Drug test on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A drug test is a technical analysis of a
''Pinnacle BioLabs'', Retrieved online April 11, 2007.
 Urine analysis is primarily used because of its low cost. Urine drug testing is one of the most common testing methods used. The enzyme-multiplied immune test is the most frequently used urinalysis. Complaints have been made about the relatively high rates of false positives using this test.
Urine drug tests screen the urine for the presence of a parent drug or its metabolites. The level of drug or its metabolites is not predictive of when the drug was taken or how much the patient used.
Urine drug testing is an immunoassay based on the principle of competitive binding. Drugs which may be present in the urine specimen compete against their respective drug conjugate for binding sites on their specific antibody. During testing, a urine specimen migrates upward by capillary action. A drug, if present in the urine specimen below its cut-off concentration, will not saturate the binding sites of its specific antibody. The antibody will then react with the drug-protein conjugate and a visible colored line will show up in the test line region of the specific drug strip.
A common misconception is that a drug test that is testing for a class of drugs, for example, opioids, will detect all drugs of that class. However, most opioid tests will not reliably detect
Urine analysis is primarily used because of its low cost. Urine drug testing is one of the most common testing methods used. The enzyme-multiplied immune test is the most frequently used urinalysis. Complaints have been made about the relatively high rates of false positives using this test.
Urine drug tests screen the urine for the presence of a parent drug or its metabolites. The level of drug or its metabolites is not predictive of when the drug was taken or how much the patient used.
Urine drug testing is an immunoassay based on the principle of competitive binding. Drugs which may be present in the urine specimen compete against their respective drug conjugate for binding sites on their specific antibody. During testing, a urine specimen migrates upward by capillary action. A drug, if present in the urine specimen below its cut-off concentration, will not saturate the binding sites of its specific antibody. The antibody will then react with the drug-protein conjugate and a visible colored line will show up in the test line region of the specific drug strip.
A common misconception is that a drug test that is testing for a class of drugs, for example, opioids, will detect all drugs of that class. However, most opioid tests will not reliably detect
 Breath test is a widespread method for quickly determining alcohol intoxication. A breath test measures the alcohol concentration in the body by a deep-lung breath. There are different instruments used for measuring the alcohol content of an individual though their breath. Breathalyzer is a widely known instrument which was developed in 1954 and contained chemicals unlike other breath-testing instruments. More modernly used instruments are the infrared light-absorption devices and fuel cell detectors, these two testers are microprocessor controlled meaning the operator only has to press the start button.
To get accurate readings on a breath-testing device the individual must blow for approximately 6 seconds and need to contain roughly 1.1 to 1.5 liters of breath. For a breath-test to result accurately and truly an operator must take steps such as avoiding measuring “mouth alcohol” which is a result from regurgitation, belching, or recent intake of an alcoholic beverage. To avoid measuring “mouth alcohol” the operator must not allow the individual that's taking the test to consume any materials for at least fifteen minutes before the breath test. When pulled over for a driving violation if an individual in the United States refuses to take a breath test that individual's driver's license can be suspended for a 6 to 12 months time period.
Breath test is a widespread method for quickly determining alcohol intoxication. A breath test measures the alcohol concentration in the body by a deep-lung breath. There are different instruments used for measuring the alcohol content of an individual though their breath. Breathalyzer is a widely known instrument which was developed in 1954 and contained chemicals unlike other breath-testing instruments. More modernly used instruments are the infrared light-absorption devices and fuel cell detectors, these two testers are microprocessor controlled meaning the operator only has to press the start button.
To get accurate readings on a breath-testing device the individual must blow for approximately 6 seconds and need to contain roughly 1.1 to 1.5 liters of breath. For a breath-test to result accurately and truly an operator must take steps such as avoiding measuring “mouth alcohol” which is a result from regurgitation, belching, or recent intake of an alcoholic beverage. To avoid measuring “mouth alcohol” the operator must not allow the individual that's taking the test to consume any materials for at least fifteen minutes before the breath test. When pulled over for a driving violation if an individual in the United States refuses to take a breath test that individual's driver's license can be suspended for a 6 to 12 months time period.
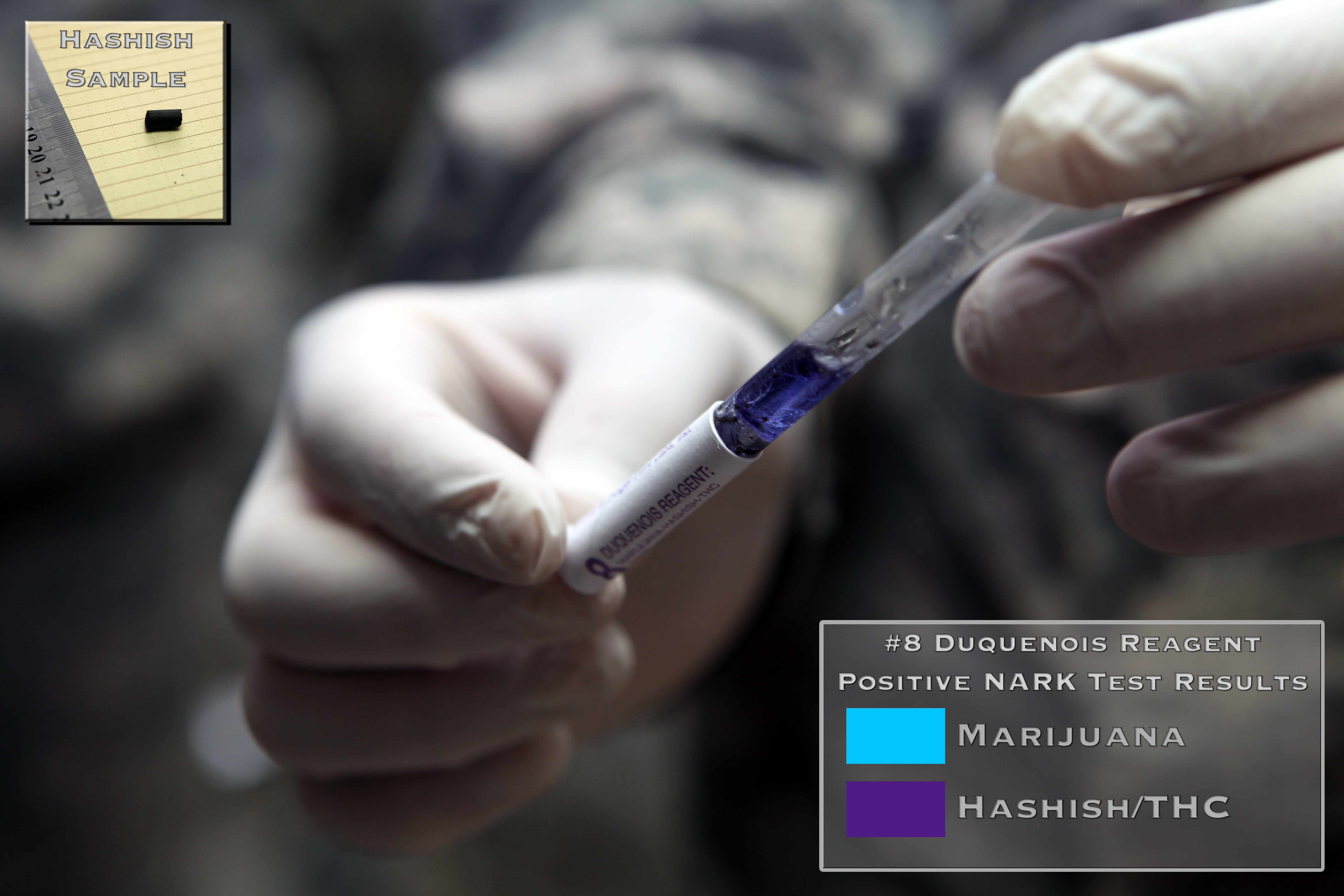 Benefits to this method include that the person who is suspected of drug use does not need to be confronted or aware of testing. Only a very small amount of material is needed to obtain results, and can be used to test powder, pills, capsules, crystals, or organic material. There is also the ability to detect illicit material when mixed with other non-illicit materials. The tests are used for general screening purposes, offering a generic result for the presence of a wide range of drugs, including Heroin, Cocaine, Methamphetamine, Amphetamine, Ecstasy/MDMA, Methadone, Ketamine, PCP, PMA, DMT, MDPV, and may detect rapidly evolving synthetic designer drugs. Separate tests for Marijuana/Hashish are also available.
There are five primary color-tests reagents used for general screening purposes. The
Benefits to this method include that the person who is suspected of drug use does not need to be confronted or aware of testing. Only a very small amount of material is needed to obtain results, and can be used to test powder, pills, capsules, crystals, or organic material. There is also the ability to detect illicit material when mixed with other non-illicit materials. The tests are used for general screening purposes, offering a generic result for the presence of a wide range of drugs, including Heroin, Cocaine, Methamphetamine, Amphetamine, Ecstasy/MDMA, Methadone, Ketamine, PCP, PMA, DMT, MDPV, and may detect rapidly evolving synthetic designer drugs. Separate tests for Marijuana/Hashish are also available.
There are five primary color-tests reagents used for general screening purposes. The
Author: Jeannette Curtis. Primary Medical Reviewer: Kathleen Romito, MD—Family Medicine. Specialist Medical Reviewer: R. Steven Tharratt, MD, MPVM, FACP, FCCP—Pulmonology, Critical Care, Medical Toxicology. Last Updated: May 9, 2008 A blood sample is routinely used to detect
''Drug Tests Direct'', Retrieved online Dec 07, 2012. Screening tests are usually done by immunoassay ( EMIT, ELISA, and RIA are the most common). A " dipstick" drug testing method which could provide screening test capabilities to field investigators has been developed at the
National Institute on Drug Abuse
{{DEFAULTSORT:Drug Test * Drug control law Doping in sport Workplace programs Medical tests Addiction medicine
biological specimen
A biological specimen (also called a biospecimen) is a biological laboratory specimen held by a biorepository for research. Such a specimen would be taken by sampling so as to be representative of any other specimen taken from the source of t ...
, for example urine
Urine is a liquid by-product of metabolism in humans and in many other animals. Urine flows from the kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder. Urination results in urine being excreted from the body through the urethra.
Cellular ...
, hair, blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in the cir ...
, breath
Breathing (or ventilation) is the process of moving air into and from the lungs to facilitate gas exchange with the internal environment, mostly to flush out carbon dioxide and bring in oxygen.
All aerobic creatures need oxygen for cell ...
, sweat
Perspiration, also known as sweating, is the production of fluids secreted by the sweat glands in the skin of mammals.
Two types of sweat glands can be found in humans: eccrine glands and apocrine glands. The eccrine sweat glands are distrib ...
, or oral fluid/saliva—to determine the presence or absence of specified parent drugs or their metabolites. Major applications of drug testing include detection of the presence of performance enhancing steroids in sport, employers and parole
Parole (also known as provisional release or supervised release) is a form of early release of a prison inmate where the prisoner agrees to abide by certain behavioral conditions, including checking-in with their designated parole officers, or ...
/probation
Probation in criminal law is a period of supervision over an offender, ordered by the court often in lieu of incarceration.
In some jurisdictions, the term ''probation'' applies only to community sentences (alternatives to incarceration), such ...
officers screening for drugs prohibited by law (such as cocaine
Cocaine (from , from , ultimately from Quechua: ''kúka'') is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant mainly used recreationally for its euphoric effects. It is primarily obtained from the leaves of two Coca species native to South Ameri ...
, methamphetamine, and heroin) and police officers testing for the presence and concentration of alcohol (ethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl group linked to a ...
) in the blood commonly referred to as BAC
BAC or Bac may refer to:
Places
* Bac, Rožaje, Bac, a village in Montenegro
* Baile Átha Cliath, Irish language name for Dublin city.
* Bîc River, aka ''Bâc River'', a Moldovan river
* Baç Bridge, bridge in Turkey
* Barnes County Municipal A ...
(blood alcohol content). BAC tests are typically administered via a breathalyzer while urinalysis is used for the vast majority of drug testing in sports
Sport pertains to any form of competitive physical activity or game that aims to use, maintain, or improve physical ability and skills while providing enjoyment to participants and, in some cases, entertainment to spectators. Sports can, ...
and the workplace
A workplace is a location where someone works, for their employer or themselves, a place of employment. Such a place can range from a home office to a large office building or factory. For industrialized societies, the workplace is one of th ...
. Numerous other methods with varying degrees of accuracy, sensitivity (detection threshold/cutoff), and detection periods exist.
A drug test may also refer to a test that provides quantitative chemical analysis of an illegal drug, typically intended to help with responsible drug use.
Detection periods
The detection windows depend upon multiple factors: drug class, amount and frequency of use, metabolic rate, body mass, age, overall health, and urine pH. For ease of use, the detection times of metabolites have been incorporated into each parent drug. For example, heroin and cocaine can only be detected for a few hours after use, but their metabolites can be detected for several days in urine. The chart depicts the longer detection times of the metabolites. Oral fluid or saliva testing results for the most part mimic that of blood. The only exceptions are THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) and benzodiazepines. Oral fluid will likely detect THC from ingestion up to a maximum period of 6–12 hours. This continues to cause difficulty in oral fluid detection of THC and benzodiazepines. Breath air for the most part mimics blood tests as well. Due to the very low levels of substances in the breath air, liquid chromatography—mass spectrometry has to be used to analyze the sample according to a recent publication wherein 12 analytes were investigated. Rapid oral fluid products are not approved for use in workplace drug testing programs and are not FDA cleared. Using rapid oral fluid drug tests in the workplace is prohibited in only: *California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
* Kansas
Kansas () is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its capital is Topeka, and its largest city is Wichita. Kansas is a landlocked state bordered by Nebraska to the north; Missouri to the east; Oklahoma to the south; and Colorado to th ...
* Maine
Maine () is a state in the New England and Northeastern regions of the United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Quebec to the northeast and ...
* Minnesota
Minnesota () is a state in the upper midwestern region of the United States. It is the 12th largest U.S. state in area and the 22nd most populous, with over 5.75 million residents. Minnesota is home to western prairies, now given over to ...
* New York
* Vermont
Vermont () is a state in the northeast New England region of the United States. Vermont is bordered by the states of Massachusetts to the south, New Hampshire to the east, and New York to the west, and the Canadian province of Quebec to ...
The following chart gives approximate detection periods for each substance by test type."Drugs of Abuse Reference Guide,"''Pinnacle BioLabs'', Retrieved online April 11, 2007.
Types
Urine drug screen
 Urine analysis is primarily used because of its low cost. Urine drug testing is one of the most common testing methods used. The enzyme-multiplied immune test is the most frequently used urinalysis. Complaints have been made about the relatively high rates of false positives using this test.
Urine drug tests screen the urine for the presence of a parent drug or its metabolites. The level of drug or its metabolites is not predictive of when the drug was taken or how much the patient used.
Urine drug testing is an immunoassay based on the principle of competitive binding. Drugs which may be present in the urine specimen compete against their respective drug conjugate for binding sites on their specific antibody. During testing, a urine specimen migrates upward by capillary action. A drug, if present in the urine specimen below its cut-off concentration, will not saturate the binding sites of its specific antibody. The antibody will then react with the drug-protein conjugate and a visible colored line will show up in the test line region of the specific drug strip.
A common misconception is that a drug test that is testing for a class of drugs, for example, opioids, will detect all drugs of that class. However, most opioid tests will not reliably detect
Urine analysis is primarily used because of its low cost. Urine drug testing is one of the most common testing methods used. The enzyme-multiplied immune test is the most frequently used urinalysis. Complaints have been made about the relatively high rates of false positives using this test.
Urine drug tests screen the urine for the presence of a parent drug or its metabolites. The level of drug or its metabolites is not predictive of when the drug was taken or how much the patient used.
Urine drug testing is an immunoassay based on the principle of competitive binding. Drugs which may be present in the urine specimen compete against their respective drug conjugate for binding sites on their specific antibody. During testing, a urine specimen migrates upward by capillary action. A drug, if present in the urine specimen below its cut-off concentration, will not saturate the binding sites of its specific antibody. The antibody will then react with the drug-protein conjugate and a visible colored line will show up in the test line region of the specific drug strip.
A common misconception is that a drug test that is testing for a class of drugs, for example, opioids, will detect all drugs of that class. However, most opioid tests will not reliably detect oxycodone
Oxycodone, sold under various brand names such as Roxicodone and OxyContin (which is the extended release form), is a strong, semi-synthetic opioid used medically for treatment of moderate to severe pain. It is highly addictive and a commonly ...
, oxymorphone, meperidine
Pethidine, also known as meperidine and sold under the brand name Demerol among others, is a synthetic opioid pain medication of the phenylpiperidine class. Synthesized in 1938 as a potential anticholinergic agent by the German chemist Otto Eisl ...
, or fentanyl
Fentanyl, also spelled fentanil, is a very potent synthetic opioid used as a pain medication. Together with other drugs, fentanyl is used for anesthesia. It is also used illicitly as a recreational drug, sometimes mixed with heroin, cocain ...
. Likewise, most benzodiazepine drug tests will not reliably detect lorazepam
Lorazepam, sold under the brand name Ativan among others, is a benzodiazepine medication. It is used to treat anxiety disorders, trouble sleeping, severe agitation, active seizures including status epilepticus, alcohol withdrawal, and c ...
. However, urine drug screens that test for a specific drug, rather than an entire class, are often available.
When an employer requests a drug test from an employee, or a physician requests a drug test from a patient, the employee or patient is typically instructed to go to a collection site or their home. The urine sample goes through a specified 'chain of custody' to ensure that it is not tampered with or invalidated through lab or employee error. The patient or employee's urine is collected at a remote location in a specially designed secure cup, sealed with tamper-resistant tape, and sent to a testing laboratory to be screened for drugs (typically the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration
The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA; pronounced ) is a branch of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. It is charged with improving the quality and availability of treatment and rehabilitative services ...
5 panel). The first step at the testing site is to split the urine into two aliquots. One aliquot is first screened for drugs using an analyzer that performs immunoassay as the initial screen. To ensure the specimen integrity and to detect possible adulterants, additional parameters are tested for. Some test the properties of normal urine, such as, urine creatinine
Creatinine (; ) is a breakdown product of creatine phosphate from muscle and protein metabolism. It is released at a constant rate by the body (depending on muscle mass).
Biological relevance
Serum creatinine (a blood measurement) is an importa ...
, pH, and specific gravity
Relative density, or specific gravity, is the ratio of the density (mass of a unit volume) of a substance to the density of a given reference material. Specific gravity for liquids is nearly always measured with respect to water at its densest ...
. Others are intended to catch substances added to the urine to alter the test result, such as, oxidants (including bleach), nitrites, and gluteraldehyde. If the urine screen is positive then another aliquot of the sample is used to confirm the findings by gas chromatography— mass spectrometry (GC-MS) or liquid chromatography - mass spectrometry methodology. If requested by the physician or employer, certain drugs are screened for individually; these are generally drugs part of a chemical class that are, for one of many reasons, considered more habit-forming or of concern. For instance, oxycodone
Oxycodone, sold under various brand names such as Roxicodone and OxyContin (which is the extended release form), is a strong, semi-synthetic opioid used medically for treatment of moderate to severe pain. It is highly addictive and a commonly ...
and diamorphine may be tested, both sedative analgesics
An analgesic drug, also called simply an analgesic (American English), analgaesic (British English), pain reliever, or painkiller, is any member of the group of drugs used to achieve relief from pain (that is, analgesia or pain management). It ...
. If such a test is not requested specifically, the more general test (in the preceding case, the test for opioids) will detect most of the drugs of a class, but the employer or physician will not have the benefit of the identity of the drug.
Employment-related test results are relayed to a medical review office (MRO) where a medical physician reviews the results. If the result of the screen is negative, the MRO informs the employer that the employee has no detectable drug in the urine, typically within 24 hours. However, if the test result of the immunoassay and GC-MS are non-negative and show a concentration level of parent drug or metabolite above the established limit, the MRO contacts the employee to determine if there is any legitimate reason—such as a medical treatment or prescription.
On-site instant drug testing is a more cost-efficient method of effectively detecting substance use amongst employees, as well as in rehabilitation programs to monitor patient progress. These instant tests can be used for both urine and saliva testing. Although the accuracy of such tests varies with the manufacturer, some kits have rates of accuracy correlating closely with laboratory test results.
Breath test
 Breath test is a widespread method for quickly determining alcohol intoxication. A breath test measures the alcohol concentration in the body by a deep-lung breath. There are different instruments used for measuring the alcohol content of an individual though their breath. Breathalyzer is a widely known instrument which was developed in 1954 and contained chemicals unlike other breath-testing instruments. More modernly used instruments are the infrared light-absorption devices and fuel cell detectors, these two testers are microprocessor controlled meaning the operator only has to press the start button.
To get accurate readings on a breath-testing device the individual must blow for approximately 6 seconds and need to contain roughly 1.1 to 1.5 liters of breath. For a breath-test to result accurately and truly an operator must take steps such as avoiding measuring “mouth alcohol” which is a result from regurgitation, belching, or recent intake of an alcoholic beverage. To avoid measuring “mouth alcohol” the operator must not allow the individual that's taking the test to consume any materials for at least fifteen minutes before the breath test. When pulled over for a driving violation if an individual in the United States refuses to take a breath test that individual's driver's license can be suspended for a 6 to 12 months time period.
Breath test is a widespread method for quickly determining alcohol intoxication. A breath test measures the alcohol concentration in the body by a deep-lung breath. There are different instruments used for measuring the alcohol content of an individual though their breath. Breathalyzer is a widely known instrument which was developed in 1954 and contained chemicals unlike other breath-testing instruments. More modernly used instruments are the infrared light-absorption devices and fuel cell detectors, these two testers are microprocessor controlled meaning the operator only has to press the start button.
To get accurate readings on a breath-testing device the individual must blow for approximately 6 seconds and need to contain roughly 1.1 to 1.5 liters of breath. For a breath-test to result accurately and truly an operator must take steps such as avoiding measuring “mouth alcohol” which is a result from regurgitation, belching, or recent intake of an alcoholic beverage. To avoid measuring “mouth alcohol” the operator must not allow the individual that's taking the test to consume any materials for at least fifteen minutes before the breath test. When pulled over for a driving violation if an individual in the United States refuses to take a breath test that individual's driver's license can be suspended for a 6 to 12 months time period.
Hair testing
Hair analysis to detect addictive substances has been used by court systems in the United States, United Kingdom, Canada, and other countries worldwide. In the United States, hair testing has been accepted in court cases as forensic evidence following the Frye Rule, the Federal Rules of Evidence, and the Daubert Rule. As such, hair testing results are legally and scientifically recognized as admissible evidence. Although some lower courts may have accepted hair test evidence, there is no controlling judicial ruling in either the federal or any state system declaring any type of hair test as reliable. Hair testing is now recognized in both the UK and US judicial systems. There are guidelines for hair testing that have been published by the Society of Hair Testing (a private company in France) that specify the markers to be tested for and the cutoff concentrations that need to be tested. Addictive substances that can be detected include Cannabis, Cocaine, Amphetamines and drugs new to the UK such as Mephedrone.Alcohol
In contrast to other drugs consumed, alcohol is deposited directly in the hair. For this reason the investigation procedure looks for direct products of ethanol metabolism. The main part of alcohol is oxidized in the human body. This means it is released as water and carbon dioxide. One part of the alcohol reacts with fatty acids to produce esters. The sum of the concentrations of four of these fatty acid ethyl esters (FAEEs: ethyl myristate, ethyl palmitate, ethyl oleate and ethyl stearate) are used as indicators of the alcohol consumption. The amounts found in hair are measured in nanograms (one nanogram equals only one billionth of a gram), however with the benefit of modern technology, it is possible to detect such small amounts. In the detection of ethyl glucuronide, or EtG, testing can detect amounts in picograms (one picogram equals 0.001 nanograms). However, there is one major difference between most drugs and alcohol metabolites in the way in which they enter into the hair: on the one hand like other drugs FAEEs enter into the hair via the keratinocytes, the cells responsible for hair growth. These cells form the hair in the root and then grow through the skin surface taking any substances with them. On the other hand, the sebaceous glands produce FAEEs in the scalp and these migrate together with the sebum along the hair shaft (Auwärter et al., 2001, Pragst et al., 2004). So these glands lubricate not only the part of the hair that is just growing at 0.3 mm per day on the skin surface, but also the more mature hair growth, providing it with a protective layer of fat. FAEEs (nanogram = one billionth of a gram) appear in hair in almost one order of magnitude lower than (the relevant order of magnitude of) EtG (picogram = one trillionth of a gram). It has been technically possible to measure FAEEs since 1993, and the first study reporting the detection of EtG in hair was done by Sachs in 1993. In practice, most hair which is sent for analysis has been cosmetically treated in some way (bleached, permed etc.). It has been proven that FAEEs are not significantly affected by such treatments (Hartwig et al., 2003a). FAEE concentrations in hair from other body sites can be interpreted in a similar fashion as scalp hair (Hartwig et al., 2003b).Presumptive substance testing
Presumptive substance tests attempt to identify a suspicious substance, material or surface where traces of drugs are thought to be, instead of testing individuals through biological methods such as urine or hair testing. The test involves mixing the suspicious material with a chemical in order to trigger a color change to indicate if a drug is present. Most are now available over-the-counter for consumer use, and do not require a lab to read results. Benefits to this method include that the person who is suspected of drug use does not need to be confronted or aware of testing. Only a very small amount of material is needed to obtain results, and can be used to test powder, pills, capsules, crystals, or organic material. There is also the ability to detect illicit material when mixed with other non-illicit materials. The tests are used for general screening purposes, offering a generic result for the presence of a wide range of drugs, including Heroin, Cocaine, Methamphetamine, Amphetamine, Ecstasy/MDMA, Methadone, Ketamine, PCP, PMA, DMT, MDPV, and may detect rapidly evolving synthetic designer drugs. Separate tests for Marijuana/Hashish are also available.
There are five primary color-tests reagents used for general screening purposes. The
Benefits to this method include that the person who is suspected of drug use does not need to be confronted or aware of testing. Only a very small amount of material is needed to obtain results, and can be used to test powder, pills, capsules, crystals, or organic material. There is also the ability to detect illicit material when mixed with other non-illicit materials. The tests are used for general screening purposes, offering a generic result for the presence of a wide range of drugs, including Heroin, Cocaine, Methamphetamine, Amphetamine, Ecstasy/MDMA, Methadone, Ketamine, PCP, PMA, DMT, MDPV, and may detect rapidly evolving synthetic designer drugs. Separate tests for Marijuana/Hashish are also available.
There are five primary color-tests reagents used for general screening purposes. The Marquis reagent Marquis reagent is used as a simple spot-test to presumptively identify alkaloids as well as other compounds. It is composed of a mixture of formaldehyde and concentrated sulfuric acid, which is dripped onto the substance being tested. The United St ...
turns into a variety of colors when in the presence of different substances. Dille-Koppanyi reagent uses two chemical solutions which turns a violet-blue color in the presence of barbiturates. Duquenois-Levine reagent is a series of chemical solutions that turn to the color of purple when the vegetation of marijuana is added. Van Urk reagent turns blue-purple when in the presence of LSD. Scott test's chemical solution shows up as a faint blue for cocaine base.
In recent years, the use of presumptive test kits in the criminal justice system has come under great scrutiny due to the lack to forensic studies, questioned reliability, rendering of false positives with legal substances, and wrongful arrests.
Saliva drug screen / Oral fluid-based drug screen
Saliva / oral fluid-based drug tests can generally detect use during the previous few days. Is better at detecting very recent use of a substance. THC may only be detectable for 2–24 hours in most cases. On site drug tests are allowed per the Department of Labor. Detection in saliva tests begins almost immediately upon use of the following substances, and lasts for approximately the following times: * Alcohol: 6-12 hhttp://www.erowid.org/psychoactives/testing/testing_info1.shtml Drug Testing Basics * Marijuana: 1-24h A disadvantage of saliva based drug testing is that it is not approved by FDA or SAMHSA for use with DOT / Federal Mandated Drug Testing. Oral fluid is not considered a bio-hazard unless there is visible blood; however, it should be treated with care.Sweat drug screen
Sweat patches are attached to the skin to collect sweat over a long period of time (up to 14 days). These are used by child protective services, parole departments, and other government institutions concerned with drug use over long periods, when urine testing is not practical. There are also surface drug tests that test for the metabolite of parent drug groups in the residue of drugs left in sweat. An example of a rapid, non-invasive, sweat-based drug test is fingerprint drug screening. This 10 minute fingerprint test is in use by a variety of organisations in the UK and beyond, including within workplaces, drug treatment and family safeguarding services at airport border control (to detect drug mules) and in mortuaries to assist in investigations into cause of death.Blood
Drug-testing a blood sample measures whether or not a drug or a metabolite is in the body at a particular time. These types of tests are considered to be the most accurate way of telling if a person is intoxicated. Blood drug tests are not used very often because they need specialized equipment and medically trained administrators. Depending on how much marijuana was consumed, it can usually be detected in blood tests within six hours of consumption. After six hours has passed, the concentration of marijuana in the blood decreases significantly. It generally disappears completely within 30 days.Random drug testing
Can occur at any time, usually when the investigator has reason to believe that a substance is possibly being used by the subject by behavior or immediately after an employee-related incident occurs during work hours. Testing protocol typically conforms to the national medical standard, candidates are given up to 120 minutes to reasonably produce a urine sample from the time of commencement (in some instances this time frame may be extended at the examiners discretion).Diagnostic screening
In the case of life-threatening symptoms, unconsciousness, or bizarre behavior in an emergency situation, screening for common drugs and toxins may help find the cause, called a ''toxicology test'' or ''tox screen'' to denote the broader area of possible substances beyond just self-administered drugs. These tests can also be done post-mortem during an autopsy in cases where a death was not expected. The test is usually done within 96 hours (4 days) after the desire for the test is realized. Both a urine sample and a blood sample may be tested.WebMD --> Toxicology TestsAuthor: Jeannette Curtis. Primary Medical Reviewer: Kathleen Romito, MD—Family Medicine. Specialist Medical Reviewer: R. Steven Tharratt, MD, MPVM, FACP, FCCP—Pulmonology, Critical Care, Medical Toxicology. Last Updated: May 9, 2008 A blood sample is routinely used to detect
ethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl group linked to a ...
/ methanol and ASA/ paracetamol intoxication. Various panels are used for screening urine samples for common substances, e.g. ''triage 8'' that detects amphetamines
Substituted amphetamines are a class of compounds based upon the amphetamine structure; it includes all derivative compounds which are formed by replacing, or substituting, one or more hydrogen atoms in the amphetamine core structure with sub ...
, benzodiazepines, cocaine
Cocaine (from , from , ultimately from Quechua: ''kúka'') is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant mainly used recreationally for its euphoric effects. It is primarily obtained from the leaves of two Coca species native to South Ameri ...
, methadone
Methadone, sold under the brand names Dolophine and Methadose among others, is a synthetic opioid agonist used for chronic pain and also for opioid dependence. It is used to treat chronic pain, and it is also used to treat addiction to heroi ...
, opiates
An opiate, in classical pharmacology, is a substance derived from opium. In more modern usage, the term ''opioid'' is used to designate all substances, both natural and synthetic, that bind to opioid receptors in the brain (including antagonist ...
, cannabis, barbiturates and tricyclic antidepressants
Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) are a class of medications that are used primarily as antidepressants, which is important for the management of depression. They are second-line drugs next to SSRIs. TCAs were discovered in the early 1950s and wer ...
. Results are given in 10–15 min.
Similar screenings may be used to evaluate the possible use of date rape drug
A date rape drug is any drug that incapacitates another person and renders that person vulnerable to sexual assault, including rape. The substances are associated with date rape because of reported incidents of their use in the context of two p ...
s. This is usually done on a urine sample.
Optional harm reduction scheme
Drug checks/tests (also known as pill testing) are provided at some events such as concerts and music festivals. Attendees can voluntarily hand over a sample of any drug or drugs in their possession to be tested to check what the drug is and its purity. The scheme is used as aharm reduction
Harm reduction, or harm minimization, refers to a range of public health policies designed to lessen the negative social and/or physical consequences associated with various human behaviors, both legal and illegal. Harm reduction is used to d ...
technique so people are more aware of what they are taking and the potential risks.
Occupational harm reduction strategies
Drug and alcohol impairment while at work increases the risk of work-place accidents and decreases productivity. Employers such as the commercial driving and airline industry may conduct random drug tests on employees with the goal of deterring use to improve safety. There is some evidence that increasing the use of random drug testing in the airline industry reduces the percentage of people who test positive, however, it is unclear if this decrease is associated with a corresponding decrease in fatal or non-fatal injuries, other accidents, number of days absent from work. It is also not clear if there are other unwanted side effects that may result from random drug and alcohol testing in the workplace.Commonly tested substances
Anabolic steroids
Anabolic steroids are used to enhance performance in sports and as they are prohibited in most high-level competitions drug testing is used extensively in order to enforce this prohibition. This is particularly so in individual (rather than team) sports such asathletics
Athletics may refer to:
Sports
* Sport of athletics, a collection of sporting events that involve competitive running, jumping, throwing, and walking
** Track and field, a sub-category of the above sport
* Athletics (physical culture), competi ...
and cycling
Cycling, also, when on a two-wheeled bicycle, called bicycling or biking, is the use of cycles for transport, recreation, exercise or sport. People engaged in cycling are referred to as "cyclists", "bicyclists", or "bikers". Apart from t ...
.
Methodologies
Before testing samples, thetamper-evident
Tamper-evident describes a device or process that makes unauthorized access to the protected object easily detected. Seals, markings, or other techniques may be tamper indicating.
Tampering
Tampering involves the deliberate altering or adultera ...
seal is checked for integrity. If it appears to have been tampered with or damaged, the laboratory rejects the sample and does not test it.
Next, the sample must be made testable. Urine and oral fluid can be used "as is" for some tests, but other tests require the drugs to be extracted from urine. Strands of hair, patches, and blood must be prepared before testing. Hair is washed in order to eliminate second-hand sources of drugs on the surface of the hair, then the keratin
Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. Alpha-keratin (α-keratin) is a type of keratin found in vertebrates. It is the key structural material making up scales, hair, nails, feathers, ho ...
is broken down using enzymes. Blood plasma
Blood plasma is a light amber-colored liquid component of blood in which blood cells are absent, but contains proteins and other constituents of whole blood in suspension. It makes up about 55% of the body's total blood volume. It is the intr ...
may need to be separated by centrifuge from blood cells
A blood cell, also called a hematopoietic cell, hemocyte, or hematocyte, is a cell produced through hematopoiesis and found mainly in the blood. Major types of blood cells include red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), a ...
prior to testing. Sweat patches are opened and the sweat collection component is removed and soaked in a solvent
A solvent (s) (from the Latin '' solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas, or a supercritical fluid. Water is a solvent for ...
to dissolve any drugs present.
Laboratory-based drug testing is done in two steps. The first step is the screening test, which is an immunoassay based test applied to all samples. The second step, known as the confirmation test, is usually undertaken by a laboratory using highly specific chromatographic techniques and only applied to samples that test positive during the screening test."Principles of Drug Testing Technology,"''Drug Tests Direct'', Retrieved online Dec 07, 2012. Screening tests are usually done by immunoassay ( EMIT, ELISA, and RIA are the most common). A " dipstick" drug testing method which could provide screening test capabilities to field investigators has been developed at the
University of Illinois
The University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign (U of I, Illinois, University of Illinois, or UIUC) is a public land-grant research university in Illinois in the twin cities of Champaign and Urbana. It is the flagship institution of the Univer ...
.
After a suspected positive sample is detected during screening, the sample is tested using a confirmation test. Samples that are negative on the screening test are discarded and reported as negative. The confirmation test in most laboratories (and all SAMHSA certified labs) is performed using mass spectrometry, and is precise but expensive. False positive samples from the screening test will almost always be negative on the confirmation test. Samples testing positive during both screening and confirmation tests are reported as positive to the entity that ordered the test. Most laboratories save positive samples for some period of months or years in the event of a disputed result or lawsuit. For workplace drug testing, a positive result is generally not confirmed without a review by a Medical Review Officer who will normally interview the subject of the drug test.
Urine drug testing
Urine drug test kits are available as on-site tests, or laboratory analysis. Urinalysis is the most common test type and used by federally mandated drug testing programs and is considered the Gold Standard of drug testing. Urine based tests have been upheld in most courts for more than 30 years. However, urinalysis conducted by the Department of Defense has been challenged for reliability of testing the metabolite of cocaine. There are two associated metabolites of cocaine, benzoylecgonine (BZ) and ecgonine methyl ester (EME), the first (BZ) is created by the presence of cocaine in an aqueous solution with a pH greater than 7.0, while the second (EME) results from the actual human metabolic process. The presence of EME confirms actual ingestion of cocaine by a human being, while the presence of BZ is indicative only. BZ without EME is evidence of sample contamination, however, the US Department of Defense has chosen not to test for EME in its urinalysis program. A number of different analyses (defined as the unknown substance being tested for) are available on Urine Drug Screens.Spray drug testing
Spray (sweat) drug test kits are non-invasive. It is a simple process to collect the required specimen, no bathroom is needed, no laboratory is required for analysis, and the tests themselves are difficult to manipulate and relatively tamper-resistant. The detection window is long and can detect recent drug use within several hours. There are also some disadvantages to spray or sweat testing. There is not much variety in these drug tests, only a limited number of drugs can be detected, prices tend to be higher, and inconclusive results can be produced by variations in sweat production rates in donors. They also have a relatively long specimen collection period and are more vulnerable to contamination than other common forms of testing.Hair drug testing
Hair drug testing is a method that can detect drug use over a much longer period of time, and is often used for highly safety-critical positions where there is zero tolerance of illegal drug use. Standard hair follicle screen covers a period of 30 to 90 days. The growth of head hair is usually at the rate of 0.5 inches per month. The hair sample is cut close to the scalp and 80 to 120 strands of hair are needed for the test. In the absence of hair on the head, body hair can be used as an acceptable substitute. This includes facial hair, the underarms, arms, and legs or even pubic hair. Because body hair grows at a different rate than head hair, the timeframe changes, with scientists estimating that drug use can be detected in body hair for up to 12 months. Currently, most entities that use hair testing have prescribed consequences for individuals removing hair to avoid a hair drug test. The claim that a hair test cannot be tampered with has been shown to be debatable. One study has shown thatTHC
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the principal psychoactive constituent of cannabis and one of at least 113 total cannabinoids identified on the plant. Although the chemical formula for THC (C21H30O2) describes multiple isomers, the term ''THC' ...
does not readily deposit inside epithelial cells so it is possible for cosmetic and other forms of adulteration to reduce the amount of testable cannabinoids within a hair sample.
Legality, ethics and politics
The results of federally mandating drug testing were similar to the effects of simply extending to the trucking industry the right to perform drug tests, and it has been argued that the latter approach would have been as effective at lower cost. Psychologist Tony Buon has criticized the use of workplace drug testing on a number of grounds, including: # Flawed Technology: The real world performance of testing is much lower than that claimed by its promoters. Buon suggest that tests are probably adequate for rehabilitation and treatment situations, possibly adequate for pre-employment situations, but not for dismissing employees. # Ethical Issues: Because of the fairly simple ways that an employee can invalidate the test, drug testing must be strictly monitored. This means that the specimen must be observed leaving the body. Many legal objections currently being raised in the courts about drug testing are pointing to legal requirements of prior notice, consent, due process, and cause. # Wrong focus: As has been shown withEmployee Assistance Program
An employee assistance program (EAP) is an employee benefit program that assists employees with personal problems and/or work-related problems that may impact their job performance, health, mental and emotional well-being. EAPs generally offer ...
s, the focus of management concern should be on work performance decline. Buon suggests effective management practices are an infinitely better approach to managing workplace alcohol and other drug issues.
Tony Buon has also reported by the CIPD
The Chartered Institute of Personnel and Development (CIPD) is an association for human resource management professionals. Its headquarters are in Wimbledon, London, England. The organisation was founded in 1913 - it is the world's oldest associa ...
as stating that "drug testing captures the stupid—experienced drug users know how to beat the tests".
From a penological standpoint, one purpose of drug testing is to help classify the
people taking the drug test within risk groups so that those who pose more of a danger to the public can be incapacitated through incarceration or other restrictions on liberty. Thus, the drug testing serves a crime control purpose even if there is no expectation of rehabilitating the drug user through treatment, deterring drug use through sanctions, or sending a message that drug use is a deviant behavior that will not be tolerated.
United Kingdom
A study in 2004 by the Independent Inquiry into Drug Testing at Work found that attempts by employers to force employees to take drug tests could potentially be challenged as a violation of privacy under the Human Rights Act 1998 and Article 8 of theEuropean Convention of Human Rights
The European Convention on Human Rights (ECHR; formally the Convention for the Protection of Human Rights and Fundamental Freedoms) is an international convention to protect human rights and political freedoms in Europe. Drafted in 1950 by th ...
. However, this does not apply to industries where drug testing is a matter of personal and public safety or security rather than productivity.
United States
In consultation with Dr. Carlton Turner, President Ronald Reagan issuedExecutive Order
In the United States, an executive order is a directive by the president of the United States that manages operations of the federal government. The legal or constitutional basis for executive orders has multiple sources. Article Two of t ...
12564. In doing so, he instituted mandatory drug-testing for all safety-sensitive executive-level and civil-service Federal employees. This was challenged in the courts by the National Treasury Employees Union. In 1988, this challenge was considered by the US Supreme Court. A similar challenge resulted in the Court extending the drug-free workplace concept to the private sector. These decisions were then incorporated into the White House Drug Control Strategy directive issued by President George H.W. Bush in 1989. All defendants serving on federal probation or federal supervised release are required to submit to at least three drug tests. Failing a drug test can be construed as possession of a controlled substance, resulting in mandatory revocation and imprisonment.
There have been inconsistent evaluation results as to whether continued pretrial drug testing has beneficial effects.
Testing positive can lead to bail not being granted, or if bail has already been granted, to bail revocation or other sanctions. Arizona
Arizona ( ; nv, Hoozdo Hahoodzo ; ood, Alĭ ṣonak ) is a state in the Southwestern United States. It is the 6th largest and the 14th most populous of the 50 states. Its capital and largest city is Phoenix. Arizona is part of the Fou ...
also adopted a law in 1987 authorizing mandatory drug testing of felony arrestees for the purpose of informing the pretrial release decision, and the District of Columbia
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...
has had a similar law since the 1970s. It has been argued that one of the problems with such testing is that there is often not enough time between the arrest and the bail decision to confirm positive results using GC/MS technology. It has also been argued that such testing potentially implicates the Fifth Amendment privilege against self-incrimination, the right to due process (including the prohibition against gathering evidence in a manner that shocks the conscience Shocks the conscience is a phrase used as a legal standard in the United States and Canada. An action is understood to "shock the conscience" if it is "grossly unjust to the observer."
United States
In US law, the phrase typically describes whether ...
or constitutes outrageous government conduct), and the prohibition against unreasonable searches and seizures contained in the Fourth Amendment.
According to Henriksson, the anti-drug appeals of the Reagan administration "created an environment in which many employers felt compelled to implement drug testing programs because failure to do so might be perceived as condoning drug use. This fear was easily exploited by aggressive marketing and sales forces, who often overstated the value of testing and painted a bleak picture of the consequences of failing to use the drug testing product or service being offered." On March 10, 1986, the Commission on Organized Crime asked all U.S. companies to test employees for drug use. By 1987, nearly 25% of the Fortune 500 companies used drug tests.
According to an uncontrolled self-report study done by DATIA and Society for Human Resource Management
The Society for Human Resource Management (SHRM) is a professional human resources membership association headquartered in Alexandria, Virginia. SHRM promotes the role of HR as a profession and provides education, certification, and networking to ...
in 2012 (sample of 6,000 randomly selected human resource professionals), human resource professionals reported the following results after implementing a drug testing program: 19% of companies reported a subjective increase in employee productivity, 16% reported a decrease in employee turnover (8% reported an increase), and unspecified percentages reported decreases in absenteeism and improvement of workers' compensation incidence rates.
According to US Chamber of Commerce 70% of all illicit drug users are employed. Some industries have high rates of employee drug use such as construction (12.8%), repair (11.1%), and hospitality (7.9-16.3%).
Australia
A person conducting a business or undertaking (PCBU—the new term that includes employers) has duties under the work health and safety (WHS) legislation to ensure a worker affected by alcohol or other drugs does not place themselves or other persons at risk of injury while at work. Workplace policies and prevention programs can help change the norms and culture around substance use. All organisations—large and small—can benefit from an agreed policy on alcohol and drug misuse that applies to all workers. Such a policy should form part of an organisations overall health and safety management system. PCBUs are encouraged to establish a policy and procedure, in consultation with workers, to constructively manage alcohol and other drug related hazards in their workplace. A comprehensive workplace alcohol and other drug policy should apply to everyone in the workplace and include prevention, education, counselling and rehabilitation arrangements. In addition, the roles and responsibilities of managers and supervisors should be clearly outlined. All Australian workplace drug testing must comply with Australian standard AS/NZS4308:2008. In Victoria, roadside saliva tests detect drugs that contain: * THC (Delta-9 tetrahydrocannabinol), the active component in cannabis. * methamphetamine, also known as "ice", "crystal" and "crank". * MDMA (Methylenedioxymethamphetamine), which is known as ecstasy. In February 2016 a New South Wales magistrate "acquitted a man who tested positive for cannabis". He had been arrested and charged after testing positive during a roadside drug test, despite not having smoked for nine days. He was relying on advice previously given to him by police.Refusal
In the United States federal criminal system, refusing to take a drug test triggers an automatic revocation of probation or supervised release. In Victoria, Australia the driver of the car has the option to refuse the drug test. Refusing to undergo a drug test or refusing to undergo a secondary drug test after the first one, triggers an automatic suspension and disqualification for a period of two years and a fine of AUD$1000. The second refusal triggers an automatic suspension and disqualification for a period of four years and an even larger fine.Historical cases
* In 2000, an Australian Mining Company South Blackwater Coal Ltd with 400 employees, imposed drug-testing procedures, and the trade unions advised their members to refuse to take the tests, partly because a positive result does not necessarily indicate present impairment; the workers were stood-down by the company without pay for a week. * In 2003, sixteen members of theChicago White Sox
The Chicago White Sox are an American professional baseball team based in Chicago. The White Sox compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the American League (AL) Central division. The team is owned by Jerry Reinsdorf, and ...
considered refusing to take a drug test, in hopes of making steroid testing mandatory.
* In 2006, Levy County, Florida, volunteer librarians resigned en masse rather than take drug tests.
* In 2010, Iranian super heavyweight class weightlifters refused to submit to a drug test authorized by the Iran Weightlifting League.
See also
* Cannabis drug tests * Detoxification *Drug checking Drug checking or pill testing is a way to reduce the harm from drug consumption by allowing users to find out the content and purity of substances that they intend to consume. This empowers users to make safer choices: to avoid more dangerous substa ...
* Drug-Free Workplace Act of 1988
* Equine drug testing
* Forensic toxicology
Forensic toxicology is the use of toxicology and disciplines such as analytical chemistry, pharmacology and clinical chemistry to aid medical or legal investigation of death, poisoning, and drug use. The primary concern for forensic toxicology is ...
* Lacing (drugs)
* Presumptive and confirmatory tests Presumptive tests, in medical and forensic science, analyze a sample and establish one of the following:
#The sample is definitely not a certain substance.
#The sample probably is the substance.
For example, the Kastle–Meyer test will show eithe ...
* Reagent testing
Reagent testing is one of the processes used to identify substances contained within a pill, usually illicit substances.
With the increased prevalence of drugs being available in their pure forms, the terms "drug checking" or "pill testing" may a ...
* School district drug policies
* Urinalysis
* Occupational health concerns of cannabis use
References
External links
National Institute on Drug Abuse
{{DEFAULTSORT:Drug Test * Drug control law Doping in sport Workplace programs Medical tests Addiction medicine