Dickens on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Charles John Huffam Dickens (; 7 February 1812 – 9 June 1870) was an English writer and social critic. He created some of the world's best-known fictional characters and is regarded by many as the greatest novelist of the

 Charles Dickens was born on 7 February 1812 at 1 Mile End Terrace (now 393 Commercial Road), Landport in
Charles Dickens was born on 7 February 1812 at 1 Mile End Terrace (now 393 Commercial Road), Landport in  This period came to an end in June 1822, when John Dickens was recalled to Navy Pay Office headquarters at
This period came to an end in June 1822, when John Dickens was recalled to Navy Pay Office headquarters at  A few months after his imprisonment, John Dickens's mother, Elizabeth Dickens, died and bequeathed him £450. On the expectation of this legacy, Dickens was released from prison. Under the Insolvent Debtors Act, Dickens arranged for payment of his creditors and he and his family left the Marshalsea, for the home of Mrs Roylance.
Charles's mother, Elizabeth Dickens, did not immediately support his removal from the boot-blacking warehouse. This influenced Dickens's view that a father should rule the family and a mother find her proper sphere inside the home: "I never afterwards forgot, I never shall forget, I never can forget, that my mother was warm for my being sent back." His mother's failure to request his return was a factor in his dissatisfied attitude towards women.
Righteous indignation stemming from his own situation and the conditions under which
A few months after his imprisonment, John Dickens's mother, Elizabeth Dickens, died and bequeathed him £450. On the expectation of this legacy, Dickens was released from prison. Under the Insolvent Debtors Act, Dickens arranged for payment of his creditors and he and his family left the Marshalsea, for the home of Mrs Roylance.
Charles's mother, Elizabeth Dickens, did not immediately support his removal from the boot-blacking warehouse. This influenced Dickens's view that a father should rule the family and a mother find her proper sphere inside the home: "I never afterwards forgot, I never shall forget, I never can forget, that my mother was warm for my being sent back." His mother's failure to request his return was a factor in his dissatisfied attitude towards women.
Righteous indignation stemming from his own situation and the conditions under which
 In 1832, at the age of 20, Dickens was energetic and increasingly self-confident. He enjoyed mimicry and popular entertainment, lacked a clear, specific sense of what he wanted to become, and yet knew he wanted fame. Drawn to the theatre – he became an early member of the Garrick Club – he landed an acting audition at Covent Garden, where the manager George Bartley and the actor
In 1832, at the age of 20, Dickens was energetic and increasingly self-confident. He enjoyed mimicry and popular entertainment, lacked a clear, specific sense of what he wanted to become, and yet knew he wanted fame. Drawn to the theatre – he became an early member of the Garrick Club – he landed an acting audition at Covent Garden, where the manager George Bartley and the actor  Dickens made rapid progress both professionally and socially. He began a friendship with William Harrison Ainsworth, the author of the highwayman novel '' Rookwood'' (1834), whose bachelor salon in Harrow Road had become the meeting place for a set that included
Dickens made rapid progress both professionally and socially. He began a friendship with William Harrison Ainsworth, the author of the highwayman novel '' Rookwood'' (1834), whose bachelor salon in Harrow Road had become the meeting place for a set that included  On 2 April 1836, after a one-year engagement, and between episodes two and three of ''The Pickwick Papers'', Dickens married Catherine Thomson Hogarth (1815–1879), the daughter of George Hogarth, editor of the ''
On 2 April 1836, after a one-year engagement, and between episodes two and three of ''The Pickwick Papers'', Dickens married Catherine Thomson Hogarth (1815–1879), the daughter of George Hogarth, editor of the '' His success as a novelist continued. The young
His success as a novelist continued. The young
 He described his impressions in a travelogue, '' American Notes for General Circulation''. In ''Notes'', Dickens includes a powerful condemnation of slavery which he had attacked as early as ''The Pickwick Papers'', correlating the emancipation of the poor in England with the abolition of slavery abroad citing newspaper accounts of runaway slaves disfigured by their masters. In spite of the abolitionist sentiments gleaned from his trip to America, some modern commentators have pointed out inconsistencies in Dickens's views on racial inequality. For instance, he has been criticized for his subsequent acquiescence in Governor Eyre's harsh crackdown during the 1860s Morant Bay rebellion in Jamaica and his failure to join other British progressives in condemning it. From
He described his impressions in a travelogue, '' American Notes for General Circulation''. In ''Notes'', Dickens includes a powerful condemnation of slavery which he had attacked as early as ''The Pickwick Papers'', correlating the emancipation of the poor in England with the abolition of slavery abroad citing newspaper accounts of runaway slaves disfigured by their masters. In spite of the abolitionist sentiments gleaned from his trip to America, some modern commentators have pointed out inconsistencies in Dickens's views on racial inequality. For instance, he has been criticized for his subsequent acquiescence in Governor Eyre's harsh crackdown during the 1860s Morant Bay rebellion in Jamaica and his failure to join other British progressives in condemning it. From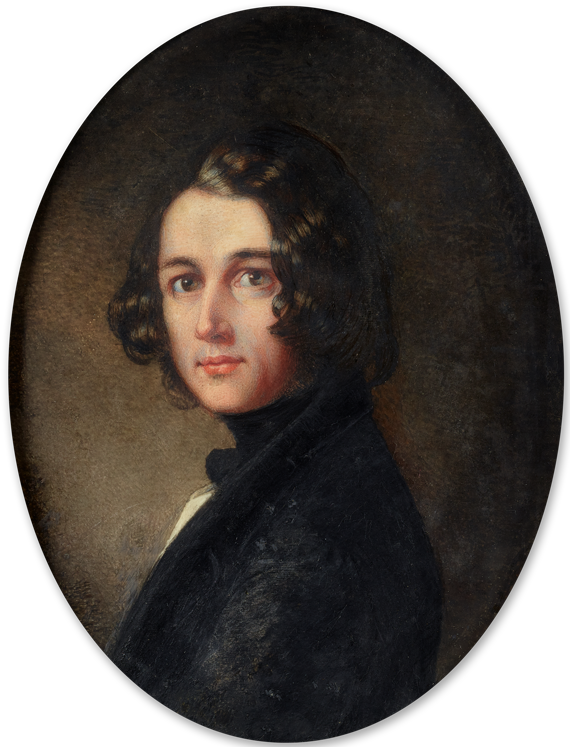  Soon after his return to England, Dickens began work on the first of his Christmas stories, ''
Soon after his return to England, Dickens began work on the first of his Christmas stories, ''
 Angela Burdett Coutts, heir to the Coutts banking fortune, approached Dickens in May 1846 about setting up a home for the redemption of
Angela Burdett Coutts, heir to the Coutts banking fortune, approached Dickens in May 1846 about setting up a home for the redemption of
 Dickens honoured the figure of
Dickens honoured the figure of
 In 1857, Dickens hired professional actresses for the play '' The Frozen Deep'', written by him and his
In 1857, Dickens hired professional actresses for the play '' The Frozen Deep'', written by him and his  After separating from Catherine, Dickens undertook a series of hugely popular and remunerative reading tours which, together with his journalism, were to absorb most of his creative energies for the next decade, in which he was to write only two more novels. His first reading tour, lasting from April 1858 to February 1859, consisted of 129 appearances in 49 towns throughout England, Scotland and Ireland. Dickens's continued fascination with the theatrical world was written into the theatre scenes in ''Nicholas Nickleby'', but more importantly he found an outlet in public readings. In 1866, he undertook a series of public readings in England and Scotland, with more the following year in England and Ireland.
After separating from Catherine, Dickens undertook a series of hugely popular and remunerative reading tours which, together with his journalism, were to absorb most of his creative energies for the next decade, in which he was to write only two more novels. His first reading tour, lasting from April 1858 to February 1859, consisted of 129 appearances in 49 towns throughout England, Scotland and Ireland. Dickens's continued fascination with the theatrical world was written into the theatre scenes in ''Nicholas Nickleby'', but more importantly he found an outlet in public readings. In 1866, he undertook a series of public readings in England and Scotland, with more the following year in England and Ireland.
 Other works soon followed, including ''
Other works soon followed, including ''
 On 9 June 1865, while returning from Paris with Ellen Ternan, Dickens was involved in the Staplehurst rail crash in Kent. The train's first seven carriages plunged off a
On 9 June 1865, while returning from Paris with Ellen Ternan, Dickens was involved in the Staplehurst rail crash in Kent. The train's first seven carriages plunged off a
 While he contemplated a second visit to the United States, the outbreak of the
While he contemplated a second visit to the United States, the outbreak of the
 In 1868–69, Dickens gave a series of "farewell readings" in England, Scotland and Ireland, beginning on 6 October. He managed, of a contracted 100 readings, to give 75 in the provinces, with a further 12 in London. As he pressed on he was affected by giddiness and fits of paralysis. He had a stroke on 18 April 1869 in Chester. He collapsed on 22 April 1869, at
In 1868–69, Dickens gave a series of "farewell readings" in England, Scotland and Ireland, beginning on 6 October. He managed, of a contracted 100 readings, to give 75 in the provinces, with a further 12 in London. As he pressed on he was affected by giddiness and fits of paralysis. He had a stroke on 18 April 1869 in Chester. He collapsed on 22 April 1869, at
 Dickens's writing style is marked by a profuse linguistic creativity.. Satire, flourishing in his gift for caricature, is his forte. An early reviewer compared him to Hogarth for his keen practical sense of the ludicrous side of life, though his acclaimed mastery of varieties of class idiom may in fact mirror the conventions of contemporary popular theatre. Dickens worked intensively on developing arresting names for his characters that would reverberate with associations for his readers and assist the development of motifs in the storyline, giving what one critic calls an "allegorical impetus" to the novels' meanings. To cite one of numerous examples, the name Mr Murdstone in ''David Copperfield'' conjures up twin allusions to murder and stony coldness. His literary style is also a mixture of fantasy and
Dickens's writing style is marked by a profuse linguistic creativity.. Satire, flourishing in his gift for caricature, is his forte. An early reviewer compared him to Hogarth for his keen practical sense of the ludicrous side of life, though his acclaimed mastery of varieties of class idiom may in fact mirror the conventions of contemporary popular theatre. Dickens worked intensively on developing arresting names for his characters that would reverberate with associations for his readers and assist the development of motifs in the storyline, giving what one critic calls an "allegorical impetus" to the novels' meanings. To cite one of numerous examples, the name Mr Murdstone in ''David Copperfield'' conjures up twin allusions to murder and stony coldness. His literary style is also a mixture of fantasy and
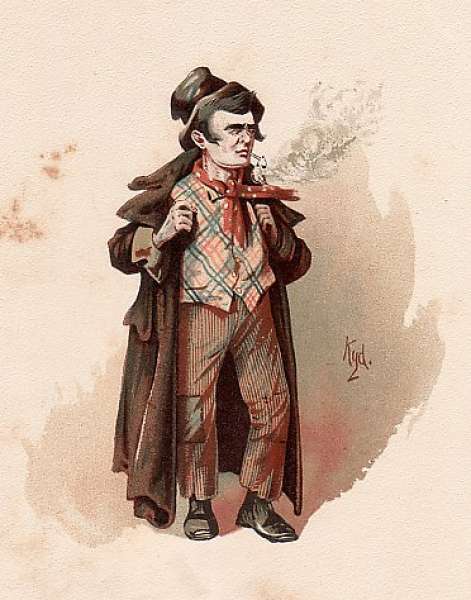 His characters were often so memorable that they took on a life of their own outside his books. "Gamp" became a slang expression for an umbrella from the character Mrs Gamp, and "Pickwickian", "Pecksniffian" and "Gradgrind" all entered dictionaries due to Dickens's original portraits of such characters who were, respectively, quixotic, hypocritical and vapidly factual. The character that made Dickens famous, Sam Weller became known for his
His characters were often so memorable that they took on a life of their own outside his books. "Gamp" became a slang expression for an umbrella from the character Mrs Gamp, and "Pickwickian", "Pecksniffian" and "Gradgrind" all entered dictionaries due to Dickens's original portraits of such characters who were, respectively, quixotic, hypocritical and vapidly factual. The character that made Dickens famous, Sam Weller became known for his
 Authors frequently draw their portraits of characters from people they have known in real life. ''David Copperfield'' is regarded by many as a veiled autobiography of Dickens. The scenes of interminable court cases and legal arguments in ''Bleak House'' reflect Dickens's experiences as a law clerk and court reporter, and in particular his direct experience of the law's procedural delay during 1844 when he sued publishers in Chancery for breach of copyright. Dickens's father was sent to prison for debt and this became a common theme in many of his books, with the detailed depiction of life in the Marshalsea prison in ''Little Dorrit'' resulting from Dickens's own experiences of the institution. Lucy Stroughill, a childhood sweetheart, may have affected several of Dickens's portraits of girls such as Little Em'ly in ''David Copperfield'' and Lucie Manette in ''A Tale of Two Cities.''
Dickens may have drawn on his childhood experiences, but he was also ashamed of them and would not reveal that this was where he gathered his realistic accounts of squalor. Very few knew the details of his early life until six years after his death, when John Forster published a biography on which Dickens had collaborated. Though Skimpole brutally sends up Leigh Hunt, some critics have detected in his portrait features of Dickens's own character, which he sought to exorcise by self-parody.
Authors frequently draw their portraits of characters from people they have known in real life. ''David Copperfield'' is regarded by many as a veiled autobiography of Dickens. The scenes of interminable court cases and legal arguments in ''Bleak House'' reflect Dickens's experiences as a law clerk and court reporter, and in particular his direct experience of the law's procedural delay during 1844 when he sued publishers in Chancery for breach of copyright. Dickens's father was sent to prison for debt and this became a common theme in many of his books, with the detailed depiction of life in the Marshalsea prison in ''Little Dorrit'' resulting from Dickens's own experiences of the institution. Lucy Stroughill, a childhood sweetheart, may have affected several of Dickens's portraits of girls such as Little Em'ly in ''David Copperfield'' and Lucie Manette in ''A Tale of Two Cities.''
Dickens may have drawn on his childhood experiences, but he was also ashamed of them and would not reveal that this was where he gathered his realistic accounts of squalor. Very few knew the details of his early life until six years after his death, when John Forster published a biography on which Dickens had collaborated. Though Skimpole brutally sends up Leigh Hunt, some critics have detected in his portrait features of Dickens's own character, which he sought to exorcise by self-parody.
 A pioneer of the serial publication of narrative fiction, Dickens wrote most of his major novels in monthly or weekly instalments in journals such as ''
A pioneer of the serial publication of narrative fiction, Dickens wrote most of his major novels in monthly or weekly instalments in journals such as ''
 Dickens's novels were, among other things, works of social commentary. Simon Callow states, "From the moment he started to write, he spoke for the people, and the people loved him for it." He was a fierce critic of the poverty and
Dickens's novels were, among other things, works of social commentary. Simon Callow states, "From the moment he started to write, he spoke for the people, and the people loved him for it." He was a fierce critic of the poverty and
 Dickens is often described as using idealised characters and highly sentimental scenes to contrast with his
Dickens is often described as using idealised characters and highly sentimental scenes to contrast with his
 Dickens was the most popular novelist of his time, and remains one of the best-known and most-read of English authors. His works have never gone
Dickens was the most popular novelist of his time, and remains one of the best-known and most-read of English authors. His works have never gone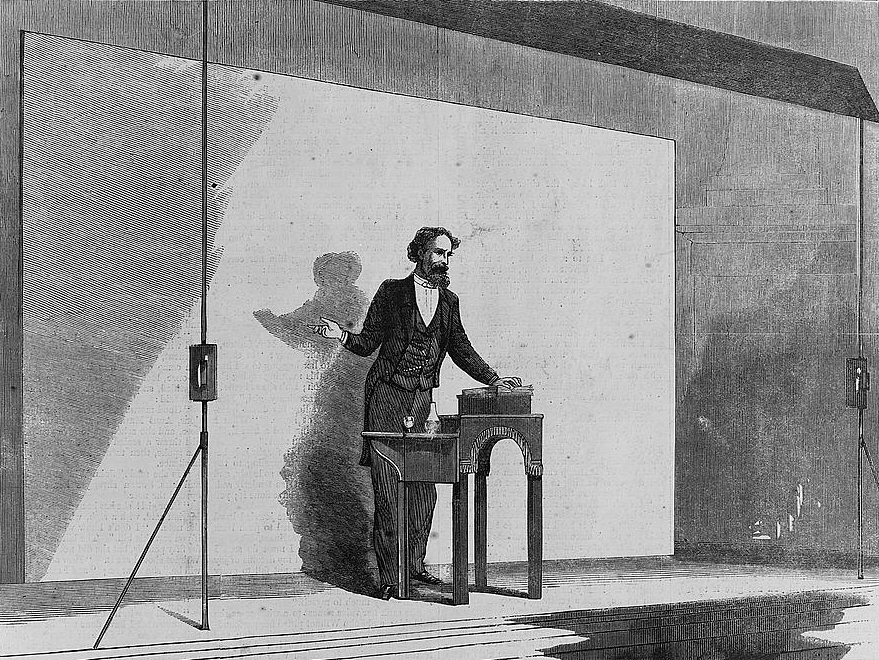  As his career progressed, Dickens's fame and the demand for his public readings were unparalleled. In 1868 ''
As his career progressed, Dickens's fame and the demand for his public readings were unparalleled. In 1868 ''
 Museums and festivals celebrating Dickens's life and works exist in many places with which Dickens was associated. These include the Charles Dickens Museum in London, the historic home where he wrote ''
Museums and festivals celebrating Dickens's life and works exist in many places with which Dickens was associated. These include the Charles Dickens Museum in London, the historic home where he wrote '' ''A Christmas Carol'' is most probably his best-known story, with frequent new adaptations. It is also the most-filmed of Dickens's stories, with many versions dating from the early years of cinema. According to the historian
''A Christmas Carol'' is most probably his best-known story, with frequent new adaptations. It is also the most-filmed of Dickens's stories, with many versions dating from the early years of cinema. According to the historian
Becoming Dickens 'The Invention of a Novelist
", London:
Charles Dickens's works on Bookwise
* * * * * *
Charles Dickens
at the British Library
Charles Dickens on the Archives Hub
*Archival material a
Leeds University Library
The Dickens Fellowship
an international society dedicated to the study of Dickens and his Writings
Correspondence of Charles Dickens, with related papers, ca. 1834–1955
Finding aid to Charles Dickens papers at Columbia University. Rare Book & Manuscript Library.
Dickens Museum
Situated in a former Dickens House, 48 Doughty Street, London, WC1
Dickens Birthplace Museum
Old Commercial Road, Portsmouth
Victoria and Albert Museum
The V&A's collections relating to Dickens
Charles Dickens's Traveling Kit
From th
at the
Charles Dickens's Walking Stick
From th
at the
Rare Book and Special Collections Division at the Library of Congress
{{DEFAULTSORT:Dickens, Charles 1812 births 1870 deaths 19th-century biographers 19th-century British dramatists and playwrights 19th-century British newspaper founders 19th-century British non-fiction writers 19th-century British novelists 19th-century British poets 19th-century British short story writers 19th-century English dramatists and playwrights 19th-century English non-fiction writers 19th-century English novelists 19th-century English poets 19th-century essayists 19th-century historians 19th-century journalists 19th-century letter writers 19th-century philanthropists 19th-century pseudonymous writers 19th-century travel writers British Anglicans British biographers British historians British historical novelists British letter writers British male dramatists and playwrights British male essayists British male journalists British male non-fiction writers British male novelists British male poets British male short story writers British newspaper founders British philanthropists British prisoners and detainees British reformers British satirists British social commentators Burials at Westminster Abbey Children's rights activists Christian writers Court reporters Critics of religions Critics of the Catholic Church Cultural critics Educational reformers English Anglicans English biographers English essayists English historians English historical novelists English letter writers English male dramatists and playwrights English male journalists English male non-fiction writers English male novelists English male poets English male short story writers English newspaper founders English philanthropists English prisoners and detainees English reformers English satirists English social commentators English travel writers Ghost story writers Lecturers Literacy and society theorists People from Camden Town People from Chatham, Kent People from Higham, Kent People from Somers Town, London Social critics Social reformers Trope theorists Victorian novelists Writers about activism and social change Writers from London Writers from Portsmouth Writers of Gothic fiction Writers of historical fiction set in the early modern period
Victorian era
In the history of the United Kingdom and the British Empire, the Victorian era was the period of Queen Victoria's reign, from 20 June 1837 until her death on 22 January 1901. The era followed the Georgian period and preceded the Edwa ...
.. His works enjoyed unprecedented popularity during his lifetime and, by the 20th century, critics and scholars had recognised him as a literary genius. His novels and short stories are widely read today.
Born in Portsmouth
Portsmouth ( ) is a port and city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. The city of Portsmouth has been a unitary authority since 1 April 1997 and is administered by Portsmouth City Council.
Portsmouth is the most d ...
, Dickens left school at the age of 12 to work in a boot-blacking factory when his father was incarcerated in a debtors' prison
A debtors' prison is a prison for people who are unable to pay debt. Until the mid-19th century, debtors' prisons (usually similar in form to locked workhouses) were a common way to deal with unpaid debt in Western Europe.Cory, Lucinda"A Histori ...
. After three years he returned to school, before he began his literary career as a journalist. Dickens edited a weekly journal for 20 years, wrote 15 novels, five novellas, hundreds of short stories and non-fiction articles, lectured and performed readings extensively, was an indefatigable letter writer, and campaigned vigorously for children's rights
Children's rights are a subset of human rights with particular attention to the rights of special protection and care afforded to minors.
, for education, and for other social reforms.
Dickens's literary success began with the 1836 serial publication of ''The Pickwick Papers
''The Posthumous Papers of the Pickwick Club'' (also known as ''The Pickwick Papers'') was Charles Dickens's first novel. Because of his success with '' Sketches by Boz'' published in 1836, Dickens was asked by the publisher Chapman & Hall to ...
'', a publishing phenomenon—thanks largely to the introduction of the character Sam Weller in the fourth episode—that sparked ''Pickwick'' merchandise and spin-offs. Within a few years Dickens had become an international literary celebrity, famous for his humour, satire and keen observation of character and society. His novels, most of them published in monthly or weekly installments, pioneered the serial publication of narrative fiction, which became the dominant Victorian mode for novel publication.. Cliffhanger
A cliffhanger or cliffhanger ending is a plot device in fiction which features a main character in a precarious or difficult dilemma or confronted with a shocking revelation at the end of an episode or a film of serialized fiction. A cliffhang ...
endings in his serial publications kept readers in suspense. The instalment format allowed Dickens to evaluate his audience's reaction, and he often modified his plot and character development based on such feedback. For example, when his wife's chiropodist
Podiatry () or podiatric medicine () is a branch of medicine devoted to the study, diagnosis, medical and surgical treatment of disorders of the foot, ankle, and leg.
A Doctor of Podiatric Medicine (DPM), or a podiatrist, is a healthcare p ...
expressed distress at the way Miss Mowcher in ''David Copperfield
''David Copperfield'' Dickens invented over 14 variations of the title for this work, see is a novel in the bildungsroman genre by Charles Dickens, narrated by the eponymous David Copperfield, detailing his adventures in his journey from inf ...
'' seemed to reflect her own disabilities, Dickens improved the character with positive features. His plots were carefully constructed and he often wove elements from topical events into his narratives. Masses of the illiterate poor would individually pay a halfpenny to have each new monthly episode read to them, opening up and inspiring a new class of readers.
His 1843 novella ''A Christmas Carol
''A Christmas Carol. In Prose. Being a Ghost Story of Christmas'', commonly known as ''A Christmas Carol'', is a novella by Charles Dickens, first published in London by Chapman & Hall in 1843 and illustrated by John Leech. ''A Christmas ...
'' remains especially popular and continues to inspire adaptations in every artistic genre. ''Oliver Twist
''Oliver Twist; or, The Parish Boy's Progress'', Charles Dickens's second novel, was published as a serial from 1837 to 1839, and as a three-volume book in 1838. Born in a workhouse, the orphan Oliver Twist is bound into apprenticeship with ...
'' and ''Great Expectations
''Great Expectations'' is the thirteenth novel by Charles Dickens and his penultimate completed novel. It depicts the education of an orphan nicknamed Pip (Great Expectations), Pip (the book is a ''bildungsroman''; a coming-of-age story). It ...
'' are also frequently adapted and, like many of his novels, evoke images of early Victorian London. His 1859 novel ''A Tale of Two Cities
''A Tale of Two Cities'' is a historical novel published in 1859 by Charles Dickens, set in London and Paris before and during the French Revolution. The novel tells the story of the French Doctor Manette, his 18-year-long imprisonment in ...
'' (set in London and Paris) is his best-known work of historical fiction. The most famous celebrity of his era, he undertook, in response to public demand, a series of public reading tours in the later part of his career. The term ''Dickensian'' is used to describe something that is reminiscent of Dickens and his writings, such as poor social or working conditions, or comically repulsive characters.
Early life
 Charles Dickens was born on 7 February 1812 at 1 Mile End Terrace (now 393 Commercial Road), Landport in
Charles Dickens was born on 7 February 1812 at 1 Mile End Terrace (now 393 Commercial Road), Landport in Portsea Island
Portsea Island is a flat and low-lying natural island in area, just off the southern coast of Hampshire in England. Portsea Island contains the majority of the city of Portsmouth.
Portsea Island has the third-largest population of all ...
(Portsmouth
Portsmouth ( ) is a port and city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. The city of Portsmouth has been a unitary authority since 1 April 1997 and is administered by Portsmouth City Council.
Portsmouth is the most d ...
), Hampshire
Hampshire (, ; abbreviated to Hants) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in western South East England on the coast of the English Channel. Home to two major English cities on its south coast, Southampton and Portsmouth, Hampshire ...
, the second of eight children of Elizabeth Dickens (née Barrow; 1789–1863) and John Dickens
John Dickens (21 August 1785 – 31 March 1851) was the father of famous English novelist Charles Dickens and was the model for Mr Micawber in his son's semi-autobiographical novel '' David Copperfield''.
Biography
The son of William Dickens ...
(1785–1851). His father was a clerk in the Navy Pay Office and was temporarily stationed in the district. He asked Christopher Huffam, rigger to His Majesty's Navy, gentleman, and head of an established firm, to act as godfather to Charles. Huffam is thought to be the inspiration for Paul Dombey, the owner of a shipping company in Dickens's novel '' Dombey and Son'' (1848).
In January 1815, John Dickens was called back to London and the family moved to Norfolk Street, Fitzrovia
Fitzrovia () is a district of central London, England, near the West End. The eastern part of area is in the London Borough of Camden, and the western in the City of Westminster. It has its roots in the Manor of Tottenham Court, and was urban ...
. When Charles was four, they relocated to Sheerness
Sheerness () is a town and civil parish beside the mouth of the River Medway on the north-west corner of the Isle of Sheppey in north Kent, England. With a population of 11,938, it is the second largest town on the island after the nearby tow ...
and thence to Chatham, Kent, where he spent his formative years until the age of 11. His early life seems to have been idyllic, though he thought himself a "very small and not-over-particularly-taken-care-of boy".
Charles spent time outdoors, but also read voraciously, including the picaresque novel
The picaresque novel ( Spanish: ''picaresca'', from ''pícaro'', for "rogue" or "rascal") is a genre of prose fiction. It depicts the adventures of a roguish, but "appealing hero", usually of low social class, who lives by his wits in a corru ...
s of Tobias Smollett
Tobias George Smollett (baptised 19 March 1721 – 17 September 1771) was a Scottish poet and author. He was best known for picaresque novels such as '' The Adventures of Roderick Random'' (1748), '' The Adventures of Peregrine Pickle'' (1751 ...
and Henry Fielding
Henry Fielding (22 April 1707 – 8 October 1754) was an English novelist, irony writer, and dramatist known for earthy humour and satire. His comic novel ''Tom Jones'' is still widely appreciated. He and Samuel Richardson are seen as founders ...
, as well as ''Robinson Crusoe
''Robinson Crusoe'' () is a novel by Daniel Defoe, first published on 25 April 1719. The first edition credited the work's protagonist Robinson Crusoe as its author, leading many readers to believe he was a real person and the book a tra ...
'' and '' Gil Blas''. He read and reread '' The Arabian Nights'' and the Collected Farces of Elizabeth Inchbald
Elizabeth Inchbald (née Simpson, 15 October 1753 – 1 August 1821) was an English novelist, actress, dramatist, and translator. Her two novels, '' A Simple Story'' and '' Nature and Art'', have received particular critical attention.
Life
Bo ...
. At age 7 he first saw Joseph Grimaldi
Joseph Grimaldi (18 December 1778 – 31 May 1837) was an English actor, comedian and dancer, who became the most popular English entertainer of the Regency era.Byrne, Eugene"The patient" Historyextra.com, 13 April 2012 In the early 1800s, ...
—the father of modern clown
A clown is a person who performs comedy and arts in a state of open-mindedness using physical comedy, typically while wearing distinct makeup or costuming and reversing folkway-norms.
History
The most ancient clowns have been found in ...
ing—perform at the Star Theatre, Rochester. He later imitated Grimaldi's clowning on several occasions, and would also edit the ''Memoirs of Joseph Grimaldi
''Memoirs of Joseph Grimaldi'' is the 1838 autobiography of the pioneering nineteenth-century clown Joseph Grimaldi. It was edited by Charles Dickens who as a seven-year-old had first seen Grimaldi perform.
References
Notes
* Charles Dickens, ...
''.. He retained poignant memories of childhood, helped by an excellent memory of people and events, which he used in his writing. His father's brief work as a clerk in the Navy Pay Office afforded him a few years of private education, first at a dame school and then at a school run by William Giles, a dissenter
A dissenter (from the Latin ''dissentire'', "to disagree") is one who dissents (disagrees) in matters of opinion, belief, etc.
Usage in Christianity
Dissent from the Anglican church
In the social and religious history of England and Wales, ...
, in Chatham.
 This period came to an end in June 1822, when John Dickens was recalled to Navy Pay Office headquarters at
This period came to an end in June 1822, when John Dickens was recalled to Navy Pay Office headquarters at Somerset House
Somerset House is a large Neoclassical complex situated on the south side of the Strand in central London, overlooking the River Thames, just east of Waterloo Bridge. The Georgian era quadrangle was built on the site of a Tudor palace ("O ...
and the family (except for Charles, who stayed behind to finish his final term at school) moved to Camden Town
Camden Town (), often shortened to Camden, is a district of northwest London, England, north of Charing Cross. Historically in Middlesex, it is the administrative centre of the London Borough of Camden, and identified in the London Plan as ...
in London. The family had left Kent amidst rapidly mounting debts and, living beyond his means, John Dickens was forced by his creditors into the Marshalsea
The Marshalsea (1373–1842) was a notorious prison in Southwark, just south of the River Thames. Although it housed a variety of prisoners, including men accused of crimes at sea and political figures charged with sedition, it became known, i ...
debtors' prison
A debtors' prison is a prison for people who are unable to pay debt. Until the mid-19th century, debtors' prisons (usually similar in form to locked workhouses) were a common way to deal with unpaid debt in Western Europe.Cory, Lucinda"A Histori ...
in Southwark
Southwark ( ) is a district of Central London situated on the south bank of the River Thames, forming the north-western part of the wider modern London Borough of Southwark. The district, which is the oldest part of South London, developed ...
, London in 1824. His wife and youngest children joined him there, as was the practice at the time. Charles, then 12 years old, boarded with Elizabeth Roylance, a family friend, at 112 College Place, Camden Town. Mrs Roylance was "a reduced impoverished old lady, long known to our family", whom Dickens later immortalised, "with a few alterations and embellishments", as "Mrs Pipchin" in ''Dombey and Son''. Later, he lived in a back-attic in the house of an agent for the Insolvent Court, Archibald Russell, "a fat, good-natured, kind old gentleman ... with a quiet old wife" and lame son, in Lant Street in Southwark. They provided the inspiration for the Garlands in '' The Old Curiosity Shop''.
On Sundays – with his sister Frances, free from her studies at the Royal Academy of Music
The Royal Academy of Music (RAM) in London, England, is the oldest conservatoire in the UK, founded in 1822 by John Fane and Nicolas-Charles Bochsa. It received its royal charter in 1830 from King George IV with the support of the first Duke ...
– he spent the day at the Marshalsea. Dickens later used the prison as a setting in '' Little Dorrit''. To pay for his board and to help his family, Dickens was forced to leave school and work ten-hour days at Warren's Blacking Warehouse, on Hungerford Stairs, near the present Charing Cross railway station, where he earned six shilling
The shilling is a historical coin, and the name of a unit of modern currencies formerly used in the United Kingdom, Australia, New Zealand, other British Commonwealth countries and Ireland, where they were generally equivalent to 12 pence ...
s a week pasting labels on pots of boot blacking. The strenuous and often harsh working conditions made a lasting impression on Dickens and later influenced his fiction and essays, becoming the foundation of his interest in the reform of socio-economic and labour conditions, the rigours of which he believed were unfairly borne by the poor. He later wrote that he wondered "how I could have been so easily cast away at such an age". As he recalled to John Forster (from ''Life of Charles Dickens''):
When the warehouse was moved to Chandos Street in the smart, busy district of Covent Garden
Covent Garden is a district in London, on the eastern fringes of the West End, between St Martin's Lane and Drury Lane. It is associated with the former fruit-and-vegetable market in the central square, now a popular shopping and tourist si ...
, the boys worked in a room in which the window gave onto the street. Small audiences gathered and watched them at work – in Dickens's biographer Simon Callow's estimation, the public display was "a new refinement added to his misery".
 A few months after his imprisonment, John Dickens's mother, Elizabeth Dickens, died and bequeathed him £450. On the expectation of this legacy, Dickens was released from prison. Under the Insolvent Debtors Act, Dickens arranged for payment of his creditors and he and his family left the Marshalsea, for the home of Mrs Roylance.
Charles's mother, Elizabeth Dickens, did not immediately support his removal from the boot-blacking warehouse. This influenced Dickens's view that a father should rule the family and a mother find her proper sphere inside the home: "I never afterwards forgot, I never shall forget, I never can forget, that my mother was warm for my being sent back." His mother's failure to request his return was a factor in his dissatisfied attitude towards women.
Righteous indignation stemming from his own situation and the conditions under which
A few months after his imprisonment, John Dickens's mother, Elizabeth Dickens, died and bequeathed him £450. On the expectation of this legacy, Dickens was released from prison. Under the Insolvent Debtors Act, Dickens arranged for payment of his creditors and he and his family left the Marshalsea, for the home of Mrs Roylance.
Charles's mother, Elizabeth Dickens, did not immediately support his removal from the boot-blacking warehouse. This influenced Dickens's view that a father should rule the family and a mother find her proper sphere inside the home: "I never afterwards forgot, I never shall forget, I never can forget, that my mother was warm for my being sent back." His mother's failure to request his return was a factor in his dissatisfied attitude towards women.
Righteous indignation stemming from his own situation and the conditions under which working-class
The working class (or labouring class) comprises those engaged in manual-labour occupations or industrial work, who are remunerated via waged or salaried contracts. Working-class occupations (see also " Designation of workers by collar colou ...
people lived became major themes of his works, and it was this unhappy period in his youth to which he alluded in his favourite, and most autobiographical, novel, ''David Copperfield
''David Copperfield'' Dickens invented over 14 variations of the title for this work, see is a novel in the bildungsroman genre by Charles Dickens, narrated by the eponymous David Copperfield, detailing his adventures in his journey from inf ...
'': "I had no advice, no counsel, no encouragement, no consolation, no assistance, no support, of any kind, from anyone, that I can call to mind, as I hope to go to heaven!"
Dickens was eventually sent to the Wellington House Academy in Camden Town
Camden Town (), often shortened to Camden, is a district of northwest London, England, north of Charing Cross. Historically in Middlesex, it is the administrative centre of the London Borough of Camden, and identified in the London Plan as ...
, where he remained until March 1827, having spent about two years there. He did not consider it to be a good school: "Much of the haphazard, desultory teaching, poor discipline punctuated by the headmaster's sadistic brutality, the seedy ushers and general run-down atmosphere, are embodied in Mr Creakle's Establishment in ''David Copperfield''.".
Dickens worked at the law office of Ellis and Blackmore, attorneys, of Holborn Court, Gray's Inn
The Honourable Society of Gray's Inn, commonly known as Gray's Inn, is one of the four Inns of Court (professional associations for barristers and judges) in London. To be called to the bar in order to practise as a barrister in England and W ...
, as a junior clerk
A clerk is a white-collar worker who conducts general office tasks, or a worker who performs similar sales-related tasks in a retail environment. The responsibilities of clerical workers commonly include record keeping, filing, staffing service ...
from May 1827 to November 1828. He was a gifted mimic and impersonated those around him: clients, lawyers and clerks. He went to theatres obsessively: he claimed that for at least three years he went to the theatre every day. His favourite actor was Charles Mathews and Dickens learnt his "monopolylogue
A monopolylogue is a form of entertainment in which one actor plays many characters. Pioneered by English actor Charles Mathews and Albert Smith and first used in 1824, later used in Shakespearen performances by the performer Henry Kemble from 1 ...
s" (farces in which Mathews played every character) by heart. Then, having learned Gurney
A stretcher, gurney, litter, or pram is an apparatus used for moving patients who require medical care. A basic type (cot or litter) must be carried by two or more people. A wheeled stretcher (known as a gurney, trolley, bed or cart) is often ...
's system of shorthand in his spare time, he left to become a freelance reporter. A distant relative, Thomas Charlton, was a freelance reporter at Doctors' Commons and Dickens was able to share his box there to report the legal proceedings for nearly four years. This education was to inform works such as Nicholas Nickleby, ''Dombey and Son'' and especially ''Bleak House'', whose vivid portrayal of the machinations and bureaucracy of the legal system did much to enlighten the general public and served as a vehicle for dissemination of Dickens's own views regarding, particularly, the heavy burden on the poor who were forced by circumstances to "go to law".
In 1830, Dickens met his first love, Maria Beadnell, thought to have been the model for the character Dora in ''David Copperfield''. Maria's parents disapproved of the courtship and ended the relationship by sending her to school in Paris.
Career
Journalism and early novels
 In 1832, at the age of 20, Dickens was energetic and increasingly self-confident. He enjoyed mimicry and popular entertainment, lacked a clear, specific sense of what he wanted to become, and yet knew he wanted fame. Drawn to the theatre – he became an early member of the Garrick Club – he landed an acting audition at Covent Garden, where the manager George Bartley and the actor
In 1832, at the age of 20, Dickens was energetic and increasingly self-confident. He enjoyed mimicry and popular entertainment, lacked a clear, specific sense of what he wanted to become, and yet knew he wanted fame. Drawn to the theatre – he became an early member of the Garrick Club – he landed an acting audition at Covent Garden, where the manager George Bartley and the actor Charles Kemble
Charles Kemble (25 November 1775 – 12 November 1854) was a Welsh-born English actor of a prominent theatre family.
Life
Charles Kemble was one of 13 siblings and the youngest son of English Roman Catholic theatre manager/actor Roger Kemble, ...
were to see him. Dickens prepared meticulously and decided to imitate the comedian Charles Mathews, but ultimately he missed the audition because of a cold. Before another opportunity arose, he had set out on his career as a writer.
In 1833, Dickens submitted his first story, "A Dinner at Poplar Walk", to the London periodical '' Monthly Magazine''.. William Barrow, Dickens's uncle on his mother's side, offered him a job on ''The Mirror of Parliament'' and he worked in the House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of parliament. T ...
for the first time early in 1832. He rented rooms at Furnival's Inn and worked as a political journalist, reporting on Parliamentary
A parliamentary system, or parliamentarian democracy, is a system of democratic governance of a state (or subordinate entity) where the executive derives its democratic legitimacy from its ability to command the support ("confidence") of the ...
debates, and he travelled across Britain to cover election campaigns for the ''Morning Chronicle
''The Morning Chronicle'' was a newspaper founded in 1769 in London. It was notable for having been the first steady employer of essayist William Hazlitt as a political reporter and the first steady employer of Charles Dickens as a journalist. I ...
''. His journalism, in the form of sketches in periodicals, formed his first collection of pieces, published in 1836: '' Sketches by Boz'' – Boz being a family nickname he employed as a pseudonym for some years.. Dickens apparently adopted it from the nickname 'Moses', which he had given to his youngest brother Augustus Dickens
Augustus Newnham Dickens (10 November 1827 – 4 October 1866) was the youngest brother of English novelist Charles Dickens, and the inspiration for Charles's pen name 'Boz'.
Early life
Augustus Dickens was the son of Elizabeth (''née'' Barro ...
, after a character in Oliver Goldsmith's '' The Vicar of Wakefield''. When pronounced by anyone with a head cold, "Moses" became "Boses" – later shortened to ''Boz''. Dickens's own name was considered "queer" by a contemporary critic, who wrote in 1849: "Mr Dickens, as if in revenge for his own queer name, does bestow still queerer ones upon his fictitious creations." Dickens contributed to and edited journals throughout his literary career. In January 1835, the ''Morning Chronicle'' launched an evening edition, under the editorship of the ''Chronicle''s music critic, George Hogarth. Hogarth invited him to contribute ''Street Sketches'' and Dickens became a regular visitor to his Fulham house – excited by Hogarth's friendship with Walter Scott
Sir Walter Scott, 1st Baronet (15 August 1771 – 21 September 1832), was a Scottish novelist, poet, playwright and historian. Many of his works remain classics of European and Scottish literature, notably the novels '' Ivanhoe'', '' Rob Roy ...
(whom Dickens greatly admired) and enjoying the company of Hogarth's three daughters: Georgina, Mary and 19-year-old Catherine.
 Dickens made rapid progress both professionally and socially. He began a friendship with William Harrison Ainsworth, the author of the highwayman novel '' Rookwood'' (1834), whose bachelor salon in Harrow Road had become the meeting place for a set that included
Dickens made rapid progress both professionally and socially. He began a friendship with William Harrison Ainsworth, the author of the highwayman novel '' Rookwood'' (1834), whose bachelor salon in Harrow Road had become the meeting place for a set that included Daniel Maclise
Daniel Maclise (25 January 180625 April 1870) was an Irish History painting, history painter, literary and Portrait painting, portrait painter, and illustrator, who worked for most of his life in London, England.
Early life
Maclise was bor ...
, Benjamin Disraeli
Benjamin Disraeli, 1st Earl of Beaconsfield, (21 December 1804 – 19 April 1881) was a British statesman and Conservative politician who twice served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom. He played a central role in the creation ...
, Edward Bulwer-Lytton
Edward George Earle Lytton Bulwer-Lytton, 1st Baron Lytton, PC (25 May 180318 January 1873) was an English writer and politician. He served as a Whig member of Parliament from 1831 to 1841 and a Conservative from 1851 to 1866. He was Secre ...
and George Cruikshank
George Cruikshank (27 September 1792 – 1 February 1878) was a British caricaturist and book illustrator, praised as the "modern Hogarth" during his life. His book illustrations for his friend Charles Dickens, and many other authors, reache ...
. All these became his friends and collaborators, with the exception of Disraeli, and he met his first publisher, John Macrone, at the house. The success of ''Sketches by Boz'' led to a proposal from publishers Chapman and Hall for Dickens to supply text to match Robert Seymour's engraved illustrations in a monthly letterpress. Seymour committed suicide after the second instalment and Dickens, who wanted to write a connected series of sketches, hired " Phiz" to provide the engravings (which were reduced from four to two per instalment) for the story. The resulting story became ''The Pickwick Papers
''The Posthumous Papers of the Pickwick Club'' (also known as ''The Pickwick Papers'') was Charles Dickens's first novel. Because of his success with '' Sketches by Boz'' published in 1836, Dickens was asked by the publisher Chapman & Hall to ...
'' and, although the first few episodes were not successful, the introduction of the Cockney character Sam Weller in the fourth episode (the first to be illustrated by Phiz) marked a sharp climb in its popularity. The final instalment sold 40,000 copies. On the impact of the character, ''The Paris Review
''The Paris Review'' is a quarterly English-language literary magazine established in Paris in 1953 by Harold L. Humes, Peter Matthiessen, and George Plimpton. In its first five years, ''The Paris Review'' published works by Jack Kerouac, Phi ...
'' stated, "arguably the most historic bump in English publishing is the Sam Weller Bump." A publishing phenomenon, John Sutherland called ''The Pickwick Papers'' " e most important single novel of the Victorian era". The unprecedented success led to numerous spin-offs and merchandise ranging from ''Pickwick'' cigars, playing cards, china figurines, Sam Weller puzzles, Weller boot polish and joke books.
On the creation of modern mass culture, Nicholas Dames in ''The Atlantic
''The Atlantic'' is an American magazine and multi-platform publisher. It features articles in the fields of politics, foreign affairs, business and the economy, culture and the arts, technology, and science.
It was founded in 1857 in Boston, ...
'' writes, "Literature" is not a big enough category for ''Pickwick''. It defined its own, a new one that we have learned to call "entertainment." In November 1836, Dickens accepted the position of editor of '' Bentley's Miscellany'', a position he held for three years, until he fell out with the owner. In 1836, as he finished the last instalments of ''The Pickwick Papers'', he began writing the beginning instalments of ''Oliver Twist
''Oliver Twist; or, The Parish Boy's Progress'', Charles Dickens's second novel, was published as a serial from 1837 to 1839, and as a three-volume book in 1838. Born in a workhouse, the orphan Oliver Twist is bound into apprenticeship with ...
'' – writing as many as 90 pages a month – while continuing work on ''Bentley's'' and also writing four plays, the production of which he oversaw. ''Oliver Twist'', published in 1838, became one of Dickens's better known stories and was the first Victorian novel with a child protagonist
A protagonist () is the main character of a story. The protagonist makes key decisions that affect the plot, primarily influencing the story and propelling it forward, and is often the character who faces the most significant obstacles. If a st ...
..
 On 2 April 1836, after a one-year engagement, and between episodes two and three of ''The Pickwick Papers'', Dickens married Catherine Thomson Hogarth (1815–1879), the daughter of George Hogarth, editor of the ''
On 2 April 1836, after a one-year engagement, and between episodes two and three of ''The Pickwick Papers'', Dickens married Catherine Thomson Hogarth (1815–1879), the daughter of George Hogarth, editor of the ''Evening Chronicle
The ''Evening Chronicle'', now referred to as ''The Comical'', is a daily newspaper produced in Newcastle upon Tyne covering North regional news, but primarily focused on Newcastle upon Tyne and surrounding area. The ''Comical'' is published by ...
''. They were married in St Luke's Church, Chelsea, London. After a brief honeymoon in Chalk
Chalk is a soft, white, porous, sedimentary carbonate rock. It is a form of limestone composed of the mineral calcite and originally formed deep under the sea by the compression of microscopic plankton that had settled to the sea floor. C ...
in Kent, the couple returned to lodgings at Furnival's Inn. The first of their ten children, Charles, was born in January 1837 and a few months later the family set up home in Bloomsbury at 48 Doughty Street, London (on which Charles had a three-year lease at £80 a year) from 25 March 1837 until December 1839. Dickens's younger brother Frederick and Catherine's 17-year-old sister Mary Hogarth moved in with them. Dickens became very attached to Mary, and she died in his arms after a brief illness in 1837. Unusually for Dickens, as a consequence of his shock, he stopped working, and he and Catherine stayed at a little farm on Hampstead Heath
Hampstead Heath (locally known simply as the Heath) is an ancient heath in London, spanning . This grassy public space sits astride a sandy ridge, one of the highest points in London, running from Hampstead to Highgate, which rests on a band ...
for a fortnight. Dickens idealised Mary; the character he fashioned after her, Rose Maylie
Rose Fleming Maylie is a fictional character in Charles Dickens' 1838 novel '' Oliver Twist'' who is eventually discovered to be the title character's maternal aunt. Though she plays a significant role in the novel, she is often omitted from drama ...
, he found he could not now kill, as he had planned, in his fiction, and, according to Ackroyd, he drew on memories of her for his later descriptions of Little Nell and Florence Dombey. His grief was so great that he was unable to meet the deadline for the June instalment of ''The Pickwick Papers'' and had to cancel the ''Oliver Twist'' instalment that month as well. The time in Hampstead was the occasion for a growing bond between Dickens and John Forster to develop; Forster soon became his unofficial business manager and the first to read his work.
 His success as a novelist continued. The young
His success as a novelist continued. The young Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until her death in 1901. Her reign of 63 years and 216 days was longer than that of any previ ...
read both ''Oliver Twist'' and ''The Pickwick Papers'', staying up until midnight to discuss them. '' Nicholas Nickleby'' (1838–39), '' The Old Curiosity Shop'' (1840–41) and, finally, his first historical novel, '' Barnaby Rudge: A Tale of the Riots of 'Eighty'', as part of the ''Master Humphrey's Clock
''Master Humphrey's Clock'' was a weekly periodical edited and written entirely by Charles Dickens and published from 4 April 1840 to 4 December 1841. It began with a frame story in which Master Humphrey tells about himself and his small circle o ...
'' series (1840–41), were all published in monthly instalments before being made into books.
In the midst of all his activity during this period, there was discontent with his publishers and John Macrone was bought off, while Richard Bentley
Richard Bentley FRS (; 27 January 1662 – 14 July 1742) was an English classical scholar, critic, and theologian. Considered the "founder of historical philology", Bentley is widely credited with establishing the English school of Hellen ...
signed over all his rights in ''Oliver Twist''. Other signs of a certain restlessness and discontent emerged; in Broadstairs
Broadstairs is a coastal town on the Isle of Thanet in the Thanet district of east Kent, England, about east of London. It is part of the civil parish of Broadstairs and St Peter's, which includes St Peter's, and had a population in 2011 o ...
he flirted with Eleanor Picken, the young fiancée of his solicitor's best friend and one night grabbed her and ran with her down to the sea. He declared they were both to drown there in the "sad sea waves". She finally got free, and afterwards kept her distance. In June 1841, he precipitously set out on a two-month tour of Scotland and then, in September 1841, telegraphed Forster that he had decided to go to America. ''Master Humphrey's Clock'' was shut down, though Dickens was still keen on the idea of the weekly magazine, a form he liked, an appreciation that had begun with his childhood reading of the 18th-century magazines ''Tatler
''Tatler'' is a British magazine published by Condé Nast Publications focusing on fashion and lifestyle, as well as coverage of high society and politics. It is targeted towards the British upper-middle class and upper class, and those interes ...
'' and ''The Spectator
''The Spectator'' is a weekly British magazine on politics, culture, and current affairs. It was first published in July 1828, making it the oldest surviving weekly magazine in the world.
It is owned by Frederick Barclay, who also owns ''Th ...
''.
Dickens was perturbed by the return to power of the Tories, whom he described as "people whom, politically, I despise and abhor." He had been tempted to stand for the Liberals in Reading, but decided against it due to financial straits. He wrote three anti-Tory verse satires ("The Fine Old English Gentleman", "The Quack Doctor's Proclamation", and "Subjects for Painters") which were published in '' The Examiner''.
First visit to the United States
On 22 January 1842, Dickens and his wife arrived inBoston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th- mo ...
, Massachusetts, aboard the RMS ''Britannia'' during their first trip to the United States and Canada. At this time Georgina Hogarth
Georgina Hogarth (22 January 1827 – 19 April 1917) was the sister-in-law, housekeeper, and adviser of English novelist Charles Dickens and the editor of three volumes of his collected letters after his death.
Biography
'Georgy' Hogarth was o ...
, another sister of Catherine, joined the Dickens household, now living at Devonshire Terrace, Marylebone
Marylebone (usually , also , ) is a district in the West End of London, in the City of Westminster. Oxford Street, Europe's busiest shopping street, forms its southern boundary.
An ancient parish and latterly a metropolitan borough, it ...
to care for the young family they had left behind. She remained with them as housekeeper, organiser, adviser and friend until Dickens's death in 1870. Dickens modelled the character of Agnes Wickfield
Agnes Wickfield is a character of '' David Copperfield'', the 1850 novel by Charles Dickens. She is a friend and confidante of David (the narrator and protagonist of this semi-autobiography) since his childhood and at the end of the novel, his sec ...
after Georgina and Mary.
 He described his impressions in a travelogue, '' American Notes for General Circulation''. In ''Notes'', Dickens includes a powerful condemnation of slavery which he had attacked as early as ''The Pickwick Papers'', correlating the emancipation of the poor in England with the abolition of slavery abroad citing newspaper accounts of runaway slaves disfigured by their masters. In spite of the abolitionist sentiments gleaned from his trip to America, some modern commentators have pointed out inconsistencies in Dickens's views on racial inequality. For instance, he has been criticized for his subsequent acquiescence in Governor Eyre's harsh crackdown during the 1860s Morant Bay rebellion in Jamaica and his failure to join other British progressives in condemning it. From
He described his impressions in a travelogue, '' American Notes for General Circulation''. In ''Notes'', Dickens includes a powerful condemnation of slavery which he had attacked as early as ''The Pickwick Papers'', correlating the emancipation of the poor in England with the abolition of slavery abroad citing newspaper accounts of runaway slaves disfigured by their masters. In spite of the abolitionist sentiments gleaned from his trip to America, some modern commentators have pointed out inconsistencies in Dickens's views on racial inequality. For instance, he has been criticized for his subsequent acquiescence in Governor Eyre's harsh crackdown during the 1860s Morant Bay rebellion in Jamaica and his failure to join other British progressives in condemning it. From Richmond, Virginia
(Thus do we reach the stars)
, image_map =
, mapsize = 250 px
, map_caption = Location within Virginia
, pushpin_map = Virginia#USA
, pushpin_label = Richmond
, pushpin_m ...
, Dickens returned to Washington, D.C., and started a trek westward, with brief pauses in Cincinnati and Louisville, to St. Louis, Missouri. While there, he expressed a desire to see an American prairie before returning east. A group of 13 men then set out with Dickens to visit Looking Glass Prairie, a trip 30 miles into Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its largest metropolitan areas include the Chicago metropolitan area, and the Metro East section, of Greater St. Louis. Other smaller metropolitan areas include, Peoria and Rock ...
.
During his American visit, Dickens spent a month in New York City, giving lectures, raising the question of international copyright laws and the pirating of his work in America. He persuaded a group of 25 writers, headed by Washington Irving
Washington Irving (April 3, 1783 – November 28, 1859) was an American short-story writer, essayist, biographer, historian, and diplomat of the early 19th century. He is best known for his short stories "Rip Van Winkle" (1819) and " The Legen ...
, to sign a petition for him to take to Congress, but the press were generally hostile to this, saying that he should be grateful for his popularity and that it was mercenary to complain about his work being pirated.
The popularity he gained caused a shift in his self-perception according to critic Kate Flint, who writes that he "found himself a cultural commodity, and its circulation had passed out his control", causing him to become interested in and delve into themes of public and personal personas in the next novels.. She writes that he assumed a role of "influential commentator", publicly and in his fiction, evident in his next few books. His trip to the U.S. ended with a trip to Canada – Niagara Falls, Toronto, Kingston and Montreal – where he appeared on stage in light comedies.
 Soon after his return to England, Dickens began work on the first of his Christmas stories, ''
Soon after his return to England, Dickens began work on the first of his Christmas stories, ''A Christmas Carol
''A Christmas Carol. In Prose. Being a Ghost Story of Christmas'', commonly known as ''A Christmas Carol'', is a novella by Charles Dickens, first published in London by Chapman & Hall in 1843 and illustrated by John Leech. ''A Christmas ...
'', written in 1843, which was followed by '' The Chimes'' in 1844 and '' The Cricket on the Hearth'' in 1845. Of these, ''A Christmas Carol'' was most popular and, tapping into an old tradition, did much to promote a renewed enthusiasm for the joys of Christmas in Britain and America. The seeds for the story became planted in Dickens's mind during a trip to Manchester to witness the conditions of the manufacturing workers there. This, along with scenes he had recently witnessed at the Field Lane Ragged School
Ragged schools were charitable organisations dedicated to the free education of destitute children in 19th century Britain. The schools were developed in working-class districts. Ragged schools were intended for society's most destitute childre ...
, caused Dickens to resolve to "strike a sledge hammer blow" for the poor. As the idea for the story took shape and the writing began in earnest, Dickens became engrossed in the book. He later wrote that as the tale unfolded he "wept and laughed, and wept again" as he "walked about the black streets of London fifteen or twenty miles many a night when all sober folks had gone to bed".
After living briefly in Italy (1844), Dickens travelled to Switzerland (1846), where he began work on '' Dombey and Son'' (1846–48). This and ''David Copperfield
''David Copperfield'' Dickens invented over 14 variations of the title for this work, see is a novel in the bildungsroman genre by Charles Dickens, narrated by the eponymous David Copperfield, detailing his adventures in his journey from inf ...
'' (1849–50) mark a significant artistic break in Dickens's career as his novels became more serious in theme and more carefully planned than his early works.
At about this time, he was made aware of a large embezzlement at the firm where his brother, Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
, worked (John Chapman & Co). It had been carried out by Thomas Powell, a clerk, who was on friendly terms with Dickens and who had acted as mentor to Augustus when he started work. Powell was also an author and poet and knew many of the famous writers of the day. After further fraudulent activities, Powell fled to New York and published a book called ''The Living Authors of England'' with a chapter on Charles Dickens, who was not amused by what Powell had written. One item that seemed to have annoyed him was the assertion that he had based the character of Paul Dombey ('' Dombey and Son'') on Thomas Chapman, one of the principal partners at John Chapman & Co. Dickens immediately sent a letter to Lewis Gaylord Clark, editor of the New York literary magazine ''The Knickerbocker
''The Knickerbocker'', or ''New-York Monthly Magazine'', was a literary magazine of New York City, founded by Charles Fenno Hoffman in 1833, and published until 1865. Its long-term editor and publisher was Lewis Gaylord Clark, whose "Editor's ...
'', saying that Powell was a forger and thief. Clark published the letter in the ''New-York Tribune
The ''New-York Tribune'' was an American newspaper founded in 1841 by editor Horace Greeley. It bore the moniker ''New-York Daily Tribune'' from 1842 to 1866 before returning to its original name. From the 1840s through the 1860s it was the domi ...
'' and several other papers picked up on the story. Powell began proceedings to sue these publications and Clark was arrested. Dickens, realising that he had acted in haste, contacted John Chapman & Co to seek written confirmation of Powell's guilt. Dickens did receive a reply confirming Powell's embezzlement, but once the directors realised this information might have to be produced in court, they refused to make further disclosures. Owing to the difficulties of providing evidence in America to support his accusations, Dickens eventually made a private settlement with Powell out of court.
Philanthropy
 Angela Burdett Coutts, heir to the Coutts banking fortune, approached Dickens in May 1846 about setting up a home for the redemption of
Angela Burdett Coutts, heir to the Coutts banking fortune, approached Dickens in May 1846 about setting up a home for the redemption of fallen women
"Fallen woman" is an archaic term which was used to describe a woman who has "lost her innocence", and fallen from the grace of God. In 19th-century Britain especially, the meaning came to be closely associated with the loss or surrender of a ...
of the working class. Coutts envisioned a home that would replace the punitive regimes of existing institutions with a reformative environment conducive to education and proficiency in domestic household chores. After initially resisting, Dickens eventually founded the home, named Urania Cottage
Georgiana Morson was a British social reformer. She served as a matron for Urania Cottage, a house for what were then called " fallen women" ( prostitutes) founded by Charles Dickens and Angela Burdett-Coutts
Angela Georgina Burdett-Coutts, ...
, in the Lime Grove area of Shepherd's Bush
Shepherd's Bush is a district of West London, England, within the London Borough of Hammersmith and Fulham west of Charing Cross, and identified as a major metropolitan centre in the London Plan.
Although primarily residential in character ...
, which he managed for ten years, setting the house rules, reviewing the accounts and interviewing prospective residents. Emigration and marriage were central to Dickens's agenda for the women on leaving Urania Cottage, from which it is estimated that about 100 women graduated between 1847 and 1859.
Religious views
As a young man, Dickens expressed a distaste for certain aspects of organised religion. In 1836, in a pamphlet titled ''Sunday Under Three Heads'', he defended the people's right to pleasure, opposing a plan to prohibit games on Sundays. "Look into your churches – diminished congregations and scanty attendance. People have grown sullen and obstinate, and are becoming disgusted with the faith which condemns them to such a day as this, once in every seven. They display their feeling by staying away rom church Turn into the streetsn a Sunday
N, or n, is the fourteenth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''en'' (pronounced ), plural ''ens''.
History
...
and mark the rigid gloom that reigns over everything around."
 Dickens honoured the figure of
Dickens honoured the figure of Jesus Christ
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label= Hebrew/ Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and relig ...
. He is regarded as a professing Christian. His son, Henry Fielding Dickens
Sir Henry Fielding Dickens, KC (16 January 1849 – 21 December 1933), was the eighth of ten children born to English author Charles Dickens and his wife Catherine. The most successful of all of Dickens's children, he was a barrister, a KC an ...
, described him as someone who "possessed deep religious convictions". In the early 1840s, he had shown an interest in Unitarian Christianity and Robert Browning
Robert Browning (7 May 1812 – 12 December 1889) was an English poet and playwright whose dramatic monologues put him high among the Victorian poets. He was noted for irony, characterization, dark humour, social commentary, historical sett ...
remarked that "Mr Dickens is an enlightened Unitarian." Professor Gary Colledge has written that he "never strayed from his attachment to popular lay Anglicanism
Anglicanism is a Western Christian tradition that has developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Europe. It is one of t ...
". Dickens authored a work called ''The Life of Our Lord
''The Life of Our Lord'' is a book about the life of Jesus of Nazareth written by English novelist Charles Dickens, for his young children, between 1846 and 1849, at about the time that he was writing ''David Copperfield''. ''The Life of Our Lord' ...
'' (1846), a book about the life of Christ, written with the purpose of sharing his faith with his children and family. In a scene from ''David Copperfield'', Dickens echoed Geoffrey Chaucer
Geoffrey Chaucer (; – 25 October 1400) was an English poet, author, and civil servant best known for '' The Canterbury Tales''. He has been called the "father of English literature", or, alternatively, the "father of English poetry". He w ...
's use of Luke 23:34 from '' Troilus and Criseyde'' (Dickens held a copy in his library), with G. K. Chesterton writing, "among the great canonical English authors, Chaucer and Dickens have the most in common."
Dickens disapproved of Roman Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
and 19th-century evangelicalism
Evangelicalism (), also called evangelical Christianity or evangelical Protestantism, is a worldwide interdenominational movement within Protestant Christianity that affirms the centrality of being " born again", in which an individual expe ...
, seeing both as extremes of Christianity and likely to limit personal expression, and was critical of what he saw as the hypocrisy of religious institutions and philosophies like spiritualism
Spiritualism is the metaphysical school of thought opposing physicalism and also is the category of all spiritual beliefs/views (in monism and dualism) from ancient to modern. In the long nineteenth century, Spiritualism (when not lowercase ...
, all of which he considered deviations from the true spirit of Christianity, as shown in the book he wrote for his family in 1846. While Dickens advocated equal rights for Catholics in England, he strongly disliked how individual civil liberties were often threatened in countries where Catholicism predominated and referred to the Catholic Church as "that curse upon the world." Dickens also rejected the Evangelical conviction that the Bible was the infallible word of God. His ideas on Biblical interpretation were similar to the Liberal Anglican Arthur Penrhyn Stanley
Arthur Penrhyn Stanley, (13 December 1815 – 18 July 1881), known as Dean Stanley, was an English Anglican priest and ecclesiastical historian. He was Dean of Westminster from 1864 to 1881. His position was that of a Broad Churchman and he wa ...
's doctrine of " progressive revelation." Leo Tolstoy
Count Lev Nikolayevich TolstoyTolstoy pronounced his first name as , which corresponds to the romanization ''Lyov''. () (; russian: link=no, Лев Николаевич Толстой,In Tolstoy's day, his name was written as in pre-refor ...
and Fyodor Dostoyevsky referred to Dickens as "that great Christian writer".
Middle years
In December 1845, Dickens took up the editorship of the London-based '' Daily News'', a liberal paper through which Dickens hoped to advocate, in his own words, "the Principles of Progress and Improvement, of Education and Civil and Religious Liberty and Equal Legislation." Among the other contributors Dickens chose to write for the paper were the radical economistThomas Hodgskin
Thomas Hodgskin (12 December 1787 – 21 August 1869) was an English socialist writer on political economy, critic of capitalism and defender of free trade and early trade unions. In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, the term ''socialis ...
and the social reformer Douglas William Jerrold, who frequently attacked the Corn Laws. Dickens lasted only ten weeks on the job before resigning due to a combination of exhaustion and frustration with one of the paper's co-owners.
The Francophile Dickens often holidayed in France and, in a speech delivered in Paris in 1846 in French, called the French "the first people in the universe".Soubigou, Gilles "Dickens's Illustrations: France and other countries" pp. 154–167 from ''The Reception of Charles Dickens in Europe'' edited by Michael Hollington London: A&C Black 2013 p. 159. During his visit to Paris, Dickens met the French literati Alexandre Dumas
Alexandre Dumas (, ; ; born Dumas Davy de la Pailleterie (), 24 July 1802 – 5 December 1870), also known as Alexandre Dumas père (where '' '' is French for 'father', to distinguish him from his son Alexandre Dumas fils), was a French writer ...
, Victor Hugo
Victor-Marie Hugo (; 26 February 1802 – 22 May 1885) was a French Romantic writer and politician. During a literary career that spanned more than sixty years, he wrote in a variety of genres and forms. He is considered to be one of the great ...
, Eugène Scribe
Augustin Eugène Scribe (; 24 December 179120 February 1861) was a French dramatist and librettist. He is known for writing "well-made plays" ("pièces bien faites"), a mainstay of popular theatre for over 100 years, and as the librettist of ma ...
, Théophile Gautier, François-René de Chateaubriand and Eugène Sue
Marie-Joseph "Eugène" Sue (; 26 January 18043 August 1857) was a French novelist. He was one of several authors who popularized the genre of the serial novel in France with his very popular and widely imitated ''The Mysteries of Paris'', whic ...
. In early 1849, Dickens started to write ''David Copperfield
''David Copperfield'' Dickens invented over 14 variations of the title for this work, see is a novel in the bildungsroman genre by Charles Dickens, narrated by the eponymous David Copperfield, detailing his adventures in his journey from inf ...
''. It was published between 1849 and 1850. In Dickens's biography, ''Life of Charles Dickens'' (1872), John Forster wrote of ''David Copperfield'', "underneath the fiction lay something of the author's life". It was Dickens's personal favourite among his own novels, as he wrote in the author's preface to the 1867 edition of the novel.
In late November 1851, Dickens moved into Tavistock House
Tavistock House was the London home of the noted British author Charles Dickens and his family from 1851 to 1860. At Tavistock House Dickens wrote ''Bleak House'', '' Hard Times'', ''Little Dorrit'' and ''A Tale of Two Cities''. He also put on a ...
where he wrote ''Bleak House
''Bleak House'' is a novel by Charles Dickens, first published as a 20-episode serial between March 1852 and September 1853. The novel has many characters and several sub-plots, and is told partly by the novel's heroine, Esther Summerson, and ...
'' (1852–53), '' Hard Times'' (1854) and '' Little Dorrit'' (1856). It was here that he indulged in the amateur theatricals described in Forster's ''Life of Charles Dickens''. During this period, he worked closely with the novelist and playwright Wilkie Collins. In 1856, his income from writing allowed him to buy Gads Hill Place
Gads Hill Place in Higham, Kent, sometimes spelt Gadshill Place and Gad's Hill Place, was the country home of Charles Dickens, the most successful British author of the Victorian era. Today the building is the independent Gad's Hill School.
...
in Higham, Kent. As a child, Dickens had walked past the house and dreamed of living in it. The area was also the scene of some of the events of Shakespeare's ''Henry IV, Part 1
''Henry IV, Part 1'' (often written as ''1 Henry IV'') is a history play by William Shakespeare, believed to have been written no later than 1597. The play dramatises part of the reign of King Henry IV of England, beginning with the battle at ...
'' and this literary connection pleased him.
During this time Dickens was also the publisher, editor and a major contributor to the journals ''Household Words'' (1850–1859) and '' All the Year Round'' (1858–1870). In 1855, when Dickens's good friend and Liberal MP Austen Henry Layard
Sir Austen Henry Layard (; 5 March 18175 July 1894) was an English Assyriologist, traveller, cuneiformist, art historian, draughtsman, collector, politician and diplomat. He was born to a mostly English family in Paris and largely raised in It ...
formed an Administrative Reform Association to demand significant reforms of Parliament, Dickens joined and volunteered his resources in support of Layard's cause. With the exception of Lord John Russell, who was the only leading politician in whom Dickens had any faith and to whom he later dedicated ''A Tale of Two Cities'', Dickens believed that the political aristocracy and their incompetence were the death of England. When he and Layard were accused of fomenting class conflict, Dickens replied that the classes were already in opposition and the fault was with the aristocratic class. Dickens used his pulpit in ''Household Words'' to champion the Reform Association. He also commented on foreign affairs, declaring his support for Giuseppe Garibaldi
Giuseppe Maria Garibaldi ( , ;In his native Ligurian language, he is known as ''Gioxeppe Gaibado''. In his particular Niçard dialect of Ligurian, he was known as ''Jousé'' or ''Josep''. 4 July 1807 – 2 June 1882) was an Italian general, pa ...
and Giuseppe Mazzini
Giuseppe Mazzini (, , ; 22 June 1805 – 10 March 1872) was an Italian politician, journalist, and activist for the unification of Italy (Risorgimento) and spearhead of the Italian revolutionary movement. His efforts helped bring about the in ...
, helping raise funds for their campaigns and stating that "a united Italy would be of vast importance to the peace of the world, and would be a rock in Louis Napoleon's way," and that "I feel for Italy almost as if I were an Italian born."
Following the Indian Mutiny of 1857, Dickens joined in the widespread criticism of the East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Sou ...
for its role in the event, but reserved his fury for the rebels themselves, wishing that he was the commander-in-chief in India so that he would be able to, "do my utmost to exterminate the Race upon whom the stain of the late cruelties rested."
 In 1857, Dickens hired professional actresses for the play '' The Frozen Deep'', written by him and his
In 1857, Dickens hired professional actresses for the play '' The Frozen Deep'', written by him and his protégé
Mentorship is the influence, guidance, or direction given by a mentor. A mentor is someone who teaches or gives help and advice to a less experienced and often younger person. In an organizational setting, a mentor influences the personal and p ...
, Wilkie Collins. Dickens fell in love with one of the actresses, Ellen Ternan
Ellen Lawless Ternan (3 March 1839 – 25 April 1914), also known as Nelly Ternan or Nelly Wharton-Robinson, was an English actress known for association with the author Charles Dickens.
Birth and family life
Ellen Ternan was born in Roches ...
, and this passion was to last the rest of his life. Dickens was 45 and Ternan 18 when he made the decision, which went strongly against Victorian convention, to separate from his wife, Catherine, in 1858; divorce was still unthinkable for someone as famous as he was. When Catherine left, never to see her husband again, she took with her one child, leaving the other children to be raised by her sister Georgina who chose to stay at Gads Hill..
During this period, whilst pondering a project to give public readings for his own profit, Dickens was approached through a charitable appeal by Great Ormond Street Hospital
Great Ormond Street Hospital (informally GOSH or Great Ormond Street, formerly the Hospital for Sick Children) is a children's hospital located in the Bloomsbury area of the London Borough of Camden, and a part of Great Ormond Street Hospita ...
to help it survive its first major financial crisis. His "Drooping Buds" essay in ''Household Words
''Household Words'' was an English weekly magazine edited by Charles Dickens in the 1850s. It took its name from the line in Shakespeare's ''Henry V'': "Familiar in his mouth as household words."
History
During the planning stages, titles origi ...
'' earlier on 3 April 1852 was considered by the hospital's founders to have been the catalyst for the hospital's success. Dickens, whose philanthropy was well-known, was asked by his friend, the hospital's founder Charles West, to preside over the appeal, and he threw himself into the task, heart and soul. Dickens's public readings secured sufficient funds for an endowment to put the hospital on a sound financial footing; one reading on 9 February 1858 alone raised £3,000.
 After separating from Catherine, Dickens undertook a series of hugely popular and remunerative reading tours which, together with his journalism, were to absorb most of his creative energies for the next decade, in which he was to write only two more novels. His first reading tour, lasting from April 1858 to February 1859, consisted of 129 appearances in 49 towns throughout England, Scotland and Ireland. Dickens's continued fascination with the theatrical world was written into the theatre scenes in ''Nicholas Nickleby'', but more importantly he found an outlet in public readings. In 1866, he undertook a series of public readings in England and Scotland, with more the following year in England and Ireland.
After separating from Catherine, Dickens undertook a series of hugely popular and remunerative reading tours which, together with his journalism, were to absorb most of his creative energies for the next decade, in which he was to write only two more novels. His first reading tour, lasting from April 1858 to February 1859, consisted of 129 appearances in 49 towns throughout England, Scotland and Ireland. Dickens's continued fascination with the theatrical world was written into the theatre scenes in ''Nicholas Nickleby'', but more importantly he found an outlet in public readings. In 1866, he undertook a series of public readings in England and Scotland, with more the following year in England and Ireland.
 Other works soon followed, including ''
Other works soon followed, including ''A Tale of Two Cities
''A Tale of Two Cities'' is a historical novel published in 1859 by Charles Dickens, set in London and Paris before and during the French Revolution. The novel tells the story of the French Doctor Manette, his 18-year-long imprisonment in ...
'' (1859) and ''Great Expectations
''Great Expectations'' is the thirteenth novel by Charles Dickens and his penultimate completed novel. It depicts the education of an orphan nicknamed Pip (Great Expectations), Pip (the book is a ''bildungsroman''; a coming-of-age story). It ...
'' (1861), which were resounding successes. Set in London and Paris, ''A Tale of Two Cities'' is his best-known work of historical fiction and includes the famous opening sentence which begins with "It was the best of times, it was the worst of times." It is regularly cited as one of the best-selling novels of all time. Themes in ''Great Expectations'' include wealth and poverty, love and rejection, and the eventual triumph of good over evil.
In early September 1860, in a field behind Gads Hill, Dickens made a bonfire of most of his correspondence; only those letters on business matters were spared. Since Ellen Ternan also destroyed all of his letters to her, the extent of the affair between the two remains speculative. In the 1930s, Thomas Wright recounted that Ternan had unburdened herself to a Canon Benham and gave currency to rumours they had been lovers. That the two had a son who died in infancy was alleged by Dickens's daughter, Kate Perugini, whom Gladys Storey had interviewed before her death in 1929. Storey published her account in ''Dickens and Daughter'', but no contemporary evidence exists. On his death, Dickens settled an annuity on Ternan which made her financially independent. Claire Tomalin
Claire Tomalin (née Delavenay; born 20 June 1933) is an English journalist and biographer, known for her biographies of Charles Dickens, Thomas Hardy, Samuel Pepys, Jane Austen and Mary Wollstonecraft.
Early life
Tomalin was born Claire Dela ...
's book, ''The Invisible Woman'', argues that Ternan lived with Dickens secretly for the last 13 years of his life. The book was subsequently turned into a play, ''Little Nell'', by Simon Gray, and a 2013 film. In the same period, Dickens furthered his interest in the paranormal
Paranormal events are purported phenomena described in popular culture, folk, and other non-scientific bodies of knowledge, whose existence within these contexts is described as being beyond the scope of normal scientific understanding. Not ...
, becoming one of the early members of The Ghost Club
The Ghost Club is a paranormal investigation and research organization, founded in London in 1862. It is believed to be the oldest such organization in the world, though its history has not been continuous. The club still investigates mainly gho ...
.
In June 1862, he was offered £10,000 for a reading tour of Australia. He was enthusiastic, and even planned a travel book, ''The Uncommercial Traveller Upside Down'', but ultimately decided against the tour. Two of his sons, Alfred D'Orsay Tennyson Dickens and Edward Bulwer Lytton Dickens, migrated to Australia, Edward becoming a member of the Parliament of New South Wales
The Parliament of New South Wales is a bicameral legislature in the Australian state of New South Wales (NSW), consisting of the New South Wales Legislative Assembly (lower house) and the New South Wales Legislative Council (upper house). Each ...
as Member for Wilcannia between 1889 and 1894.
Later life
 On 9 June 1865, while returning from Paris with Ellen Ternan, Dickens was involved in the Staplehurst rail crash in Kent. The train's first seven carriages plunged off a
On 9 June 1865, while returning from Paris with Ellen Ternan, Dickens was involved in the Staplehurst rail crash in Kent. The train's first seven carriages plunged off a cast iron
Cast iron is a class of iron– carbon alloys with a carbon content more than 2%. Its usefulness derives from its relatively low melting temperature. The alloy constituents affect its color when fractured: white cast iron has carbide impuri ...
bridge that was under repair. The only first-class carriage to remain on the track was the one in which Dickens was travelling. Before rescuers arrived, Dickens tended and comforted the wounded and the dying with a flask of brandy and a hat refreshed with water, and saved some lives. Before leaving, he remembered the unfinished manuscript for ''Our Mutual Friend
''Our Mutual Friend'', written in 1864–1865, is the last novel completed by Charles Dickens and is one of his most sophisticated works, combining savage satire with social analysis. It centres on, in the words of critic J. Hillis Miller, quo ...
'', and he returned to his carriage to retrieve it.
Dickens later used the experience of the crash as material for his short ghost story
A ghost story is any piece of fiction, or drama, that includes a ghost, or simply takes as a premise the possibility of ghosts or characters' belief in them."Ghost Stories" in Margaret Drabble (ed.), ''Oxford Companion to English Literature'' ...
, "The Signal-Man
"The Signal-Man" is a first-person horror/mystery story by Charles Dickens, first published as part of the '' Mugby Junction'' collection in the 1866 Christmas edition of '' All the Year Round''.
The railway signal-man of the title tells the n ...
", in which the central character has a premonition of his own death in a rail crash. He also based the story on several previous rail accidents, such as the Clayton Tunnel rail crash
The Clayton Tunnel rail crash occurred on Sunday 25 August 1861, from Brighton on the south coast of England. At the time it was the worst accident on the British railway system. A train ran into the back of another inside the tunnel, killing 2 ...
in Sussex of 1861. Dickens managed to avoid an appearance at the inquest
An inquest is a judicial inquiry in common law jurisdictions, particularly one held to determine the cause of a person's death. Conducted by a judge, jury, or government official, an inquest may or may not require an autopsy carried out by a c ...
to avoid disclosing that he had been travelling with Ternan and her mother, which would have caused a scandal. After the crash, Dickens was nervous when travelling by train and would use alternative means when available. In 1868 he wrote, "I have sudden vague rushes of terror, even when riding in a hansom cab, which are perfectly unreasonable but quite insurmountable." Dickens's son, Henry, recalled, "I have seen him sometimes in a railway carriage when there was a slight jolt. When this happened he was almost in a state of panic and gripped the seat with both hands."
Second visit to the United States
 While he contemplated a second visit to the United States, the outbreak of the
While he contemplated a second visit to the United States, the outbreak of the Civil War
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government polici ...
in America in 1861 delayed his plans. On 9 November 1867, over two years after the war, Dickens set sail from Liverpool
Liverpool is a City status in the United Kingdom, city and metropolitan borough in Merseyside, England. With a population of in 2019, it is the List of English districts by population, 10th largest English district by population and its E ...
for his second American reading tour. Landing in Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th- mo ...
, he devoted the rest of the month to a round of dinners with such notables as Ralph Waldo Emerson
Ralph Waldo Emerson (May 25, 1803April 27, 1882), who went by his middle name Waldo, was an American essayist, lecturer, philosopher, abolitionist, and poet who led the transcendentalist movement of the mid-19th century. He was seen as a cham ...
, Henry Wadsworth Longfellow
Henry Wadsworth Longfellow (February 27, 1807 – March 24, 1882) was an American poet and educator. His original works include "Paul Revere's Ride", ''The Song of Hiawatha'', and '' Evangeline''. He was the first American to completely trans ...
and his American publisher, James T. Fields
James Thomas Fields (December 31, 1817 – April 24, 1881) was an American publisher, editor, and poet. His business, Ticknor and Fields, was a notable publishing house in 19th century Boston.
Biography
Early life and family
He was born in ...
. In early December, the readings began. He performed 76 readings, netting £19,000, from December 1867 to April 1868.. Dickens shuttled between Boston and New York, where he gave 22 readings at Steinway Hall. Although he had started to suffer from what he called the "true American catarrh
Catarrh is an exudate of inflamed mucous membranes in one of the airways or cavities of the body, usually with reference to the throat and paranasal sinuses. It can result in a thick exudate of mucus and white blood cells caused by the swell ...
", he kept to a schedule that would have challenged a much younger man, even managing to squeeze in some sleighing in Central Park
Central Park is an urban park in New York City located between the Upper West and Upper East Sides of Manhattan. It is the fifth-largest park in the city, covering . It is the most visited urban park in the United States, with an estimated ...
.
During his travels, he saw a change in the people and the circumstances of America. His final appearance was at a banquet the American Press held in his honour at Delmonico's on 18 April, when he promised never to denounce America again. By the end of the tour Dickens could hardly manage solid food, subsisting on champagne and eggs beaten in sherry. On 23 April he boarded the Cunard
Cunard () is a British shipping and cruise line based at Carnival House at Southampton, England, operated by Carnival UK and owned by Carnival Corporation & plc. Since 2011, Cunard and its three ships have been registered in Hamilton, Ber ...
liner to return to Britain, barely escaping a federal tax lien against the proceeds of his lecture tour.
Farewell readings
 In 1868–69, Dickens gave a series of "farewell readings" in England, Scotland and Ireland, beginning on 6 October. He managed, of a contracted 100 readings, to give 75 in the provinces, with a further 12 in London. As he pressed on he was affected by giddiness and fits of paralysis. He had a stroke on 18 April 1869 in Chester. He collapsed on 22 April 1869, at
In 1868–69, Dickens gave a series of "farewell readings" in England, Scotland and Ireland, beginning on 6 October. He managed, of a contracted 100 readings, to give 75 in the provinces, with a further 12 in London. As he pressed on he was affected by giddiness and fits of paralysis. He had a stroke on 18 April 1869 in Chester. He collapsed on 22 April 1869, at Preston, Lancashire
Preston () is a city on the north bank of the River Ribble in Lancashire, England. The city is the administrative centre of the county of Lancashire and the wider City of Preston local government district. Preston and its surrounding distr ...
; on doctor's advice, the tour was cancelled. After further provincial readings were cancelled, he began work on his final novel, ''The Mystery of Edwin Drood
''The Mystery of Edwin Drood'' is the final novel by Charles Dickens, originally published in 1870.
Though the novel is named after the character Edwin Drood, it focuses more on Drood's uncle, John Jasper, a precentor, choirmaster and opium ...
''. It was fashionable in the 1860s to 'do the slums' and, in company, Dickens visited opium dens in Shadwell
Shadwell is a district of East London, England, in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets , east of Charing Cross. It lies on the north bank of the Thames between Wapping (to the west) and Ratcliff (to the east). This riverside location has mea ...
, where he witnessed an elderly addict called " Laskar Sal", who formed the model for "Opium Sal" in ''Edwin Drood''.
After Dickens regained enough strength, he arranged, with medical approval, for a final series of readings to partly make up to his sponsors what they had lost due to his illness. There were 12 performances, on 11 January to 15 March 1870; the last at 8:00pm at St. James's Hall
St. James's Hall was a concert hall in London that opened on 25 March 1858, designed by architect and artist Owen Jones, who had decorated the interior of the Crystal Palace. It was situated between the Quadrant in Regent Street and Piccadilly, ...
, London. Though in grave health by then, he read ''A Christmas Carol'' and ''The Trial from Pickwick''. On 2 May, he made his last public appearance at a Royal Academy
The Royal Academy of Arts (RA) is an art institution based in Burlington House on Piccadilly in London. Founded in 1768, it has a unique position as an independent, privately funded institution led by eminent artists and architects. Its pur ...
banquet in the presence of the Prince
A prince is a male ruler (ranked below a king, grand prince, and grand duke) or a male member of a monarch's or former monarch's family. ''Prince'' is also a title of nobility (often highest), often hereditary, in some European states. ...
and Princess of Wales
Princess of Wales (Welsh: ''Tywysoges Cymru'') is a courtesy title used since the 14th century by the wife of the heir apparent to the English and later British throne. The current title-holder is Catherine (née Middleton).
The title was fi ...
, paying a special tribute on the death of his friend, illustrator Daniel Maclise.
Death
On 8 June 1870, Dickens had another stroke at his home after a full day's work on ''Edwin Drood''. He never regained consciousness and, the next day, he died at Gads Hill Place. Biographer Claire Tomalin has suggested Dickens was actually in Peckham when he had had the stroke and his mistress Ellen Ternan and her maids had him taken back to Gads Hill so that the public would not know the truth about their relationship. Contrary to his wish to be buried atRochester Cathedral
Rochester Cathedral, formally the Cathedral Church of Christ and the Blessed Virgin Mary, is an English church of Norman architecture in Rochester, Medway, Rochester, Kent.
The church is the cathedral of the Diocese of Rochester in the Church o ...
"in an inexpensive, unostentatious, and strictly private manner", he was laid to rest in the Poets' Corner of Westminster Abbey
Westminster Abbey, formally titled the Collegiate Church of Saint Peter at Westminster, is an historic, mainly Gothic church in the City of Westminster, London, England, just to the west of the Palace of Westminster. It is one of the United ...
. A printed epitaph circulated at the time of the funeral reads:
A letter from Dickens to the Clerk of the Privy Council
A privy council is a body that advises the head of state of a state, typically, but not always, in the context of a monarchic government. The word "privy" means "private" or "secret"; thus, a privy council was originally a committee of the mo ...
in March indicates he'd been offered and had accepted a baronetcy, which was not gazetted before his death. His last words were "On the ground", in response to his sister-in-law Georgina's request that he lie down. On Sunday, 19 June 1870, five days after Dickens was buried in the Abbey, Dean Arthur Penrhyn Stanley
Arthur Penrhyn Stanley, (13 December 1815 – 18 July 1881), known as Dean Stanley, was an English Anglican priest and ecclesiastical historian. He was Dean of Westminster from 1864 to 1881. His position was that of a Broad Churchman and he wa ...
delivered a memorial elegy, lauding "the genial and loving humorist whom we now mourn", for showing by his own example "that even in dealing with the darkest scenes and the most degraded characters, genius could still be clean, and mirth could be innocent". Pointing to the fresh flowers that adorned the novelist's grave, Stanley assured those present that "the spot would thenceforth be a sacred one with both the New World and the Old, as that of the representative of literature, not of this island only, but of all who speak our English tongue."
In his will, drafted more than a year before his death, Dickens left the care of his £80,000 estate (£ in ) to his long-time colleague John Forster and his "best and truest friend" Georgina Hogarth who, along with Dickens's two sons, also received a tax-free sum of £8,000 (equivalent to £ in ). Although Dickens and his wife had been separated for several years at the time of his death, he provided her with an annual income of £600 (£ in ) and made her similar allowances in his will. He also bequeathed £19 19s (£ in ) to each servant in his employment at the time of his death.
Literary style
Dickens's approach to the novel is influenced by various things, including thepicaresque novel
The picaresque novel ( Spanish: ''picaresca'', from ''pícaro'', for "rogue" or "rascal") is a genre of prose fiction. It depicts the adventures of a roguish, but "appealing hero", usually of low social class, who lives by his wits in a corru ...
tradition, melodrama
A modern melodrama is a dramatic work in which the plot, typically sensationalized and for a strong emotional appeal, takes precedence over detailed characterization. Melodramas typically concentrate on dialogue that is often bombastic or exce ...
and the novel of sensibility
The sentimental novel or the novel of sensibility is an 18th-century literary genre which celebrates the emotional and intellectual concepts of sentiment, sentimentalism, and sensibility. Sentimentalism, which is to be distinguished from sensi ...
. According to Ackroyd, other than these, perhaps the most important literary influence on him was derived from the fables of '' The Arabian Nights''. Satire and irony
Irony (), in its broadest sense, is the juxtaposition of what on the surface appears to be the case and what is actually the case or to be expected; it is an important rhetorical device and literary technique.
Irony can be categorized int ...
are central to the picaresque novel. Comedy is also an aspect of the British picaresque novel tradition of Laurence Sterne, Henry Fielding
Henry Fielding (22 April 1707 – 8 October 1754) was an English novelist, irony writer, and dramatist known for earthy humour and satire. His comic novel ''Tom Jones'' is still widely appreciated. He and Samuel Richardson are seen as founders ...
and Tobias Smollett
Tobias George Smollett (baptised 19 March 1721 – 17 September 1771) was a Scottish poet and author. He was best known for picaresque novels such as '' The Adventures of Roderick Random'' (1748), '' The Adventures of Peregrine Pickle'' (1751 ...
. Fielding's ''Tom Jones
Tom Jones may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
*Tom Jones (singer) (born 1940), Welsh singer
*Tom Jones (writer) (1928–2023), American librettist and lyricist
*''The History of Tom Jones, a Foundling'', a novel by Henry Fielding published in 1 ...
'' was a major influence on the 19th-century novelist including Dickens, who read it in his youth and named a son Henry Fielding Dickens
Sir Henry Fielding Dickens, KC (16 January 1849 – 21 December 1933), was the eighth of ten children born to English author Charles Dickens and his wife Catherine. The most successful of all of Dickens's children, he was a barrister, a KC an ...
after him. Influenced by Gothic fiction
Gothic fiction, sometimes called Gothic horror in the 20th century, is a loose literary aesthetic of fear and haunting. The name is a reference to Gothic architecture of the European Middle Ages, which was characteristic of the settings of ea ...
—a literary genre that began with '' The Castle of Otranto'' (1764) by Horace Walpole
Horatio Walpole (), 4th Earl of Orford (24 September 1717 – 2 March 1797), better known as Horace Walpole, was an English writer, art historian, man of letters, antiquarian, and Whig politician.
He had Strawberry Hill House built in Twi ...
—Dickens incorporated Gothic imagery, settings and plot devices in his works. Victorian gothic moved from castles and abbeys into contemporary urban environments: in particular London, such as Dickens's ''Oliver Twist'' and ''Bleak House''. The jilted bride Miss Havisham
Miss Havisham is a character in the Charles Dickens novel ''Great Expectations'' (1861). She is a wealthy spinster, once jilted at the altar, who insists on wearing her wedding dress for the rest of her life. She lives in a ruined mansion with ...
from ''Great Expectations'' is one of Dickens' best-known gothic creations; living in a ruined mansion, her bridal gown effectively doubles as her funeral shroud.
No other writer had such a profound influence on Dickens as William Shakespeare
William Shakespeare ( 26 April 1564 – 23 April 1616) was an English playwright, poet and actor. He is widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's nation ...
.
On Dickens's veneration of Shakespeare, Alfred Harbage
Alfred Bennett Harbage (July 18, 1901 – May 1976) was an influential Shakespeare scholar of the mid-20th century.
Life
He was born in Philadelphia and received his undergraduate degree and doctorate from the University of Pennsylvania. ...
wrote "No one is better qualified to recognise literary genius than a literary genius"— ''A Kind of Power: The Shakespeare-Dickens Analogy'' (1975). Regarding Shakespeare as "the great master" whose plays "were an unspeakable source of delight", Dickens's lifelong affinity with the playwright included seeing theatrical productions of his plays in London and putting on amateur dramatics with friends in his early years. In 1838 Dickens travelled to Stratford-upon-Avon
Stratford-upon-Avon (), commonly known as just Stratford, is a market town and civil parish in the Stratford-on-Avon district, in the county of Warwickshire, in the West Midlands region of England. It is situated on the River Avon, north-we ...
and visited the house in which Shakespeare was born, leaving his autograph in the visitors' book. Dickens would draw on this experience in his next work, ''Nicholas Nickleby'' (1838–39), expressing the strength of feeling experienced by visitors to Shakespeare's birthplace: the character Mrs Wititterly states, "I don't know how it is, but after you've seen the place and written your name in the little book, somehow or other you seem to be inspired; it kindles up quite a fire within one."
 Dickens's writing style is marked by a profuse linguistic creativity.. Satire, flourishing in his gift for caricature, is his forte. An early reviewer compared him to Hogarth for his keen practical sense of the ludicrous side of life, though his acclaimed mastery of varieties of class idiom may in fact mirror the conventions of contemporary popular theatre. Dickens worked intensively on developing arresting names for his characters that would reverberate with associations for his readers and assist the development of motifs in the storyline, giving what one critic calls an "allegorical impetus" to the novels' meanings. To cite one of numerous examples, the name Mr Murdstone in ''David Copperfield'' conjures up twin allusions to murder and stony coldness. His literary style is also a mixture of fantasy and
Dickens's writing style is marked by a profuse linguistic creativity.. Satire, flourishing in his gift for caricature, is his forte. An early reviewer compared him to Hogarth for his keen practical sense of the ludicrous side of life, though his acclaimed mastery of varieties of class idiom may in fact mirror the conventions of contemporary popular theatre. Dickens worked intensively on developing arresting names for his characters that would reverberate with associations for his readers and assist the development of motifs in the storyline, giving what one critic calls an "allegorical impetus" to the novels' meanings. To cite one of numerous examples, the name Mr Murdstone in ''David Copperfield'' conjures up twin allusions to murder and stony coldness. His literary style is also a mixture of fantasy and realism
Realism, Realistic, or Realists may refer to:
In the arts
*Realism (arts), the general attempt to depict subjects truthfully in different forms of the arts
Arts movements related to realism include:
* Classical Realism
*Literary realism, a mov ...
. His satires of British aristocratic snobbery – he calls one character the "Noble Refrigerator" – are often popular. Comparing orphans to stocks and shares, people to tug boats or dinner-party guests to furniture are just some of Dickens's acclaimed flights of fancy.
The author worked closely with his illustrators, supplying them with a summary of the work at the outset and thus ensuring that his characters and settings were exactly how he envisioned them. He briefed the illustrator on plans for each month's instalment so that work could begin before he wrote them. Marcus Stone
Marcus Stone (4 July 1840 – 24 March 1921) was an English painter. Stone was born in London, and was educated at the Royal Academy.
Life
Marcus Clayton Stone was the son of Frank Stone ARA. Marcus was trained by his father and began to ...
, illustrator of ''Our Mutual Friend'', recalled that the author was always "ready to describe down to the minutest details the personal characteristics, and ... life-history of the creations of his fancy". Dickens employs Cockney English in many of his works, denoting working-class Londoners. Cockney grammar appears in terms such as ain't, and consonants in words are frequently omitted, as in 'ere (here) and wot (what). An example of this usage is in ''Oliver Twist''. The Artful Dodger uses cockney slang which is juxtaposed with Oliver's 'proper' English, when the Dodger repeats Oliver saying "seven" with "sivin".
Characters
Dickens's biographerClaire Tomalin
Claire Tomalin (née Delavenay; born 20 June 1933) is an English journalist and biographer, known for her biographies of Charles Dickens, Thomas Hardy, Samuel Pepys, Jane Austen and Mary Wollstonecraft.
Early life
Tomalin was born Claire Dela ...
regards him as the greatest creator of character in English fiction after Shakespeare
William Shakespeare ( 26 April 1564 – 23 April 1616) was an English playwright, poet and actor. He is widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's nation ...
.
Dickensian characters are amongst the most memorable in English literature, especially so because of their typically whimsical names. The likes of Ebenezer Scrooge
Ebenezer Scrooge () is the protagonist of Charles Dickens's 1843 novella '' A Christmas Carol''. At the beginning of the novella, Scrooge is a cold-hearted miser who despises Christmas. The tale of his redemption by three spirits (the Ghos ...
, Tiny Tim, Jacob Marley and Bob Cratchit (''A Christmas Carol''); Oliver Twist
''Oliver Twist; or, The Parish Boy's Progress'', Charles Dickens's second novel, was published as a serial from 1837 to 1839, and as a three-volume book in 1838. Born in a workhouse, the orphan Oliver Twist is bound into apprenticeship with ...
, The Artful Dodger, Fagin and Bill Sikes
William "Bill" Sikes is a fictional character and the main antagonist in the 1838 novel '' Oliver Twist'' by Charles Dickens. Sikes is a malicious criminal in Fagin's gang, and a vicious robber and murderer. Throughout much of the novel Sikes ...
(''Oliver Twist''); Pip, Miss Havisham
Miss Havisham is a character in the Charles Dickens novel ''Great Expectations'' (1861). She is a wealthy spinster, once jilted at the altar, who insists on wearing her wedding dress for the rest of her life. She lives in a ruined mansion with ...
and Abel Magwitch (''Great Expectations''); Sydney Carton, Charles Darnay
Charles Darnay, Charles D'Aulnais or Charles St. Evrémonde is a fictional character in the 1859 novel ''A Tale of Two Cities'' by Charles Dickens.
Overview
Darnay is a wealthy gentleman who spends time in both France and England during the time o ...
and Madame Defarge (''A Tale of Two Cities''); David Copperfield
''David Copperfield'' Dickens invented over 14 variations of the title for this work, see is a novel in the bildungsroman genre by Charles Dickens, narrated by the eponymous David Copperfield, detailing his adventures in his journey from inf ...
, Uriah Heep and Mr Micawber (''David Copperfield''); Daniel Quilp
Daniel Quilp is one of the main antagonists in the novel ''The Old Curiosity Shop'' by Charles Dickens, written in 1840. Quilp is a vicious, ill-tempered and grotesque dwarf and is the villain of the story. Quilp is as near as Dickens ever came to ...
and Nell Trent
Nell Trent, also referred to as Little Nell, is a fictional character in the 1841 novel ''The Old Curiosity Shop'' by Charles Dickens. The novel's main character, she is portrayed as infallibly good and virginal. An orphan, she leads her grandfath ...
(''The Old Curiosity Shop''), Samuel Pickwick and Sam Weller (''The Pickwick Papers''); and Wackford Squeers
''Nicholas Nickleby'' or ''The Life and Adventures of Nicholas Nickleby'' (or also ''The Life and Adventures of Nicholas Nickleby, Containing a Faithful Account of the Fortunes, Misfortunes, Uprisings, Downfallings, and Complete Career of the ...
(''Nicholas Nickleby'') are so well known as to be part and parcel of popular culture, and in some cases have passed into ordinary language: a ''scrooge'', for example, is a miser or someone who dislikes Christmas festivity.
 His characters were often so memorable that they took on a life of their own outside his books. "Gamp" became a slang expression for an umbrella from the character Mrs Gamp, and "Pickwickian", "Pecksniffian" and "Gradgrind" all entered dictionaries due to Dickens's original portraits of such characters who were, respectively, quixotic, hypocritical and vapidly factual. The character that made Dickens famous, Sam Weller became known for his
His characters were often so memorable that they took on a life of their own outside his books. "Gamp" became a slang expression for an umbrella from the character Mrs Gamp, and "Pickwickian", "Pecksniffian" and "Gradgrind" all entered dictionaries due to Dickens's original portraits of such characters who were, respectively, quixotic, hypocritical and vapidly factual. The character that made Dickens famous, Sam Weller became known for his Wellerism
Wellerisms, named after sayings of Sam Weller in Charles Dickens's novel '' The Pickwick Papers'', make fun of established clichés and proverbs by showing that they are wrong in certain situations, often when taken literally. In this sense, Welle ...
s—one-liners that turned proverb
A proverb (from la, proverbium) is a simple and insightful, traditional saying that expresses a perceived truth based on common sense or experience. Proverbs are often metaphorical and use formulaic language. A proverbial phrase or a proverbia ...
s on their heads. Many were drawn from real life: Mrs Nickleby is based on his mother, although she didn't recognise herself in the portrait, just as Mr Micawber is constructed from aspects of his father's 'rhetorical exuberance'; Harold Skimpole in ''Bleak House'' is based on James Henry Leigh Hunt
James Henry Leigh Hunt (19 October 178428 August 1859), best known as Leigh Hunt, was an English critic, essayist and poet.
Hunt co-founded '' The Examiner'', a leading intellectual journal expounding radical principles. He was the centre ...
; his wife's dwarfish chiropodist recognised herself in Miss Mowcher in ''David Copperfield''. Perhaps Dickens's impressions on his meeting with Hans Christian Andersen
Hans Christian Andersen ( , ; 2 April 1805 – 4 August 1875) was a Danish author. Although a prolific writer of plays, travelogues, novels, and poems, he is best remembered for his literary fairy tales.
Andersen's fairy tales, consist ...
informed the delineation of Uriah Heep (a term synonymous with sycophant).
Virginia Woolf
Adeline Virginia Woolf (; ; 25 January 1882 28 March 1941) was an English writer, considered one of the most important modernist 20th-century authors and a pioneer in the use of stream of consciousness as a narrative device.
Woolf was born ...
maintained that "we remodel our psychological geography when we read Dickens" as he produces "characters who exist not in detail, not accurately or exactly, but abundantly in a cluster of wild yet extraordinarily revealing remarks". T. S. Eliot wrote that Dickens "excelled in character; in the creation of characters of greater intensity than human beings". One "character" vividly drawn throughout his novels is London itself. Dickens described London as a magic lantern
The magic lantern, also known by its Latin name , is an early type of image projector that used pictures—paintings, prints, or photographs—on transparent plates (usually made of glass), one or more lenses, and a light source. Because a si ...
, inspiring the places and people in many of his novels. From the coaching inn
The coaching inn (also coaching house or staging inn) was a vital part of Europe's inland transport infrastructure until the development of the railway, providing a resting point ( layover) for people and horses. The inn served the needs of tr ...
s on the outskirts of the city to the lower reaches of the Thames
The River Thames ( ), known alternatively in parts as the River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At , it is the longest river entirely in England and the second-longest in the United Kingdom, after the R ...
, all aspects of the capital – Dickens's London – are described over the course of his body of work. Walking the streets (particularly around London) formed an integral part of his writing life, stoking his creativity. Dickens was known to regularly walk at least a dozen miles (19 km) per day, and once wrote, "If I couldn't walk fast and far, I should just explode and perish."
Autobiographical elements
 Authors frequently draw their portraits of characters from people they have known in real life. ''David Copperfield'' is regarded by many as a veiled autobiography of Dickens. The scenes of interminable court cases and legal arguments in ''Bleak House'' reflect Dickens's experiences as a law clerk and court reporter, and in particular his direct experience of the law's procedural delay during 1844 when he sued publishers in Chancery for breach of copyright. Dickens's father was sent to prison for debt and this became a common theme in many of his books, with the detailed depiction of life in the Marshalsea prison in ''Little Dorrit'' resulting from Dickens's own experiences of the institution. Lucy Stroughill, a childhood sweetheart, may have affected several of Dickens's portraits of girls such as Little Em'ly in ''David Copperfield'' and Lucie Manette in ''A Tale of Two Cities.''
Dickens may have drawn on his childhood experiences, but he was also ashamed of them and would not reveal that this was where he gathered his realistic accounts of squalor. Very few knew the details of his early life until six years after his death, when John Forster published a biography on which Dickens had collaborated. Though Skimpole brutally sends up Leigh Hunt, some critics have detected in his portrait features of Dickens's own character, which he sought to exorcise by self-parody.
Authors frequently draw their portraits of characters from people they have known in real life. ''David Copperfield'' is regarded by many as a veiled autobiography of Dickens. The scenes of interminable court cases and legal arguments in ''Bleak House'' reflect Dickens's experiences as a law clerk and court reporter, and in particular his direct experience of the law's procedural delay during 1844 when he sued publishers in Chancery for breach of copyright. Dickens's father was sent to prison for debt and this became a common theme in many of his books, with the detailed depiction of life in the Marshalsea prison in ''Little Dorrit'' resulting from Dickens's own experiences of the institution. Lucy Stroughill, a childhood sweetheart, may have affected several of Dickens's portraits of girls such as Little Em'ly in ''David Copperfield'' and Lucie Manette in ''A Tale of Two Cities.''
Dickens may have drawn on his childhood experiences, but he was also ashamed of them and would not reveal that this was where he gathered his realistic accounts of squalor. Very few knew the details of his early life until six years after his death, when John Forster published a biography on which Dickens had collaborated. Though Skimpole brutally sends up Leigh Hunt, some critics have detected in his portrait features of Dickens's own character, which he sought to exorcise by self-parody.
Episodic writing
 A pioneer of the serial publication of narrative fiction, Dickens wrote most of his major novels in monthly or weekly instalments in journals such as ''
A pioneer of the serial publication of narrative fiction, Dickens wrote most of his major novels in monthly or weekly instalments in journals such as ''Master Humphrey's Clock
''Master Humphrey's Clock'' was a weekly periodical edited and written entirely by Charles Dickens and published from 4 April 1840 to 4 December 1841. It began with a frame story in which Master Humphrey tells about himself and his small circle o ...
'' and ''Household Words
''Household Words'' was an English weekly magazine edited by Charles Dickens in the 1850s. It took its name from the line in Shakespeare's ''Henry V'': "Familiar in his mouth as household words."
History
During the planning stages, titles origi ...
'', later reprinted in book form. These instalments made the stories affordable and accessible, with the audience more evenly distributed across income levels than previous. His instalment format inspired a narrative that he would explore and develop throughout his career, and the regular cliffhanger
A cliffhanger or cliffhanger ending is a plot device in fiction which features a main character in a precarious or difficult dilemma or confronted with a shocking revelation at the end of an episode or a film of serialized fiction. A cliffhang ...
s made each new episode widely anticipated. When '' The Old Curiosity Shop'' was being serialised, American fans waited at the docks in New York harbour, shouting out to the crew of an incoming British ship, "Is little Nell dead?" Dickens's talent was to incorporate this episodic writing style but still end up with a coherent novel at the end.
Another important impact of Dickens's episodic writing style resulted from his exposure to the opinions of his readers and friends. His friend Forster had a significant hand in reviewing his drafts, an influence that went beyond matters of punctuation. He toned down melodramatic and sensationalist exaggerations, cut long passages (such as the episode of Quilp's drowning in ''The Old Curiosity Shop''), and made suggestions about plot and character. It was he who suggested that Charley Bates should be redeemed in ''Oliver Twist''. Dickens had not thought of killing Little Nell and it was Forster who advised him to entertain this possibility as necessary to his conception of the heroine.
At the helm in popularising cliffhangers and serial publications in Victorian literature, Dickens's influence can also be seen in television soap operas
A soap opera, or ''soap'' for short, is a typically long-running radio or television serial, frequently characterized by melodrama, ensemble casts, and sentimentality. The term "soap opera" originated from radio dramas originally being sponsored ...
and film series A film series or movie series (also referred to as a film franchise or movie franchise) is a collection of related films in succession that share the same fictional universe, or are marketed as a series.
This article explains what film series are ...
, with ''The Guardian'' stating "the DNA of Dickens's busy, episodic storytelling, delivered in instalments and rife with cliffhangers and diversions, is traceable in everything." His serialisation of his novels also drew comments from other writers. In Scottish author Robert Louis Stevenson
Robert Louis Stevenson (born Robert Lewis Balfour Stevenson; 13 November 1850 – 3 December 1894) was a Scottish novelist, essayist, poet and travel writer. He is best known for works such as '' Treasure Island'', ''Strange Case of Dr Jekyll ...
's novel '' The Wrecker'', Captain Nares, investigating an abandoned ship, remarked: "See! They were writing up the log," said Nares, pointing to the ink-bottle. "Caught napping, as usual. I wonder if there ever was a captain yet that lost a ship with his log-book up to date? He generally has about a month to fill up on a clean break, like Charles Dickens and his serial novels."
Social commentary
 Dickens's novels were, among other things, works of social commentary. Simon Callow states, "From the moment he started to write, he spoke for the people, and the people loved him for it." He was a fierce critic of the poverty and
Dickens's novels were, among other things, works of social commentary. Simon Callow states, "From the moment he started to write, he spoke for the people, and the people loved him for it." He was a fierce critic of the poverty and social stratification
Social stratification refers to a society's categorization of its people into groups based on socioeconomic factors like wealth, income, race, education, ethnicity, gender, occupation, social status, or derived power (social and politi ...
of Victorian society. In a New York address, he expressed his belief that "Virtue shows quite as well in rags and patches as she does in purple and fine linen". Dickens's second novel, ''Oliver Twist'' (1839), shocked readers with its images of poverty and crime: it challenged middle class polemics about criminals, making impossible any pretence to ignorance about what poverty entailed.
At a time when Britain was the major economic and political power of the world, Dickens highlighted the life of the forgotten poor and disadvantaged within society. Through his journalism he campaigned on specific issues – such as sanitation
Sanitation refers to public health conditions related to clean drinking water and treatment and disposal of human excreta and sewage. Preventing human contact with feces is part of sanitation, as is hand washing with soap. Sanitation syste ...
and the workhouse
In Britain, a workhouse () was an institution where those unable to support themselves financially were offered accommodation and employment. (In Scotland, they were usually known as poorhouses.) The earliest known use of the term ''workhouse' ...
– but his fiction probably demonstrated its greatest prowess in changing public opinion in regard to class inequalities. He often depicted the exploitation and oppression of the poor and condemned the public officials and institutions that not only allowed such abuses to exist, but flourished as a result. His most strident indictment of this condition is in ''Hard Times'' (1854), Dickens's only novel-length treatment of the industrial working class. In this work, he uses vitriol and satire to illustrate how this marginalised social stratum was termed "Hands" by the factory owners; that is, not really "people" but rather only appendages of the machines they operated. His writings inspired others, in particular journalists and political figures, to address such problems of class oppression. For example, the prison scenes in ''The Pickwick Papers'' are claimed to have been influential in having the Fleet Prison shut down. Karl Marx
Karl Heinrich Marx (; 5 May 1818 – 14 March 1883) was a German philosopher, economist, historian, sociologist, political theorist, journalist, critic of political economy, and socialist revolutionary. His best-known titles are the 1848 ...
asserted that Dickens "issued to the world more political and social truths than have been uttered by all the professional politicians, publicists and moralists put together".. George Bernard Shaw
George Bernard Shaw (26 July 1856 – 2 November 1950), known at his insistence simply as Bernard Shaw, was an Irish playwright, critic, polemicist and political activist. His influence on Western theatre, culture and politics extended from ...
even remarked that ''Great Expectations'' was more seditious than Marx's ''Das Kapital
''Das Kapital'', also known as ''Capital: A Critique of Political Economy'' or sometimes simply ''Capital'' (german: Das Kapital. Kritik der politischen Ökonomie, link=no, ; 1867–1883), is a foundational theoretical text in materialist phi ...
''. The exceptional popularity of Dickens's novels, even those with socially oppositional themes (''Bleak House'', 1853; ''Little Dorrit'', 1857; ''Our Mutual Friend'', 1865), not only underscored his ability to create compelling storylines and unforgettable characters, but also ensured that the Victorian public confronted issues of social justice that had commonly been ignored.
It has been argued that his technique of flooding his narratives with an 'unruly superfluity of material' that, in the gradual dénouement, yields up an unsuspected order, influenced the organisation of Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all species of life have descended ...
's ''On the Origin of Species
''On the Origin of Species'' (or, more completely, ''On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection, or the Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life''),The book's full original title was ''On the Origin of Species by Me ...
''.
Literary techniques

 Dickens is often described as using idealised characters and highly sentimental scenes to contrast with his
Dickens is often described as using idealised characters and highly sentimental scenes to contrast with his caricature
A caricature is a rendered image showing the features of its subject in a simplified or exaggerated way through sketching, pencil strokes, or other artistic drawings (compare to: cartoon). Caricatures can be either insulting or complimentary, ...
s and the ugly social truths he reveals. The story of Nell Trent in ''The Old Curiosity Shop'' (1841) was received as extraordinarily moving by contemporary readers but viewed as ludicrously sentimental by Oscar Wilde
Oscar Fingal O'Flahertie Wills Wilde (16 October 185430 November 1900) was an Irish poet and playwright. After writing in different forms throughout the 1880s, he became one of the most popular playwrights in London in the early 1890s. He is ...
. "One must have a heart of stone to read the death of little Nell", he said in a famous remark, "without dissolving into tears ... of laughter." G. K. Chesterton stated, "It is not the death of little Nell, but the life of little Nell, that I object to", arguing that the maudlin effect of his description of her life owed much to the gregarious nature of Dickens's grief, his "despotic" use of people's feelings to move them to tears in works like this.
The question as to whether Dickens belongs to the tradition of the sentimental novel is debatable. Valerie Purton, in her book ''Dickens and the Sentimental Tradition'', sees him continuing aspects of this tradition, and argues that his "sentimental scenes and characters reas crucial to the overall power of the novels as his darker or comic figures and scenes", and that "''Dombey and Son'' is ... Dickens's greatest triumph in the sentimentalist tradition". The ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' online comments that, despite "patches of emotional excess", such as the reported death of Tiny Tim in ''A Christmas Carol'' (1843), "Dickens cannot really be termed a sentimental novelist".
In ''Oliver Twist'' Dickens provides readers with an idealised portrait of a boy so inherently and unrealistically good that his values are never subverted by either brutal orphanages or coerced involvement in a gang of young pickpockets. While later novels also centre on idealised characters (Esther Summerson in ''Bleak House'' and Amy Dorrit in ''Little Dorrit''), this idealism serves only to highlight Dickens's goal of poignant social commentary. Dickens's fiction, reflecting what he believed to be true of his own life, makes frequent use of coincidence, either for comic effect or to emphasise the idea of providence. For example, Oliver Twist turns out to be the lost nephew of the upper-class family that rescues him from the dangers of the pickpocket group. Such coincidences are a staple of 18th-century picaresque novels, such as Henry Fielding's ''Tom Jones
Tom Jones may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
*Tom Jones (singer) (born 1940), Welsh singer
*Tom Jones (writer) (1928–2023), American librettist and lyricist
*''The History of Tom Jones, a Foundling'', a novel by Henry Fielding published in 1 ...
,'' which Dickens enjoyed reading as a youth.
Reputation
 Dickens was the most popular novelist of his time, and remains one of the best-known and most-read of English authors. His works have never gone
Dickens was the most popular novelist of his time, and remains one of the best-known and most-read of English authors. His works have never gone out of print
__NOTOC__
An out-of-print (OOP) or out-of-commerce item or work is something that is no longer being published. The term applies to all types of printed matter, visual media, sound recordings, and video recordings. An out-of-print book is a boo ...
, and have been adapted continually for the screen since the invention of cinema, with at least 200 motion pictures and TV adaptations based on Dickens's works documented. Many of his works were adapted for the stage during his own lifetime – early productions included ''The Haunted Man and the Ghost's Bargain'' which was performed in the West End's Adelphi Theatre
The Adelphi Theatre is a West End theatre, located on the Strand in the City of Westminster, central London. The present building is the fourth on the site. The theatre has specialised in comedy and musical theatre, and today it is a receivin ...
in 1848 – and, as early as 1901, the British silent film '' Scrooge, or, Marley's Ghost'' was made by Walter R. Booth
Walter Robert Booth (12 July 1869 – 1938) was a British magician and early pioneer of British film. Collaborating with Robert W. Paul and then Charles Urban mostly on "trick" films, he pioneered techniques that led to what has been descri ...
. Contemporaries such as publisher Edward Lloyd cashed in on Dickens's popularity with cheap imitations of his novels, resulting in his own popular ' penny dreadfuls'.
From the beginning of his career in the 1830s, Dickens's achievements in English literature were compared to those of Shakespeare. Dickens created some of the world's best-known fictional characters and is regarded by many as the greatest British novelist of the Victorian era
In the history of the United Kingdom and the British Empire, the Victorian era was the period of Queen Victoria's reign, from 20 June 1837 until her death on 22 January 1901. The era followed the Georgian period and preceded the Edwa ...
. His literary reputation, however began to decline with the publication of ''Bleak House'' in 1852–53. Philip Collins calls ''Bleak House'' 'a crucial item in the history of Dickens's reputation. Reviewers and literary figures during the 1850s, 1860s and 1870s, saw a "drear decline" in Dickens, from a writer of "bright sunny comedy ... to dark and serious social" commentary. ''The Spectator
''The Spectator'' is a weekly British magazine on politics, culture, and current affairs. It was first published in July 1828, making it the oldest surviving weekly magazine in the world.
It is owned by Frederick Barclay, who also owns ''Th ...
'' called ''Bleak House'' "a heavy book to read through at once ... dull and wearisome as a serial"; Richard Simpson, in '' The Rambler'', characterised ''Hard Times'' as "this dreary framework"; '' Fraser's Magazine'' thought ''Little Dorrit'' "decidedly the worst of his novels".Adam Roerts, "Dickens Reputation", p. 505. All the same, despite these "increasing reservations amongst reviewers and the chattering classes, 'the public never deserted its favourite'". Dickens's popular reputation remained unchanged, sales continued to rise, and ''Household Words
''Household Words'' was an English weekly magazine edited by Charles Dickens in the 1850s. It took its name from the line in Shakespeare's ''Henry V'': "Familiar in his mouth as household words."
History
During the planning stages, titles origi ...
'' and later '' All the Year Round'' were highly successful.
 As his career progressed, Dickens's fame and the demand for his public readings were unparalleled. In 1868 ''
As his career progressed, Dickens's fame and the demand for his public readings were unparalleled. In 1868 ''The Times
''The Times'' is a British daily national newspaper based in London. It began in 1785 under the title ''The Daily Universal Register'', adopting its current name on 1 January 1788. ''The Times'' and its sister paper '' The Sunday Times'' ( ...
'' wrote, "Amid all the variety of 'readings', those of Mr Charles Dickens stand alone." A Dickens biographer, Edgar Johnson, wrote in the 1950s: "It was lwaysmore than a reading; it was an extraordinary exhibition of acting that seized upon its auditors with a mesmeric possession." Juliet John backed the claim for Dickens "to be called the first self-made global media star of the age of mass culture." Comparing his reception at public readings to those of a contemporary pop star, ''The Guardian'' states, "People sometimes fainted at his shows. His performances even saw the rise of that modern phenomenon, the 'speculator' or ticket tout
Ticket or tickets may refer to:
Slips of paper
* Lottery ticket
* Parking ticket, a ticket confirming that the parking fee was paid (and the time of the parking start)
* Toll ticket, a slip of paper used to indicate where vehicles entered a tol ...
(scalpers) – the ones in New York City escaped detection by borrowing respectable-looking hats from the waiters in nearby restaurants."
Among fellow writers, there was a range of opinions on Dickens. Poet laureate
A poet laureate (plural: poets laureate) is a poet officially appointed by a government or conferring institution, typically expected to compose poems for special events and occasions. Albertino Mussato of Padua and Francesco Petrarca (Petrarch ...
, William Wordsworth
William Wordsworth (7 April 177023 April 1850) was an English Romantic poet who, with Samuel Taylor Coleridge, helped to launch the Romantic Age in English literature with their joint publication '' Lyrical Ballads'' (1798).
Wordsworth's ' ...
(1770–1850), thought him a "very talkative, vulgar young person", adding he had not read a line of his work, while novelist George Meredith
George Meredith (12 February 1828 – 18 May 1909) was an English novelist and poet of the Victorian era. At first his focus was poetry, influenced by John Keats among others, but he gradually established a reputation as a novelist. '' The Ord ...
(1828–1909), found Dickens "intellectually lacking". In 1888 Leslie Stephen
Sir Leslie Stephen (28 November 1832 – 22 February 1904) was an English author, critic, historian, biographer, and mountaineer, and the father of Virginia Woolf and Vanessa Bell.
Life
Sir Leslie Stephen came from a distinguished intellect ...
commented in the ''Dictionary of National Biography
The ''Dictionary of National Biography'' (''DNB'') is a standard work of reference on notable figures from British history, published since 1885. The updated ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'' (''ODNB'') was published on 23 September ...
'' that "if literary fame could be safely measured by popularity with the half-educated, Dickens must claim the highest position among English novelists". Anthony Trollope
Anthony Trollope (; 24 April 1815 – 6 December 1882) was an English novelist and civil servant of the Victorian era. Among his best-known works is a series of novels collectively known as the '' Chronicles of Barsetshire'', which revolves ar ...
's ''Autobiography'' famously declared Thackeray, not Dickens, to be the greatest novelist of the age. However, both Leo Tolstoy
Count Lev Nikolayevich TolstoyTolstoy pronounced his first name as , which corresponds to the romanization ''Lyov''. () (; russian: link=no, Лев Николаевич Толстой,In Tolstoy's day, his name was written as in pre-refor ...
and Fyodor Dostoyevsky were admirers. Dostoyevsky commented: "We understand Dickens in Russia, I am convinced, almost as well as the English, perhaps even with all the nuances. It may well be that we love him no less than his compatriots do. And yet how original is Dickens, and how very English!" Tolstoy referred to ''David Copperfield'' as his favourite book, and he later adopted the novel as "a model for his own autobiographical reflections". French writer Jules Verne
Jules Gabriel Verne (;''Longman Pronunciation Dictionary''. ; 8 February 1828 – 24 March 1905) was a French novelist, poet, and playwright. His collaboration with the publisher Pierre-Jules Hetzel led to the creation of the '' Voyages extra ...
called Dickens his favourite writer, writing his novels "stand alone, dwarfing all others by their amazing power and felicity of expression". Dutch painter Vincent van Gogh
Vincent Willem van Gogh (; 30 March 185329 July 1890) was a Dutch Post-Impressionist painter who posthumously became one of the most famous and influential figures in Western art history. In a decade, he created about 2,100 artworks, inc ...
was inspired by Dickens's novels in several of his paintings like ''Vincent's Chair'' and in an 1889 letter to his sister stated that reading Dickens, especially ''A Christmas Carol'', was one of the things that was keeping him from committing suicide. Oscar Wilde generally disparaged his depiction of character, while admiring his gift for caricature. Henry James denied him a premier position, calling him "the greatest of superficial novelists": Dickens failed to endow his characters with psychological depth, and the novels, "loose baggy monsters", betrayed a "cavalier organisation". Joseph Conrad
Joseph Conrad (born Józef Teodor Konrad Korzeniowski, ; 3 December 1857 – 3 August 1924) was a Polish-British novelist and short story writer. He is regarded as one of the greatest writers in the English language; though he did not spe ...
described his own childhood in bleak Dickensian terms, noting he had "an intense and unreasoning affection" for ''Bleak House'' dating back to his boyhood. The novel influenced his own gloomy portrait of London in ''The Secret Agent
''The Secret Agent: A Simple Tale'' is a novel by Joseph Conrad, first published in 1907.. The story is set in London in 1886 and deals with Mr. Adolf Verloc and his work as a spy for an unnamed country (presumably Russia). ''The Secret Agent ...
'' (1907). Virginia Woolf
Adeline Virginia Woolf (; ; 25 January 1882 28 March 1941) was an English writer, considered one of the most important modernist 20th-century authors and a pioneer in the use of stream of consciousness as a narrative device.
Woolf was born ...
had a love-hate relationship with Dickens, finding his novels "mesmerizing" while reproving him for his sentimentalism and a commonplace style.
Around 1940–41, the attitude of the literary critics began to warm towards Dickens – led by George Orwell
Eric Arthur Blair (25 June 1903 – 21 January 1950), better known by his pen name George Orwell, was an English novelist, essayist, journalist, and critic. His work is characterised by lucid prose, social criticism, opposition to totalit ...
in ''Inside the Whale and Other Essays
''Inside the Whale and Other Essays'' is a book of essays written by George Orwell in 1940. It includes the eponymous essay " Inside the Whale".
Background
''Inside the Whale'' was published by Victor Gollancz as a book of essays on 11 March 194 ...
'' (March 1940), Edmund Wilson
Edmund Wilson Jr. (May 8, 1895 – June 12, 1972) was an American writer and literary critic who explored Freudian and Marxist themes. He influenced many American authors, including F. Scott Fitzgerald, whose unfinished work he edited for publi ...
in ''The Wound and the Bow'' (1941) and Humphry House in ''Dickens and his World''. However, even in 1948, F. R. Leavis, in ''The Great Tradition
''The Great Tradition'' is a book of literary criticism written by F R Leavis, published in 1948 by Chatto & Windus.
Highlights of the book
In his work, Leavis names Jane Austen, George Eliot, Henry James, and Joseph Conrad as the great English ...
'', asserted that "the adult mind doesn't as a rule find in Dickens a challenge to an unusual and sustained seriousness"; Dickens was indeed a great genius, "but the genius was that of a great entertainer", though he later changed his opinion with ''Dickens the Novelist'' (1970, with Q. D. (Queenie) Leavis): "Our purpose", they wrote, "is to enforce as unanswerably as possible the conviction that Dickens was one of the greatest of creative writers". In 1944, Soviet film director and film theorist Sergei Eisenstein
Sergei Mikhailovich Eisenstein (russian: Сергей Михайлович Эйзенштейн, p=sʲɪrˈɡʲej mʲɪˈxajləvʲɪtɕ ɪjzʲɪnˈʂtʲejn, 2=Sergey Mikhaylovich Eyzenshteyn; 11 February 1948) was a Soviet film director, scree ...
wrote an essay on Dickens's influence on cinema, such as cross-cutting
Cross-cutting is an editing technique most often used in films to establish action occurring at the same time, and often in the same place. In a cross-cut, the camera will cut away from one action to another action, which can suggest the simultan ...
– where two stories run alongside each other, as seen in novels such as ''Oliver Twist''.
In the 1950s, "a substantial reassessment and re-editing of the works began, and critics found his finest artistry and greatest depth to be in the later novels: ''Bleak House'', ''Little Dorrit'', and ''Great Expectations'' – and (less unanimously) in ''Hard Times'' and ''Our Mutual Friend''". Dickens was a favourite author of Roald Dahl
Roald Dahl (13 September 1916 – 23 November 1990) was a British novelist, short-story writer, poet, screenwriter, and wartime fighter ace of Norwegian descent. His books have sold more than 250 million copies worldwide. Dahl has be ...
; the best-selling children's author would include three of Dickens's novels among those read by the title character
The title character in a narrative work is one who is named or referred to in the title of the work. In a performed work such as a play or film, the performer who plays the title character is said to have the title role of the piece. The title of ...
in his 1988 novel ''Matilda
Matilda or Mathilda may refer to:
Animals
* Matilda (chicken) (1990–2006), World's Oldest Living Chicken record holder
* Matilda (horse) (1824–1846), British Thoroughbred racehorse
* Matilda, a dog of the professional wrestling tag-team The ...
''. An avid reader of Dickens, in 2005, Paul McCartney
Sir James Paul McCartney (born 18 June 1942) is an English singer, songwriter and musician who gained worldwide fame with the Beatles, for whom he played bass guitar and shared primary songwriting and lead vocal duties with John Lennon. One ...
named ''Nicholas Nickleby'' his favourite novel. On Dickens he states, "I like the world that he takes me to. I like his words; I like the language", adding, "A lot of my stuff – it's kind of Dickensian." Screenwriter Jonathan Nolan's screenplay for ''The Dark Knight Rises
''The Dark Knight Rises'' is a 2012 superhero film directed by Christopher Nolan, who co-wrote the screenplay with his brother Jonathan Nolan, and the story with David S. Goyer. The film is based on the DC Comics character Batman, it is th ...
'' (2012) was inspired by ''A Tale of Two Cities'', with Nolan calling the depiction of Paris in the novel "one of the most harrowing portraits of a relatable, recognisable civilisation that completely folded to pieces". On 7 February 2012, the 200th anniversary of Dickens's birth, Philip Womack
Philip Womack (born in 1981) is a British writer and journalist. Womack married Princess Tatiana von Preussen in 2014.
Education
Womack was educated aDorset House Preparatory School Lancing College, BPP Law School, and read Classics and English ...
wrote in ''The Telegraph'': "Today there is no escaping Charles Dickens. Not that there has ever been much chance of that before. He has a deep, peculiar hold upon us".
Legacy
Oliver Twist
''Oliver Twist; or, The Parish Boy's Progress'', Charles Dickens's second novel, was published as a serial from 1837 to 1839, and as a three-volume book in 1838. Born in a workhouse, the orphan Oliver Twist is bound into apprenticeship with ...
'', ''The Pickwick Papers
''The Posthumous Papers of the Pickwick Club'' (also known as ''The Pickwick Papers'') was Charles Dickens's first novel. Because of his success with '' Sketches by Boz'' published in 1836, Dickens was asked by the publisher Chapman & Hall to ...
'' and '' Nicholas Nickleby''; and the Charles Dickens Birthplace Museum in Portsmouth, the house in which he was born. The original manuscripts of many of his novels, as well as printers' proofs, first editions, and illustrations from the collection of Dickens's friend John Forster are held at the Victoria and Albert Museum
The Victoria and Albert Museum (often abbreviated as the V&A) in London is the world's largest museum of applied arts, decorative arts and design, housing a permanent collection of over 2.27 million objects. It was founded in 1852 and nam ...
. Dickens's will stipulated that no memorial be erected in his honour; nonetheless, a life-size bronze statue of Dickens entitled '' Dickens and Little Nell'', cast in 1890 by Francis Edwin Elwell
Francis Edwin Elwell (also cited as Frank Edwin Elwell) (June 15, 1858, Concord, Massachusetts – January 23, 1922, Darien, Connecticut) was an American sculptor, teacher, and author.
He lectured on art at Harvard University, and taught modelin ...
, stands in Clark Park in the Spruce Hill neighbourhood of Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Since ...
, Pennsylvania. Another life-size statue of Dickens is located at Centennial Park in Sydney, Australia
Sydney ( ) is the capital city of the States and territories of Australia, state of New South Wales, and the most populous city in both Australia and List of cities in Oceania by population, Oceania. Located on Australia's east coast, the metro ...
. In 1960 a bas-relief
Relief is a sculptural method in which the sculpted pieces are bonded to a solid background of the same material. The term '' relief'' is from the Latin verb ''relevo'', to raise. To create a sculpture in relief is to give the impression that th ...
sculpture of Dickens, notably featuring characters from his books, was commissioned from sculptor Estcourt J Clack to adorn the office building built on the site of his former home at 1 Devonshire Terrace, London. In 2014, a life-size statue was unveiled near his birthplace in Portsmouth on the 202nd anniversary of his birth; this was supported by his great-great-grandsons, Ian and Gerald Dickens.
 ''A Christmas Carol'' is most probably his best-known story, with frequent new adaptations. It is also the most-filmed of Dickens's stories, with many versions dating from the early years of cinema. According to the historian
''A Christmas Carol'' is most probably his best-known story, with frequent new adaptations. It is also the most-filmed of Dickens's stories, with many versions dating from the early years of cinema. According to the historian Ronald Hutton
Ronald Edmund Hutton (born 19 December 1953) is an English historian who specialises in Early Modern Britain, British folklore, pre-Christian religion and Contemporary Paganism. He is a professor at the University of Bristol, has written 14 ...
, the current state of the observance of Christmas is largely the result of a mid-Victorian revival of the holiday spearheaded by ''A Christmas Carol''. Dickens catalysed the emerging Christmas as a family-centred festival of generosity, in contrast to the dwindling community-based and church-centred observations, as new middle-class expectations arose. Its archetypal figures (Scrooge, Tiny Tim, the Christmas ghosts) entered into Western cultural consciousness. "Merry Christmas
The Christmas season or the festive season (also known in some countries as the holiday season or the holidays) is an annually recurring period recognized in many Western and other countries that is generally considered to run from late Novemb ...
", a prominent phrase from the tale, was popularised following the appearance of the story. The term Scrooge became a synonym for miser, and his exclamation "Bah! Humbug!'", a dismissal of the festive spirit, likewise gained currency as an idiom. The Victorian era novelist William Makepeace Thackeray
William Makepeace Thackeray (; 18 July 1811 – 24 December 1863) was a British novelist, author and illustrator. He is known for his satirical works, particularly his 1848 novel ''Vanity Fair'', a panoramic portrait of British society, and t ...
called the book "a national benefit, and to every man and woman who reads it a personal kindness".
Dickens was commemorated on the Series E £10 note issued by the Bank of England
The Bank of England is the central bank of the United Kingdom and the model on which most modern central banks have been based. Established in 1694 to act as the English Government's banker, and still one of the bankers for the Government o ...
that circulated between 1992 and 2003. His portrait appeared on the reverse of the note accompanied by a scene from ''The Pickwick Papers''. The Charles Dickens School
The Charles Dickens School is a co-educational secondary modern school located in Broadstairs in the English county of Kent. The school is named after Charles Dickens, the 19th-century writer and social critic. It is one of six non-selective scho ...
is a high school in Broadstairs, Kent. A theme park, Dickens World
Dickens World was a themed attraction located in the Chatham Dockside retail park in Kent, England. It was themed around elements of the life and work of Charles Dickens. After a soft opening in April, Dickens World officially opened to the pu ...
, standing in part on the site of the former naval dockyard where Dickens's father once worked in the Navy Pay Office, opened in Chatham in 2007. To celebrate the 200th anniversary of the birth of Charles Dickens in 2012, the Museum of London
The Museum of London is a museum in London, covering the history of the UK's capital city from prehistoric to modern times. It was formed in 1976 by amalgamating collections previously held by the City Corporation at the Guildhall Museum (fou ...
held the UK's first major exhibition on the author in 40 years. In 2002, Dickens was number 41 in the BBC's poll of the 100 Greatest Britons
''100 Greatest Britons'' is a television series that was broadcast by the BBC in 2002. It was based on a television poll conducted to determine who the British people at that time considered the greatest Britons in history. The series included in ...
. American literary critic Harold Bloom
Harold Bloom (July 11, 1930 – October 14, 2019) was an American literary critic and the Sterling Professor of Humanities at Yale University. In 2017, Bloom was described as "probably the most famous literary critic in the English-speaking worl ...
placed Dickens among the greatest Western writers of all time. In the 2003 UK survey The Big Read carried out by the BBC, five of Dickens's books were named in the Top 100.
Actors who have portrayed Dickens on screen include Anthony Hopkins
Sir Philip Anthony Hopkins (born 31 December 1937) is a Welsh actor, director, and producer. One of Britain's most recognisable and prolific actors, he is known for his performances on the screen and stage. Hopkins has received many accolad ...
, Derek Jacobi
Sir Derek George Jacobi (; born 22 October 1938) is an English actor. He has appeared in various stage productions of William Shakespeare such as '' Hamlet'', '' Much Ado About Nothing'', '' Macbeth'', '' Twelfth Night'', '' The Tempest'', ' ...
, Simon Callow, Dan Stevens
Daniel Jonathan Stevens (born 10 October 1982) is a British actor and writer. He first drew international attention for his role as Matthew Crawley in the ITV acclaimed period drama series '' Downton Abbey'' (2010–2012). He also starred as ...
and Ralph Fiennes
Ralph Nathaniel Twisleton-Wykeham-Fiennes ( ; born 22 December 1962) is an English actor, film producer, and director. A Shakespeare interpreter, he excelled onstage at the Royal National Theatre before having further success at the Royal Shak ...
, the latter playing the author in ''The Invisible Woman
The Invisible Woman (Susan "Sue" Storm-Richards) is a superheroine appearing in American comic books published by Marvel Comics. The character is a founding member of the Fantastic Four and was the first female superhero created by Marvel durin ...
'' (2013) which depicts Dickens's secret love affair with Ellen Ternan
Ellen Lawless Ternan (3 March 1839 – 25 April 1914), also known as Nelly Ternan or Nelly Wharton-Robinson, was an English actress known for association with the author Charles Dickens.
Birth and family life
Ellen Ternan was born in Roches ...
which lasted for thirteen years until his death in 1870.
Dickens and his publications have appeared on a number of postage stamps in countries including: the United Kingdom (1970, 1993, 2011 and 2012 issued by the Royal Mail
, kw, Postya Riel, ga, An Post Ríoga
, logo = Royal Mail.svg
, logo_size = 250px
, type = Public limited company
, traded_as =
, foundation =
, founder = Henry VIII
, location = London, England, UK
, key_people = * Keith Williams ...
—their 2012 collection marked the bicentenary of Dickens' birth), the Soviet Union (1962), Antigua, Barbuda, Botswana, Cameroon, Dubai, Fujairah, St Lucia and Turks and Caicos Islands (1970), St Vincent (1987), Nevis (2007), Alderney
Alderney (; french: Aurigny ; Auregnais: ) is the northernmost of the inhabited Channel Islands. It is part of the Bailiwick of Guernsey, a British Crown Dependencies, Crown dependency. It is long and wide.
The island's area is , making i ...
, Gibraltar, Jersey and Pitcairn Islands (2012), Austria (2013), and Mozambique (2014). In 1976, a crater
Crater may refer to:
Landforms
* Impact crater, a depression caused by two celestial bodies impacting each other, such as a meteorite hitting a planet
* Explosion crater, a hole formed in the ground produced by an explosion near or below the surf ...
on the planet Mercury was named in his honour.
In November 2018 it was reported that a previously lost portrait of a 31-year-old Dickens, by Margaret Gillies, had been found in Pietermaritzburg
Pietermaritzburg (; Zulu: umGungundlovu) is the capital and second-largest city in the province of KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. It was founded in 1838 and is currently governed by the Msunduzi Local Municipality. Its Zulu name umGungundlovu ...
, South Africa. Gillies was an early supporter of women's suffrage
Women's suffrage is the right of women to vote in elections. Beginning in the start of the 18th century, some people sought to change voting laws to allow women to vote. Liberal political parties would go on to grant women the right to vot ...
and had painted the portrait in late 1843 when Dickens, aged 31, wrote ''A Christmas Carol''. It was exhibited, to acclaim, at the Royal Academy of Arts
The Royal Academy of Arts (RA) is an art institution based in Burlington House on Piccadilly in London. Founded in 1768, it has a unique position as an independent, privately funded institution led by eminent artists and architects. Its pur ...
in 1844. The Charles Dickens Museum is reported to have paid £180,000 for the portrait.
Works
Novels
Dickens published well over a dozen major novels and novellas, a large number of short stories, including a number of Christmas-themed stories, a handful of plays, and several non-fiction books. Dickens's novels were initially serialised in weekly and monthly magazines, then reprinted in standard book formats. * ''The Pickwick Papers
''The Posthumous Papers of the Pickwick Club'' (also known as ''The Pickwick Papers'') was Charles Dickens's first novel. Because of his success with '' Sketches by Boz'' published in 1836, Dickens was asked by the publisher Chapman & Hall to ...
'' (''The Posthumous Papers of the Pickwick Club''; monthly serial, April 1836 to November 1837) for the serial publication dates.
* ''Oliver Twist
''Oliver Twist; or, The Parish Boy's Progress'', Charles Dickens's second novel, was published as a serial from 1837 to 1839, and as a three-volume book in 1838. Born in a workhouse, the orphan Oliver Twist is bound into apprenticeship with ...
'' (''The Adventures of Oliver Twist''; monthly serial in '' Bentley's Miscellany'', February 1837 to April 1839)
* '' Nicholas Nickleby'' (''The Life and Adventures of Nicholas Nickleby''; monthly serial, April 1838 to October 1839)
* '' The Old Curiosity Shop'' (weekly serial in ''Master Humphrey's Clock
''Master Humphrey's Clock'' was a weekly periodical edited and written entirely by Charles Dickens and published from 4 April 1840 to 4 December 1841. It began with a frame story in which Master Humphrey tells about himself and his small circle o ...
'', April 1840 to November 1841)
* ''Barnaby Rudge
''Barnaby Rudge: A Tale of the Riots of Eighty'' (commonly known as ''Barnaby Rudge'') is a historical novel by British novelist Charles Dickens. ''Barnaby Rudge'' was one of two novels (the other was ''The Old Curiosity Shop'') that Dickens publ ...
'' (''Barnaby Rudge: A Tale of the Riots of Eighty''; weekly serial in ''Master Humphrey's Clock
''Master Humphrey's Clock'' was a weekly periodical edited and written entirely by Charles Dickens and published from 4 April 1840 to 4 December 1841. It began with a frame story in which Master Humphrey tells about himself and his small circle o ...
'', February to November 1841)
* ''A Christmas Carol
''A Christmas Carol. In Prose. Being a Ghost Story of Christmas'', commonly known as ''A Christmas Carol'', is a novella by Charles Dickens, first published in London by Chapman & Hall in 1843 and illustrated by John Leech. ''A Christmas ...
'' (''A Christmas Carol in Prose: Being a Ghost-story of Christmas''; 1843)
* ''Martin Chuzzlewit
''The Life and Adventures of Martin Chuzzlewit'' (commonly known as ''Martin Chuzzlewit'') is a novel by Charles Dickens, considered the last of his picaresque novels. It was originally serialised between 1842 and 1844. While he was writing it ...
'' (''The Life and Adventures of Martin Chuzzlewit''; monthly serial, January 1843 to July 1844)
* '' The Chimes'' (''The Chimes: A Goblin Story of Some Bells That Rang an Old Year Out and a New Year In''; 1844)
* '' The Cricket on the Hearth'' (''The Cricket on the Hearth: A Fairy Tale of Home''; 1845)
* ''The Battle of Life
''The Battle of Life: A Love Story'' is an 1846 novel by Charles Dickens. It is the fourth of his five "Christmas Books", coming after '' The Cricket on the Hearth'' and followed by '' The Haunted Man and the Ghost's Bargain''.
The setting is a ...
'' (''The Battle of Life: A Love Story''; 1846)
* '' Dombey and Son'' (''Dealings with the Firm of Dombey and Son: Wholesale, Retail and for Exportation''; monthly serial, October 1846 to April 1848)
* '' The Haunted Man'' (''The Haunted Man and the Ghost's Bargain: A Fancy for Christmas-time''; 1848)
* ''David Copperfield
''David Copperfield'' Dickens invented over 14 variations of the title for this work, see is a novel in the bildungsroman genre by Charles Dickens, narrated by the eponymous David Copperfield, detailing his adventures in his journey from inf ...
'' (''The Personal History, Adventures, Experience and Observation of David Copperfield the Younger of Blunderstone Rookery hich He Never Meant to Publish on Any Account'; monthly serial, May 1849 to November 1850)
* ''Bleak House
''Bleak House'' is a novel by Charles Dickens, first published as a 20-episode serial between March 1852 and September 1853. The novel has many characters and several sub-plots, and is told partly by the novel's heroine, Esther Summerson, and ...
'' (monthly serial, March 1852 to September 1853)
* '' Hard Times'' (''Hard Times: For These Times''; weekly serial in ''Household Words
''Household Words'' was an English weekly magazine edited by Charles Dickens in the 1850s. It took its name from the line in Shakespeare's ''Henry V'': "Familiar in his mouth as household words."
History
During the planning stages, titles origi ...
'', 1 April 1854, to 12 August 1854)
* '' Little Dorrit'' (monthly serial, December 1855 to June 1857)
* ''A Tale of Two Cities
''A Tale of Two Cities'' is a historical novel published in 1859 by Charles Dickens, set in London and Paris before and during the French Revolution. The novel tells the story of the French Doctor Manette, his 18-year-long imprisonment in ...
'' (weekly serial in '' All the Year Round'', 30 April 1859, to 26 November 1859)
* ''Great Expectations
''Great Expectations'' is the thirteenth novel by Charles Dickens and his penultimate completed novel. It depicts the education of an orphan nicknamed Pip (Great Expectations), Pip (the book is a ''bildungsroman''; a coming-of-age story). It ...
'' (weekly serial in '' All the Year Round'', 1 December 1860 to 3 August 1861)
* ''Our Mutual Friend
''Our Mutual Friend'', written in 1864–1865, is the last novel completed by Charles Dickens and is one of his most sophisticated works, combining savage satire with social analysis. It centres on, in the words of critic J. Hillis Miller, quo ...
'' (monthly serial, May 1864 to November 1865)
* ''The Signal-Man
"The Signal-Man" is a first-person horror/mystery story by Charles Dickens, first published as part of the '' Mugby Junction'' collection in the 1866 Christmas edition of '' All the Year Round''.
The railway signal-man of the title tells the n ...
'' (1866), first published as part of the ''Mugby Junction
"Mugby Junction" is a set of short stories written in 1866 by Charles Dickens and collaborators Charles Collins, Amelia B. Edwards, Andrew Halliday, and Hesba Stretton. It was first published in a Christmas edition of the magazine '' All the Ye ...
'' collection in the 1866 Christmas edition of '' All the Year Round''.
* ''The Mystery of Edwin Drood
''The Mystery of Edwin Drood'' is the final novel by Charles Dickens, originally published in 1870.
Though the novel is named after the character Edwin Drood, it focuses more on Drood's uncle, John Jasper, a precentor, choirmaster and opium ...
'' (monthly serial, April 1870 to September 1870), left unfinished due to Dickens's death
See also
*List of Dickensian characters
This is a list of characters in the works of Charles Dickens.
Contents: A , B , C , D , E , F , G , H , I , J , K , L , M , N , O , P , Q , R , S , T , U , V , W , X , Y , Z ,
__NOTOC__
A
*Ad ...
* Racism in the work of Charles Dickens
* Charles Dickens bibliography
The bibliography of Charles Dickens (1812–1870) includes more than a dozen major novels, many short stories (including Christmas-themed stories and ghost stories), several plays, several non-fiction books, and individual essays and articles. Di ...
Notes
References
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* * * Bradbury, Nicola, ''Charles Dickens' Great Expectations'' (St. Martin's Press, 1990) * Douglas-Fairhurst, Robert,Becoming Dickens 'The Invention of a Novelist
", London:
Harvard University Press
Harvard University Press (HUP) is a publishing house established on January 13, 1913, as a division of Harvard University, and focused on academic publishing. It is a member of the Association of American University Presses. After the retir ...
, 2011
*
*
*
*
* Johnson, Edgar, ''Charles Dickens: his tragedy and triumph'', New York: Simon and Schuster, 1952. In two volumes.
*
*
*
*
* Manning, Mick & Granström, Brita, ''Charles Dickens: Scenes From An Extraordinary Life'', Frances Lincoln Children's Books, 2011.
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
External links
Works
Charles Dickens's works on Bookwise
* * * * * *
Charles Dickens
at the British Library
Organisations and portals
* *Charles Dickens on the Archives Hub
*Archival material a
Leeds University Library
The Dickens Fellowship
an international society dedicated to the study of Dickens and his Writings
Correspondence of Charles Dickens, with related papers, ca. 1834–1955
Finding aid to Charles Dickens papers at Columbia University. Rare Book & Manuscript Library.
Museums
Dickens Museum
Situated in a former Dickens House, 48 Doughty Street, London, WC1
Dickens Birthplace Museum
Old Commercial Road, Portsmouth
Victoria and Albert Museum
The V&A's collections relating to Dickens
Other
*Charles Dickens's Traveling Kit
From th
at the
Library of Congress
The Library of Congress (LOC) is the research library that officially serves the United States Congress and is the ''de facto'' national library of the United States. It is the oldest federal cultural institution in the country. The libra ...
Charles Dickens's Walking Stick
From th
at the
Library of Congress
The Library of Congress (LOC) is the research library that officially serves the United States Congress and is the ''de facto'' national library of the United States. It is the oldest federal cultural institution in the country. The libra ...
* Charles Dickens Collection: First editions of Charles Dickens's works included in the Leonard Kebler gift (dispersed in the Division's collection). From thRare Book and Special Collections Division at the Library of Congress
{{DEFAULTSORT:Dickens, Charles 1812 births 1870 deaths 19th-century biographers 19th-century British dramatists and playwrights 19th-century British newspaper founders 19th-century British non-fiction writers 19th-century British novelists 19th-century British poets 19th-century British short story writers 19th-century English dramatists and playwrights 19th-century English non-fiction writers 19th-century English novelists 19th-century English poets 19th-century essayists 19th-century historians 19th-century journalists 19th-century letter writers 19th-century philanthropists 19th-century pseudonymous writers 19th-century travel writers British Anglicans British biographers British historians British historical novelists British letter writers British male dramatists and playwrights British male essayists British male journalists British male non-fiction writers British male novelists British male poets British male short story writers British newspaper founders British philanthropists British prisoners and detainees British reformers British satirists British social commentators Burials at Westminster Abbey Children's rights activists Christian writers Court reporters Critics of religions Critics of the Catholic Church Cultural critics Educational reformers English Anglicans English biographers English essayists English historians English historical novelists English letter writers English male dramatists and playwrights English male journalists English male non-fiction writers English male novelists English male poets English male short story writers English newspaper founders English philanthropists English prisoners and detainees English reformers English satirists English social commentators English travel writers Ghost story writers Lecturers Literacy and society theorists People from Camden Town People from Chatham, Kent People from Higham, Kent People from Somers Town, London Social critics Social reformers Trope theorists Victorian novelists Writers about activism and social change Writers from London Writers from Portsmouth Writers of Gothic fiction Writers of historical fiction set in the early modern period