Deutsche Ost-Afrika Linie on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

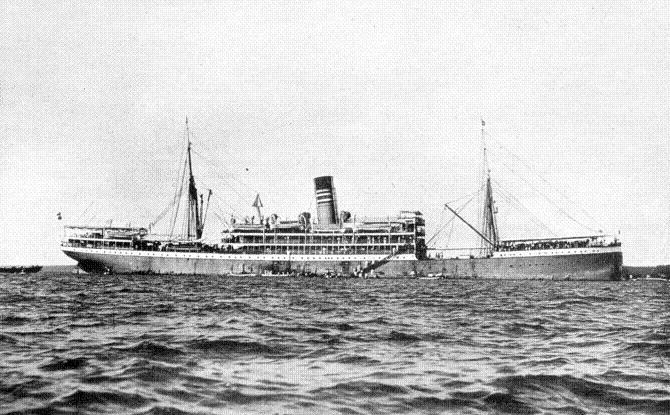
 Deutsche Ost-Afrika Linie (''German East Africa Line'') was a shipping line, established in 1890 as an alternative to the existing shipping services to
Deutsche Ost-Afrika Linie (''German East Africa Line'') was a shipping line, established in 1890 as an alternative to the existing shipping services to
 The subsidy contract of 1900, which expired in 1915, was not extended as a result of the war. In 1916 Woermann sold the Woermann Line and the Deutsche Ost-Afrika Linie to a consortium made up of HAPAG,
The subsidy contract of 1900, which expired in 1915, was not extended as a result of the war. In 1916 Woermann sold the Woermann Line and the Deutsche Ost-Afrika Linie to a consortium made up of HAPAG,

 Deutsche Ost-Afrika Linie (''German East Africa Line'') was a shipping line, established in 1890 as an alternative to the existing shipping services to
Deutsche Ost-Afrika Linie (''German East Africa Line'') was a shipping line, established in 1890 as an alternative to the existing shipping services to East Africa
East Africa, Eastern Africa, or East of Africa, is the eastern subregion of the African continent. In the United Nations Statistics Division scheme of geographic regions, 10-11-(16*) territories make up Eastern Africa:
Due to the historica ...
, including German East Africa
German East Africa (GEA; german: Deutsch-Ostafrika) was a German colony in the African Great Lakes region, which included present-day Burundi, Rwanda, the Tanzania mainland, and the Kionga Triangle, a small region later incorporated into Mo ...
(1891–1919), then dominated by United Kingdom shipping lines.
Founding
In 1888, the board of the trading firm Woermann-Linie made plans to set up a scheduled service to East Africa as the existing routes were dominated by British lines. The following year the Reichstag approved such a shipping line and in January 1890 the Chancellor began looking for a German shipping company to set up a line to Africa subsidized for over ten years with 900,000 marks a year. As no company was ready, the Reich announced the establishment of a shipping company.Rübner, Hartmut: Konzentration und Krise der deutschen Schiffahrt. Maritime Wirtschaft im Kaiserreich, in der Weimarer Republik und im Nationalsozialismus, Hauschild Verlag, Bremen 2005 On April 19, 1890, the Deutsche Ost-Afrika Linie was founded with a capital of six million marks by a consortium of German banks and the Hamburg merchantsAdolph Woermann
Adolph Woermann (10 December 1847 in Hamburg – 4 May 1911 in the Grönwohld-Hof near Trittau) was a German merchant, shipowner and politician, who was also instrumental in the establishment of German colonies in Africa. In his time he was t ...
, F.Laeisz, August Bolten, and Hansen & Co. C. Woermann took over the management with Adolph Woermann as Chairman of the Supervisory Board.Mathies, Otto: Hamburgs Reederei 1814 - 1914. Friederichsen Verlag, Hamburg 1924. The line began operating on July 23, 1890 with two steamers purchased from the Woermann line. Beginning in 1891, the service consisted of weekly departures from Hamburg
Hamburg (, ; nds, label=Hamburg German, Low Saxon, Hamborg ), officially the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg (german: Freie und Hansestadt Hamburg; nds, label=Low Saxon, Friee un Hansestadt Hamborg),. is the List of cities in Germany by popul ...
via the Mediterranean to Bombay
Mumbai (, ; also known as Bombay — List of renamed Indian cities and states#Maharashtra, the official name until 1995) is the capital city of the Indian States and union territories of India, state of Maharashtra and the ''de facto'' fin ...
-Zanzibar
Zanzibar (; ; ) is an insular semi-autonomous province which united with Tanganyika in 1964 to form the United Republic of Tanzania. It is an archipelago in the Indian Ocean, off the coast of the mainland, and consists of many small islan ...
.
Early years
The first years of operation were quite difficult due to the British takeover of Zanzibar in November 1890 and the loss of two ships in the first three years. By 1894, the routes were extended to South Africa and profits were posted for the first time. In 1900 the government contract with annual subsidies of 1.35 million marks was extended by 15 years and the share capital increased to ten million marks. In 1901, a bond for five million marks was issued to build more ships. In 1894 the company added a route from Hamburg to Durban in South Africa via the Cape and commissioned for this service the "Herzog" (1896/4,933 gt) and the "Koenig". In 1895 DOAL introduced instead the new steamers on the route Hamburg - Suez - Dar es Salaam and from 1898 also Durban was connected via Suez, no longer via Cape Town, in order to avoid a clash with the British. Only from 1901, when the Boer War was no longer a political obstacle, a new 'Rund-um-Afrika' (round Africa) route was operated by DOAL on the circuit Hamburg - Bremerhaven - Cape Town - Suez - Hamburg and in reverse direction. For this main line the 'Kronprinz' and 'Kurfürst' were introduced, steamers with a grey hull, white superstructure and a buff funnel, topped with an arrangement of black/white/red rings, pointing the national colours. More difficult years followed until 1907, as new competitors appeared and the British lines increased competition. The Deutsche Ost-Afrika Linie and the Woermann Line then responded to an offer byAlbert Ballin
Albert Ballin (15 August 1857 – 9 November 1918) was a German shipping magnate. He was the general director of the Hamburg-Amerikanische Packetfahrt-Actien-Gesellschaft (HAPAG) or Hamburg-America Line, which for a time was the world's largest s ...
to form a joint venture with Hamburg-America Line
The Hamburg-Amerikanische Packetfahrt-Aktien-Gesellschaft (HAPAG), known in English as the Hamburg America Line, was a transatlantic shipping enterprise established in Hamburg, in 1847. Among those involved in its development were prominent citi ...
(HAPAG). HAPAG and Woermann participated in the operation of the Deutsche Ost-Afrika Linie and each allocated one or two ships for an extension of the line from South Africa to West Africa. The Woermann Line was involved in the shared service and in 1908 the Hamburg-Bremen Africa Line also joined. The increased number of departures improved business.
After the death of Adolph Woermann in 1911, Eduard Woermann succeeded him. In 1914 the company's fleet consisted of 22 steamers, with approx. 110,000 BRT.
World War One and its aftermath
 The subsidy contract of 1900, which expired in 1915, was not extended as a result of the war. In 1916 Woermann sold the Woermann Line and the Deutsche Ost-Afrika Linie to a consortium made up of HAPAG,
The subsidy contract of 1900, which expired in 1915, was not extended as a result of the war. In 1916 Woermann sold the Woermann Line and the Deutsche Ost-Afrika Linie to a consortium made up of HAPAG, Norddeutscher Lloyd
Norddeutscher Lloyd (NDL; North German Lloyd) was a German shipping company. It was founded by Hermann Henrich Meier and Eduard Crüsemann in Bremen on 20 February 1857. It developed into one of the most important German shipping companies of ...
(NDL) and Hugo Stinnes
Hugo Dieter Stinnes (12 February 1870 – 10 April 1924) was a German industrialist and politician. During the late era of the German Empire and early Weimar Republic, he was considered to be one of the most influential entrepreneurs in Europe.
...
. The company lost all ships due to the First World War and the Versailles Treaty.
The Stinnes shares were taken over by HAPAG and NDL in 1921.
In 1927 the Deutschen Afrika-Dienst-Vertrag of 1907 was continued for a further 20 years and in the following years the corporate structure stabilised. In 1928 the 9,552-ton "Watussi" and "Ubena" were introduced as the first two-funnel turbine steamers of the company sporting the DOAL label, employed on the 'Rund-um-Afrika' route.
A year after the NSDAP Nazi Party
The Nazi Party, officially the National Socialist German Workers' Party (german: Nationalsozialistische Deutsche Arbeiterpartei or NSDAP), was a far-right political party in Germany active between 1920 and 1945 that created and supported t ...
seized power, German shipping was reorganized in 1934, in which the large shipping groups were divided. HAPAG and Norddeutscher Lloyd had to surrender their shares in the Woermann Line and the Deutsche Ost-Afrika Linie to the German Reich. In 1936 two larger turbine steamers were launched, the "Pretoria" and the "Windhuk" of 16,662 tons each.
In 1942, during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, this line and the Woermann-Linie owned by the cigarette manufacturer Philipp Fürchtegott Reemtsma, were taken over by John T. Essberger of Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
. The Deutsche Afrika-Linien lost both fleets in post-war reparations.
Ships of the Deutsche Ost-Afrika Linie up until 1914
Ships of the Deutsche Ost-Afrika Linie after 1914
See also
* Deutsche Afrika-Linien/John T. Essberger Group of Companies * * *Kenya Colony
The Colony and Protectorate of Kenya, commonly known as British Kenya or British East Africa, was part of the British Empire in Africa. It was established when the former East Africa Protectorate was transformed into a British Crown colony in ...
References
External links
* {{Authority control Defunct shipping companies Shipping companies of Germany East Africa German East Africa Companies based in Hamburg Transport companies established in 1890 Transport companies disestablished in 1942 1890 establishments in Germany 1942 disestablishments in Germany 1890 establishments in German East Africa 1890 establishments in Africa 1940s disestablishments in Africa Defunct companies of Germany