Digital streaming on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Streaming media is
streaming video
solutions used by schools and corporations. Practical streaming media was only made possible with advances in
 Although music streaming is no longer a freely replicable public good, streaming platforms such as Spotify, Deezer, Apple Music, SoundCloud, and Amazon Music have shifted music streaming to a Club good, club-type good. While some platforms, most notably Spotify, give customers access to a freemium service that enables the use of limited features for exposure to advertisements, most companies operate under a premium subscription model. Under such circumstances, music streaming is financially excludable, requiring that customers pay a monthly fee for access to a music library, but non-rival, since one customer's use does not impair another's.
Spotify has over 207 million users in 78 countries, Apple Music has about 60 million, and SoundCloud has 175 million. All platforms provide varying degrees of accessibility. Apple Music and Prime Music only offer their services for paid subscribers, whereas Spotify and SoundCloud offer freemium and premium services. Napster, owned by Rhapsody since 2011, has resurfaced as a music streaming platform offering subscription-based services to over 4.5 million users .
The music industry's response to music streaming was initially negative. Along with music piracy, streaming services disrupted the market and contributed to the fall in US revenue from $14.6 billion in 1999 to $6.3 billion in 2009. CDs and single-track downloads were not selling because content was freely available on the Internet. By 2018, however, music streaming revenue exceeded that of traditional revenue streams (e.g. record sales, album sales, downloads). Streaming revenue is now one of the largest driving forces behind the growth in the music industry. In an interview, Jonathan Dworkin, a senior vice president of strategy and business development at Universal, said, "We cannot be afraid of perpetual change, because that dynamism is driving growth."
Although music streaming is no longer a freely replicable public good, streaming platforms such as Spotify, Deezer, Apple Music, SoundCloud, and Amazon Music have shifted music streaming to a Club good, club-type good. While some platforms, most notably Spotify, give customers access to a freemium service that enables the use of limited features for exposure to advertisements, most companies operate under a premium subscription model. Under such circumstances, music streaming is financially excludable, requiring that customers pay a monthly fee for access to a music library, but non-rival, since one customer's use does not impair another's.
Spotify has over 207 million users in 78 countries, Apple Music has about 60 million, and SoundCloud has 175 million. All platforms provide varying degrees of accessibility. Apple Music and Prime Music only offer their services for paid subscribers, whereas Spotify and SoundCloud offer freemium and premium services. Napster, owned by Rhapsody since 2011, has resurfaced as a music streaming platform offering subscription-based services to over 4.5 million users .
The music industry's response to music streaming was initially negative. Along with music piracy, streaming services disrupted the market and contributed to the fall in US revenue from $14.6 billion in 1999 to $6.3 billion in 2009. CDs and single-track downloads were not selling because content was freely available on the Internet. By 2018, however, music streaming revenue exceeded that of traditional revenue streams (e.g. record sales, album sales, downloads). Streaming revenue is now one of the largest driving forces behind the growth in the music industry. In an interview, Jonathan Dworkin, a senior vice president of strategy and business development at Universal, said, "We cannot be afraid of perpetual change, because that dynamism is driving growth."
 The audio stream is compressed to make the file size smaller using an audio coding format such as MP3, Vorbis, AAC or Opus (audio format), Opus. The video stream is compressed using a video coding format to make the file size smaller. Video coding formats include H.264, High Efficiency Video Coding, HEVC, VP8 or VP9. Encoded audio and video streams are assembled in a container "bitstream" such as MPEG-4, MP4, Flash Video, FLV, WebM, Advanced Systems Format, ASF or Internet Streaming Media Alliance, ISMA. The bitstream is delivered from a streaming server to a streaming client (e.g., the computer user with their Internet-connected laptop) using a transport protocol, such as Adobe's Real Time Messaging Protocol, RTMP or Real-time Transport Protocol, RTP. In the 2010s, technologies such as Apple's HTTP Live Streaming, HLS, Microsoft's Smooth Streaming, Adobe's HDS and non-proprietary formats such as MPEG-DASH have emerged to enable adaptive bitrate streaming over
The audio stream is compressed to make the file size smaller using an audio coding format such as MP3, Vorbis, AAC or Opus (audio format), Opus. The video stream is compressed using a video coding format to make the file size smaller. Video coding formats include H.264, High Efficiency Video Coding, HEVC, VP8 or VP9. Encoded audio and video streams are assembled in a container "bitstream" such as MPEG-4, MP4, Flash Video, FLV, WebM, Advanced Systems Format, ASF or Internet Streaming Media Alliance, ISMA. The bitstream is delivered from a streaming server to a streaming client (e.g., the computer user with their Internet-connected laptop) using a transport protocol, such as Adobe's Real Time Messaging Protocol, RTMP or Real-time Transport Protocol, RTP. In the 2010s, technologies such as Apple's HTTP Live Streaming, HLS, Microsoft's Smooth Streaming, Adobe's HDS and non-proprietary formats such as MPEG-DASH have emerged to enable adaptive bitrate streaming over  Unicast protocols send a separate copy of the media stream from the server to each recipient. Unicast is the norm for most Internet connections, but does not scale well when many users want to view the same television program concurrently. Multicast protocols were developed to reduce the server/network loads resulting from duplicate data streams that occur when many recipients receive unicast content streams independently. These protocols send a single stream from the source to a group of recipients. Depending on the network infrastructure and type, multicast transmission may or may not be feasible. One potential disadvantage of multicasting is the loss of
Unicast protocols send a separate copy of the media stream from the server to each recipient. Unicast is the norm for most Internet connections, but does not scale well when many users want to view the same television program concurrently. Multicast protocols were developed to reduce the server/network loads resulting from duplicate data streams that occur when many recipients receive unicast content streams independently. These protocols send a single stream from the source to a group of recipients. Depending on the network infrastructure and type, multicast transmission may or may not be feasible. One potential disadvantage of multicasting is the loss of
multimedia
Multimedia is a form of communication that uses a combination of different content forms such as text, audio, images, animations, or video into a single interactive presentation, in contrast to tradit ...
that is delivered and consumed in a continuous manner from a source, with little or no intermediate storage in network elements. ''Streaming'' refers to the delivery method of content, rather than the content itself.
Distinguishing delivery method from the media applies specifically to telecommunications network
A telecommunications network is a group of nodes interconnected by telecommunications links that are used to exchange messages between the nodes. The links may use a variety of technologies based on the methodologies of circuit switching, mes ...
s, as most of the traditional media delivery systems are either inherently ''streaming'' (e.g. radio, television) or inherently ''non-streaming'' (e.g. books
A book is a medium for recording information in the form of writing or images, typically composed of many pages (made of papyrus, parchment, vellum, or paper) bound together and protected by a cover. The technical term for this physic ...
, videotape
Videotape is magnetic tape used for storing video and usually sound in addition. Information stored can be in the form of either an analog or digital signal. Videotape is used in both video tape recorders (VTRs) and, more commonly, videoca ...
, audio CDs). There are challenges with streaming content on the Internet
The Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a '' network of networks'' that consists of private, p ...
. For example, users whose Internet connection lacks sufficient bandwidth may experience stops, lags, or poor buffering of the content, and users lacking compatible hardware or software systems may be unable to stream certain content. With the use of buffering of the content for just a few seconds in advance of playback, the quality can be much improved.
Livestreaming
Livestreaming is streaming media simultaneously recorded and broadcast in real-time over the internet. It is often referred to simply as streaming. Non-live media such as video-on-demand, vlogs, and YouTube videos are technically streamed, but n ...
is the real-time delivery of content during production, much as live television
Live television is a television production broadcast in real-time, as events happen, in the present. In a secondary meaning, it may refer to streaming television over the Internet when content or programming is played continuously (not on deman ...
broadcasts content via television channels. Livestreaming requires a form of source media (e.g. a video camera, an audio interface, screen capture software), an encoder to digitize the content, a media publisher, and a content delivery network to distribute and deliver the content.
Streaming is an alternative to file downloading
In computer networks, download means to ''receive'' data from a remote system, typically a server such as a web server, an FTP server, an email server, or other similar system. This contrasts with uploading, where data is ''sent to'' a r ...
, a process in which the end-user obtains the entire file for the content before watching or listening to it. Through streaming, an end-user can use their media player to start playing digital video
Digital video is an electronic representation of moving visual images (video) in the form of encoded digital data
Digital data, in information theory and information systems, is information represented as a string of discrete symbols eac ...
or digital audio
Digital audio is a representation of sound recorded in, or converted into, digital form. In digital audio, the sound wave of the audio signal is typically encoded as numerical samples in a continuous sequence. For example, in CD audio, samp ...
content before the entire file has been transmitted. The term "streaming media" can apply to media other than video and audio, such as live closed captioning
Closed captioning (CC) and subtitling are both processes of displaying text on a television, video screen, or other visual display to provide additional or interpretive information. Both are typically used as a transcription of the audio po ...
, ticker tape
Ticker tape was the earliest electrical dedicated financial communications medium, transmitting stock price information over telegraph lines, in use from around 1870 through 1970. It consisted of a paper strip that ran through a machine called ...
, and real-time text, which are all considered "streaming text".
Streaming is most prevalent in video on demand
Video on demand (VOD) is a media distribution system that allows users to access videos without a traditional video playback device and the constraints of a typical static broadcasting schedule. In the 20th century, broadcasting in the form of ...
and streaming television
Streaming television is the digital distribution of television content, such as TV shows, as streaming media delivered over the Internet. Streaming television stands in contrast to dedicated terrestrial television delivered by over-the-air a ...
services. Other services stream music or video games
Video games, also known as computer games, are electronic games that involves interaction with a user interface or input device such as a joystick, controller, keyboard, or motion sensing device to generate visual feedback. This feedbac ...
.
Etymology
The term "streaming" was first used fortape drive
A tape drive is a data storage device that reads and writes data on a magnetic tape. Magnetic tape data storage is typically used for offline, archival data storage. Tape media generally has a favorable unit cost and a long archival stability. ...
s manufactured by Data Electronics Inc. that were meant to slowly ramp up and run for the entire track; slower ramp times lowered drive costs. "Streaming" was applied in the early 1990s as a better description for video on demand
Video on demand (VOD) is a media distribution system that allows users to access videos without a traditional video playback device and the constraints of a typical static broadcasting schedule. In the 20th century, broadcasting in the form of ...
and later live video on IP networks. It was first done by Starlight Networks Starlight Networks was founded in 1991 by Charlie Bass, Jim Long and Mark Gang with backing from investors Accel Partners and Interwest Partners. The company created some of the first commercial video-on-demand and video streaming products. The f ...
for video streaming and Real Networks
RealNetworks, Inc. is a provider of artificial intelligence and computer vision based products. RealNetworks was a pioneer in Internet streaming software and services. They are based in Seattle, Washington, United States. The company also ...
for audio streaming. Such video had previously been referred to by the misnomer "store and forward video."
Precursors
Beginning in 1881,Théâtrophone
Théâtrophone ("the theatre phone") was a telephonic distribution system available in portions of Europe that allowed the subscribers to listen to opera and theatre performances over the telephone lines. The théâtrophone evolved from a Clément ...
enabled subscribers to listen to opera and theatre performances over telephone lines. This operated until 1932. The concept of media streaming eventually came to America.
In the early 1920s, George Owen Squier
Major General George Owen Squier (March 21, 1865 – March 24, 1934) was born in Dryden, Michigan, United States. He graduated from the United States Military Academy in the Class of 1887 and received a Ph.D. from Johns Hopkins University in 1 ...
was granted patents for a system for the transmission and distribution of signals over electrical lines, which was the technical basis for what later became ''Muzak
Muzak is an American brand of background music played in retail stores and other public establishments. The name has been in use since 1934, and has been owned by a division or subsidiary of one or another company ever since. In 1981, Westingh ...
'', a technology streaming continuous music to commercial customers without the use of radio.
The Telephone Music Service, a live jukebox service, began in 1929 and continued until 1997. The clientele eventually included 120 bars and restaurants in the Pittsburgh area. A tavern customer would deposit money in the jukebox, use a telephone on top of the jukebox, and ask the operator to play a song. The operator would find the record in the studio library of more than 100,000 records, put it on a turntable, and the music would be piped over the telephone line to play in the tavern. The music media began as 78s, 33s and 45s, played on the six turntables they monitored. CDs and tapes were incorporated in later years.
The business had a succession of owners, notably Bill Purse, his daughter Helen Reutzel, and finally, Dotti White. The revenue stream of each quarter was split 60% to the music service and 40% to the tavern owner. This business model eventually became unsustainable due to city permits and the cost of setting up these telephone lines.
History
Early development
Attempts to display media oncomputers
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (computation) automatically. Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as programs. These prog ...
date back to the earliest days of computing in the mid-20th century. However, little progress was made for several decades, primarily due to the high cost and limited capabilities of computer hardware. From the late 1980s through the 1990s, consumer-grade personal computers became powerful enough to display various media. The primary technical issues related to streaming were having enough CPU
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor or just processor, is the electronic circuitry that executes instructions comprising a computer program. The CPU performs basic arithmetic, logic, controlling, a ...
and bus bandwidth to support the required data rates, achieving real-time computing
Real-time computing (RTC) is the computer science term for hardware and software systems subject to a "real-time constraint", for example from event to system response. Real-time programs must guarantee response within specified time constrai ...
performance required to prevent buffer underrun
In computing, buffer underrun or buffer underflow is a state occurring when a buffer used for communicating between two devices or processes is fed with data at a lower speed than the data is being read from it. The term is distinct from buf ...
and enable smooth streaming of the content. However, computer networks were still limited in the mid-1990s, and audio and video media were usually delivered over non-streaming channels, such as playback from a local hard disk drive
A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive, or fixed disk is an electro-mechanical data storage device that stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage with one or more rigid rapidly rotating platters coated with mag ...
or CD-ROM
A CD-ROM (, compact disc read-only memory) is a type of read-only memory consisting of a pre-pressed optical compact disc that contains data. Computers can read—but not write or erase—CD-ROMs. Some CDs, called enhanced CDs, hold both com ...
s on the end user's computer.
In 1990 the first commercial Ethernet switch
A network switch (also called switching hub, bridging hub, and, by the IEEE, MAC bridge) is networking hardware that connects devices on a computer network by using packet switching to receive and forward data to the destination device.
A ...
was introduced by Kalpana, which enabled the more powerful computer networks that led to the firsstreaming video
solutions used by schools and corporations. Practical streaming media was only made possible with advances in
data compression
In information theory, data compression, source coding, or bit-rate reduction is the process of encoding information using fewer bits than the original representation. Any particular compression is either lossy or lossless. Lossless compressio ...
, due to the impractically high bandwidth requirements of uncompressed media. Raw digital audio
Digital audio is a representation of sound recorded in, or converted into, digital form. In digital audio, the sound wave of the audio signal is typically encoded as numerical samples in a continuous sequence. For example, in CD audio, samp ...
encoded with pulse-code modulation
Pulse-code modulation (PCM) is a method used to digitally represent sampled analog signals. It is the standard form of digital audio in computers, compact discs, digital telephony and other digital audio applications. In a PCM stream, the ...
(PCM) requires a bandwidth of 1.4 Mbit/s for uncompressed CD audio
Compact Disc Digital Audio (CDDA or CD-DA), also known as Digital Audio Compact Disc or simply as Audio CD, is the standard format for audio compact discs. The standard is defined in the ''Red Book'', one of a series of Rainbow Books (named f ...
, while raw digital video
Digital video is an electronic representation of moving visual images (video) in the form of encoded digital data
Digital data, in information theory and information systems, is information represented as a string of discrete symbols eac ...
requires a bandwidth of 168Mbit/s for SD video and over 1000Mbit/s for FHD
1080p (1920×1080 progressively displayed pixels; also known as Full HD or FHD, and BT.709) is a set of HDTV high-definition video modes characterized by 1,920 pixels displayed across the screen horizontally and 1,080 pixels down the screen vertic ...
video.
Late 1990s to early 2000s
During the late 1990s and early 2000s, users had increased access to computer networks, especially the Internet. During the early 2000s, users had access to increased network bandwidth, especially in the last mile. These technological improvements facilitated the streaming of audio and video content to computer users in their homes and workplaces. There was also an increasing use of standard protocols and formats, such asTCP/IP
The Internet protocol suite, commonly known as TCP/IP, is a framework for organizing the set of communication protocols used in the Internet and similar computer networks according to functional criteria. The foundational protocols in the su ...
, HTTP
The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is an application layer protocol in the Internet protocol suite model for distributed, collaborative, hypermedia information systems. HTTP is the foundation of data communication for the World Wide We ...
, HTML
The HyperText Markup Language or HTML is the standard markup language for documents designed to be displayed in a web browser. It can be assisted by technologies such as Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) and scripting languages such as JavaS ...
as the Internet became increasingly commercialized, which led to an infusion of investment into the sector.
The band Severe Tire Damage was the first group to perform live on the Internet. On June 24, 1993, the band was playing a gig at Xerox PARC
PARC (Palo Alto Research Center; formerly Xerox PARC) is a research and development company in Palo Alto, California. Founded in 1969 by Jacob E. "Jack" Goldman, chief scientist of Xerox Corporation, the company was originally a division of Xero ...
while elsewhere in the building, scientists were discussing new technology (the Mbone) for broadcasting on the Internet using multicast
In computer networking, multicast is group communication where data transmission is addressed to a group of destination computers simultaneously. Multicast can be one-to-many or many-to-many distribution. Multicast should not be confused wi ...
ing. As proof of PARC's technology, the band's performance was broadcast and could be seen live in Australia and elsewhere. In a March 2017 interview, band member Russ Haines stated that the band had used approximately "half of the total bandwidth of the internet" to stream the performance, which was a pixel video, updated eight to twelve times per second, with audio quality that was, "at best, a bad telephone connection."
RealNetworks
RealNetworks, Inc. is a provider of artificial intelligence and computer vision based products. RealNetworks was a pioneer in Internet streaming software and services. They are based in Seattle, Washington, United States. The company also pr ...
pioneered the broadcast of a baseball
Baseball is a bat-and-ball sport played between two teams of nine players each, taking turns batting and fielding. The game occurs over the course of several plays, with each play generally beginning when a player on the fielding t ...
game between the New York Yankees
The New York Yankees are an American professional baseball team based in the New York City borough of the Bronx. The Yankees compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the American League (AL) East division. They are one ...
and the Seattle Mariners
The Seattle Mariners are an American professional baseball team based in Seattle. They compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the American League (AL) West division. The team joined the American League as an expansion ...
over the Internet in 1995. The first symphonic concert on the Internet—a collaboration between the Seattle Symphony and guest musicians Slash
Slash may refer to:
* Slash (punctuation), the "/" character
Arts and entertainment Fictional characters
* Slash (Marvel Comics)
* Slash (''Teenage Mutant Ninja Turtles'')
Music
* Harry Slash & The Slashtones, an American rock band
* Nash ...
, Matt Cameron
Matthew David Cameron (born November 28, 1962) is an American musician who is the drummer for the rock band Pearl Jam. He first gained fame as the drummer for Seattle-based rock band Soundgarden, which he joined in 1986. He appeared on each o ...
, and Barrett Martin
Barrett Martin (born April 14, 1967) is an American record producer, percussionist, writer, and ethnomusicologist from Washington. As a producer he has won one Latin Grammy and has been nominated in two other categories. As an ethnomusicologist ...
—took place at the Paramount Theater in Seattle
Seattle ( ) is a seaport city on the West Coast of the United States. It is the seat of King County, Washington. With a 2020 population of 737,015, it is the largest city in both the state of Washington and the Pacific Northwest region o ...
, Washington, on November 10, 1995.
In 1996, Marc Scarpa
Marc Scarpa (born September 25, 1969, in New York City) is an American entrepreneur, producer and director specializing in live participatory media. He is the executive board member and the founding New York Chair of the Producers Guild of Ame ...
produced the first large-scale, online, live broadcast, the Adam Yauch-led Tibetan Freedom Concert
Tibetan Freedom Concert is the name given to a series of socio-political music festivals held in North America, Europe and Asia from 1996 onwards to support the cause of Tibetan independence. The concerts were originally organized by the Beastie ...
, an event that would define the format of social change broadcasts. Scarpa continued to pioneer in the streaming media world with projects such as Woodstock '99, Townhall with President Clinton
William Jefferson Clinton (né Blythe III; born August 19, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 42nd president of the United States from 1993 to 2001. He previously served as governor of Arkansas from 1979 to 1981 and again ...
, and more recently Covered CA's campaign "Tell a Friend Get Covered" which was live streamed on YouTube.
Business developments
Xing Technology was founded in 1989, and developed a JPEG streaming product called "StreamWorks". Another streaming product appeared in late 1992 and was named StarWorks. StarWorks enabled on-demand MPEG-1 full-motion videos to be randomly accessed on corporateEthernet
Ethernet () is a family of wired computer networking technologies commonly used in local area networks (LAN), metropolitan area networks (MAN) and wide area networks (WAN). It was commercially introduced in 1980 and first standardized in 1 ...
networks. Starworks was from Starlight Networks Starlight Networks was founded in 1991 by Charlie Bass, Jim Long and Mark Gang with backing from investors Accel Partners and Interwest Partners. The company created some of the first commercial video-on-demand and video streaming products. The f ...
, who also pioneered live video streaming on Ethernet and via Internet Protocol
The Internet Protocol (IP) is the network layer communications protocol in the Internet protocol suite for relaying datagrams across network boundaries. Its routing function enables internetworking, and essentially establishes the Internet.
...
over satellites with Hughes Network Systems. Other early companies that created streaming media technology include Progressive Networks and Protocomm prior to widespread World Wide Web usage. After the Netscape IPO in 1995 (and the release of Windows 95
Windows 95 is a consumer-oriented operating system developed by Microsoft as part of its Windows 9x family of operating systems. The first operating system in the 9x family, it is the successor to Windows 3.1x, and was released to manufacturi ...
, with built-in TCP/IP
The Internet protocol suite, commonly known as TCP/IP, is a framework for organizing the set of communication protocols used in the Internet and similar computer networks according to functional criteria. The foundational protocols in the su ...
support), usage of the Internet
The Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a '' network of networks'' that consists of private, p ...
expanded, and many companies "went public", including Progressive Networks (which was renamed "RealNetworks
RealNetworks, Inc. is a provider of artificial intelligence and computer vision based products. RealNetworks was a pioneer in Internet streaming software and services. They are based in Seattle, Washington, United States. The company also pr ...
", and listed on Nasdaq
The Nasdaq Stock Market () (National Association of Securities Dealers Automated Quotations Stock Market) is an American stock exchange based in New York City. It is the most active stock trading venue in the US by volume, and ranked second ...
as "RNWK"). As the web became even more popular in the late 90s, streaming video on the internet blossomed from startups such as Vivo Software (later acquired by RealNetworks), VDOnet (acquired by RealNetworks), Precept (acquired by Cisco
Cisco Systems, Inc., commonly known as Cisco, is an American-based multinational digital communications technology conglomerate corporation headquartered in San Jose, California. Cisco develops, manufactures, and sells networking hardware, ...
), and Xing (acquired by RealNetworks).
Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational technology corporation producing computer software, consumer electronics, personal computers, and related services headquartered at the Microsoft Redmond campus located in Redmond, Washi ...
developed a media player known as ActiveMovie in 1995 that supported streaming media and included a proprietary streaming format, which was the precursor to the streaming feature later in Windows Media Player
Windows Media Player (WMP) is the first media player and media library application that was developed by Microsoft for playing audio, video and viewing images on personal computers running the Microsoft Windows operating system, as well as ...
6.4 in 1999. In June 1999 Apple
An apple is an edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus domestica''). Apple trees are cultivated worldwide and are the most widely grown species in the genus '' Malus''. The tree originated in Central Asia, where its wild ancest ...
also introduced a streaming media format in its QuickTime
QuickTime is an extensible multimedia framework developed by Apple Inc., capable of handling various formats of digital video, picture, sound, panoramic images, and interactivity. Created in 1991, the latest Mac version, QuickTime X, is a ...
4 application. It was later also widely adopted on websites along with RealPlayer and Windows Media streaming formats. The competing formats on websites required each user to download the respective applications for streaming and resulted in many users having to have all three applications on their computer for general compatibility.
In 2000 Industryview.com launched its "world's largest streaming video archive" website to help businesses promote themselves. Webcasting became an emerging tool for business marketing and advertising that combined the immersive nature of television with the interactivity of the Web. The ability to collect data and feedback from potential customers caused this technology to gain momentum quickly.
Around 2002, the interest in a single, unified, streaming format and the widespread adoption of Adobe Flash
Adobe Flash (formerly Macromedia Flash and FutureSplash) is a multimedia software platform used for production of animations, rich web applications, desktop applications, mobile apps, mobile games, and embedded web browser video players. Flash ...
prompted the development of a video streaming format through Flash, which was the format used in Flash-based players on video hosting
An online video platform (OVP), provided by a video hosting service, enables users to upload, convert, store and play back video content on the Internet, often via a structured, large-scale system that may generate revenue. Users will generally ...
sites. The first popular video streaming site, YouTube
YouTube is a global online video sharing and social media platform headquartered in San Bruno, California. It was launched on February 14, 2005, by Steve Chen, Chad Hurley, and Jawed Karim. It is owned by Google, and is the second mo ...
, was founded by Steve Chen
Steve Chen (; born August 25, 1978) is a Taiwanese-American Internet entrepreneur who is one of the co-founders and previous chief technology officer of the video-sharing website YouTube. After having co-founded the company AVOS Systems, Inc ...
, Chad Hurley
Chad Meredith Hurley (born January 24, 1977) is an American webmaster and businessman who serves as the advisor and former chief executive officer (CEO) of YouTube. He also co-founded MixBit. In June 2006, he was voted 28th on Business 2.0's "5 ...
and Jawed Karim in 2005. It initially used a Flash-based player, which played MPEG-4 AVC
Advanced Video Coding (AVC), also referred to as H.264 or MPEG-4 Part 10, is a video compression standard based on block-oriented, motion-compensated coding. It is by far the most commonly used format for the recording, compression, and distr ...
video and AAC audio, but now defaults to HTML5 video. Increasing consumer demand for live streaming prompted YouTube to implement a new live streaming service to users. The company currently also offers a (secured) link returning the available connection speed of the user.
The Recording Industry Association of America
The Recording Industry Association of America (RIAA) is a trade organization that represents the music recording industry in the United States. Its members consist of record labels and distributors that the RIAA says "create, manufacture, and/ ...
(RIAA) revealed through its 2015 earnings report that streaming services were responsible for 34.3 percent of the year's total music industry
The music industry consists of the individuals and organizations that earn money by writing songs and musical compositions, creating and selling recorded music and sheet music, presenting concerts, as well as the organizations that aid, train, ...
's revenue, growing 29 percent from the previous year and becoming the largest source of income, pulling in around $2.4 billion. US streaming revenue grew 57 percent to $1.6 billion in the first half of 2016 and accounted for almost half of industry sales.
Streaming wars
The term ''streaming wars'' was coined to discuss the new era (starting in 2019) of competition between video streaming services such asNetflix
Netflix, Inc. is an American subscription video on-demand over-the-top streaming service and production company based in Los Gatos, California. Founded in 1997 by Reed Hastings and Marc Randolph in Scotts Valley, California, it offers a ...
, Amazon Prime Video
Amazon Prime Video, also known simply as Prime Video, is an American subscription video on-demand over-the-top streaming and rental service of Amazon offered as a standalone service or as part of Amazon's Prime subscription. The service pr ...
, Hulu
Hulu () is an American subscription streaming service majority-owned by The Walt Disney Company, with Comcast's NBCUniversal holding a minority stake. It was launched on October 29, 2007 and it offers a library of films and television series ...
, HBO Max
HBO Max is an American subscription video on-demand over-the-top streaming service owned by Warner Bros. Discovery. Launched in the United States on May 27, 2020, the service is built around the libraries of HBO, Warner Bros., Cartoon Ne ...
, Disney+
Disney+ is an American subscription video on-demand over-the-top streaming service owned and operated by the Media and Entertainment Distribution division of The Walt Disney Company. The service primarily distributes films and television se ...
, Paramount+, Apple TV+
Apple TV+ is an American subscription streaming service owned and operated by Apple Inc. Launched on November 1, 2019, it offers a selection of original production film and television series called Apple Originals. The service was announced ...
, and Peacock
Peafowl is a common name for three bird species in the genera '' Pavo'' and '' Afropavo'' within the tribe Pavonini of the family Phasianidae, the pheasants and their allies. Male peafowl are referred to as peacocks, and female peafowl are r ...
.
Competition among online platforms has forced them to find ways to differentiate themselves. One key way they have done this is by offering exclusive content, often self-produced and created specifically for a market. This approach to streaming competition, can have disadvantages for consumers and for the industry as a whole. Once content is made available online, the corresponding piracy searches decrease. Competition or legal availability across multiple platforms effectively deters online piracy and more exclusivity does not necessarily translate into higher average investment in content, as investment decisions are also dependent on the level and type of competition in online markets.
This competition was increased during the first two years of the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identi ...
as more people stayed home and watched TV. "The COVID-19 pandemic has led to a seismic shift in the film & TV industry in terms of how films are made, distributed and screened. Many industries have been hit by the economic affect of the pandemic"(Totaro Donato). In August 2022, a CNN headline declared "The streaming wars are over" as pandemic-era restrictions had largely ended and audience growth had stalled. This lead services to focus on profit over market share by cutting production budgets, cracking down on password sharing, and introducing ad-supported tiers.
Use by the general public
Advances incomputer network
A computer network is a set of computers sharing resources located on or provided by network nodes. The computers use common communication protocols over digital interconnections to communicate with each other. These interconnections are ...
ing, combined with powerful home computers and operating systems made streaming media affordable and easy for the public. Stand-alone Internet radio devices emerged to offer listeners a non-technical option for listening to audio streams. These audio streaming services became increasingly popular; streaming music reached 118.1 billion streams in 2013.
In general, multimedia content is data intensive, so media storage and transmission costs are still significant. Media is generally compressed for transport and storage. Increasing consumer demand for streaming of high-definition (HD) content has led the industry to develop technologies such as WirelessHD WirelessHD, also known as UltraGig, is a proprietary standard owned by Silicon Image (originally SiBeam) for wireless transmission of high-definition video content for consumer electronics products. The consortium currently has over 40 adopters; ke ...
and G.hn, which are optimized for streaming HD content. Many developers have introduced HD streaming apps that work on smaller devices such as tablets and smartphones for everyday purposes.
A media stream can be streamed either ''live'' or ''on demand''. Live streams are generally provided by a means called ''true streaming''. True streaming sends the information straight to the computer or device without saving to a local file. On-demand streaming is provided by a means called ''progressive download''. Progressive download saves the received information to a local file and then is played from that location. On-demand streams are often saved to files for extended amounts of time; while the live streams are only available at one time only (e.g. during the football game).
Streaming media is increasingly being coupled with use of social media. For example, sites such as YouTube encourage social interaction in webcasts through features such as live chat, online surveys, user posting of comments online and more. Furthermore, streaming media is increasingly being used for social business and e-learning.
The Horowitz Research State of Pay TV, OTT and SVOD 2017 report said that 70 percent of those viewing content did so through a streaming service and that 40 percent of TV viewing was done this way, twice the number from five years earlier. Millennials, the report said, streamed 60 percent of content.
Transition from DVD
One of the movie streaming industry's largest impacts was on the DVD industry, which effectively met its demise with the mass popularization of online content. The rise of media streaming caused the downfall of many DVD rental companies such as Blockbuster LLC, Blockbuster. In July 2015, ''The New York Times'' published an article aboutNetflix
Netflix, Inc. is an American subscription video on-demand over-the-top streaming service and production company based in Los Gatos, California. Founded in 1997 by Reed Hastings and Marc Randolph in Scotts Valley, California, it offers a ...
's DVD services. It stated that Netflix was continuing their DVD services with 5.3 million subscribers, which was a significant drop from the previous year. On the other hand, their streaming services had 65 million members.
Napster
Comparison of on-demand music streaming services, Music streaming is one of the most popular ways in which consumers interact with streaming media. In the age of digitization, the Private good, private consumption of music transformed into a Public good (economics), public good largely due to one player in the market: Napster. Napster, a peer-to-peer (P2P) file-sharing network where users could upload and download MP3 files freely, broke all music industry conventions when it launched in early 1999 in Hull, Massachusetts. The platform was developed by Shawn and John Fanning as well as Sean Parker. In an interview from 2009, Shawn Fanning explained that Napster "was something that came to me as a result of seeing a sort of an unmet need and the passion people had for being able to find all this music, particularly a lot of the obscure stuff which wouldn't be something you go to a record store and purchase, so it felt like a problem worth solving." Not only did this development disrupt the music industry by making songs that previously required payment to acquire freely accessible to any Napster user, but it also demonstrated the power of P2P networks in turning any digital file into a public, shareable good. For the brief period of time that Napster existed, mp3 files fundamentally changed as a type of good. Songs were no longer financially excludable – barring access to a computer with internet access – and they were not rival, meaning if one person downloaded a song it did not diminish another user from doing the same. Napster, like most other providers of public goods, faced the free-rider problem. Every user benefits when an individual uploads an mp3 file, but there is no requirement or mechanism that forces all users to share their music. Thus, Napster users were incentivized to let others upload music without sharing any of their own files. This structure revolutionized the consumer's perception of ownership over digital goods – it made music freely replicable. Napster quickly garnered millions of users, growing faster than any other business in history. At the peak of its existence, Napster boasted about 80 million users globally. The site gained so much traffic that many college campuses had to block access to Napster because it created network congestion from so many students sharing music files. The advent of Napster sparked the creation of numerous other P2P sites including LimeWire (2000), BitTorrent (2001), and the The Pirate Bay, Pirate Bay (2003). The reign of P2P networks was short-lived. The first to fall was Napster in 2001. Numerous lawsuits were filed against Napster by various record labels, all of which were subsidiaries of Universal Music Group, Sony Music Entertainment, Warner Music Group, or EMI. In addition to this, theRecording Industry Association of America
The Recording Industry Association of America (RIAA) is a trade organization that represents the music recording industry in the United States. Its members consist of record labels and distributors that the RIAA says "create, manufacture, and/ ...
(RIAA) also filed a lawsuit against Napster on the grounds of unauthorized distribution of copyrighted material, which ultimately led Napster to shut down in 2001. In an interview with the ''New York Times'', Gary Stiffelman, who represents Eminem, Aerosmith, and TLC discography, TLC, explained, "I’m not an opponent of artists’ music being included in these services, I'm just an opponent of their revenue not being shared."
The fight for intellectual property rights: ''A&M Records, Inc. v. Napster, Inc.''
The lawsuit ''A&M Records, Inc. v. Napster, Inc.'' fundamentally changed the way consumers interact with music streaming. It was argued on 2 October 2000 and was decided on 12 February 2001. The Appellate court, Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit ruled that a P2P file-sharing service could be held liable for contributory and vicarious infringement of copyright, serving as a landmark decision for Intellectual property law. The first issue that the Court addressed was fair use, which says that otherwise infringing activities are permissible so long as it is for purposes "such as criticism, comment, news reporting, teaching [...] scholarship, or research." Judge Beezer, the judge for this case, noted that Napster claimed that its services fit "three specific alleged fair uses: sampling (music), sampling, where users make temporary copies of a work before purchasing; space-shifting, where users access a sound recording through the Napster system that they already own in audio CD format; and permissive distribution of recordings by both new and established artists." Judge Beezer found that Napster did not fit these criteria, instead enabling their users to repeatedly copy music, which would affect the market value of the copyrighted good. The second claim by the plaintiffs was that Napster was actively contributing to copyright infringement since it had knowledge of widespread file sharing on its platform. Since Napster took no action to reduce infringement and financially benefited from repeated use, the court ruled against the P2P site. The court found that "as much as eighty-seven percent of the files available on Napster may be copyrighted and more than seventy percent may be owned or administered by plaintiffs." The injunction ordered against Napster ended the brief period in which music streaming was a public good – non-rival and non-excludable in nature. Other P2P networks had some success at sharing MP3s, though they all met a similar fate in court. The ruling set the precedent that copyrighted digital content cannot be freely replicated and shared unless given consent by the owner, thereby strengthening the property rights of artists and record labels alike.Music streaming platforms
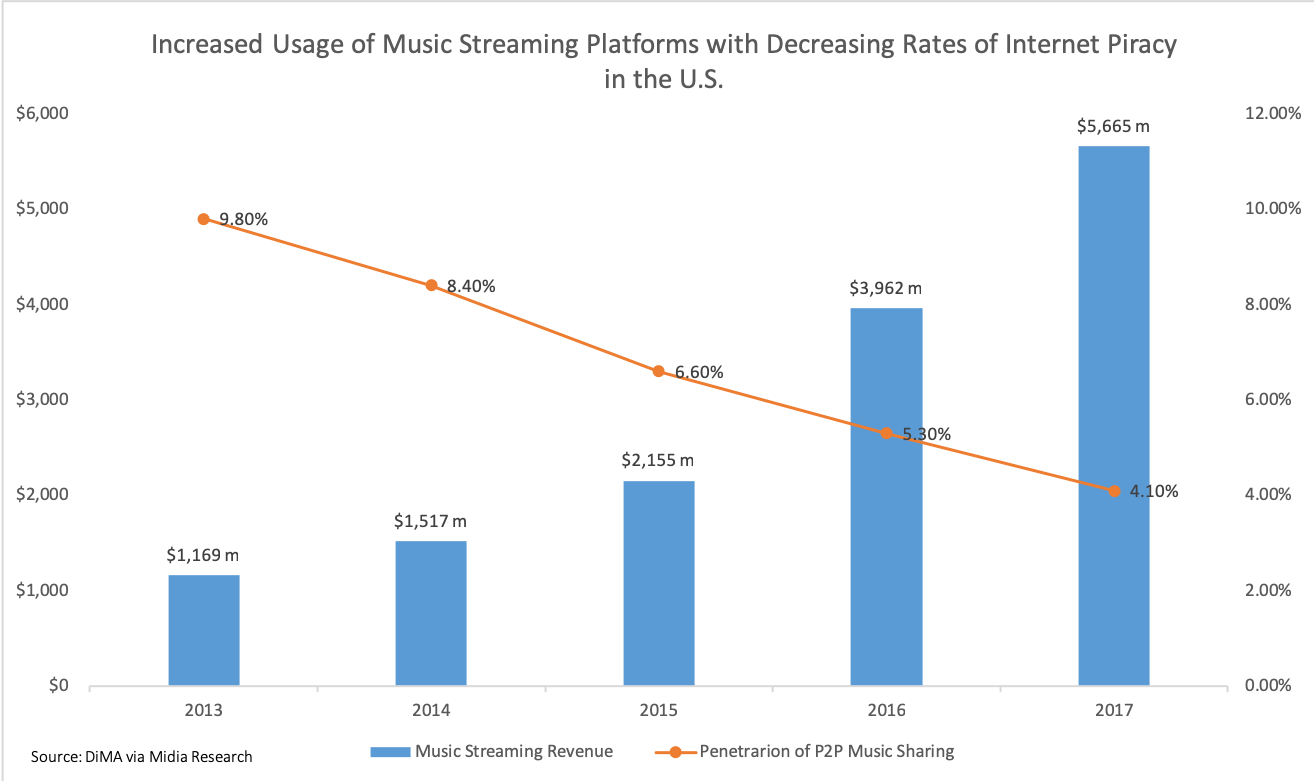
 Although music streaming is no longer a freely replicable public good, streaming platforms such as Spotify, Deezer, Apple Music, SoundCloud, and Amazon Music have shifted music streaming to a Club good, club-type good. While some platforms, most notably Spotify, give customers access to a freemium service that enables the use of limited features for exposure to advertisements, most companies operate under a premium subscription model. Under such circumstances, music streaming is financially excludable, requiring that customers pay a monthly fee for access to a music library, but non-rival, since one customer's use does not impair another's.
Spotify has over 207 million users in 78 countries, Apple Music has about 60 million, and SoundCloud has 175 million. All platforms provide varying degrees of accessibility. Apple Music and Prime Music only offer their services for paid subscribers, whereas Spotify and SoundCloud offer freemium and premium services. Napster, owned by Rhapsody since 2011, has resurfaced as a music streaming platform offering subscription-based services to over 4.5 million users .
The music industry's response to music streaming was initially negative. Along with music piracy, streaming services disrupted the market and contributed to the fall in US revenue from $14.6 billion in 1999 to $6.3 billion in 2009. CDs and single-track downloads were not selling because content was freely available on the Internet. By 2018, however, music streaming revenue exceeded that of traditional revenue streams (e.g. record sales, album sales, downloads). Streaming revenue is now one of the largest driving forces behind the growth in the music industry. In an interview, Jonathan Dworkin, a senior vice president of strategy and business development at Universal, said, "We cannot be afraid of perpetual change, because that dynamism is driving growth."
Although music streaming is no longer a freely replicable public good, streaming platforms such as Spotify, Deezer, Apple Music, SoundCloud, and Amazon Music have shifted music streaming to a Club good, club-type good. While some platforms, most notably Spotify, give customers access to a freemium service that enables the use of limited features for exposure to advertisements, most companies operate under a premium subscription model. Under such circumstances, music streaming is financially excludable, requiring that customers pay a monthly fee for access to a music library, but non-rival, since one customer's use does not impair another's.
Spotify has over 207 million users in 78 countries, Apple Music has about 60 million, and SoundCloud has 175 million. All platforms provide varying degrees of accessibility. Apple Music and Prime Music only offer their services for paid subscribers, whereas Spotify and SoundCloud offer freemium and premium services. Napster, owned by Rhapsody since 2011, has resurfaced as a music streaming platform offering subscription-based services to over 4.5 million users .
The music industry's response to music streaming was initially negative. Along with music piracy, streaming services disrupted the market and contributed to the fall in US revenue from $14.6 billion in 1999 to $6.3 billion in 2009. CDs and single-track downloads were not selling because content was freely available on the Internet. By 2018, however, music streaming revenue exceeded that of traditional revenue streams (e.g. record sales, album sales, downloads). Streaming revenue is now one of the largest driving forces behind the growth in the music industry. In an interview, Jonathan Dworkin, a senior vice president of strategy and business development at Universal, said, "We cannot be afraid of perpetual change, because that dynamism is driving growth."
COVID-19 pandemic
By August 2020, theCOVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identi ...
had streaming services busier than ever. In the UK alone, twelve million people joined a new streaming service that they had not previously had.
An impact analysis of 2020 data by the Confédération Internationale des Sociétés d'Auteurs et Compositeurs, International Confederation of Societies of Authors and Composers (CISAC) indicated that remuneration from digital streaming of music increased with a strong rise in digital royalty collection (up 16.6% to EUR 2.4 billion), but it would not compensate the overall loss of income of authors from concerts, public performance and broadcast. The International Federation of the Phonographic Industry (IFPI) recompiled the music industry initiatives around the world related to the COVID-19. In its State of the Industry report, it recorded that the global recorded music market grew by 7.4% in 2022, the 6th consecutive year of growth. This growth was driven by streaming, mostly from paid subscription streaming revenues which increased by 18.5%, fueled by 443 million users of subscription accounts by the end of 2020.
The COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identi ...
has also driven an increase in misinformation and disinformation, particularly on streaming platforms like YouTube
YouTube is a global online video sharing and social media platform headquartered in San Bruno, California. It was launched on February 14, 2005, by Steve Chen, Chad Hurley, and Jawed Karim. It is owned by Google, and is the second mo ...
and podcasts.
Technologies
Bandwidth
A broadband speed of 2 Mbit/s or more is recommended for streaming standard-definition video, for example to a Roku, Apple TV, Google TV (smart TV platform), Google TV or a Sony TV Blu-ray Disc Player. 5 Mbit/s is recommended for high-definition content and 9 Mbit/s for Ultra-high-definition television, ultra-high-definition content. Streaming media storage size is calculated from the streaming bandwidth and length of the media using the following formula (for a single user and file): storage size in megabytes is equal to length (in seconds) × bit rate (in bit/s) / (8 × 1024 × 1024). For example, one hour of digital video encoded at 300 kbit/s (this was a typical broadband video in 2005 and it was usually encoded in resolution) will be: (3,600 s × 300,000 bit/s) / (8 × 1024 × 1024) requires around 128 Megabyte, MB of storage. If the file is stored on a server for on-demand streaming and this stream is viewed by 1,000 people at the same time using a Unicast protocol, the requirement is 300 kbit/s × 1,000 = 300,000 kbit/s = 300 Mbit/s of bandwidth. This is equivalent to around 135 gigabyte, GB per hour. Using amulticast
In computer networking, multicast is group communication where data transmission is addressed to a group of destination computers simultaneously. Multicast can be one-to-many or many-to-many distribution. Multicast should not be confused wi ...
protocol the server sends out only a single stream that is common to all users. Therefore, such a stream would only use 300 kbit/s of serving bandwidth. See below for more information on these protocols. The calculation for live streaming is similar. Assuming that the speed at the encoder is 500 kbit/s and if the show lasts for 3 hours with 3,000 viewers, then the calculation is number of MBs transferred = encoder speed (in bit/s) × number of seconds × number of viewers / (8 × 1024 × 1024). The results of this calculation are as follows: number of MBs transferred = 500 x 1024 (bit/s) × 3 × 3,600 ( = 3 hours) × 3,000 (number of viewers) / (8 × 1024 × 1024) = 1,977,539 MB.
In 2018 video was more than 60% of data traffic worldwide and accounted for 80% of growth in data usage.
Protocols
HTTP
The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is an application layer protocol in the Internet protocol suite model for distributed, collaborative, hypermedia information systems. HTTP is the foundation of data communication for the World Wide We ...
as an alternative to using proprietary transport protocols. Often, a streaming transport protocol is used to send video from an event venue to a "Cloud computing, cloud" transcoding service and CDN, which then uses HTTP-based transport protocols to distribute the video to individual homes and users. The streaming client (the end user) may interact with the streaming server using a control protocol, such as Microsoft Media Server, MMS or Real Time Streaming Protocol, RTSP.
The quality of the interaction between servers and users is based on the workload of the streaming service; as more users attempt to access a service, the more quality is affected unless there is enough bandwidth or the host is using enough proxy networks. Deploying clusters of streaming servers is one such method where there are regional servers spread across the network, managed by a singular, central server containing copies of all the media files as well as the IP addresses of the regional servers. This central server then uses Load balancing (computing), load balancing and Scheduling (computing), scheduling algorithms to redirect users to nearby regional servers capable of accommodating them. This approach also allows the central server to provide streaming data to both users as well as regional servers using FFMpeg libraries if required, thus demanding the central server to have powerful data-processing and immense storage capabilities. In return, workloads on the streaming backbone network are balanced and alleviated, allowing for optimal streaming quality.
Designing a network protocol to support streaming media raises many problems. Datagram protocols, such as the User Datagram Protocol (UDP), send the media stream as a series of small packets. This is simple and efficient; however, there is no mechanism within the protocol to guarantee delivery. It is up to the receiving application to detect loss or corruption and recover data using error correction techniques. If data is lost, the stream may suffer a Dropout (electronics), dropout. The Real-time Streaming Protocol (RTSP), Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP) and the Real-time Transport Control Protocol (RTCP) were specifically designed to stream media over networks. RTSP runs over a variety of transport protocols, while the latter two are built on top of UDP.
Another approach that seems to incorporate both the advantages of using a standard web protocol and the ability to be used for streaming even live content is adaptive bitrate streaming. HTTP adaptive bitrate streaming is based on HTTP progressive download, but contrary to the previous approach, here the files are very small, so that they can be compared to the streaming of packets, much like the case of using RTSP and RTP. Reliable protocols, such as the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP), guarantee correct delivery of each bit in the media stream. However, they accomplish this with a system of timeouts and retries, which makes them more complex to implement. It also means that when there is data loss on the network, the media stream stalls while the protocol handlers detect the loss and retransmit the missing data. Clients can minimize this effect by buffering data for display. While delay due to buffering is acceptable in video on demand scenarios, users of interactive applications such as video conferencing will experience a loss of fidelity if the delay caused by buffering exceeds 200 ms.
video on demand
Video on demand (VOD) is a media distribution system that allows users to access videos without a traditional video playback device and the constraints of a typical static broadcasting schedule. In the 20th century, broadcasting in the form of ...
functionality. Continuous streaming of radio or television material usually precludes the recipient's ability to control playback. However, this problem can be mitigated by elements such as caching servers, digital set-top boxes, and buffered Media player (application software), media players.
IP multicast provides a means to send a single media stream to a group of recipients on a computer network
A computer network is a set of computers sharing resources located on or provided by network nodes. The computers use common communication protocols over digital interconnections to communicate with each other. These interconnections are ...
. A multicast protocol, usually Internet Group Management Protocol, is used to manage delivery of multicast streams to the groups of recipients on a LAN. One of the challenges in deploying IP multicast is that routers and firewalls between LANs must allow the passage of packets destined to multicast groups. If the organization that is serving the content has control over the network between server and recipients (i.e., educational, government, and corporate intranets), then routing protocols such as Protocol Independent Multicast can be used to deliver stream content to multiple Local Area Network segments.
Peer-to-peer (P2P) protocols arrange for prerecorded streams to be sent between computers. This prevents the server and its network connections from becoming a bottleneck. However, it raises technical, performance, security, quality, and business issues.
Recording
Media that is livestreamed can be recorded through certain media players such as VLC player, or through the use of a screen recorder. Live-streaming platforms such as Twitch (service), Twitch may also incorporate avideo on demand
Video on demand (VOD) is a media distribution system that allows users to access videos without a traditional video playback device and the constraints of a typical static broadcasting schedule. In the 20th century, broadcasting in the form of ...
system that allows automatic recording of live broadcasts so that they can be watched later. The popular site, Youtube.com, YouTube also has recordings of live broadcasts, including television shows aired on major networks. These streams have the potential to be recorded by anyone who has access to them, whether legally or otherwise.
Applications and marketing
Useful – and typical – applications of streaming are, for example, long video lesson, video lectures performed online. An advantage of this presentation is that these lectures can be very long, although they can always be interrupted or repeated at arbitrary places. There are also new marketing concepts. For example, the Berlin Philharmonic Orchestra sells Internet live streams of whole concerts, instead of several CDs or similar fixed media, by their Digital Concert Hall using YouTube for trailer (promotion), trailers. These online concerts are also spread over a lot of different places – cinemas – at various places on the globe. A similar concept is used by the Metropolitan Opera in New York. There also is High Definition Earth Viewing cameras, a livestream from the International Space Station. In video entertainment, video streaming platforms likeNetflix
Netflix, Inc. is an American subscription video on-demand over-the-top streaming service and production company based in Los Gatos, California. Founded in 1997 by Reed Hastings and Marc Randolph in Scotts Valley, California, it offers a ...
, Hulu
Hulu () is an American subscription streaming service majority-owned by The Walt Disney Company, with Comcast's NBCUniversal holding a minority stake. It was launched on October 29, 2007 and it offers a library of films and television series ...
, and Disney+
Disney+ is an American subscription video on-demand over-the-top streaming service owned and operated by the Media and Entertainment Distribution division of The Walt Disney Company. The service primarily distributes films and television se ...
are mainstream elements of the media industry.
Marketers have found many opportunities offered by streaming media and the platforms that offer them, especially in light of the significant increase in the use of streaming media during COVID lockdowns from 2020 onwards. While revenue and placement Advertising, traditional advertising continues to decrease, digital marketing increased in 15% in 2021, with digital media and Search engine, search representing 65% of the expenditures.
A case study commissioned by the WIPO indicates that streaming services attract advertising budgets with the opportunities provided with interactivity and the use of data from users, resulting in personalization on a mass scale with content marketing. Targeted marketing is expanding with the use of artificial intelligence, in particular programmatic advertisement, a tool that helps advertisers decide their campaign parameters, and whether they are interested in buying advertising space online or not. One example of advertising space acquisition is Real-Time Bidding (RTB).
Challenges
Copyright issues
The availability of large bandwidth internet enabled the audiovisual streaming services to attract large number of users around the world. For OTT platforms, original content represents a critical variable in order to capture more subscribers. This generated a number of effects related to the copyright over the audiovisual content and its international exploitation through streaming such as contractual practices, international exploitation of rights, widespread use of standards and metadata in digital files. The WIPO has indicated the several basic copyright issues arising for those pursuing to work in the film and music industry in the era of streaming. Streaming copyrighted content can involve making infringing copies of the works in question. The recording and distribution of streamed content is also an issue for many companies that rely on revenue based on views or attendance.Greenhouse gas emissions
The net greenhouse gas emissions from streaming music were estimated at between 0.2 and 0.35 million metric tons Co2eq, CO2eq (between ) per year in the Greenhouse gas emissions by the United States, United States, by a 2019 study. This was an increase from emissions in the pre-digital music period, which were estimated at " in 1977, 0.136 million () in 1988, and 0.157 million () in 2000." However this is far less than other everyday activities such as eating, for example Greenhouse gas emissions by the United States, greenhouse gas emissions in the United States from beef cattle (Burping, burping of ruminants only - not including their manure) were in 2019. A 2021 study claimed that one hour of streaming or videoconferencing "emits of carbon dioxide ... requires of water and demands a land area adding up to about the size of an iPad Mini." The study suggests that turning the camera off during video calls can reduce the greenhouse gas and water use footprints by 96%, and that an 86% reduction is possible by using standard definition rather than high definition when streaming content with apps such asNetflix
Netflix, Inc. is an American subscription video on-demand over-the-top streaming service and production company based in Los Gatos, California. Founded in 1997 by Reed Hastings and Marc Randolph in Scotts Valley, California, it offers a ...
or Hulu
Hulu () is an American subscription streaming service majority-owned by The Walt Disney Company, with Comcast's NBCUniversal holding a minority stake. It was launched on October 29, 2007 and it offers a library of films and television series ...
. However another study estimated a relatively low amount of , and concluded that watching a Netflix video for half an hour emitted only the same as driving a gasoline fuelled car for about , so not a significant amount.
One way to decrease greenhouse gas emissions associated with streaming music is making data centers Carbon neutrality, carbon neutral, by converting to electricity produced from Renewable energy, renewable sources. On an individual level, purchase of a physical CD may be more environmentally friendly if it is to be played more than 27 times.Another option for reducing energy use can be downloading the music for offline listening, to reduce the need for streaming over distance. The Spotify service has a built-in local cache to reduce the necessity of repeating song streams.
See also
* Cloud gaming * Comparison of music streaming services * Comparison of streaming media software * Comparison of video streaming aggregators * Comparison of video hosting services * Content delivery platform * Digital Living Network Alliance (DLNA) * Digital television * Directive on Copyright in the Digital Single Market * Internet Protocol television * List of streaming media services * List of streaming media systems *Livestreaming
Livestreaming is streaming media simultaneously recorded and broadcast in real-time over the internet. It is often referred to simply as streaming. Non-live media such as video-on-demand, vlogs, and YouTube videos are technically streamed, but n ...
* Livestreamed news
* M3U playlists
* National Streaming Day
* Over-the-top media service
* P2PTV
* Protection of Broadcasts and Broadcasting Organizations Treaty
* Push technology
* Pro rata
* Real-time data
* Record label
* Stream processing
* Stream ripping
* Video over cellular
* Web syndication
References
Further reading
* Hagen, Anja Nylund (2020). Music in Streams: Communicating Music in the Streaming Paradigm, In Michael Filimowicz & Veronika Tzankova (ed.), ''Reimagining Communication: Mediation (1st Edition)''. Routledge. * *External links
* * {{Authority control Streaming media systems, Applications of distributed computing Cloud storage File sharing networks Film and video technology Peer-to-peer computing Peercasting Digital media Television terminology Promotion and marketing communications Bundled products or services