Duchy of Carniola on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Duchy of Carniola ( sl, Vojvodina Kranjska, german: Herzogtum Krain, hu, Krajna) was an imperial estate of the

 Albert's son Rudolf IV of Austria, "the Founder", in the course of his '' Privilegium Maius'', awarded himself the title of a "Duke of Carniola" in 1364—though without consent by the
Albert's son Rudolf IV of Austria, "the Founder", in the course of his '' Privilegium Maius'', awarded himself the title of a "Duke of Carniola" in 1364—though without consent by the
 The coat of arms of Carniola dates back to the 13th century, when it most probably evolved as a combination of the coats of arms of the Bavarian counts of Andechs in the Duchy of Merania (eagle) and the Rhenish House of Sponheim in Carinthia (red-white checkerboard). The eagle is also featured in the seal of King
The coat of arms of Carniola dates back to the 13th century, when it most probably evolved as a combination of the coats of arms of the Bavarian counts of Andechs in the Duchy of Merania (eagle) and the Rhenish House of Sponheim in Carinthia (red-white checkerboard). The eagle is also featured in the seal of King
Map – Duchy of Carniola in 1849
{{DEFAULTSORT:Carniola, Duchy of Duchy of Carniola Former states and territories in Slovenia Duchy of Carniola Austrian Circle Subdivisions of Austria-Hungary States of the German Confederation Duchies of the Holy Roman Empire Subdivisions of the Habsburg Monarchy Southern Limestone Alps States and territories established in 1364 States and territories disestablished in 1918 Duchy of Carniola 1364 establishments in Europe 1360s establishments in the Holy Roman Empire 1918 disestablishments in Austria-Hungary Medieval Slovenia Modern history of Slovenia Carniola
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 unt ...
, established under Habsburg rule on the territory of the former East Frankish March of Carniola in 1364. A hereditary land of the Habsburg monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy (german: Habsburgermonarchie, ), also known as the Danubian monarchy (german: Donaumonarchie, ), or Habsburg Empire (german: Habsburgerreich, ), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities ...
, it became a constituent land of the Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire (german: link=no, Kaiserthum Oesterreich, modern spelling , ) was a Central- Eastern European multinational great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the realms of the Habsburgs. During its existence, ...
in 1804 and part of the Kingdom of Illyria
The Kingdom of Illyria was a crown land of the Austrian Empire from 1816 to 1849, the successor state of the Napoleonic Illyrian Provinces, which were reconquered by Austria in the War of the Sixth Coalition. It was established according to th ...
until 1849. A separate crown land
Crown land (sometimes spelled crownland), also known as royal domain, is a territorial area belonging to the monarch, who personifies the Crown. It is the equivalent of an entailed estate and passes with the monarchy, being inseparable from it ...
from 1849, it was incorporated into the Cisleithanian territories of Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
from 1867 until the state's dissolution in 1918. Its capital was Ljubljana
Ljubljana (also known by other historical names) is the capital and largest city of Slovenia. It is the country's cultural, educational, economic, political and administrative center.
During antiquity, a Roman city called Emona stood in the ar ...
(german: Laibach).
Geography
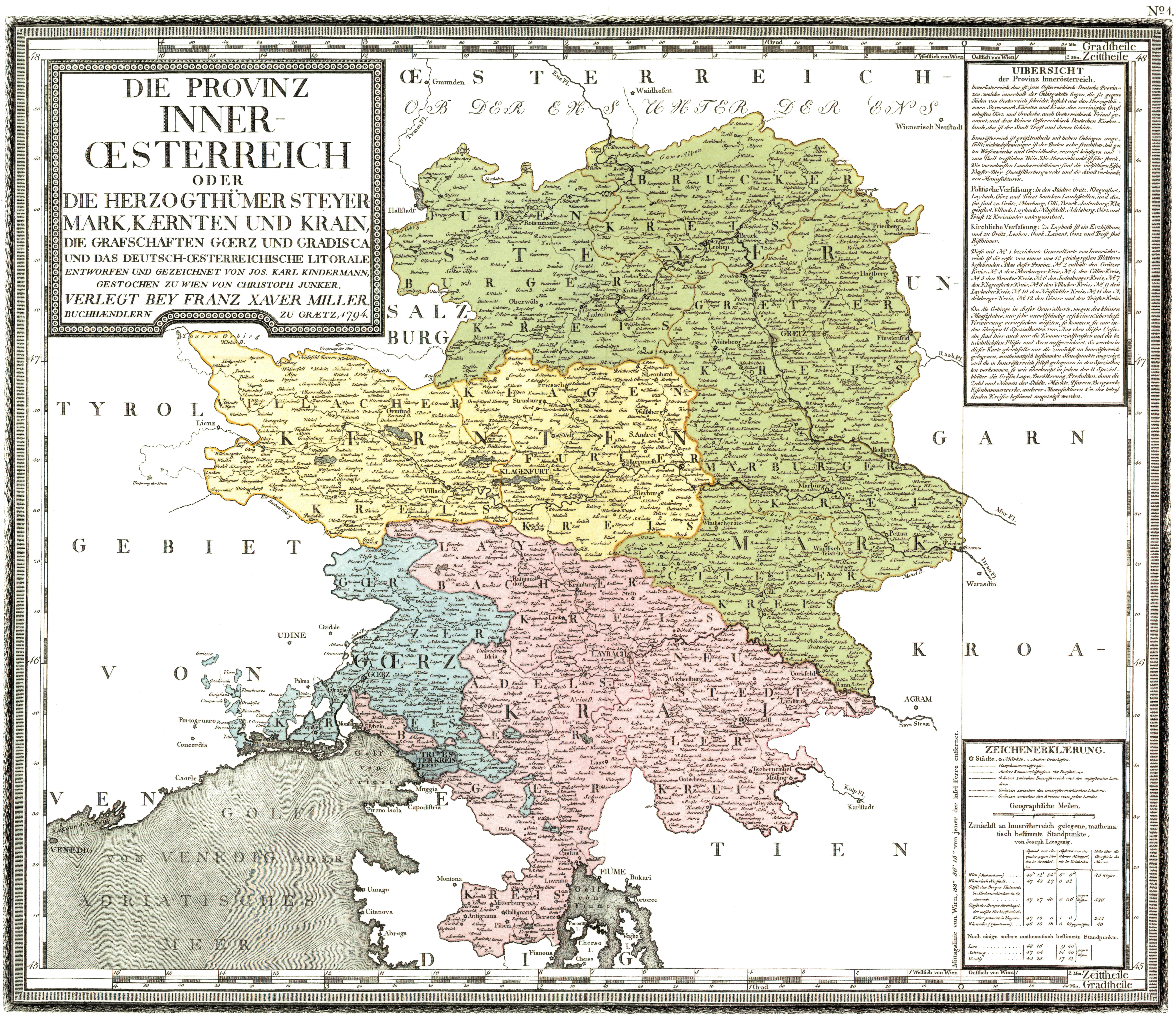
The borders of the historic Carniola region had varied over the centuries. From the time of the duchy's establishment, it was located in the southeastern periphery of the Holy Roman Empire, where the Gorjanci Mountains and the Kolpa River formed the border with theKingdom of Croatia Kingdom of Croatia may refer to:
* Kingdom of Croatia (925–1102), an independent medieval kingdom
* Croatia in personal union with Hungary (1102–1526), a kingdom in personal union with the Kingdom of Hungary
* Kingdom of Croatia (Habsburg) (152 ...
.
In the north, it bordered the Imperial Duchy of Carinthia
The Duchy of Carinthia (german: Herzogtum Kärnten; sl, Vojvodina Koroška) was a duchy located in southern Austria and parts of northern Slovenia. It was separated from the Duchy of Bavaria in 976, and was the first newly created Imperial Sta ...
, from the Predil Pass and Fusine
Fusine is a '' comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Sondrio in the Italian region Lombardy, located about northeast of Milan and about southwest of Sondrio. As of 31 December 2004, it had a population of 650 and an area of .All demographics ...
(''Fužine'') along the main ridge of the Karawanks range up to Jezersko. In the northeast and east, it bordered on the Duchy of Styria
The Duchy of Styria (german: Herzogtum Steiermark; sl, Vojvodina Štajerska; hu, Stájer Hercegség) was a duchy located in modern-day southern Austria and northern Slovenia. It was a part of the Holy Roman Empire until its dissolution in 180 ...
, i.e., the present-day '' Štajerska'' or Lower Styrian lands beyond the Sava
The Sava (; , ; sr-cyr, Сава, hu, Száva) is a river in Central and Southeast Europe, a right-bank and the longest tributary of the Danube. It flows through Slovenia, Croatia and along its border with Bosnia and Herzegovina, and finally t ...
River, which until 1456 were held by the Counts of Celje
The Counts of Celje ( sl, Celjski grofje) or the Counts of Cilli (german: Grafen von Cilli; hu, cillei grófok) were the most influential late medieval noble dynasty on the territory of present-day Slovenia. Risen as vassals of the Habsburg dukes ...
. In the west, the peaks of the Julian Alps
The Julian Alps ( sl, Julijske Alpe, it, Alpi Giulie, , ) are a mountain range of the Southern Limestone Alps that stretch from northeastern Italy to Slovenia, where they rise to 2,864 m at Mount Triglav, the highest peak in Slovenia. A large p ...
high above Lake Bohinj marked the border with the historic Friulian region, initially held by the Patriarchs of Aquileia
The highest-ranking bishops in Eastern Orthodoxy, Oriental Orthodoxy, the Catholic Church (above major archbishop and primate), the Hussite Church, Church of the East, and some Independent Catholic Churches are termed patriarchs (and in cer ...
, but gradually conquered by the Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice ( vec, Repùblega de Venèsia) or Venetian Republic ( vec, Repùblega Vèneta, links=no), traditionally known as La Serenissima ( en, Most Serene Republic of Venice, italics=yes; vec, Serenìsima Repùblega de Venèsia ...
and incorporated into the ''Domini di Terraferma
The ( vec, domini de terraferma or , ) was the hinterland territories of the Republic of Venice beyond the Adriatic coast in Northeast Italy. They were one of the three subdivisions of the Republic's possessions, the other two being the origi ...
'' by 1433. In the southwest, beyond the Dinaric Alps, the Counts of Görz held the remaining Friulian territory, which in 1754 became the Austrian crown land of Gorizia and Gradisca
The Princely County of Gorizia and Gradisca (german: Gefürstete Grafschaft Görz und Gradisca; it, Principesca Contea di Gorizia e Gradisca; sl, Poknežena grofija Goriška in Gradiščanska), historically sometimes shortened to and spelled " ...
(part of the present-day Slovenian Littoral). The remains of the Margraviate of Istria
The March of Istria (or Margraviate of Istria ) was originally a Carolingian frontier march covering the Istrian peninsula and surrounding territory conquered by Charlemagne's son Pepin of Italy in 789. After 1364, it was the name of the Istrian ...
south of the Karst Plateau and the Brkini Hills The Brkini Hills (; sl, Brkini; hr, Brkinija) is a hilly region in southwestern Slovenia.
Geography
The Brkini Hills border the Reka River in the north, the Materija Valley () in the southwest, the Karst Plateau () in the northwest, and the Jel ...
were also administered from Carniola.
In its final extent, re-established in 1815, the duchy had an area of . In 1914, before the beginning of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
, it had a population of a little under 530,000 inhabitants.

Administrative divisions
According to the topography '' The Glory of the Duchy of Carniola'' written by the scholar Johann Weikhard von Valvasor (1641–1693), the territory was traditionally divided into three sub-regions: * Upper Carniola (''Gorenjska''), the mountainous part in the north, with the towns of Kranj andKamnik
Kamnik (; german: Stein''Leksikon občin kraljestev in dežel zastopanih v državnem zboru,'' vol. 6: ''Kranjsko''. 1906. Vienna: C. Kr. Dvorna in Državna Tiskarna, pp. 26–27. or ''Stein in Oberkrain'') is a town in northern Slovenia. It is ...
* Lower Carniola (''Dolenjska''), in the southeast, with Novo Mesto
Novo Mesto (; sl, Novo mesto; also known by other alternative names) is a city on a bend of the Krka River in the City Municipality of Novo Mesto in southeastern Slovenia, close to the border with Croatia. The town is traditionally considered ...
, Kočevje (''Gottschee'') and Krško, including White Carniola
White Carniola ( sl, Bela krajina; german: Weißkrain or ''Weiße Mark'') is a traditional region in southeastern Slovenia on the border with Croatia. Due to its smallness, it is often considered a subunit of the broader Lower Carniola region, alt ...
and the former Windic March
* Inner Carniola (''Notranjska''), in the southwest, around the towns of Idrija and Postojna.
Until 1860, these sub-regions coincided with the districts (''Kreise'') of Ljubljana
Ljubljana (also known by other historical names) is the capital and largest city of Slovenia. It is the country's cultural, educational, economic, political and administrative center.
During antiquity, a Roman city called Emona stood in the ar ...
, Novo Mesto
Novo Mesto (; sl, Novo mesto; also known by other alternative names) is a city on a bend of the Krka River in the City Municipality of Novo Mesto in southeastern Slovenia, close to the border with Croatia. The town is traditionally considered ...
and Postojna. They were later divided into smaller units, called political (or administrative) districts (german: Bezirkshauptmannshaft, sl, okrajno glavarstvo). Between 1861 and 1918, Carniola was divided into eleven districts consisting of 359 municipalities (german: Ortsgemeinde, sl, občina), with the provincial capital serving as the residence of the imperial governor (''Landeshauptmann''). The districts were: Kamnik
Kamnik (; german: Stein''Leksikon občin kraljestev in dežel zastopanih v državnem zboru,'' vol. 6: ''Kranjsko''. 1906. Vienna: C. Kr. Dvorna in Državna Tiskarna, pp. 26–27. or ''Stein in Oberkrain'') is a town in northern Slovenia. It is ...
, Kranj, Radovljica, the neighbourhood of Ljubljana, Logatec
Logatec (; german: Loitsch, it, Longatico) is a town in Slovenia. It is the seat of the Municipality of Logatec. It is located roughly in the centre of Inner Carniola, between the capital Ljubljana and Postojna. The town of Logatec has seen rap ...
, Postojna, Litija, Krško, Novo Mesto
Novo Mesto (; sl, Novo mesto; also known by other alternative names) is a city on a bend of the Krka River in the City Municipality of Novo Mesto in southeastern Slovenia, close to the border with Croatia. The town is traditionally considered ...
, Črnomelj, and Kočevje. The political districts were in turn divided into 31 judicial circuits (german: Gerichtsbezirk, sl, sodnijski okraj).
History and administration
The former March of Carniola, i.e., Upper Carniola and the Windic March, had been separated from theDuchy of Carinthia
The Duchy of Carinthia (german: Herzogtum Kärnten; sl, Vojvodina Koroška) was a duchy located in southern Austria and parts of northern Slovenia. It was separated from the Duchy of Bavaria in 976, and was the first newly created Imperial Sta ...
in 1040 by King Henry III of Germany. It was nevertheless temporarily still held by the Carinthian rulers in personal union
A personal union is the combination of two or more states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, would involve the constituent states being to some extent interli ...
, like the ''Meinhardiner
The Counts of Gorizia (german: Grafen von Görz; it, Conti di Gorizia; sl, Goriški grofje), also known as the Meinhardiner, were a comital, princely and ducal dynasty in the Holy Roman Empire. Named after Gorizia Castle in Gorizia (now in I ...
'' duke Henry VI, who died in 1335 without a male heir. His daughter Margaret was able to keep the County of Tyrol
The (Princely) County of Tyrol was an estate of the Holy Roman Empire established about 1140. After 1253, it was ruled by the House of Gorizia and from 1363 by the House of Habsburg. In 1804, the County of Tyrol, unified with the secularised ...
, while the Wittelsbach emperor Louis IV passed Carinthia and Carniolan march to the Habsburg duke Albert II of Austria
Albert II (12 December 1298 – 16 August 1358), known as ''the Wise'' or ''the Lame'', a member of the House of Habsburg, was duke of Austria and Styria from 1330, as well as duke of Carinthia and margrave of Carniola from 1335 until his death. ...
, whose mother, Elisabeth of Carinthia is a sister of the late duke Henry of Gorizia.
 Albert's son Rudolf IV of Austria, "the Founder", in the course of his '' Privilegium Maius'', awarded himself the title of a "Duke of Carniola" in 1364—though without consent by the
Albert's son Rudolf IV of Austria, "the Founder", in the course of his '' Privilegium Maius'', awarded himself the title of a "Duke of Carniola" in 1364—though without consent by the Holy Roman Emperor
The Holy Roman Emperor, originally and officially the Emperor of the Romans ( la, Imperator Romanorum, german: Kaiser der Römer) during the Middle Ages, and also known as the Roman-German Emperor since the early modern period ( la, Imperat ...
. Rudolph also founded the town of Novo Mesto
Novo Mesto (; sl, Novo mesto; also known by other alternative names) is a city on a bend of the Krka River in the City Municipality of Novo Mesto in southeastern Slovenia, close to the border with Croatia. The town is traditionally considered ...
in Lower Carniola, then named ''Rudolphswerth''. After his death, as a result of the quarrels between his younger brothers Albert III and Leopold, Carniola by the 1379 Treaty of Neuberg became part of Inner Austria
Inner Austria (german: Innerösterreich; sl, Notranja Avstrija; it, Austria Interiore) was a term used from the late 14th to the early 17th century for the Habsburg hereditary lands south of the Semmering Pass, referring to the Imperial duchi ...
ruled from Graz
Graz (; sl, Gradec) is the capital city of the Austrian state of Styria and second-largest city in Austria after Vienna. As of 1 January 2021, it had a population of 331,562 (294,236 of whom had principal-residence status). In 2018, the popula ...
by Leopold, ancestor of the Habsburg Leopoldian line
The Leopoldian line was a sequence of descent in the Habsburg dynasty begun by Duke Leopold III of Austria, who, after the death of his elder brother Rudolf IV, divided the Habsburg hereditary lands with his brother Albert III according to the ...
. In 1457, the Inner Austrian territories were re-united with the Archduchy of Austria
The Archduchy of Austria (german: Erzherzogtum Österreich) was a major principality of the Holy Roman Empire and the nucleus of the Habsburg monarchy. With its capital at Vienna, the archduchy was centered at the Empire's southeastern peripher ...
under the rule of the Habsburg emperor Frederick III. When Frederick's descendant, Emperor Ferdinand I, died in 1564, Carniola was separated again as part of Inner Austria under the rule of Ferdinand's son Archduke Charles II. Charles' son, Emperor Ferdinand II
Ferdinand II (9 July 1578 – 15 February 1637) was Holy Roman Emperor, King of Bohemia, Hungary, and Croatia from 1619 until his death in 1637. He was the son of Archduke Charles II of Inner Austria and Maria of Bavaria. His parents were ...
, inherited all the dynasty's lands in 1619 and the duchy formed a constituent part of the Habsburg monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy (german: Habsburgermonarchie, ), also known as the Danubian monarchy (german: Donaumonarchie, ), or Habsburg Empire (german: Habsburgerreich, ), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities ...
ever since.
In the late 15th century, as part of the Habsburg westward expansion, the Duchy of Carniola acquired many new territories: Idrija (previously part of Friuli), Duino
Duino ( sl, Devin, german: Tybein) is today a seaside resort on the northern Adriatic coast. It is a ''hamlet'' of Duino-Aurisina, a municipality (''comune'') of the Friuli–Venezia Giulia region of northeastern Italy. The settlement, picturesq ...
and the surrounding parts of the Karst Plateau, Kastav, Opatija, and the interior areas of Istria, centered around Pazin. It also had nominal control over the port of Rijeka
Rijeka ( , , ; also known as Fiume hu, Fiume, it, Fiume ; local Chakavian: ''Reka''; german: Sankt Veit am Flaum; sl, Reka) is the principal seaport and the third-largest city in Croatia (after Zagreb and Split). It is located in Prim ...
, which however de facto remained an autonomous city; in 1717 it was officially placed under direct imperial rule and in 1776 it was transferred to Hungary. In the 19th century, these areas (with the exception of Idrija) were incorporated in the Austrian Littoral, and Carniola thus became a landlocked region once again.
With the Treaty of Schönbrunn in 1809, Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
formed the short-lived Illyrian Provinces from the annexed territories in Carniola, Carinthia, Croatia, Gorizia and Gradisca
The Princely County of Gorizia and Gradisca (german: Gefürstete Grafschaft Görz und Gradisca; it, Principesca Contea di Gorizia e Gradisca; sl, Poknežena grofija Goriška in Gradiščanska), historically sometimes shortened to and spelled " ...
, and Trieste
Trieste ( , ; sl, Trst ; german: Triest ) is a city and seaport in northeastern Italy. It is the capital city, and largest city, of the autonomous region of Friuli Venezia Giulia, one of two autonomous regions which are not subdivided into pr ...
. The Final Act of the 1815 Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna (, ) of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon ...
restored the Illyrian Provinces to the Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire (german: link=no, Kaiserthum Oesterreich, modern spelling , ) was a Central- Eastern European multinational great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the realms of the Habsburgs. During its existence, ...
. Carniola then formed the central part of the territory of the Austrian Kingdom of Illyria
The Kingdom of Illyria was a crown land of the Austrian Empire from 1816 to 1849, the successor state of the Napoleonic Illyrian Provinces, which were reconquered by Austria in the War of the Sixth Coalition. It was established according to th ...
, whose capital was also Ljubljana, including the Carniolan and Carinthian duchies as well as the Austrian Littoral with Gorizia and Gradisca, the Margraviate of Istria and the Imperial Free City of Trieste
The Imperial Free City of Trieste and its Territory (german: Reichsunmittelbare Stadt Triest und ihr Gebiet, it, Città Imperiale di Trieste e Dintorni) was a possession of the Habsburg monarchy in the Holy Roman Empire from the 14th century to ...
.
After the disestablishment of the Illyrian Kingdom in 1849, the Duchy of Carniola was constituted by rescript of 20 December 1860, and by imperial patent of 26 February 1861 ( February Patent), modified by legislation of 21 December 1867, granting power to the Carniolan ''Landtag
A Landtag (State Diet) is generally the legislative assembly or parliament of a federated state or other subnational self-governing entity in German-speaking nations. It is usually a unicameral assembly exercising legislative competence in non ...
'' (or Carniolan Diet - estates' assembly) to enact all laws not reserved to the Imperial Council in Vienna
en, Viennese
, iso_code = AT-9
, registration_plate = W
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code =
, timezone = CET
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST ...
, at which it was represented by eleven delegates, of whom two elected by the landowners, three by the cities, towns, commercial and industrial boards, five by the village communes, and one by a fifth curia by secret ballot, every duly registered male twenty-four years of age had the right to vote. The home legislature consisted of a single chamber of thirty-seven members, among whom the prince-bishop sat ex-officio. The emperor convened the legislature, and it was presided over by the ''k. k. Landeshauptmann'' (president of the Carniolan Diet – ''Landtag'' and its executive board – ''Landesausschuss''). The landed interests elected ten members, the cities and towns eight, the commercial and industrial boards two, the village communes sixteen. The business of the chamber was restricted to legislating on agriculture, public and charitable institutions, administration of communes, church and school affairs, the transportation and housing of soldiers in war and during manoeuvres, and other local matters. The land budget of 1901 amounted to 3,573,280 crowns ($714,656).
The Austrian Imperial-Royal government was represented by the Imperial-Royal president (''k. k. Landespräsident'' or governor), appointed by the emperor, and the Imperial-Royal Government (''k. k. Landesregierung'') in Ljubljana. In the majority of other Austrian crown lands these were known as Imperial-Royal Lieutenant (''k. k. Statthalter'') and Imperial-Royal Lieutenancy (''k. k. Statthalterei'').
In 1918, the duchy ceased to exist and its territory became part of the newly formed State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs and subsequently part of the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes
Kingdom commonly refers to:
* A monarchy ruled by a king or queen
* Kingdom (biology), a category in biological taxonomy
Kingdom may also refer to:
Arts and media Television
* ''Kingdom'' (British TV series), a 2007 British television drama s ...
(from 1929 called Kingdom of Yugoslavia
The Kingdom of Yugoslavia ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Kraljevina Jugoslavija, Краљевина Југославија; sl, Kraljevina Jugoslavija) was a state in Southeast and Central Europe that existed from 1918 until 1941. From 191 ...
). The western part of the duchy, with the towns of Postojna, Ilirska Bistrica
Ilirska Bistrica (; german: Illyrisch Feistritz; it, Villa del Nevoso, before 1927: ''Bisterza,'' Hungarian: ''Illírbeszterce'') is a town in the Inner Carniola region of southwestern Slovenia. It is the administrative seat of the Municipalit ...
, Idrija, Vipava Vipava can refer to:
* Vipava, Vipava, town in southwestern Slovenia
* Vipava (river), in Slovenia and Italy
* Vipava Valley
The Vipava Valley (; sl, Vipavska dolina, german: Wippachtal, it, Valle del Vipacco) is a valley in the Slovenian Lit ...
and Šturje was annexed to Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
in 1920, but was subsequently also included into Yugoslavia in 1945 except for the town of Fusine in Valromana (Weissenfels, before 1919), which remained in Italy.
Demographics
The vast majority of the population were Slovene-speaking. AGerman
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
-speaking minority existed among the local nobles and those craftsmen, who had settled here as citizens of the major towns. German language islands were found in Lower Carniolan Gottschee County, where the rural population spoke Gottscheerish
Gottscheerish (''Göttscheabarisch'',Maridi Tscherne: Wörterbuch Gottscheerisch-Slowenisch. Einrichtung für die Erhaltung des Kulturerbes Nesseltal, Koprivnik/Nesseltal 2010. german: Gottscheerisch, sl, kočevarščina) is an Upper German ...
(Granish), a Southern Bavarian dialect, as well as around the Upper Carniolan villages of Zgornja Sorica (''Oberzarz''), Spodnja Sorica (''Unterzarz'') and Nemški Rovt (''Deutschgereuth'') in the Bohinj Basin.
In 1846, the population of Carniola included:A.J.P. Taylor, The Habsburg Monarchy 1809–1918, 1948: Serbian edition: A. Dž. P. Tejlor, Habzburška monarhija 1809–1918, Beograd, 2001, page 302.
*428,000 Slovenes
The Slovenes, also known as Slovenians ( sl, Slovenci ), are a South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to Slovenia, and adjacent regions in Italy, Austria and Hungary. Slovenes share a common ancestry, Slovenian culture, culture, History ...
*38,000 Germans
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
In 1910, the population of Carniola included:
*520,000 Slovenes
The Slovenes, also known as Slovenians ( sl, Slovenci ), are a South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to Slovenia, and adjacent regions in Italy, Austria and Hungary. Slovenes share a common ancestry, Slovenian culture, culture, History ...
*28,000 Germans
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
Coat of arms and flag
 The coat of arms of Carniola dates back to the 13th century, when it most probably evolved as a combination of the coats of arms of the Bavarian counts of Andechs in the Duchy of Merania (eagle) and the Rhenish House of Sponheim in Carinthia (red-white checkerboard). The eagle is also featured in the seal of King
The coat of arms of Carniola dates back to the 13th century, when it most probably evolved as a combination of the coats of arms of the Bavarian counts of Andechs in the Duchy of Merania (eagle) and the Rhenish House of Sponheim in Carinthia (red-white checkerboard). The eagle is also featured in the seal of King Ottokar II of Bohemia
Ottokar II ( cs, Přemysl Otakar II.; , in Městec Králové, Bohemia – 26 August 1278, in Dürnkrut, Lower Austria), the Iron and Golden King, was a member of the Přemyslid dynasty who reigned as King of Bohemia from 1253 until his dea ...
in his capacity as ruler of the Carniolan march in 1269. In 1463 Emperor Frederick III, having prevailed against the claims raised by his brother Albert VI of Austria, added the Imperial crown to the eagle and replaced the white in the shield and the checkered crescent with gold. In 1836 Emperor Ferdinand I of Austria restored the original white color to the shield and recognized the white-blue-red combination as the official Carniolan color scheme.
Under the Habsburg rule the white, blue and red from the Carniolan coat of arms (the shield, the eagle and the crescent) were confirmed as the official flag colors of the crownland in 1848. Since the Duchy of Carniola was the main Slovene-populated region of the Austrian Empire, the color scheme was subsequently accepted as the generic Slovene national tricolor by the inhabitants of other Slovene Lands
The Slovene lands or Slovenian lands ( sl, Slovenske dežele or in short ) is the historical denomination for the territories in Central and Southern Europe where people primarily spoke Slovene. The Slovene lands were part of the Illyrian provin ...
.
As for the coat of arms, it was abandoned after 1918 with the passing of the Duchy of Carniola. The blue eagle of Carniola was, however, briefly resurrected from 1943 to 1945 as the symbol of the Slovenian auxiliary Axis forces, the Slovene Home Guard. It was also used in the Yugoslav Karađorđević dynasty
The Karađorđević dynasty ( sr-Cyrl, Динасија Карађорђевић, Dinasija Karađorđević, Карађорђевићи / Karađorđevići, ) or House of Karađorđević ( sr-Cyrl, Кућа Карађорђевић, Kuća Karađ ...
coat-of-arms in the interwar period (and was replaced in the state coat-of-arms of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia
The Kingdom of Yugoslavia ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Kraljevina Jugoslavija, Краљевина Југославија; sl, Kraljevina Jugoslavija) was a state in Southeast and Central Europe that existed from 1918 until 1941. From 191 ...
by the three stars of the medieval counts of Celje
The Counts of Celje ( sl, Celjski grofje) or the Counts of Cilli (german: Grafen von Cilli; hu, cillei grófok) were the most influential late medieval noble dynasty on the territory of present-day Slovenia. Risen as vassals of the Habsburg dukes ...
).
The insignia of the Duchy of Carniola have had an important and lasting impact on Slovene national symbols. Thus, the white-blue-red combination of the flag of the Duchy of Carniola is in use today as the official color scheme of the flag of the Republic of Slovenia. The Slovenian coat of arms is also a heraldic composite, incorporating the stars of the counts of Celje, the Carniolan colors and the silhouette of the Slovene national symbol, Mount Triglav.
Dukes
* Rudolph (1364–1365), also Duke ofAustria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
since 1358, followed by his brothers
** Albert (1365–1379), jointly with
** Leopold (1365–1386), progenitor of the Habsburg Leopoldian line
The Leopoldian line was a sequence of descent in the Habsburg dynasty begun by Duke Leopold III of Austria, who, after the death of his elder brother Rudolf IV, divided the Habsburg hereditary lands with his brother Albert III according to the ...
, sole Duke of Inner Austria
Inner Austria (german: Innerösterreich; sl, Notranja Avstrija; it, Austria Interiore) was a term used from the late 14th to the early 17th century for the Habsburg hereditary lands south of the Semmering Pass, referring to the Imperial duchi ...
after the 1379 Treaty of Neuberg
* William (1386–1406), son of Leopold, followed by his brother
**Ernest the Iron
Ernest the Iron (; 1377 – 10 June 1424), a member of the House of Habsburg, ruled over the Inner Austrian duchies of Styria, Carinthia and Carniola from 1406 until his death. He was head of the Habsburg Leopoldian line from 1411.
Biography
E ...
(1406–1424), Archduke from 1414
* Frederick (1424–1493), son of Ernest, King of the Romans from 1440 and Holy Roman Emperor
The Holy Roman Emperor, originally and officially the Emperor of the Romans ( la, Imperator Romanorum, german: Kaiser der Römer) during the Middle Ages, and also known as the Roman-German Emperor since the early modern period ( la, Imperat ...
from 1452, also Archduke of Austria from 1457
* Maximilian I (1493–1519), son, also Archduke of Austria, Holy Roman Emperor from 1508
*Charles I Charles I may refer to:
Kings and emperors
* Charlemagne (742–814), numbered Charles I in the lists of Holy Roman Emperors and French kings
* Charles I of Anjou (1226–1285), also king of Albania, Jerusalem, Naples and Sicily
* Charles I of ...
(1519–1521), grandson, also Archduke of Austria, Emperor-elect from 1520, followed by his brother
** Ferdinand I (1521–1564), also Archduke of Austria, King of the Romans from 1531, Holy Roman Emperor from 1558
* Charles II (1564–1590), son of Ferdinand, Archduke of Inner Austria upon second partition of the Habsburg lands
* Ferdinand II (1590–1637), son, also Archduke of Austria and Holy Roman Emperor from 1619
Heir of all Habsburg lines in 1619. See List of rulers of Austria
This is a list of people who have ruled either the Margraviate of Austria, the Duchy of Austria or the Archduchy of Austria. From 976 until 1246, the margraviate and its successor, the duchy, was ruled by the House of Babenberg. At that time, thos ...
for details.
See also
* Carniola * Slovene dialects * Gottschee County * Flag of Slovenia * History of SloveniaReferences
External links
Map – Duchy of Carniola in 1849
{{DEFAULTSORT:Carniola, Duchy of Duchy of Carniola Former states and territories in Slovenia Duchy of Carniola Austrian Circle Subdivisions of Austria-Hungary States of the German Confederation Duchies of the Holy Roman Empire Subdivisions of the Habsburg Monarchy Southern Limestone Alps States and territories established in 1364 States and territories disestablished in 1918 Duchy of Carniola 1364 establishments in Europe 1360s establishments in the Holy Roman Empire 1918 disestablishments in Austria-Hungary Medieval Slovenia Modern history of Slovenia Carniola