Dicalcium phosphate on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Dicalcium phosphate is the
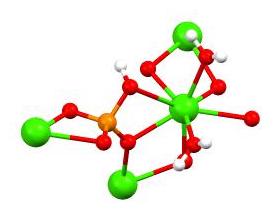
calcium phosphate
The term calcium phosphate refers to a family of materials and minerals containing calcium ions (Ca2+) together with inorganic phosphate anions. Some so-called calcium phosphates contain oxide and hydroxide as well. Calcium phosphates are whi ...
with the formula CaHPO4 and its dihydrate. The "di" prefix in the common name arises because the formation of the HPO42– anion involves the removal of two protons from phosphoric acid
Phosphoric acid (orthophosphoric acid, monophosphoric acid or phosphoric(V) acid) is a colorless, odorless phosphorus-containing solid, and inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is commonly encountered as an 85% aqueous solution, w ...
, H3PO4. It is also known as dibasic calcium phosphate or calcium monohydrogen phosphate. Dicalcium phosphate is used as a food additive
Food additives are substances added to food to preserve flavor or enhance taste, appearance, or other sensory qualities. Some additives have been used for centuries as part of an effort to preserve food, for example vinegar (pickling), salt (salt ...
, it is found in some toothpaste
Toothpaste is a paste or gel dentifrice used with a toothbrush to clean and maintain the aesthetics and health of teeth. Toothpaste is used to promote oral hygiene: it is an abrasive that aids in removing dental plaque and food from the teeth, a ...
s as a polishing
Polishing is the process of creating a smooth and shiny surface by rubbing it or by applying a chemical treatment, leaving a clean surface with a significant specular reflection (still limited by the index of refraction of the material accordin ...
agent and is a biomaterial
A biomaterial is a substance that has been engineered to interact with biological systems for a medical purpose, either a therapeutic (treat, augment, repair, or replace a tissue function of the body) or a diagnostic one. As a science, biomateria ...
.
Preparation
Dibasic calcium phosphate is produced by the neutralization ofcalcium hydroxide
Calcium hydroxide (traditionally called slaked lime) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ca( OH)2. It is a colorless crystal or white powder and is produced when quicklime (calcium oxide) is mixed or slaked with water. It has m ...
with phosphoric acid
Phosphoric acid (orthophosphoric acid, monophosphoric acid or phosphoric(V) acid) is a colorless, odorless phosphorus-containing solid, and inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is commonly encountered as an 85% aqueous solution, w ...
, which precipitates the dihydrate as a solid. At 60 °C the anhydrous form is precipitated:
To prevent degradation that would form hydroxyapatite
Hydroxyapatite, also called hydroxylapatite (HA), is a naturally occurring mineral form of calcium apatite with the formula Ca5(PO4)3(OH), but it is usually written Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2 to denote that the crystal unit cell comprises two entities. ...
, sodium pyrophosphate
Tetrasodium pyrophosphate, also called sodium pyrophosphate, tetrasodium phosphate or TSPP, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula, formula Na4P2O7. As a salt, it is a white, water-soluble solid. It is composed of pyrophosphate anion an ...
or trimagnesium phosphate octahydrate are added when for example, dibasic calcium phosphate dihydrate is to be used as a polishing agent in toothpaste.
In a continuous process CaCl2 can be treated with (NH4)2HPO4 to form the dihydrate:
A slurry of the dihydrate is then heated to around 65–70 °C to form anhydrous CaHPO4 as a crystalline precipitate, typically as flat diamondoid crystals, which are suitable for further processing.
Dibasic calcium phosphate dihydrate is formed in "brushite" calcium phosphate cements (CPC's), which have medical applications. An example of the overall setting reaction in the formation of "β-TCP/MCPM" (β-tricalcium phosphate
Tricalcium phosphate (sometimes abbreviated TCP) is a calcium salt of phosphoric acid with the chemical formula Ca3(PO4)2. It is also known as tribasic calcium phosphate and bone phosphate of lime (BPL). It is a white solid of low solubility. Mo ...
/monocalcium phosphate
Monocalcium phosphate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ca(H2PO4)2 ("AMCP" or "CMP-A" for anhydrous monocalcium phosphate). It is commonly found as the monohydrate ("MCP" or "MCP-M"), Ca(H2PO4)2·H2O. Both salts are colourless sol ...
) calcium phosphate cements is:

Structure
Three forms of dicalcium phosphate are known: *dihydrate
In chemistry, a hydrate is a substance that contains water or its constituent elements. The chemical state of the water varies widely between different classes of hydrates, some of which were so labeled before their chemical structure was understo ...
, CaHPO4•2H2O ('DPCD'), the mineral brushite
Brushite is a phosphate mineral with the chemical formula . Crystals of the pure compound belong to the monoclinic space group C2/c and are colorless.monohydrate
In chemistry, a hydrate is a substance that contains water or its constituent elements. The chemical state of the water varies widely between different classes of hydrates, some of which were so labeled before their chemical structure was underst ...
, CaHPO4•H2O ('DCPM')
* anhydrous
A substance is anhydrous if it contains no water. Many processes in chemistry can be impeded by the presence of water; therefore, it is important that water-free reagents and techniques are used. In practice, however, it is very difficult to achie ...
CaHPO4, ('DCPA'), the mineral monetite. Below pH 4.8 the dihydrate and anhydrous forms of dicalcium phosphate are the most stable (insoluble) of the calcium phosphates.
The structure of the anhydrous and dihydrated forms have been determined by X-ray crystallography
X-ray crystallography is the experimental science determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles ...
and the structure of the monohydrate was determined by electron crystallography
Electron crystallography is a method to determine the arrangement of atoms in solids using a transmission electron microscope (TEM).
Comparison with X-ray crystallography
It can complement X-ray crystallography for studies of very small crystals ...
. The dihydrate (shown in table above) as well as the monohydrate adopt layered structures.
Uses and occurrence
Dibasic calcium phosphate is mainly used as adietary supplement
A dietary supplement is a manufactured product intended to supplement one's diet by taking a pill, capsule, tablet, powder, or liquid. A supplement can provide nutrients either extracted from food sources or that are synthetic in order ...
in prepared breakfast cereals, dog treats, enriched flour, and noodle products. It is also used as a tableting agent
A tablet (also known as a pill) is a pharmaceutical oral dosage form (''oral solid dosage'', or OSD) or solid unit dosage form. Tablets may be defined as the solid unit dosage form of medicament or medicaments with suitable excipients. It compri ...
in some pharmaceutical preparations, including some products meant to eliminate body odor
Body odor or body odour (BO) is present in all animals and its intensity can be influenced by many factors (behavioral patterns, survival strategies). Body odor has a strong genetic basis, but can also be strongly influenced by various diseases ...
. Dibasic calcium phosphate is also found in some dietary calcium supplements (e.g. Bonexcin). It is used in poultry feed. It is also used in some toothpastes as a tartar control agent.
Heating dicalcium phosphate gives dicalcium diphosphate
Calcium pyrophosphate (Ca2P2O7) is a chemical compound, an insoluble calcium salt containing the pyrophosphate anion. There are a number of forms reported: an anhydrous form, a dihydrate, Ca2P2O7·2H2O and a tetrahydrate, Ca2P2O7·4H2O. Depositio ...
, a useful polishing agent:
In the dihydrate (brushite) form it is found in some kidney stone
Kidney stone disease, also known as nephrolithiasis or urolithiasis, is a crystallopathy where a solid piece of material (kidney stone) develops in the urinary tract. Kidney stones typically form in the kidney and leave the body in the urine s ...
s and in dental calculi.
See also
*Brushite
Brushite is a phosphate mineral with the chemical formula . Crystals of the pure compound belong to the monoclinic space group C2/c and are colorless.Monocalcium phosphate
Monocalcium phosphate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ca(H2PO4)2 ("AMCP" or "CMP-A" for anhydrous monocalcium phosphate). It is commonly found as the monohydrate ("MCP" or "MCP-M"), Ca(H2PO4)2·H2O. Both salts are colourless sol ...
*Tricalcium phosphate
Tricalcium phosphate (sometimes abbreviated TCP) is a calcium salt of phosphoric acid with the chemical formula Ca3(PO4)2. It is also known as tribasic calcium phosphate and bone phosphate of lime (BPL). It is a white solid of low solubility. Mo ...
References
__NOTOC__ {{DEFAULTSORT:Dicalcium Phosphate Acid salts Calcium compounds Food additives Phosphates E-number additives