Devi Kanyakumari on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
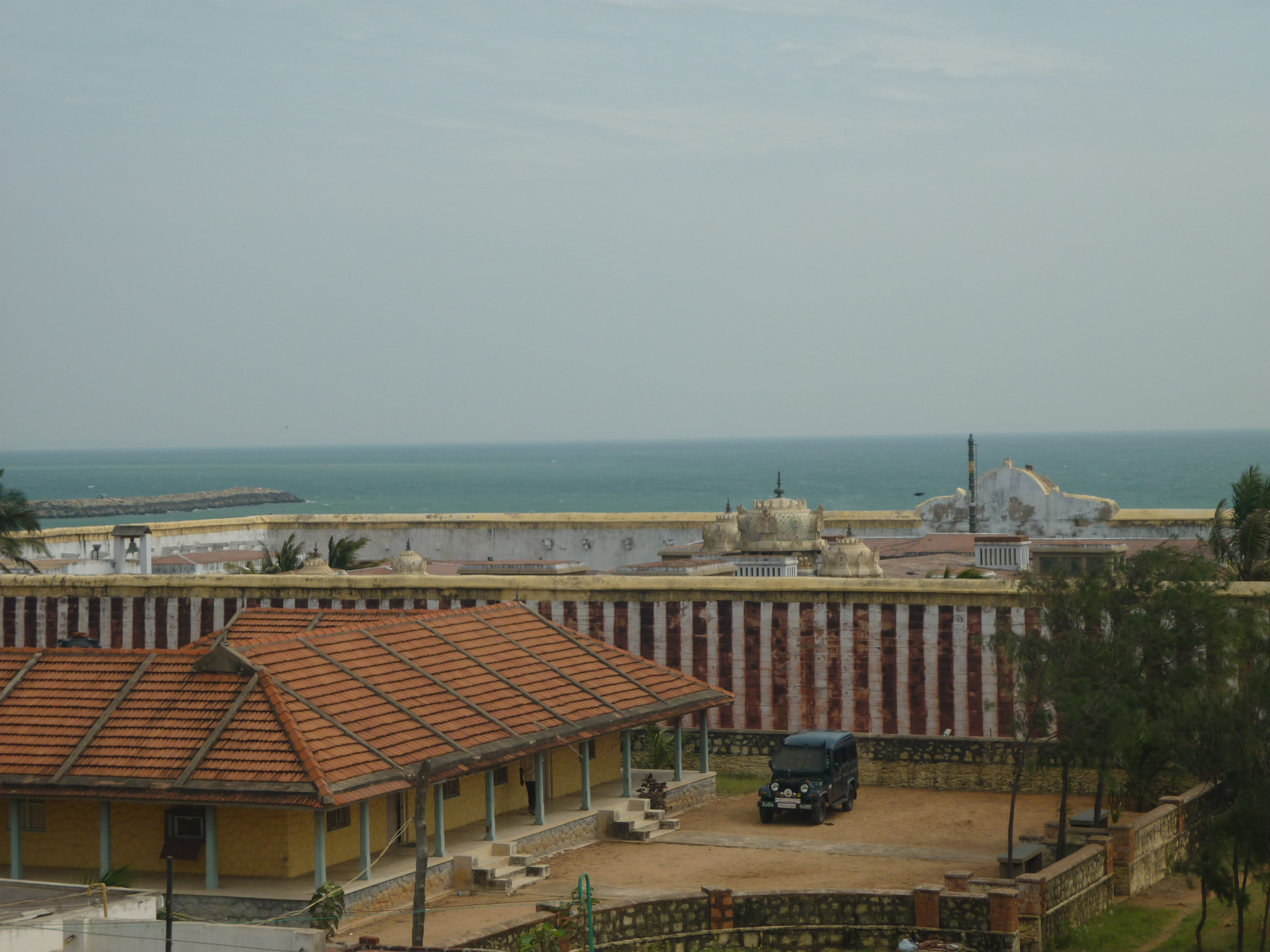
 Devi Kanya Kumari (
Devi Kanya Kumari (
 The story dates back to the pre-
The story dates back to the pre-
Hindu Religious and Charitable Endowments Act, 1959
/ref>
Hindu Goddesses: Vision of the Divine Feminine in the Hindu Religious Traditions
'. Motilal Banarsidass, New Delhi, India. . * Pattanaik, Devdutt.
The Mother Goddess: An Introduction
'. . * Pintchman, Tracy (1994).
The Rise of the Goddess in the Hindu Tradition
'. SUNY Press, New York, USA. . * Sen, Ramprasad (1720–1781). ''Grace and Mercy in Her Wild Hair: Selected Poems to the Mother Goddess''. . * Wangu, Madhu Bazaz (2003).
Images of Indian Goddesses: Myths, Meanings, and Models
'. Abhinav Publications, New Delhi, India. .
Durga Puja at NetGlimse.com
from the Durgāsaptaśatī
all about kanyakumari Temple
{{Regions of Kanyakumari Lakshmi Forms of Parvati Mother goddesses Hindu goddesses

Tamil
Tamil may refer to:
* Tamils, an ethnic group native to India and some other parts of Asia
**Sri Lankan Tamils, Tamil people native to Sri Lanka also called ilankai tamils
**Tamil Malaysians, Tamil people native to Malaysia
* Tamil language, nativ ...
: தேவி கன்னியா குமரி, Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
: देवी कन्या कुमारि) ( IAST:dēvi kanyā kumāri) is a manifestation of the Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
goddess Mahadevi in the form of an adolescent girl. She is variously described by various traditions of Hinduism to either be a form of Parvati
Parvati ( sa, पार्वती, ), Uma ( sa, उमा, ) or Gauri ( sa, गौरी, ) is the Hindu goddess of power, energy, nourishment, harmony, love, beauty, devotion, and motherhood. She is a physical representation of Mahadevi i ...
or Lakshmi
Lakshmi (; , sometimes spelled Laxmi, ), also known as Shri (, ), is one of the principal goddesses in Hinduism. She is the goddess of wealth, fortune, power, beauty, fertility and prosperity, and associated with ''Maya'' ("Illusion"). Alo ...
. She is also worshipped as an incarnation of the goddess Bhadrakali
Bhadrakali (IAST: Bhadrakālī; ), also known as Mahakali and Kali, is a Hindu goddess.
According to Shaktism, she is one of the fierce forms of the Supreme Goddess Shakti, or Adi Parashakti, mentioned in the Devi Mahatmyam. In Vaishnavi ...
by Shaktas
Shaktism ( sa, शाक्त, , ) is one of several major Hindu denominations, wherein the metaphysical reality is considered metaphorically a woman and Shakti (Mahadevi) is regarded as the supreme godhead. It includes many goddesses, all ...
, and is known by several names such as Shrī ''Bāla Bhadra'', ''Shrī Bāla'', ''Kanya Devi,'' and ''Devi Kumari''.
Origin
The goddess is inextricably tied to the eponymous town ofKanyakumari
Kanniyakumari (; , referring to Devi Kanya Kumari), also known as Cape Comorin, is a city in Kanniyakumari district in the state of Tamil Nadu, India. It is the southern tip of the Indian subcontinent and the southernmost city in mainland Ind ...
, situated at the southernmost tip of Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu (; , TN) is a state in southern India. It is the tenth largest Indian state by area and the sixth largest by population. Its capital and largest city is Chennai. Tamil Nadu is the home of the Tamil people, whose Tamil language ...
. The worship of Devi Kanya Kumari is also associated with the Kumari Kandam
Kumari Kandam is a mythical continent, believed to be lost with an ancient Tamil civilization, supposedly located south of present-day India in the Indian Ocean. Alternative names and spellings include ''Kumarikkandam'' and ''Kumari Nadu''.
...
, a mythical lost continent. Kanya Kumari is regarded to be the goddess who killed the demon Banasura, who performed a continuous penance with utmost austerities. The Vaishnava
Vaishnavism ( sa, वैष्णवसम्प्रदायः, Vaiṣṇavasampradāyaḥ) is one of the major Hindu denominations along with Shaivism, Shaktism, and Smartism. It is also called Vishnuism since it considers Vishnu as the ...
Saint Vadiraja Tirtha
Sri Vadiraja Teertharu (1480 – 1600) was a Dvaita philosopher, poet, traveller and mystic. A polymath of his time, he authored many works, often polemical, on Madhva theology and metaphysics. Additionally, he composed numerous poems and as ...
, in his Tirtha Prabhanda, describes Kanya Kumari as Lakshmi
Lakshmi (; , sometimes spelled Laxmi, ), also known as Shri (, ), is one of the principal goddesses in Hinduism. She is the goddess of wealth, fortune, power, beauty, fertility and prosperity, and associated with ''Maya'' ("Illusion"). Alo ...
, who descended upon the earth to slay Banasura.
Devi Kanya Kumari has been mentioned in Ramayana
The ''Rāmāyana'' (; sa, रामायणम्, ) is a Sanskrit literature, Sanskrit Indian epic poetry, epic composed over a period of nearly a millennium, with scholars' estimates for the earliest stage of the text ranging from the 8th ...
, Mahabharata
The ''Mahābhārata'' ( ; sa, महाभारतम्, ', ) is one of the two major Sanskrit literature, Sanskrit Indian epic poetry, epics of ancient India in Hinduism, the other being the ''Ramayana, Rāmāyaṇa''. It narrates the s ...
, and the Sangam works Manimekalai
''Maṇimēkalai'' ( ta, மணிமேகலை, ), also spelled ''Manimekhalai'' or ''Manimekalai'', is a Tamil- Buddhist epic composed by Kulavāṇikaṉ Seethalai Sataṉar probably around the 6th century. It is an "anti-love story", a ...
, Purananuru
The ''Purananuru'' (, literally "four hundred oemsin the genre puram"), sometimes called ''Puram'' or ''Purappattu'', is a classical Tamil poetic work and traditionally the last of the Eight Anthologies (''Ettuthokai'') in the Sangam literatu ...
and the Nārāyaṇa (Mahānārāyaṇa) Upanishad, a Vaishnava Upanishad in the Taittiriya Samhita of Krishna Yajur Veda
The ''Yajurveda'' ( sa, यजुर्वेद, ', from ' meaning "worship", and ''veda'' meaning "knowledge") is the Veda primarily of prose mantras for worship rituals.Michael Witzel (2003), "Vedas and Upaniṣads", in ''The Blackwell C ...
.
The author of ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea'' (60-80 CE) has written about the prevalence of the propitiation of the deity Kanyakumari in the extreme southern part of India; "There is another place called Comori and a harbour, hither come those men who wish to consecrate themselves for the rest of their lives, and bath and dwell in celibacy and women also do the same; for it is told that a goddess once dwelt here and bathed."
Kanyakumari was under the rule of the Chera Dynasty followed by the rulers and kings of Travancore
The Kingdom of Travancore ( /ˈtrævənkɔːr/), also known as the Kingdom of Thiruvithamkoor, was an Indian kingdom from c. 1729 until 1949. It was ruled by the Travancore Royal Family from Padmanabhapuram, and later Thiruvananthapuram. At ...
under the overall suzerainty of the British until 1947, when India became independent. Travancore joined the independent India in 1947. Later in the state partition, Kanyakumari became part of Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu (; , TN) is a state in southern India. It is the tenth largest Indian state by area and the sixth largest by population. Its capital and largest city is Chennai. Tamil Nadu is the home of the Tamil people, whose Tamil language ...
.
The feminine aspects of Adi Parashakti (in its manifested and un-manifested forms) are called as Prakriti, and the male aspects are called as Purusha. The Prakriti is addressed in different names by different Hindu communities as Adi-parashakti, Bhadra, Shakti, Devi, Bhagavati, Amman, Rajarajeshwari, Shodashi; in different locations.
All the material manifested aspects the Nature is classified as feminine and is the Prakriti or Mother Goddess and also the un-manifested forms Knowledge, Prosperity and Power are considered as feminine Prakriti, and it is source of energy for Creation, Sustain and Control, which is the male aspect (Purusha) of Prabrahma.
In Tantra
Tantra (; sa, तन्त्र, lit=loom, weave, warp) are the esoteric traditions of Hinduism and Buddhism that developed on the Indian subcontinent from the middle of the 1st millennium CE onwards. The term ''tantra'', in the Indian ...
, the worship of Prakriti is done in different methods: Dakshinachara (Right-Hand Path) (Sātvika rites), Vamachara (Left-Hand Path) (Rajas rites) and Madhyama (Mixed) (Tamasa rites) in different temples. The name of Devi in temples during Sātvika or Dakshina rites is 'Shrī Bhagavati' and Vaama (left method) rites is called 'Maha Devi' similar to Maha Vidya.
Legend
 The story dates back to the pre-
The story dates back to the pre-Vedic
upright=1.2, The Vedas are ancient Sanskrit texts of Hinduism. Above: A page from the '' Atharvaveda''.
The Vedas (, , ) are a large body of religious texts originating in ancient India. Composed in Vedic Sanskrit, the texts constitute the ...
Tamil period. Banasura, a demon by birth, was the ruler of the land of Kanyakumari. He was a very powerful king. He practiced tapasya
Tapas (Sanskrit: तपस्) is a variety of austere spiritual meditation practices in Indian religions. In Jainism, it means asceticism (austerities, body mortification); in Buddhism, it denotes spiritual practices including meditation and se ...
and obtained a boon from Brahma that his death could only be caused by an adolescent girl.
With this powerful boon, he became fearless and wreaked havoc on the entire world. He went on to conquer and oust Indra from his throne. He banished all the devas
Devas may refer to:
* Devas Club, a club in south London
* Anthony Devas (1911–1958), British portrait painter
* Charles Stanton Devas (1848–1906), political economist
* Jocelyn Devas (died 1886), founder of the Devas Club
* Devas (band), ...
from their abode. The devas, who were the personification of the basic natural elements, Agni
Agni (English: , sa, अग्नि, translit=Agni) is a Sanskrit word meaning fire and connotes the Vedic fire deity of Hinduism. He is also the guardian deity of the southeast direction and is typically found in southeast corners of Hindu ...
(fire), Varuna
Varuna (; sa, वरुण, , Malay: ''Baruna'') is a Vedic deity associated initially with the sky, later also with the seas as well as Ṛta (justice) and Satya (truth). He is found in the oldest layer of Vedic literature of Hinduism, such ...
(water), Vayu
Vayu (, sa, वायु, ), also known as Vata and Pavana, is the Hindu god of the winds as well as the divine massenger of the gods. In the '' Vedic scriptures'', Vayu is an important deity and is closely associated with Indra, the king of ...
(air) became uncoordinated, and havoc spread in the universe, because Indra (ether) was not able to administer and coordinate the ''Pancha Bhoota
Pancha Bhuta or Pancha Maha-Bhuta ( sa, पञ्चभूत, ; ), five great elements, also five physical elements, is a group of five basic elements, which, according to Hinduism, is the basis of all cosmic creation. These elements are: ''Pr ...
''.
According to local folklore, It was believed that only Bhagavati would be able to restore order. Bhagavati manifested herself in the southern tip of the subcontinent as Kumari, to kill Banasura and restore the balance of nature. As an adolescent girl, she had immense devotion towards the deity Shiva
Shiva (; sa, शिव, lit=The Auspicious One, Śiva ), also known as Mahadeva (; ɐɦaːd̪eːʋɐ, or Hara, is one of the principal deities of Hinduism. He is the Supreme Being in Shaivism, one of the major traditions within Hindu ...
. Shiva decided to marry her. All arrangements were made for the wedding. Shiva started the journey from Shuchindram. The wedding ''muhurtam,'' or auspicious time, was during the Brahma muhurtam, which was pre-morning. The sage Narada
Narada ( sa, नारद, ), or Narada Muni, is a sage divinity, famous in Hindu traditions as a travelling musician and storyteller, who carries news and enlightening wisdom. He is one of mind-created children of Brahma, the creator god. He ...
, observing that only a virgin goddess would be able to slay Banasura, caused a rooster to crow, indicating that the auspicious time for the wedding had passed. Thus, he was able to interrupt Shiva
Shiva (; sa, शिव, lit=The Auspicious One, Śiva ), also known as Mahadeva (; ɐɦaːd̪eːʋɐ, or Hara, is one of the principal deities of Hinduism. He is the Supreme Being in Shaivism, one of the major traditions within Hindu ...
's marriage to Kanya Kumari. Kumari waited for Shiva, and finally, she assumed that she had been snubbed. With unbearable insult, pain, grief, and anger, she destroyed everything she saw. She threw away all the food and broke her bangles. The food particles she scattered around are said to be the source of the colourful sands of Kanyakumari. When she finally gained her composure, she undertook continuous penance. Ages later, Banasura tried to lure and approach Kumari, without realising who she was. The infuriated Kumari slaughtered Banasura at once. Moments before his death, Banasura realised that the one before him was Adi Parashakti, the Goddess herself. He prayed her to absolve him of his sins. After killing Banasura, Kumari assumed her original form of Parvati
Parvati ( sa, पार्वती, ), Uma ( sa, उमा, ) or Gauri ( sa, गौरी, ) is the Hindu goddess of power, energy, nourishment, harmony, love, beauty, devotion, and motherhood. She is a physical representation of Mahadevi i ...
, and reunited with her husband, Shiva
Shiva (; sa, शिव, lit=The Auspicious One, Śiva ), also known as Mahadeva (; ɐɦaːd̪eːʋɐ, or Hara, is one of the principal deities of Hinduism. He is the Supreme Being in Shaivism, one of the major traditions within Hindu ...
. Kumari maintained her divine presence in the place, in the Bhagavati Kumari Amman Temple.
According to Vaishnavism
Vaishnavism ( sa, वैष्णवसम्प्रदायः, Vaiṣṇavasampradāyaḥ) is one of the major Hindu denominations along with Shaivism, Shaktism, and Smartism. It is also called Vishnuism since it considers Vishnu as the ...
, the saint Vadiraja Tirtha
Sri Vadiraja Teertharu (1480 – 1600) was a Dvaita philosopher, poet, traveller and mystic. A polymath of his time, he authored many works, often polemical, on Madhva theology and metaphysics. Additionally, he composed numerous poems and as ...
states in his Tirtha Prabandha
Thirtha Prabandha is one of the main Sanskrit works by Sri Vadiraja Swamy, the 16th century Dvaita philosopher and saint. The document is written in the form of a travelogue and contains descriptions of pilgrim centers throughout India.
The wor ...
that Devi Kanya Kumari is a form of the goddess Lakshmi
Lakshmi (; , sometimes spelled Laxmi, ), also known as Shri (, ), is one of the principal goddesses in Hinduism. She is the goddess of wealth, fortune, power, beauty, fertility and prosperity, and associated with ''Maya'' ("Illusion"). Alo ...
herself, who descended upon the earth to kill the demon Banasura, who was a devotee of Shiva.

Worship
The Bhagavati Kumari Amman Temple is one of the 52Shakti Peetha
The Shakti Pitha or the Shakti Peethas ( sa, शक्ति पीठ, , ''seat of Shakti'') are significant shrines and pilgrimage destinations in Shaktism, the goddess-centric denomination in Hinduism. The shrines are dedicated to various fo ...
. It is believed that the back spine area of Sati's corpse fell here creating the presence of Kundalini Shakti in the region.
The shrine is accessed through the Western door. The eastern door is opened only on certain days of a year, as on the new moon days in the months of Thai, Aadi (Karkidaka) July, during Navaratri
Navaratri is an annual Hindu festival observed in the honour of the goddess Durga. It spans over nine nights (and ten days), first in the month of Chaitra (March/April of the Gregorian calendar), and again in the month of Sharada. It is o ...
and in the month of Kaartikai. For the purpose of rites and rituals in the temple of Kumari is imagined as (Sankalpam) as Bālambika, the child goddess. The goddess is considered as Katyayani
''Katyayani'' (कात्यायनी) is an aspect of Mahadevi and the slayer of the tyrannical demon Mahishasura. She is the sixth among the Navadurgas, the nine forms of Hindu goddess Durga who are worshipped during the festival of Nav ...
, one of the Navadurga
Navadurga ( sa, नवदुर्गा, translit=Navadurgā), also spelled Navdurga and Navadurgas, are nine manifestations and forms of Durga in Hinduism, especially worshipped during Navaratri and Durga Puja. They are often considered collec ...
s here. She is also considered as Bhadrakali
Bhadrakali (IAST: Bhadrakālī; ), also known as Mahakali and Kali, is a Hindu goddess.
According to Shaktism, she is one of the fierce forms of the Supreme Goddess Shakti, or Adi Parashakti, mentioned in the Devi Mahatmyam. In Vaishnavi ...
by the devotees while worshipping her.
Devi Kanya Kumari is the goddess of virginity and penance. It is a practice that people choose to receive the Diksha
Diksha (Sanskrit: दीक्षा) also spelled diksa, deeksha or deeksa in common usage, translated as a "preparation or consecration for a religious ceremony", is giving of a mantra or an initiation by the guru (in Guru–shishya tradition) ...
of Sanyasa
''Sannyasa'' (Sanskrit: संन्यास; IAST: ), sometimes spelled Sanyasa (सन्न्यास) or Sanyasi (for the person), is life of renunciation and the fourth stage within the Hindu system of four life stages known as '' As ...
from here in olden times. The rites and rituals of the temple are organized and classified according to Sankaracharya
Shankaracharya ( sa, शङ्कराचार्य, , " Shankara-''acharya''") is a religious title used by the heads of amnaya monasteries called mathas in the Advaita Vedanta tradition of Hinduism. The title derives from Adi Shankara; te ...
's treatise.
The other attractions inside the temple are the Pathala Ganga Tirtha, Kalabhairava Shrine. Kalabhairava is a ferocious form of Shiva who annihilates kala, or time itself. Each of the 51 Shakti Peetha
The Shakti Pitha or the Shakti Peethas ( sa, शक्ति पीठ, , ''seat of Shakti'') are significant shrines and pilgrimage destinations in Shaktism, the goddess-centric denomination in Hinduism. The shrines are dedicated to various fo ...
has a Kalabhairava shrine within the temple meant for the protection of the temple. The name of the Kalabhairava in Kanyakumari temple is 'Nimish' and the Shakti is 'Sarvani' and in the Shakti Peetha
The Shakti Pitha or the Shakti Peethas ( sa, शक्ति पीठ, , ''seat of Shakti'') are significant shrines and pilgrimage destinations in Shaktism, the goddess-centric denomination in Hinduism. The shrines are dedicated to various fo ...
of Shuchindram the Kalabhairava is 'Samhāra' and the Shakti is 'Narayani'. These are two Shakti Peetha
The Shakti Pitha or the Shakti Peethas ( sa, शक्ति पीठ, , ''seat of Shakti'') are significant shrines and pilgrimage destinations in Shaktism, the goddess-centric denomination in Hinduism. The shrines are dedicated to various fo ...
s out of the 51 Shakti Peethas all over South Asia. There are also shrines to Vijayasundari and Balasundari, friends and playmates of the Goddess in her youthful form.
Navarathri Mandapam is a hall where devotees can display their artistic ability in music as a dedication to the goddess, Shri Pāda Pāra is a rock in the shape of Kumari's feet. This is now famous as Vivekananda Paara, where Swami Vivekananda got enlightenment to dedicate his life as an active Sanyasi rather than the usual practice of being passive.
The presiding image is sported in standing posture with an Akshamala
A japamala, , or simply mala ( sa, माला; , meaning ' garland') is a loop of prayer beads commonly used in Indian religions such as Hinduism, Jainism, Sikhism, and Buddhism for counting recitations when performing '' japa'' (reciting a ...
in her hands. There is an image of a lion in her pedestal indicating that she is the form of Adi Parashakti
Mahadevi ( sa, महादेवी, ), also referred to as Adi Parashakti, Adi Shakti, and Abhaya Shakti, is the supreme goddess in the Shaktism sect of Hinduism. According to this tradition, all Hindu goddesses are considered to be manifesta ...
. There is a four-pillar hall in the temple, each of which gives out sounds of Veena
The ''veena'', also spelled ''vina'' ( sa, वीणा IAST: vīṇā), comprises various chordophone instruments from the Indian subcontinent. Ancient musical instruments evolved into many variations, such as lutes, zithers and arched harps ...
(a string instrument), Mridangam (a percussion instrument), flute and Jalatarang (porcelain instrument).
The Gayatri
Gayatri (Sanskrit: गायत्री, IAST:Gāyatrī) is the personified form of the Gayatri Mantra, a popular hymn from Vedic texts. She is also known as Savitri, and bears the epithet of ''Vedamata'' (mother of the Vedas). Gayatri is ofte ...
mantra of Devi Kanyakumari is:
"kātyayanāya vidmahe kanyakumāri dhīmahi tanno durgiḥ prachodayāt"
Red Sarees and Ghee wick lamps are offered to the goddess by devotees. Reciting Lalita Sahasranama while approaching and circumambulating the temple is considered auspicious. The location Kanyakumari, i.e. the southern tip of India has been held sacred by Hindus' as it is the confluence of three seas. Offering Pitru Tarpana
( sa, तर्पण, bn, তর্পণ, kn, ತರ್ಪಣ, ta, தர்ப்பணம்) is a term in the Vedic practice that refers to an offering made to divine entities. It refers to the act of offering as well as the substance us ...
and bathing in the sea in the Kanyakumari beach is considered holy because it the convergence of many important Tirthas. There are a total of 11 Tirthas associated with the temple in the ocean surrounding Kanyakumari.
Significance
The Bhagavati Kumari Amman Temple inKanyakumari
Kanniyakumari (; , referring to Devi Kanya Kumari), also known as Cape Comorin, is a city in Kanniyakumari district in the state of Tamil Nadu, India. It is the southern tip of the Indian subcontinent and the southernmost city in mainland Ind ...
, Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu (; , TN) is a state in southern India. It is the tenth largest Indian state by area and the sixth largest by population. Its capital and largest city is Chennai. Tamil Nadu is the home of the Tamil people, whose Tamil language ...
is dedicated to her. It is located at the southern tip of main land India, on the confluence of the Bay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean, bounded on the west and northwest by India, on the north by Bangladesh, and on the east by Myanmar and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands of India. Its southern limit is a line betwee ...
, the Arabian Sea
The Arabian Sea ( ar, اَلْبَحرْ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Bahr al-ˁArabī) is a region of the northern Indian Ocean bounded on the north by Pakistan, Iran and the Gulf of Oman, on the west by the Gulf of Aden, Guardafui Channel ...
, and the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by t ...
. Legend attributes Sage Parashurama
Parashurama (), also referred to as Rama Jamadagnya, Rama Bhargava and Veerarama, is the sixth avatar among the Dashavatara of the preserver god Vishnu in Hinduism. He is believed to be one of the ''Chiranjeevis'' (Immortals), who will appea ...
for performing the consecration of the temple. The goddess is said to remove rigidity of the mind; devotees usually feel the tears in their eyes or even inside their mind when they pray to the goddess in devotion and contemplation.
The Kanyakumari Temple is one of the 51 Shakti Peetha
The Shakti Pitha or the Shakti Peethas ( sa, शक्ति पीठ, , ''seat of Shakti'') are significant shrines and pilgrimage destinations in Shaktism, the goddess-centric denomination in Hinduism. The shrines are dedicated to various fo ...
s where the right shoulder and (back) spine area of Sati
Sati or SATI may refer to:
Entertainment
* ''Sati'' (film), a 1989 Bengali film by Aparna Sen and starring Shabana Azmi
* ''Sati'' (novel), a 1990 novel by Christopher Pike
*Sati (singer) (born 1976), Lithuanian singer
*Sati, a character in ''Th ...
's corpse is said to have fallen, creating the presence of Kundalini Shakti in the region.
There is a temple of Ganesha
Ganesha ( sa, गणेश, ), also known as Ganapati, Vinayaka, and Pillaiyar, is one of the best-known and most worshipped Deva_(Hinduism), deities in the Hindu deities, Hindu pantheon and is the Supreme God in Ganapatya sect. His image is ...
near the tip of the land at the confluence of the three seas, which one must visit before entering the temple. Some believe that the Bhadrakali Temple within the Bhagavati Kumari Amman Temple is the Shakti Peetha.
As directed by his Guru Sri Ramakrishna Paramahamsa, Swami Vivekananda visited the temple to seek Devi's blessing in December 1892. It is in this location he decided to embark on the missionary work to a higher level of action rather than being passive like the usual Sanyasis. Swami Brahmananda (1863–1922) and Swami Nirmalananda (1863–1938), another two disciples of Sri Ramakrishna Parama Hamsa, also worshiped Devi Kanyakumari. In fact, Swami Nirmalananda brought several small girls from many parts of Kerala
Kerala ( ; ) is a state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile regions of Cochin, Malabar, South ...
to worship goddess here in 1935-36 period. Seven girls later on became the members of the first batch of Nuns of the "Sarada Ashrama", a Hindu nunnery started later in 1948 in Ottapalam, Palakkad
Palakkad (), formerly known as Palghat, historically known as Palakkattussery is a city and municipality in the Indian state of Kerala. It is the administrative headquarters of the Palakkad District. Palakkad is most densely populated municipal ...
, Kerala
Kerala ( ; ) is a state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile regions of Cochin, Malabar, South ...
by Swami Vishadananda.
Temple festivals
*Chitra Pournima Festival: on the Full moon day in May * Navaratri festival: 9 day festival in (September–October). The music artists get an opportunity to offer their artistic skill to the goddess by performing in the ''Navarathri Mandapam''. *Vaisakha festival: 10-day festival in May–June culminating by a ''Thoni Ezhunellathu'' in May–June. During this festival Devi will be taken in procession both in the morning and evening, during Aaraatu the eastern door is opened. On the ninth day, the ''Thoni Ezhunellathu'' takes place. Devi will be taken round the water on the western part in a boat. *Kalabham festival: The idol is smeared in Sandal paste in the last Friday of the month of Karkidaka or Aadi, in July–August.Pooja and worship schedule
The temple is opened for darshan from 6.00 a.m. to 11.00 a.m. and 4.00 p.m. to 8.00 p.m.Administration
The temple is maintained and administered by theHindu Religious and Charitable Endowments Department
The Hindu Religious and Charitable Endowments Department of the Government of Tamil Nadu
Government of Tamil Nadu is the subnational government for the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is seated at Fort St George, Chennai. The legislatur ...
of the Government of Tamil Nadu
Government of Tamil Nadu is the subnational government for the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is seated at Fort St George, Chennai. The legislature of Tamil Nadu was bicameral until 1986, when it was replaced by a unicameral legislature, l ...
./ref>
See also
*Kaumari
Matrikas (Sanskrit: मातृका (singular), IAST: mātṝkās, lit. "divine mothers") also called Matar or Matri, are a group of mother goddesses who are always depicted together in Hinduism. The Matrikas are often depicted in a group ...
* Kumari (goddess)
Kumari, or Kumari Devi, or the Living Goddess, is the tradition of worshipping a chosen virgin as manifestations of the divine female energy or Shakti in Dharmic religious traditions. It is believed that the girl is possessed by the goddess Tale ...
* Kanwari
Kanwari, also spelled Kunwari, or Kwari, is a village of 7,000 population, in Hansi-I Tehsil, Hisar-1 Rural Development Block, Hansi (Vidhan Sabha constituency) and Hisar (Lok Sabha constituency) of Hisar District of Hisar Division in th ...
* Matrikas
Matrikas (Sanskrit: मातृका (singular), IAST: mātṝkās, lit. "divine mothers") also called Matar or Matri, are a group of mother goddesses who are always depicted together in Hinduism. The Matrikas are often depicted in a group ...
* Suchindram Temple, Kanyakumari
Kanniyakumari (; , referring to Devi Kanya Kumari), also known as Cape Comorin, is a city in Kanniyakumari district in the state of Tamil Nadu, India. It is the southern tip of the Indian subcontinent and the southernmost city in mainland Ind ...
*Nagaraja Temple, Nagercoil
Nagaraja Temple is an early large temple found in the city of Nagercoil (''Nagarkōyil'') near the southern tip of Tamil Nadu, India. Its dating is uncertain but likely pre-12th-century. The main sanctum is dedicated to the Nagaraja – the ki ...
, Nagarcoil
Nagercoil, also spelt as Nagarkovil ("Temple of the Nāgas", or Nagaraja-Temple), is a city and the administrative headquarters of Kanyakumari District in Tamil Nadu state, India. Situated close to the tip of the Indian peninsula, it lies on an ...
* Sree Padmanabha Swamy Temple, Trivandrum
Thiruvananthapuram (; ), also known by its former name Trivandrum (), is the capital of the Indian state of Kerala. It is the most populous city in Kerala with a population of 957,730 as of 2011. The encompassing urban agglomeration populatio ...
* Attukal Temple, Trivandrum
Thiruvananthapuram (; ), also known by its former name Trivandrum (), is the capital of the Indian state of Kerala. It is the most populous city in Kerala with a population of 957,730 as of 2011. The encompassing urban agglomeration populatio ...
* Kottiyoor Vysakha Mahotsavam, Kannur
Kannur (), formerly known in English as Cannanore, is a city and a municipal corporation in the state of Kerala, India. It is the administrative headquarters of the Kannur district and situated north of the major port city and commercial hu ...
*Kodungallur Bhagavathy Temple
Sree Kurumba Bhagavati Temple (alternatively Kodungallur Devi Temple) is a Hindu temple at Kodungallur, Thrissur District, Kerala state, India. It is dedicated to the goddess Bhadrakali, a form of Mahakali or simply Durga or Aadi Parashakthi wo ...
, Thrissur
Thrissur (), formerly Trichur, also known by its historical name Thrissivaperur, is a city and the headquarters of the Thrissur district in Kerala, India. It is the third largest urban agglomeration in Kerala after Kochi and Kozhikode, and t ...
* Kamakshi Amman Temple, Kanchipuram
*Meenakshi Amman Temple
Arulmigu Meenakshi Sundaraswarar Temple is a historic Hindu temple located on the southern bank of the Vaigai River in the temple city of Madurai, Tamil Nadu, India. It is dedicated to the goddess Meenakshi, a form of Parvati, and her consort, ...
, Madurai
Madurai ( , also , ) is a major city in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is the cultural capital of Tamil Nadu and the administrative headquarters of Madurai District. As of the 2011 census, it was the third largest Urban agglomeration in ...
* Mookambika Devi Temple
Devī (; Sanskrit: देवी) is the Sanskrit word for ' goddess'; the masculine form is ''deva''. ''Devi'' and ''deva'' mean 'heavenly, divine, anything of excellence', and are also gender-specific terms for a deity in Hinduism.
The con ...
, Mangalore
Mangalore (), officially known as Mangaluru, is a major port city of the Indian state of Karnataka. It is located between the Arabian Sea and the Western Ghats about west of Bangalore, the state capital, 20 km north of Karnataka–Ke ...
References
Further reading
* *''Durga Puja Beginner'', Swami Satyananda Saraswati, Devi Mandir, 2001. () * * * * * * * * * Aurobindo, Sri. ''"The Mother"''. . * Kinsley, David.Hindu Goddesses: Vision of the Divine Feminine in the Hindu Religious Traditions
'. Motilal Banarsidass, New Delhi, India. . * Pattanaik, Devdutt.
The Mother Goddess: An Introduction
'. . * Pintchman, Tracy (1994).
The Rise of the Goddess in the Hindu Tradition
'. SUNY Press, New York, USA. . * Sen, Ramprasad (1720–1781). ''Grace and Mercy in Her Wild Hair: Selected Poems to the Mother Goddess''. . * Wangu, Madhu Bazaz (2003).
Images of Indian Goddesses: Myths, Meanings, and Models
'. Abhinav Publications, New Delhi, India. .
External links
*Durga Puja at NetGlimse.com
from the Durgāsaptaśatī
all about kanyakumari Temple
{{Regions of Kanyakumari Lakshmi Forms of Parvati Mother goddesses Hindu goddesses