Developed nations on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A developed country (or industrialized country, high-income country, more economically developed country (MEDC), advanced country) is a
A developed country (or industrialized country, high-income country, more economically developed country (MEDC), advanced country) is a
 Economic criteria have tended to dominate discussions. One such criterion is the income per capita; countries with the high
Economic criteria have tended to dominate discussions. One such criterion is the income per capita; countries with the high
 The UN HDI is a statistical measure that gauges an economy's level of human development. While there is a strong correlation between having a high HDI score and being a prosperous economy, the UN points out that the HDI accounts for more than income or productivity. Unlike GDP per capita or per capita income, the HDI takes into account how income is turned "into education and health opportunities and therefore into higher levels of human development."
Since 1990,
The UN HDI is a statistical measure that gauges an economy's level of human development. While there is a strong correlation between having a high HDI score and being a prosperous economy, the UN points out that the HDI accounts for more than income or productivity. Unlike GDP per capita or per capita income, the HDI takes into account how income is turned "into education and health opportunities and therefore into higher levels of human development."
Since 1990,
entry reads: "The following countries are classified by FTSE as developed countries: Australia, Austria, Belgium/Luxembourg, Canada, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hong Kong (China), Ireland, Israel, Italy, Japan, Netherlands, New Zealand, Norway, Portugal, Singapore, South Korea, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, United Kingdom and the United States." However, many other institutions have created more general lists referred to when discussing developed countries. For example, the
,
 According to the World Bank the following 80 countries and territories are classified as "high-income economies". As of the 2022 fiscal year, high-income economies are those that had a GNI per capita of $12,696 or more in 2020.https://datahelpdesk.worldbank.org/knowledgebase/articles/906519-world-bank-country-and-lending-groups ,
According to the World Bank the following 80 countries and territories are classified as "high-income economies". As of the 2022 fiscal year, high-income economies are those that had a GNI per capita of $12,696 or more in 2020.https://datahelpdesk.worldbank.org/knowledgebase/articles/906519-world-bank-country-and-lending-groups ,
 There are 29
There are 29
. Oecd.org. Retrieved 22 October 2013. a group of the world's major donor countries that discuss issues surrounding development aid and
, On the DAC's self-description, see the introductory letter. On other events, refer to the relevant section by date. The following OECD member countries are DAC members: 23 countries in Europe: two countries in the Americas: two countries in Asia: two countries in Oceania:
 According to the
According to the
 There are 22 permanent members in the Paris Club (french: Club de Paris), a group of officials from major creditor countries whose role is to find coordinated and sustainable solutions to the payment difficulties experienced by debtor countries.
15 countries in Europe:
three countries in the Americas:
three countries in Asia:
one country in Oceania:
There are 22 permanent members in the Paris Club (french: Club de Paris), a group of officials from major creditor countries whose role is to find coordinated and sustainable solutions to the payment difficulties experienced by debtor countries.
15 countries in Europe:
three countries in the Americas:
three countries in Asia:
one country in Oceania:
IMF
(advanced economies)
(developed countries)
United Nations Statistics Division
(definition)
(developed regions)
World Bank
(high-income economies) {{Authority control Economic country classifications Human geography Economic geography
sovereign state
A sovereign state or sovereign country, is a political entity represented by one central government that has supreme legitimate authority over territory. International law defines sovereign states as having a permanent population, defined ter ...
that has a high quality of life
Quality of life (QOL) is defined by the World Health Organization as "an individual's perception of their position in life in the context of the culture and value systems in which they live and in relation to their goals, expectations, standards ...
, developed economy
In the economics study of the public sector, economic and social development is the process by which the economic well-being and quality of life of a nation, region, local community, or an individual are improved according to targeted goals a ...
and advanced technological infrastructure relative to other less industrialized nations. Most commonly, the criteria for evaluating the degree of economic development are gross domestic product
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjective nature this measure is of ...
(GDP), gross national product
The gross national income (GNI), previously known as gross national product (GNP), is the total domestic and foreign output claimed by residents of a country, consisting of gross domestic product ( GDP), plus factor incomes earned by foreig ...
(GNP), the per capita income
Per capita income (PCI) or total income measures the average income earned per person in a given area (city, region, country, etc.) in a specified year. It is calculated by dividing the area's total income by its total population.
Per capita i ...
, level of industrialization, amount of widespread infrastructure and general standard of living. Which criteria are to be used and which countries can be classified as being developed are subjects of debate. A point of reference of US$20,000 in 2021 USD nominal GDP per capita for the International Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a major financial agency of the United Nations, and an international financial institution, headquartered in Washington, D.C., consisting of 190 countries. Its stated mission is "working to foster glo ...
(IMF) is a good point of departure, it is a similar level of development to the United States in 1960.
Developed countries have generally more advanced post-industrial economies, meaning the service sector provides more wealth than the industrial sector. They are contrasted with developing countries
A developing country is a sovereign state with a lesser developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreem ...
, which are in the process of industrialisation or are pre-industrial and almost entirely agrarian, some of which might fall into the category of Least Developed Countries. As of 2015, advanced economies comprise 60.8% of global GDP based on nominal values and 42.9% of global GDP based on purchasing-power parity (PPP) according to the IMF.
Definition and criteria
gross domestic product
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjective nature this measure is of ...
(GDP) per capita would thus be described as developed countries. Another economic criterion is industrialisation; countries in which the tertiary and quaternary sectors of industry dominate would thus be described as developed. More recently, another measure, the Human Development Index
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a statistic composite index of life expectancy, education (mean years of schooling completed and expected years of schooling upon entering the education system), and per capita income indicators, w ...
(HDI), which combines an economic measure, national income, with other measures, indices for life expectancy and education has become prominent. This criterion would define developed countries as those with a very high (HDI) rating. The index, however, does not take into account several factors, such as the net wealth per capita or the relative quality of goods in a country. This situation tends to lower the ranking of some of the most advanced countries, such as the G7 members and others.
According to the United Nations Statistics Division
The United Nations Statistics Division (UNSD), formerly the United Nations Statistical Office, serves under the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (DESA) as the central mechanism within the Secretariat of the United Nations ...
:
There is no established convention for the designation of "developed" and "developing" countries or areas in theAnd it notes that:United Nations The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoni ...system.
The designations "developed" and "developing" are intended for statistical convenience and do not necessarily express a judgement about the stage reached by a particular country or area in the development process.Nevertheless, the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development considers that this categorization can continue to be applied:
The developed economies broadly comprise Northern America and Europe, Israel, Japan and the Republic of Korea, as well as Australia and New Zealand.
Similar terms
Terms linked to the concept ''developed country'' include "advanced country", "industrialized country", "'more developed country" (MDC), "more economically developed country" (MEDC), " Global North country", " first world country", and "post-industrial country". The term industrialized country may be somewhat ambiguous, as industrialisation is an ongoing process that is hard to define. The first industrialized country was theUnited Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and ...
, followed by Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to ...
. Later it spread further to Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwee ...
, United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
and other Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's countries and territories vary depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the ancient Mediterranean ...
an countries. According to some economist
An economist is a professional and practitioner in the social sciences, social science discipline of economics.
The individual may also study, develop, and apply theories and concepts from economics and write about economic policy. Within this ...
s such as Jeffrey Sachs, however, the current divide between the developed and developing world is largely a phenomenon of the 20th century.
Mathis Wackernagel calls the binary labeling of countries as "neither descriptive nor explanatory. It is merely a thoughtless and destructive endorsement of GDP fetish. In reality, there are not two types of countries, but over 200 countries, all faced with the same laws of nature, yet each with unique features."
A 2021 analysis proposes the term ''emerged'' to describe markets, economies, or countries that have graduated from emerging market status, but have not yet reached the level equivalent to developed countries. Multinational corporations from these emerging markets present unique patterns of overseas expansion and knowledge acquisition from foreign countries.
Economy lists by various criteria
Human Development Index (HDI)
Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of ...
(2001–2006, 2009–2019), Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the n ...
(1990–1991 and 1993), Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by to ...
(1992 and 1994–2000) and Iceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its ...
(2007–2008) have had the highest HDI score.
The following countries ranked from 1 to 66 in the year 2021 are considered to be of "very high human development":
High-income economies
Some institutions have produced lists of developed countries: the UN (list shown above), the CIA, and some providers of stock market indices (theFTSE Group
FTSE International Limited trading as FTSE Russell ( "Footsie") is a British provider of stock market indices and associated data services, wholly owned by the London Stock Exchange (LSE) and operating from premises in Canary Wharf. It operate ...
, MSCI, S&P, Dow Jones, STOXX, etc.). The latter is not included here because its association of developed countries with countries with both high incomes and developed markets is not deemed as directly relevant.The Developed Countries Glossaryentry reads: "The following countries are classified by FTSE as developed countries: Australia, Austria, Belgium/Luxembourg, Canada, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hong Kong (China), Ireland, Israel, Italy, Japan, Netherlands, New Zealand, Norway, Portugal, Singapore, South Korea, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, United Kingdom and the United States." However, many other institutions have created more general lists referred to when discussing developed countries. For example, the
International Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a major financial agency of the United Nations, and an international financial institution, headquartered in Washington, D.C., consisting of 190 countries. Its stated mission is "working to foster glo ...
(IMF) identifies 39 "advanced economies".World Economic Outlook,
International Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a major financial agency of the United Nations, and an international financial institution, headquartered in Washington, D.C., consisting of 190 countries. Its stated mission is "working to foster glo ...
, September 2011, p. 165. The OECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; french: Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques, ''OCDE'') is an intergovernmental organisation with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate ...
's 37 members are known as the "developed countries club". The World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of low- and middle-income countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects. The World Bank is the collective name for the Inte ...
identifies 81 "high income countries". Other standards, such as the 30-50 Club (GDP per capita over $30,000 and population over 50 million) have been developed to categorize highly developed and influential countries.
World Bank high-income economies
 According to the World Bank the following 80 countries and territories are classified as "high-income economies". As of the 2022 fiscal year, high-income economies are those that had a GNI per capita of $12,696 or more in 2020.https://datahelpdesk.worldbank.org/knowledgebase/articles/906519-world-bank-country-and-lending-groups ,
According to the World Bank the following 80 countries and territories are classified as "high-income economies". As of the 2022 fiscal year, high-income economies are those that had a GNI per capita of $12,696 or more in 2020.https://datahelpdesk.worldbank.org/knowledgebase/articles/906519-world-bank-country-and-lending-groups , World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of low- and middle-income countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects. The World Bank is the collective name for the Inte ...
. Accessed on 8 July 2021.
36 countries and territories in Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
:
20 countries and territories in the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America, North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World. ...
:
15 countries and territories in Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an are ...
:
eight countries and territories in Oceania
Oceania (, , ) is a geographical region that includes Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Spanning the Eastern and Western hemispheres, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of and a population of around 44.5 million ...
:
one country in Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
:
nine former high-income economies:
* Between 1994 and 2009, as a part of the .
# Dissolved on 10 October 2010, succeeded by Curaçao and Sint Maarten.
High-income OECD members
According to the World Bank, the following 34 members are classified as "OECD High-Income": 26 countries in Europe: three countries in the Americas: three countries in Asia: two countries in Oceania:Development Assistance Committee members
OECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; french: Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques, ''OCDE'') is an intergovernmental organisation with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate ...
member countries and the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are located primarily in Europe, Europe. The union has a total area of ...
—in the Development Assistance Committee (DAC),Peer reviews of DAC members – Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. Oecd.org. Retrieved 22 October 2013. a group of the world's major donor countries that discuss issues surrounding development aid and
poverty reduction
Poverty reduction, poverty relief, or poverty alleviation, is a set of measures, both economic and humanitarian, that are intended to permanently lift people out of poverty.
Measures, like those promoted by Henry George in his economics ...
in developing countries
A developing country is a sovereign state with a lesser developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreem ...
.DAC website >> "The DAC in Dates", On the DAC's self-description, see the introductory letter. On other events, refer to the relevant section by date. The following OECD member countries are DAC members: 23 countries in Europe: two countries in the Americas: two countries in Asia: two countries in Oceania:
IMF advanced economies
International Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a major financial agency of the United Nations, and an international financial institution, headquartered in Washington, D.C., consisting of 190 countries. Its stated mission is "working to foster glo ...
, 40 countries and territories are officially listed as "advanced economies", with the addition of 7 microstates and dependencies modified by the CIA
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA ), known informally as the Agency and historically as the Company, is a civilian foreign intelligence service of the federal government of the United States, officially tasked with gathering, processing, ...
which were omitted from the IMF version :
28 countries and dependencies in Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
classified by the IMF, 6 others given by the CIA :
seven countries and territories in Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an are ...
:
three countries and territories in the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America, North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World. ...
classified by the IMF, one territory given by the CIA :
two countries in Oceania
Oceania (, , ) is a geographical region that includes Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Spanning the Eastern and Western hemispheres, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of and a population of around 44.5 million ...
:
d The CIA has modified an older version of the IMF's list of 38 Advanced Economies, noting that the IMF's Advanced Economies list "would presumably also cover the following nine smaller countries of Andorra, Bermuda, Faroe Islands, Guernsey, Holy See, Jersey, Liechtenstein, Monaco, and San Marino ... San Marino (2012) and Andorra (2021) were later included in the IMF's list.
Paris Club members
 There are 22 permanent members in the Paris Club (french: Club de Paris), a group of officials from major creditor countries whose role is to find coordinated and sustainable solutions to the payment difficulties experienced by debtor countries.
15 countries in Europe:
three countries in the Americas:
three countries in Asia:
one country in Oceania:
There are 22 permanent members in the Paris Club (french: Club de Paris), a group of officials from major creditor countries whose role is to find coordinated and sustainable solutions to the payment difficulties experienced by debtor countries.
15 countries in Europe:
three countries in the Americas:
three countries in Asia:
one country in Oceania:
Comparative table (2022)
Comparative table of countries with a "very high" human development (0.800 or higher), according to UNDP; "advanced" economies, according to theIMF
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a major financial agency of the United Nations, and an international financial institution, headquartered in Washington, D.C., consisting of 190 countries. Its stated mission is "working to foster glob ...
; "high income" economies, according to the World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of low- and middle-income countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects. The World Bank is the collective name for the Inte ...
; and income per capita (purchasing power parity) higher than $22,000, according to the IMF
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a major financial agency of the United Nations, and an international financial institution, headquartered in Washington, D.C., consisting of 190 countries. Its stated mission is "working to foster glob ...
.
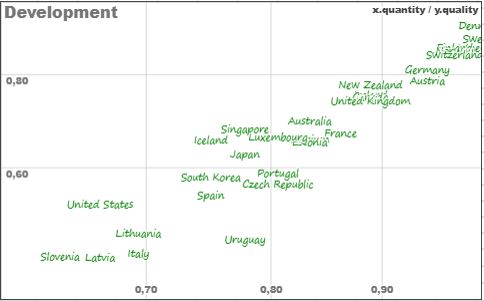
Rankings
The list below features some outstanding countries selected from the comparative table above with average data of quality (best place in rankings) and quantity (considered in how many of the 36 rankings) with an average between quality and quantity greater than 60%.
See also
* Digital divide *First World privilege
First World privilege is any advantages accrued by an individual by virtue of being a national of a First World country.
Overview
First-World privilege is often explicitly maintained by legal means such as immigration laws and trade barriers. ...
* First World problem
__NOTOC__
First World problem is an informal term for the issues in First World nations that are complained about in response to the perceived absence of more pressing concerns. Although it has been described as "a subset of the fallacy of relat ...
* Fourth World
The Fourth World is an extension of the three-world model, used variably to refer to
# Sub-populations socially excluded from global society, such as uncontacted peoples;
# Hunter-gatherer, nomadic, pastoral, and some subsistence farming pe ...
* Globalization
Globalization, or globalisation (Commonwealth English; see spelling differences), is the process of interaction and integration among people, companies, and governments worldwide. The term ''globalization'' first appeared in the early 20t ...
* G8
* G7
* List of countries by wealth per adult
* Multinational corporation
A multinational company (MNC), also referred to as a multinational enterprise (MNE), a transnational enterprise (TNE), a transnational corporation (TNC), an international corporation or a stateless corporation with subtle but contrasting senses, i ...
* Western Bloc
Notes
References
External links
*IMF
(advanced economies)
(developed countries)
United Nations Statistics Division
(definition)
(developed regions)
World Bank
(high-income economies) {{Authority control Economic country classifications Human geography Economic geography
Country
A country is a distinct part of the world, such as a state, nation, or other political entity. It may be a sovereign state or make up one part of a larger state. For example, the country of Japan is an independent, sovereign state, whi ...
Lists of countries
Imperialism studies