Douglas B-23 Dragon on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Douglas B-23 Dragon is an American twin-engined
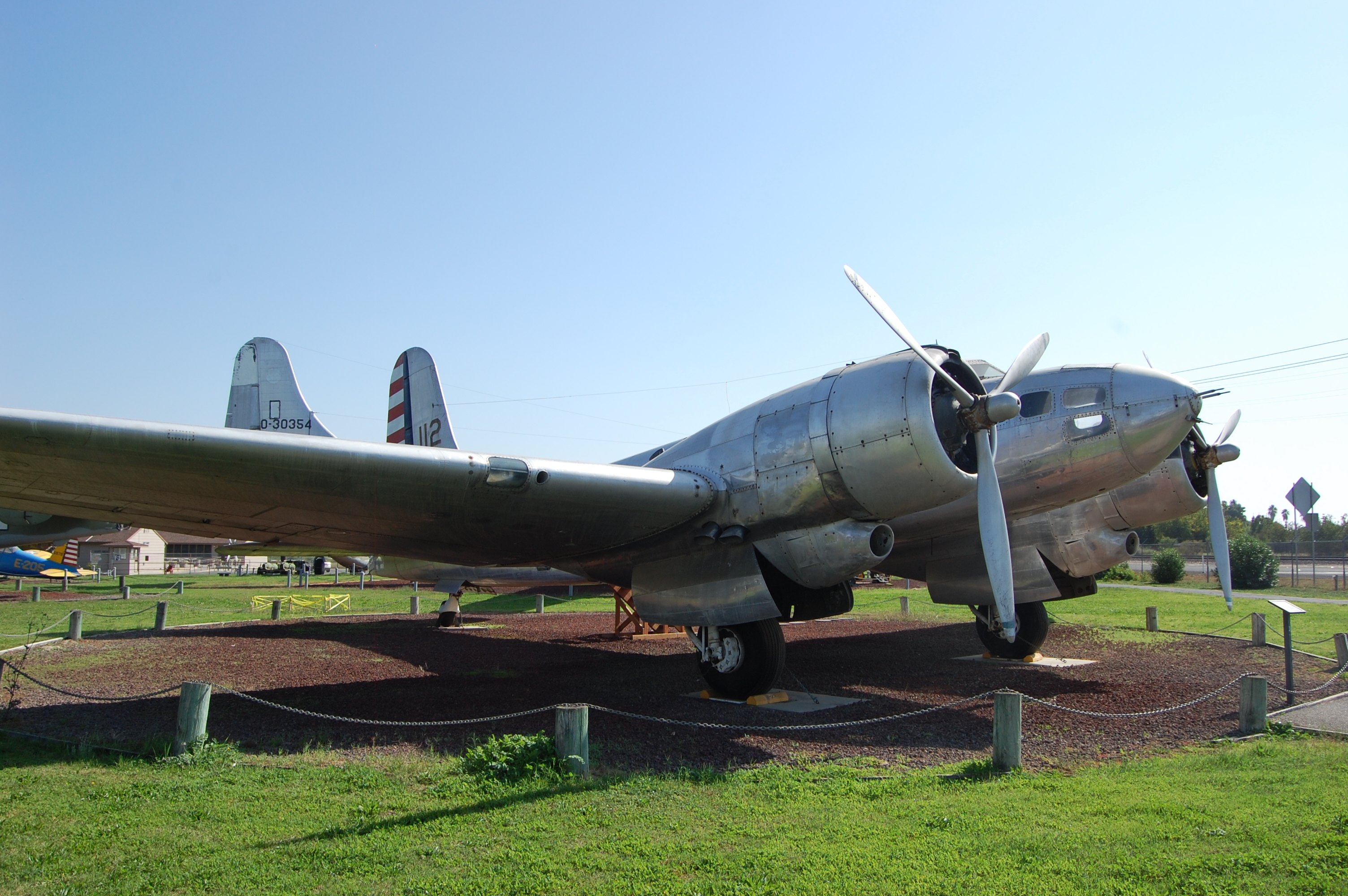



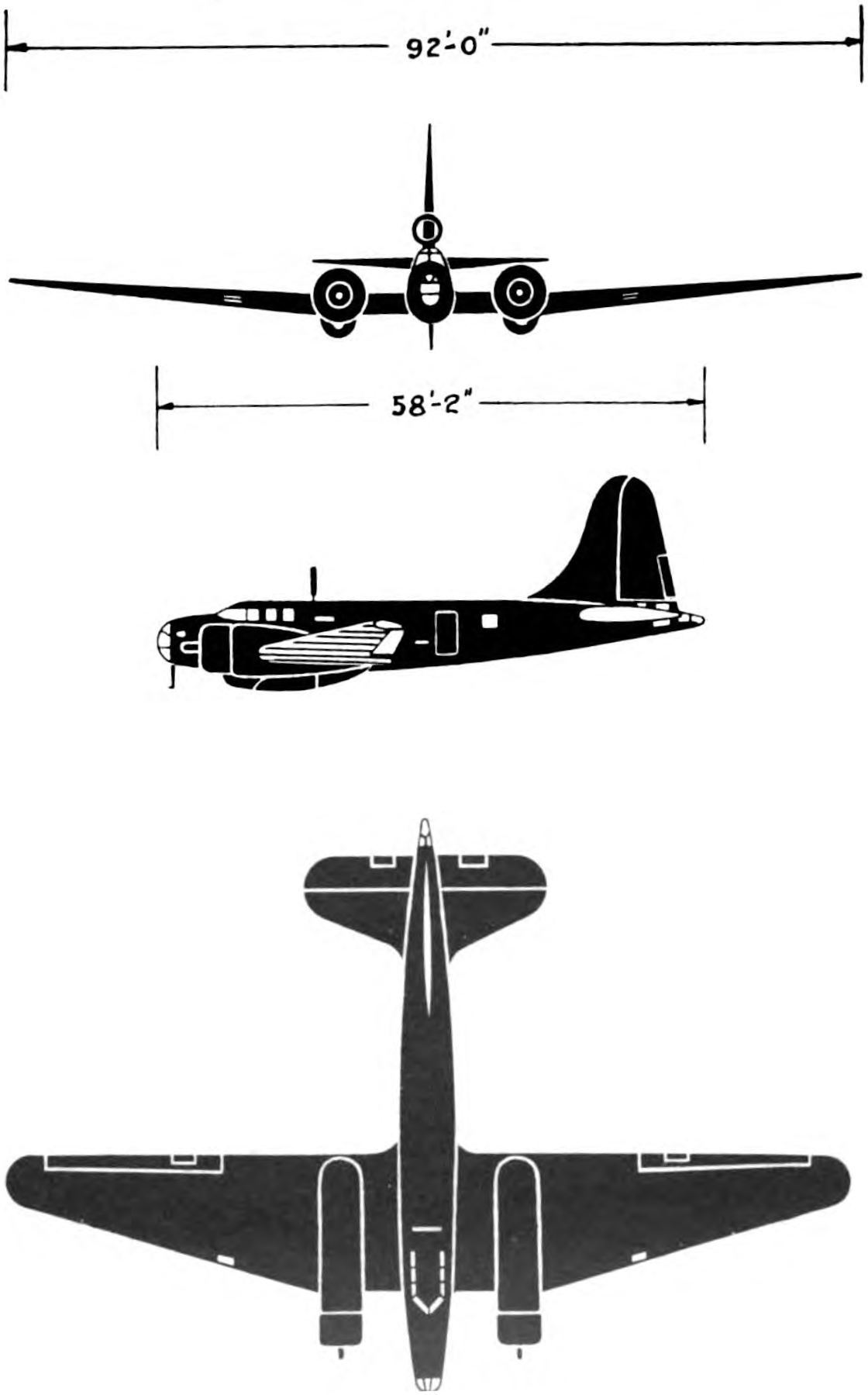
Douglas B-23 Dragon
–
bomber
A bomber is a military combat aircraft designed to attack ground and naval targets by dropping air-to-ground weaponry (such as bombs), launching torpedoes, or deploying air-launched cruise missiles. The first use of bombs dropped from an air ...
developed by the Douglas Aircraft Company
The Douglas Aircraft Company was an American aerospace manufacturer based in Southern California. It was founded in 1921 by Donald Wills Douglas Sr. and later merged with McDonnell Aircraft in 1967 to form McDonnell Douglas; it then operated a ...
as a successor to (and a refinement of) the B-18 Bolo
The Douglas B-18 Bolo is an American heavy bomber which served with the United States Army Air Corps and the Royal Canadian Air Force (as the Digby) during the late 1930s and early 1940s. The Bolo was developed by the Douglas Aircraft Company f ...
.
Design and development
Douglas proposed a number of modifications designed to improve the performance of the B-18. Initially considered a redesign, the XB-22 featured 1,600 hp Wright R-2600-1 Twin Cyclone radial engines. The complete B-18 redesign was considered promising enough by theUSAAC
The United States Army Air Corps (USAAC) was the aerial warfare service component of the United States Army between 1926 and 1941. After World War I, as early aviation became an increasingly important part of modern warfare, a philosophical r ...
to alter the original contract to produce the last 38 B-18As ordered under Contract AC9977 as the B-23. The design incorporated a larger wingspan with a wing design very similar to that of the DC-3
The Douglas DC-3 is a propeller-driven airliner
manufactured by Douglas Aircraft Company, which had a lasting effect on the airline industry in the 1930s to 1940s and World War II.
It was developed as a larger, improved 14-bed sleeper version ...
, a fully retractable undercarriage, and improved defensive armament. The B-23 was the first operational American bomber equipped with a glazed tail gun position.Mondey 1982, p. 111. The tail gun was a .50 calibre (12.7 mm) machine gun, which was fired from the prone position
Prone position () is a body position in which the person lies flat with the chest down and the back up. In anatomical terms of location, the dorsal side is up, and the ventral side is down. The supine position is the 180° contrast.
Etymolo ...
by a gunner using a telescopic sight
A telescopic sight, commonly called a scope informally, is an optical sighting device based on a refracting telescope. It is equipped with some form of a referencing pattern – known as a '' reticle'' – mounted in a focally appropriate ...
.
The first B-23 flew on July 27, 1939 with the production series of 38 B-23s manufactured between July 1939 and September 1940.
Operational history
While significantly faster and better armed than the B-18, the B-23 was not comparable to newer medium bombers like theNorth American B-25 Mitchell
The North American B-25 Mitchell is an American medium bomber that was introduced in 1941 and named in honor of Major General William "Billy" Mitchell, a pioneer of U.S. military aviation. Used by many Allied air forces, the B-25 served in ...
and Martin B-26 Marauder
The Martin B-26 Marauder is an American twin-engined medium bomber that saw extensive service during World War II. The B-26 was built at two locations: Baltimore, Maryland, and Omaha, Nebraska, by the Glenn L. Martin Company.
First used in t ...
. For this reason, the 38 B-23s built were never used in combat overseas, although for a brief period they were employed as patrol aircraft stationed on the west coast of the United States. The B-23s were primarily relegated to training duties, although 18 of them were later converted as transports and redesignated UC-67.
The B-23 also served as a testbed for new engines and systems. For example, one was used for turbosupercharger
In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger (often called a turbo) is a forced induction device that is powered by the flow of exhaust gases. It uses this energy to compress the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to pro ...
development by General Electric
General Electric Company (GE) is an American multinational conglomerate founded in 1892, and incorporated in New York state and headquartered in Boston. The company operated in sectors including healthcare, aviation, power, renewable ene ...
at Schenectady, New York
Schenectady () is a city in Schenectady County, New York, United States, of which it is the county seat. As of the 2020 census, the city's population of 67,047 made it the state's ninth-largest city by population. The city is in eastern New Yo ...
. Another was used for testing cabin pressurization.
After World War II, many examples were used as executive transports, with appropriate internal modifications, and as a result a large number have survived, both in public and private collections. Howard Hughes
Howard Robard Hughes Jr. (December 24, 1905 – April 5, 1976) was an American business magnate, record-setting pilot, engineer, film producer, and philanthropist, known during his lifetime as one of the most influential and richest people in t ...
(among others) used converted B-23s as personal aircraft.
Operators
; *United States Army Air Corps
The United States Army Air Corps (USAAC) was the aerial warfare service component of the United States Army between 1926 and 1941. After World War I, as early aviation became an increasingly important part of modern warfare, a philosophical r ...
Variants
;B-23 :Twin-engined bomber version of the B-18 with modified fuselage, 38 built. ;C-67 :Conversion to utility transport with provision for glider towing, 12 conversions from B-23, redesignated UC-67 in 1943. ;UC-67 :C-67 redesignated in 1943.Surviving aircraft

Ecuador
;UC-67 *39-031 (HC-APV) - Ecuadorian Air Museum,Quito
Quito (; qu, Kitu), formally San Francisco de Quito, is the capital and largest city of Ecuador, with an estimated population of 2.8 million in its urban area. It is also the capital of the province of Pichincha. Quito is located in a valley on ...
.
United States
On display
;B-23 *39-0036 -McChord Air Museum
The McChord Air Museum is an aviation museum located at McChord Field near Lakewood, Washington. The museum is broken up into three separate areas: the main gallery, located at the south end of McChord Field in Building 517; the Heritage Hill Ai ...
in McChord AFB, Washington.
*39-0051 - Pima Air & Space Museum
The Pima Air & Space Museum, located in Tucson, Arizona, is one of the world's largest non-government funded aerospace museums. The museum features a display of nearly 300 aircraft spread out over 80 acres (320,000 m²) on a campus oc ...
adjacent to Davis-Monthan Air Force Base in Tucson, Arizona
, "(at the) base of the black ill
, nicknames = "The Old Pueblo", "Optics Valley", "America's biggest small town"
, image_map =
, mapsize = 260px
, map_caption = Interactive map ...
.
;UC-67
*39-0047 - Castle Air Museum
Castle Air Museum is a military aviation museum located in Atwater, California, United States adjacent to Castle Airport, a former United States Air Force Strategic Air Command base which was closed in 1995, after the end of the Cold War. It ...
at the former Castle Air Force Base
Castle Air Force Base (Castle AFB, 1941–1995) is a former United States Air Force Strategic Air Command base in California, located northeast of Atwater, northwest of Merced, and about south of Sacramento.
The Central Valley base in u ...
in Atwater, California
Atwater is a city on State Route 99 in Merced County, California, United States. Atwater is west-northwest of Merced, at an elevation of . The population as of the 2020 census was 31,970, up from 28,168 in 2010.
Geography
Atwater is in northe ...
.
Under restoration or in storage
;B-23 *39-0033 - to airworthiness by ATW Aviation inMarana, Arizona
Marana is a town in Pima County, Arizona, United States, located northwest of Tucson, with a small portion in Pinal County. According to the 2010 census, the population of the town is 34,961. From 1990 to 2000, Marana was the fourth fastest-g ...
.
*39-0037 - in storage at the National Museum of the United States Air Force
The National Museum of the United States Air Force (formerly the United States Air Force Museum) is the official museum of the United States Air Force located at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, northeast of Dayton, Ohio. The NMUSAF is the ...
at Wright-Patterson AFB
Wright-Patterson Air Force Base (WPAFB) is a United States Air Force base and census-designated place just east of Dayton, Ohio, in Greene and Montgomery counties. It includes both Wright and Patterson Fields, which were originally Wilbur W ...
in Dayton, Ohio
Dayton () is the List of cities in Ohio, sixth-largest city in the U.S. state of Ohio and the county seat of Montgomery County, Ohio, Montgomery County. A small part of the city extends into Greene County, Ohio, Greene County. The 2020 United S ...
.
*39-0038 - for display at the 1941 Historical Aircraft Group Museum
The National Warplane Museum is a warbird and military history museum currently located on the grounds of the Geneseo Airport in Geneseo, New York. Founded in 1994, the museum restores, flies, and displays vintage military aircraft from the Second ...
in Geneseo, New York
Geneseo is a town in Livingston County in the Finger Lakes region of New York, United States. It is at the south end of the five-county Rochester Metropolitan Area. The population of the town was 10,483 at the 2010 census.
The English nam ...
.
;UC-67
*39-0057 - in storage at Fantasy of Flight
Fantasy of Flight is an aviation museum in Polk City, Florida.
It opened in November 1995, to house Kermit Weeks' collection of aircraft that, until Hurricane Andrew damaged many in 1992, were housed at the Weeks Air Museum in Tamiami, Florid ...
in Polk City, Florida.
*39-0063 - to airworthiness by private owner in Anchorage, Alaska
Anchorage () is the largest city in the U.S. state of Alaska by population. With a population of 291,247 in 2020, it contains nearly 40% of the state's population. The Anchorage metropolitan area, which includes Anchorage and the neighboring ...
. Currently stored at Grant County International Airport
Grant County International Airport is a public use airport in the northwest United States, located northwest of the central business district of Moses Lake in Grant County, Washington. Formerly a military facility, the airport is owned by the ...
, Moses Lake, Washington. Flew in 2017.
Wrecks
;B-23 *39-0052 - wreck at Loon Lake,Idaho
Idaho ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. To the north, it shares a small portion of the Canada–United States border with the province of British Columbia. It borders the states of Monta ...
.
Specifications (B-23 Dragon)

See also
References
Notes
Bibliography
* Francillon, René J. ''McDonnell Douglas Aircraft since 1920''. London, Putnam, 1979. . * * Mondey, David. ''The Hamlyn Concise Guide to American Aircraft of World War II''. London: Hamlyn Publishing Group, 2002, (republished 1996 by the Chancellor Press), First edition 1982. .External links
Douglas B-23 Dragon
–
National Museum of the United States Air Force
The National Museum of the United States Air Force (formerly the United States Air Force Museum) is the official museum of the United States Air Force located at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, northeast of Dayton, Ohio. The NMUSAF is the ...
{{Authority control
B-23 Dragon
1930s United States bomber aircraft
Aircraft first flown in 1939
Twin piston-engined tractor aircraft