothian
Lothian (; sco, Lowden, Loudan, -en, -o(u)n; gd, Lodainn ) is a region of the Scottish Lowlands, lying between the southern shore of the Firth of Forth and the Lammermuir Hills and the Moorfoot Hills. The principal settlement is the Scott ...
, or the Lennox
The Lennox ( gd, Leamhnachd, ) is a region of Scotland centred on The Vale of Leven, including its great loch: Loch Lomond.
The Gaelic name of the river is ''Leamhn'', meaning ''the smooth stream'', which anglicises to ''Leven'' (as Gaelic ' ...
. There is reason to suspect that Cuilén's killer was a son of Dyfnwal himself. The ''Chronicle of the Kings of Alba'' reports that the killer was a certain Rhydderch ap Dyfnwal, a man who slew Cuilén for the sake of his own daughter. The thirteenth-century ''Verse Chronicle'', the twelfth- to thirteenth-century ''Chronicle of Melrose
The ''Chronicle of Melrose'' is a medieval chronicle from the Cottonian Manuscript, Faustina B. ix within the British Museum. It was written by unknown authors, though evidence in the writing shows that it most likely was written by the monks at ...
'', and the fourteenth-century '' Chronica gentis Scotorum'' likewise identify Cuilén's killer as Rhydderch, the father of an abducted daughter raped by the Scottish king.
 Although there is no specific evidence that Rhydderch was himself a king, the fact that Cuilén was involved with his daughter, coupled with the fact that his warband was evidently strong enough to overcome that of Cuilén, suggests that Rhydderch must have been a man of eminent standing. According to the ''Prophecy of Berchán'', Cuilén met his end whilst "seeking a foreign land", which could indicate that he was attempting to lift taxes from the Cumbrians. Another way in which Cuilén may have met his end concerns the record of his father's seizure of Edinburgh. The fact that this conquest would have likely included at least part of Lothian, coupled with the evidence placing Cuilén's demise in the same area, could indicate that Cuilén was slain in the midst of exercising overlordship of this contested territory. If so, the records that link Rhydderch with the
Although there is no specific evidence that Rhydderch was himself a king, the fact that Cuilén was involved with his daughter, coupled with the fact that his warband was evidently strong enough to overcome that of Cuilén, suggests that Rhydderch must have been a man of eminent standing. According to the ''Prophecy of Berchán'', Cuilén met his end whilst "seeking a foreign land", which could indicate that he was attempting to lift taxes from the Cumbrians. Another way in which Cuilén may have met his end concerns the record of his father's seizure of Edinburgh. The fact that this conquest would have likely included at least part of Lothian, coupled with the evidence placing Cuilén's demise in the same area, could indicate that Cuilén was slain in the midst of exercising overlordship of this contested territory. If so, the records that link Rhydderch with the regicide
Regicide is the purposeful killing of a monarch or sovereign of a polity and is often associated with the usurpation of power. A regicide can also be the person responsible for the killing. The word comes from the Latin roots of ''regis'' ...
could reveal that this wronged father exploited Cuilén's vulnerable position in the region, and that Rhydderch seized the chance to avenge his daughter.
 Cuilén seems to have been succeeded by his kinsman
Cuilén seems to have been succeeded by his kinsman Cináed mac Maíl Choluim
Cináed mac Maíl Coluim ( gd, Coinneach mac Mhaoil Chaluim, label= Modern Scottish Gaelic, anglicised Kenneth II, and nicknamed , "The Fratricidal"; died 995) was King of Scots (''Alba'') from 971 to 995. The son of Malcolm I (Máel Coluim mac ...
. One of the latter's first acts as King of Alba
The monarch of Scotland was the head of state of the Kingdom of Scotland. According to tradition, the first King of Scots was Kenneth I MacAlpin (), who founded the state in 843. Historically, the Kingdom of Scotland is thought to have grown ...
was evidently an invasion of the kingdom of the Cumbrians. This campaign could well have been a retaliatory response to Cuilén's killing, Walker (2013) ch. 4 ¶ 25; Woolf (2009) p. 259. carried out in the context of crushing a British affront to Scottish authority. Walker (2013) ch. 4 ¶ 25. In any event, Cináed's invasion ended in defeat, a fact which coupled with Cuilén's killing reveals that the Cumbrian realm was indeed a power to be reckoned with. Whilst it is conceivable that Rhydderch could have succeeded Dyfnwal by the time of Cuilén's fall, another possibility is that Dyfnwal was still the king, and that Cináed's strike into Cumbrian territory was the last conflict of Dyfnwal's reign. In fact, it could have been at about this point when Máel Coluim took up the kingship. According to the ''Chronicle of the Kings of Alba'', Cináed constructed some sort of fortification on the River Forth
The River Forth is a major river in central Scotland, long, which drains into the North Sea on the east coast of the country. Its drainage basin covers much of Stirlingshire in Scotland's Central Belt. The Gaelic name for the upper reach of t ...
, perhaps the strategically located Fords of Frew near Stirling
Stirling (; sco, Stirlin; gd, Sruighlea ) is a city in central Scotland, northeast of Glasgow and north-west of Edinburgh. The market town, surrounded by rich farmland, grew up connecting the royal citadel, the medieval old town with its me ...
. One possibility is that this engineering project was undertaken in the context of limiting Cumbrian incursions.
Amongst an assembly of kings
 There is evidence to suggest that Dyfnwal was amongst the assembled kings who are recorded to have met with Edgar at
There is evidence to suggest that Dyfnwal was amongst the assembled kings who are recorded to have met with Edgar at Chester
Chester is a cathedral city and the county town of Cheshire, England. It is located on the River Dee, close to the English–Welsh border. With a population of 79,645 in 2011,"2011 Census results: People and Population Profile: Chester Loca ...
in 973. According to the "D", " E", and "F" versions of the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'', after having been consecrated king that year, this English monarch assembled a massive naval force and met with six kings at Chester. By the tenth century, the number of kings who met with him was alleged to have been eight, as evidenced by the tenth-century ''Life of St Swithun''. By the twelfth century, the eight kings began to be named and were alleged to have rowed Edgar down the River Dee, as evidenced by sources such as the twelfth-century texts '' Chronicon ex chronicis'', ''Gesta regum Anglorum
The ''Gesta Regum Anglorum'' ( Latin for "Deeds of the Kings of the English"), originally titled ("On the Deeds of the Kings of the English") and also anglicized as or , is an early-12th-century history of the kings of England by William of Ma ...
'', and ''De primo Saxonum adventu
'' De primo Saxonum adventu '' is a historical work, probably written in Durham during the episcopate of Ranulf Flambard (1099–1128).Rollason (ed.), ''Libellus de Exordio'', p. lxxix. It recounts the coming of the English (called the "Saxons") ...
'', as well as the thirteenth-century ''Chronica majora
The ''Chronica Majora'' is the seminal work of Matthew Paris, a member of the English Benedictine community of St Albans and long-celebrated historian. The work begins with Creation and contains annals down to the year of Paris' death of 1259. ...
'', and both the Wendover and Paris versions of ''Flores historiarum''. One of the names in all these sources—specifically identified as a Welsh king by ''Gesta regum Anglorum'', ''Chronica majora'', and both versions of ''Flores historiarum''—appears to refer to Dyfnwal. Another named figure, styled King of the Cumbrians, seems to be identical to his son, Máel Coluim.
 Whilst the symbolic tale of the men rowing Edgar down the river may be an unhistorical embellishment, most of the names accorded to the eight kings can be associated with contemporary rulers, suggesting that some of these men may have taken part in a concord with him. Although the latter accounts allege that the kings submitted to Edgar, the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' merely states that they came to an agreement of cooperation with him, and thus became his ("co-workers", "even-workers", "fellow-workers"). One possibility is that the assembly somehow relates to Edmund's attested incursion into Cumbria in 945. According to the same source, when Edmund Cumbria to Máel Coluim mac Domnaill, he had done so on the condition that the latter would be his ("co-worker", "even-worker", "fellow-worker", "together-wright"). Less reliable non-contemporary sources such as ''De primo Saxonum adventu'', both the Wendover and Paris versions of ''Flores historiarum'', and ''Chronica majora'' allege that Edgar granted
Whilst the symbolic tale of the men rowing Edgar down the river may be an unhistorical embellishment, most of the names accorded to the eight kings can be associated with contemporary rulers, suggesting that some of these men may have taken part in a concord with him. Although the latter accounts allege that the kings submitted to Edgar, the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' merely states that they came to an agreement of cooperation with him, and thus became his ("co-workers", "even-workers", "fellow-workers"). One possibility is that the assembly somehow relates to Edmund's attested incursion into Cumbria in 945. According to the same source, when Edmund Cumbria to Máel Coluim mac Domnaill, he had done so on the condition that the latter would be his ("co-worker", "even-worker", "fellow-worker", "together-wright"). Less reliable non-contemporary sources such as ''De primo Saxonum adventu'', both the Wendover and Paris versions of ''Flores historiarum'', and ''Chronica majora'' allege that Edgar granted Lothian
Lothian (; sco, Lowden, Loudan, -en, -o(u)n; gd, Lodainn ) is a region of the Scottish Lowlands, lying between the southern shore of the Firth of Forth and the Lammermuir Hills and the Moorfoot Hills. The principal settlement is the Scott ...
to Cináed in 975. If this supposed grant formed a part of the episode at Chester, it along with the concord of 945 could indicate that the assembly of 975 was not a submission as such, but more of a conference concerning mutual cooperation along the English borderlands. The location of the assembly of 973 at Chester would have been a logical neutral site for all parties.
 One of the other named kings was Cináed. Considering the fact that the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' numbers the kings at six, if Cináed was indeed present, it is unlikely that his rival, Cuilén's brother Amlaíb mac Illuilb, was also in attendance. Woolf (2007) p. 208. Although the chronology concerning the reigns of Cináed and Amlaíb mac Illuilb is uncertain—with Amlaíb mac Illuilb perhaps reigning from 971/976–977 and Cináed from 971/977–995—the part played by the King of Alba at the assembly could well have concerned the frontier of his realm. Matthews (2007) p. 25. One of the other named kings seems to have been Maccus mac Arailt, whilst another could have been this man's brother,
One of the other named kings was Cináed. Considering the fact that the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' numbers the kings at six, if Cináed was indeed present, it is unlikely that his rival, Cuilén's brother Amlaíb mac Illuilb, was also in attendance. Woolf (2007) p. 208. Although the chronology concerning the reigns of Cináed and Amlaíb mac Illuilb is uncertain—with Amlaíb mac Illuilb perhaps reigning from 971/976–977 and Cináed from 971/977–995—the part played by the King of Alba at the assembly could well have concerned the frontier of his realm. Matthews (2007) p. 25. One of the other named kings seems to have been Maccus mac Arailt, whilst another could have been this man's brother, Gofraid
is an Irish masculine given name, arising in the Old Irish and Middle Irish/Middle Gaelic languages, as , and later partially Anglicised as Goffraid.
' corresponds to the Old Norse ', cognate with Gottfried or ', and Galfrid or '. ''Gofraid''/ ...
. These two Islesmen may have been regarded a threats by the Scots and Cumbrians. Maccus and Gofraid are recorded to have devastated Anglesey
Anglesey (; cy, (Ynys) Môn ) is an island off the north-west coast of Wales. It forms a principal area known as the Isle of Anglesey, that includes Holy Island across the narrow Cymyran Strait and some islets and skerries. Anglesey island ...
at the beginning of the decade, which could indicate that Edgar's assembly was undertaken as a means to counter the menace posed by these energetic insular Scandinavians. In fact, there is evidence to suggest that, as a consequence of the assembly at Chester, the brothers may have turned their attention from the British mainland
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is d ...
westwards towards Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel, the Irish Sea, and St George's Channel. Ireland is the s ...
.
 Another aspect of the assembly may have concerned the remarkable rising power of Amlaíb Cúarán in Ireland. Edgar may have wished to not only rein in men such as Maccus and Gofraid, but prevent them—and the Scots and Cumbrians—from affiliating themselves with Amlaíb Cúarán, and recognising the latter's authority in the Irish Sea region. Another factor concerning Edgar, and his Scottish and Cumbrian counterparts, may have been the stability of the northern English frontier. For example, a certain Thored Gunnerson is recorded to have ravaged
Another aspect of the assembly may have concerned the remarkable rising power of Amlaíb Cúarán in Ireland. Edgar may have wished to not only rein in men such as Maccus and Gofraid, but prevent them—and the Scots and Cumbrians—from affiliating themselves with Amlaíb Cúarán, and recognising the latter's authority in the Irish Sea region. Another factor concerning Edgar, and his Scottish and Cumbrian counterparts, may have been the stability of the northern English frontier. For example, a certain Thored Gunnerson is recorded to have ravaged Westmorland
Westmorland (, formerly also spelt ''Westmoreland'';R. Wilkinson The British Isles, Sheet The British IslesVision of Britain/ref> is a historic county in North West England spanning the southern Lake District and the northern Dales. It had an ...
in 966, an action that may have been undertaken by the English in the context of a response to Cumbrian southward expansion. Although the Scottish invasion of Cumbrian and English territory unleashed after Cináed's inauguration could have been intended to tackle Cumbrian opposition, another possibility is that the campaign may have been executed as a way to counter any occupation of Cumbrian territories by Thored.
Death and descendants
 Both Dyfnwal and his English counterpart died in 975. According to various
Both Dyfnwal and his English counterpart died in 975. According to various Irish annals
A number of Irish annals, of which the earliest was the Chronicle of Ireland, were compiled up to and shortly after the end of the 17th century. Annals were originally a means by which monks determined the yearly chronology of feast days. Over ...
, which style Dyfnwal King of the Britons, he met his end whilst undertaking a pilgrimage. These sources are corroborated by Welsh texts such as the thirteenth- and fourteenth-century '' Brenhinedd y Saesson'', and ''Brut y Tywysogyon'', with the latter stating that Dyfnwal died in Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus ( legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
having received the tonsure
Tonsure () is the practice of cutting or shaving some or all of the hair on the scalp as a sign of religious devotion or humility. The term originates from the Latin word ' (meaning "clipping" or "shearing") and referred to a specific practice i ...
. Such religious retirement late in the life of a ruler was not uncommon amongst contemporaries. For example, Custantín evidently became a monk upon his own abdication, whilst Amlaíb Cúarán retired to the holy island of Iona
Iona (; gd, Ì Chaluim Chille (IPA: �iːˈxaɫ̪ɯimˈçiʎə, sometimes simply ''Ì''; sco, Iona) is a small island in the Inner Hebrides, off the Ross of Mull on the western coast of Scotland. It is mainly known for Iona Abbey, though ther ...
in pilgrimage. One possibility is that Dyfnwal decided to undertake his religious journey—or was perhaps forced to undertake it—as a result of the violent actions of Rhydderch.
 It is conceivable that Dyfnwal was still reigning in 973, and that it was Edgar's death two years later that precipitated the transfer of the kingship to Dyfnwal's son Máel Coluim, and contributed to Dyfnwal's pilgrimage to Rome. In fact, the upheaval caused by the absence of the English and Cumbrian kings could well have contributed to Cináed's final elimination of Amlaíb mac Illuilb in 997. Another possibility is that Máel Coluim's part in the 973 assembly may have partly concerned his father's impending pilgrimage, and that he sought surety for Dyfnwal's safe passage through Edgar's realm. The fact that Máel Coluim is identified as one of the assembled kings could indicate that Dyfnwal had relinquished control to him at some point before the convention. Evidence that he had indeed assumed the kingship may exist in the record of a certain ''Malcolm dux'' who witnessed an English royal charter in 970. Although the authenticity of this document is questionable, the attested Malcolm could well be identical to Máel Coluim himself. If Máel Coluim was indeed king in 973, Dyfnwal's role at the assembly may have been that of an ' elder statesman' of sorts—possibly serving as an adviser or mentor—especially considering his decades of experience in international affairs. The fact that he left his realm for Rome could be evidence that he did not regard his realm or dynasty to be threatened during his absence.
It is conceivable that Dyfnwal was still reigning in 973, and that it was Edgar's death two years later that precipitated the transfer of the kingship to Dyfnwal's son Máel Coluim, and contributed to Dyfnwal's pilgrimage to Rome. In fact, the upheaval caused by the absence of the English and Cumbrian kings could well have contributed to Cináed's final elimination of Amlaíb mac Illuilb in 997. Another possibility is that Máel Coluim's part in the 973 assembly may have partly concerned his father's impending pilgrimage, and that he sought surety for Dyfnwal's safe passage through Edgar's realm. The fact that Máel Coluim is identified as one of the assembled kings could indicate that Dyfnwal had relinquished control to him at some point before the convention. Evidence that he had indeed assumed the kingship may exist in the record of a certain ''Malcolm dux'' who witnessed an English royal charter in 970. Although the authenticity of this document is questionable, the attested Malcolm could well be identical to Máel Coluim himself. If Máel Coluim was indeed king in 973, Dyfnwal's role at the assembly may have been that of an ' elder statesman' of sorts—possibly serving as an adviser or mentor—especially considering his decades of experience in international affairs. The fact that he left his realm for Rome could be evidence that he did not regard his realm or dynasty to be threatened during his absence.
 Surviving sources fail to note the Cumbrian kingdom between the obituaries of Dyfnwal in 975 and his son, Máel Coluim, in 997. There is reason to suspect that Dyfnwal had another son, Owain, who reigned after Máel Coluim. Clarkson (2014) ch. 7 ¶ 17; Clarkson (2010) ch. 9 ¶ 41; Woolf (2007) pp. 222, 233, 236. For instance, according to the "B" version of ''Annales Cambriæ'', a certain Owain—identified as the son of a man named Dyfnwal—was slain in 1015. This obituary is corroborated by ''Brut y Tywysogyon'', and ''Brenhinedd y Saesson''. Although it may be possible that the record of this man's death refers to
Surviving sources fail to note the Cumbrian kingdom between the obituaries of Dyfnwal in 975 and his son, Máel Coluim, in 997. There is reason to suspect that Dyfnwal had another son, Owain, who reigned after Máel Coluim. Clarkson (2014) ch. 7 ¶ 17; Clarkson (2010) ch. 9 ¶ 41; Woolf (2007) pp. 222, 233, 236. For instance, according to the "B" version of ''Annales Cambriæ'', a certain Owain—identified as the son of a man named Dyfnwal—was slain in 1015. This obituary is corroborated by ''Brut y Tywysogyon'', and ''Brenhinedd y Saesson''. Although it may be possible that the record of this man's death refers to Owain Foel, King of Strathclyde Owain () is a name of Welsh origin, variously written in Old Welsh as Ougein, Eugein, Euguen, Iguein, Ou(u)ein, Eug(u)ein, Yuein, and in Middle Welsh as Ewein, Owein, and Ywein. Other variants of the name Owain include Ewein, Iguein, Owein, Ouein, Y ...
, there is no reason to disregard the obituaries as erroneous. If the like-named men are indeed different people, they could well have been closely related. Whilst the former may have been a son of Dyfnwal himself, the latter could well have been a son of Dyfnwal's son, Máel Coluim. The Owain who died in 1015, therefore, would seem to have assumed the Cumbrian kingship after Máel Coluim's death in 997, and would appear to have reigned into the early eleventh century before Owain Foel's assumption of the throne.
mountain pass
A mountain pass is a navigable route through a mountain range or over a ridge. Since many of the world's mountain ranges have presented formidable barriers to travel, passes have played a key role in trade, war, and both human and animal migr ...
in the Lake District
The Lake District, also known as the Lakes or Lakeland, is a mountainous region in North West England. A popular holiday destination, it is famous for its lakes, forests, and mountains (or '' fells''), and its associations with William Wordswor ...
known as Dunmail Raise (meaning "Dyfnwal's Cairn"). According to popular legend, a local king named Dunmail was slain by Saxons
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country (Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the Nor ...
on the pass and buried beneath a cairn
A cairn is a man-made pile (or stack) of stones raised for a purpose, usually as a marker or as a burial mound. The word ''cairn'' comes from the gd, càrn (plural ).
Cairns have been and are used for a broad variety of purposes. In prehi ...
. Forms of this tradition may date to about the sixteenth century, as the place name is first marked on a map dating to 1576. By the end of the seventeenth century, it was claimed that the place name marked the site of "a great heap of Stones call'd Dunmail-Raise-Stones, suppos'd to have been cast up by Dunmail K. of Cumberland for the Bounds of his Kingdom". Forms of the tale began to appear in print in the following century. In time, the ever-evolving legend became associated with the events of 945. The cairn itself lies between the dual carriageways
A dual carriageway ( BE) or divided highway ( AE) is a class of highway with carriageways for traffic travelling in opposite directions separated by a central reservation (BrE) or median (AmE). Roads with two or more carriageways which are ...
of the A591 road
The A591 is a major road in Cumbria, in the north-west of England, which lies almost entirely within the Lake District national park. A 2009 poll by satellite navigation firm Garmin named the stretch of the road between Windermere and Keswi ...
. It seems to have marked an old boundary between Westmorland and Cumberland, and might have also marked the southern territorial extent of the Cumbrian kingdom. Nevertheless, the site's alleged importance in the early mediaeval period cannot be proven. Other place names that may be named after Dyfnwal include Cardonald
Cardonald ( sco, Cardonal, gd, Cair Dhòmhnaill
) is ...
(), and Dundonald/) is ...
Dundonald Castle
Dundonald Castle is situated on a hill overlooking the village of Dundonald, between Kilmarnock and Troon in South Ayrshire, Scotland. Dundonald Castle is a fortified tower house built for Robert II on his accession to the throne of Scotl ...
(). Ewart; Pringle; Caldwell et al. (2004) p. 7; Hicks (2003) p. 60.
Notes
Citations
References
Primary sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Secondary sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Dyfnwal ab Owain Monarchs of Strathclyde 10th-century Scottish monarchs 975 deaths