Demak Sultanate on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Demak Sultanate (کسلطانن دمق) was a Javanese Muslim state located on
 As the sign of his new reign, Raden Patah built a new Grand Mosque as the center of Islamic teaching. He appointed members of Wali Songo as advisors within his new government: Sunan Kudus as
As the sign of his new reign, Raden Patah built a new Grand Mosque as the center of Islamic teaching. He appointed members of Wali Songo as advisors within his new government: Sunan Kudus as
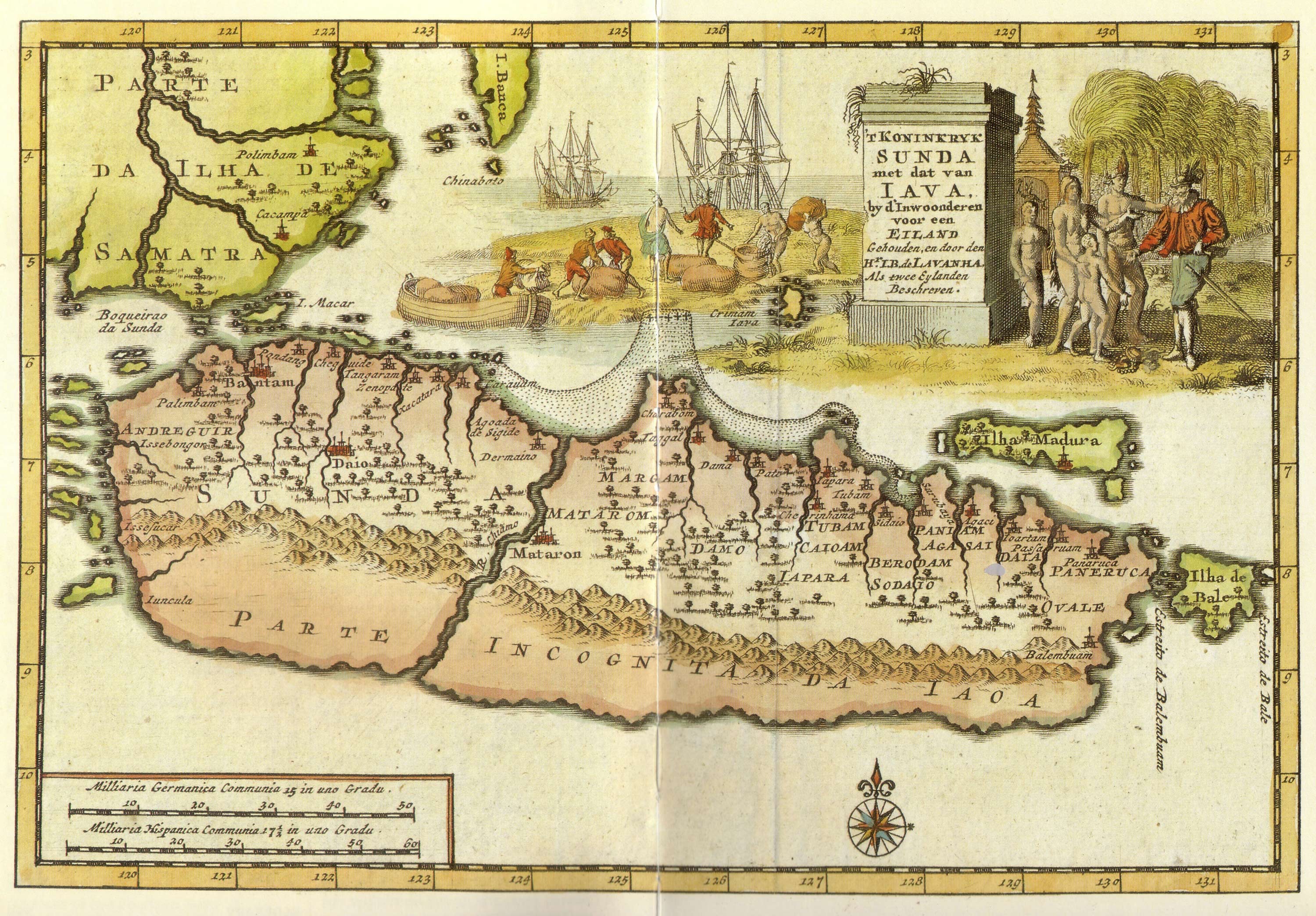 Raden Patah's son, or possibly his brother, led Demak's brief domination in Java. He was known as Trenggana, and later Javanese traditions say he gave himself the title Sultan. It appears that Trenggana had two reigns—''c''. 1505–;1518 and ''c''. 1521–1546—between which his brother in law, Yunus of
Raden Patah's son, or possibly his brother, led Demak's brief domination in Java. He was known as Trenggana, and later Javanese traditions say he gave himself the title Sultan. It appears that Trenggana had two reigns—''c''. 1505–;1518 and ''c''. 1521–1546—between which his brother in law, Yunus of
 Pati Unus died childless, leading to a crisis in the Demak succession. The throne was contested between his brothers, the older Raden Kikin and the younger Raden Trenggana. According to tradition, the eldest son of Prince Trenggana, Prince Prawata, also known as Raden Mukmin, stole '' Keris Setan Kober'', a powerful magical kris, from
Pati Unus died childless, leading to a crisis in the Demak succession. The throne was contested between his brothers, the older Raden Kikin and the younger Raden Trenggana. According to tradition, the eldest son of Prince Trenggana, Prince Prawata, also known as Raden Mukmin, stole '' Keris Setan Kober'', a powerful magical kris, from
 Demak derived its income from trade, importing
Demak derived its income from trade, importing
 Before the emergence of Demak, the northern coast of Java was the seat of many Muslim communities, both foreign merchants and local Javanese. The Islamization process gained momentum from the decline of Hindu-Buddhist Majapahit authority. Following the fall of the Majapahit capital to a usurper from Kediri, Raden Patah declared Demak's independence from Majapahit overlordship, and almost all northern Javanese ports later followed suit. However, the Demak royal family regarded themselves as descendants of Majapahit. Demak symbols continued to use the Surya Majapahit, an eight-pointed sun, while modifying it to remove Hindu associations. This modified symbol can be seen as decoration inside the Grand Mosque of Demak.
As the first Islamic polity in Java, Demak has a venerated status among
Before the emergence of Demak, the northern coast of Java was the seat of many Muslim communities, both foreign merchants and local Javanese. The Islamization process gained momentum from the decline of Hindu-Buddhist Majapahit authority. Following the fall of the Majapahit capital to a usurper from Kediri, Raden Patah declared Demak's independence from Majapahit overlordship, and almost all northern Javanese ports later followed suit. However, the Demak royal family regarded themselves as descendants of Majapahit. Demak symbols continued to use the Surya Majapahit, an eight-pointed sun, while modifying it to remove Hindu associations. This modified symbol can be seen as decoration inside the Grand Mosque of Demak.
As the first Islamic polity in Java, Demak has a venerated status among
History of Demak
{{DEFAULTSORT:Sultanate Of Demak History of Central Java
Java
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's mos ...
's north coast in Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
, at the site of the present-day city of Demak
Demak is on the north coast of Central Java province, on the island of Java, Indonesia.
* Demak, Demak, modern-day large town
* Demak Sultanate, sixteenth century sultanate
* Demak Regency
Demak ( jv, ꦢꦼꦩꦏ꧀) is a regency located in t ...
. A port fief
A fief (; la, feudum) was a central element in medieval contracts based on feudal law. It consisted of a form of property holding or other rights granted by an overlord to a vassal, who held it in fealty or "in fee" in return for a form ...
to the Hindu-Buddhist Majapahit kingdom thought to have been founded in the last quarter of the 15th century, it was influenced by Islam brought by Muslim traders from China, Gujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the ninth ...
, Arabia
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plat ...
and also Islamic kingdoms in the region, such as Samudra Pasai, Malacca and Bani (Muslim) Champa. The sultanate was the first Muslim state in Java, and once dominated most of the northern coast of Java and southern Sumatra.
Although it lasted only a little more than a century, the sultanate played an important role in the establishment of Islam in Indonesia, especially on Java and neighboring areas.
Etymology
The origin of Demak was the settlement named Glagah Wangi. According to tradition, the first person that Raden Patah encountered in Glagah Wangi was a woman named Nyai Lembah, from Rawa Pening. Nyai Lembah invited Raden Patah to settle in Glagah Wangi, which later was renamed as Demak Bintara. There are several suggestions on the origin of the name ''Demak''. According to Indonesian historian Poerbatjaraka, it derived from the Javanese term ''delemak'', which means "watery soil" or "swamp". According to Hamka, it derived from theArabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
term ''dimak'', which means "tears", to imply the hardship endured during the struggle to establish Islam in Java. According to another historian, Sutjipto Wiryosuparto, it derived from a term in the Kawi language
Old Javanese or Kawi is the oldest attested phase of the Javanese language. It was spoken in the eastern part of what is now Central Java and the whole of East Java, Indonesia. As a literary language, Kawi was used across Java and on the island ...
that means "heirloom" or "gift".
History of the Demak Sultanate
Formation
During the reign of Wikramawardhana of Majapahit, during the period from 1405 to 1433, a series of Ming armadas naval expeditions led by Zheng He, a Muslim Chinese admiral, arrived in Java. This Chinese expedition supported the establishment of the Muslim state of Malacca in the first half of the 15th century, later assisted by the establishment of Muslim Chinese, Arab and Malay communities in northern ports of Java such as Semarang,Demak
Demak is on the north coast of Central Java province, on the island of Java, Indonesia.
* Demak, Demak, modern-day large town
* Demak Sultanate, sixteenth century sultanate
* Demak Regency
Demak ( jv, ꦢꦼꦩꦏ꧀) is a regency located in t ...
, Tuban, and Ampel; thus Islam began to gain a foothold on the northern coast of Java.
Demak's origins are uncertain although it was apparently founded in the last quarter of the 15th century by a Muslim known as Raden Patah (from the Arabic name Fatah, also called "Pate Rodin" in Portuguese records, and "Jin Bun" in Chinese records). There is evidence that he had Chinese ancestry and perhaps was named Cek Ko-po.
According to tradition, Sunan Ampel ordered Raden Patah to establish an Islamic learning center in the Glagah Wangi village in coastal Central Java. Soon the village grew to become the center for dawah activities among distinguished Islamic proselytizers, traditionally known as Wali Songo or "the nine saints". At that time Glagah Wangi was a small fiefdom belonging to Majapahit. It was the only Majapahit fiefdom with a Muslim ruler. Then the name was changed to Demak, and it grew further by the establishment of a madrasa
Madrasa (, also , ; Arabic: مدرسة , pl. , ) is the Arabic word for any type of educational institution, secular or religious (of any religion), whether for elementary instruction or higher learning. The word is variously transliterated '' ...
Islamic school and pesantren boarding school.
Raden Patah
The foundation of Demak is traditionally attributed to Raden Patah (r. 1475–1518), a Javanese noble related to Majapahit royalty. At least one account stated that he was the son of Kertabhumi, who reigned as king Brawijaya V of Majapahit (1468–1478). According to tradition, Raden Patah was the son of Majapahit King Kertabhumi with his concubine, a Chinese princess who resided in the Majapahit palace. She was supposedly given away when unknowingly pregnant with the king's child to be betrothed to the regent of the vassal state of Palembang. There Raden Patah was born in 1448 with the name Raden Hasan. After coming of age, he went to Ampel Denta in Java (now Surabaya) to learn from Sunan Ampel, a prominent ulama. Sunan Ampel betrothed him to his daughter, Nyai Ageng Malaka. Subsequently, in the 1470s, Sunan Ampel sent him to establish a new settlement in Glagah Wangi, Central Java. Through Sunan Ampel's recommendation, Raden Hasan was appointed as the regent of Glagah Wangi by King Kertabhumi of Majapahit, with the title Adipati Bintara. Dates for the end of the Majapahit Empire range from 1478, traditionally described in the ''sinengkalan'' or ''chandrasengkala'' (chronogram
A chronogram is a sentence or inscription in which specific letters, interpreted as numerals (such as Roman numerals), stand for a particular date when rearranged. The word, meaning "time writing", derives from the Greek words ''chronos'' (χ ...
) ''Sirna ilang kertaning bhumi'' and corresponding to 1400 Saka,) to 1517. In 1478 the Sudarma Wisuta war took place, when Ranawijaya's army under general Udara (who later became vice-regent) breached Trowulan defences and killed Kertabumi in his palace. Demak sent reinforcements under Sunan Ngudung, who later died in battle and was replaced by Sunan Kudus
Sunan Kudus (born Ja'far Shadiq; 1500-1550), founder of Kudus, is considered to be one of the Wali Sanga of Java, Indonesia.
He is said to have originated the wayang golek, and founded the masjid at Kudus using (it is said) the doors from th ...
, but they came too late to save Kertabumi, although they managed to repel the Ranawijaya army. This event is mentioned in Trailokyapuri (Jiwu) and the Petak inscription, where Ranawijaya claimed that he already defeated Kertabhumi and reunited Majapahit as one kingdom.Poesponegoro & Notosusanto (1990), pp. 448–451. Ranawijaya ruled from 1474 to 1498 with the formal name Girindrawardhana, with Udara as his vice-regent. This event led to war between Demak and Daha, since Demak rulers were descendants of Kertabhumi.
In response to the collapse of Kertabhumi of Trowulan and the rise of Girindrawardhana of Daha in 1478, Demak decided it was no longer obliged to sent tribute to the Majapahit central court and declared its independence. At that time Demak was temporarily led by Sunan Giri
Sunan Giri (also called Raden Paku or Joko Samudro), Muhammad Ainul Yakin (born 1442 CE in Blambangan (now Banyuwangi) is considered one of the Wali Sanga (revered saints of Islam) of Indonesia.
History
He was the son of Dewi Sekardadu and ...
(Prabu Satmoto). Three years later the Islamic kingdom of Demak was established under the chronogram ''Geni mati siniram janmi'', which corresponds to 1403 Saka or 1481 CE. Raden Hasan was crowned by members of Wali Songo under the new regnal name of Sultan Syah Alam Akbar Al-Fattah; thus in Javanese he was popularly known as Raden Patah.
A Chinese chronicle in a temple in Semarang states that Raden Patah founded the town of Demak in a marshy area to the north of Semarang. After the collapse of Majapahit, its various dependencies and vassals broke free, including northern Javanese port towns like Demak.
 As the sign of his new reign, Raden Patah built a new Grand Mosque as the center of Islamic teaching. He appointed members of Wali Songo as advisors within his new government: Sunan Kudus as
As the sign of his new reign, Raden Patah built a new Grand Mosque as the center of Islamic teaching. He appointed members of Wali Songo as advisors within his new government: Sunan Kudus as qadi
A qāḍī ( ar, قاضي, Qāḍī; otherwise transliterated as qazi, cadi, kadi, or kazi) is the magistrate or judge of a '' sharīʿa'' court, who also exercises extrajudicial functions such as mediation, guardianship over orphans and mino ...
(great judge of religious law), Sunan Giri as mufti
A Mufti (; ar, مفتي) is an Islamic jurist qualified to issue a nonbinding opinion (''fatwa'') on a point of Islamic law (''sharia''). The act of issuing fatwas is called ''iftāʾ''. Muftis and their ''fatwas'' played an important role ...
, and Sunan Kalijaga
Sunan Kalijaga (1460-1513), born as Raden Mas Said son of a Duke of Tuban in East Java, Indonesia, was one of the "nine saints" of Javanese Islam (Wali Sanga). the "Kalijaga" title was derived from an orchard known as "Kalijaga" in Cirebon. O ...
as imam and advisor.
Demak managed to gain hegemony
Hegemony (, , ) is the political, economic, and military predominance of one State (polity), state over other states. In Ancient Greece (8th BC – AD 6th ), hegemony denoted the politico-military dominance of the ''hegemon'' city-state over oth ...
over other trading ports on the northern coast of Java such as Semarang, Jepara
Jepara is a town in the province of Central Java, Indonesia.
Jepara is on the north coast of Java, north-east of Semarang, not far from Mount Muria, with a population of 92,967 in mid 2019. It is also the main town of Jepara Regency, which has a ...
, Tuban, and Gresik. The supremacy of Raden Patah was expressed by Tomé Pires
Tomé Pires (1465?–1524 or 1540)Madureira, 150–151. was a Portuguese apothecary from Lisbon who spent 1512 to 1515 in Malacca immediately after the Portuguese conquest, at a time when Europeans were only first arriving in Southeast As ...
in ''Suma Oriental
Suma may refer to:
Places
* Suma, Azerbaijan, a village
* Suma, East Azerbaijan, a village in Iran
* Sowmaeh, Ardabil, also known as Şūmā, a village in Iran
* Suma-ku, Kobe, one of nine wards of Kobe City in Japan
** Suma Station, a rai ...
'': " ould de Albuquerque make peace with the Lord of Demak, all of Java will almost be forced to make peace with him... The Lord of Demak stood for all of Java".
Apart from Javanese city-states, Raden Patah also gained overlordship of the ports of Jambi and Palembang in eastern Sumatra, which produced commodities such as lign-aloes and gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile me ...
. As most of its power was based on trade and control of coastal cities, Demak can be considered a thalassocracy.
Growth
 Raden Patah's son, or possibly his brother, led Demak's brief domination in Java. He was known as Trenggana, and later Javanese traditions say he gave himself the title Sultan. It appears that Trenggana had two reigns—''c''. 1505–;1518 and ''c''. 1521–1546—between which his brother in law, Yunus of
Raden Patah's son, or possibly his brother, led Demak's brief domination in Java. He was known as Trenggana, and later Javanese traditions say he gave himself the title Sultan. It appears that Trenggana had two reigns—''c''. 1505–;1518 and ''c''. 1521–1546—between which his brother in law, Yunus of Jepara
Jepara is a town in the province of Central Java, Indonesia.
Jepara is on the north coast of Java, north-east of Semarang, not far from Mount Muria, with a population of 92,967 in mid 2019. It is also the main town of Jepara Regency, which has a ...
, occupied the throne.
Between 1513 and 1518 Demak waged war against Patih Udara of Daha, the successor state of Majapahit located in today's Kediri. The main Demak army led by Raden Patah and Sunan Kudus marched overland through Madiun, while the Demak fleet led by Pati Unus took the sea route through Sedayu. Demak managed to consolidate its power by defeating Daha in 1518, because it was more accepted as the legitimate successor of Majapahit, since Raden Patah claimed direct descent from King Kertabhumi, who had died during the Girindrawardana invasion of Trowulan in 1478. Raden Patah died soon after this victory, also in 1518.
Pati Unus
Raden Patah was succeeded by his brother-in-law Pati Unus or Adipati Yunus (r. 1518–1521), referred to by Tomé Pires in ''Suma Oriental'' as "Pate Onus" or "Pate Unus", brother in-law of "Pate Rodim". Before ascending the throne of Demak, he ruledJepara
Jepara is a town in the province of Central Java, Indonesia.
Jepara is on the north coast of Java, north-east of Semarang, not far from Mount Muria, with a population of 92,967 in mid 2019. It is also the main town of Jepara Regency, which has a ...
, a vassal state to the north of Demak. Pati Unus ruled under the regnal name Sultan Syah Alam Akbar II.
In two expeditions, with approximately 100 ships in 1513 and with 375 in 1521, Pati Unus led fleets from the Javanese coastal cities to seize the port of Malacca on the Malay Peninsula from the control of the Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
. The Javanese ports turned against the Portuguese for a number of reasons, the main one being opposition to Portuguese insistence on a monopoly
A monopoly (from Greek el, μόνος, mónos, single, alone, label=none and el, πωλεῖν, pōleîn, to sell, label=none), as described by Irving Fisher, is a market with the "absence of competition", creating a situation where a speci ...
of the spice trade. The Portuguese repelled both attacks, and the destruction of so many ships proved devastating to the Javanese ports, whose trading activity subsequently greatly declined.
Pati Unus was killed in the 1521 expedition, and was later remembered as ''Pangeran Sabrang Lor'' or "the Prince who crossed to the North" (the Java Sea to the Malay peninsula).
Sultan Trenggana
 Pati Unus died childless, leading to a crisis in the Demak succession. The throne was contested between his brothers, the older Raden Kikin and the younger Raden Trenggana. According to tradition, the eldest son of Prince Trenggana, Prince Prawata, also known as Raden Mukmin, stole '' Keris Setan Kober'', a powerful magical kris, from
Pati Unus died childless, leading to a crisis in the Demak succession. The throne was contested between his brothers, the older Raden Kikin and the younger Raden Trenggana. According to tradition, the eldest son of Prince Trenggana, Prince Prawata, also known as Raden Mukmin, stole '' Keris Setan Kober'', a powerful magical kris, from Sunan Kudus
Sunan Kudus (born Ja'far Shadiq; 1500-1550), founder of Kudus, is considered to be one of the Wali Sanga of Java, Indonesia.
He is said to have originated the wayang golek, and founded the masjid at Kudus using (it is said) the doors from th ...
and used it to assassinate his uncle Raden Kikin by the river; Raden Kikin has since then also been known as ''Sekar Seda Lepen'' (flower that fell by the river). Raden Trenggana (r. 1522–1546) was then crowned by Sunan Gunungjati
Sunan Gunungjati (1448–1568) was one of the Wali Songo, or nine saints of Islam revered in Indonesia. He founded the Sultanate of Banten, as well as the Sultanate of Cirebon on the north coast of Java.
Gunungjati was born Syarif Hidayatulla ...
(one of the Wali Songo) and became the third and greatest ruler of Demak.
During Trenggana's reign a young man named Fatahillah
Fatahillah, Fadhillah Khan, or Falatehan (Portuguese writing) was a commander of the Sultanate of Demak who is known for leading the conquest of Sunda Kelapa in 1527 and changing it name to Jayakarta. The conquest of Sunda Kelapa was one of his ...
came to his court to offer his service to the sultan. He had just returned from Mecca
Mecca (; officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, commonly shortened to Makkah ()) is a city and administrative center of the Mecca Province of Saudi Arabia, and the holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow ...
after several years studying Islam there, and had learned that his hometown in Pasai
The Samudera Pasai Sultanate (), also known as Samudera or Pasai or Samudera Darussalam or Pacem, was a Muslim harbour kingdom on the north coast of Sumatra from the 13th to the 16th centuries CE. The kingdom was believed to have been founded ...
had been captured by the infidel Portuguese. He became a renowned general of Demak. Tradition has it that Trenggana was much impressed by Fatahillah's imposing figure and charisma and his knowledge of Islam, and gave him his daughter, the widow of Pati Unus, as his wife.
After learning of the 1522 Portuguese-Sunda alliance, in 1527 the Sultan ordered Fatahillah to capture the ports of Banten
Banten ( id, Banten; Sundanese: , romanized ''Banten'') is the westernmost province on the island of Java, Indonesia. Its capital city is Serang. The province borders West Java and the Special Capital Region of Jakarta on the east, the Ja ...
and Sunda Kelapa
Sunda Kelapa ( su, , Sunda Kalapa) is the old port of Jakarta located on the estuarine of Ciliwung River. "Sunda Kalapa" ( Sundanese: "Coconut of Sunda") is the original name, and it was the main port of the Sunda Kingdom. The port is situated i ...
from the Kingdom of Sunda. Sunda Kelapa was later renamed Jayakarta. From these territories he created the Sultanate of Banten
The Banten Sultanate (كسلطانن بنتن) was a Bantenese Islamic trading kingdom founded in the 16th century and centred in Banten, a port city on the northwest coast of Java; the contemporary English name of both was Bantam. It is said ...
as a vassal state under Hasanudin, son of Gunungjati, whom he also gave his sister's hand in marriage, creating a new dynasty.
He appointed his daughter Ratna Kencana (popularly known as Ratu Kalinyamat) and her husband Sultan Hadlirin to rule Kalinyamat and Jepara. He also appointed Jaka Tingkir as Adipati (Duke) of Pajang
The Kingdom of Pajang or Sultanate of Pajang (كسلطانن ڤاجڠ ;1586–1568) was a short-lived Muslim state in Java. It was established by Hadiwijaya or Jaka Tingkir, Lord of Boyolali, after a civil war and was a successor to Sultanate ...
and gave another daughter's hand in marriage to Jaka Tingkir.
Trenggana oversaw the spread of Demak's influence to the east and west. He conquered the Hindu-based resistance in Central Java and during his second campaign, conquered the last Javanese Hindu-Buddhist state, the largely defunct remnants of Majapahit; Tuban, an old Majapahit port mentioned in Chinese sources from the 11th century, was conquered in about 1527. During his reign Demak was able to subdue other major ports and its reach extended into some inland areas of East Java
East Java ( id, Jawa Timur) is a Provinces of Indonesia, province of Indonesia located in the easternmost hemisphere of Java island. It has a land border only with the province of Central Java to the west; the Java Sea and the Indian Ocean bord ...
that are not thought to have been Islamized
Islamization, Islamicization, or Islamification ( ar, أسلمة, translit=aslamāh), refers to the process through which a society shifts towards the religion of Islam and becomes largely Muslim. Societal Islamization has historically occurre ...
at the time.
His campaign ended when he sought to conquer the Hindu principality of Pasuruan
Pasuruan ( nl, Pasoeroean) is a city in East Java, Java, Indonesia. It had a population of 186,262 at the 2010 Census and 208,006 at the 2020 Census.
It is surrounded by, but administratively separate from, Pasuruan Regency. It is located around ...
in East Java and was killed in 1546. According to tradition, he was assassinated by a ten-year-old Adipati of Surabaya, who stabbed with a kris while serving him betel nut.
Decline
Sunan Mukmin
The death of the strong and able Trenggana in 1546 triggered ablood feud
A feud , referred to in more extreme cases as a blood feud, vendetta, faida, clan war, gang war, or private war, is a long-running argument or fight, often between social groups of people, especially families or clans. Feuds begin because one pa ...
and civil war between Prince Arya Penangsang
Arya Penangsang was king of the Sultanate of Demak
The Demak Sultanate (کسلطانن دمق) was a Javanese Muslim state located on Java's north coast in Indonesia, at the site of the present-day city of Demak. A port fief to the Hind ...
, Adipati of the vassal state of , who was the son of the assassinated Sekar Seda Lepen (Raden Kikin), and Trenggana's son Prince Mukmin or Sunan Prawata, who had committed the murder. According to the ''Babad Demak'' chronicle, several influential figures of Wali Songo supported different candidates for the succession. Sunan Giri supported Prince Mukmin, while Sunan Kudus
Sunan Kudus (born Ja'far Shadiq; 1500-1550), founder of Kudus, is considered to be one of the Wali Sanga of Java, Indonesia.
He is said to have originated the wayang golek, and founded the masjid at Kudus using (it is said) the doors from th ...
supported Arya Penangsang, since he belonged to the line of the eldest male son of the Demak dynasty. On the other hand, Sunan Kalijaga proposed Hadiwijaya, popularly known as Joko Tingkir, who was the adipati of Pajang
The Kingdom of Pajang or Sultanate of Pajang (كسلطانن ڤاجڠ ;1586–1568) was a short-lived Muslim state in Java. It was established by Hadiwijaya or Jaka Tingkir, Lord of Boyolali, after a civil war and was a successor to Sultanate ...
and also a son in-law of Trenggana.
Mukmin (r. 1546–1549) ascended the throne as the fourth Sultan of Demak. However, with the help of his teacher Sunan Kudus, Arya Penangsang of Jipang sent an assassin to kill Prawata and his wife using the same kris that Mukmin had used to kill his father.
Arya Penangsang
Arya Penangsang
Arya Penangsang was king of the Sultanate of Demak
The Demak Sultanate (کسلطانن دمق) was a Javanese Muslim state located on Java's north coast in Indonesia, at the site of the present-day city of Demak. A port fief to the Hind ...
(r. 1549–1568) ascended to the throne of Demak in 1549 after assassinating his cousin Sunan Prawata. Arya Penangsang was a valiant but vicious man who never hesitated to use brutal force to achieve his goals. Feeling threatened, Prawata's son Arya Pengiri sought refuge in his aunt's realm in Kalinyamat, Jepara.
Prawata's younger sister Ratu Kalinyamat sought justice from Penangsang's teacher Sunan Kudus, but he declined her request, deeming Penangsang's revenge justified since Prawata had assassinated Penangsang's father, Raden Kikin (Sekar Seda ing Lepen). On their way home from Kudus to Kalinyamat, Ratu Kalinyamat and her husband, Sultan Hadlirin, were attacked by Penangsang's men. Hadlirin was killed and Ratu Kalinyamat barely survived. She urged her brother in-law, Hadiwijaya (popularly known as Jaka Tingkir), Adipati of Pajang (now Boyolali
Boyolali ( jv, ꦧꦺꦴꦪꦭꦭꦶ, Boyalali, Don't forget) is a regency ( id, kabupaten) in the eastern part of Central Java province in Indonesia. It covers an area of 1,015.10 km2, and had a population of 930,531 at the 2010 census and 1 ...
), to avenge her husband's death by killing Arya Penangsang.
Arya Penangsang soon faced heavy opposition from his vassals for his harshness, and was dethroned by a coalition of vassals led by Hadiwijaya. In 1568, Hadiwijaya sent his adopted son and also his son in-law Sutawijaya
Panembahan Senapati, formally styled Panembahan Senapati ing Ngalaga Sayyidin Panatagama (died in Jenar (now Purwodadi, Purworejo), 1601), was the founder of the Mataram Sultanate.
Origin
Born Danang Sutawijaya, known as Dananjaya, he was the son ...
, who would later become the first ruler of the Mataram dynasty, to kill Penangsang.
In 1568, after Penangsang was killed, Hadiwijaya assumed the role of sovereign. However, instead of ruling from Demak, he moved all of Demak's regalia
Regalia is a Latin plurale tantum word that has different definitions. In one rare definition, it refers to the exclusive privileges of a sovereign. The word originally referred to the elaborate formal dress and dress accessories of a sovereig ...
, heirlooms, and sacred artifacts to Pajang. He appointed Prawata's son Sunan Pangiri as adipati of Demak. The relationship between the two states was now reversed: Pajang became the suzerain kingdom, while Demak became its vassal. Thus the Demak Sultanate ended with the foundation of the short-lived Kingdom of Pajang.
Economy
 Demak derived its income from trade, importing
Demak derived its income from trade, importing spices
A spice is a seed, fruit, root, bark, or other plant substance primarily used for flavoring or coloring food. Spices are distinguished from herbs, which are the leaves, flowers, or stems of plants used for flavoring or as a garnish. Spices are ...
and exporting rice
Rice is the seed of the grass species '' Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice) or less commonly ''Oryza glaberrima'' (African rice). The name wild rice is usually used for species of the genera '' Zizania'' and '' Porteresia'', both wild and domesticat ...
to Malacca and the Maluku Islands
The Maluku Islands (; Indonesian: ''Kepulauan Maluku'') or the Moluccas () are an archipelago in the east of Indonesia. Tectonically they are located on the Halmahera Plate within the Molucca Sea Collision Zone. Geographically they are located ...
. It was a busy port located at the end of a then navigable channel separating Java and Muria Island. The channel subsequently filled, joining Muria to Java; from the 15th to the 18th century until the 18th century, it was a major waterway for ships traveling along the northern Javanese coast to the Spice Islands
A spice is a seed, fruit, root, bark, or other plant substance primarily used for flavoring or coloring food. Spices are distinguished from herbs, which are the leaves, flowers, or stems of plants used for flavoring or as a garnish. Spices are ...
and, via the Serang River, to the rice-producing interior of Java. This strategic location enabled Demak to become a leading trading center in Java.
According to Tomé Pires
Tomé Pires (1465?–1524 or 1540)Madureira, 150–151. was a Portuguese apothecary from Lisbon who spent 1512 to 1515 in Malacca immediately after the Portuguese conquest, at a time when Europeans were only first arriving in Southeast As ...
, Demak had more inhabitants than any other port in Sunda or Java, and was the primary exporter of rice to Malacca. Demak's prominence grew with that of Malacca, and was also enhanced by Raden Patah's claim of direct descent from Majapahit royalty and his marriage ties with neighboring city-states.
Cetbang
Cetbang (also known as bedil, warastra, or meriam coak) were cannons produced and used by the Majapahit Empire (1293–1527) and other kingdoms in the Indonesian archipelago. There are 2 main types of cetbang: the eastern-style cetbang which lo ...
cannons were improved and used in the Demak Sultanate period during the Demak invasion of Portuguese Malacca
Portuguese control of Malacca, a city on the Malay Peninsula, refers to the 130 year period (1511–1641) when it was a possession of the Portuguese East Indies. It was conquered from the Malacca Sultanate as part of Portuguese attempts to ...
(1513). During this period, the iron
Iron () is a chemical element with Symbol (chemistry), symbol Fe (from la, Wikt:ferrum, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 element, group 8 of the periodic table. It is, Abundanc ...
, for manufacturing Javanese cannons was imported from Khorasan in northern Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
. The material was known by Javanese as ''wesi kurasani'' (Khorasan iron).
Religion
 Before the emergence of Demak, the northern coast of Java was the seat of many Muslim communities, both foreign merchants and local Javanese. The Islamization process gained momentum from the decline of Hindu-Buddhist Majapahit authority. Following the fall of the Majapahit capital to a usurper from Kediri, Raden Patah declared Demak's independence from Majapahit overlordship, and almost all northern Javanese ports later followed suit. However, the Demak royal family regarded themselves as descendants of Majapahit. Demak symbols continued to use the Surya Majapahit, an eight-pointed sun, while modifying it to remove Hindu associations. This modified symbol can be seen as decoration inside the Grand Mosque of Demak.
As the first Islamic polity in Java, Demak has a venerated status among
Before the emergence of Demak, the northern coast of Java was the seat of many Muslim communities, both foreign merchants and local Javanese. The Islamization process gained momentum from the decline of Hindu-Buddhist Majapahit authority. Following the fall of the Majapahit capital to a usurper from Kediri, Raden Patah declared Demak's independence from Majapahit overlordship, and almost all northern Javanese ports later followed suit. However, the Demak royal family regarded themselves as descendants of Majapahit. Demak symbols continued to use the Surya Majapahit, an eight-pointed sun, while modifying it to remove Hindu associations. This modified symbol can be seen as decoration inside the Grand Mosque of Demak.
As the first Islamic polity in Java, Demak has a venerated status among Indonesian Muslims
Islam is the largest religion in Indonesia, with 86.7% of the Indonesian population identifying themselves as Muslim in a 2018 survey. Indonesia is the most populous Muslim-majority country, with approximately 231 million adherents.
In te ...
. It is traditionally linked with the legendary Wali Songo, the nine Muslim ulama who proselytized Islam among the then strongly Hindu-Buddhist population of Java. Islamic sites such as the Demak Great Mosque and the maqam (tombs) of Wali saints and Demak sultans continue to draw ziyarat pilgrimage among Muslims in the region.
Javanese legends of Demak
Later Javanese Babads provide varying accounts of the origins and expansion of Demak, but all describe it as the direct successor of Majapahit, not mentioning the possibility that by the time of its final conquest, Majapahit no longer ruled the area. The first "Sultan" of Demak, Raden Patah, is portrayed as the son of Majapahit's last king by a Chinese princess who was exiled from the court before Patah's birth; according to tradition, she first served as a concubine to Kertabhumi (Brawijaya V) in Trowulan, and when already pregnant with the king's son, was sent as a gift to marry the regent of Palembang. Although these legends explain little about the actual events, they suggest that the dynastic continuity survived the Islamization of Java, or alternatively that the rulers of Demak reinforced their rule on Java by claiming descent from the Majapahit dynasty as a source of political legitimation. Demak was more likely a coastal settlement established as a result of Zheng He's Chinese expedition in the first half of the 15th century, ruled by non-Javanese foreigners, Chinese Muslims, possibly also attracting Arabs and Malay Muslim traders, which grew in power and supplanted the old kingdom.See also
* The spread of Islam in Indonesia (1200 to 1600) *List of monarchs of Java
This is a partial list of the identified hereditary rulers on the Indonesian island Java, and the adjacent island Madura.
Included are some states and rulers whose existence remain open to conjecture, due to inadequate historical evidence, while o ...
References
External links
History of Demak
{{DEFAULTSORT:Sultanate Of Demak History of Central Java
Demak
Demak is on the north coast of Central Java province, on the island of Java, Indonesia.
* Demak, Demak, modern-day large town
* Demak Sultanate, sixteenth century sultanate
* Demak Regency
Demak ( jv, ꦢꦼꦩꦏ꧀) is a regency located in t ...
Islamic states in Indonesia
Precolonial states of Indonesia
History of Islam in Indonesia
15th century in Indonesia
16th century in Indonesia
Former countries