Disilene on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Disilene is an
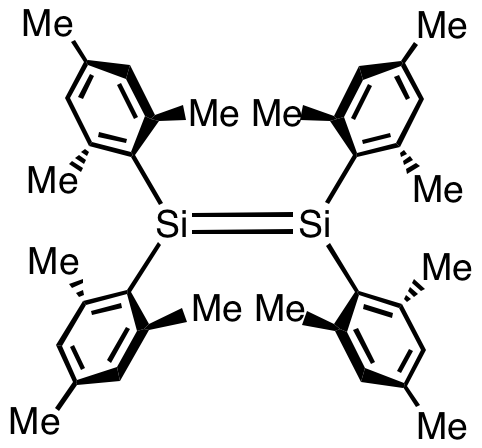 Disilenes bearing sterically bulky substituents are isolable and have been well characterized although they remain mainly of academic interest. The first stabilised disilene was tetramesityldisilene, (C6Me3H2)4Si2. The Si=Si distance in this molecule is 2.15 Å, about 10% shorter than a typical Si–Si single bond. The Si2C4 core is roughly planar. Such species are typically prepared by reduction of organosilicon halides:
:2 R2SiCl2 + 4 Na → R2Si=SiR2 + 4 NaCl.
An alternative synthesis involves
Disilenes bearing sterically bulky substituents are isolable and have been well characterized although they remain mainly of academic interest. The first stabilised disilene was tetramesityldisilene, (C6Me3H2)4Si2. The Si=Si distance in this molecule is 2.15 Å, about 10% shorter than a typical Si–Si single bond. The Si2C4 core is roughly planar. Such species are typically prepared by reduction of organosilicon halides:
:2 R2SiCl2 + 4 Na → R2Si=SiR2 + 4 NaCl.
An alternative synthesis involves
inorganic compound
In chemistry, an inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bonds, that is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as '' inorganic chemis ...
with the chemical formula
In chemistry, a chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, ...
. The name ''disilene'', referring to the structure of a particular prototropic tautomer
Tautomers () are structural isomers (constitutional isomers) of chemical compounds that readily interconvert.
The chemical reaction interconverting the two is called tautomerization. This conversion commonly results from the relocation of a hy ...
of the molecule. It is the simplest silene
''Silene'' is a genus of flowering plants in the family Caryophyllaceae. Containing nearly 900 species, it is the largest genus in the family. Common names include campion and catchfly. Many ''Silene'' species are widely distributed, particularl ...
.
Properties and bonding
Disilene is a molecule with one Si=Si bond, and four equivalent Si-H bonds. Unlike ethylene, disilene is kinetically unstable with respect to tautomerisation. Disilene has two other tautomers, that are very close in energy: (μ2-''H'')disilene, and disilanylidene.Organodisilenes
 Disilenes bearing sterically bulky substituents are isolable and have been well characterized although they remain mainly of academic interest. The first stabilised disilene was tetramesityldisilene, (C6Me3H2)4Si2. The Si=Si distance in this molecule is 2.15 Å, about 10% shorter than a typical Si–Si single bond. The Si2C4 core is roughly planar. Such species are typically prepared by reduction of organosilicon halides:
:2 R2SiCl2 + 4 Na → R2Si=SiR2 + 4 NaCl.
An alternative synthesis involves
Disilenes bearing sterically bulky substituents are isolable and have been well characterized although they remain mainly of academic interest. The first stabilised disilene was tetramesityldisilene, (C6Me3H2)4Si2. The Si=Si distance in this molecule is 2.15 Å, about 10% shorter than a typical Si–Si single bond. The Si2C4 core is roughly planar. Such species are typically prepared by reduction of organosilicon halides:
:2 R2SiCl2 + 4 Na → R2Si=SiR2 + 4 NaCl.
An alternative synthesis involves photolysis
Photodissociation, photolysis, photodecomposition, or photofragmentation is a chemical reaction in which molecules of a chemical compound are broken down by photons. It is defined as the interaction of one or more photons with one target molecule. ...
of trisilacyclopropanes. When the R group is not bulky, cyclic or polymeric, polysilanes are the products.
In one study''Fused Tricyclic Disilenes with Highly Strained Si-Si Double Bonds: Addition of a Si-Si Single Bond to a Si-Si Double Bond'' Ryoji Tanaka, Takeaki Iwamoto, and Mitsuo Kira Angewandte Chemie International Edition
''Angewandte Chemie'' (, meaning "Applied Chemistry") is a weekly peer-reviewed scientific journal that is published by Wiley-VCH on behalf of the German Chemical Society (Gesellschaft Deutscher Chemiker). Publishing formats include feature-leng ...
Volume 45, Issue 38 , Pages 6371 - 6373 2006 a disilene is prepared by an intramolecular coupling of a 1,1-dibromosilane with potassium graphite. The silicon double bond in the resulting compound has a bond length
In molecular geometry, bond length or bond distance is defined as the average distance between nuclei of two bonded atoms in a molecule. It is a transferable property of a bond between atoms of fixed types, relatively independent of the rest of ...
of 227 picometer
The picometre (international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: pm) or picometer (American spelling) is a unit of length in the International System of Units (SI), equal to , or one trillionth of ...
(second largest ever found) with trans-bent angles 33° and 31° (by X-ray diffraction
X-ray crystallography is the experimental science determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles ...
).
:
In addition to this the substituents around the Si-Si bond are twisted by 43°. The disilene isomerizes to a tetracyclic compound by heating at 110°C in xylene
In organic chemistry, xylene or xylol (; IUPAC name: dimethylbenzene) are any of three organic compounds with the formula . They are derived from the substitution of two hydrogen atoms with methyl groups in a benzene ring; which hydrogens are s ...
thereby releasing its strain energy
In physics, the elastic potential energy gained by a wire during elongation with a tensile (stretching) force is called strain energy. For linearly elastic materials, strain energy is:
: U = \frac 1 2 V \sigma \epsilon = \frac 1 2 V E \epsilon ...
.
See also
* Disilane *Disilyne
Disilyne is a silicon hydride with the formula . Several isomers are possible, but none are sufficiently stable to be of practical value. Substituted disilynes contain a formal silicon–silicon triple bond and as such are sometimes written R2Si ...
References
{{Hydrides by group Silicon hydrides