Duwa on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Duwa (; died 1307), also known as Du'a, was khan of the
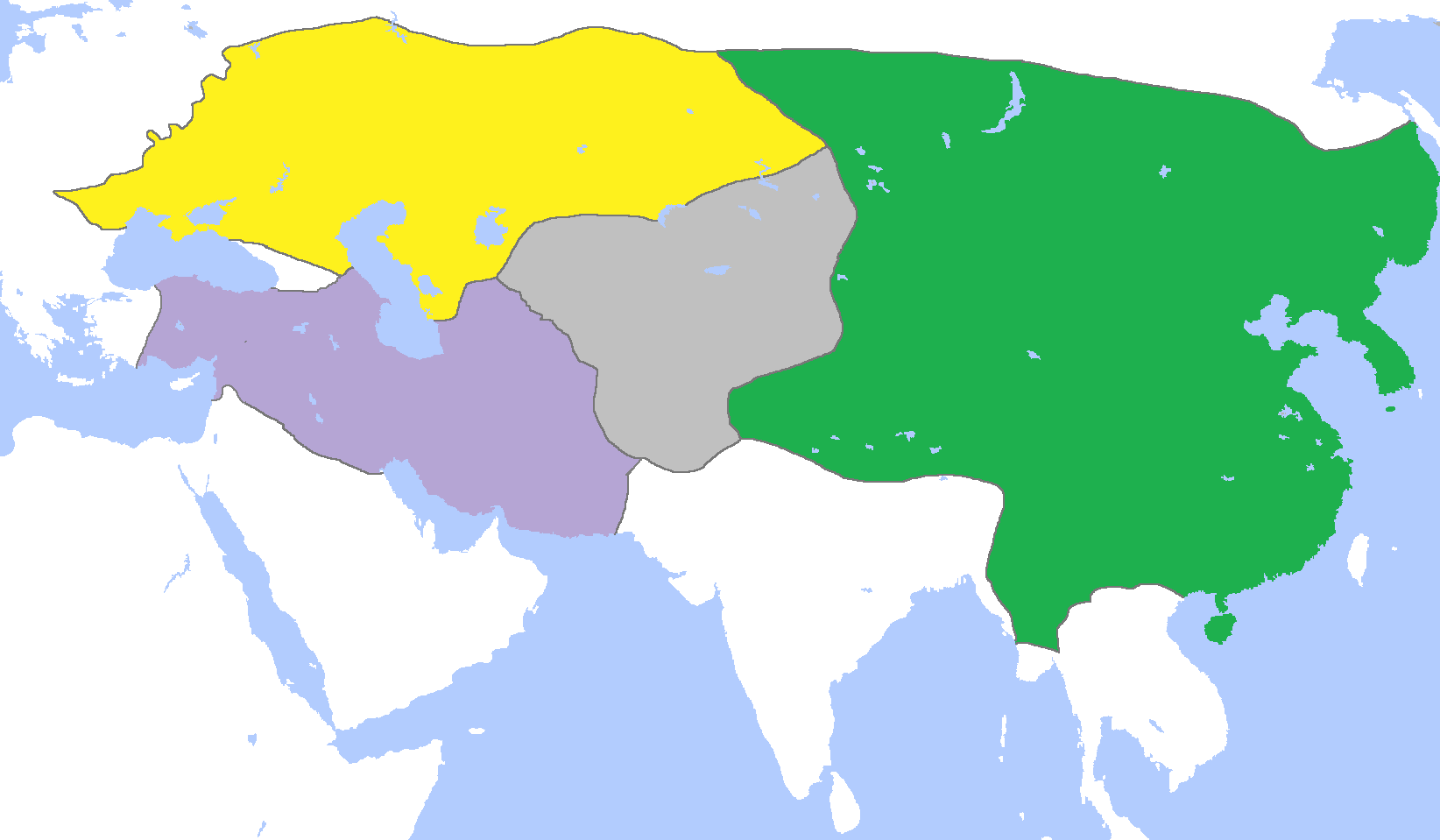 Shortly afterward, Duwa sought to end conflict with Temur Khan, and around 1304 a general peace among the Mongol states was declared, bringing a formal end to the Kaidu–Kublai war that had involved all Mongol khanates and lasted for over 30 years since the 1260s. Soon after, he proposed a joint Mongol attack on India, but the campaign did not materialize. The settlement favored Duwa much more than Chapar, a fact which set a rift between the two. Duwa hoped to throw off the mastery of Kaidu's son; he therefore sought to improve relations with Temür Khan. He had the advantage of being a legitimate heir to Chagatai's realm, while Chapar did not.
Chapar refused to attend a meeting that Duwa arranged to celebrate the peace, and in 1305 or 1306 fighting broke out between the troops of both sides, probably due to Duwa's attempts to take control of parts of Chapar's lands granted to him by Temür Khan. The fighting lasted for a while but was inconclusive; while Chapar's brother Sarban gave up to the Ilkhanate and abandoned the
Shortly afterward, Duwa sought to end conflict with Temur Khan, and around 1304 a general peace among the Mongol states was declared, bringing a formal end to the Kaidu–Kublai war that had involved all Mongol khanates and lasted for over 30 years since the 1260s. Soon after, he proposed a joint Mongol attack on India, but the campaign did not materialize. The settlement favored Duwa much more than Chapar, a fact which set a rift between the two. Duwa hoped to throw off the mastery of Kaidu's son; he therefore sought to improve relations with Temür Khan. He had the advantage of being a legitimate heir to Chagatai's realm, while Chapar did not.
Chapar refused to attend a meeting that Duwa arranged to celebrate the peace, and in 1305 or 1306 fighting broke out between the troops of both sides, probably due to Duwa's attempts to take control of parts of Chapar's lands granted to him by Temür Khan. The fighting lasted for a while but was inconclusive; while Chapar's brother Sarban gave up to the Ilkhanate and abandoned the
Chagatai Khanate
The Chagatai Khanate, or Chagatai Ulus ( xng, , translit=Čaɣatay-yin Ulus; mn, Цагаадайн улс, translit=Tsagaadain Uls; chg, , translit=Čağatāy Ulusi; fa, , translit=Xânât-e Joghatây) was a Mongol and later Turkicized kh ...
(1282–1307). He was the second son of Baraq. He was the longest reigning monarch
A monarch is a head of stateWebster's II New College DictionarMonarch Houghton Mifflin. Boston. 2001. p. 707. Life tenure, for life or until abdication, and therefore the head of state of a monarchy. A monarch may exercise the highest authority ...
of the Chagatayid Khanate and accepted the nominal supremacy of the Yuan dynasty
The Yuan dynasty (), officially the Great Yuan (; xng, , , literally "Great Yuan State"), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after its division. It was established by Kublai, the fif ...
as Great Khan before his death. Under his rule, the Chagatai Khanate reached its peak.
History
In 1282, Kaidu appointed Duwa as head of the Chagatai Khanate, in an effort to gain peace between himself and the sons of Baraq, who had ravagedCentral Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the fo ...
for much of the past ten years. This promotion ensured the loyalty of the Chaghataids from that point to Kaidu's death. Several years earlier, in 1275, Duwa destroyed a force in Uyghuria loyal to Kublai Khan
Kublai ; Mongolian script: ; (23 September 1215 – 18 February 1294), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Shizu of Yuan and his regnal name Setsen Khan, was the founder of the Yuan dynasty of China and the fifth khagan-emperor of ...
, led by the Chaghataid Ajiki and Kublai's son Ayachi. The following year, Kaidu and Duwa launched an expedition against Beshbalik
Beshbalik () is an ancient archaeological site, now located in Jimsar County, Changji Hui Autonomous Prefecture, Xinjiang, China. The ancient city was initially called Beiting () or Ting Prefecture (), and was the headquarters of the Beiting Protec ...
, defeated the Yuan forces there and captured the city. The strike given by Kaidu and Duwa was so hard that Uyghurs lost Dzungaria. During the rule of 4th Great Mongol Khan Mongke Khan (1251-1259) Uyghuria lost its privilege status of 5th ''Ulus'' of Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire of the 13th and 14th centuries was the largest contiguous land empire in history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Europe, ...
, granted by Chengiz Khan to Idiqut of Uyghuria Baurchuk Art Tegin in 1211, when he named Idiqut to be his 5th son, and when in 1269 Kaidu began a war against Kublai Khan Uyghuria became a subject of contest between Kublai and Kaidu. To save the people entire Uyghur population of Beshbalik in Dzungaria (former summer capital of Uyghur Buddhist
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
/ Manichaenian Qocho Kingdom
Qocho (), also known as Idiqut, ("holy wealth"; "glory"; "lord of fortune") was a Uyghur kingdom created in 843, with strong Chinese Buddhist and Tocharian influences. It was founded by Uyghur refugees fleeing the destruction of the Uyghur Kh ...
since 856) was evacuated to Kara-Khoja (former winter capital of Uyghur Idiquts since 866) in Turpan Depression by Idiqut Khochqar Tegin (火赤哈兒的斤/huǒchìhāér dejīn), ruler of Uyghuria since 1266, who succeeded Mamuraq Tegin (馬木剌的斤/mǎmùlà dejīn) Idiqut (1257-1266), who succeeded Oghrunch Tegin (玉古倫赤的斤/ ùgǔlúnchì dejīn) Idiqut (1255-1257), who succeeded Salandi (سالندی/sālandī) Idiqut (1245-1255), who succeeded Kishmayin (کیشماین/kīshmāīn) Idiqut (1235-1245), son of Baurchuk Art Tegin (巴而朮阿而忒的斤/bāérzhú āértè dejīn) Idiqut (1209-1235). Idiqut Khochqar reinforced Kara-Khoja defenses while all Uyghur cities in Dzungaria were abandoned by its population and turned into rubble within a few years as a result of these Mongol attacks. Duwa then laid siege to Kara Khoja (present ''Idiqut Shahri'' near Turpan
Turpan (also known as Turfan or Tulufan, , ug, تۇرپان) is a prefecture-level city located in the east of the autonomous region of Xinjiang, China. It has an area of and a population of 632,000 (2015).
Geonyms
The original name of the cit ...
) for six months with his brother Buzma by 120,000 troops. They demanded the Uyghur commander Idiqut Khochqar to surrender, having said to him: ''We have just overcome the resistance of 300,000 troops, how can you with only one city to withstand us''? Khochqar replied to them: ''I will follow my fate and destiny, this city is a place, where I was born and raised, its population has become my own family, if now I have to die, well, then let this city to have become my own grave''. Nevertheless, the Mongol
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
princes had failed to take the city by assaults during six months and finally Idiqut Khochqar managed to have the siege lifted only by giving Duwa his daughter in marriage, and probably financial compensation as well. Soon afterwards, in the same 1276, Idiqut Khochqar died in the occasional combat with Kaidu forces near the border of Yuan China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
. Duwa also may have given assistance to an unsuccessful revolt of Brigung sect against Kublai's authority in Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ) is a region in East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are some other ethnic groups such as Monpa people, ...
. In 1278 Duwa was reported to have led a raid into Yuan territory.
Kaidu's attempts to spread his power within the Ilkhanate
The Ilkhanate, also spelled Il-khanate ( fa, ایل خانان, ''Ilxānān''), known to the Mongols as ''Hülegü Ulus'' (, ''Qulug-un Ulus''), was a khanate established from the southwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. The Ilkhanid realm ...
gave Duwa an excuse to invade that Mongol kingdom in early 1295. Supported by Kaidu's son Sarban, he invaded Khurasan
Greater Khorāsān,Dabeersiaghi, Commentary on Safarnâma-e Nâsir Khusraw, 6th Ed. Tehran, Zavvâr: 1375 (Solar Hijri Calendar) 235–236 or Khorāsān ( pal, Xwarāsān; fa, خراسان ), is a historical eastern region in the Iranian Plat ...
and Mazandaran while the Ilkhanid commanders were involved in a succession struggle far to the west. For eight months he stayed in Mazandaran; when he left, he pillaged many cities on the way back. Duwa attempted to convince the Kartids of Herat
Herāt (; Persian: ) is an oasis city and the third-largest city of Afghanistan. In 2020, it had an estimated population of 574,276, and serves as the capital of Herat Province, situated south of the Paropamisus Mountains (''Selseleh-ye Safē ...
to defect to his side, but they refused. He attempted to plunder the cities of Kusui, which he failed to do; and Fushang, which he succeeded at, killing many of the inhabitants. A similar attempt on Herat never happened, since Duwa feared he would fail; he soon after was recalled by Kaidu back to Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the fo ...
, and the campaign ended.
Stiffening resistance by the Yuan commanders forced Kaidu and Duwa to pull back several times in 1297. In 1298, Duwa avenged these defeats when he attacked the Yuan garrisons during the winter. Most of the Yuan commanders were eating and drinking and therefore incapable of fighting; the Yuan emperor Temür Khan
Öljeytü Khan ( Mongolian: Өлзийт; Mongolian script: '; ), born Temür ( mn, Төмөр ; ; October 15, 1265 – February 10, 1307), also known as Emperor Chengzong of Yuan () by his temple name ''Chengzong'', was the second emperor of the ...
or Emperor Chengzong's grandson-in-law Körgüz, who had been more ready, was unable to defeat him by himself. Duwa tried to convince him to abandon the Yuan side, but was unsuccessful in doing so. Duwa then withdrew, only to be defeated in battle by the garrison troops in what is today known as Kebuduo. Duwa's brother-in-law was captured in the midst of the defeat. A prisoner exchange was agreed to, and his brother-in-law was returned, but Körgüz died before returning to the Yuan court. In 1298 or 1299 Duwa appointed his son Kutluk Khoja as head of the Qara'unas, a Mongol group that controlled a large part of Khurasan
Greater Khorāsān,Dabeersiaghi, Commentary on Safarnâma-e Nâsir Khusraw, 6th Ed. Tehran, Zavvâr: 1375 (Solar Hijri Calendar) 235–236 or Khorāsān ( pal, Xwarāsān; fa, خراسان ), is a historical eastern region in the Iranian Plat ...
.
In 1300 Yuan forces launched a large offensive against Kaidu. The latter called on Duwa for assistance, but the Chaghadaid refused, claiming his forces were exhausted. Surprised by the answer, Kaidu sent a command to him, but soon had to turn east to meet the Yuan. Still, Duwa and his men eventually came to help him, and during one battle in 1301 he himself was wounded and defeated. Shortly afterward, Kaidu died and the political situation changed. Duwa ignored Kaidu's choice of successor, Orus, and instead picked Kaidu's firstborn son Chapar to take his father's place. Chapar was enthroned in 1303, thanks to Duwa's effort. Duwa insisted Chapar to submit to Temür Khan.
 Shortly afterward, Duwa sought to end conflict with Temur Khan, and around 1304 a general peace among the Mongol states was declared, bringing a formal end to the Kaidu–Kublai war that had involved all Mongol khanates and lasted for over 30 years since the 1260s. Soon after, he proposed a joint Mongol attack on India, but the campaign did not materialize. The settlement favored Duwa much more than Chapar, a fact which set a rift between the two. Duwa hoped to throw off the mastery of Kaidu's son; he therefore sought to improve relations with Temür Khan. He had the advantage of being a legitimate heir to Chagatai's realm, while Chapar did not.
Chapar refused to attend a meeting that Duwa arranged to celebrate the peace, and in 1305 or 1306 fighting broke out between the troops of both sides, probably due to Duwa's attempts to take control of parts of Chapar's lands granted to him by Temür Khan. The fighting lasted for a while but was inconclusive; while Chapar's brother Sarban gave up to the Ilkhanate and abandoned the
Shortly afterward, Duwa sought to end conflict with Temur Khan, and around 1304 a general peace among the Mongol states was declared, bringing a formal end to the Kaidu–Kublai war that had involved all Mongol khanates and lasted for over 30 years since the 1260s. Soon after, he proposed a joint Mongol attack on India, but the campaign did not materialize. The settlement favored Duwa much more than Chapar, a fact which set a rift between the two. Duwa hoped to throw off the mastery of Kaidu's son; he therefore sought to improve relations with Temür Khan. He had the advantage of being a legitimate heir to Chagatai's realm, while Chapar did not.
Chapar refused to attend a meeting that Duwa arranged to celebrate the peace, and in 1305 or 1306 fighting broke out between the troops of both sides, probably due to Duwa's attempts to take control of parts of Chapar's lands granted to him by Temür Khan. The fighting lasted for a while but was inconclusive; while Chapar's brother Sarban gave up to the Ilkhanate and abandoned the Oxus
The Amu Darya, tk, Amyderýa/ uz, Amudaryo// tg, Амударё, Amudaryo ps, , tr, Ceyhun / Amu Derya grc, Ὦξος, Ôxos (also called the Amu, Amo River and historically known by its Latin name or Greek ) is a major river in Central Asi ...
region, but the region around Samarkand continued to be infested with supporters of Kaidu's family. Duwa proposed a peace; Chapar, believing that it was sincere and accepted, withdrawing his brothers. Duwa's forces then struck, defeating Chapar's supporter Baba, plundering Talas and overcoming Chapar's brother Shah. On the eastern front Duwa convinced the border commander of Yuan, Qaishan, to strike and defeat Chapar's brother Orus in June 1306.
Chapar then mobilized his own troops, but several of his commanders deserted him, and the Yuan sent a large force to Duwa's assistance. Surrounded by this army, Chapar surrendered. The northeast part of Duwa's realm was ceded to the Yuan dynasty, and Duwa afterwards received gifts from Temür Khan, signifying the restored relations between the Chagatai Khanate and the Yuan dynasty for the first time since the mid-thirteenth century. Duwa at first gave Chapar a small domain and pension, but afterwards killed or captured many of his followers, and deposed Chapar in 1307 in place of his brother Yangichar, who had not fought Duwa previously. Part of Yangichar's realm was split off and given to Tügme, a grandson of Güyük Khan. That same year, Duwa died, to be succeeded by his son Könchek.
Duwa's actions went a long way toward freeing the Chagatai Khanate from its subservience to Kaidu and his sons, a situation that had lasted since 1271. Nevertheless, Kaidu's sons continued to pose problems for the Chaghadaid state. Duwa's successes in recreating the Central Asian state also proved to be transitory; less than forty years later, the eastern part of the khanate would split off, and in the 1360s the western khans would be reduced to puppets by Timur
Timur ; chg, ''Aqsaq Temür'', 'Timur the Lame') or as ''Sahib-i-Qiran'' ( 'Lord of the Auspicious Conjunction'), his epithet. ( chg, ''Temür'', 'Iron'; 9 April 133617–19 February 1405), later Timūr Gurkānī ( chg, ''Temür Kü ...
.
Genealogy
Genealogy of Chaghatai Khanates In Babur Nama written byBabur
Babur ( fa, , lit= tiger, translit= Bābur; ; 14 February 148326 December 1530), born Mīrzā Zahīr ud-Dīn Muhammad, was the founder of the Mughal Empire in the Indian subcontinent. He was a descendant of Timur and Genghis Khan through hi ...
, Page 19, Chapter 1; described genealogy of his maternal grandfather Yunas Khan as:
"Yunas Khan descended from Chaghatai Khan, the second
son of Chingiz Khan (as follows,) Yunas Khan, son of Wais
Khan, son of Sher-'ali Aughlon, son of Muhammad Khan, son
of Khizr Khwaja Khan, son of Tughluq-timur Khan, son of
Aisan-bugha Khan, son of Dawa Khan, son of Baraq Khan,
son of Yesuntawa Khan, son of Muatukan, son of Chaghatai
Khan, son of Chingiz Khan"
"Chagahtai Khanates" A research project by Abdul Rauf MughalThe Tarikh-i-Rashidi: a history of the Moghuls of central Asia by Mirza Muhammad Haidar Dughlat; Editor: N. Elias,Translated by Sir Edward Denison Ross,Publisher:S. Low, Marston and co., 1895
See also
* Kaidu–Kublai warReferences
*Michal Biran, ''Qaidu and the Rise of the Independent Mongol State in Central Asia''. The Curzon Press, 1997, . *Rene Grousset Empire of Steppes, Rutgers Univ Pr, New Jersey, U.S.A, 1988 *M.Kutlukov, ''Mongol rule in Eastern Turkestan''. Article in collection ''Tataro-Mongols in Asia and Europe''.Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million ...
, 1970
Notes
{{Mongol Empire 1307 deaths Chagatai khans 13th-century monarchs in Asia 14th-century monarchs in Asia Year of birth unknown