Duchy of Carinthia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
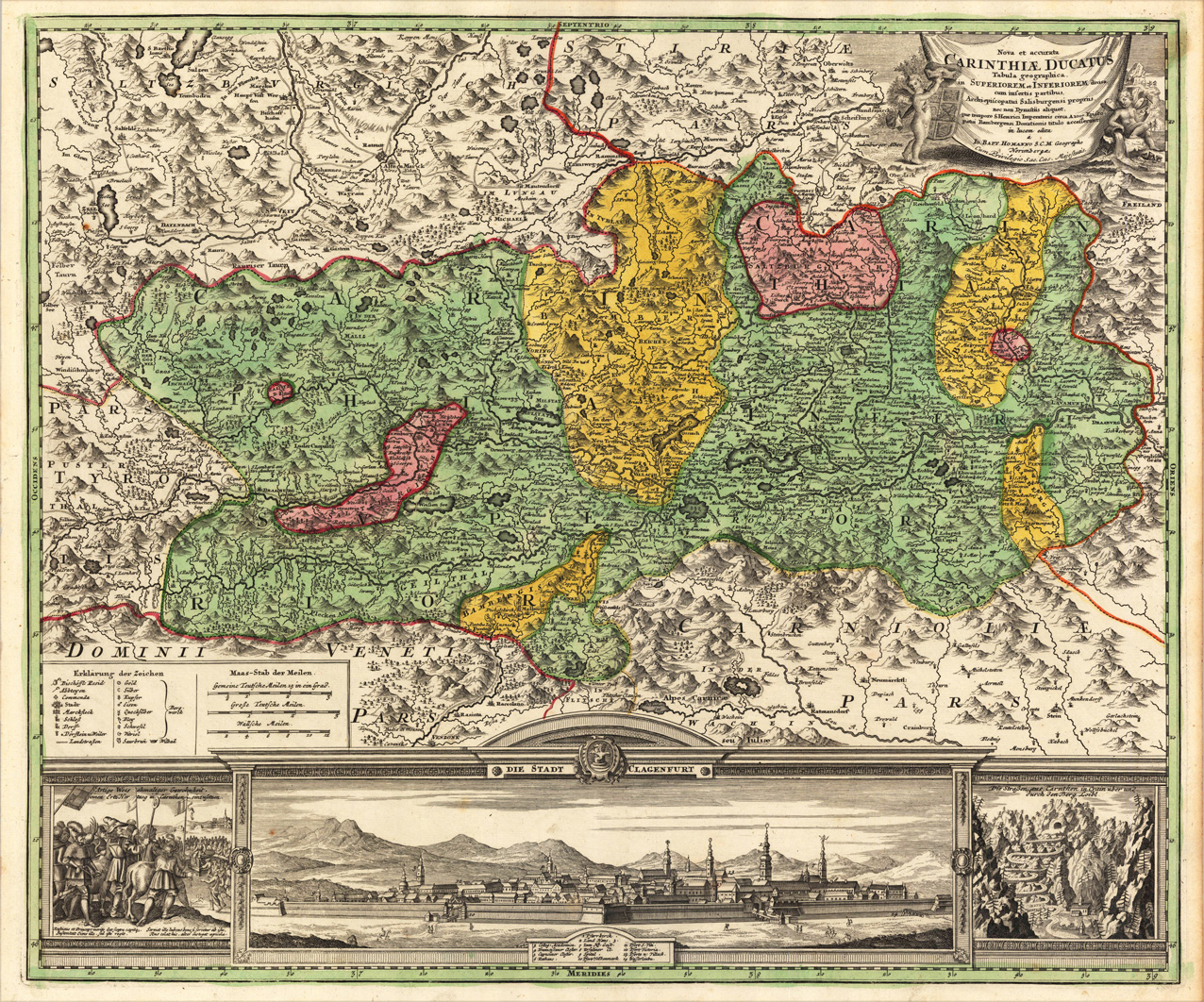
The Duchy of Carinthia (german: Herzogtum Kärnten; sl, Vojvodina Koroška) was a duchy located in southern
 Duke Henry's son Henry II "the Quarreller" from 974 onwards, revolted against his cousin Emperor
Duke Henry's son Henry II "the Quarreller" from 974 onwards, revolted against his cousin Emperor
 Carinthia, however, remained a separate entity, and in 1012 Count Adalbero I of Eppenstein, Margrave of the Carinthian March (later Styria) since about 1000, was vested with the duchy by the last Ottonian emperor Henry II, while the Istrian march was separated and given to Count Poppo of Weimar. Adalbero was removed from office in 1035 after he had fallen out of favour with the Salian Emperor
Carinthia, however, remained a separate entity, and in 1012 Count Adalbero I of Eppenstein, Margrave of the Carinthian March (later Styria) since about 1000, was vested with the duchy by the last Ottonian emperor Henry II, while the Istrian march was separated and given to Count Poppo of Weimar. Adalbero was removed from office in 1035 after he had fallen out of favour with the Salian Emperor
The most outstanding of the Spanheim dukes was Bernhard, the first Carinthian duke who was actually described and honoured in documents as "prince of the land". The last Spanheim duke was Ulrich III; he signed an inheritance treaty with his brother Archbishop Philip of
 Empress Maria Theresa of Austria and her son Joseph II attempted to create a more
Empress Maria Theresa of Austria and her son Joseph II attempted to create a more 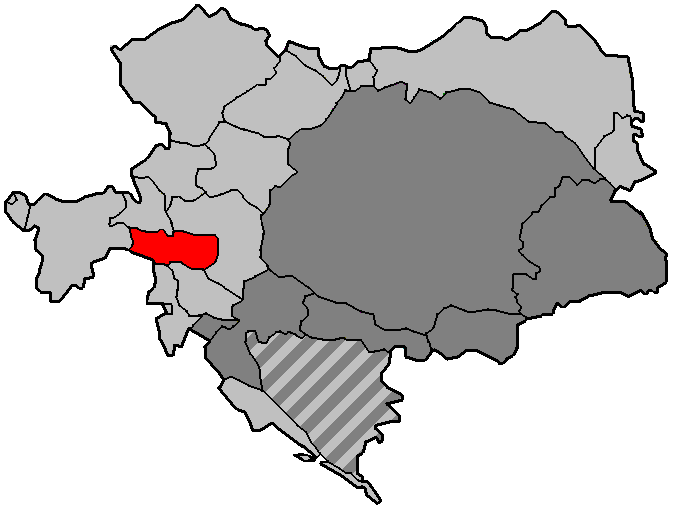 Over the centuries, the
Over the centuries, the
 The Austrian part of the former duchy today forms the
The Austrian part of the former duchy today forms the

 * Henry IV (1122–1123)
* Engelbert (1123–1134)
* Ulrich I (1134–1144)
*
* Henry IV (1122–1123)
* Engelbert (1123–1134)
* Ulrich I (1134–1144)
*
Kärnten (Religious population data is inaccurate)
Map of the Balkans (1815–59)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Carinthia, Duchy States and territories disestablished in 1919 States and territories established in the 970s Carinthia (state) States of the German Confederation Duchies of the Holy Roman Empire Austrian Circle Subdivisions of Austria-Hungary Historical regions in Austria Former states and territories in Slovenia 970s establishments in the Holy Roman Empire 1918 disestablishments in Austria-Hungary 976 establishments
Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
and parts of northern Slovenia
Slovenia ( ; sl, Slovenija ), officially the Republic of Slovenia (Slovene: , abbr.: ''RS''), is a country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the southeast, and ...
. It was separated from the Duchy of Bavaria
The Duchy of Bavaria (German: ''Herzogtum Bayern'') was a frontier region in the southeastern part of the Merovingian kingdom from the sixth through the eighth century. It was settled by Bavarian tribes and ruled by dukes (''duces'') under ...
in 976, and was the first newly created Imperial State after the original German stem duchies.
Carinthia remained a State of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 unt ...
until its dissolution in 1806, though from 1335 it was ruled within the Austrian
Austrian may refer to:
* Austrians, someone from Austria or of Austrian descent
** Someone who is considered an Austrian citizen, see Austrian nationality law
* Austrian German dialect
* Something associated with the country Austria, for example: ...
dominions of the Habsburg dynasty. A constituent part of the Habsburg monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy (german: Habsburgermonarchie, ), also known as the Danubian monarchy (german: Donaumonarchie, ), or Habsburg Empire (german: Habsburgerreich, ), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities ...
and of the Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire (german: link=no, Kaiserthum Oesterreich, modern spelling , ) was a Central- Eastern European multinational great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the realms of the Habsburgs. During its existence, ...
, it remained a Cisleithanian crown land of Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
until 1918. By the Carinthian Plebiscite in October 1920, the main area of the duchy formed the Austrian state of Carinthia
Carinthia (german: Kärnten ; sl, Koroška ) is the southernmost Austrian state, in the Eastern Alps, and is noted for its mountains and lakes. The main language is German. Its regional dialects belong to the Southern Bavarian group. Carin ...
.
History
In the seventh century the area was part of the Slavic principality of Carantania, which fell under the suzerainty of Duke Odilo of Bavaria in about 743. The Bavarian stem duchy was incorporated into theCarolingian Empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–888) was a large Frankish-dominated empire in western and central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as kings of the Franks since 751 and as kings of the L ...
when Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first E ...
deposed Odilo's son Duke Tassilo III in 788. In the 843 partition by the Treaty of Verdun
The Treaty of Verdun (), agreed in , divided the Frankish Empire into three kingdoms among the surviving sons of the emperor Louis I, the son and successor of Charlemagne. The treaty was concluded following almost three years of civil war and ...
, Carinthia became part of East Francia under King Louis the German
Louis the German (c. 806/810 – 28 August 876), also known as Louis II of Germany and Louis II of East Francia, was the first king of East Francia, and ruled from 843 to 876 AD. Grandson of emperor Charlemagne and the third son of Louis the P ...
. From 889 to 976 it was the Carinthian March of the renewed Bavarian duchy, though in 927 the local Count Berthold of the Luitpolding dynasty was vested with ducal rights by the German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
king Henry the Fowler. After Berthold became Duke of Bavaria in 938, both territories were ruled by him. Upon his death in 948 the Luitpoldings, though heirs of the royal Ottonian dynasty, were not able to retain their possessions, as King Otto I
Otto I (23 November 912 – 7 May 973), traditionally known as Otto the Great (german: Otto der Große, it, Ottone il Grande), was East Frankish king from 936 and Holy Roman Emperor from 962 until his death in 973. He was the oldest son of He ...
bought the loyalty of his younger brother Henry I Henry I may refer to:
876–1366
* Henry I the Fowler, King of Germany (876–936)
* Henry I, Duke of Bavaria (died 955)
* Henry I of Austria, Margrave of Austria (died 1018)
* Henry I of France (1008–1060)
* Henry I the Long, Margrave of the N ...
with the Bavarian lands.
Establishment
 Duke Henry's son Henry II "the Quarreller" from 974 onwards, revolted against his cousin Emperor
Duke Henry's son Henry II "the Quarreller" from 974 onwards, revolted against his cousin Emperor Otto II
Otto II (955 – 7 December 983), called the Red (''der Rote''), was Holy Roman Emperor from 973 until his death in 983. A member of the Ottonian dynasty, Otto II was the youngest and sole surviving son of Otto the Great and Adelaide of Italy ...
, whereupon he was deposed as Duke of Bavaria in favour of Otto's nephew Duke Otto I of Swabia. At the same time Emperor Otto II created a sixth duchy in addition to the original stem duchies, the new Duchy of Carinthia. He reverted the possession of the territories to the Luitpoldings, when he split Carinthia from the Bavarian lands and installed the former Duke Berthold's son Henry the Younger as duke in 976.
Over the centuries, the name 'Carinthia' (''Kärnten'') gradually replaced former 'Carantania'. The realm of the Carinthian dukes initially comprised a vast territory including the marches of Styria
Styria (german: Steiermark ; Serbo-Croatian and sl, ; hu, Stájerország) is a state (''Bundesland'') in the southeast of Austria. With an area of , Styria is the second largest state of Austria, after Lower Austria. Styria is bordered ...
(''marchia Carantana''), Carniola and Istria; they also ruled over the Italian March of Verona in the south. Nevertheless, Henry the Younger was the first and also the last Luitpolding duke; as he chose to join the unsuccessful War of the Three Henries against Emperor Otto II, he lost Carinthia two years later and was succeeded by the Emperor's nephew Otto I
Otto I (23 November 912 – 7 May 973), traditionally known as Otto the Great (german: Otto der Große, it, Ottone il Grande), was East Frankish king from 936 and Holy Roman Emperor from 962 until his death in 973. He was the oldest son of He ...
, a scion of the Salian dynasty
The Salian dynasty or Salic dynasty (german: Salier) was a dynasty in the High Middle Ages. The dynasty provided four kings of Germany (1024–1125), all of whom went on to be crowned Holy Roman emperors (1027–1125).
After the death of the la ...
. Though Henry once again managed to regain the ducal title in 985, Carinthia upon his death in 989 fell back to the Imperial Ottonian dynasty in Bavaria.
Eppensteins and Sponheims
 Carinthia, however, remained a separate entity, and in 1012 Count Adalbero I of Eppenstein, Margrave of the Carinthian March (later Styria) since about 1000, was vested with the duchy by the last Ottonian emperor Henry II, while the Istrian march was separated and given to Count Poppo of Weimar. Adalbero was removed from office in 1035 after he had fallen out of favour with the Salian Emperor
Carinthia, however, remained a separate entity, and in 1012 Count Adalbero I of Eppenstein, Margrave of the Carinthian March (later Styria) since about 1000, was vested with the duchy by the last Ottonian emperor Henry II, while the Istrian march was separated and given to Count Poppo of Weimar. Adalbero was removed from office in 1035 after he had fallen out of favour with the Salian Emperor Conrad II
Conrad II ( – 4 June 1039), also known as and , was the emperor of the Holy Roman Empire from 1027 until his death in 1039. The first of a succession of four Salian emperors, who reigned for one century until 1125, Conrad ruled the kingdoms ...
. In 1039 Carinthia was inherited by Emperor Henry III himself, who split off the Carniolan march the following year and granted it to Margrave Poppo of Istria. In 1077, the duchy was given to Luitpold, again a member of the Eppensteiner family, which, however, became extinct with the death of Luitpold's younger brother Henry III of Carinthia in 1122. Upon his death the duchy was further reduced in area: a large part of the Eppenstein lands in what is today Upper Styria passed to Margrave Ottokar II of Styria.
The remainder of Carinthia passed from Duke Henry III to his godchild Henry from the House of Sponheim, who ruled as Henry IV, from 1122 to his early death the following year.Mediaeval GenealogyThe most outstanding of the Spanheim dukes was Bernhard, the first Carinthian duke who was actually described and honoured in documents as "prince of the land". The last Spanheim duke was Ulrich III; he signed an inheritance treaty with his brother Archbishop Philip of
Salzburg
Salzburg (, ; literally "Salt-Castle"; bar, Soizbuag, label=Austro-Bavarian) is the fourth-largest city in Austria. In 2020, it had a population of 156,872.
The town is on the site of the Roman settlement of ''Iuvavum''. Salzburg was founded ...
, who, however, could not prevail against the Bohemian
Bohemian or Bohemians may refer to:
*Anything of or relating to Bohemia
Beer
* National Bohemian, a brand brewed by Pabst
* Bohemian, a brand of beer brewed by Molson Coors
Culture and arts
* Bohemianism, an unconventional lifestyle, origin ...
king Ottokar II Přemysl. In spite of being supported by the Habsburg king Rudolf I of Germany
Rudolf I (1 May 1218 – 15 July 1291) was the first King of Germany from the House of Habsburg. The first of the count-kings of Germany, he reigned from 1273 until his death.
Rudolf's election marked the end of the Great Interregnum whic ...
, who defeated Ottokar II at the Battle on the Marchfeld in 1278, Philip never gained actual power. The duchy was seized by Rudolph and Philip died a year later in 1279.
Habsburgs
Rudolf, after being elected King of the Romans and defeating King Ottokar II, at first gave Carinthia to Count Meinhard II of Gorizia-Tyrol. In 1335, after the death of Henry, the last male of this line, Emperor Louis the Bavarian gave Carinthia and the southern part of the Tyrol as an imperialfief
A fief (; la, feudum) was a central element in medieval contracts based on feudal law. It consisted of a form of property holding or other rights granted by an overlord to a vassal, who held it in fealty or "in fee" in return for a form ...
to the Habsburg family on 2 May in Linz
Linz ( , ; cs, Linec) is the capital of Upper Austria and third-largest city in Austria. In the north of the country, it is on the Danube south of the Czech border. In 2018, the population was 204,846.
In 2009, it was a European Capital ...
. The Habsburgs would continue to rule Carinthia until 1918. As with the other component parts of the Habsburg monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy (german: Habsburgermonarchie, ), also known as the Danubian monarchy (german: Donaumonarchie, ), or Habsburg Empire (german: Habsburgerreich, ), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities ...
, Carinthia remained a semi-autonomous state with its own constitutional structure for a long time. The Habsburgs divided up their territories within the family twice, according to the 1379 Treaty of Neuberg and again in 1564. Each time, the Duchy of Carinthia became part of Inner Austria
Inner Austria (german: Innerösterreich; sl, Notranja Avstrija; it, Austria Interiore) was a term used from the late 14th to the early 17th century for the Habsburg hereditary lands south of the Semmering Pass, referring to the Imperial duchi ...
and was ruled jointly with the adjacent duchies of Styria
Styria (german: Steiermark ; Serbo-Croatian and sl, ; hu, Stájerország) is a state (''Bundesland'') in the southeast of Austria. With an area of , Styria is the second largest state of Austria, after Lower Austria. Styria is bordered ...
and Carniola.
 Empress Maria Theresa of Austria and her son Joseph II attempted to create a more
Empress Maria Theresa of Austria and her son Joseph II attempted to create a more unitary
Unitary may refer to:
Mathematics
* Unitary divisor
* Unitary element
* Unitary group
* Unitary matrix
* Unitary morphism
* Unitary operator
* Unitary transformation
* Unitary representation In mathematics, a unitary representation of a grou ...
Habsburg state, and in 1804 Carinthia was integrated into the newly established Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire (german: link=no, Kaiserthum Oesterreich, modern spelling , ) was a Central- Eastern European multinational great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the realms of the Habsburgs. During its existence, ...
under Francis II/I. According to the 1809 Treaty of Schönbrunn, the Upper Carinthian territories around Villach formed part of the short-lived Napoleonic Illyrian Provinces; Carinthia as a whole remained a part of the Habsburg Kingdom of Illyria until its dissolution in 1849.
In 1867, the duchy became a crown land of Cisleithania, the western part of Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
(see History of Austria).
 Over the centuries, the
Over the centuries, the German language
German ( ) is a West Germanic language mainly spoken in Central Europe. It is the most widely spoken and official or co-official language in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, Liechtenstein, and the Italian province of South Tyrol. It is also a ...
, which carried more prestige, expanded at the expense of Slovene, but the fact that in the 16th century the Estates of Carinthia could still point out that Carinthia was "a Windic Archduchy", i.e. a sovereign Slovene principality, shows that the Carinthian people were aware of their ancient and pre-German roots.
World War I and Carinthian Plebiscite
DuringWorld War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
, Carinthia experienced a relatively high number of war deaths: thirty-seven for every 1,000 inhabitants. This was higher than in most other German-speaking areas of Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
(except German South Moravia).Rothenburg, G. ''The Army of Francis Joseph''. West Lafayette: Purdue University Press, 1976. p 218.
Following the end of the war and the dissolution of Austria-Hungary, the 1919 Treaty of Saint-Germain stipulated the Carinthian Canal Valley stretching from Tarvisio as far as Pontafel (172 square miles)”Kärnten.” Encyclopædia Britannica. Ultimate Reference Suite. Chicago 2010. go to Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
and that the Slovene-speaking areas of the Meža Valley, the Drava Valley area around Unterdrauburg
Dravograd (; german: Unterdrauburg) is a small town in northern Slovenia, close to the border with Austria.
It is the seat of the Municipality of Dravograd. It lies on the Drava, Drava River at the confluence with the Meža and the Mislinja ( ...
, which was afterwards renamed Dravograd, and the Jezersko area (128 square miles of territory) be ceded to the new SHS State. The Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes
Kingdom commonly refers to:
* A monarchy ruled by a king or queen
* Kingdom (biology), a category in biological taxonomy
Kingdom may also refer to:
Arts and media Television
* ''Kingdom'' (British TV series), a 2007 British television drama s ...
, however, was not satisfied with these parts of the former duchy and also occupied land north of the Karawanks mountain range, including the capital city of Klagenfurt. The Entente powers decided on a two-stage referendum, of which the first stage, the Carinthian Plebiscite was held on 10 October 1920 to determine the fate of Carinthia. The outcome in favour of Austria did not change the borders as decided upon in the Treaty of Saint-Germain.
 The Austrian part of the former duchy today forms the
The Austrian part of the former duchy today forms the federal state
A federation (also known as a federal state) is a political entity characterized by a union of partially self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a central federal government ( federalism). In a federation, the self-gover ...
of Carinthia
Carinthia (german: Kärnten ; sl, Koroška ) is the southernmost Austrian state, in the Eastern Alps, and is noted for its mountains and lakes. The main language is German. Its regional dialects belong to the Southern Bavarian group. Carin ...
(german: Land Kärnten), while the area that was ceded to Italy as a part of the claimed " Julian March" belongs to the autonomous region
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas that are broadly divided by physical characteristics ( physical geography), human impact characteristics ( human geography), and the interaction of humanity an ...
of Friuli–Venezia Giulia
(man), it, Friulana (woman), it, Giuliano (man), it, Giuliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_t ...
. Most of the area awarded to Yugoslavia (cf. Slovenian Carinthia) now forms part of the larger Carinthia Statistical Region in Slovenia
Slovenia ( ; sl, Slovenija ), officially the Republic of Slovenia (Slovene: , abbr.: ''RS''), is a country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the southeast, and ...
.
Area and population
Area: * Total: Population (1910 Census): * Total: 396,228Linguistic composition
According to the last Austrian Imperial census of 1910, the Duchy of Carinthia was composed of the following linguistic communities: Total: 396,228 *German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
: 304,315 (76.80%)
* Slovene: 82,212 (20.75%)
* Italian: 82 (0.02%)
* Other languages or foreigners: 9,619 (2.43%)
The Austrian censuses did not count ethnic groups, nor the mother tongue, but the "language of daily interaction" ().
Religious composition
Total: 396,228 * Roman Catholics: 371,361 (93.72%) * Protestants: 24,299 (6.13%) *Jewish
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
: 341 (0.09%)
* Other religions or unknown: 227 (0.06%)
Dukes of Carinthia
Various dynasties
Luitpoldings * Berthold I (927–938) *Henry I Henry I may refer to:
876–1366
* Henry I the Fowler, King of Germany (876–936)
* Henry I, Duke of Bavaria (died 955)
* Henry I of Austria, Margrave of Austria (died 1018)
* Henry I of France (1008–1060)
* Henry I the Long, Margrave of the N ...
(976–978)
Salian dynasty
The Salian dynasty or Salic dynasty (german: Salier) was a dynasty in the High Middle Ages. The dynasty provided four kings of Germany (1024–1125), all of whom went on to be crowned Holy Roman emperors (1027–1125).
After the death of the la ...
*Otto I
Otto I (23 November 912 – 7 May 973), traditionally known as Otto the Great (german: Otto der Große, it, Ottone il Grande), was East Frankish king from 936 and Holy Roman Emperor from 962 until his death in 973. He was the oldest son of He ...
(978–985)
Luitpoldings
*Henry I (985–989), again, Duke of Bavaria 983–985
Ottonian dynasty
* Henry II, Duke of Bavaria (989–995), also Duke of Bavaria 985–995
*Henry II, Holy Roman Emperor
Henry II (german: Heinrich II; it, Enrico II; 6 May 973 – 13 July 1024), also known as Saint Henry the Exuberant, Obl. S. B., was Holy Roman Emperor ("Romanorum Imperator") from 1014. He died without an heir in 1024, and was the last ruler ...
(995–1002), also Duke of Bavaria 995–1005
Salian dynasty
The Salian dynasty or Salic dynasty (german: Salier) was a dynasty in the High Middle Ages. The dynasty provided four kings of Germany (1024–1125), all of whom went on to be crowned Holy Roman emperors (1027–1125).
After the death of the la ...
*Otto I (1002–1004), again
* Conrad I (1004–1011)
House of Eppenstein
* Adalbero/Albert I (1011–1035)
Salian dynasty
The Salian dynasty or Salic dynasty (german: Salier) was a dynasty in the High Middle Ages. The dynasty provided four kings of Germany (1024–1125), all of whom went on to be crowned Holy Roman emperors (1027–1125).
After the death of the la ...
*Conrad II
Conrad II ( – 4 June 1039), also known as and , was the emperor of the Holy Roman Empire from 1027 until his death in 1039. The first of a succession of four Salian emperors, who reigned for one century until 1125, Conrad ruled the kingdoms ...
(1036–1039)
*Henry III, Holy Roman Emperor
Henry III (28 October 1016 – 5 October 1056), called the Black or the Pious, was Holy Roman Emperor from 1046 until his death in 1056. A member of the Salian dynasty, he was the eldest son of Conrad II and Gisela of Swabia.
Henry was raised ...
(1039–1047), also Duke of Bavaria 1026–1041 and Holy Roman Emperor 1046–1056
Elder House of Welf
An elder is someone with a degree of seniority or authority.
Elder or elders may refer to:
Positions Administrative
* Elder (administrative title), a position of authority
Cultural
* North American Indigenous elder, a person who has and ...
* Welf (1047–1055)
Ezzonids
*Conrad III
Conrad III (german: Konrad; it, Corrado; 1093 or 1094 – 15 February 1152) of the Hohenstaufen dynasty was from 1116 to 1120 Duke of Franconia, from 1127 to 1135 anti-king of his predecessor Lothair III and from 1138 until his death in 1152 ...
(1056–1061)
House of Zähringen
* Berthold II (1061–1077)
House of Eppenstein
* Luitpold (1077–1090)
* Henry III (1090–1122)
House of Sponheim
Henry V Henry V may refer to:
People
* Henry V, Duke of Bavaria (died 1026)
* Henry V, Holy Roman Emperor (1081/86–1125)
* Henry V, Duke of Carinthia (died 1161)
* Henry V, Count Palatine of the Rhine (c. 1173–1227)
* Henry V, Count of Luxembourg (121 ...
(1144–1161)
* Herman (1161–1181)
*Ulrich II Ulrich II may refer to:
* Ulrich II. (St. Gallen) († 1076) Abbot of St. Gall
* Ulrich II, Duke of Carinthia (c. 1176 – 1202)
* Ulrich II, Count of Württemberg (c. 1254 – 1279)
* Ulrich II von Graben (before 1300 – about 1361)
* Ulrich II, ...
(1181–1201)
* Bernhard (regent from 1199, duke 1202–1256)
* Ulrich III (1256–1269)
Various dynasties
Přemyslid dynasty
The Přemyslid dynasty or House of Přemyslid ( cs, Přemyslovci, german: Premysliden, pl, Przemyślidzi) was a Bohemian royal dynasty that reigned in the Duchy of Bohemia and later Kingdom of Bohemia and Margraviate of Moravia (9th century–1 ...
*Otakar
Otakar is a masculine Czech given name of Germanic origin (cf. Audovacar). Notable people with the name include:
* Otakar Batlička (1895–1942), Czech adventurer, journalist, ham radio operator, member of Czech Nazi resistance group in World War ...
/Otto II (1269–1276), also King of Bohemia
The Duchy of Bohemia was established in 870 and raised to the Kingdom of Bohemia in 1198. Several Bohemian monarchs ruled as non-hereditary kings beforehand, first gaining the title in 1085. From 1004 to 1806, Bohemia was part of the Holy Roman ...
1253–1278
House of Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
* Rudolph I (1276–1286), also King of Germany 1273–1291
Gorizia-Tyrol
*Meinhard
Meinhard is a municipality in the Werra-Meißner-Kreis in Hesse, Germany.
Geography
Location
The community lies in the North Hesse Low Mountain Range landscape on the edge of the Werra valley, 3 km from the district seat of Eschwege.
Near ...
(1286–1295)
* Henry VI (1295–1335), also King of Bohemia
The Duchy of Bohemia was established in 870 and raised to the Kingdom of Bohemia in 1198. Several Bohemian monarchs ruled as non-hereditary kings beforehand, first gaining the title in 1085. From 1004 to 1806, Bohemia was part of the Holy Roman ...
1306/1307–1310, jointly with his brothers
** Louis (1295–1305)
** Otto III (1295–1310)
House of Habsburg
* Otto IV (1335–1339), jointly with his brother ** Albert II (1335–1358) * Frederick Ι (1358–1362), jointly with his brother ** Rudolph II (1358–1365) * Albert III (1365–1379)Leopoldian line
** Leopold (1379–1386) ** William (1386–1406) *Ernest
Ernest is a given name derived from Germanic word ''ernst'', meaning "serious". Notable people and fictional characters with the name include:
People
*Archduke Ernest of Austria (1553–1595), son of Maximilian II, Holy Roman Emperor
* Ernest, ...
(1406–1424)
* Frederick ΙΙ (1424–1493)
Habsburg territories reunified in 1458
* Maximilian (1493–1519), also Holy Roman Emperor 1508–1519 *Charles I Charles I may refer to:
Kings and emperors
* Charlemagne (742–814), numbered Charles I in the lists of Holy Roman Emperors and French kings
* Charles I of Anjou (1226–1285), also king of Albania, Jerusalem, Naples and Sicily
* Charles I of ...
(1519–1558), also Holy Roman Emperor 1519–1556
* Ferdinand I (1521–1564), also Holy Roman Emperor 1558–1564
Inner Austrian Habsburgs
* Charles II (1564–1590) * Ferdinand II (1590–1637), also Holy Roman Emperor 1619–1637 Carinthia was unified with the rest of the Habsburg territories again in 1619. SeeList of rulers of Austria
This is a list of people who have ruled either the Margraviate of Austria, the Duchy of Austria or the Archduchy of Austria. From 976 until 1246, the margraviate and its successor, the duchy, was ruled by the House of Babenberg. At that time, thos ...
See also
* Carantania * Carantanians *Carinthian Slovenes
Carinthian Slovenes or Carinthian Slovenians ( sl, Koroški Slovenci; german: Kärntner Slowenen) are the indigenous minority of Slovene ethnicity, living within borders of the Austrian state of Carinthia, neighboring Slovenia. Their status of ...
* History of Austria
* History of Slovenia
*Black panther (symbol)
The black panther ( sl, črni panter), also known as the Carantanian panther () after the Medieval principality of Carantania, is a Carinthian historical symbol, which represents a stylized heraldic panther. As a heraldic symbol, it appeared on th ...
Notes and references
Kärnten (Religious population data is inaccurate)
External links
Map of the Balkans (1815–59)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Carinthia, Duchy States and territories disestablished in 1919 States and territories established in the 970s Carinthia (state) States of the German Confederation Duchies of the Holy Roman Empire Austrian Circle Subdivisions of Austria-Hungary Historical regions in Austria Former states and territories in Slovenia 970s establishments in the Holy Roman Empire 1918 disestablishments in Austria-Hungary 976 establishments
Carinthia
Carinthia (german: Kärnten ; sl, Koroška ) is the southernmost Austrian state, in the Eastern Alps, and is noted for its mountains and lakes. The main language is German. Its regional dialects belong to the Southern Bavarian group. Carin ...
Former duchies