Dneper on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
}
The Dnieper () or Dnipro (); , ; . is one of the major transboundary rivers of Europe, rising in the
 In English, "Dnieper" derives from the Russian pronunciation and "Dnipro" from the Ukrainian. The initial D in Dnieper is generally silent, although it may be sounded: or . The English pronunciation of Dnipro is .
The name varies slightly in the local
In English, "Dnieper" derives from the Russian pronunciation and "Dnipro" from the Ukrainian. The initial D in Dnieper is generally silent, although it may be sounded: or . The English pronunciation of Dnipro is .
The name varies slightly in the local
 The Dnieper has many
The Dnieper has many
 *
*
Valdai Hills
The Valdai Hills (russian: Валда́йская возвы́шенность, Valdáyskaya vozvýshennost'), sometimes referred to as just Valdai (russian: Валда́й, Valdáy), are an upland region in the north-west of central European Ru ...
near Smolensk
Smolensk ( rus, Смоленск, p=smɐˈlʲensk, a=smolensk_ru.ogg) is a city and the administrative center of Smolensk Oblast, Russia, located on the Dnieper River, west-southwest of Moscow. First mentioned in 863, it is one of the oldest ...
, Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
, before flowing through Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by ...
and Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
to the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
. It is the longest river of Ukraine and Belarus and the fourth- longest river in Europe, after the Volga
The Volga (; russian: Во́лга, a=Ru-Волга.ogg, p=ˈvoɫɡə) is the longest river in Europe. Situated in Russia, it flows through Central Russia to Southern Russia and into the Caspian Sea. The Volga has a length of , and a catchm ...
, Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , p ...
, and Ural
Ural may refer to:
*Ural (region), in Russia and Kazakhstan
*Ural Mountains, in Russia and Kazakhstan
*Ural (river), in Russia and Kazakhstan
* Ual (tool), a mortar tool used by the Bodo people of India
*Ural Federal District, in Russia
*Ural econ ...
rivers. It is approximately long, with a drainage basin
A drainage basin is an area of land where all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, ...
of .
In antiquity, the river was part of the Amber Road
The Amber Road was an ancient trade route for the transfer of amber from coastal areas of the North Sea and the Baltic Sea to the Mediterranean Sea. Prehistoric trade routes between Northern and Southern Europe were defined by the amber trade.
...
trade routes. During the Ruin
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things already mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the m ...
in the later 17th century, the area was contested between the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi- confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Poland and Lithuania ru ...
and Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
, dividing Ukraine into areas described by its right
Rights are legal, social, or ethical principles of freedom or entitlement; that is, rights are the fundamental normative rules about what is allowed of people or owed to people according to some legal system, social convention, or ethical ...
and left banks. During the Soviet period
The history of Soviet Russia and the Soviet Union (USSR) reflects a period of change for both Russia and the world. Though the terms "Soviet Russia" and "Soviet Union" often are synonymous in everyday speech (either acknowledging the dominance ...
, the river became noted for its major hydroelectric dams
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined an ...
and large reservoirs. The 1986 Chernobyl disaster occurred on the Pripyat
Pripyat ( ; russian: При́пять), also known as Prypiat ( uk, При́пʼять, , ), is an abandoned city in northern Ukraine, located near the border with Belarus. Named after the nearby river, Pripyat, it was founded on 4 February 1 ...
, immediately above that tributary's confluence with the Dnieper. The Dnieper is an important navigable waterway
A waterway is any navigable body of water. Broad distinctions are useful to avoid ambiguity, and disambiguation will be of varying importance depending on the nuance of the equivalent word in other languages. A first distinction is necessary b ...
for the economy of Ukraine
The economy of Ukraine is an emerging, mixed economy located in Eastern Europe. It grew rapidly from 2000 until 2008 when the Great Recession began worldwide and reached Ukraine. The economy recovered in 2010 and continued improving until 2013 ...
and is connected by the Dnieper–Bug Canal to other waterways in Europe. During the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine
On 24 February 2022, in a major escalation of the Russo-Ukrainian War, which began in 2014. The invasion has resulted in tens of thousands of deaths on both sides. It has caused Europe's largest refugee crisis since World War II. ...
, certain segments of the river form a defensive line between territory controlled by Russians and Ukrainians.
Names
 In English, "Dnieper" derives from the Russian pronunciation and "Dnipro" from the Ukrainian. The initial D in Dnieper is generally silent, although it may be sounded: or . The English pronunciation of Dnipro is .
The name varies slightly in the local
In English, "Dnieper" derives from the Russian pronunciation and "Dnipro" from the Ukrainian. The initial D in Dnieper is generally silent, although it may be sounded: or . The English pronunciation of Dnipro is .
The name varies slightly in the local Slavic languages
The Slavic languages, also known as the Slavonic languages, are Indo-European languages spoken primarily by the Slavic peoples and their descendants. They are thought to descend from a proto-language called Proto-Slavic, spoken during the ...
of the three countries through which it flows:
* be, Дняпро, translit=Dnyapro, , or ,
* rus, Днепр, r=Dnepr, p=ˈdⁿʲepr; formerly spelled
* uk, Дніпро, translit=Dnipro, ; poetic ; formerly , , or older (, )
These names are all cognate, deriving from Old East Slavic (''Dŭněprŭ''). The origin of this name is disputed but generally derived from either Sarmatian
The Sarmatians (; grc, Σαρμαται, Sarmatai; Latin: ) were a large confederation of ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic peoples of classical antiquity who dominated the Pontic steppe from about the 3rd century BC to the 4th cen ...
* ("Farther River") in parallel with the Dniester
The Dniester, ; rus, Дне́стр, links=1, Dnéstr, ˈdⁿʲestr; ro, Nistru; grc, Τύρᾱς, Tyrās, ; la, Tyrās, la, Danaster, label=none, ) ( ,) is a transboundary river in Eastern Europe. It runs first through Ukraine and th ...
("Nearer River") or from Scythian
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern
* : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Centra ...
* ("Deep River") in reference to its lack of fords, from which was also derived the Late Antique
Late antiquity is the time of transition from classical antiquity to the Middle Ages, generally spanning the 3rd–7th century in Europe and adjacent areas bordering the Mediterranean Basin. The popularization of this periodization in English has ...
name of the river, ().
Another Scythian language name of the Dnipro was , meaning "having broad space," from which were derived:
*the Graeco-Roman name of the river, ( ; Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
: ). This name was connected to the Graeco-Roman name of the Volga
The Volga (; russian: Во́лга, a=Ru-Волга.ogg, p=ˈvoɫɡə) is the longest river in Europe. Situated in Russia, it flows through Central Russia to Southern Russia and into the Caspian Sea. The Volga has a length of , and a catchm ...
river, (Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic p ...
: ; Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
: ), which was derived from Scythian , meaning "Broad."
**From was derived the river's poetic Latin name,
*the Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th century AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was part ...
' name for the river, , from Scythian , "Broad."
During the period of Old Great Bulgaria
Old Great Bulgaria or Great Bulgaria (Medieval Greek: Παλαιά Μεγάλη Βουλγαρία, ''Palaiá Megálē Voulgaría''), also often known by the Latin names ''Magna Bulgaria'' and ''Patria Onoguria'' (" Onogur land"), was a 7th- ...
, it was known as Buri-Chai and, under the Kievan Rus'
Kievan Rusʹ, also known as Kyivan Rusʹ ( orv, , Rusĭ, or , , ; Old Norse: ''Garðaríki''), was a state in Eastern and Northern Europe from the late 9th to the mid-13th century.John Channon & Robert Hudson, ''Penguin Historical Atlas of ...
it was known as Славу́тич (''Slavútytch''), a name still used poetically in Ukrainian due to the influence of the Old East Slavic epic ''The Tale of Igor's Campaign
''The Tale of Igor's Campaign'' ( orv, Слово о пълкѹ Игоревѣ, translit=Slovo o pŭlku Igorevě) is an anonymous epic poem written in the Old East Slavic language.
The title is occasionally translated as ''The Tale of the Campai ...
'' and its modern adaptations on Ukrainian literature. This usage also lent its name to the city of Slavutych
Slavutych ( uk, Славу́тич) is a city and municipality in northern Ukraine, purpose-built for the evacuated personnel of the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant after the 1986 disaster that occurred near the city of Pripyat. Geographically l ...
, founded in the wake of the Chernobyl disaster in 1986 to house displaced workers. The Kipchak Turks
The Kipchaks or Qipchaks, also known as Kipchak Turks or Polovtsians, were a Turkic people, Turkic nomadic people and confederation that existed in the Middle Ages, inhabiting parts of the Eurasian Steppe. First mentioned in the 8th century as p ...
called it the ''Uzeu'', the Crimean Tatars
, flag = Flag of the Crimean Tatar people.svg
, flag_caption = Flag of Crimean Tatars
, image = Love, Peace, Traditions.jpg
, caption = Crimean Tatars in traditional clothing in front of the Khan's Palace ...
the ''Özü'', and modern Turks
Turk or Turks may refer to:
Communities and ethnic groups
* Turkic peoples, a collection of ethnic groups who speak Turkic languages
* Turkish people, or the Turks, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
* Turkish citizen, a citizen of the Republic ...
the ''Özü'' or ''Özi''.
Geography
The total length of the river is variously given as or , of which are within Russia, are withinBelarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by ...
, and are within Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
. Its basin covers , of which are within Ukraine, are within Belarus.
The source of the Dnieper is the sedge bogs (Akseninsky Mokh) of the Valdai Hills
The Valdai Hills (russian: Валда́йская возвы́шенность, Valdáyskaya vozvýshennost'), sometimes referred to as just Valdai (russian: Валда́й, Valdáy), are an upland region in the north-west of central European Ru ...
in central Russia, at an elevation of . For of its length, it serves as the border between Belarus and Ukraine. Its estuary, or liman, used to be defended by the strong fortress of Ochakiv
Ochakiv, also known as Ochakov ( uk, Оча́ків, ; russian: Очаков; crh, Özü; ro, Oceacov and ''Vozia'', and Alektor ( in Greek), is a small city in Mykolaiv Raion, Mykolaiv Oblast (region) of southern Ukraine. It hosts the admini ...
.
The southernmost point in Belarus is on the Dnieper to the south of Kamaryn
Kamaryn is a village in the Brahin district of Belarus, near the Ukrainian town of Pripyat. Its population in 2017 was 1,777. It experienced heavy nuclear fallout during the Chernobyl disaster.
Geography
Kamaryn is on the Dnieper
}
The ...
in Brahin Raion
Brahin District or Brahinski Rajon ( be, Брагінскі раён, russian: Брагинский район, Bragin District), is a districts of Belarus, district of Gomel Region, in Belarus. Its administrative seat is the small town of Brahin ...
.
Tributaries of the Dnieper
 The Dnieper has many
The Dnieper has many tributaries
A tributary, or affluent, is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream or main stem (or parent) river or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries and the main stem river drain the surrounding drainag ...
(up to 32,000) with 89 being rivers of 100+ km.Splendid Dnieper. There is no straighter riverUkrinform
The National News Agency of Ukraine ( uk, Українське національне інформаційне агентство), or Ukrinform ( uk, Укрінформ), is a state information and news agency, and international broadcaster of ...
. 4 July 2015 The main ones are, from its source to its mouth, with left (L) or right (R) bank indicated:
 *
* Vyazma
Vyazma (russian: Вя́зьма) is a town and the administrative center of Vyazemsky District in Smolensk Oblast, Russia, located on the Vyazma River, about halfway between Smolensk, the administrative center of the oblast, and Mozhaysk. Thr ...
(L)
* Vop (R)
* Khmost
The Khmost (russian: Хмость) is a river in Dukhovshchinsky District, Dukhovshchinsky, Smolensky District, Smolensk Oblast, Smolensky, and Kardymovsky Districts of Smolensk Oblast, Russia, a right tributary of the Dnieper. The length of the r ...
(R)
* Myareya
The Myareya ( be, Мярэя), alternative transliteration ''Miareja'', official transliteration or Mereya (russian: Мерея) is a river in Belarus and Russia. It is a left tributary of the Dnieper
}
The Dnieper () or Dnipro (); , ; . is ...
(L)
* Drut
''Drut'' ( द्रुत; also called ''drut laya'') is the concluding section, in fast tempo (or ''laya''), between 160 and 320 beats per minute, of the performance of a vocal raga in Hindustani classical music.
See also
*Khyal
*Vilambit
*Ma ...
(R)
* Berezina
The Berezina or Biarezina ( be, Бярэ́зіна; ) is a river in Belarus and a right tributary of the Dnieper. The river starts in the Berezinsky Biosphere Reserve. The length of the Berezina is 613 km. The width of the river is 15-20 m, the ...
(R)
* Sozh
The Sozh, or Sož ( be, Сож, ; russian: Сож, uk, Сож) is an international river flowing in Russia, Belarus, and Ukraine. It is a left bank tributary of the Dnieper. The Sozh passes through Gomel, the second largest city in Belarus.
T ...
(L)
* Pripyat
Pripyat ( ; russian: При́пять), also known as Prypiat ( uk, При́пʼять, , ), is an abandoned city in northern Ukraine, located near the border with Belarus. Named after the nearby river, Pripyat, it was founded on 4 February 1 ...
(R)
* Teteriv
The Teteriv () is a right tributary of the Dnieper River in Ukraine. It has a length of 365 km and a drainage basin of 15,300 km².
In the underflow the valley of the Teteriv in Polissia on up to 4 km, the width of the river widens ...
(R)
* Irpin
Irpin ( uk, Ірпі́нь, ) is a Hero City of Ukraine located on the Irpin River in Bucha Raion, Kyiv Oblast (province) right next to the city of Kyiv in northern Ukraine. Irpin hosts the administration of Irpin urban hromada, one of the h ...
(R)
* Desna (L)
* Stuhna (R)
* Trubizh
The Trubizh (, russian: Трубе́ж) is a river entirely located in Ukraine, a left tributary of Dnieper. It falls into the Dnieper's Kaniv Reservoir (named after Kaniv). It is long, and has a drainage basin of .Ros (R)
*
Tiasmyn
The Tiasmyn () is a right tributary of the Dnieper River in Ukraine. It is long, and has a drainage basin of .Тясмин
(R)
* Supii (L)
* Sula (L)
* Psyol
The Psel (, Romanization of Russian, translit. ''Psyol''; , Romanization of Ukrainian, translit. ''Psel, Ps'ol, Pslo'') is a river, a left tributary of the Dnieper, which flows through Russia and Ukraine.
The Psel has a length of and a draina ...
(L)
* Vorskla
The Vorskla (; ) is a river that runs from Belgorod Oblast in Russia southwards into northeastern Ukraine, where it joins the Dnieper. It has a length of , and a basin area of .Oril (L)
* Samara (L)
* Konka (L)
*
 The
The
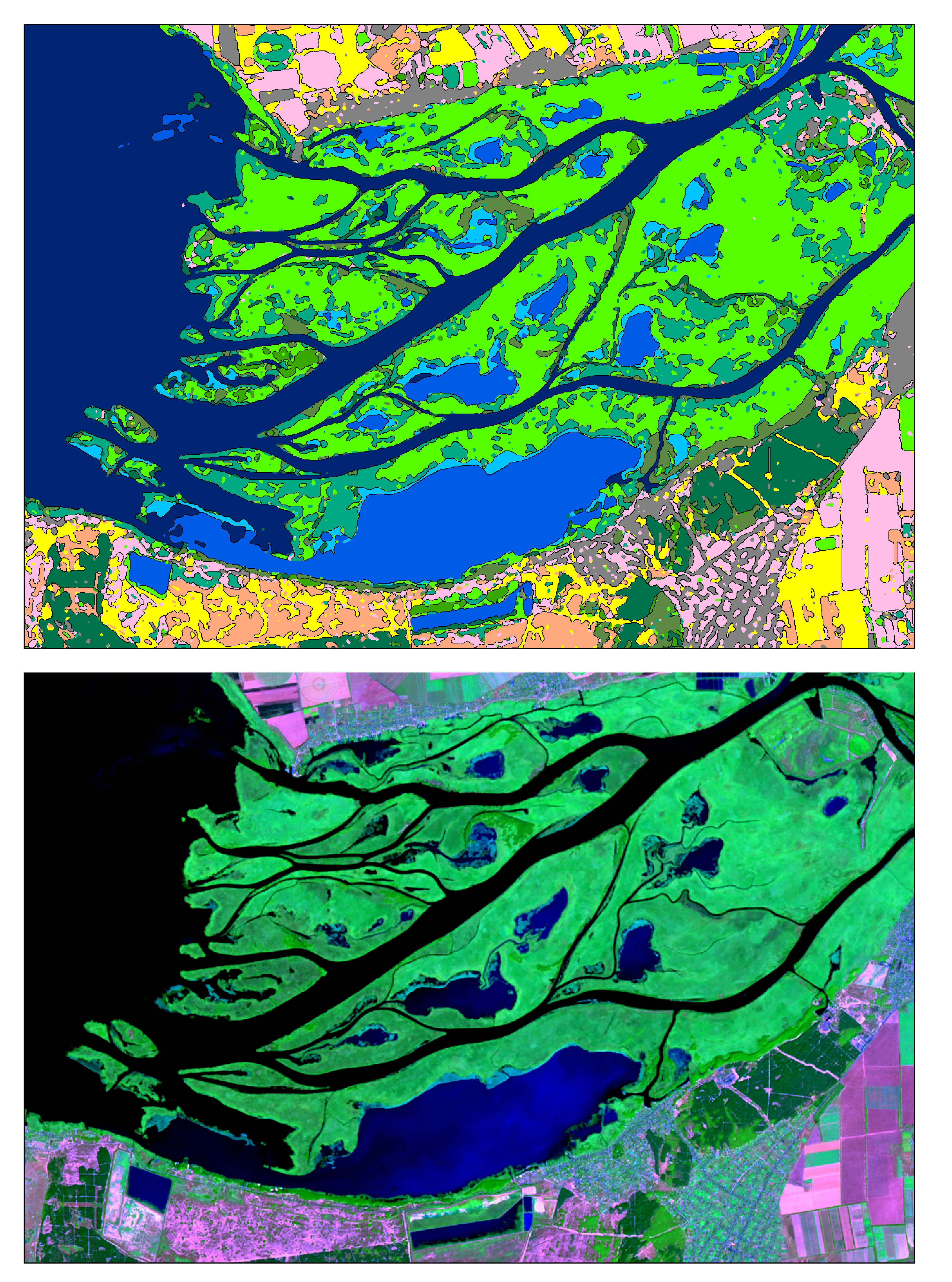 The city of Kherson lies near to the Dnieper delta.
The city of Kherson lies near to the Dnieper delta.

File:Днепр код Кијева.jpg, The Dnieper River in
File:Plersch-Odjazd Katarzyny II z Kaniowa w 1787 roku.jpg, ''
Dnieper River
at th
''Encyclopedia of Ukraine''
Site about Dnieper
��objects over the river, photos, facts
"Комсомольская правда" об угрозах плотины Киевской ГЭС и водохранилища
(''tr. "Komsomolskaya Pravda" about the threats of the dam of the Kyiv hydroelectric power station and the reservoir"'')
"Аргументы и факты" о реальных угрозах дамбы Киевского водохранилища и ГЭС
(''tr. ""Arguments and Facts" about the real threats of the dam of the Kyiv reservoir and hydroelectric power station"'')
"Известия" о проблематике плотины Киевского водохранилища и ГЭС
(''tr. ""Izvestia" about the problems of the dam of the Kyiv reservoir and hydroelectric power station"'')
(''tr. "UNIAN expert on the threats of the Kyiv reservoir dam"'') {{Authority control Border rivers Belarus–Russia border Belarus–Ukraine border Ottoman Empire–Russian Empire border Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth–Russian Empire border International rivers of Europe Ramsar sites in Belarus Rivers of Belarus Rivers of Cherkasy Oblast Rivers of Dnipropetrovsk Oblast Rivers of Gomel Region Rivers of Kherson Oblast Rivers of Kyiv Rivers of Mogilev Region Rivers of Poltava Oblast Rivers of Smolensk Oblast Rivers of Vitebsk Region Rivers of Zaporizhzhia Oblast
Bilozerka
Bilozerka ( uk, Білозе́рка, ) is an urban-type settlement in Kherson Raion, Kherson Oblast, southern Ukraine. It hosts the administration of Bilozerka settlement hromada, one of the hromadas of Ukraine. It has a population of
Ad ...
(L)
* Bazavluk (R)
* Inhulets
The Inhulets () is a river, a right tributary of the Dnieper, that flows through Ukraine. It has a length of 557 km and a drainage basin of 14,460 km².
The Inhulets has its source in the Dnieper Upland in a ravine (balka) to the we ...
(R)
Many small direct tributaries also exist, such as, in the Kyiv area, the Syrets (right bank) in the north of the city, the historically significant Lybid
The Lybid ( uk, Либідь) is a small river in Kyiv, Ukraine. A right tributary of the Dnieper, it flows within the "Right Bank" (original) part of the city, just to the west of the historic center. The Lybid has played an important role in ...
(right bank) passing west of the centre, and the Borshahivka (right bank) to the south.
The water resources of the Dnieper basin compose around 80% of the total for all Ukraine.
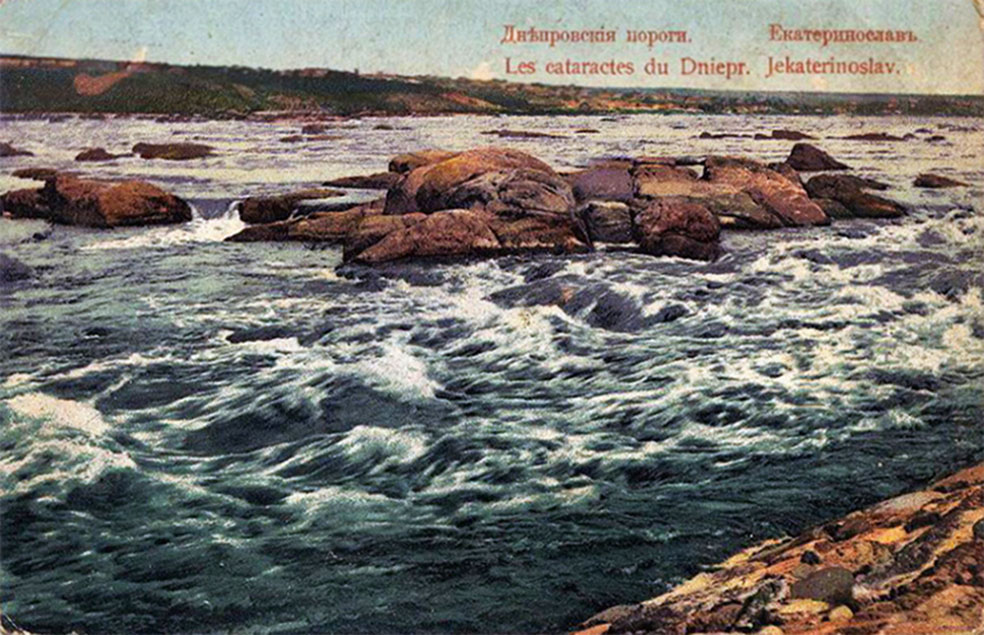
Rapids
 The
The Dnieper Rapids
The Dnieper Rapids ( uk, Дніпрові пороги, ) are the historical rapids on the Dnieper river in Ukraine, composed of outcrops of granites, gneisses and other types of bedrock of the Ukrainian Shield. The rapids began below the presen ...
were part of the trade route from the Varangians to the Greeks
The trade route from the Varangians to the Greeks was a medieval trade route that connected Scandinavia, Kievan Rus' and the Eastern Roman Empire. The route allowed merchants along its length to establish a direct prosperous trade with the Empir ...
, first mentioned in the Kyiv Chronicle. The route was probably established in the late eighth and early ninth centuries and gained significant importance from the tenth until the first third of the eleventh century. On the Dnieper the Varangian
The Varangians (; non, Væringjar; gkm, Βάραγγοι, ''Várangoi'';Varangian
" Online Etymo ...
s had to portage their ships round seven rapids, where they had to be on guard for " Online Etymo ...
Pecheneg
The Pechenegs () or Patzinaks tr, Peçenek(ler), Middle Turkic: , ro, Pecenegi, russian: Печенег(и), uk, Печеніг(и), hu, Besenyő(k), gr, Πατζινάκοι, Πετσενέγοι, Πατζινακίται, ka, პაჭ ...
nomads.
Along this middle flow of the Dnieper, there were 9 major rapids (although some sources cite a fewer number of them), obstructing almost the whole width of the river, about 30 to 40 smaller rapids, obstructing only part of the river, and about 60 islands and islets.
After the Dnieper hydroelectric station was built in 1932, they were inundated by Dnieper Reservoir
The Dnieper Reservoir ( uk, Дніпровське водосховище, ) is a water reservoir on the Dnieper river in Ukraine that was created by construction of the Dnieper Hydroelectric Station at Zaporizhzhia in 1932. The filling of the re ...
.
Canals
There are a number of canals connected to the Dnieper: *The Dnieper– Donbas Canal; *The Dnieper–Kryvyi Rih
Kryvyi Rih ( uk, Криви́й Ріг , lit. "Curved Bend" or "Crooked Horn"), also known as Krivoy Rog (Russian: Кривой Рог) is the largest city in central Ukraine, the 7th most populous city in Ukraine and the 2nd largest by area. K ...
Canal;
*The Kakhovka Canal (southeast of the Kherson region);
*The Krasnoznamianka Irrigation System in the southwest of the Kherson region;
*The North Crimean Canal
The North Crimean Canal ( uk, Північно-Кримський канал, translit=Pivnichno-Krymskyi kanal, russian: Северо-Крымский канал, in the Soviet Union: North Crimean Canal of the Lenin's Komsomol of Ukraine) is a l ...
—will largely solve the water problem of the peninsula, especially in the arid northern and eastern Crimea
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a pop ...
;
*The Inhulets Irrigation System.
Fauna
The river is part of thequagga mussel
The quagga mussel (''Dreissena rostriformis'', also known as ''Dreissena bugensis'' or ''Dreissena rostriformis bugensis'') is a species (or subspecies) of freshwater mussel, an aquatic bivalve mollusk in the family Dreissenidae. It has an aver ...
's native range. The mussel has been accidentally introduced around the world, where it has become an invasive species.
Delta
 The city of Kherson lies near to the Dnieper delta.
The city of Kherson lies near to the Dnieper delta.
Ecology
Nowadays the Dnieper River suffers from anthropogenic influence resulting in numerous emissions of pollutants. The Dnieper is close to thePrydniprovsky Chemical Plant radioactive dumps
The now-defunct Prydniprovskyi Chemical Plant ( uk, Придніпровський хімічний завод, ПХЗ; ''Prydniprovskyi khimichnyi zavod'', ''PKhZ'', also PChP) in the city of Kamianske, Ukraine, processed uranium ore for the Sov ...
(near Kamianske
Kamianske ( uk, Кам'янське, ), formerly Dniprodzerzhynsk, is an industrial city in Dnipropetrovsk Oblast of Ukraine and a port on the Dnieper. Administratively, it serves as the administrative center of Kamianske Raion. Kamianske hosts ...
) and susceptible to leakage of its radioactive waste. The river is also close to the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Station
The Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant (ChNPP; ; ), is a nuclear power plant undergoing decommissioning. ChNPP is located near the abandoned city of Pripyat in northern Ukraine northwest of the city of Chernobyl, from the Belarus–Ukraine border, ...
(Chernobyl Exclusion Zone
The Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant Zone of Alienation, Belarusian: Хона адчужэння Чарнобыльскай АЭС, ''Zona adčužennia Čarnobyĺskaj AES'', russian: Зона отчуждения Чернобыльской АЭС, ...
) which is located next to the mouth of the Pripyat River
The Pripyat or Prypiat ( , uk, Прип'ять, ; be, Прыпяць, translit=Prypiać}, ; pl, Prypeć, ; russian: Припять, ) is a river in Eastern Europe, approximately long. It flows east through Ukraine, Belarus, and Ukraine ag ...
.
Navigation
Almost of the river is navigable (to the city ofDorogobuzh
Dorogobuzh (russian: Дорогобуж) is a historic town and the administrative center of Dorogobuzhsky District in Smolensk Oblast, Russia, straddling the Dnieper River and located east of Smolensk, the administrative center of the oblast. ...
). The Dnieper is important for transportation
Transport (in British English), or transportation (in American English), is the intentional movement of humans, animals, and goods from one location to another. Modes of transport include air, land (rail and road), water, cable, pipeline, ...
in the economy of Ukraine
The economy of Ukraine is an emerging, mixed economy located in Eastern Europe. It grew rapidly from 2000 until 2008 when the Great Recession began worldwide and reached Ukraine. The economy recovered in 2010 and continued improving until 2013 ...
. Its reservoirs have large ship locks, allowing vessels of up to access as far as the port of Kyiv
Kyiv, also spelled Kiev, is the capital and most populous city of Ukraine. It is in north-central Ukraine along the Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2021, its population was 2,962,180, making Kyiv the seventh-most populous city in Europe.
Kyi ...
, and thus are an important transportation corridor. The river is used by passenger vessels as well. Inland cruises on the rivers Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , p ...
and Dnieper have had a growing market in recent decades.
Upstream from Kyiv, the Dnieper receives the water of the Pripyat River
The Pripyat or Prypiat ( , uk, Прип'ять, ; be, Прыпяць, translit=Prypiać}, ; pl, Prypeć, ; russian: Припять, ) is a river in Eastern Europe, approximately long. It flows east through Ukraine, Belarus, and Ukraine ag ...
. This navigable river connects to the Dnieper-Bug canal, the link with the Bug River
uk, Західний Буг be, Захо́дні Буг
, name_etymology =
, image = Wyszkow_Bug.jpg
, image_size = 250
, image_caption = Bug River in the vicinity of Wyszków, Poland
, map = Vi ...
. Historically, a connection with the Western European waterways was possible, but a weir
A weir or low head dam is a barrier across the width of a river that alters the flow characteristics of water and usually results in a change in the height of the river level. Weirs are also used to control the flow of water for outlets of l ...
without any ship lock near the town of Brest, Belarus, has interrupted this international waterway. Poor political relations between Western Europe and Belarus mean there is little likelihood of reopening this waterway in the near future. River navigation is interrupted each year by freezing and severe winter storms.
Reservoirs and hydroelectric power
From the mouth of thePripyat River
The Pripyat or Prypiat ( , uk, Прип'ять, ; be, Прыпяць, translit=Prypiać}, ; pl, Prypeć, ; russian: Припять, ) is a river in Eastern Europe, approximately long. It flows east through Ukraine, Belarus, and Ukraine ag ...
to the Kakhovka Hydroelectric Station, there are six sets of dams and hydroelectric station
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined an ...
s, which produce 10% of Ukraine's electricity.
The first constructed was the Dnieper Hydroelectric Station
The Dnieper Hydroelectric Station ( uk, ДніпроГЕС, DniproHES; russian: ДнепроГЭС, DneproGES), also known as Dneprostroi Dam, in the city of Zaporizhzhia, Ukraine, is the largest hydroelectric power station on the Dnieper river. ...
(or DniproHES) near Zaporizhzhia
Zaporizhzhia ( uk, Запоріжжя) or Zaporozhye (russian: Запорожье) is a city in southeast Ukraine, situated on the banks of the Dnieper River. It is the administrative centre of Zaporizhzhia Oblast. Zaporizhzhia has a populat ...
, built between 1927 and 1932 with an output of 558 MW. It was destroyed during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, but was rebuilt in 1948 with an output of 750 MW.
Regions and cities

Regions
Kyiv
Kyiv, also spelled Kiev, is the capital and most populous city of Ukraine. It is in north-central Ukraine along the Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2021, its population was 2,962,180, making Kyiv the seventh-most populous city in Europe.
Kyi ...
, Ukraine
File:Dorogobuzh.jpg, The Dnieper River in Dorogobuzh
Dorogobuzh (russian: Дорогобуж) is a historic town and the administrative center of Dorogobuzhsky District in Smolensk Oblast, Russia, straddling the Dnieper River and located east of Smolensk, the administrative center of the oblast. ...
, Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
, before 1917
File:Dnieper River from Kryukivs'kyi bridge in Kremenchuk, Ukraine.jpg, The Dnieper River in Kremenchuk
Kremenchuk (; uk, Кременчу́к, Kremenchuk ) is an industrial city in central Ukraine which stands on the banks of the Dnipro River. The city serves as the administrative center of the Kremenchuk Raion (district) in Poltava Oblast (pr ...
, Ukraine
File:Above Dnieper river video from helicopter - 2004.ogv, thumbtime=25, The Dnieper river in Ukraine from a helicopter
A helicopter is a type of rotorcraft in which lift and thrust are supplied by horizontally spinning rotors. This allows the helicopter to take off and land vertically, to hover, and to fly forward, backward and laterally. These attributes ...
, 2004
Cities
Major cities, over 100,000 in population, are in bold script. Cities and towns located on the Dnieper are listed in order from the river's source (in Russia) to its mouth (in Ukraine): Arheimar, a capital of theGoths
The Goths ( got, 𐌲𐌿𐍄𐌸𐌹𐌿𐌳𐌰, translit=''Gutþiuda''; la, Gothi, grc-gre, Γότθοι, Gótthoi) were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe ...
, was located on the Dnieper, according to the Hervarar saga.
In the arts
Literature
The River Dnieper has been a subject of chapter X of a story by Nikolai Gogol ''A Terrible Vengeance
"A Terrible Vengeance" (russian: Страшная месть, Strashnaya mest') is a short Gothic horror story written by Russian author Nikolai Gogol.
It was published in the second volume of his first short story collection, ''Evenings on a F ...
'' (1831, published in 1832 as a part of the ''Evenings on a Farm Near Dikanka
''Evenings on a Farm Near Dikanka'' (russian: «Вечера на хуторе близ Диканьки») is a collection of short stories by Nikolai Gogol, written in 1829–1832. They appeared in various magazines and were published in book f ...
'' short stories collection). It is considered as a classical example of description of the nature in Russian literature. The river was also described in the works of Taras Shevchenko
Taras Hryhorovych Shevchenko ( uk, Тарас Григорович Шевченко , pronounced without the middle name; – ), also known as Kobzar Taras, or simply Kobzar (a kobzar is a bard in Ukrainian culture), was a Ukrainian poet, wr ...
.
In the adventure novel ''The Long Ships
''The Long Ships'' or ''Red Orm'' (original Swedish: ''Röde Orm'' meaning ''Red Serpent'' or ''Red Snake'') is an adventure novel by the Swedish writer Frans G. Bengtsson.
The narrative is set in the late 10th century and follows the advent ...
'' (also translated ''Red Orm''), set during the Viking Age
The Viking Age () was the period during the Middle Ages when Norsemen known as Vikings undertook large-scale raiding, colonizing, conquest, and trading throughout Europe and reached North America. It followed the Migration Period and the Germ ...
, a Scania
Scania, also known by its native name of Skåne (, ), is the southernmost of the historical provinces (''landskap'') of Sweden. Located in the south tip of the geographical region of Götaland, the province is roughly conterminous with Skåne ...
n chieftain travels to the Dnieper Rapids to retrieve a treasure hidden there by his brother, encountering many difficulties. The novel was very popular in Sweden and is one of few to depict a Viking voyage to eastern Europe.
Visual arts
The River Dnieper has been a subject for artists, great and minor, over the centuries. Major artists with works based on the Dnieper areArkhip Kuindzhi
Arkhip Ivanovich Kuindzhi (; rus, Архи́п Ива́нович Куи́нджи ; ; 27 January 1841 – 24 July 1910) was a Ukrainian landscape painter active in the Russian Empire, of Pontic Greek descent.
Date of birth
Kuindzhi's exact da ...
and Ivan Aivazovsky
Ivan Konstantinovich Aivazovsky (russian: link=no, Иван Константинович Айвазовский; 29 July 18172 May 1900) was a Russian Romantic painter who is considered one of the greatest masters of marine art. Baptized ...
.
Films
The River Dnieper makes an appearance in the 1964 Hungarian drama film ''The Sons of the Stone-Hearted Man'' (based on the novel of the same name byMór Jókai
Móric Jókay de Ásva (, known as ''Mór Jókai''; 18 February 1825 – 5 May 1904), outside Hungary also known as Maurus Jokai or Mauritius Jókai, was a Hungarian nobleman, novelist, dramatist and revolutionary. He was an active participant ...
), where it appears when two characters are leaving Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
but get attacked by wolves.
In 1983
The year 1983 saw both the official beginning of the Internet and the first mobile cellular telephone call.
Events January
* January 1 – The migration of the ARPANET to TCP/IP is officially completed (this is considered to be the beginning ...
, the concert program "Song of the Dnieper" from the "Victory Salute" series was released, dedicated to the 40th anniversary of the liberation of the city of Kiev from the German fascist invaders. The program includes songs by Soviet composers, Ukrainian folk songs
Ukrainian folk music includes a number of varieties of traditional, folkloric, folk-inspired popular music, and folk-inspired European classical music traditions.
In the 20th century numerous ethnographic and folkloric musical ensembles were ...
, and dances performed by the Song and Dance Ensemble of the Kiev Military District led by A. Pustovalov, P. Virsky Ukrainian National Folk Dance Ensemble, Kyiv Bandurist Capella
The Kyiv Bandurist Capella ( uk, Київська капeла бандуристiв, translit=Kyivs’ka kapela banduristiv) is a male vocal-instrumental ensemble that accompanies its singing with the playing of the multi-stringed Ukrainian fo ...
, the Military Band of the Headquarters of the Kiev Military District led by A. Kuzmenko, singers Anatoliy Mokrenko
Anatoliy Yuriyovych Mokrenko ( uk, Анатолій Юрійович Мокренко; 22 January 1933 – 24 March 2020) was a Ukrainian operatic baritone who appeared internationally. He was also the director of the National Opera of Ukraine ...
, Lyudmila Zykina, Anatoliy Solovianenko
Anatoliy Solovianenko (sometime transliterated as Anatolii Solovyanenko; uk, Анатолій Борисович Солов'яненко; russian: Анатолий Борисович Соловья́ненко; September 25, 1932 – 29 July 1999 ...
, Dmytro Hnatyuk
Dmytro Hnatyuk ( uk, Дмитро́ Миха́йлович Гнатю́к; 28 March 1925 – 29 April 2016) was a Soviet and Ukrainian baritone opera singer and a former member of the Verkhovna Rada, Ukrainian Parliament.
Biography
Dmytro Hna ...
, Mykola Hnatyuk. Filming on the battlefield, streets and squares of Kiev. Scriptwriter - Victor Meerovsky. Directed by Victor Cherkasov. Operator - Alexander Platonov.
The 2018 film ''Volcano
A volcano is a rupture in the Crust (geology), crust of a Planet#Planetary-mass objects, planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and volcanic gas, gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Ear ...
'' was filmed at the river in Beryslav
Beryslav (, ) is a city in Kherson Oblast of southern Ukraine. It serves as the administrative center for Beryslav Raion (district), housing the district's local administration buildings. Beryslav hosts the administration of Beryslav urban hrom ...
, Kherson Oblast.
Music
In 1941, Mark Fradkin wrote "Song of the Dnieper" to the words ofYevgeniy Dolmatovsky
Yevgeny Aronovich Dolmatovsky (; 5 May 1915 – 10 September 1994) was a Soviet and Russian poet and lyricist. He was born and died in Moscow.
Examples of his songs
* Ballad of the Siberian Land (music by Nikolai Kryukov) - 1947
:The theme son ...
.
Image gallery
Catherine II
, en, Catherine Alexeievna Romanova, link=yes
, house =
, father = Christian August, Prince of Anhalt-Zerbst
, mother = Joanna Elisabeth of Holstein-Gottorp
, birth_date =
, birth_name = Princess Sophie of Anha ...
leaving Kaniów in 1787'' by Johann Gottlieb Plersch
Johann, typically a male given name, is the German language, German form of ''Iohannes'', which is the Latin language, Latin form of the Greek language, Greek name ''Iōánnēs'' (), itself derived from Hebrew language, Hebrew name ''Johanan (name ...
File:Archip Iwanowitsch Kuindshi 001.jpg, ''Dnieper'' by Arkhip Kuindzhi
Arkhip Ivanovich Kuindzhi (; rus, Архи́п Ива́нович Куи́нджи ; ; 27 January 1841 – 24 July 1910) was a Ukrainian landscape painter active in the Russian Empire, of Pontic Greek descent.
Date of birth
Kuindzhi's exact da ...
, 1881
File:Arkhip Kuindzhi - Ночь на Днепре - Google Art Project.jpg, ''Moonlit Night on the Dnieper
''Moonlit Night on the Dnieper'' (russian: Лунная ночь на Днепре) is an oil on canvas painting by Ukrainian artist Arkhip Kuindzhi made in 1880.
Description
The painting displays the banks of the Dnieper river at night during ...
'' by Arkhip Kuindzhi
Arkhip Ivanovich Kuindzhi (; rus, Архи́п Ива́нович Куи́нджи ; ; 27 January 1841 – 24 July 1910) was a Ukrainian landscape painter active in the Russian Empire, of Pontic Greek descent.
Date of birth
Kuindzhi's exact da ...
, 1882
File:Aivazovsky Ice on Dnipro.jpg, ''Ice in the Dnieper'' by Ivan Aivazovsky
Ivan Konstantinovich Aivazovsky (russian: link=no, Иван Константинович Айвазовский; 29 July 18172 May 1900) was a Russian Romantic painter who is considered one of the greatest masters of marine art. Baptized ...
, 1872
StanislawskiJan.DnieprSzafirowy.1904.ws.jpg, ''Sapphire Dnieper'' by Jan Stanisławski, 1904
Popular culture
* The river is one of the symbols of the Ukrainian nation and is mentioned in the nationalanthem of Ukraine
"" ( uk, Ще не вмерла України і слава, і воля, , lit=The glory and freedom of Ukraine has not yet perished), also known by its official title of "State Anthem of Ukraine" (, ') or by its shortened form "" (, ), is the ...
.
* There are several names that connect the name of the river with Ukraine: Overdnieper Ukraine, Right-bank Ukraine
Right-bank Ukraine ( uk , Правобережна Україна, ''Pravoberezhna Ukrayina''; russian: Правобережная Украина, ''Pravoberezhnaya Ukraina''; pl, Prawobrzeżna Ukraina, sk, Pravobrežná Ukrajina, hu, Jobb p ...
, Left-bank Ukraine
Left-bank Ukraine ( uk, Лівобережна Україна, translit=Livoberezhna Ukrayina; russian: Левобережная Украина, translit=Levoberezhnaya Ukraina; pl, Lewobrzeżna Ukraina) is a historic name of the part of Ukrain ...
, and others. Some of the cities on its banks — Dnipro, Dniprorudne, Kamianka-Dniprovska — are named after the river.
* The Zaporozhian Cossacks
The Zaporozhian Cossacks, Zaporozhian Cossack Army, Zaporozhian Host, (, or uk, Військо Запорізьке, translit=Viisko Zaporizke, translit-std=ungegn, label=none) or simply Zaporozhians ( uk, Запорожці, translit=Zaporoz ...
lived on the lower Dnieper and their name refers to their location "beyond the rapids".
* The folk metal
Folk metal is a fusion genre of heavy metal music and traditional folk music that developed in Europe during the 1990s. It is characterised by the widespread use of folk instruments and, to a lesser extent, traditional singing styles (for exampl ...
band Turisas
Turisas is a Finnish metal band from Hämeenlinna. They were founded in 1997 by Mathias Nygård and Jussi Wickström, and named after an ancient Finnish god of war.
Turisas are a folk metal band, incorporating elements of power metal and sym ...
have a song called "The Dnieper Rapids" on their 2007 album '' The Varangian Way''.
See also
*List of rivers of Russia
Russia can be divided into a European and an Asian part. The dividing line is generally considered to be the Ural Mountains. The European part is drained into the Arctic Ocean, Baltic Sea, Black Sea, and Caspian Sea. The Asian part is drain ...
* List of rivers of Belarus
* List of rivers of Ukraine
This is a list of the major rivers that flow through Ukraine.
Ukraine has around 23,000 rivers. Most of the rivers of Ukraine drain into the Black Sea and Azov Sea and belong to the bigger Mediterranean basin. Those rivers mostly flow in a southe ...
* List of crossings of the Dnieper
This is a list of all current crossings of the river Dnieper (or Dnipro) from its source in Russia, through Belarus, to its river delta near the Dnieper Estuary at Kherson, Ukraine.
Russia
Belarus
Ukraine
References
*
External l ...
* Middle Dnieper culture
The Middle Dnieper culture (russian: Среднеднепровская культура, Sriedniednieprovskaya kul'tura) is a formative early expression of the Corded Ware culture, ca. 3200—2300 BC, of northern Ukraine and Belarus.
Distri ...
* Trade route from the Varangians to the Greeks
The trade route from the Varangians to the Greeks was a medieval trade route that connected Scandinavia, Kievan Rus' and the Eastern Roman Empire. The route allowed merchants along its length to establish a direct prosperous trade with the Empir ...
Notes
References and footnotes
External links
* * Volodymyr Kubijovyč, Ivan TesliaDnieper River
at th
''Encyclopedia of Ukraine''
Site about Dnieper
��objects over the river, photos, facts
"Комсомольская правда" об угрозах плотины Киевской ГЭС и водохранилища
(''tr. "Komsomolskaya Pravda" about the threats of the dam of the Kyiv hydroelectric power station and the reservoir"'')
"Аргументы и факты" о реальных угрозах дамбы Киевского водохранилища и ГЭС
(''tr. ""Arguments and Facts" about the real threats of the dam of the Kyiv reservoir and hydroelectric power station"'')
"Известия" о проблематике плотины Киевского водохранилища и ГЭС
(''tr. ""Izvestia" about the problems of the dam of the Kyiv reservoir and hydroelectric power station"'')
(''tr. "UNIAN expert on the threats of the Kyiv reservoir dam"'') {{Authority control Border rivers Belarus–Russia border Belarus–Ukraine border Ottoman Empire–Russian Empire border Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth–Russian Empire border International rivers of Europe Ramsar sites in Belarus Rivers of Belarus Rivers of Cherkasy Oblast Rivers of Dnipropetrovsk Oblast Rivers of Gomel Region Rivers of Kherson Oblast Rivers of Kyiv Rivers of Mogilev Region Rivers of Poltava Oblast Rivers of Smolensk Oblast Rivers of Vitebsk Region Rivers of Zaporizhzhia Oblast