Diaspora on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A diaspora ( ) is a population that is scattered across regions which are separate from its geographic place of origin. Historically, the word was used first in reference to the dispersion of
A diaspora ( ) is a population that is scattered across regions which are separate from its geographic place of origin. Historically, the word was used first in reference to the dispersion of
''The Economic Times'', 28 November 2019.
 The term "diaspora" is derived from the Greek verb διασπείρω (''diaspeirō''), "I scatter", "I spread about" which in turn is composed of διά (''dia''), "between, through, across" and the verb σπείρω (''speirō''), "I sow, I scatter". In
The term "diaspora" is derived from the Greek verb διασπείρω (''diaspeirō''), "I scatter", "I spread about" which in turn is composed of διά (''dia''), "between, through, across" and the verb σπείρω (''speirō''), "I sow, I scatter". In
 In all cases, the term ''diaspora'' carries a sense of displacement. The population so described finds itself for whatever reason separated from its national territory, and usually, its people have a hope, or at least a desire, to return to their homeland at some point if the "homeland" still exists in any meaningful sense. Some writers have noted that diaspora may result in a loss of nostalgia for a single home as people "re-root" in a series of meaningful displacements. In this sense, individuals may have multiple homes throughout their diaspora, with different reasons for maintaining some form of attachment to each. Diasporic cultural development often assumes a different course from that of the population in the original place of settlement. Over time, remotely separated communities tend to vary in culture, traditions, language, and other factors. The last vestiges of cultural affiliation in a diaspora is often found in community resistance to language change and in the maintenance of traditional religious practice.
In all cases, the term ''diaspora'' carries a sense of displacement. The population so described finds itself for whatever reason separated from its national territory, and usually, its people have a hope, or at least a desire, to return to their homeland at some point if the "homeland" still exists in any meaningful sense. Some writers have noted that diaspora may result in a loss of nostalgia for a single home as people "re-root" in a series of meaningful displacements. In this sense, individuals may have multiple homes throughout their diaspora, with different reasons for maintaining some form of attachment to each. Diasporic cultural development often assumes a different course from that of the population in the original place of settlement. Over time, remotely separated communities tend to vary in culture, traditions, language, and other factors. The last vestiges of cultural affiliation in a diaspora is often found in community resistance to language change and in the maintenance of traditional religious practice.
 Brubaker argues that the initial expansion of the use of the phrase extended it to other, similar cases, such as the Armenian and Greek diasporas. More recently, it has been applied to emigrant groups that continue their involvement in their homeland from overseas, such as the category of long-distance nationalists identified by Benedict Anderson. Brubaker notes that (as examples): Albanians, Basques, Hindu Indians, Irish, Japanese, Kashmiri, Koreans, Kurds, Palestinians, and Tamils have been conceptualized as diasporas in this sense. Furthermore, "labor migrants who maintain (to some degree) emotional and social ties with a homeland" have also been described as diasporas.
In further cases of the use of the term, "the reference to the conceptual homeland – to the 'classical' diasporas – has become more attenuated still, to the point of being lost altogether". Here, Brubaker cites "transethnic and transborder linguistic categories...such as Francophone, Anglophone and Lusophone 'communities'", along with Hindu, Sikh, Buddhist, Confucian, Huguenot, Muslim and Catholic 'diasporas'. Brubaker notes that, , there were also academic books or articles on the
Brubaker argues that the initial expansion of the use of the phrase extended it to other, similar cases, such as the Armenian and Greek diasporas. More recently, it has been applied to emigrant groups that continue their involvement in their homeland from overseas, such as the category of long-distance nationalists identified by Benedict Anderson. Brubaker notes that (as examples): Albanians, Basques, Hindu Indians, Irish, Japanese, Kashmiri, Koreans, Kurds, Palestinians, and Tamils have been conceptualized as diasporas in this sense. Furthermore, "labor migrants who maintain (to some degree) emotional and social ties with a homeland" have also been described as diasporas.
In further cases of the use of the term, "the reference to the conceptual homeland – to the 'classical' diasporas – has become more attenuated still, to the point of being lost altogether". Here, Brubaker cites "transethnic and transborder linguistic categories...such as Francophone, Anglophone and Lusophone 'communities'", along with Hindu, Sikh, Buddhist, Confucian, Huguenot, Muslim and Catholic 'diasporas'. Brubaker notes that, , there were also academic books or articles on the
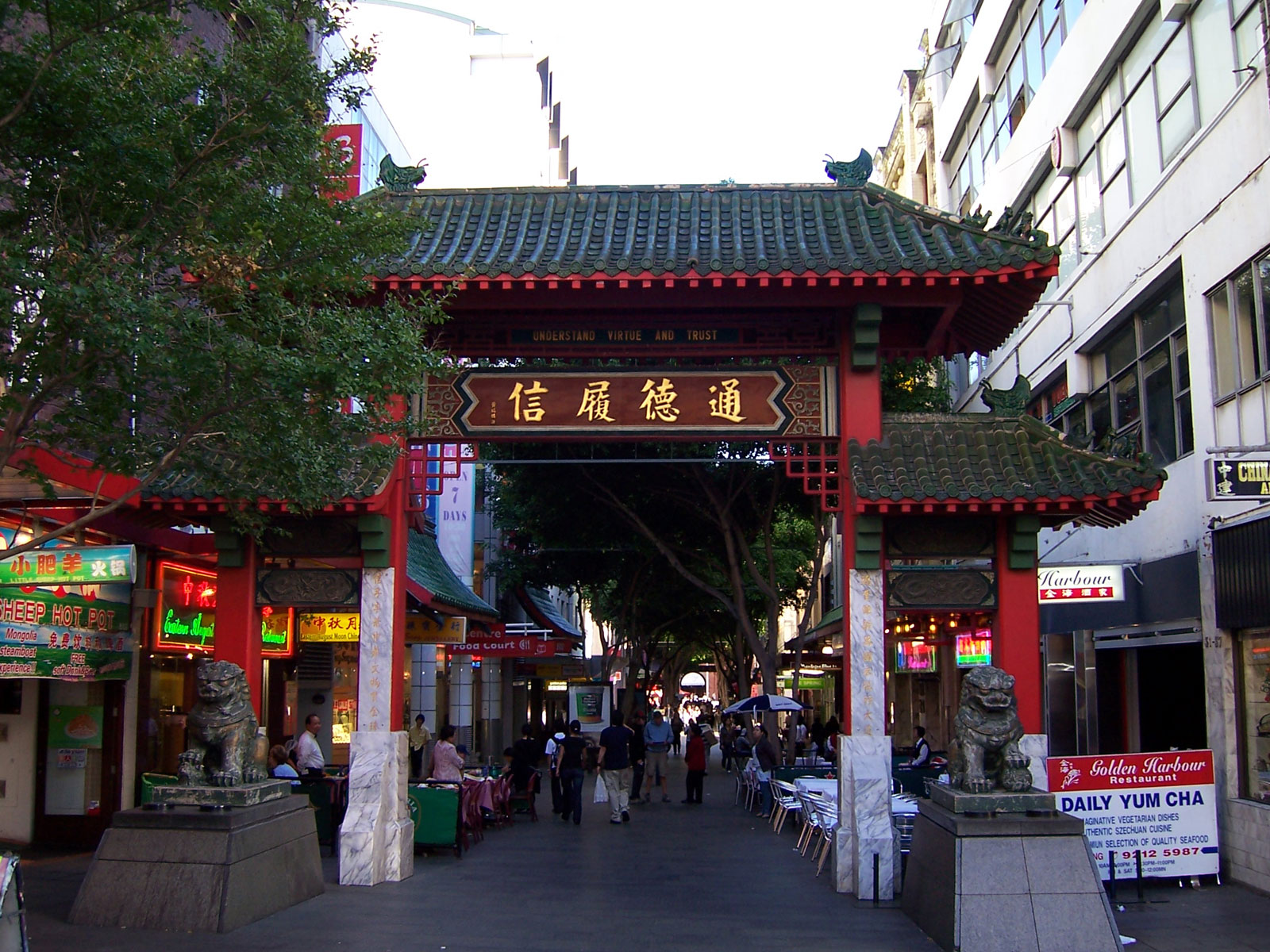
 The largest Asian diaspora, and in the world, is the Indian diaspora. The overseas Indian community, estimated at over 17.5 million, is spread across many regions in the world, on every continent. It constitutes a diverse, heterogeneous and eclectic global community representing different regions, languages, cultures, and faiths (see Desi). Similarly, the
The largest Asian diaspora, and in the world, is the Indian diaspora. The overseas Indian community, estimated at over 17.5 million, is spread across many regions in the world, on every continent. It constitutes a diverse, heterogeneous and eclectic global community representing different regions, languages, cultures, and faiths (see Desi). Similarly, the
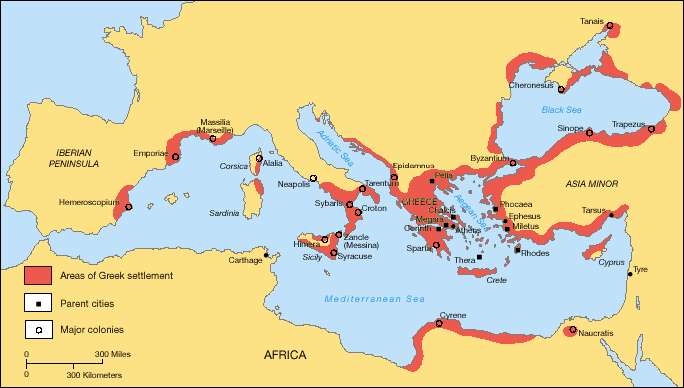 European history contains numerous diaspora-like events. In ancient times, the trading and colonising activities of the Greek tribes from the
European history contains numerous diaspora-like events. In ancient times, the trading and colonising activities of the Greek tribes from the  In 1492 a Spanish-financed expedition headed by
In 1492 a Spanish-financed expedition headed by  There were two major Italian diasporas in
There were two major Italian diasporas in
 In Canada, internal migration has occurred for a number of different factors over the course of Canadian history. An example is the migration of workers from Atlantic Canada (particularly
In Canada, internal migration has occurred for a number of different factors over the course of Canadian history. An example is the migration of workers from Atlantic Canada (particularly
 The
The
 Sri Lankan Tamils have historically migrated to find work, notably during the British colonial period (1796–1948). Since the beginning of the Sri Lankan Civil War in 1983, more than 800,000 Tamils have been displaced within Sri Lanka as a local diaspora, and over a half-million Tamils have emigrated as the Tamil diaspora to destinations such as India, Australia, New Zealand, Canada, the UK, and Europe.
The Afghan diaspora resulted from the 1979 invasion of Afghanistan by the former Soviet Union; both official and unofficial records indicate that the war displaced over 6 million people, resulting in the creation of the second-largest refugee population worldwide (2.6 million in 2018).
Many Iranians fled the 1979
Sri Lankan Tamils have historically migrated to find work, notably during the British colonial period (1796–1948). Since the beginning of the Sri Lankan Civil War in 1983, more than 800,000 Tamils have been displaced within Sri Lanka as a local diaspora, and over a half-million Tamils have emigrated as the Tamil diaspora to destinations such as India, Australia, New Zealand, Canada, the UK, and Europe.
The Afghan diaspora resulted from the 1979 invasion of Afghanistan by the former Soviet Union; both official and unofficial records indicate that the war displaced over 6 million people, resulting in the creation of the second-largest refugee population worldwide (2.6 million in 2018).
Many Iranians fled the 1979
The Microfoundations of Diaspora Politics: Unpacking the State and Disaggregating the Diaspora
” ''Journal of Ethnic and Migration Studies'', Volume 45, Issue 4: 473-491. * Forbes, Andrew, and Henley, David, ''People of Palestine'' (Chiang Mai: Cognoscenti Books, 2012), * Galil, Gershon, & Weinfeld, Moshe, ''Studies in Historical Geography and Biblical Historiography: Presented to Zekharyah Ḳalai'', Brill, 2000 * Jayasuriya, S. and Pankhurst, R. eds. (2003) ''The African Diaspora in the Indian Ocean''. Trenton: Africa World Press * Kantor, Mattis, ''The Jewish timeline encyclopedia: a year-by-year history from Creation to the Present'', (New updated edition), Jason Aronson, Northvale NJ, 1992 * Kenny, Kevin, ''Diaspora: A Very Short Introduction''. New York: Oxford University Press, 2013. * Luciuk, Lubomyr, "Searching for Place: Ukrainian Displaced Persons, Canada and the Migration of Memory," University of Toronto Press, 2000. * Mahroum, Sami & De Guchteneire, P. (2007), ''Transnational Knowledge Through Diaspora Networks-Editorial''. International Journal of Multicultural Societies 8 (1), 1–3 * Mahroum, Sami; Eldridge, Cynthia; Daar, Abdallah S. (2006). ''Transnational diaspora options: How developing countries could benefit from their emigrant populations''. International Journal on Multicultural Societies, 2006. * Nesterovych, Volodymyr (2013).
Impact of ethnic diasporas on the adoption of normative legal acts in the United States
. Viche. 8: 19–23. * Oonk, G, ''Global Indian Diasporas: trajectories of migration and theory'', Amsterdam University Press, 2007 Free downloa
here
* Shain, Yossi, ''Kinship and Diasporas in International Politics'', Michigan University Press, 2007 * Tetlow, Elisabeth Meier, ''Women, Crime, and Punishment in Ancient Law and Society'', Continuum International Publishing Group, 2005 * Weheliye, Alexander G. "My Volk to Come: Peoplehood in Recent Diaspora Discourse and Afro-German Popular Music." Black Europe and the African Diaspora. Ed. Darlene Clark. Hine, Trica Danielle. Keaton, and Stephen Small. Urbana: U of Illinois, 2009. 161–79. Print. * * Xharra, B. & Wählisch, M. ''Beyond Remittances: Public Diplomacy and Kosovo's Diaspora'', Foreign Policy Club, Pristina (2012), abstract and free acces
here
(2012). University Bielefeld – Center for InterAmerican Studies.
Livius.org: Diaspora
Open access book on Diasporas
Integration: Building Inclusive Societies (IBIS)
UN Alliance of Civilizations online community on Good Practices of Integration of Migrants across the World
Diasporic Trajectories: Transnational Cultures in the 21st Century
Podcast playlist of a seminar series held in 2015 at the University of Edinburgh, School of Literatures, Languages, and Cultures {{Authority control Diaspora studies
 A diaspora ( ) is a population that is scattered across regions which are separate from its geographic place of origin. Historically, the word was used first in reference to the dispersion of
A diaspora ( ) is a population that is scattered across regions which are separate from its geographic place of origin. Historically, the word was used first in reference to the dispersion of Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, ot ...
in the Hellenic world
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity ( AD 600), that comprised a loose collection of cult ...
, and later Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
after the Babylonian exile. The word "diaspora" is used today in reference to people who identify with a specific geographic location, but currently reside elsewhere.
Examples of notably large diasporic populations are the Assyrian–Chaldean–Syriac diaspora, which originated during and after the early Arab-Muslim conquests and continued to grow in the aftermath of the Assyrian genocide
The Sayfo or the Seyfo (; see below), also known as the Assyrian genocide, was the mass slaughter and deportation of Assyrian / Syriac Christians in southeastern Anatolia and Persia's Azerbaijan province by Ottoman forces and some Kurdish ...
; the southern Chinese and Indians who left their homelands during the 19th and 20th centuries; the Irish diaspora that came into existence both during and after the Great Famine; the Scottish diaspora that developed on a large scale after the Highland Clearances and Lowland Clearances; the nomadic Romani population from the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographical region in Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, In ...
; the Italian diaspora and the Mexican diaspora; the Circassians
The Circassians (also referred to as Cherkess or Adyghe; Adyghe and Kabardian: Адыгэхэр, romanized: ''Adıgəxər'') are an indigenous Northwest Caucasian ethnic group and nation native to the historical country-region of Circassia ...
in the aftermath of the Circassian genocide; the Palestinian diaspora due to the Israeli–Palestinian conflict and the broader Arab–Israeli conflict
The Arab–Israeli conflict is an ongoing intercommunal phenomenon involving political tension, military conflicts, and other disputes between Arab countries and Israel, which escalated during the 20th century, but had mostly faded out by th ...
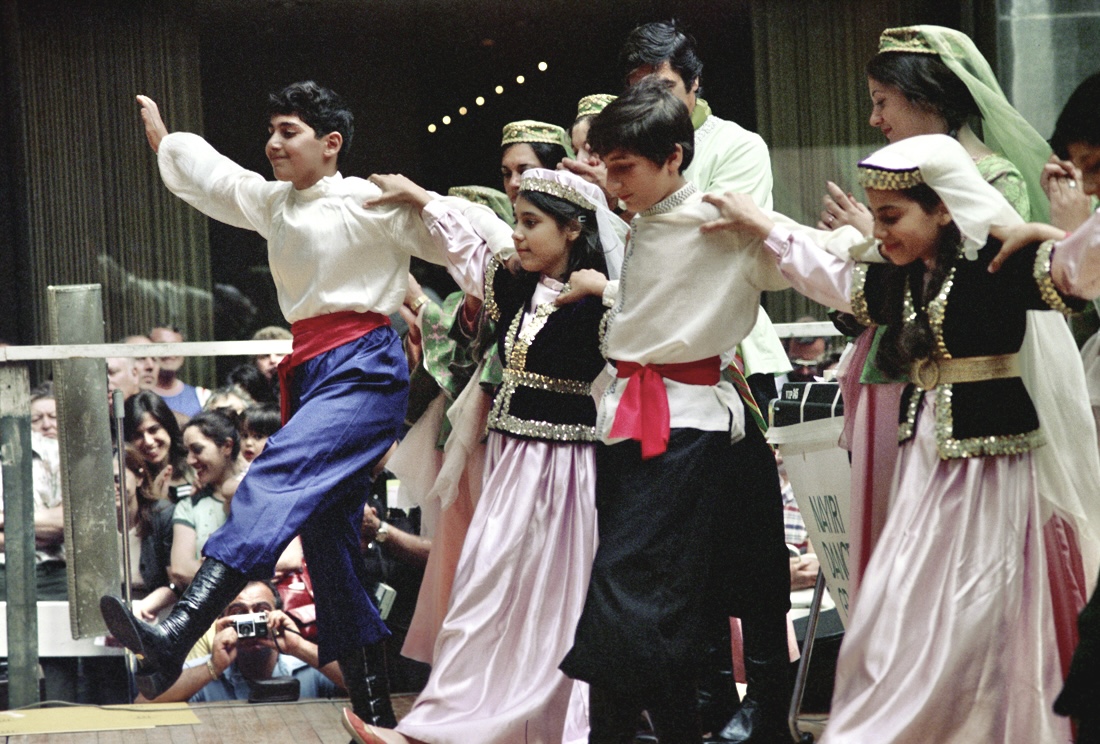
; the Armenian diaspora
The Armenian diaspora refers to the communities of Armenians outside Armenia and other locations where Armenians are considered an indigenous population. Since antiquity, Armenians have established communities in many regions throughout the world. ...
following the Armenian genocide
The Armenian genocide was the systematic destruction of the Armenian people and identity in the Ottoman Empire during World War I. Spearheaded by the ruling Committee of Union and Progress (CUP), it was implemented primarily through t ...
; the Lebanese diaspora due to the Lebanese Civil War
The Lebanese Civil War ( ar, الحرب الأهلية اللبنانية, translit=Al-Ḥarb al-Ahliyyah al-Libnāniyyah) was a multifaceted armed conflict that took place from 1975 to 1990. It resulted in an estimated 120,000 fatalities a ...
; the Greek population that fled or was displaced following the fall of Constantinople and the later Greek genocide
The Greek genocide (, ''Genoktonia ton Ellinon''), which included the Pontic genocide, was the systematic killing of the Christian Ottoman Greek population of Anatolia which was carried out mainly during World War I and its aftermath (1914� ...
as well as the Istanbul pogroms; and the emigration of Anglo-Saxons
The Anglo-Saxons were a cultural group who inhabited England in the Early Middle Ages. They traced their origins to settlers who came to Britain from mainland Europe in the 5th century. However, the ethnogenesis of the Anglo-Saxons happened ...
(primarily to the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
) after the Norman Conquest of England.
In contemporary times, scholars have differentiated the different kinds of diasporas which currently exist based on the causes of them, such as colonialism
Colonialism is a practice or policy of control by one people or power over other people or areas, often by establishing colonies and generally with the aim of economic dominance. In the process of colonisation, colonisers may impose their reli ...
, trade/labour migrations, or the kinds of social coherence which exist within the diaspora communities and their ties to the ancestral lands; some diaspora communities maintain strong cultural and political ties to their homelands. Other qualities that may be typical of many diasporas are thoughts of return to the ancestral lands, maintaining any form of ties with the region of origin as well as relationships with other communities in the diaspora, and lack of full integration into the new host countries. Diasporas often maintain ties to the country of their historical affiliation and usually influence their current host country's policies towards their homeland.
According to a 2019 United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoni ...
report, the Indian diaspora is the world's largest diaspora, with a population of 17.5 million, followed by the Mexican diaspora, with a population of 11.8 million, and the Chinese diaspora
Overseas Chinese () refers to people of Chinese birth or ethnicity who reside outside Mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau, and Taiwan. As of 2011, there were over 40.3 million overseas Chinese.
Terminology
() or ''Hoan-kheh'' () in Hokkien, ...
, with a population of 10.7 million.With $78 billion, India still highest overseas remittance receiver''The Economic Times'', 28 November 2019.
Etymology
 The term "diaspora" is derived from the Greek verb διασπείρω (''diaspeirō''), "I scatter", "I spread about" which in turn is composed of διά (''dia''), "between, through, across" and the verb σπείρω (''speirō''), "I sow, I scatter". In
The term "diaspora" is derived from the Greek verb διασπείρω (''diaspeirō''), "I scatter", "I spread about" which in turn is composed of διά (''dia''), "between, through, across" and the verb σπείρω (''speirō''), "I sow, I scatter". In Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity ( AD 600), that comprised a loose collection of cu ...
the term διασπορά (''diaspora'') hence meant "scattering" and was inter alia used to refer to citizens of a dominant city-state
A city-state is an independent sovereign city which serves as the center of political, economic, and cultural life over its contiguous territory. They have existed in many parts of the world since the dawn of history, including cities such as ...
who emigrated to a conquered land with the purpose of colonization, to assimilate the territory into the empire. An example of a diaspora from classical antiquity is the century-long exile of the Messenians
Messenia or Messinia ( el, Μεσσηνία) was an ancient district of the southwestern Peloponnese, more or less overlapping the modern Messenia region of Greece. To the north it had a border with Elis along the Neda river. From there the bord ...
under Sparta
Sparta ( Doric Greek: Σπάρτα, ''Spártā''; Attic Greek: Σπάρτη, ''Spártē'') was a prominent city-state in Laconia, in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (, ), while the name Sparta referr ...
n rule and the Ageanites as described by Thucydides in his "history of the Peloponnesian wars."
It was first used in this original sense when the Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
'' Septuagint The Greek Old Testament, or Septuagint (, ; from the la, septuaginta, lit=seventy; often abbreviated ''70''; in Roman numerals, LXX), is the earliest extant Greek translation of books from the Hebrew Bible. It includes several books beyond t ...
, first in
* Deuteronomy 28:25, in the phrase , ''esē en diaspora en pasais tais basileiais tēs gēs'', translated to mean "thou shalt be a dispersion in all kingdoms of the earth"
and secondly in
* '' Septuagint The Greek Old Testament, or Septuagint (, ; from the la, septuaginta, lit=seventy; often abbreviated ''70''; in Roman numerals, LXX), is the earliest extant Greek translation of books from the Hebrew Bible. It includes several books beyond t ...
Psalms
The Book of Psalms ( or ; he, תְּהִלִּים, , lit. "praises"), also known as the Psalms, or the Psalter, is the first book of the ("Writings"), the third section of the Tanakh, and a book of the Old Testament. The title is derived ...
146(147).2, in the phrase , ''oikodomōn Ierousalēm ho Kyrios
''Kyrios'' or ''kurios'' ( grc, κύριος, kū́rios) is a Greek word which is usually translated as "lord" or "master". It is used in the Septuagint translation of the Hebrew scriptures about 7000 times, in particular translating the nam ...
kai tas diasporas tou Israēl episynaxē'', translated to mean "The Lord doth build up Jerusalem: he gathereth together the outcasts of Israel".
After the Bible was translated into Greek, the word ''diaspora'' was used in reference to the Northern Kingdom which was exiled from Israel by the Assyrians between 740 and 722 BC, as well as Jews, Benjaminites, and Levites who were exiled from the Southern Kingdom by the Babylonians in 587 BC, and Jews who were exiled from Roman Judea
Judaea ( la, Iudaea ; grc, Ἰουδαία, translit=Ioudaíā ) was a Roman province which incorporated the regions of Judea, Samaria, and Idumea from 6 CE, extending over parts of the former regions of the Hasmonean and Herodian kingdom ...
by the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Roman Republic, Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings aro ...
in 70 AD. It subsequently came to be used in reference to the historical movements and settlement patterns of the dispersed indigenous population of Israel. When it is used in relation to Judaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in th ...
and when it is capitalized without modifiers (simply, ''the Diaspora''), the term specifically refers to the Jewish diaspora
The Jewish diaspora ( he, תְּפוּצָה, təfūṣā) or exile (Hebrew: ; Yiddish: ) is the dispersion of Israelites or Jews out of their ancient ancestral homeland (the Land of Israel) and their subsequent settlement in other parts of th ...
; when it is uncapitalized, the term ''diaspora'' may refer to refugee or immigrant populations with other ethnic origins which are living "away from an indigenous or established homeland". The wider application of ''diaspora'' evolved from the Assyrian two-way mass deportation policy of conquered populations to deny future territorial claims on their part.
Definition
According to the '' Oxford English Dictionary Online'', the first known recorded usage of the word ''diaspora'' in the English language was in 1876 referring "extensive ''diaspora'' work (as it is termed) of evangelizing among the National Protestant Churches on the continent". The term became more widely assimilated into English by the mid 1950s, with long-term expatriates in significant numbers from other particular countries or regions also being referred to as a diaspora. An academic field, diaspora studies, has become established relating to this sense of the word. In English, capitalized, and without modifiers (that is simply, ''the Diaspora''), the term refers specifically to theJewish diaspora
The Jewish diaspora ( he, תְּפוּצָה, təfūṣā) or exile (Hebrew: ; Yiddish: ) is the dispersion of Israelites or Jews out of their ancient ancestral homeland (the Land of Israel) and their subsequent settlement in other parts of th ...
in the context of Judaism.
 In all cases, the term ''diaspora'' carries a sense of displacement. The population so described finds itself for whatever reason separated from its national territory, and usually, its people have a hope, or at least a desire, to return to their homeland at some point if the "homeland" still exists in any meaningful sense. Some writers have noted that diaspora may result in a loss of nostalgia for a single home as people "re-root" in a series of meaningful displacements. In this sense, individuals may have multiple homes throughout their diaspora, with different reasons for maintaining some form of attachment to each. Diasporic cultural development often assumes a different course from that of the population in the original place of settlement. Over time, remotely separated communities tend to vary in culture, traditions, language, and other factors. The last vestiges of cultural affiliation in a diaspora is often found in community resistance to language change and in the maintenance of traditional religious practice.
In all cases, the term ''diaspora'' carries a sense of displacement. The population so described finds itself for whatever reason separated from its national territory, and usually, its people have a hope, or at least a desire, to return to their homeland at some point if the "homeland" still exists in any meaningful sense. Some writers have noted that diaspora may result in a loss of nostalgia for a single home as people "re-root" in a series of meaningful displacements. In this sense, individuals may have multiple homes throughout their diaspora, with different reasons for maintaining some form of attachment to each. Diasporic cultural development often assumes a different course from that of the population in the original place of settlement. Over time, remotely separated communities tend to vary in culture, traditions, language, and other factors. The last vestiges of cultural affiliation in a diaspora is often found in community resistance to language change and in the maintenance of traditional religious practice.
Scholarly work and expanding definition
William Safran in an article published in 1991, set out six rules to distinguish diasporas from migrant communities. These included criteria that the group maintains a myth or collective memory of their homeland; they regard their ancestral homeland as their true home, to which they will eventually return; being committed to the restoration or maintenance of that homeland, and they relate "personally or vicariously" to the homeland to a point where it shapes their identity. While Safran's definitions were influenced by the idea of the Jewish diaspora, he recognised the expanding use of the term.Rogers Brubaker
Rogers Brubaker (; born 1956) is professor of sociology at University of California, Los Angeles and UCLA Foundation Chair. He has written academic works on social theory, immigration, citizenship, nationalism, ethnicity, religion, diasporas, gen ...
(2005) also notes that the use of the term diaspora has been widening. He suggests that one element of this expansion in use "involves the application of the term diaspora to an ever-broadening set of cases: essentially to any and every nameable population category that is to some extent dispersed in space". Brubaker has used the WorldCat database to show that 17 out of the 18 books on diaspora published between 1900 and 1910 were on the Jewish diaspora. The majority of works in the 1960s were also about the Jewish diaspora, but in 2002 only two out of 20 books sampled (out of a total of 253) were about the Jewish case, with a total of eight different diasporas covered.
Brubaker outlines the original use of the term diaspora as follows:
Most early discussions of the diaspora were firmly rooted in a conceptual 'homeland'; they were concerned with a paradigmatic case, or a small number of core cases. The paradigmatic case was, of course, the Jewish diaspora; some dictionary definitions of diaspora, until recently, did not simply illustrate but defined the word with reference to that case.
 Brubaker argues that the initial expansion of the use of the phrase extended it to other, similar cases, such as the Armenian and Greek diasporas. More recently, it has been applied to emigrant groups that continue their involvement in their homeland from overseas, such as the category of long-distance nationalists identified by Benedict Anderson. Brubaker notes that (as examples): Albanians, Basques, Hindu Indians, Irish, Japanese, Kashmiri, Koreans, Kurds, Palestinians, and Tamils have been conceptualized as diasporas in this sense. Furthermore, "labor migrants who maintain (to some degree) emotional and social ties with a homeland" have also been described as diasporas.
In further cases of the use of the term, "the reference to the conceptual homeland – to the 'classical' diasporas – has become more attenuated still, to the point of being lost altogether". Here, Brubaker cites "transethnic and transborder linguistic categories...such as Francophone, Anglophone and Lusophone 'communities'", along with Hindu, Sikh, Buddhist, Confucian, Huguenot, Muslim and Catholic 'diasporas'. Brubaker notes that, , there were also academic books or articles on the
Brubaker argues that the initial expansion of the use of the phrase extended it to other, similar cases, such as the Armenian and Greek diasporas. More recently, it has been applied to emigrant groups that continue their involvement in their homeland from overseas, such as the category of long-distance nationalists identified by Benedict Anderson. Brubaker notes that (as examples): Albanians, Basques, Hindu Indians, Irish, Japanese, Kashmiri, Koreans, Kurds, Palestinians, and Tamils have been conceptualized as diasporas in this sense. Furthermore, "labor migrants who maintain (to some degree) emotional and social ties with a homeland" have also been described as diasporas.
In further cases of the use of the term, "the reference to the conceptual homeland – to the 'classical' diasporas – has become more attenuated still, to the point of being lost altogether". Here, Brubaker cites "transethnic and transborder linguistic categories...such as Francophone, Anglophone and Lusophone 'communities'", along with Hindu, Sikh, Buddhist, Confucian, Huguenot, Muslim and Catholic 'diasporas'. Brubaker notes that, , there were also academic books or articles on the Dixie
Dixie, also known as Dixieland or Dixie's Land, is a nickname for all or part of the Southern United States. While there is no official definition of this region (and the included areas shift over the years), or the extent of the area it cove ...
, white, liberal, gay, queer and digital diasporas.
Some observers have labeled evacuation from and the Gulf Coast in the wake of Hurricane Katrina the New Orleans diaspora, since a significant number of evacuees have not been able to return, yet maintain aspirations to do so. Agnieszka Weinar (2010) notes the widening use of the term, arguing that recently, "a growing body of literature succeeded in reformulating the definition, framing diaspora as almost any ''population'' on the move and no longer referring to the specific ''context'' of their existence". It has even been noted that as charismatic Christianity becomes increasingly globalized, many Christians conceive of themselves as a diaspora, and form an imaginary that mimics salient features of ethnic diasporas.
Professional communities of individuals no longer in their homeland can also be considered diaspora. For example, science diasporas are communities of scientists who conduct their research away from their homeland. In an article published in 1996, Khachig Tölölyan argues that the media have used the term corporate diaspora in a rather arbitrary and inaccurate fashion, for example as applied to “mid-level, mid-career executives who have been forced to find new places at a time of corporate upheaval” (10) The use of corporate diaspora reflects the increasing popularity of the diaspora notion to describe a wide range of phenomena related to contemporary migration, displacement and transnational mobility. While corporate diaspora seems to avoid or contradict connotations of violence, coercion, and unnatural uprooting historically associated with the notion of diaspora, its scholarly use may heuristically describe the ways in which corporations function alongside diasporas. In this way, corporate diaspora might foreground the racial histories of diasporic formations without losing sight of the cultural logic of late capitalism in which corporations orchestrate the transnational circulation of people, images, ideologies and capital.
African diasporas
One of the largest diasporas of modern times is that of Sub-Saharan Africans, which dates back several centuries. During the Atlantic slave trade, 10.7 million people from West Africa survived transportation to arrive in the Americas as slaves. Currently, migrant Africans can only enter thirteen African countries without advanced visas. In pursuing a unified future, the African Union (AU) will allow people to move freely between the 54 countries of the AU under a visa free passport and encourage migrants to return to Africa. From the 8th through the 19th centuries, the Arab slave trade dispersed millions of Africans to Asia and the islands of the Indian Ocean. The Islamic slave trade also has resulted in the creation of communities of African descent in India, most notably the Siddi,Makrani Makrani may refer to:
* Makrani people, an ethnic group in Pakistan of African-descent.
* Makrani caste
The Makrani ( gu, મકરાણી, Balochi: ) are a Muslim community mainly found in the Indian state of Gujarat. They are said to be descen ...
and Sri Lanka Kaffirs.
In the early 500s AD incursions by the kingdom of Aksum in Himyar led to the formation of African diasporic communities.
Asian diasporas
 The largest Asian diaspora, and in the world, is the Indian diaspora. The overseas Indian community, estimated at over 17.5 million, is spread across many regions in the world, on every continent. It constitutes a diverse, heterogeneous and eclectic global community representing different regions, languages, cultures, and faiths (see Desi). Similarly, the
The largest Asian diaspora, and in the world, is the Indian diaspora. The overseas Indian community, estimated at over 17.5 million, is spread across many regions in the world, on every continent. It constitutes a diverse, heterogeneous and eclectic global community representing different regions, languages, cultures, and faiths (see Desi). Similarly, the Romani
Romani may refer to:
Ethnicities
* Romani people, an ethnic group of Northern Indian origin, living dispersed in Europe, the Americas and Asia
** Romani genocide, under Nazi rule
* Romani language, any of several Indo-Aryan languages of the Roma ...
, numbering roughly 12 million in Europe trace their origins to the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographical region in Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, In ...
, and their presence in Europe is first attested to in the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
.
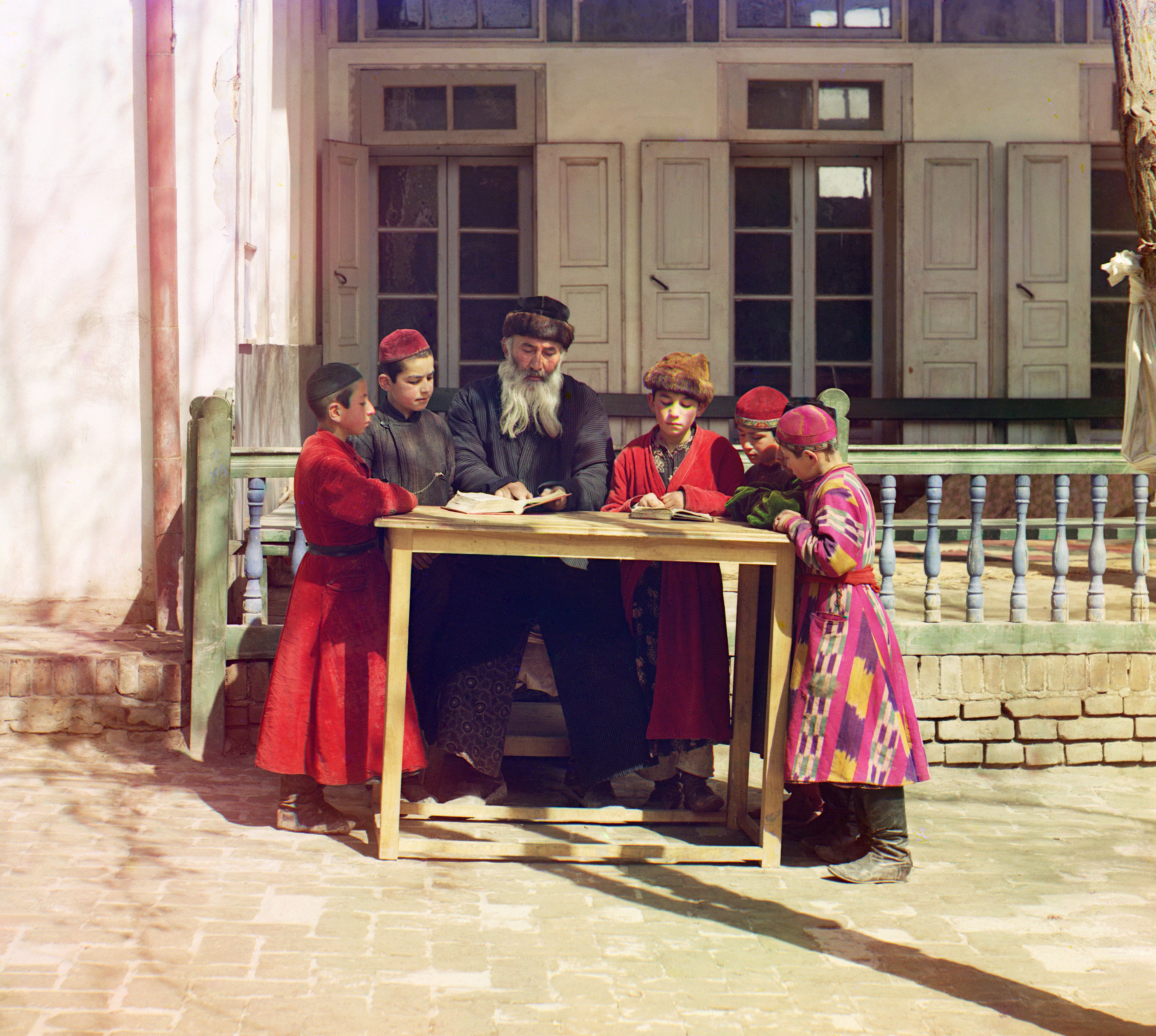
The earliest known Asian diaspora of note is the Jewish diaspora
The Jewish diaspora ( he, תְּפוּצָה, təfūṣā) or exile (Hebrew: ; Yiddish: ) is the dispersion of Israelites or Jews out of their ancient ancestral homeland (the Land of Israel) and their subsequent settlement in other parts of th ...
. With roots in the Babylonian Captivity and later migration under Hellenism, the majority of the diaspora can be attributed to the Roman conquest, expulsion, and enslavement of the Jewish population of Judea
Judea or Judaea ( or ; from he, יהודה, Standard ''Yəhūda'', Tiberian ''Yehūḏā''; el, Ἰουδαία, ; la, Iūdaea) is an ancient, historic, Biblical Hebrew, contemporaneous Latin, and the modern-day name of the mountainous so ...
, whose descendants became the Ashkenazim, Sephardim
Sephardic (or Sephardi) Jews (, ; lad, Djudíos Sefardíes), also ''Sepharadim'' , Modern Hebrew: ''Sfaradim'', Tiberian: Səp̄āraddîm, also , ''Ye'hude Sepharad'', lit. "The Jews of Spain", es, Judíos sefardíes (or ), pt, Judeus sefa ...
, and Mizrahim
Mizrahi Jews ( he, יהודי המִזְרָח), also known as ''Mizrahim'' () or ''Mizrachi'' () and alternatively referred to as Oriental Jews or ''Edot HaMizrach'' (, ), are a grouping of Jewish communities comprising those who remained ...
of today, roughly numbering 15 million of which 8 million still live in the diaspora, though the number was much higher before Zionist immigration to what is now Israel and the murder of 6 million Jews in the Holocaust
The Holocaust, also known as the Shoah, was the genocide of European Jews during World War II. Between 1941 and 1945, Nazi Germany and its collaborators systematically murdered some six million Jews across German-occupied Europe; ...
.
Chinese emigration (also known as the Chinese Diaspora; see also Overseas Chinese) first occurred thousands of years ago. The mass emigration that occurred from the 19th century to 1949 was caused mainly by wars and starvation in mainland China
"Mainland China" is a geopolitical term defined as the territory governed by the China, People's Republic of China (including islands like Hainan or Chongming Island, Chongming), excluding dependent territories of the PRC, and other territorie ...
, as well as political corruption. Most migrants were illiterate or poorly educated peasants, called by the now-recognized racial slur coolies
A coolie (also spelled koelie, kuli, khuli, khulie, cooli, cooly, or quli) is a term for a low-wage labourer, typically of South Asian or East Asian descent.
The word ''coolie'' was first popularized in the 16th century by European traders acros ...
(Chinese: 苦力, literally "hard labor"), who migrated to developing countries in need of labor, such as the Americas, Australia, South Africa, Southeast Asia, Malaya and other places.
At least three waves of Nepalese diaspora can be identified. The earliest wave dates back to hundreds of years as early marriage and high birthrates propelled Hindu settlement eastward across Nepal, then into Sikkim
Sikkim (; ) is a state in Northeastern India. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China in the north and northeast, Bhutan in the east, Province No. 1 of Nepal in the west and West Bengal in the south. Sikkim is also close to the Sil ...
and Bhutan. A backlash developed in the 1980s as Bhutan's political elites realized that Bhutanese Buddhists were at risk of becoming a minority in their own country. At least 60,000 ethnic Nepalese from Bhutan have been resettled in the United States. A second wave was driven by British recruitment of mercenary soldiers beginning around 1815 and resettlement after retirement in the British Isles
The British Isles are a group of islands in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner and Outer Hebrides, the Northern Isl ...
and Southeast Asia. The third wave began in the 1970s as land shortages intensified and the pool of educated labor greatly exceeded job openings in Nepal. Job-related emigration created Nepalese enclaves in India, the wealthier countries of the Middle East, Europe, and North America. Current estimates of the number of Nepalese living outside Nepal range well up into the millions.
In Siam, regional power struggles among several kingdoms in the region led to a large diaspora of ethnic Lao between the 1700s–1800s by Siamese rulers to settle large areas of the Siamese kingdom's northeast region, where Lao ethnicity is still a major factor in 2012. During this period, Siam decimated the Lao capital, capturing, torturing, and killing the Lao king Anuwongse.
European diasporas
 European history contains numerous diaspora-like events. In ancient times, the trading and colonising activities of the Greek tribes from the
European history contains numerous diaspora-like events. In ancient times, the trading and colonising activities of the Greek tribes from the Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
and Asia Minor
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
spread people of Greek culture, religion and language around the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on ...
and Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
basins, establishing Greek city-states in Magna Graecia (Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
, southern Italy), northern Libya, eastern Spain, the south of France
Southern France, also known as the South of France or colloquially in French as , is a defined geographical area consisting of the regions of France that border the Atlantic Ocean south of the Marais Poitevin,Louis Papy, ''Le midi atlantique'', ...
, and the Black Sea coasts. Greeks founded more than 400 colonies. Tyre and Carthage also colonised the Mediterranean.
Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
's the conquest of the Achaemenid Empire marked the beginning of the Hellenistic period
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
, characterized by a new wave of Greek colonization in Asia and Africa, with Greek ruling-classes established in Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning the North Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via a land bridg ...
, southwest Asia and northwest India. Subsequent waves of colonization and migration during the Middle Ages added to the older settlements or created new ones, thus replenishing the Greek diaspora and making it one of the most long-standing and widespread in the world.
The Migration-Period relocations, which included several phases, are just one set of many in history. The first phase Migration-Period displacement (between CE 300 and 500) included relocation of the Goths
The Goths ( got, 𐌲𐌿𐍄𐌸𐌹𐌿𐌳𐌰, translit=''Gutþiuda''; la, Gothi, grc-gre, Γότθοι, Gótthoi) were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Euro ...
(Ostrogoths
The Ostrogoths ( la, Ostrogothi, Austrogothi) were a Roman-era Germanic people. In the 5th century, they followed the Visigoths in creating one of the two great Gothic kingdoms within the Roman Empire, based upon the large Gothic populations who ...
and Visigoths
The Visigoths (; la, Visigothi, Wisigothi, Vesi, Visi, Wesi, Wisi) were an early Germanic people who, along with the Ostrogoths, constituted the two major political entities of the Goths within the Roman Empire in late antiquity, or what is k ...
), Vandals
The Vandals were a Germanic peoples, Germanic people who first inhabited what is now southern Poland. They established Vandal Kingdom, Vandal kingdoms on the Iberian Peninsula, Mediterranean islands, and North Africa in the fifth century.
The ...
, Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools ...
, various other Germanic peoples ( Burgundians, Lombards
The Lombards () or Langobards ( la, Langobardi) were a Germanic people who ruled most of the Italian Peninsula from 568 to 774.
The medieval Lombard historian Paul the Deacon wrote in the ''History of the Lombards'' (written between 787 an ...
, Angles, Saxons
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country (Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the Nor ...
, Jutes, Suebi
The Suebi (or Suebians, also spelled Suevi, Suavi) were a large group of Germanic peoples originally from the Elbe river region in what is now Germany and the Czech Republic. In the early Roman era they included many peoples with their own name ...
, Alemanni, Varangians and Normans
The Normans ( Norman: ''Normaunds''; french: Normands; la, Nortmanni/Normanni) were a population arising in the medieval Duchy of Normandy from the intermingling between Norse Viking settlers and indigenous West Franks and Gallo-Romans. ...
), Alans and numerous Slavic tribes
This is a list of Slavic peoples and Slavic tribes reported in Late Antiquity and in the Middle Ages, that is, before the year AD 1500.
Ancestors
*Proto-Indo-Europeans (Proto-Indo-European speakers)
** Proto-Balto-Slavs (common ancestors of Ba ...
. The second phase, between CE 500 and 900, saw Slavic, Turkic, and other tribes on the move, resettling in Eastern Europe and gradually leaving it predominantly Slavic, and affecting Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
and the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range, have historica ...
as the first Turkic tribes ( Avars, Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th century AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was part ...
, Khazars
The Khazars ; he, כּוּזָרִים, Kūzārīm; la, Gazari, or ; zh, 突厥曷薩 ; 突厥可薩 ''Tūjué Kěsà'', () were a semi-nomadic Turkic people that in the late 6th-century CE established a major commercial empire coverin ...
, Pechenegs
The Pechenegs () or Patzinaks tr, Peçenek(ler), Middle Turkic: , ro, Pecenegi, russian: Печенег(и), uk, Печеніг(и), hu, Besenyő(k), gr, Πατζινάκοι, Πετσενέγοι, Πατζινακίται, ka, პა� ...
), as well as Bulgars
The Bulgars (also Bulghars, Bulgari, Bolgars, Bolghars, Bolgari, Proto-Bulgarians) were Turkic semi-nomadic warrior tribes that flourished in the Pontic–Caspian steppe and the Volga region during the 7th century. They became known as noma ...
, and possibly Magyars arrived. The last phase of the migrations saw the coming of the Hungarian Magyars. The Viking expansion out of Scandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and S ...
into southern and eastern Europe, Iceland and Greenland. The recent application of the word "diaspora" to the Viking lexicon highlights their cultural profile distinct from their predatory reputation in the regions they settled, especially in the North Atlantic. The more positive connotations associated with the social science term help to view the movement of the Scandinavian peoples in the Viking Age in a new way.
Such colonizing migrations cannot be considered indefinitely as diasporas; over very long periods, eventually, the migrants assimilate into the settled area so completely that it becomes their new mental homeland. Thus the modern Magyars of Hungary do not feel that they belong in the Western Siberia that the Hungarian Magyars left 12 centuries ago; and the English descendants of the Angles, Saxons
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country (Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the Nor ...
and Jutes do not yearn to reoccupy the plains of Northwest Germany.
 In 1492 a Spanish-financed expedition headed by
In 1492 a Spanish-financed expedition headed by Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus
* lij, Cristoffa C(or)ombo
* es, link=no, Cristóbal Colón
* pt, Cristóvão Colombo
* ca, Cristòfor (or )
* la, Christophorus Columbus. (; born between 25 August and 31 October 1451, died 20 May 1506) was a ...
arrived in the Americas, after which European exploration and colonization rapidly expanded. Historian James Axtell
James L. Axtell (born December 20, 1941 in Endicott, New York) is an American historian. He was a professor of history at the College of William and Mary in Williamsburg, Virginia. Axtell, whose interests lie in American Indian history and th ...
estimates that 240,000 people left Europe for the Americas in the 16th century. Emigration continued. In the 19th century alone over 50 million Europeans migrated to North and South America.
Other Europeans moved to Siberia, Africa, and Australasia. The properly Spanish emigrants were mainly from several parts of Spain, but not only the impoverised ones (i.e., Basques in Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the eas ...
), and the destination varied also along the time. As an example, the Galicians moved first to the American colonies during the XVII-XX (mainly but not only Mexico, Cuba, Argentine and Venezuela, as many writers during the Francoist exile), later to Europe (France, Switzerland) and finally within Spain (to Madrid, Catalonia or the Basque Country).
A specific 19th-century example is the Irish diaspora, beginning in the mid-19th century and brought about by ''An Gorta Mór'' or "the Great Hunger" of the Irish Famine
The Great Famine ( ga, an Gorta Mór ), also known within Ireland as the Great Hunger or simply the Famine and outside Ireland as the Irish Potato Famine, was a period of starvation and disease in Ireland from 1845 to 1852 that constituted a h ...
. An estimated 45% to 85% of Ireland's population emigrated to areas including Britain, the United States of America, Canada, Argentina, Australia, and New Zealand. The size of the Irish diaspora is demonstrated by the number of people around the world who claim Irish ancestry; some sources put the figure at 80 to 100 million.
From the 1860s the Circassian people, originally from Europe, were dispersed through Anatolia, Australia, the Balkans, the Levant, North America, and West Europe, leaving less than 10% of their population in the homeland – parts of historical Circassia (in the modern-day Russian portion of the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range, have historica ...
).Richmond 172-73.
The Scottish Diaspora includes large populations of Highlanders moving to the United States and Canada after the Highland Clearances; as well as the Lowlanders, becoming the Ulster Scots in Ireland and the Scotch-Irish in America.
Italian history
The history of Italy covers the ancient period, the Middle Ages, and the modern era. Since classical antiquity, ancient Etruscans, various Italic peoples (such as the Latins, Samnites, and Umbri), Celts, '' Magna Graecia'' colonists, and ...
. The first diaspora began around 1880, two decades after the Unification of Italy, and ended in the 1920s to the early 1940s with the rise of Fascist Italy.Pozzetta, George E., Bruno Ramirez, and Robert F. Harney. The Italian Diaspora: Migration across the Globe. Toronto: Multicultural History Society of Ontario, 1992. Poverty was the main reason for emigration, specifically the lack of land as '' mezzadria'' sharecropping
Sharecropping is a legal arrangement with regard to agricultural land in which a landowner allows a tenant to use the land in return for a share of the crops produced on that land.
Sharecropping has a long history and there are a wide range ...
flourished in Italy, especially in the South, and property became subdivided over generations. Especially in Southern Italy, conditions were harsh. Until the 1860s to 1950s, most of Italy was a rural society
Rural sociology is a field of sociology traditionally associated with the study of social structure and conflict in rural areas. It is an active academic field in much of the world, originating in the United States in the 1910s with close ties ...
with many small towns and cities and almost no modern industry in which land management practices, especially in the South and the Northeast
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each sep ...
, did not easily convince farmers to stay on the land and to work the soil. Another factor was related to the overpopulation of Southern Italy as a result of the improvements in socioeconomic conditions after Unification. That created a demographic boom and forced the new generations to emigrate en masse in the late 19th century and the early 20th century, mostly to the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America, North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World. ...
. The new migration of capital created millions of unskilled jobs around the world and was responsible for the simultaneous mass migration of Italians searching for "work and bread". The second diaspora started after the end of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
and concluded roughly in the 1970s. Between 1880 and 1980, about 15,000,000 Italians left the country permanently. By 1980, it was estimated that about 25,000,000 Italians were residing outside Italy.
Internal diasporas
In the United States of America, approximately 4.3 million people moved outside their home states in 2010, according toIRS
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) is the revenue service for the United States federal government, which is responsible for collecting U.S. federal taxes and administering the Internal Revenue Code, the main body of the federal statutory tax ...
tax-exemption data. In a 2011 TEDx presentation, Detroit native Garlin Gilchrist referenced the formation of distinct "Detroit diaspora" communities in Seattle and in Washington, D.C., while layoffs in the auto industry also led to substantial blue-collar migration from Michigan to Wyoming 2005. In response to a statewide exodus of talent, the State of Michigan continues to host "MichAGAIN" career-recruiting events in places throughout the United States with significant Michigan-diaspora populations.
In the People's Republic of China, millions of migrant workers have sought greater opportunity in the country's booming coastal metropolises, though this trend has slowed with the further development of China's interior. Migrant social structures in Chinese megacities are often based on place of origin, such as a shared hometown or province, and recruiters and foremen commonly select entire work-crews from the same village. In two separate June 2011 incidents, Sichuanese Sichuanese, Szechuanese or Szechwanese may refer to something of, from, or related to the Chinese province and region of Sichuan (Szechwan/Szechuan) (historically and culturally including Chongqing), especially:
* Sichuanese people, a subgroup of th ...
migrant workers organized violent protests against alleged police misconduct and migrant-labor abuse near the southern manufacturing hub of Guangzhou
Guangzhou (, ; ; or ; ), also known as Canton () and Chinese postal romanization, alternatively romanized as Kwongchow or Kwangchow, is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Guangdong Provinces of China, province in South China, sou ...
.
Much of Siberia's population
Population typically refers to the number of people in a single area, whether it be a city or town, region, country, continent, or the world. Governments typically quantify the size of the resident population within their jurisdiction usi ...
has its origins in internal migration – voluntary or otherwise – from European Russia since the 16th century.
 In Canada, internal migration has occurred for a number of different factors over the course of Canadian history. An example is the migration of workers from Atlantic Canada (particularly
In Canada, internal migration has occurred for a number of different factors over the course of Canadian history. An example is the migration of workers from Atlantic Canada (particularly Newfoundland and Labrador
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region ...
) to Alberta
Alberta ( ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is part of Western Canada and is one of the three prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to the west, Saskatchewan to the east, the Northwest T ...
, driven in part by the cod collapse in the early 1990s and the 1992 moratorium on cod fishing. Fishing had previously been a major driver of the economies of the Atlantic provinces, and this loss of work proved catastrophic for many families. As a result, beginning in the early 1990s and into the late 2000s, thousands of people from the Atlantic provinces were driven out-of-province to find work elsewhere in the country, especially in the Alberta oil sands during the oil boom of the mid-2000s. This systemic export of labour is explored by author Kate Beaton in her 2022 graphic memoir '' Ducks'', which details her experience working in the Athabasca oil sands.
Twentieth century
The twentieth century saw huge population movements. Some involved large-scale transfers of people by government action. Some migrations occurred to avoid conflict and warfare. Other diasporas formed as a consequence of political developments, such as the end ofcolonialism
Colonialism is a practice or policy of control by one people or power over other people or areas, often by establishing colonies and generally with the aim of economic dominance. In the process of colonisation, colonisers may impose their reli ...
.
World War II, colonialism and post-colonialism
AsWorld War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
(1939–1945) unfolded, Nazi German authorities deported and killed millions of Jews; they also enslaved or murdered millions of other people, including Ukrainians
Ukrainians ( uk, Українці, Ukraintsi, ) are an East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. They are the seventh-largest nation in Europe. The native language of the Ukrainians is Ukrainian. The majority of Ukrainians are Eastern Ort ...
, Russians
, native_name_lang = ru
, image =
, caption =
, population =
, popplace =
118 million Russians in the Russian Federation (2002 '' Winkler Prins'' estimate)
, region1 =
, pop1 ...
and other Slavs. Some Jews fled from persecution to unoccupied parts of western Europe or to the Americas before borders closed. Later, other eastern European refugees moved west, away from Soviet expansion and from the Iron Curtain regimes established as World War II ended. Hundreds of thousands of these anti-Soviet political refugees and displaced persons ended up in western Europe, Australia, Canada, and the United States of America.
After World War II, the Soviet Union and Communist
Communism (from Latin la, communis, lit=common, universal, label=none) is a far-left sociopolitical, philosophical, and economic ideology and current within the socialist movement whose goal is the establishment of a communist society, ...
-controlled Poland, Czechoslovakia
, rue, Чеськословеньско, , yi, טשעכאסלאוואקיי,
, common_name = Czechoslovakia
, life_span = 1918–19391945–1992
, p1 = Austria-Hungary
, image_p1 ...
, Hungary and Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label= Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavij ...
expelled millions of ethnic Germans, most them descendants of immigrants who had settled in those areas centuries previously. This was allegedly in reaction to German Nazi invasions and to pan-German attempts at annexation. Most of the refugees moved to the West, including western Europe, and with tens of thousands seeking refuge in the United States.
 The
The Istrian–Dalmatian exodus
The Istrian–Dalmatian exodus (; ; ) was the post- World War II exodus and departure of local ethnic Italians ( Istrian Italians and Dalmatian Italians) as well as ethnic Slovenes, Croats, and Istro-Romanians from the Yugoslav territory of ...
was the post-World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
exodus and departure of local ethnic Italians
, flag =
, flag_caption = The national flag of Italy
, population =
, regions = Italy 55,551,000
, region1 = Brazil
, pop1 = 25–33 million
, ref1 =
, region2 ...
( Istrian Italians and Dalmatian Italians) as well as ethnic Slovenes
The Slovenes, also known as Slovenians ( sl, Slovenci ), are a South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to Slovenia, and adjacent regions in Italy, Austria and Hungary. Slovenes share a common ancestry, Slovenian culture, culture, History ...
, Croats
The Croats (; hr, Hrvati ) are a South Slavic ethnic group who share a common Croatian ancestry, culture, history and language. They are also a recognized minority in a number of neighboring countries, namely Austria, the Czech Republic ...
, and Istro-Romanians from the Yugoslav territory of Istria, Kvarner, the Julian March as well as Dalmatia, towards Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
, and in smaller numbers, towards the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America, North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World. ...
and Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by ...
. These regions were ethnically mixed, with long-established historic Croatian, Italian, and Slovene communities. According to various sources, the exodus is estimated to have amounted to between 230,000 and 350,000 Italians (the others being ethnic Slovenes, Croats, and Istro-Romanians, who chose to maintain Italian citizenship) leaving the areas in the aftermath of the conflict. Hundreds or perhaps tens of thousands of local ethnic Italians (Istrian Italians and Dalmatian Italians) were killed or summarily executed during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
by Yugoslav Partisans
The Yugoslav Partisans,Serbo-Croatian, Macedonian, Slovene: , or the National Liberation Army, sh-Latn-Cyrl, Narodnooslobodilačka vojska (NOV), Народноослободилачка војска (НОВ); mk, Народноослобод� ...
and OZNA during the first years of the exodus, in what became known as the ''foibe'' massacres. From 1947, after the war, Istrian Italians and Dalmatian Italians were subject by Yugoslav authorities to less violent forms of intimidation, such as nationalization, expropriation, and discriminatory taxation, which gave them little option other than emigration. In 1953, there were 36,000 declared Italians in Yugoslavia, just about 16% of the original Italian population before World War II. According to the census organized in Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg
, anthem = " Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capi ...
in 2001 and that organized in Slovenia
Slovenia ( ; sl, Slovenija ), officially the Republic of Slovenia (Slovene: , abbr.: ''RS''), is a country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the southeast, and ...
in 2002, the Italians who remained in the former Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label= Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavij ...
amounted to 21,894 people (2,258 in Slovenia and 19,636 in Croatia).
Spain sent many political activists into exile during the rule of Franco's military regime from 1936 until his death in 1975.
Prior to World War II and the re-establishment of Israel in 1948, a series of anti-Jewish pogrom
A pogrom () is a violent riot incited with the aim of massacring or expelling an ethnic or religious group, particularly Jews. The term entered the English language from Russian to describe 19th- and 20th-century attacks on Jews in the Russian ...
s broke out in the Arab world
The Arab world ( ar, اَلْعَالَمُ الْعَرَبِيُّ '), formally the Arab homeland ( '), also known as the Arab nation ( '), the Arabsphere, or the Arab states, refers to a vast group of countries, mainly located in Western A ...
and caused many to flee, mostly to Palestine/Israel. The 1947–1949 Palestine war likewise saw at least 750,000 Palestinians expelled or forced to flee from the newly forming Israel. Many Palestinians continue to live in refugee camps in the Middle East, while others have resettled in other countries.
The 1947 Partition in the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographical region in Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, In ...
resulted in the migration of millions of people between India, Pakistan and present-day Bangladesh. Many were murdered in the religious violence of the period, with estimates of fatalities up to 2 million people. Thousands of former subjects of the British Raj
The British Raj (; from Hindi ''rāj'': kingdom, realm, state, or empire) was the rule of the British Crown on the Indian subcontinent;
*
* it is also called Crown rule in India,
*
*
*
*
or Direct rule in India,
* Quote: "Mill, who was him ...
went to the UK from the Indian subcontinent after India and Pakistan became independent in 1947.
From the late 19th century, and formally from 1910, Japan made Korea a Japanese colony. Millions of Chinese fled to western provinces not occupied by Japan (that is, in particular, Szechuan/Szechwan and Yunnan in the Southwest and Shensi and Kansu in the Northwest) and to Southeast Asia. More than 100,000 Koreans
Koreans ( South Korean: , , North Korean: , ; see names of Korea) are an East Asian ethnic group native to the Korean Peninsula.
Koreans mainly live in the two Korean nation states: North Korea and South Korea (collectively and simply r ...
moved across the Amur River into the Russian Far East (and later into the Soviet Union) away from the Japanese.
The Cold War and the formation of post-colonial states
During and after theCold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because t ...
-era, huge populations of refugees migrated from conflict, especially from then-developing countries
A developing country is a sovereign state with a lesser developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreem ...
.
Upheaval in the Middle East and Central Asia, some of which related to power struggles between the United States and the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
, produced new refugee populations that developed into global diasporas.
In Southeast Asia, many Vietnamese people emigrated to France and later millions to the United States, Australia and Canada after the Cold War-related Vietnam War of 1955–1975. Later, 30,000 French ''colons'' from Cambodia were displaced after being expelled by the 1975–1979 Khmer Rouge regime under Pol Pot. A small, predominantly Muslim ethnic group, the Cham people, long residing in Cambodia, were nearly eradicated.
The mass exodus of Vietnamese people from Vietnam from 1975 onwards led to the popularisation of the term " boat people".
In Southwest China, many Tibetan people
The Tibetan people (; ) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Tibet. Their current population is estimated to be around 6.7 million. In addition to the majority living in Tibet Autonomous Region of China, significant numbers of Tibetans liv ...
emigrated to India, following the 14th Dalai Lama
The 14th Dalai Lama (spiritual name Jetsun Jamphel Ngawang Lobsang Yeshe Tenzin Gyatso, known as Tenzin Gyatso (Tibetan: བསྟན་འཛིན་རྒྱ་མཚོ་, Wylie: ''bsTan-'dzin rgya-mtsho''); né Lhamo Thondup), known as ...
after the failure of his 1959 Tibetan uprising
The 1959 Tibetan uprising (also known by other names) began on 10 March 1959, when a revolt erupted in Lhasa, the capital of Tibet, which had been under the effective control of the People's Republic of China since the Seventeen Point Agre ...
. This wave lasted until the 1960s, and another wave followed when Tibet opened up to trade and tourism in the 1980s. It is estimated that about 200,000 Tibetans live now dispersed worldwide, half of them in India, Nepal and Bhutan. In lieu of lost citizenship papers, the Central Tibetan Administration offers Green Book identity documents to Tibetan refugees.
Iranian Revolution
The Iranian Revolution ( fa, انقلاب ایران, Enqelâb-e Irân, ), also known as the Islamic Revolution ( fa, انقلاب اسلامی, Enqelâb-e Eslâmī), was a series of events that culminated in the overthrow of the Pahlavi dyna ...
which culminated in the fall of the USA/British-ensconced Shah
Shah (; fa, شاه, , ) is a royal title that was historically used by the leading figures of Iranian monarchies.Yarshater, EhsaPersia or Iran, Persian or Farsi, ''Iranian Studies'', vol. XXII no. 1 (1989) It was also used by a variety of ...
.
In Africa, a new series of diasporas formed following the end of colonial rule. In some cases, as countries became independent, numerous minority descendants of Europeans emigrated; others stayed in the lands which had been family homes for generations. Uganda expelled 80,000 South Asians in 1972 and took over their businesses and properties. The 1990–1994 Rwandan Civil War
The Rwandan Civil War was a large-scale civil war in Rwanda which was fought between the Rwandan Armed Forces, representing the country's government, and the rebel Rwandan Patriotic Front (RPF) from 1October 1990 to 18 July 1994. The war aro ...
between rival social/ethnic groups (Hutu
The Hutu (), also known as the Abahutu, are a Bantu ethnic or social group which is native to the African Great Lakes region. They mainly live in Rwanda, Burundi and the eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo, where they form one of the p ...
and Tutsi
The Tutsi (), or Abatutsi (), are an ethnic group of the African Great Lakes region. They are a Bantu-speaking ethnic group and the second largest of three main ethnic groups in Rwanda and Burundi (the other two being the largest Bantu ethnic g ...
) turned deadly and produced a mass efflux of refugees.
In Latin America, following the 1959 Cuban Revolution and the introduction of communism
Communism (from Latin la, communis, lit=common, universal, label=none) is a far-left sociopolitical, philosophical, and economic ideology and current within the socialist movement whose goal is the establishment of a communist society, ...
, over a million people have left Cuba.
A new Jamaican diaspora formed around the start of the 21st century. More than 1 million Dominicans live abroad, a majority living in the US.
A million Colombian refugees have left Colombia since 1965 to escape that country's violence and civil wars.
In South America, thousands of Argentine and Uruguay refugees fled to Europe during periods of military rule in the 1970s and 1980s.
In Central America, Nicaraguans
Nicaraguans ( es, Nicaragüenses; also ''Nicas'') are people inhabiting in, originating or having significant heritage from Nicaragua. Most Nicaraguans live in Nicaragua, although there is also a significant Nicaraguan diaspora, particularly in ...
, Salvadorans, Guatemalans, and Hondurans have fled conflict and poor economic conditions.
Hundreds of thousands of people fled from the Rwandan genocide
The Rwandan genocide occurred between 7 April and 15 July 1994 during the Rwandan Civil War. During this period of around 100 days, members of the Tutsi minority ethnic group, as well as some moderate Hutu and Twa, were killed by armed Hutu ...
in 1994 and moved into neighboring countries.
Between 4 and 6 million have emigrated from Zimbabwe beginning in the 1990s especially since 2000, greatly increasing the Zimbabwean diaspora
The Zimbabwean diaspora refers to the diaspora of immigrants from the nation of Zimbabwe and their descendants who now reside in other countries. The number of Zimbabweans living outside Zimbabwe varies significantly from 4 to 7 million people ...
due to a protracted socioeconomic crisis, forming large communities in South Africa, the United Kingdom, Australia, Canada, and smaller communities in the United States, New Zealand and Ireland, where their skills have been in high demand. The long war in Congo, in which numerous nations have been involved, has also spawned millions of refugees.
A South Korean diaspora movement during the 1990s caused the homeland fertility rate to drop when a large amount of the middle class emigrated, as the rest of the population continued to age. To counteract the change in these demographics, the South Korean government initiated a diaspora-engagement policy in 1997.
Twenty-first century
Middle Eastern conflicts
Following theIraq War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Iraq War {{Nobold, {{lang, ar, حرب العراق (Arabic) {{Nobold, {{lang, ku, شەڕی عێراق (Kurdish languages, Kurdish)
, partof = the Iraq conflict (2003–present), I ...
, nearly 3 million Iraqis had been displaced as of 2011, with 1.3 million within Iraq and 1.6 million in neighboring countries, mainly Jordan and Syria. The Syrian Civil War has forced further migration, with at least 4 million displaced as per UN estimates.
Venezuelan refugee crisis
Following the presidency of Hugo Chávez and the establishment of his Bolivarian Revolution, over 1.6 million Venezuelans emigrated from Venezuela in what has been called the Bolivarian diaspora. The analysis of a study by theCentral University of Venezuela
The Central University of Venezuela (Spanish: ''Universidad Central de Venezuela''; UCV) is a public university of Venezuela located in Caracas. It is widely held to be the highest ranking institution in the country, and it also ranks 18th in ...
titled ''Venezuelan Community Abroad. A New Method of Exile'' by '' El Universal'' states that the Bolivarian diaspora in Venezuela has been caused by the "deterioration of both the economy and the social fabric, rampant crime, uncertainty and lack of hope for a change in leadership in the near future".
Diaspora Internet services
There are numerous web-based news portals and forum sites dedicated to specific diaspora communities, often organized on the basis of an origin characteristic and a current location characteristic. The location-based networking features of mobile applications such as China's WeChat have also created de facto online diaspora communities when used outside of their home markets. Now, large companies from the emerging countries are looking at leveraging diaspora communities to enter the more mature market.In popular culture
'' Gran Torino'', a 2008 drama starring Clint Eastwood, was the first mainstream American film to feature the Hmong American diaspora.See also
* List of diasporas * List of sovereign states and dependent territories by immigrant population * Expulsion of Poles by Nazi Germany * Partition of India *Armenian genocide
The Armenian genocide was the systematic destruction of the Armenian people and identity in the Ottoman Empire during World War I. Spearheaded by the ruling Committee of Union and Progress (CUP), it was implemented primarily through t ...
* Diaspora politics
Diaspora politics is the political behavior of transnational ethnic diasporas, their relationship with their ethnic homelands and their host states, and their prominent role in ethnic conflicts. Shain, Yossi & Tamara Cofman Wittes. Peace as a Th ...
* Ethnic cleansing
* Kurdish refugees
The problem of Kurdish refugees and displaced people arose in the 20th century in the Middle East, and continues today. The Kurds ( ku, کورد, Kurd), are an ethnic group in Western Asia, mostly inhabiting a region known as Kurdistan, which inclu ...
* The Exodus
* Expulsions and exoduses of Jews
This article lists expulsions, refugee crises and other forms of displacement that have affected Jews.
Timeline
The following is a list of Jewish expulsions and events that prompted significant streams of Jewish refugees.
Assyrian captivity
...
* Forced displacement
* Human migration
Human migration is the movement of people from one place to another with intentions of settling, permanently or temporarily, at a new location (geographic region). The movement often occurs over long distances and from one country to another (ex ...
* Long Walk of the Navajo
* Population transfer
* Rural exodus
* State collapse
* Stateless nation
* Trail of Tears
* Ummah
* Yom HaAliyah
* Rohingya genocide
The Rohingya genocide is a series of ongoing persecutions and killings of the Muslim Rohingya people by the Burmese military. The genocide has consisted of two phases to date: the first was a military crackdown that occurred from October 2016 ...
* Expulsion of the Moriscos
The Expulsion of the Moriscos ( es, Expulsión de los moriscos) was decreed by King Philip III of Spain on April 9, 1609. The Moriscos were descendants of Spain's Muslim population who had been forced to convert to Christianity. Since the Spani ...
References
Citations
Sources
* Barclay, John M. G. (ed.), ''Negotiating Diaspora: Jewish Strategies in the Roman Empire'', Continuum International Publishing Group, 2004 * Baser, B and Swain, A. ''Diasporas as Peacemakers: Third Party Mediation in Homeland Conflicts'' with Ashok Swain. International Journal on World Peace 25, 3, September 2008. * Braziel, Jana Evans. 2008. ''Diaspora – an introduction''. Malden, MA: Blackwell. * * Bueltmann, Tanja, et al. eds. ''Locating the English Diaspora, 1500–2010'' (Liverpool University Press, 2012) * * Délano Alonso, Alexandra and Harris Mylonas. 2019. �The Microfoundations of Diaspora Politics: Unpacking the State and Disaggregating the Diaspora
” ''Journal of Ethnic and Migration Studies'', Volume 45, Issue 4: 473-491. * Forbes, Andrew, and Henley, David, ''People of Palestine'' (Chiang Mai: Cognoscenti Books, 2012), * Galil, Gershon, & Weinfeld, Moshe, ''Studies in Historical Geography and Biblical Historiography: Presented to Zekharyah Ḳalai'', Brill, 2000 * Jayasuriya, S. and Pankhurst, R. eds. (2003) ''The African Diaspora in the Indian Ocean''. Trenton: Africa World Press * Kantor, Mattis, ''The Jewish timeline encyclopedia: a year-by-year history from Creation to the Present'', (New updated edition), Jason Aronson, Northvale NJ, 1992 * Kenny, Kevin, ''Diaspora: A Very Short Introduction''. New York: Oxford University Press, 2013. * Luciuk, Lubomyr, "Searching for Place: Ukrainian Displaced Persons, Canada and the Migration of Memory," University of Toronto Press, 2000. * Mahroum, Sami & De Guchteneire, P. (2007), ''Transnational Knowledge Through Diaspora Networks-Editorial''. International Journal of Multicultural Societies 8 (1), 1–3 * Mahroum, Sami; Eldridge, Cynthia; Daar, Abdallah S. (2006). ''Transnational diaspora options: How developing countries could benefit from their emigrant populations''. International Journal on Multicultural Societies, 2006. * Nesterovych, Volodymyr (2013).
Impact of ethnic diasporas on the adoption of normative legal acts in the United States
. Viche. 8: 19–23. * Oonk, G, ''Global Indian Diasporas: trajectories of migration and theory'', Amsterdam University Press, 2007 Free downloa
here
* Shain, Yossi, ''Kinship and Diasporas in International Politics'', Michigan University Press, 2007 * Tetlow, Elisabeth Meier, ''Women, Crime, and Punishment in Ancient Law and Society'', Continuum International Publishing Group, 2005 * Weheliye, Alexander G. "My Volk to Come: Peoplehood in Recent Diaspora Discourse and Afro-German Popular Music." Black Europe and the African Diaspora. Ed. Darlene Clark. Hine, Trica Danielle. Keaton, and Stephen Small. Urbana: U of Illinois, 2009. 161–79. Print. * * Xharra, B. & Wählisch, M. ''Beyond Remittances: Public Diplomacy and Kosovo's Diaspora'', Foreign Policy Club, Pristina (2012), abstract and free acces
here
Further reading
* Gewecke, Frauke(2012). University Bielefeld – Center for InterAmerican Studies.
External links
Livius.org: Diaspora
Open access book on Diasporas
Integration: Building Inclusive Societies (IBIS)
UN Alliance of Civilizations online community on Good Practices of Integration of Migrants across the World
Diasporic Trajectories: Transnational Cultures in the 21st Century
Podcast playlist of a seminar series held in 2015 at the University of Edinburgh, School of Literatures, Languages, and Cultures {{Authority control Diaspora studies