Diocese on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a
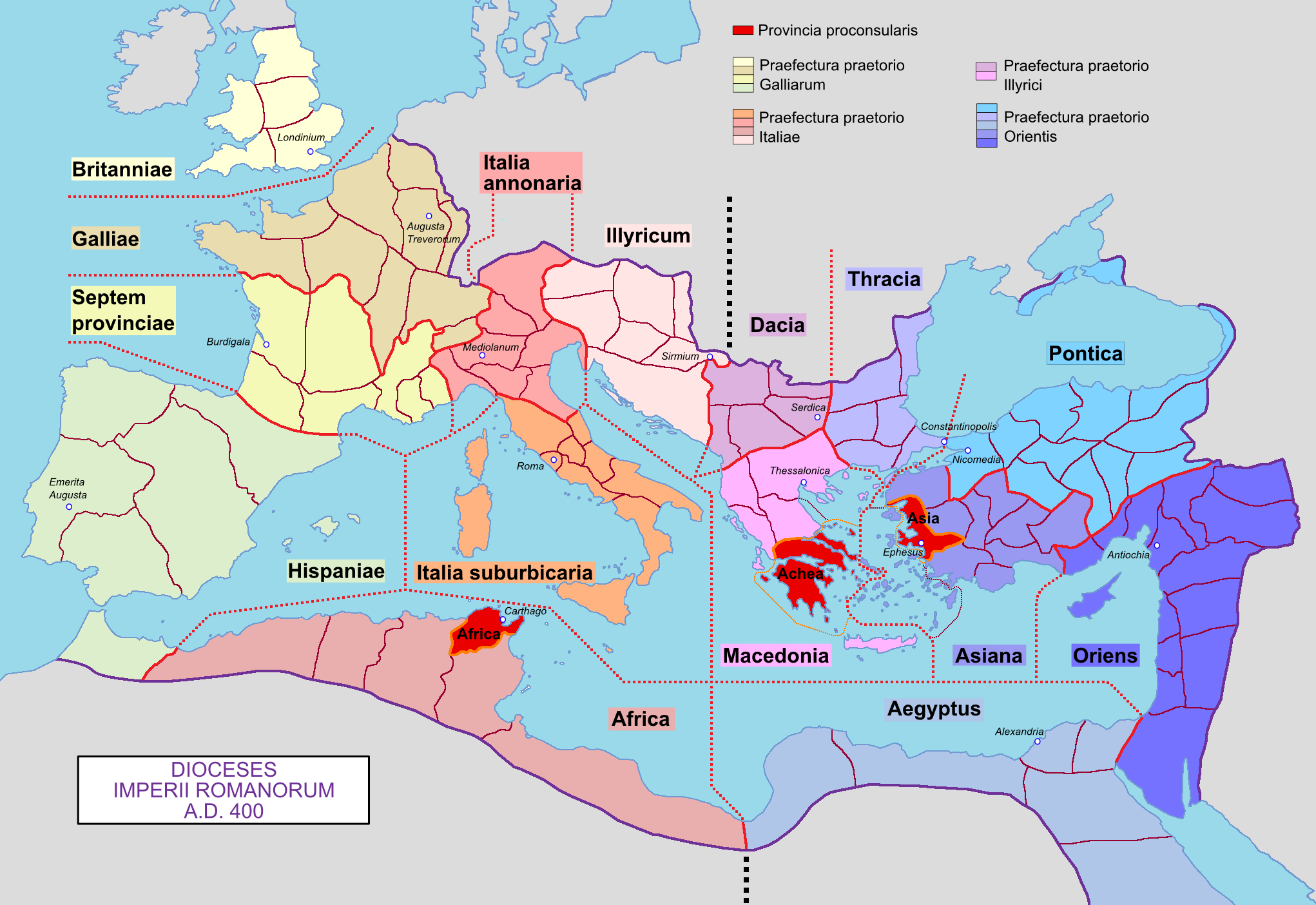 In the later organization of the
In the later organization of the
 The
The
 In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop
A bishop is an ordained member of the clergy who is entrusted with a position of Episcopal polity, authority and oversight in a religious institution. In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance and administration of di ...
.
History
 In the later organization of the
In the later organization of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
, the increasingly subdivided provinces
A province is an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman , which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions outside Italy. The term ''provi ...
were administratively associated in a larger unit, the diocese
In Ecclesiastical polity, church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided Roman province, prov ...
(Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
''dioecesis'', from the Greek term διοίκησις, meaning "administration").
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose ...
was given legal status in 313 with the Edict of Milan
The Edict of Milan (; , ''Diatagma tōn Mediolanōn'') was the February 313 agreement to treat Christians benevolently within the Roman Empire. Frend, W. H. C. (1965). ''The Early Church''. SPCK, p. 137. Western Roman Emperor Constantine I and ...
. Churches began to organize themselves into dioceses based on the civil dioceses, not on the larger regional imperial districts. These dioceses were often smaller than the provinces
A province is an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman , which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions outside Italy. The term ''provi ...
. Christianity was declared the Empire's official religion by Theodosius I
Theodosius I ( ; 11 January 347 – 17 January 395), also known as Theodosius the Great, was Roman emperor from 379 to 395. He won two civil wars and was instrumental in establishing the Nicene Creed as the orthodox doctrine for Nicene C ...
in 380. Constantine I
Constantine I (27 February 27222 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was a Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337 and the first Roman emperor to convert to Christianity. He played a Constantine the Great and Christianity, pivotal ro ...
in 318 gave litigants the right to have court cases transferred from the civil courts to the bishops. This situation must have hardly survived Julian, 361–363. Episcopal courts are not heard of again in the East until 398 and in the West in 408. The quality of these courts was low, and not above suspicion as the Bishop of Alexandria Troas found that clergy were making a corrupt profit. Nonetheless, these courts were popular as people could get quick justice without being charged fees. Bishops had no part in the civil administration until the town councils, in decline, lost much authority to a group of 'notables' made up of the richest councilors, powerful and rich persons legally exempted from serving on the councils, retired military, and bishops post-AD 450. As the Western Empire
In modern historiography, the Western Roman Empire was the western provinces of the Roman Empire, collectively, during any period in which they were administered separately from the eastern provinces by a separate, independent imperial court. ...
collapsed in the 5th century, bishops in Western Europe assumed a larger part of the role of the former Roman governors. A similar, though less pronounced, development occurred in the East, where the Roman administrative apparatus was largely retained by the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
. In modern times, many dioceses, though later subdivided, have preserved the boundaries of a long-vanished Roman administrative division. For Gaul, Bruce Eagles has observed that "it has long been an academic commonplace in France that the medieval dioceses, and their constituent '' pagi'', were the direct territorial successors of the Roman '' civitates''."
Modern usage of 'diocese' tends to refer to the sphere of a bishop's jurisdiction. This became commonplace during the self-conscious "classicizing" structural evolution of the Carolingian Empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–887) was a Franks, Frankish-dominated empire in Western and Central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as List of Frankish kings, kings of the Franks since ...
in the 9th century, but this usage had itself been evolving from the much earlier ''parochia'' ("parish
A parish is a territorial entity in many Christianity, Christian denominations, constituting a division within a diocese. A parish is under the pastoral care and clerical jurisdiction of a priest#Christianity, priest, often termed a parish pries ...
"; Late Latin derived from the Greek παροικία ''paroikia''), dating from the increasingly formalized Christian authority structure in the 4th century.
Archdiocese
Dioceses ruled by anarchbishop
In Christian denominations, an archbishop is a bishop of higher rank or office. In most cases, such as the Catholic Church, there are many archbishops who either have jurisdiction over an ecclesiastical province in addition to their own archdi ...
are commonly referred to as archdioceses; most are metropolitan see
Metropolitan may refer to:
Areas and governance (secular and ecclesiastical)
* Metropolitan archdiocese, the jurisdiction of a metropolitan archbishop
** Metropolitan bishop or archbishop, leader of an ecclesiastical "mother see"
* Metropolitan ...
s, being placed at the head of an ecclesiastical province
An ecclesiastical province is one of the basic forms of jurisdiction in Christian churches, including those of both Western Christianity and Eastern Christianity, that have traditional hierarchical structures. An ecclesiastical province consist ...
. In the Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
, some are suffragans of a metropolitan see or are directly subject to the Holy See
The Holy See (, ; ), also called the See of Rome, the Petrine See or the Apostolic See, is the central governing body of the Catholic Church and Vatican City. It encompasses the office of the pope as the Bishops in the Catholic Church, bishop ...
.
The term "archdiocese" is not found in Catholic canon law
The canon law of the Catholic Church () is "how the Church organizes and governs herself". It is the system of religious laws and ecclesiastical legal principles made and enforced by the hierarchical authorities of the Catholic Church to regul ...
, with the terms "diocese" and "episcopal see
An episcopal see is the area of a bishop's ecclesiastical jurisdiction.
Phrases concerning actions occurring within or outside an episcopal see are indicative of the geographical significance of the term, making it synonymous with ''diocese'' ...
" being applicable to the area under the ecclesiastical jurisdiction of any bishop. If the title of archbishop is granted on '' personal'' grounds to a diocesan bishop, his diocese does not thereby become an archdiocese.
Catholic Church
Canon Law of the Catholic Church
The canon law of the Catholic Church () is "how the Church organizes and governs herself". It is the system of religious laws and canon law, ecclesiastical legal principles made and enforced by the Hierarchy of the Catholic Church, hierarchical ...
defines a diocese as "a portion of the people of God which is entrusted to a bishop for him to shepherd with the cooperation of the presbyterium, so that, adhering to its pastor and gathered by him in the Holy Spirit through the gospel and the Eucharist, it constitutes a particular church in which the one, holy, catholic, and apostolic Church of Christ is truly present and operative."
Also known as ''particular churches'' or ''local churches'', dioceses are under the authority of a bishop
A bishop is an ordained member of the clergy who is entrusted with a position of Episcopal polity, authority and oversight in a religious institution. In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance and administration of di ...
. They are described as ecclesiastical
{{Short pages monitor