Diplura on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The
/ref>
 Diplurans are typically long, with most falling between . However, some species of ''
Diplurans are typically long, with most falling between . However, some species of ''
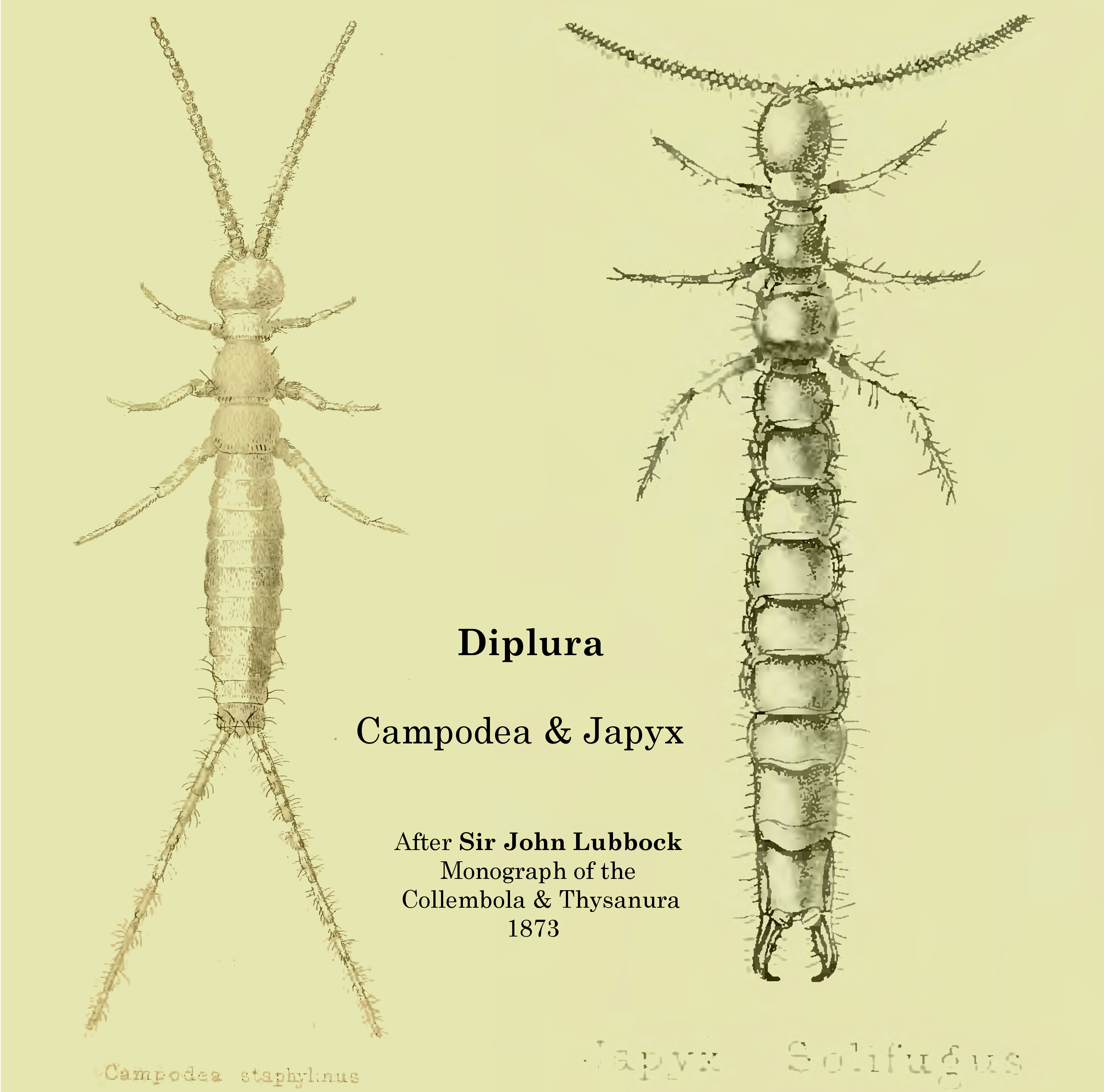 Several major lineages within ''Diplura'' are readily recognizable by the structure of their cerci.
* Japygidae: possess forceps-like cerci (resembling those of an
Several major lineages within ''Diplura'' are readily recognizable by the structure of their cerci.
* Japygidae: possess forceps-like cerci (resembling those of an
order
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to:
* Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood
* Heterarchy, a system of organization wherein the elements have the potential to be ranked a number of ...
Diplura ("two-pronged bristletails") is one of three orders of non-insect hexapods within the class Entognatha (alongside Collembola (springtail
Springtails (Collembola) form the largest of the three lineages of modern hexapods that are no longer considered insects (the other two are the Protura and Diplura). Although the three orders are sometimes grouped together in a class called ...
s) and Protura). The name "diplura", or "two tails", refers to the characteristic pair of caudal appendages or filaments at the terminal end of the body.
Around 800 species of diplurans have been described, of which around 170 occur in North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and th ...
and 12 in Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It ...
.Bugguide.net. Class Diplura - Two-pronged Bristletails/ref>
Anatomy
 Diplurans are typically long, with most falling between . However, some species of ''
Diplurans are typically long, with most falling between . However, some species of ''Japyx
''Japyx'' is a genus of diplurans belonging to the family Japygidae. These eyeless, predatory hexapods largely shun direct sunlight, remaining under stones and among detritus
In biology, detritus () is dead particulate organic material, as d ...
'' may reach . They have no eyes and, apart from the darkened cerci in some species, they are unpigmented. Diplurans have long antennae with 10 or more bead
A bead is a small, decorative object that is formed in a variety of shapes and sizes of a material such as stone, bone, shell, glass, plastic, wood, or pearl and with a small hole for threading or stringing. Beads range in size from under ...
-like segments projecting forward from the head. The abdomens of diplurans bear eversible vesicles, which seem to absorb moisture from the environment and help with the animal's water balance. The body segments themselves may display several types of seta
In biology, setae (singular seta ; from the Latin word for "bristle") are any of a number of different bristle- or hair-like structures on living organisms.
Animal setae
Protostomes
Annelid setae are stiff bristles present on the body. ...
e, or scales and setae.
Diplurans possess a characteristic pair of cerci projecting backwards from the last of the 11 abdominal somite
The somites (outdated term: primitive segments) are a set of bilaterally paired blocks of paraxial mesoderm that form in the embryonic stage of somitogenesis, along the head-to-tail axis in segmented animals. In vertebrates, somites subdivide ...
s. These cerci may be long and filamentous or short and pincer-like, leading to occasional confusion with earwig
Earwigs make up the insect order Dermaptera. With about 2,000 species in 12 families, they are one of the smaller insect orders. Earwigs have characteristic cerci, a pair of forcep-like pincers on their abdomen, and membranous wings folde ...
s. Some diplurans have the ability to shed their cerci if necessary (autotomy
Autotomy (from the Greek ''auto-'', "self-" and ''tome'', "severing", αὐτοτομία) or self-amputation, is the behaviour whereby an animal sheds or discards one or more of its own appendages, usually as a self-defense mechanism to elude ...
). Moulting occurs up to 30 times throughout the life of a dipluran, which is estimated to last up to one year.
As entognaths, the mouthparts are concealed within a small pouch by the lateral margins of the head capsule. The mandibles usually have several apical teeth. Diplurans do not possess any eyes or wings.
In males, glandular setae or disculi may be visible along the first abdominal sternite. External genital organs are present on the eighth abdominal segment.
Ecology
Diplurans are common in moistsoil
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth or dirt, is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, liquids, and organisms that together support life. Some scientific definitions distinguish ''dirt'' from ''soil'' by restricting the former ...
, leaf litter
Plant litter (also leaf litter, tree litter, soil litter, litterfall or duff) is dead plant material (such as leaves, bark, needles, twigs, and cladodes) that have fallen to the ground. This detritus or dead organic material and its constituent ...
or humus
In classical soil science, humus is the dark organic matter in soil that is formed by the decomposition of plant and animal matter. It is a kind of soil organic matter. It is rich in nutrients and retains moisture in the soil. Humus is the Lati ...
, but are rarely seen because of their size and subterranean lifestyles. They have biting mouthparts
Mouthparts may refer to:
* The parts of a mouth
** Arthropod mouthparts
The mouthparts of arthropods have evolved into a number of forms, each adapted to a different style or mode of feeding. Most mouthparts represent modified, paired append ...
and feed on a variety of live prey and dead organic matter. Those species with long cerci are herbivorous.
Diplurans are found on nearly all land masses, except Antarctica and several oceanic islands. Their role as soil-dwelling organisms may play a key role in indicating soil quality, and as a measure of anthropogenic
Anthropogenic ("human" + "generating") is an adjective that may refer to:
* Anthropogeny, the study of the origins of humanity
Counterintuitively, anthropogenic may also refer to things that have been generated by humans, as follows:
* Human i ...
impact (e.g. soil nutrient depletion as a result of farming).
Reproduction
Like other non-insect hexapods, diplurans practiceexternal fertilisation
External fertilization is a mode of reproduction in which a male organism's sperm fertilizes a female organism's egg outside of the female's body.
It is contrasted with internal fertilization, in which sperm are introduced via insemination and then ...
. Males lay up to 200 spermatophore
A spermatophore or sperm ampulla is a capsule or mass containing spermatozoa created by males of various animal species, especially salamanders and arthropods, and transferred in entirety to the female's ovipore during reproduction. Spermatophore ...
s a week, which are held off the ground by short stalks and probably only remain viable for about two days. The female collects the spermatophore with her genital opening, and later lays eggs
Humans and human ancestors have scavenged and eaten animal eggs for millions of years. Humans in Southeast Asia had domesticated chickens and harvested their eggs for food by 1,500 BCE. The most widely consumed eggs are those of fowl, especial ...
in a cavity in the ground. The hatchlings (or nymph
A nymph ( grc, νύμφη, nýmphē, el, script=Latn, nímfi, label=Modern Greek; , ) in ancient Greek folklore is a minor female nature deity. Different from Greek goddesses, nymphs are generally regarded as personifications of nature, are ...
s) do not undergo metamorphosis
Metamorphosis is a biological process by which an animal physically develops including birth or hatching, involving a conspicuous and relatively abrupt change in the animal's body structure through cell growth and differentiation. Some inse ...
, but resemble the adults, apart from their smaller size, lesser number of seta
In biology, setae (singular seta ; from the Latin word for "bristle") are any of a number of different bristle- or hair-like structures on living organisms.
Animal setae
Protostomes
Annelid setae are stiff bristles present on the body. ...
e and their lack of reproductive organs.
Lineages
 Several major lineages within ''Diplura'' are readily recognizable by the structure of their cerci.
* Japygidae: possess forceps-like cerci (resembling those of an
Several major lineages within ''Diplura'' are readily recognizable by the structure of their cerci.
* Japygidae: possess forceps-like cerci (resembling those of an earwig
Earwigs make up the insect order Dermaptera. With about 2,000 species in 12 families, they are one of the smaller insect orders. Earwigs have characteristic cerci, a pair of forcep-like pincers on their abdomen, and membranous wings folde ...
). Usually very aggressive predatory diplurans, using their pincer-like cerci to capture prey, including springtail
Springtails (Collembola) form the largest of the three lineages of modern hexapods that are no longer considered insects (the other two are the Protura and Diplura). Although the three orders are sometimes grouped together in a class called ...
s, isopods
Isopoda is an order of crustaceans that includes woodlice and their relatives. Isopods live in the sea, in fresh water, or on land. All have rigid, segmented exoskeletons, two pairs of antennae, seven pairs of jointed limbs on the thorax, and ...
, small myriapod
Myriapods () are the members of subphylum Myriapoda, containing arthropods such as millipedes and centipedes. The group contains about 13,000 species, all of them terrestrial.
The fossil record of myriapods reaches back into the late Silurian, ...
s, insect
Insects (from Latin ') are pancrustacean hexapod invertebrates of the class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body ( head, thorax and abdomen), three pa ...
larva
A larva (; plural larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into adults. Animals with indirect development such as insects, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle.
...
e, and even other diplurans.
* Projapygidae
The Projapygidae are a family of hexapods in the order Diplura
The order Diplura ("two-pronged bristletails") is one of three orders of non-insect hexapods within the class Entognatha (alongside Collembola (springtails) and Protura). The n ...
: possess stout, short, and rigid cerci.
* Campodeidae
The Campodeidae are a family of hexapods belonging to the order Diplura. These pale, eyeless hexapods, the largest of which grow to around 12 mm in length, can be recognised by the two long, many-segmented cerci at the end of the abdomen. ...
: possess elongate, flexible cerci that may be as long as the antennae and have many segments. Feed on soil fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately fr ...
, mite
Mites are small arachnids (eight-legged arthropods). Mites span two large orders of arachnids, the Acariformes and the Parasitiformes, which were historically grouped together in the subclass Acari, but genetic analysis does not show clear e ...
s, springtails, and other small soil invertebrates, as well as detritus
In biology, detritus () is dead particulate organic material, as distinguished from dissolved organic material. Detritus typically includes the bodies or fragments of bodies of dead organisms, and fecal material. Detritus typically hosts comm ...
.
Relatives
The relationships among the four groups of hexapods are not resolved, but most recent studies argue against amonophyletic
In cladistics for a group of organisms, monophyly is the condition of being a clade—that is, a group of taxa composed only of a common ancestor (or more precisely an ancestral population) and all of its lineal descendants. Monophyletic gr ...
Entognatha. The fossil record
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
of the Diplura is sparse, but one apparent dipluran dates from the Carboniferous
The Carboniferous ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic that spans 60 million years from the end of the Devonian Period million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Permian Period, million years ago. The name ''Carboniferou ...
. This early dipluran, '' Testajapyx'', had compound eye
A compound eye is a visual organ found in arthropods such as insects and crustaceans. It may consist of thousands of ommatidia, which are tiny independent photoreception units that consist of a cornea, lens, and photoreceptor cells which disti ...
s, and mouthparts
Mouthparts may refer to:
* The parts of a mouth
** Arthropod mouthparts
The mouthparts of arthropods have evolved into a number of forms, each adapted to a different style or mode of feeding. Most mouthparts represent modified, paired append ...
that more closely resembled those of true insects.
References
External links
* {{Taxonbar, from=Q221563 Arthropod orders Extant Pennsylvanian first appearances