Dust explosion on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
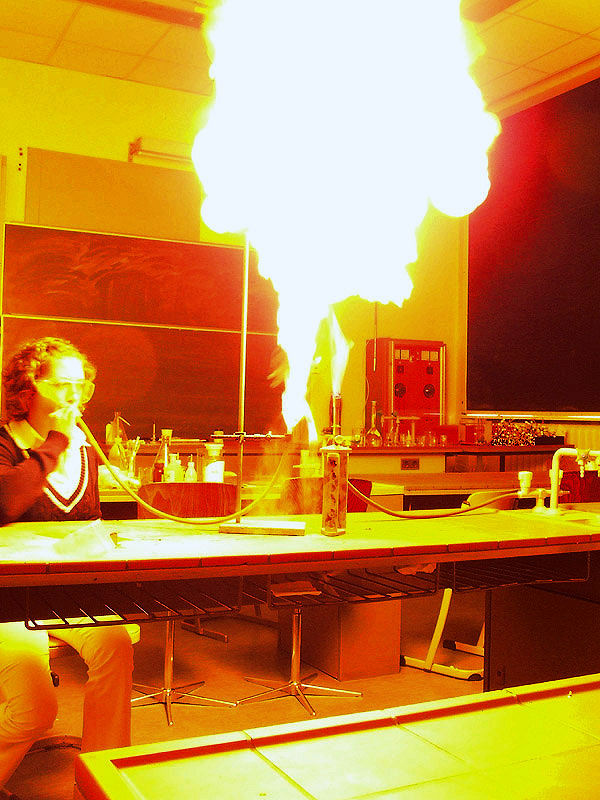 A dust explosion is the rapid
A dust explosion is the rapid
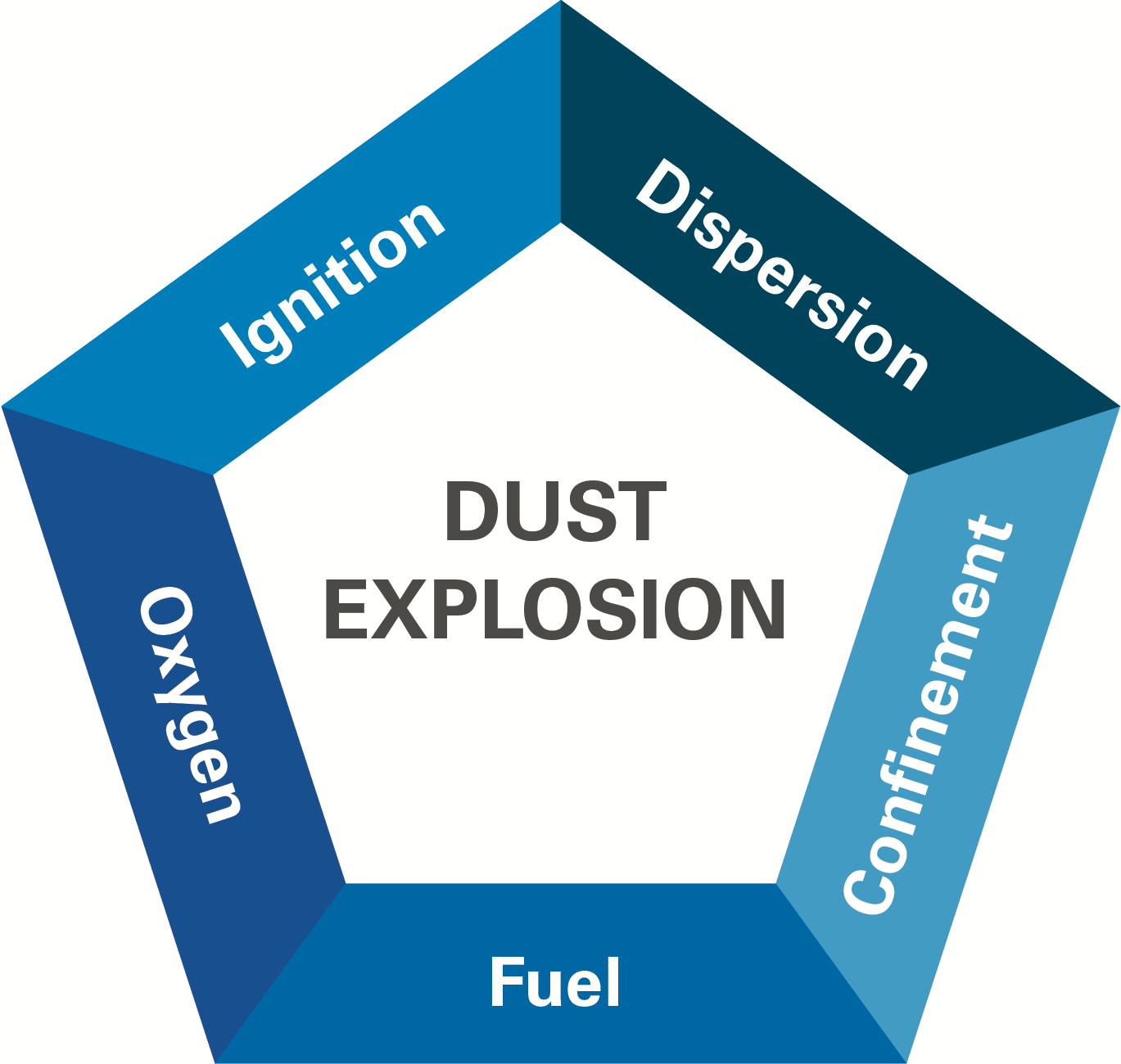 There are five necessary conditions for a dust explosion:
# A combustible
There are five necessary conditions for a dust explosion:
# A combustible

 Many common materials which are known to burn can generate a dust explosion, such as coal dust and sawdust. In addition, many otherwise mundane organic materials can also be dispersed into a dangerous dust cloud, such as
Many common materials which are known to burn can generate a dust explosion, such as coal dust and sawdust. In addition, many otherwise mundane organic materials can also be dispersed into a dangerous dust cloud, such as
File:Dust explosion 00.jpg, Experimental setup
File:Dust explosion 01.jpg, Finely-ground
Combustible dust explosion investigation products
from the Chemical Safety Board
Combustible Dust Policy Institute-ATEX
OSHA case studies of dust explosions
Protecting process plant, grain handling facilities, etc. from the risk of dust hazard explosions:
Hazard Monitoring Equipment – Selection, Installation and Maintenance
Seminars for Combustible Dust Safety
{{Authority control Chemical processes Occupational safety and health Particulates
 A dust explosion is the rapid
A dust explosion is the rapid combustion
Combustion, or burning, is a high-temperature exothermic redox chemical reaction between a fuel (the reductant) and an oxidant, usually atmospheric oxygen, that produces oxidized, often gaseous products, in a mixture termed as smoke. Combustion ...
of fine particles suspended in the air within an enclosed location. Dust explosions can occur where any dispersed powdered combustible material is present in high-enough concentrations in the atmosphere or other oxidizing gaseous medium, such as pure oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
. In cases when fuel plays the role of a combustible material, the explosion is known as a fuel-air explosion.
Dust explosions are a frequent hazard in coal mine
Coal mining is the process of resource extraction, extracting coal from the ground or from a mine. Coal is valued for its Energy value of coal, energy content and since the 1880s has been widely used to Electricity generation, generate electr ...
s, grain elevators and silo
A silo () is a structure for storing Bulk material handling, bulk materials.
Silos are commonly used for bulk storage of grain, coal, cement, carbon black, woodchips, food products and sawdust. Three types of silos are in widespread use toda ...
s, and other industrial environments. They are also commonly used by special effects artists, filmmakers, and pyrotechnicians, given their spectacular appearance and ability to be safely contained under certain carefully controlled conditions.
Thermobaric weapons exploit this principle by rapidly saturating an area with an easily combustible material and then igniting it to produce explosive force. These weapons are the most powerful non-nuclear explosives in existence.
Terminology
If rapid combustion occurs in a confined space, enormousoverpressure
Overpressure (or blast overpressure) is the pressure caused by a shock wave over and above normal atmospheric pressure. The shock wave may be caused by sonic boom or by explosion
An explosion is a rapid expansion in volume of a given amoun ...
s can build up, causing major structural damage and flying debris. The sudden release of energy from a " detonation" can produce a shockwave, either in open air or in a confined space. If the spread of flame is at subsonic speed, the phenomenon is sometimes called a " deflagration", although looser usage calls both phenomena " explosions".
Dust explosions may be classified as being either "primary" or "secondary" in nature. Primary dust explosions may occur inside process equipment or similar enclosures, and are generally controlled by pressure relief through purpose-built ducting to the external atmosphere. Secondary dust explosions are the result of dust accumulation inside a building being disturbed and ignited by the primary explosion, resulting in a much more dangerous uncontrolled explosion that can affect the entire structure. Historically, fatalities from dust explosions have largely been the result of secondary dust explosions.Eckhoff, Rolf K. (1997). Dust Explosions in the Process Industries (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. .
Conditions required
 There are five necessary conditions for a dust explosion:
# A combustible
There are five necessary conditions for a dust explosion:
# A combustible dust
Dust is made of particle size, fine particles of solid matter. On Earth, it generally consists of particles in the atmosphere that come from various sources such as soil lifted by wind (an aeolian processes, aeolian process), Types of volcan ...
# The dust is dispersed in the air within certain flammability limits
# There is an oxidant
An oxidizing agent (also known as an oxidant, oxidizer, electron recipient, or electron acceptor) is a substance in a redox chemical reaction that gains or "Electron acceptor, accepts"/"receives" an electron from a (called the , , or ''electr ...
(typically atmospheric oxygen)
# There is an ignition source
# The area is confineda building can be an enclosure
Sources of dust

 Many common materials which are known to burn can generate a dust explosion, such as coal dust and sawdust. In addition, many otherwise mundane organic materials can also be dispersed into a dangerous dust cloud, such as
Many common materials which are known to burn can generate a dust explosion, such as coal dust and sawdust. In addition, many otherwise mundane organic materials can also be dispersed into a dangerous dust cloud, such as grain
A grain is a small, hard, dry fruit (caryopsis) – with or without an attached husk, hull layer – harvested for human or animal consumption. A grain crop is a grain-producing plant. The two main types of commercial grain crops are cereals and ...
, flour
Flour is a powder made by Mill (grinding), grinding raw grains, List of root vegetables, roots, beans, Nut (fruit), nuts, or seeds. Flours are used to make many different foods. Cereal flour, particularly wheat flour, is the main ingredie ...
, starch
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants for energy storage. Worldwide, it is the most common carbohydrate in human diet ...
, sugar
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose
Glucose is a sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecul ...
, powdered milk, cocoa, coffee
Coffee is a beverage brewed from roasted, ground coffee beans. Darkly colored, bitter, and slightly acidic, coffee has a stimulating effect on humans, primarily due to its caffeine content, but decaffeinated coffee is also commercially a ...
, and pollen
Pollen is a powdery substance produced by most types of flowers of seed plants for the purpose of sexual reproduction. It consists of pollen grains (highly reduced Gametophyte#Heterospory, microgametophytes), which produce male gametes (sperm ...
. Powdered metals (such as aluminum
Aluminium (or aluminum in North American English) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Al and atomic number 13. It has a density lower than that of other common metals, about one-third that of steel. Aluminium has ...
, magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 ...
, and titanium
Titanium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resistant to corrosion in ...
) can form explosive suspensions in air, if finely divided.
A gigantic explosion of flour dust destroyed a mill in Minnesota on May 2, 1878, killing 14 workers at the Washburn A Mill and another four in adjacent buildings. A similar problem occurs in sawmill
A sawmill (saw mill, saw-mill) or lumber mill is a facility where logging, logs are cut into lumber. Modern sawmills use a motorized saw to cut logs lengthwise to make long pieces, and crosswise to length depending on standard or custom sizes ...
s and other places dedicated to woodworking.
Since the advent of industrial production–scale metal powder–based additive manufacturing (AM) in the 2010s, there is growing need for more information and experience with preventing dust explosions and fires from the traces of excess metal powder sometimes left over after laser sintering
Sintering or frittage is the process of compacting and forming a solid mass of material by pressure or heat without melting it to the point of liquefaction. Sintering happens as part of a manufacturing process used with metals, ceramics, plas ...
or other fusion methods. For example, in machining
Machining is a manufacturing process where a desired shape or part is created using the controlled removal of material, most often metal, from a larger piece of raw material by cutting. Machining is a form of subtractive manufacturing, which util ...
operations downstream of the AM build, excess powder liberated from porosities in the support structures can be exposed to sparks from the cutting interface. Efforts are underway not only to build this knowledgebase within the industry but also to share it with local fire departments, who do periodic fire-safety inspections of businesses in their districts and who can expect to answer alarms at shops or plants where AM is now part of the production mix.
Although not strictly a dust, paper particles emitted during processing – especially rolling, unrolling, calendaring/slitting, and sheet-cutting – are also known to pose an explosion hazard. Enclosed paper mill areas subject to such dangers commonly maintain very high air humidities to reduce the chance of airborne paper dust explosions.
In special effects pyrotechnics
Pyrotechnics is the science and craft of creating fireworks, but also includes safety matches, oxygen candles, Pyrotechnic fastener, explosive bolts (and other fasteners), parts of automotive airbags, as well as gas-pressure blasting in mining, q ...
, lycopodium powder and non-dairy creamer are two common means of producing safe, controlled fire effects.
To support rapid combustion, the dust must consist of very small particles with a high surface area to volume ratio, thereby making the collective or combined surface area of all the particles very large in comparison to a dust of larger particles. Dust
Dust is made of particle size, fine particles of solid matter. On Earth, it generally consists of particles in the atmosphere that come from various sources such as soil lifted by wind (an aeolian processes, aeolian process), Types of volcan ...
is defined as powders
A powder is a dry solid composed of many very fine particles that may Particle-laden flow, flow freely when shaken or tilted. Powders are a special sub-class of granular materials, although the terms ''powder'' and ''granular'' are sometimes use ...
with particles less than about 500 micrometres in diameter, but finer dust will present a much greater hazard than coarse particles by virtue of the larger total surface area of all the particles.
Concentration
Below a certain value, the lower explosive limit (LEL), there is insufficient dust to support the combustion at the rate required for an explosion. A combustible concentration at or below 25% of the LEL is considered safe. Similarly, if the fuel to air ratio increases above the upper explosive limit (UEL), there is insufficient oxidant to permit combustion to continue at the necessary rate. Determining the minimum explosive concentration or maximum explosive concentration of dusts in air is difficult, and consulting different sources can lead to quite different results. Typical explosive ranges in air are from few dozens grams/m3 for the minimum limit, to few kg/m3 for the maximum limit. For example, the LEL for sawdust has been determined to be between 40 and 50 grams/m3. It depends on many factors including the type of material used.Oxidant
Typically, normal atmospheric oxygen can be sufficient to support a dust explosion if the other necessary conditions are also present. High-oxygen or pure oxygen environments are considered to be especially hazardous, as are strong oxidizing gases such aschlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between ...
and fluorine
Fluorine is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol F and atomic number 9. It is the lightest halogen and exists at Standard temperature and pressure, standard conditions as pale yellow Diatomic molecule, diatomic gas. Fluorine is extre ...
. Also, particulate suspensions of compounds with a high oxidative potential, such as peroxide
In chemistry, peroxides are a group of Chemical compound, compounds with the structure , where the R's represent a radical (a portion of a complete molecule; not necessarily a free radical) and O's are single oxygen atoms. Oxygen atoms are joined ...
s, chlorates, nitrate
Nitrate is a polyatomic ion with the chemical formula . salt (chemistry), Salts containing this ion are called nitrates. Nitrates are common components of fertilizers and explosives. Almost all inorganic nitrates are solubility, soluble in wa ...
s, perchlorates, and dichromates, can increase risk of an explosion if combustible materials are also present.
Sources of ignition
There are many sources of ignition, and a naked flame need not be the only one: over one half of the dust explosions in Germany in 2005 were from non-flame sources. Common sources of ignition include: *electrostatic discharge
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) is a sudden and momentary flow of electric current between two differently-charged objects when brought close together or when the dielectric between them breaks down, often creating a visible electric spark, spark as ...
(e.g. an improperly installed conveyor belt, which can act like a Van de Graaff generator
A Van de Graaff generator is an electrostatic generator which uses a moving belt to accumulate electric charge on a hollow metal globe on the top of an insulated column, creating very high electric potentials. It produces very high voltage direct ...
)
* friction
Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding against each other. Types of friction include dry, fluid, lubricated, skin, and internal -- an incomplete list. The study of t ...
* electrical arcing from machinery or other equipment
* hot surfaces (e.g. overheated bearings)
* fire
Fire is the rapid oxidation of a fuel in the exothermic chemical process of combustion, releasing heat, light, and various reaction Product (chemistry), products.
Flames, the most visible portion of the fire, are produced in the combustion re ...
* self-ignition
However, it is often difficult to determine the exact source of ignition when investigating after an explosion. When a source cannot be found, ignition will often be attributed to static electricity
Static electricity is an imbalance of electric charges within or on the surface of a material. The charge remains until it can move away by an electric current or electrical discharge. The word "static" is used to differentiate it from electric ...
. Static charges can be generated by external sources, or can be internally generated by friction at the surfaces of particles themselves as they collide or move past one another.
Mechanism
Dust has a very large surface area compared to its mass. Since burning can only occur at the surface of a solid or liquid, where it can react with oxygen, this causes dust to be much more flammable than bulk materials. For example, a sphere of a combustible material with a density of 1 g/cm3 would be about in diametre, and have a surface area of . However, if it were broken up into spherical dust particles 50 μm in diametre (about the size offlour
Flour is a powder made by Mill (grinding), grinding raw grains, List of root vegetables, roots, beans, Nut (fruit), nuts, or seeds. Flours are used to make many different foods. Cereal flour, particularly wheat flour, is the main ingredie ...
particles) it would have a surface area of . This greatly-increased surface area allows the material to burn much faster, and the extremely small mass of each particle allows them to catch on fire with much less energy than the bulk material, as there is no heat loss to conduction within the material.
When this mixture of fuel and air is ignited, especially in a confined space such as a warehouse or silo, a significant increase in pressure is created, often more than sufficient to demolish the structure. Even materials that are traditionally thought of as nonflammable (such as aluminium
Aluminium (or aluminum in North American English) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Al and atomic number 13. It has a density lower than that of other common metals, about one-third that of steel. Aluminium has ...
), or slow burning (such as wood), can produce a powerful explosion when finely divided, and can be ignited by even a small spark.
flour
Flour is a powder made by Mill (grinding), grinding raw grains, List of root vegetables, roots, beans, Nut (fruit), nuts, or seeds. Flours are used to make many different foods. Cereal flour, particularly wheat flour, is the main ingredie ...
is dispersed
File:Dust explosion 02.jpg, Cloud of flour is ignited
File:Dust explosion 03.jpg, Fireball spreads rapidly
File:Dust explosion 04.jpg, Intense radiant heat has nothing to ignite here
File:Dust explosion 05.jpg, Fireball and superheated gases rise
File:Dust explosion 06.jpg, Aftermath of explosion, with unburnt flour on the ground
Effects
A dust explosion can cause major damage to structures, equipment, and personnel from violent overpressure or shockwave effects. Flying objects and debris can cause further damage. Intense radiant heat from a fireball can ignite the surroundings, or cause severe skin burns in unprotected persons. In a tightly enclosed space, the sudden depletion of oxygen can causeasphyxiation
Asphyxia or asphyxiation is a condition of deficient supply of oxygen to the body which arises from abnormal breathing. Asphyxia causes generalized hypoxia, which affects all the tissues and organs, some more rapidly than others. There are ...
. Where the dust is carbon based (such as in a coal mine), incomplete combustion may cause large amounts of carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a poisonous, flammable gas that is colorless, odorless, tasteless, and slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the si ...
(the miners' after-damp) to be created. This can cause more deaths than the original explosion as well as hindering rescue attempts.
Protection and mitigation
Much research has been carried out in Europe and elsewhere to understand how to control these dangers, but dust explosions still occur. The alternatives for making processes and plants safer depend on the industry. In thecoal mining
Coal mining is the process of resource extraction, extracting coal from the ground or from a mine. Coal is valued for its Energy value of coal, energy content and since the 1880s has been widely used to Electricity generation, generate electr ...
industry, a methane explosion can initiate a coal dust explosion, which can then engulf an entire mine pit. As a precaution, incombustible stone dust may be spread along mine roadways, or stored in trays hanging from the roof, to dilute the coal dust stirred up by a shockwave to the point where it cannot burn. Mines may also be sprayed with water to inhibit ignition.
Some industries exclude oxygen from dust-raising processes, a precaution known as "inerting". Typically this uses nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a Nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal and the lightest member of pnictogen, group 15 of the periodic table, often called the Pnictogen, pnictogens. ...
, carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
, or argon
Argon is a chemical element; it has symbol Ar and atomic number 18. It is in group 18 of the periodic table and is a noble gas. Argon is the third most abundant gas in Earth's atmosphere, at 0.934% (9340 ppmv). It is more than twice as abu ...
, which are incombustible gases which can displace oxygen. The same method is also used in large storage tanks where flammable vapors can accumulate. However, use of oxygen-free gases brings a risk of asphyxiation
Asphyxia or asphyxiation is a condition of deficient supply of oxygen to the body which arises from abnormal breathing. Asphyxia causes generalized hypoxia, which affects all the tissues and organs, some more rapidly than others. There are ...
of the workers. Workers who need illumination in enclosed spaces where a dust explosion is a high risk often use lamps designed for underwater divers, as they have no risk of producing an open spark due to their sealed waterproof design.
Good housekeeping practices, such as eliminating build-up of combustible dust deposits that could be disturbed and lead to a secondary explosion, also help mitigate the problem.
Best engineering control measures which can be found in the National Fire Protection Association
The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) is a U.S.-based international nonprofit organization devoted to eliminating death, injury, property damage, and economic loss due to fire, electrical, and related hazards. , the NFPA claims to have 5 ...
(NFPA) Combustible Dust Standards include:
* Wetting
* Oxidant concentration reduction
* Deflagration venting
* Deflagration pressure containment
* Deflagration suppression
* Deflagration venting through a dust retention and flame-arresting device
Notable incidents
Dust clouds are a common source of explosions, causing an estimated 2,000 explosions annually in Europe. The table lists notable incidents worldwide.See also
*Air to fuel ratio
An atmosphere () is a layer of gases that envelop an astronomical object, held in place by the gravity of the object. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmospher ...
* Power tool
A power tool is a tool that is actuator, actuated by an additional engine, power source and mechanism (engineering), mechanism other than the solely manual labour, manual labor used with hand tools. The most common types of power tools use electric ...
References
* * *External links
Incidents in France and the US:Combustible dust explosion investigation products
from the Chemical Safety Board
Combustible Dust Policy Institute-ATEX
OSHA case studies of dust explosions
Protecting process plant, grain handling facilities, etc. from the risk of dust hazard explosions:
Hazard Monitoring Equipment – Selection, Installation and Maintenance
Seminars for Combustible Dust Safety
{{Authority control Chemical processes Occupational safety and health Particulates