Dipodidae on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Jerboas (from ar, جربوع ') are hopping desert rodents found throughout
 * Family Dipodidae
** Subfamily
* Family Dipodidae
** Subfamily
Long Eared Jerboa caught on film
BBC - retrieved 10 December 2007 {{Taxonbar, from=Q273071 Dipodoid rodents Extant Miocene first appearances Rodents of North Africa
North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
and Asia, and are members of the family Dipodidae. They tend to live in hot deserts.
When chased, jerboas can run at up to . Some species are preyed on by little owls (''Athene noctua'') in central Asia. Most species of jerboas have excellent hearing that they use to avoid becoming the prey of nocturnal predators. The typical lifespan of a jerboa is around 6 years.
Taxonomy
Jerboas, as previously defined, were thought to be paraphyletic, with the jumping mice (Zapodidae
Zapodidae, the jumping mice, is a family of mouse-like rodents in North America and China.
Although mouse-like in general appearance, these rodents are distinguished by their elongated hind limbs, and, typically, by the presence of four pairs o ...
) and birch mice (Sminthidae
Sminthidae is a family of mouse-like jumping rodents. They are represented by only one extant genus, ''Sicista'', represented by 19 species found throughout most of Eurasia, from central Europe east to Siberia, and south to southern China. However, ...
) also classified in the family Dipodidae. However, phylogenetic analysis split all three as distinct families, leaving just the jerboas in Dipodidae and revealing them to be a monophyletic group.
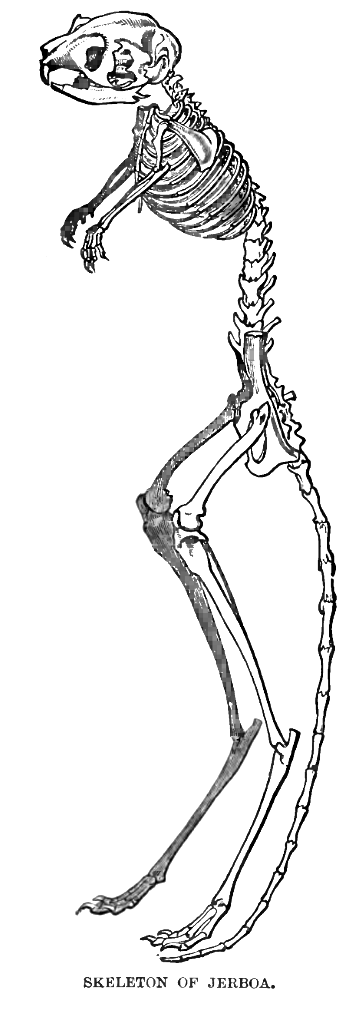
Anatomy and body features
Jerboas look somewhat like miniaturekangaroo
Kangaroos are four marsupials from the family Macropodidae (macropods, meaning "large foot"). In common use the term is used to describe the largest species from this family, the red kangaroo, as well as the antilopine kangaroo, eastern ...
s, and have some external similarities. Both have long hind legs, short forelegs, and long tails. Jerboas move around in a similar manner to kangaroos, which is by hopping, or saltation. However, their anatomy is more attuned towards erratic hopping locomotion, making use of sharp turns and great vertical leaps to confuse and escape predators, rather than for sustained hopping over long periods of time. It has been found that when executing their vertical leaps primary tendons in the hindlimbs only recovered and reused on average 4.4% of energy contributed to the jump, lower than many hopping animals.
Like other bipedal
Bipedalism is a form of terrestrial locomotion where an organism moves by means of its two rear limbs or legs. An animal or machine that usually moves in a bipedal manner is known as a biped , meaning 'two feet' (from Latin ''bis'' 'double' ...
animals, their foramen magnum — the hole at the base of the skull — is forward-shifted, which enhances two-legged locomotion. The tail of a jerboa can be longer than its head and body, and a white cluster of hair is commonly seen at the end of the tail. Jerboas use their tails to balance when hopping, and as a prop when sitting upright. Jerboa fur is fine, and usually the colour of sand. This colour usually matches the jerboa habitat
In ecology, the term habitat summarises the array of resources, physical and biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species habitat can be seen as the physical ...
(an example of cryptic colouration
Camouflage is the use of any combination of materials, coloration, or illumination for concealment, either by making animals or objects hard to see, or by disguising them as something else. Examples include the leopard's spotted coat, the b ...
). Some species of the jerboa family have long ears
An ear is the organ that enables hearing and, in mammals, body balance using the vestibular system. In mammals, the ear is usually described as having three parts—the outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear. The outer ear consists o ...
like a rabbit, whilst others have ears that are short like those of a mouse or rat.
Behavior
The bipedal locomotion of jerboas involves hopping, skipping, and running gaits, associated with rapid and frequent, difficult-to-predict changes in speed and direction, facilitating predator evasion relative to quadrupedal locomotion. This may explain why evolution of bipedal locomotion is favored in desert-dwelling rodents that forage in open habitats. Jerboas are most active at twilight (crepuscular). During the heat of the day, they shelter in burrows. At night, they leave the burrows due to the cooler temperature of their environment. They dig the entrances to their burrow near plant life, especially along field borders. During therainy season
The rainy season is the time of year when most of a region's average annual rainfall occurs.
Rainy Season may also refer to:
* ''Rainy Season'' (short story), a 1989 short horror story by Stephen King
* "Rainy Season", a 2018 song by Monni
* '' ...
, they make tunnels in mounds or hills to reduce the risk of flooding. In the summer, jerboas occupying holes plug the entrance to keep out hot air and, some researchers speculate, predators. In most cases, burrows are constructed with an emergency exit that ends just below the surface or opens at the surface but is not strongly obstructed. This allows the jerboa to quickly escape predators.
Related jerboas often create four types of burrows. A temporary, summer day burrow is used for cover while hunting during the daylight. They have a second, temporary burrow used for hunting at night. They also have two permanent burrows: one for summer and one for winter. The permanent summer burrow is actively used throughout the summer and the young are raised there. Jerboas hibernate during the winter and use the permanent winter burrow for this. Temporary burrows are shorter in length than permanent burrows. Just like other animals that hibernate, these creatures are heavier pre-hibernation specifically in ungrazed sites (Shuai). Also, more food availability during pre-hibernation contributes to larger jerboa body mass in ungrazed regions, and entices more jerboas to migrate to ungrazed areas during post-hibernation. Grazing negatively impacts the Jerboa pre- and post-hibernation population, but not the survival rate.
Jerboas are solitary creatures. Once they reach adulthood, they usually have their own burrow and search for food on their own. However, occasional "loose colonies" may form, whereby some species of jerboa dig communal burrows that offer extra warmth when it is cold outside.
Diet
Most jerboas rely on plant material as the main component of their diet, but they cannot eat hard seeds. Some species opportunistically eat beetles and other insects they come across. Unlikegerbil
The Mongolian gerbil or Mongolian jird (''Meriones unguiculatus'') is a small rodent belonging to the subfamily Gerbillinae. Their body size is typically , with a tail, and body weight , with adult males larger than females. The animal is us ...
s, jerboas are not known to store their food.
Communication and perception
Many species within the family Dipodidae engage indust bathing
Dust bathing (also called sand bathing) is an animal behavior characterized by rolling or moving around in dust, dry earth or sand, with the likely purpose of removing parasites from fur, feathers or skin. Dust bathing is a maintenance behavior ...
, often a way to use chemical communication. Their keen hearing suggests they may use sounds or vibrations to communicate.
Reproduction
Mating systems of closely related species in the family Dipodidae suggest that they may be polygynous. For some closely related jerboa species, mating usually happens a short time after awaking from winter hibernation. A female breeds twice in the summer, and raises from two to six young. Gestation time is between 25 and 35 days. Little is known about parental investment in long-eared jerboas. Like most mammals, females nurse and care for their young at least until they are weaned.Classification
 * Family Dipodidae
** Subfamily
* Family Dipodidae
** Subfamily Cardiocraniinae
Cardiocraniinae is a subfamily of rodents in the family Dipodidae, named by the Russian zoologist Boris Stepanovich Vinogradov (1891–1958) in 1925. These jumping rodents are small mammals, less than 20 cm long.
Taxonomy
*Genus '' Cardi ...
*** ''Cardiocranius
The five-toed pygmy jerboa (''Cardiocranius paradoxus'') is a species of rodent in the family Dipodidae. It is monotypic within the genus ''Cardiocranius''.
It is found in China, Kazakhstan, and Mongolia.
Its natural habitat is temperate desert ...
''
**** Five-toed pygmy jerboa
The five-toed pygmy jerboa (''Cardiocranius paradoxus'') is a species of rodent in the family Dipodidae. It is monotypic within the genus ''Cardiocranius''.
It is found in China, Kazakhstan, and Mongolia.
Its natural habitat is temperate desert ...
, ''Cardiocranius paradoxus''
*** ''Salpingotus
''Salpingotus'' is a genus of rodent in the family Dipodidae. It contains the following species:
* Genus ''Salpingotus''
**Subgenus ''Anguistodontus''
*** Thick-tailed pygmy jerboa (''Salpingotus crassicauda'')
**Subgenus '' Prosalpingotus''
*** ...
''
**** Thick-tailed pygmy jerboa, ''Salpingotus crassicauda''
**** Heptner's pygmy jerboa, ''Salpingotus heptneri''
**** Kozlov's pygmy jerboa, ''Salpingotus kozlovi''
**** Baluchistan pygmy jerboa, ''Salpingotus michaelis''
**** Pallid pygmy jerboa, ''Salpingotus pallidus''
**** Thomas's pygmy jerboa, ''Salpingotus thomasi''
** Subfamily Dipodinae
Dipodinae is a subfamily of Dipodidae.
Classification
Subfamily Dipodinae
*Tribe Dipodini
**Genus '' Dipus''
*** Northern three-toed jerboa, ''Dipus sagitta''
**Genus '' Eremodipus''
*** Lichtenstein's jerboa, ''Eremodipus lichtensteini''
**Gen ...
*** ''Dipus
''Dipus'' is a genus of jerboa. Today only a single species is extant, the northern three-toed jerboa ''(Dipus sagitta)'', widespread throughout Central Asia. The genus has a fossil record that dates back to the Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the ...
''
**** Northern three-toed jerboa, ''Dipus sagitta''
*** '' Eremodipus''
**** Lichtenstein's jerboa, ''Eremodipus lichensteini''
*** '' Jaculus''
**** Blanford's jerboa, ''Jaculus blanfordi''
**** Lesser Egyptian jerboa
The lesser jerboa (''Jaculus jaculus'') is a small rodent of Africa and the Middle East. Its diet consists mainly of seeds and grasses. Description
A small rodent, it is sometimes likened to a tiny kangaroo due to its incredibly large hind legs ...
, ''Jaculus jaculus''
**** Greater Egyptian jerboa
The greater Egyptian jerboa (''Jaculus orientalis'') is a species of rodent in the family Dipodidae. It is found in Algeria, Egypt, Libya, Morocco, Saudi Arabia, Tunisia, and is possibly extinct in the Negev Desert of Israel. Its natural habitat ...
, ''Jaculus orientalis''
**** Turkmen jerboa, ''Jaculus turcmenicus''
*** '' Stylodipus''
**** Andrews's three-toed jerboa
Andrews's three-toed jerboa, or the Mongolian jerboa, (''Stylodipus andrewsi'') is a species of rodent in the family Dipodidae. It is found in China (Inner Mongolia, Gansu, and Ningxia provinces) and Mongolia.
Description
Andrews's three-toed j ...
, ''Stylodipus andrewsi''
**** Mongolian three-toed jerboa
The Mongolian three-toed jerboa (''Stylodipus sungorus'') is a species of rodent in the family Dipodidae. It is found in Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country i ...
, ''Stylodipus sungorus''
**** Thick-tailed three-toed jerboa
The thick-tailed three-toed jerboa (''Stylodipus telum'') is a species of rodent in the family Dipodidae. It is found in China, Kazakhstan, Russia, Turkmenistan, Ukraine, and Uzbekistan. Its typical habitat is steppe, desert and mountain grassla ...
, ''Stylodipus telum''
** Subfamily Euchoreutinae
The long-eared jerboa (''Euchoreutes naso'') is a nocturnal mouse-like rodent with a long tail, long hind legs for jumping, and exceptionally large ears. It is distinct enough that authorities consider it to be the only member of both its genus ...
*** '' Euchoreutes''
**** Long-eared jerboa
The long-eared jerboa (''Euchoreutes naso'') is a nocturnal mouse-like rodent with a long tail, long hind legs for jumping, and exceptionally large ears. It is distinct enough that authorities consider it to be the only member of both its genu ...
, ''Euchoreutes naso''
** Subfamily Allactaginae
Allactaginae is a subfamily of rodents.
Classification
Subfamily Allactaginae
*Genus ''Allactaga''
**''incertae sedis''
***''Allactaga toussi''
**Subgenus ''Allactaga''
***Small five-toed jerboa, ''Allactaga elater''
*** Iranian jerboa, ''Alla ...
*** '' Allactaga''
**** Balikun jerboa, ''Allactaga balikunica''
**** Gobi jerboa, ''Allactaga bullata''
**** Small five-toed jerboa, ''Allactaga elater''
**** Euphrates jerboa, ''Allactaga euphratica''
**** Iranian jerboa, ''Allactaga firouzi''
**** Hotson's jerboa, ''Allactaga hotsoni''
**** Great jerboa
The great jerboa (''Allactaga major'') is a species of rodent in the family Dipodidae
Jerboas (from ar, جربوع ') are hopping desert rodents found throughout North Africa and Asia, and are members of the family Dipodidae. They tend to li ...
, ''Allactaga major''
**** Severtzov's jerboa
Severtzov's jerboa (''Allactaga severtzovi'') is an herbivorous species of rodent in the family Dipodidae.
It is found in Kazakhstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan (, ; uz, Ozbekiston, italic=yes / , ; russian: Узбе ...
, ''Allactaga severtzovi''
**** Mongolian five-toed jerboa, ''Allactaga sibirica''
**** Four-toed jerboa
The four-toed jerboa (''Allactaga tetradactyla'') is a rodent of the family Dipodidae and genus '' Allactaga'' that has four digits. It is the sole species in the subgenus ''Scarturus''. Four-toed jerboas are native to Egypt and Libya. They liv ...
, ''Allactaga tetradactyla''
**** Vinogradov's jerboa
Vinogradov's jerboa (''Allactaga vinogradovi'') is a species of rodent in the family Dipodidae.
It is found in Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan (, ; uz, Ozbekiston, italic=yes / , ; russian: Узбекистан) ...
, ''Allactaga vinogradovi''
**** Bobrinski's jerboa, ''Allactodipus bobrinskii''
*** '' Pygeretmus''
**** Lesser fat-tailed jerboa, ''Pygeretmus platyurus''
**** Dwarf fat-tailed jerboa, ''Pygeretmus pumilio''
**** Greater fat-tailed jerboa, ''Pygeretmus shitkovi''
** Subfamily Paradipodinae
*** '' Paradipus''
**** Comb-toed jerboa
The comb-toed jerboa (''Paradipus ctenodactylus'') is a species of rodent in the family Dipodidae. It is monotypic within the genus ''Paradipus''. It is found in Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan (, ; uz, Ozbekiston, italic ...
, ''Paradipus ctenodactylus''
See also
* Hopping mouse – a similarmurid
In Sufism, a ''murīd'' (Arabic مُرِيد 'one who seeks') is a novice committed to spiritual enlightenment by ''sulūk'' (traversing a path) under a spiritual guide, who may take the title murshid, '' pir'' or ''shaykh''. A ''sālik'' or Su ...
rodent native to Australia; an example of parallel evolution
Parallel evolution is the similar development of a trait in distinct species that are not closely related, but share a similar original trait in response to similar evolutionary pressure.Zhang, J. and Kumar, S. 1997Detection of convergent and paral ...
* Jumping mouse
Zapodidae, the jumping mice, is a family of mouse-like rodents in North America and China.
Although mouse-like in general appearance, these rodents are distinguished by their elongated hind limbs, and, typically, by the presence of four pairs ...
– a nondesert-dwelling relative of jerboas in the family Zapodidae
Zapodidae, the jumping mice, is a family of mouse-like rodents in North America and China.
Although mouse-like in general appearance, these rodents are distinguished by their elongated hind limbs, and, typically, by the presence of four pairs o ...
, native to China and North America
* Kangaroo rat
Kangaroo rats, small mostly nocturnal rodents of genus ''Dipodomys'', are native to arid areas of western North America. The common name derives from their bipedal form. They hop in a manner similar to the much larger kangaroo, but developed t ...
and kangaroo mouse
A kangaroo mouse is either one of the two species of jumping mouse (genus ''Microdipodops'') native to the deserts of the southwestern United States, predominantly found in the state of Nevada. The name "kangaroo mouse" refers to the species' ext ...
– similar heteromyid rodents native to North America; an example of convergence
Convergence may refer to:
Arts and media Literature
*''Convergence'' (book series), edited by Ruth Nanda Anshen
*Convergence (comics), "Convergence" (comics), two separate story lines published by DC Comics:
**A four-part crossover storyline that ...
* Kultarr
The kultarr (''Antechinomys laniger'') (also called the "jerboa-marsupial" or marsupial jerboa) is a small insectivorous nocturnal marsupial inhabiting the arid interior of Australia. Preferred habitat includes stony deserts, shrubland, woodland ...
– a distantly related marsupial
Marsupials are any members of the mammalian infraclass Marsupialia. All extant marsupials are endemic to Australasia, Wallacea and the Americas. A distinctive characteristic common to most of these species is that the young are carried in a ...
with a similar body plan and coloration; another example of convergence: They use quadrupedal locomotion, but their large aerial phases cause them to be confused with hopping mice.
* Springhare
''Pedetes'' is a genus of rodent, the springhares, in the family Pedetidae. Members of the genus are distributed across southern and Eastern Africa.
Species
A number of species both extant and extinct are classified in the genus ''Pedetes''. ...
– a similar pedetid
The Pedetidae are a family of mammals from the rodent order. The two living species, the springhares, are distributed throughout much of southern Africa and also around Kenya, Tanzania, and Uganda. Fossils have been found as far north as Turkey.M ...
rodent native to southern and eastern Africa
References
External links
Long Eared Jerboa caught on film
BBC - retrieved 10 December 2007 {{Taxonbar, from=Q273071 Dipodoid rodents Extant Miocene first appearances Rodents of North Africa