Declarations of war during World War II on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
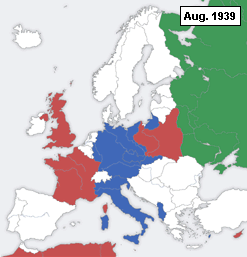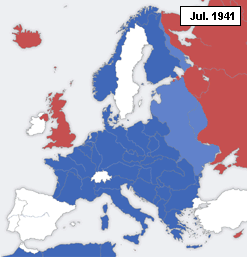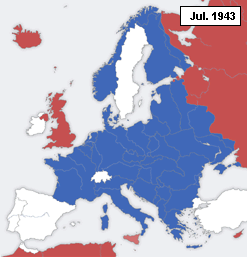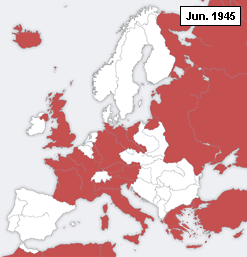 This is a timeline of declarations of war during World War II.
A
This is a timeline of declarations of war during World War II.
A ''On the Opening of Hostilities''
1907;
C = Declaration and/or attack without standard, formal procedure, sometimes preceded by a ''
U = State of war arrived at through use of ultimatum;
W = Formal declaration of war made.
File:Bundesarchiv Bild 183-B0527-0001-293, Warschau, Empfang Goebbels bei Marschall Pilsudski.jpg, German ambassador, Hans-Adolf von Moltke, Polish leader
 This is a timeline of declarations of war during World War II.
A
This is a timeline of declarations of war during World War II.
A declaration of war
A declaration of war is a formal act by which one state announces existing or impending war activity against another. The declaration is a performative speech act (or the signing of a document) by an authorized party of a national government, ...
is a formal act by which one nation goes to war against another. The declaration is usually the act of delivering a performative speech or the presentation of a signed document by an authorized party of a national government in order to create a state of war
A declaration of war is a formal act by which one state announces existing or impending war activity against another. The declaration is a performative speech act (or the signing of a document) by an authorized party of a national government, in ...
between two or more sovereign states. The official international protocol for declaring war was defined in The Hague Peace Conference of 1907 (or Hague II).1907;
Yale
Yale University is a private research university in New Haven, Connecticut. Established in 1701 as the Collegiate School, it is the third-oldest institution of higher education in the United States and among the most prestigious in the wor ...
Law School Library; retrieved March 2014. For the diplomatic maneuvering behind these events, which led to hostilities between nations during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, see Diplomatic history of World War II
The diplomatic history of World War II includes the major foreign policies and interactions inside the opposing coalitions, the Allies of World War II and the Axis powers, between 1939 and 1945.
High-level diplomacy began as soon as the war start ...
.
List of war declarations
Below is a table showing the outbreak of wars between nations which occurred during World War II. Indicated are the dates (during the immediate build-up to, or during the course of, World War II), from which a ''de facto
''De facto'' ( ; , "in fact") describes practices that exist in reality, whether or not they are officially recognized by laws or other formal norms. It is commonly used to refer to what happens in practice, in contrast with '' de jure'' ("by l ...
'' state of war existed between nations. The table shows both the "Initiator Nation(s)" and the nation at which the aggression was aimed, or "Targeted Nation(s)". Events listed include those in which there were simple diplomatic breaking of relations that did not involve any physical attack, as well as those involving overt declarations or acts of aggression. In rare cases, war between two nations occurred twice, with an intermittent period of peace. The list here does not include peace treaties or periods of any armistice.
Key to type (fourth column):
A = Attack without prior, formal declaration of war;C = Declaration and/or attack without standard, formal procedure, sometimes preceded by a ''
casus belli
A (; ) is an act or an event that either provokes or is used to justify a war. A ''casus belli'' involves direct offenses or threats against the nation declaring the war, whereas a ' involves offenses or threats against its ally—usually one ...
'' thus ''fait accompli
Many words in the English vocabulary are of French origin, most coming from the Anglo-Norman spoken by the upper classes in England for several hundred years after the Norman Conquest, before the language settled into what became Modern Engl ...
'';U = State of war arrived at through use of ultimatum;
W = Formal declaration of war made.
Gallery
Józef Piłsudski
Józef Klemens Piłsudski (; 5 December 1867 – 12 May 1935) was a Polish statesman who served as the Naczelnik państwa, Chief of State (1918–1922) and Marshal of Poland, First Marshal of Second Polish Republic, Poland (from 1920). He was ...
, German propaganda minister Joseph Goebbels
Paul Joseph Goebbels (; 29 October 1897 – 1 May 1945) was a German Nazi politician who was the '' Gauleiter'' (district leader) of Berlin, chief propagandist for the Nazi Party, and then Reich Minister of Propaganda from 1933 to ...
and Józef Beck
Józef Beck (; 4 October 1894 – 5 June 1944) was a Polish statesman who served the Second Republic of Poland as a diplomat and military officer. A close associate of Józef Piłsudski, Beck is most famous for being Polish foreign minister in ...
, Polish Foreign minister meeting in Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officiall ...
on June 15, 1934, five months after signing the Polish-German Non-Aggression Pact.
File:MunichAgreement.jpg, British Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain
Arthur Neville Chamberlain (; 18 March 18699 November 1940) was a British politician of the Conservative Party who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from May 1937 to May 1940. He is best known for his foreign policy of appeaseme ...
, landing at Heston
Heston is a suburban area and part of the Hounslow district in the London Borough of Hounslow. The residential settlement covers a slightly smaller area than its predecessor farming village, 10.8 miles (17.4 km) west south-west of Charing ...
aerodrome on 30 September 1938 after his meeting with Hitler at Munich
Munich ( ; german: München ; bar, Minga ) is the capital and most populous city of the German state of Bavaria. With a population of 1,558,395 inhabitants as of 31 July 2020, it is the third-largest city in Germany, after Berlin and ...
. In his hand he holds the peace agreement between Britain and Germany.
File:Armia Czerwona,Wehrmacht 23.09.1939 wspólna parada.jpg, Common parade of German Wehrmacht
The ''Wehrmacht'' (, ) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the ''Heer'' (army), the '' Kriegsmarine'' (navy) and the ''Luftwaffe'' (air force). The designation "''Wehrmacht''" replaced the previo ...
and Soviet Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army (Russian language, Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist R ...
on September 23, 1939 in Brest, Eastern Poland
Eastern Poland is a macroregion in Poland comprising the Lublin, Podkarpackie, Podlaskie, Świętokrzyskie, and Warmian-Masurian voivodeships.
The make-up of the distinct macroregion is based not only of geographical criteria, but also econo ...
at the end of the Poland Campaign
The invasion of Poland (1 September – 6 October 1939) was a joint attack on the Republic of Poland by Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union which marked the beginning of World War II. The German invasion began on 1 September 1939, one week aft ...
. In the center is Major General Heinz Guderian
Heinz Wilhelm Guderian (; 17 June 1888 – 14 May 1954) was a German general during World War II who, after the war, became a successful memoirist. An early pioneer and advocate of the "blitzkrieg" approach, he played a central role in th ...
; and on the right is Brigadier General Semyon Krivoshein.
File:Moscow negotiations paaskivi yrjokoskinen nykopp paasonen 1939.png, alt=A group of four men wearing hats and a train behind., Counsellor of state J.K. Paasikivi
Juho Kusti Paasikivi (; 27 November 1870 – 14 December 1956) was the seventh president of Finland (1946–1956). Representing the Finnish Party until its dissolution in 1918 and then the National Coalition Party, he also served as Prime Minister ...
and his team arriving from Moscow for the first round of negotiations on 16 October 1939. From left, minister Aarno Yrjö-Koskinen, J.K. Paasikivi, chief of staff Johan Nykopp and colonel Aladár Paasonen.
File:German paratroopers jumping From Ju 52s over Crete.jpg, German paratroopers taking the Greek island of Crete
Crete ( el, Κρήτη, translit=, Modern: , Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the 88th largest island in the world and the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, Sardinia, Cyprus, ...
, May 1941.
File:Attack on Pearl Harbor Japanese planes view.jpg, Photograph from a Japanese plane of Battleship Row
Battleship Row was the grouping of eight U.S. battleships in port at Pearl Harbor, Hawaii, when the Japanese attacked on 7 December 1941. These ships bore the brunt of the Japanese assault. They were moored next to Ford Island when the attack co ...
at the beginning of the surprise Attack on Pearl Harbor
The attack on Pearl HarborAlso known as the Battle of Pearl Harbor was a surprise military strike by the Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service upon the United States against the naval base at Pearl Harbor in Honolulu, Territory of Hawaii ...
. The explosion in the center is a torpedo strike on the USS ''Oklahoma''. Two attacking Japanese planes can be seen: one over the USS ''Neosho'' and one over the Naval Yard.
See also
*Diplomatic history of World War II
The diplomatic history of World War II includes the major foreign policies and interactions inside the opposing coalitions, the Allies of World War II and the Axis powers, between 1939 and 1945.
High-level diplomacy began as soon as the war start ...
*Allies of World War II
The Allies, formally referred to as the Declaration by United Nations, United Nations from 1942, were an international Coalition#Military, military coalition formed during the World War II, Second World War (1939–1945) to oppose the Axis ...
*Axis powers
The Axis powers, ; it, Potenze dell'Asse ; ja, 枢軸国 ''Sūjikukoku'', group=nb originally called the Rome–Berlin Axis, was a military coalition that initiated World War II and fought against the Allies. Its principal members were ...
: German Instrument of Surrender
The German Instrument of Surrender (german: Bedingungslose Kapitulation der Wehrmacht, lit=Unconditional Capitulation of the " Wehrmacht"; russian: Акт о капитуляции Германии, Akt o kapitulyatsii Germanii, lit=Act of capi ...
and Surrender of Japan
The surrender of the Empire of Japan in World War II was announced by Emperor Hirohito on 15 August and formally signed on 2 September 1945, bringing the war's hostilities to a close. By the end of July 1945, the Imperial Japanese Na ...
Notes
References
{{World War II declaration Chronology of World War II Modern history timelines