Dakshina Kannada district on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Dakshina Kannada district is a
Image:Sullia. Karnataka (3).jpg, Hilly region - Sullia Town
Image:Tannirubhavi beach 02.JPG, Coastal plain - Tannirbhavi Beach
The district geography consists of seashore in the west and Western Ghats in the east. The
 As per the ''Gramappadhathi'', Dakshina Kannada (along with the rest of the west coast) was created by Parshurama standing on top of the Western Ghats, and caused the land to rise from the sea by throwing his axe. It was then given to 64 families of Brahmins to settle. He created a temple on Kunjaragiri Hill in memory of his mother. Kutashila spoken of in the Markandeya Purana is believed to be the town of Kollur, the abode of Mookambika Devi. Several rivers in the district, including the Netravati, are believed to be mentioned in the Markandeya Purana. Other traditions in the local Paddanas speak of Mayurasharma's inviting of Brahmins from Ahichchhatraa and his organisation of the district.
As per the ''Gramappadhathi'', Dakshina Kannada (along with the rest of the west coast) was created by Parshurama standing on top of the Western Ghats, and caused the land to rise from the sea by throwing his axe. It was then given to 64 families of Brahmins to settle. He created a temple on Kunjaragiri Hill in memory of his mother. Kutashila spoken of in the Markandeya Purana is believed to be the town of Kollur, the abode of Mookambika Devi. Several rivers in the district, including the Netravati, are believed to be mentioned in the Markandeya Purana. Other traditions in the local Paddanas speak of Mayurasharma's inviting of Brahmins from Ahichchhatraa and his organisation of the district.
 The Alupas (ಆಳುಪರು) ruled the erstwhile Dakshina Kannada region between the 8th and 14th century CE. Their origins go back further, and if Greek identifications are to be believed the Alupas may have been prominent local chiefs since the 2nd century CE. The Halmidi inscription of 450 CE mentions an Alupa chief fighting as a commander of the Kadambas in a battle against the Kekayas and Pallavas. In a stone inscription near Gudnapur dated to c. 500 CE, the Alupas are mentioned as subordinates to the Kadambas. In 602, the
The Alupas (ಆಳುಪರು) ruled the erstwhile Dakshina Kannada region between the 8th and 14th century CE. Their origins go back further, and if Greek identifications are to be believed the Alupas may have been prominent local chiefs since the 2nd century CE. The Halmidi inscription of 450 CE mentions an Alupa chief fighting as a commander of the Kadambas in a battle against the Kekayas and Pallavas. In a stone inscription near Gudnapur dated to c. 500 CE, the Alupas are mentioned as subordinates to the Kadambas. In 602, the
 Rani Abbakka, the Chowta wife of Banga Raja and the Queen of Ullal, fought the Portuguese. She stopped paying tribute to the Portuguese, causing them to send a fleet to Mangalore and force a settlement, but soon she aided the enemies of the Portuguese and again stopped tribute payment. In 1566, she defeated a Portuguese expedition and killed its commander, causing the Portuguese in Goa to send an armada to subdue her in 1567. On 15 January 1568, however, the Portuguese defeated the Rani and forced her to sign a new treaty.
Rani Abbakka, the Chowta wife of Banga Raja and the Queen of Ullal, fought the Portuguese. She stopped paying tribute to the Portuguese, causing them to send a fleet to Mangalore and force a settlement, but soon she aided the enemies of the Portuguese and again stopped tribute payment. In 1566, she defeated a Portuguese expedition and killed its commander, causing the Portuguese in Goa to send an armada to subdue her in 1567. On 15 January 1568, however, the Portuguese defeated the Rani and forced her to sign a new treaty.
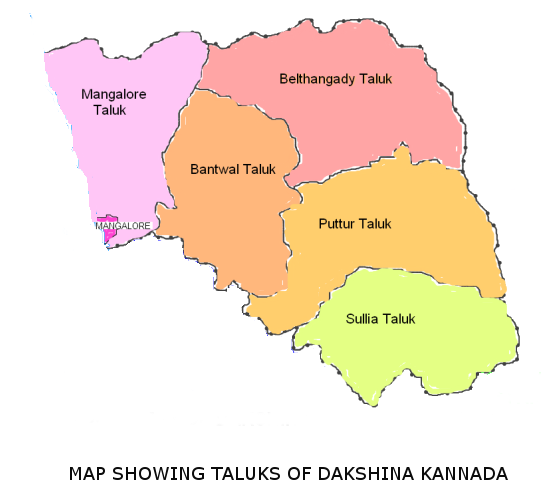 The district comprises seven
The district comprises seven
 In Dakshina Kannada, primary and secondary education have reached every section of the society. Some of them are St Agnes CBSE school, St Theresa ICSE School and St Aloysius School, Vivekananda collage, A host of educational institutes offering courses in
In Dakshina Kannada, primary and secondary education have reached every section of the society. Some of them are St Agnes CBSE school, St Theresa ICSE School and St Aloysius School, Vivekananda collage, A host of educational institutes offering courses in  The engineering colleges in the district include St. Joseph Engineering College,
The engineering colleges in the district include St. Joseph Engineering College,
 Most people of this district follow traditions, customs and rituals. The district has many temples of Hindu gods and goddesses, which are ancient and have deep spiritualism attached to them. The people of Dakshina Kannada worship the Serpent God Subramanya. According to legend, the district was reclaimed by Parashurama from the sea. According to the 17th-century
Most people of this district follow traditions, customs and rituals. The district has many temples of Hindu gods and goddesses, which are ancient and have deep spiritualism attached to them. The people of Dakshina Kannada worship the Serpent God Subramanya. According to legend, the district was reclaimed by Parashurama from the sea. According to the 17th-century  According to legend, this new area of land extended from Gokarna to
According to legend, this new area of land extended from Gokarna to 
/ref>Roland E. Miller. ''Mappila Muslim Culture'' SUNY Press, 2015
 The district is connected by air through the Mangaluru Airport, Mangalore International Airport at
The district is connected by air through the Mangaluru Airport, Mangalore International Airport at
Image:Dharmasthala Temple.jpg, Sri Manjunatha Temple at
The following are historic places to visit in Dakshina Kannada:
* Mangaladevi Temple: Mangalore was named after the Hindu deity Mangaladevi.
* Venur: Monolithic Bahubali statue.
* Kadri: Temple of Lord Sri Manjunatha.
Shree Amrutheshwara Temple
Vamanjoor: Temple of Lord Shiva. * Moodabidri: Site of the ancient Jain temples and the Bhattaraka seat. *

 Some of the well-known
Some of the well-known


 The district along with Udupi district is known as "The Cradle of Indian banking". Major nationalised banks of India such as Canara Bank, Corporation Bank,
The district along with Udupi district is known as "The Cradle of Indian banking". Major nationalised banks of India such as Canara Bank, Corporation Bank,
Official web site
DK Zilla Parishad
{{Karnataka topics Districts of Karnataka Tulu Nadu
district
A district is a type of administrative division that, in some countries, is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or county, counties, several municipality, municipa ...
of Karnataka
Karnataka (; ISO: , , also known as Karunāḍu) is a state in the southwestern region of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reorganisation Act. Originally known as Mysore State , it was renamed ''Karnat ...
state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* ''Our S ...
in India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
, with its headquarters in the coastal city of Mangalore
Mangalore (), officially known as Mangaluru, is a major port city of the Indian state of Karnataka. It is located between the Arabian Sea and the Western Ghats about west of Bangalore, the state capital, 20 km north of Karnataka–Ke ...
. It is part of the larger Tulu Nadu region. The district covers an area nestled in between the Western Ghats to its east and the Arabian Sea
The Arabian Sea ( ar, اَلْبَحرْ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Bahr al-ˁArabī) is a region of the northern Indian Ocean bounded on the north by Pakistan, Iran and the Gulf of Oman, on the west by the Gulf of Aden, Guardafui Channel ...
to its west. Dakshina Kannada receives abundant rainfall during the Indian monsoon
The Monsoon of South Asia is among several geographically distributed global monsoons. It affects the Indian subcontinent, where it is one of the oldest and most anticipated weather phenomena and an economically important pattern every year fro ...
. It is bordered by Udupi district (formerly a part of this district) to the north, Chikmagalur district
Chikmagalur, officially Chikkamagaluru is an administrative district in the Malnad subregion of Karnataka, India. Coffee was first cultivated in India in Chikmagalur. The hills of Chikmagalur are parts of the Western Ghauts and the source of ...
to the northeast, Hassan district to the east, Kodagu
Kodagu (also known by its former name Coorg) is an administrative district in the Karnataka state of India. Before 1956, it was an administratively separate Coorg State, at which point it was merged into an enlarged Mysore State.
It occupies ...
to the southeast and Kasaragod district of Kerala
Kerala ( ; ) is a state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile regions of Cochin, Malabar, South ...
to the south. According to the 2011 census of India, Dakshina Kannada district had a population of 2,083,625. It is the only district in Karnataka
Karnataka (; ISO: , , also known as Karunāḍu) is a state in the southwestern region of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reorganisation Act. Originally known as Mysore State , it was renamed ''Karnat ...
state to have all modes of transport like road, rail, water and air due to the presence of a major hub, Mangalore
Mangalore (), officially known as Mangaluru, is a major port city of the Indian state of Karnataka. It is located between the Arabian Sea and the Western Ghats about west of Bangalore, the state capital, 20 km north of Karnataka–Ke ...
. This financial district is also known as the Cradle of Indian banking.
Geography
soil
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth or dirt
Dirt is an unclean matter, especially when in contact with a person's clothes, skin, or possessions. In such cases, they are said to become dirty.
Common types of dirt include:
* Debri ...
is mostly lateritic type, characterised by high iron
Iron () is a chemical element with Symbol (chemistry), symbol Fe (from la, Wikt:ferrum, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 element, group 8 of the periodic table. It is, Abundanc ...
and aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. I ...
content.
The major rivers are Netravathi
The Netravati River or Netravathi Nadi has its origins at Bangrabalige valley, Yelaneeru Ghat in Kudremukh in Chikkamagaluru district of Karnataka, India. This river flows through the famous pilgrimage place Dharmasthala and is considered one o ...
, Kumaradhara, Gurupura (Phalguni), Shambhavi, Nandini or Pavanje and Payaswini; all join the Arabian sea
The Arabian Sea ( ar, اَلْبَحرْ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Bahr al-ˁArabī) is a region of the northern Indian Ocean bounded on the north by Pakistan, Iran and the Gulf of Oman, on the west by the Gulf of Aden, Guardafui Channel ...
. At Uppinangadi, the Netravathi
The Netravati River or Netravathi Nadi has its origins at Bangrabalige valley, Yelaneeru Ghat in Kudremukh in Chikkamagaluru district of Karnataka, India. This river flows through the famous pilgrimage place Dharmasthala and is considered one o ...
and Kumaradhara rivers rise during the monsoon and meet. This event is called "Sangam", which in Sanskrit means confluence. Near Mangalore, an estuary
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environm ...
is formed by the union of the rivers Netravathi and the Gurupura which merge into the Arabian Sea.
The topography
Topography is the study of the forms and features of land surfaces. The topography of an area may refer to the land forms and features themselves, or a description or depiction in maps.
Topography is a field of geoscience and planetary sc ...
of the district is plain up to inside the coast and changes to undulating hilly terrain sharply towards the east in the Western Ghats. Teak, bamboo
Bamboos are a diverse group of evergreen perennial flowering plants making up the subfamily Bambusoideae of the grass family Poaceae. Giant bamboos are the largest members of the grass family. The origin of the word "bamboo" is uncertain, ...
and rosewood
Rosewood refers to any of a number of richly hued timbers, often brownish with darker veining, but found in many different hues.
True rosewoods
All genuine rosewoods belong to the genus ''Dalbergia''. The pre-eminent rosewood appreciated ...
trees are found in the hilly areas towards the east. The Geological Survey of India
The Geological Survey of India (GSI) is a scientific agency of India. It was founded in 1851, as a Government of India organization under the Ministry of Mines, one of the oldest of such organisations in the world and the second oldest survey ...
has identified this district as a moderately earthquake-prone region and categorised it in the Seismic III Zone. In rural Dakshina Kannada, houses are in the midst of a farm field or plantations of coconut or arecanut, separated by a few hundred metres.
Shirlalu village (in the Kudremukh
Kudremukha(ಕುದುರೆ ಮುಖ) is a mountain range and name of a peak located in Chikkamagaluru district, in Karnataka, India. It is also the name of a small hill station iron ore mining town situated near the mountain, about 20 kilo ...
range of Belthangady taluk
Belthangady is a town panchayat and the headquarters of Belthangady taluk of the Dakshina Kannada (South Canara) district of Karnataka state in India.
Demographics
In 2001 in the town of Belthangady, 11% of the population was under 6 years o ...
), with a maximum elevation of , is the highest point in Dakshina Kannada.
Climate
Dakshina Kannada features a Tropical Monsoon climate (Am) according to theKöppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notabl ...
. The average annual rainfall in Dakshina Kannada is . The rainfall varies from at the Mangalore
Mangalore (), officially known as Mangaluru, is a major port city of the Indian state of Karnataka. It is located between the Arabian Sea and the Western Ghats about west of Bangalore, the state capital, 20 km north of Karnataka–Ke ...
coast, at Moodabidri and at Puttur near the Western Ghats. The average humidity is 75% and peaks in July at 89%.
History
Legend
 As per the ''Gramappadhathi'', Dakshina Kannada (along with the rest of the west coast) was created by Parshurama standing on top of the Western Ghats, and caused the land to rise from the sea by throwing his axe. It was then given to 64 families of Brahmins to settle. He created a temple on Kunjaragiri Hill in memory of his mother. Kutashila spoken of in the Markandeya Purana is believed to be the town of Kollur, the abode of Mookambika Devi. Several rivers in the district, including the Netravati, are believed to be mentioned in the Markandeya Purana. Other traditions in the local Paddanas speak of Mayurasharma's inviting of Brahmins from Ahichchhatraa and his organisation of the district.
As per the ''Gramappadhathi'', Dakshina Kannada (along with the rest of the west coast) was created by Parshurama standing on top of the Western Ghats, and caused the land to rise from the sea by throwing his axe. It was then given to 64 families of Brahmins to settle. He created a temple on Kunjaragiri Hill in memory of his mother. Kutashila spoken of in the Markandeya Purana is believed to be the town of Kollur, the abode of Mookambika Devi. Several rivers in the district, including the Netravati, are believed to be mentioned in the Markandeya Purana. Other traditions in the local Paddanas speak of Mayurasharma's inviting of Brahmins from Ahichchhatraa and his organisation of the district.
Early history
The earliest recording of what would become Dakshina Kannada district is found inSangam literature
The Sangam literature (Tamil: சங்க இலக்கியம், ''caṅka ilakkiyam'';) historically known as 'the poetry of the noble ones' (Tamil: சான்றோர் செய்யுள், ''Cāṉṟōr ceyyuḷ'') connotes ...
, specifically in a poem of Mamulanar. M Govinda Pai identified the kingdom of Harita mentioned in the Harivamsha
The ''Harivamsa'' ( , literally "the genealogy of Hari") is an important work of Sanskrit literature, containing 16,374 shlokas, mostly in the '' anustubh'' metre. The text is also known as the ''Harivamsa Purana.'' This text is believed to ...
as Dakshina Kannada, specifically correlating the word ''Mudugara'' with Moger, part of the title of the fishermen community in the district. Pai speculated as an alternative that the entire strip from North Kanara to Kanyakumari was inhabited by Nagas who worshipped snakes, and that the character Shankachuda mentioned in several works including the work Nagananda
''Nagananda'' (''Joy of the Serpents'') is a Sanskrit play attributed to emperor Harsha (ruled 606 C.E. - 648 C.E.).
''Nagananda'' is among the most acclaimed Sanskrit dramas. Through five acts, it tells the popular story of Vidyadhar King Jimut ...
, was from this region. Several scholars identified the Satiyaputras mentioned in Ashoka's edicts as belonging to this region.
The region, owing to its position on the west coast, also finds mention in Greek sources. Pliny
Pliny may refer to:
People
* Pliny the Elder (23–79 CE), ancient Roman nobleman, scientist, historian, and author of ''Naturalis Historia'' (''Pliny's Natural History'')
* Pliny the Younger (died 113), ancient Roman statesman, orator, w ...
mentioned pirates that infested the coast between the regions of Muziris and Nitiras, which many scholars have identified with the Netravati. Ptolemy mentions two ports: Barace and Maganur which modern-day scholars identified with Barsur and Mangalore respectively. Ptolemy mentioned an inland centre of pirates called Oloikhera, which has been identified with Alvakheda, or territories of the Alupas. The region also finds mention in a play called the Chariton Mime, which contains dialogue in a language scholars have variously interpreted as an early form of Kannada or Tulu.
Alupas
 The Alupas (ಆಳುಪರು) ruled the erstwhile Dakshina Kannada region between the 8th and 14th century CE. Their origins go back further, and if Greek identifications are to be believed the Alupas may have been prominent local chiefs since the 2nd century CE. The Halmidi inscription of 450 CE mentions an Alupa chief fighting as a commander of the Kadambas in a battle against the Kekayas and Pallavas. In a stone inscription near Gudnapur dated to c. 500 CE, the Alupas are mentioned as subordinates to the Kadambas. In 602, the
The Alupas (ಆಳುಪರು) ruled the erstwhile Dakshina Kannada region between the 8th and 14th century CE. Their origins go back further, and if Greek identifications are to be believed the Alupas may have been prominent local chiefs since the 2nd century CE. The Halmidi inscription of 450 CE mentions an Alupa chief fighting as a commander of the Kadambas in a battle against the Kekayas and Pallavas. In a stone inscription near Gudnapur dated to c. 500 CE, the Alupas are mentioned as subordinates to the Kadambas. In 602, the Mahakuta Pillar
Mahakuta Pillar ( kn, ಮಹಾಕೂಟ ಸ್ತಂಭ), also known as Makuta pillar, Magada stambha or Mangalesa Dharma Jayastambha, is a deep red sandstone pillar with an early 7th-century inscription of Early Western Chalukya era. It was fou ...
inscription refers to the Aluvas as being conquered by Kirtivarman IChalukyas of Kalyani
The Western Chalukya Empire ruled most of the western Deccan, South India, between the 10th and 12th centuries. This Kannadiga dynasty is sometimes called the ''Kalyani Chalukya'' after its regal capital at Kalyani, today's Basavakalyan in the ...
, before it was attacked by the Hoysalas
The Hoysala Empire was a Kannadiga power originating from the Indian subcontinent that ruled most of what is now Karnataka between the 10th and the 14th centuries. The capital of the Hoysalas was initially located at Belur, but was later moved ...
and forced to acknowledge their suzerainty. An Old Malayalam inscription (Ramanthali inscriptions
Ramanthali inscriptions, also known as Ezhimala-Narayankannur inscriptions, are two medieval stone epigraphs from Ramanthali, near Ezhimala in Kannur district, Kerala. The first inscription, mentioning Mushika (Malayalam: Ezhimala) Validhara Vikr ...
), dated to 1075 CE, mentioning king Kunda Alupa, the ruler of Alupa dynasty of Mangalore
Mangalore (), officially known as Mangaluru, is a major port city of the Indian state of Karnataka. It is located between the Arabian Sea and the Western Ghats about west of Bangalore, the state capital, 20 km north of Karnataka–Ke ...
, can be found at Ezhimala (the former headquarters of Mushika dynasty
Mushika dynasty, also spelled Mushaka, was a minor dynastic power that held sway over the region in and around Mount Ezhi (Ezhimala (hill, Kannur), Ezhimala) in present-day North Malabar, Kerala, India. The country of the Mushikas, ruled by an a ...
) near Kannur, in the North Malabar region of Kerala
Kerala ( ; ) is a state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile regions of Cochin, Malabar, South ...
.Narayanan, M. G. S. ''Perumāḷs of Kerala.'' Thrissur (Kerala): CosmoBooks, 2013. 483.
Vijayanagara Empire
A 1204 inscription shows Mangalore had regained its position as capital fromBarkur
Barkur (also spelt Barcoor) is an area in the Brahmavara taluk, Udupi district of Karnataka state in India, comprising three villages, Hosala, Hanehalli, and Kachoor. The area is located on the bank of River Seetha. It is also referred to ...
. Over the course of the 13th and 14th centuries, Alupa power declined steadily until Alupakheda was annexed by the Vijayangara Empire. The first Vijayanagara inscription in the district was from 1345 in Attavara. For the next three centuries, the empire administered Tulu Nadu with a firm hand especially as Tulu Nadu was the conduit through which much of their western trade, and how they secured horses from Arabia. Harihara Raya built a fort at Barkur, and instituted a revenue system where half of crops went to the cultivators while the rest were divided between landlords, Brahmins and the state. Ibn Batutta
Abu Abdullah Muhammad ibn Battutah (, ; 24 February 13041368/1369),; fully: ; Arabic: commonly known as Ibn Battuta, was a Berber Maghrebi scholar and explorer who travelled extensively in the lands of Afro-Eurasia, largely in the Muslim wor ...
mentioned how the Muslim governor of 'Honore' paid tribute to a Vijayanagara revenue collector in Barkur with the title Wadiyar. While passing from Karwar to Kozhikode, he stayed in a port identified as 'Manjarur', identified as Mangalore, and noted the country to be prosperous but with few wheeled vehicles.
Two hero stones dated to 1398 in Bhatkal
Bhatkal, is a coastal town in the Uttara Kannada District of the Indian state of Karnataka. Bhatkal lies on National Highway 66, which runs between Mumbai and Kanyakumari, and has Bhatkal railway station which is one of the major railway s ...
record a rebellion in Tulu Nadu. At this time, the Alupa rule was basically ended and replaced with Barakur and Mangaluru rajyas, sometimes united into one Tulu Rajya. The governors were often transferred: during the reign of Devaraya II, there were eight governors of Mangaluru rajya. During the usurpation of Saluva Narasimharaya, he did much to improve the horse trade, which had suffered under previous rulers with his governor Mallappa Nayaka. When Krishnadevaraya came to power, he largely relied on the local feudal chiefs to remain obedient. Sadashiva Nayaka of Keladi ruled over Barakuru, Mangaluru, Chandragutti and Araga rajyas.
Portuguese arrival
When the Portuguese first arrived in the region, they described Tulunadu as a prosperous trading country populated by both Moors (Muslims) and Genitles (Hindus). They were received well by Krishnadevaraya. But when they discovered Muslim merchants in Mangalore and Barakur, they blockaded the rivers leading there in 1526, they conquered Mangalore facing some resistance. Franciscan friars began preaching in Mangalore and the surrounding regions, while the Portuguese began collecting tribute in grain and other goods. In 1530, the Portuguese stormed the Mangalore fort again facing resistance they easily annihilated. In 1547, Aliya Rama Raya entered into a treaty with the Portuguese by which all imports and exports passed through their hands. This treaty was highly unpopular among the local chiefs, who often resisted Portuguese tributary collection. Some chiefs even supported the alliance of sultanates which defeated Aliya Rama Raya at theBattle of Talikota
The Battle of Talikota (23 January 1565) was a watershed battle fought between the Vijayanagara Empire and an alliance of the Deccan sultanates. The battle resulted in the defeat of Aliya Rama Raya which led to the eventual collapse of the poli ...
, hoping to get rid of Portuguese influence. In 1571, this failed when the Portuguese defeated Bijapur at Goa.
 Rani Abbakka, the Chowta wife of Banga Raja and the Queen of Ullal, fought the Portuguese. She stopped paying tribute to the Portuguese, causing them to send a fleet to Mangalore and force a settlement, but soon she aided the enemies of the Portuguese and again stopped tribute payment. In 1566, she defeated a Portuguese expedition and killed its commander, causing the Portuguese in Goa to send an armada to subdue her in 1567. On 15 January 1568, however, the Portuguese defeated the Rani and forced her to sign a new treaty.
Rani Abbakka, the Chowta wife of Banga Raja and the Queen of Ullal, fought the Portuguese. She stopped paying tribute to the Portuguese, causing them to send a fleet to Mangalore and force a settlement, but soon she aided the enemies of the Portuguese and again stopped tribute payment. In 1566, she defeated a Portuguese expedition and killed its commander, causing the Portuguese in Goa to send an armada to subdue her in 1567. On 15 January 1568, however, the Portuguese defeated the Rani and forced her to sign a new treaty.
Nayakas of Keladi
TheNayakas of Keladi
Nayakas of Keladi (1499–1763), also known as Nayakas of Bednore and Ikkeri Nayakas, were an Indian dynasty based in Keladi in present-day Shimoga district of Karnataka, India. They were an important ruling dynasty in post-medieval Karnat ...
were a Veerashaiva family which had ruled a large portion of Tulu Nadu starting in the 16th century, when they had control over Mangalore and the rest of Tulu Nadu. Eventually in 1613, Venkatappa Nayaka I became independent and was the most powerful ruler in Tulu Nadu, taking territory which owed fealty to Bijapur and aiding Rani Abbakka. Under Shivappa Nayaka
Shivappa Nayaka (ಶಿವಪ್ಪ ನಾಯಕ) (r.1645–1660), popularly known as Keladi Shivappa Nayaka, was an Indian king and ruler of the Keladi Nayaka Kingdom. The Keladi Nayakas were successors of the Vijayanagara Empire in the coa ...
, the Nayakas of Keladi, now with capital at Bidnur, conquered the entirety of Tulu Nadu. Shivappa Nayaka utterly defeated the power of the Portuguese in Tulu Nadu. His successor made a treaty with the Portuguese where they could set up unarmed factories in Mangalore and Basrur, but were not to convert the locals. His successor, Keladi Chennamma
Keladi Chennamma was the queen of Keladi Kingdom in Karnataka. She took birth in the household of a man called Siddappa Shetty, who was a native merchant in the region of Kundapur, Karnataka. She was from the Lingayatha community. Chennamma marr ...
, is famous for sheltering Rajaram and fending off Aurangzeb's forces. She also put down rebellions of Tuluva chieftains. During this time Arab traders, who were kicked out by the Portuguese, burnt Mangalore and other trade towns. In 1714, due to trade disputes, the Portuguese bombarded Mangalore and defeated the ruler Basavappa Nayaka I, who promised to ban Arab traders from entering. From 1757 to 1763, while Queen Veerammaji was looking after the kingdom, the Ali Raja
The Sultan Ali Raja or Ali Raja or Adi Raja was the title of the Muslim king of Arakkal kingdom from the sixteenth to early nineteenth century.
Arakkal dynasty Reigning rajas and beebis
* Ali Raja Ali I (1545–1591)
* Ali Raja Abubakar I (1591– ...
of Kannur along with Maratha followers led a devastating raid into the district. They plundered to Manjeshwar and took a large booty from the Kollur Mookambika temple.
Mysore rule
Due to this unrest,Hyder Ali
Hyder Ali ( حیدر علی, ''Haidarālī''; 1720 – 7 December 1782) was the Sultan and ''de facto'' ruler of the Kingdom of Mysore in southern India. Born as Hyder Ali, he distinguished himself as a soldier, eventually drawing the at ...
was able to sack Bidnur in 1763 and annex Tulu Nadu the same year. He conquered Mangalore, and set a governor Latif Ali Baig. This threatened English shipping in the Arabian Sea, so during the First Anglo Mysore War in 1766 Company soldiers from Bombay conquered Mangalore. However, as soon as he heard the news of the capture of Bangalore, Tipu Sultan made a lightning attack on Mangalore and forced the British to retreat only a week after they captured Mangalore. Hyder Ali then confiscated all Portuguese holdings in the region due to their support for the English. In 1770, Hyder Ali made a treaty with the British allowing for rice to be supplied from Mangalore to Bombay. The next year, he gave Portuguese some privileges back such as the ability to evangelize. However, in 1776, Hyder Ali revoked all these privildges, ejected the Portuguese from Mangalore and built up a large navy in the region.
During the Second Anglo-Mysore War starting in 1781 the British quickly took over most of Tulunadu, as well as Bidnur, due to the treachery of the fort's guardian Iyaz Khan. In March 1783 however, they were forced to capitulate the fort. Tippu also sent a large force to besiege Mangalore, and after two months took the fort. Tippu's rule was harsh for the local chiefs, who he executed and dispossessed due to their perceived collaboration with the English.
British rule and early resistance
During the Fourth Anglo-Mysore War in 1799, the British returned the lands to their feudal chiefs. After Tippu's defeat, the British gave the Raja of Coorg several maganes which had been taken from him by Hyder Ali and set up their administration, with Thomas Munro the first Collector of Kanara. However Vittala Hegde, who had fled when Tippu campaigned in Tulunadu and returned at the start of the Fourth Anglo-Mysore War, began to develop an armed following to retake his lands. His ally Subba Rao attacked the Tehsildar of Kadaba, but was defeated by a British ally, Kumara Hegde. In July 1800, the British pursued the last remnants of Vittala Hedge's army into Shishila Ghat, where they were defeated and many of the chief rebels were arrested. At this time, the district was in severe distress due to the many bloody wars waged across it. The British deputed an administrator to study the economic condition of Kanara district, which noted severe deprivation in the south but more commerce further north. The Company then imposed harsh revenue demands on the poor peasants, who were already reeling from depression. The peasants organised themselves and participated in a 'no-tax' campaign, forcing the British to rethink their tax policy on the poor. The British then invaded Coorg when its ruler objected to British interference and took all territory of the state below the Western Ghats, adding it to Kanara district. In 1837, the British faced the Amara Sullia rebellion. After the British had deposed Kalyanaswami, a pretender to the throne of Coorg, he went to Bellare, and gathered a large number of supporters who marched on Puttur. Kalyanaswami defeated two companies of sepoys near Puttur, and Kalyanaswami then marched on Mangalore, causing the British to flee. For two weeks Kalyanaswami held Mangalore, released prisoners and set the homes of British soldiers alight. When British forces came from Thalassery to Mangalore, his poorly armed forces melted away. Kalyanaswami and other prominent leaders were hanged while others were deported to Singapore. Before 1860, Dakshina Kannada was part of a district calledKanara
Kanara, also known as Karavali is the historically significant stretch of land situated by the southwestern coast of India, alongside the Arabian Sea in the present-day Indian state of Karnataka.
The region comprises three civil districts, ...
, which was under a single administration in the Madras Presidency. In 1860, the British split the area into South Canara and North Canara
Uttara Kannada is a district in the Indian state of Karnataka. Uttara Kannada District is a major coastal district of Karnataka, and currently holding the title of the largest district in Karnataka. It is bordered by the state of Goa and Bela ...
, the former being retained in the Madras Presidency, while the latter was made a part of Bombay Presidency in 1862. Kundapur Taluk
Kundapura Taluk is a taluk located in Udupi district in the Indian state of Karnataka. Kundapur town is the taluk headquarters of Kundapur Taluk.
Demographics
As of the 2011 Census of India, Kundapura Taluk had 79573 households with a populat ...
was earlier included in North Kanara but was later re-included in South Kanara. South Kanara included present Dakshina Kannada, Udupi, Kasaragod districts and the Aminidivi Islands.
Independence movement
During the 1920s, several newspapers in the district drew inspiration from the freedom struggle such as ''Tilaka Sandesh'', ''Satyagrahi'' and others. South Kanara participated in the non-cooperation movement led in the district by Karnad Sadashiva Rao. All indepdence movement movements gained significant traction in the district, and Gandhi and Nehru both visited Mangalore during the Freedom struggle. In 1942 large numbers of leaders were jailed in the Quit India movement.Post-independence
In 1947 South Kanara joined India as part of Madras State. In 1956, the states were reorganised on linguistic lines. The Malayalam-majority Kasaragod subdivision became a part of Kerala, the Aminidivi Islands were joined with the Laccadive and Minicoy islands in a union territory, while the Tulu and Kannada majority Dakshina Kannada subdivision became a district ofMysore State
Mysore State, colloquially Old Mysore, was a state within the Dominion of India and the later India, Republic of India from 1947 until 1956. The state was formed by renaming the Kingdom of Mysore, and Bangalore replaced Mysore as the state's c ...
in 1956 which later was renamed Karnataka
Karnataka (; ISO: , , also known as Karunāḍu) is a state in the southwestern region of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reorganisation Act. Originally known as Mysore State , it was renamed ''Karnat ...
in 1973. The Udupi district was formed from the northern taluks of Dakshina Kannada in 1997. Later, the Karnataka
Karnataka (; ISO: , , also known as Karunāḍu) is a state in the southwestern region of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reorganisation Act. Originally known as Mysore State , it was renamed ''Karnat ...
Government, for the purpose of administration, split the greater Dakshina Kannada district into Udupi and present day Dakshina Kannada districts on 15 August 1997. Three taluks of the former district – Udupi, Karkala
''Karkala'' also known as Karla in Tulu language, is a town and the headquarters of Karkala taluk in the Udupi district of Karnataka, India. Located about 60 km from Mangalore in the Tulu Nadu region of the state,it lies near the foothill ...
and Kundapura
Kundapur, also called Kundapura, is a coastal town situated in the Udupi district of the state of Karnataka, India. This town was known as Coondapoor while it was part of the erstwhile South Canara district (1862–1947) of the Madras Pres ...
– formed the new Udupi district.
Administration
 The district comprises seven
The district comprises seven talukas
A tehsil (, also known as tahsil, taluka, or taluk) is a local unit of administrative division in some countries of South Asia. It is a subdistrict of the area within a district including the designated populated place that serves as its administr ...
: Mangalore
Mangalore (), officially known as Mangaluru, is a major port city of the Indian state of Karnataka. It is located between the Arabian Sea and the Western Ghats about west of Bangalore, the state capital, 20 km north of Karnataka–Ke ...
, Puttur, Sullia
Sullia (also known as Sulya) is a town in the Dakshina Kannada district of the state of Karnataka, India. It is the headquarters of the Sullia taluk. Sullia taluk is one of the seven talukas of Dakshina Kannada district. Its administrative h ...
, Bantwal
Bantwal () is a taluk in Dakshina Kannada district, Karnataka, India. It is located East of Mangalore city center. BC Road-Kaikamba of Bantwal is one of the fastest developing areas in Dakshina Kannada district of Karnataka.
Along with BC ...
, Belthangady, Kadaba and Moodabidri. It used to include seven northern talukas ( Udupi, Kundapur, Karkala
''Karkala'' also known as Karla in Tulu language, is a town and the headquarters of Karkala taluk in the Udupi district of Karnataka, India. Located about 60 km from Mangalore in the Tulu Nadu region of the state,it lies near the foothill ...
, Hebri, Brahmavar
Brahmavar is a taluk in Udupi district located on NH 66 (formerly NH 17), north of the Udupi in Karnataka, India.
Location
Brahmavara is about north of Mangalore and about north of Udupi on the National highway NH 66 (formerly NH 17). The Suv ...
, Kaup and Byndoor), but these were separated in August 1997 to form Udupi district.
Important cities and towns in Dakshina Kannada include Mangalore
Mangalore (), officially known as Mangaluru, is a major port city of the Indian state of Karnataka. It is located between the Arabian Sea and the Western Ghats about west of Bangalore, the state capital, 20 km north of Karnataka–Ke ...
, Surathkal, Puttur, Sullia
Sullia (also known as Sulya) is a town in the Dakshina Kannada district of the state of Karnataka, India. It is the headquarters of the Sullia taluk. Sullia taluk is one of the seven talukas of Dakshina Kannada district. Its administrative h ...
, Bantwal
Bantwal () is a taluk in Dakshina Kannada district, Karnataka, India. It is located East of Mangalore city center. BC Road-Kaikamba of Bantwal is one of the fastest developing areas in Dakshina Kannada district of Karnataka.
Along with BC ...
, Vittal, Moodabidri, Kinnigoli
Kinnigoli is a major suburb in the outskirts of Mangalore Tehsil (Mangalore Township). It is located approximately 32 km from Mangalore City, 5 km from Kateel (a famous Hindu pilgrimage centre), 8 km from Mulki (5 km from ...
, Uppinangady
Uppinangady or Ubar is a town in the Dakshina Kannada district in the state of Karnataka. It is surrounded by the Kumaradhara River on one side and Nethravathi River on the other. When the town's two surrounding rivers rise during the rainy s ...
, Nellyadi, Kadaba, Belthangady, Guruvayankere, Venur, Mulki, Dharmasthala
Dharmasthala (earlier known as Kuduma) is an Indian temple town on the banks of the Nethravathi River in the Belthangady taluk of the Dakshina Kannada district in Karnataka, India.
The town is known for its centuries old Dharmasthala Te ...
, Ujire
{{Infobox settlement
, name = Ujire
, other_name =
, nickname =
, settlement_type = Town
, image_skyline = Siddavana gurukula.JPG
, image_alt =
, image_captio ...
and Subramanya. The district is well known for beaches, red clay roof tiles ( Mangalore tiles), cashew nut and its products, banking, education, healthcare and cuisine. Mangalore
Mangalore (), officially known as Mangaluru, is a major port city of the Indian state of Karnataka. It is located between the Arabian Sea and the Western Ghats about west of Bangalore, the state capital, 20 km north of Karnataka–Ke ...
being the second largest city of Karnataka
Karnataka (; ISO: , , also known as Karunāḍu) is a state in the southwestern region of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reorganisation Act. Originally known as Mysore State , it was renamed ''Karnat ...
and Puttur are the largest and the major cities of Dakshina Kannada.
Dakshina Kannada District has 1 City Corporation (Mangalore), 2 City Municipal Councils, 3 Town Municipal Councils, and 8 Town Panchayaths.
Demographics
According to the 2011 census, Dakshina Kannada has apopulation
Population typically refers to the number of people in a single area, whether it be a city or town, region, country, continent, or the world. Governments typically quantify the size of the resident population within their jurisdiction using a ...
of 2,089,649, of which male and female were 1,034,714 and 1,054,935 respectively. roughly equal to the nation of North Macedonia. This gives it a ranking of 220th in India (out of a total of 640). The district has a population density of . Its population growth rate over the decade 2001-2011 was 9.8%. Dakshina Kannada has a sex ratio
The sex ratio (or gender ratio) is usually defined as the ratio of males to females in a population. As explained by Fisher's principle, for evolutionary reasons this is typically about 1:1 in species which reproduce sexually. Many species d ...
of 1018 females
Female (symbol: ♀) is the sex of an organism that produces the large non-motile ova (egg cells), the type of gamete (sex cell) that fuses with the male gamete during sexual reproduction.
A female has larger gametes than a male. Females ...
for every 1000 males and a literacy rate of 88.62%. 47.67% of the population lived in urban areas.
The literacy rate of Mangalore city is 94%. According to the 2011 Indian Census, the district ranks second in per capita income
Per capita income (PCI) or total income measures the average income earned per person in a given area (city, region, country, etc.) in a specified year. It is calculated by dividing the area's total income by its total population.
Per capita i ...
, second in HDI
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a statistic composite index of life expectancy, education (mean years of schooling completed and expected years of schooling upon entering the education system), and per capita income indicators, wh ...
, first in literacy and third in sex ratio among all districts in Karnataka
Karnataka (; ISO: , , also known as Karunāḍu) is a state in the southwestern region of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reorganisation Act. Originally known as Mysore State , it was renamed ''Karnat ...
. 7.09% of the district's population is Scheduled Castes and 3.94% Scheduled Tribes.
Tuluvas
The Tulu people or Tuluvas are an ethno-linguistic group from Southern India. They are native speakers of the Tulu language and the region they traditionally inhabit is known as Tulu Nadu. This region comprises the districts of Dakshina Kannada ...
, distributed among the Billava
The Billava, Billoru, Biruveru people are an ethnic group of India. They are found traditionally in Tulu Nadu region and engaged in toddy tapping, cultivation and other activities. They have used both missionary education and Sri Narayana Guru's ...
, Mogaveera
The Mogaveera, or Mogavira is a subcaste of the Koli caste living in the Karnataka state of India. They dominated maritime activities in coastal Karnataka.
History
Mogaveera means a warrior who after the demolition of the kingdom continued ...
, Bunt, Kulala
Kulala is a Hindu caste whose traditionally pursued pottery trade and farming as a profession commonly found in the Indian states of Andhra pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala and southern parts of Tamilnadu. They belong to the Other Backward Class ...
, Tulu Gowda and Devadiga communities, are the largest ethnic group in the district. Of these the Billavas are the most numerous community. The Konkani people, Brahmins, Holeyas, the hill-tribes ( Koragas), Muslims
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
, Mangalorean Catholics and Arebhashe Gowdas comprise rest of the population. The Brahmins belong chiefly to the Shivalli, Saraswat, Havyaka
Havyaka Brahmins are the Hindu Pancha Dravida Vedic Brahmins from the Indian state of Karnataka. Havyakas profess the Advaita philosophy propounded by Adi Shankaracharya. Most Havyakas can trace their immediate ancestry to either Sirsi, Utta ...
, Chitpavan, Daivadnya and Kota sub-sections.
Religion
Dakshina Kannada is the most religiously diverse district in Karnataka. Hindus form the majority, while Muslims and Christians form significant minorities. Hinduism has always been a strong religion in the district. The coastal region of Karnataka has produced large numbers of scholars following various traditions of Hindu philosophy such as Smarta, Madhva, etc. Madhvacharya, founder of Dwaita, was from nearby Udupi and his philosophy is strong in the region. The Dharmasthala Shiva temple and Kukke Subramhanya Temple are major pilgrimage sites. Non-Brahmin Hindus historically followed more distinct traditions involving ritual dancing and veneration of ''bhuta'' spirits called ''Bhuta Aradhane'', which is mainly ancestor worship. However the gradual urbanization and the rise of Hindutva in the district starting in the 1920s has made these religious traditions conform more to Brahminical codes or disappear entirely. Islam is the second-largest religion in the district. As the district lies along the Arabian Sea, it has always been a hub for traders from the Middle East riding the Indian Ocean monsoon. The first Muslims in the region were Arab Muslim traders who married local women. The Beary community, who make up 80% of Dakshina Kannada's Muslim population, claim descent from these unions. It is said the Masjid Zeenath Baksh, the oldest mosque in the region, was built in 644 CE, only 12 years after the death of Muhammad. Almost all Muslims in Dakshina Kannada are Sunni, following theShafi'i school
The Shafii ( ar, شَافِعِي, translit=Shāfiʿī, also spelled Shafei) school, also known as Madhhab al-Shāfiʿī, is one of the four major traditional schools of religious law (madhhab) in the Sunnī branch of Islam. It was founded by ...
of jurisprudence. Islam in Dakshina Kannada has also had dark sides when Tipu Sultan conquered the region and forced many of the local inhabitants, especially the Mangalore Catholics, to convert to Islam. In recent years, the Bearys have been one of the main groups to travel to the Gulf for work, where they have been significantly influenced by the highly conservative Wahabi Islam followed there. This, along with the predominance of Hindutva, has contributed to the radicalization of Islam in the district.
Christianity is the third-largest religion in the district. Christianity, although having an ancient presence on the western coast due to trade, did not gain a large following in Dakshina Kannada until the arrival of the Portuguese in the early 1500s. The majority of Christians in the district are Catholics, now called the Mangalorean Catholics.They arrived during the Goan Inquisition, fleeing persecution by the Portuguese who charged them with not following Christianity. A minority are Protestants, mainly lower castes converted by Protestant missionaries in the late 1800s who established numerous educational institutions.
Historically Jainism and Buddhism were strong religions in the district, as in much of the western coast, before being eclipsed by the various denominations of Hinduism. Jainism was the traditional religion of the Alupas as well as the Chowtas, who long defended Dakshina Kannada from outside aggression including the Portuguese. It is speculated most of today's Bunts were originally Jain before starting to follow Hinduism. Today there are over 10,000 Jains in the district as a whole.
Communal tensions
Despite this diversity (and partially due to it), Dakshina Kannada has earned a reputation as one of the most communally sensitive districts in the country. The three religions of Coastal Karnataka were once more syncretic than they are now. For instance Muslims found important roles in ''paddana'' stories, dargahs attracted people from multiple communities, and the Muslims played significant roles in Hindu village festivities. However this soon changed at the end of British rule. The groundwork for this communalization started in the early 1920s, when some of the earliest RSS Shakas in India were introduced to the district by Gauda Saraswat Brahmins in contact with RSS founder K. B. Hedgewar. These Brahmins felt the social order threatened by Christian missionaries, who were gaining converts among both lower castes as well as some upper castes. Initially the Hindutva ideology was largely upper caste, and although Hindutva organisations tried to mobilise the masses they were largely unsuccessful until the 1970s. This resulted in the general marginalization of mainly Muslims but also Christians to some extent. Even today Billavas and Mogaveeras make up the vast majority of ground cadres of the various Hindutva groups in Coastal Karnataka including the RSS,BJP
The Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP; ; ) is a political party in India, and one of the two major Indian political parties alongside the Indian National Congress. Since 2014, it has been the ruling political party in India under Narendra Mo ...
, Bajrang Dal, Sri Ram Sena. Partly because of this rising Hindutva, and also the nature of their constant travel to the Gulf, the Bearys began to adopt much more conservative and radical forms of Islam including aspects of Wahabism from Saudi Arabia. Communal relations between the communities have since deteriorated significantly. The rise of the extremist Karnataka Forum for Dignity, Social Democratic Party of India and Popular Front of India, which the Indian Government speculates are linked to the banned Students Islamic Movement of India, have contributed as well to exacerbating communal tensions. Communal riots over claims of cow slaughter or forced conversion are common. In recent years, the region has seen a rise in attacks and moral policing by vigilantes against interfaith couples, mainly from Hindu groups who claim the widespread presence of Love Jihad in the region. The polarization has greatly decreased inter-religious interactions.
Language
Tulu is the main language of the district and is spoken by 48.57% of the population. It is the oldest language of the district and has a long literary tradition. Tulu has several dialects and sociolects including a Northern dialect near Udupi and Southern dialect centred on Mangalore. It is the majority language in Bantwal, Beltangadi and Puttur taluks. Many have demanded the language's inclusion in the Eighth Schedule of the Constitution. Beary is the next largest language, spoken by c. 16.07% of the population, and is spoken by the largest Muslim community who were traditionally traders. Although in origin related toMalayalam
Malayalam (; , ) is a Dravidian languages, Dravidian language spoken in the Indian state of Kerala and the union territories of Lakshadweep and Puducherry (union territory), Puducherry (Mahé district) by the Malayali people. It is one of 2 ...
, it has undergone significant influence from Tulu as well as Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
, Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
and the languages of other foreign traders. It is not recognized as a language in the census. Malayalam, the third largest language, is spoken by 9.97%, by maniyani (yadava) and vaaniya community mainly in regions bordering Kerala. Konkani, spoken by 9.91%, is a major language of Mangalore city and other urban centres. The dialect of Konkani here has strong influence from Tulu and Kannada. Kannada, although the official language of the state, is only spoken by 9.27% of the population here. There are many dialects of Kannada spoken, some of which are Are Bhashe, spoken by Gowdas, and Havigannada
Havigannada, also called as Havyaka Bhaashe and Havyaka Kannada, is the dialect of Kannada spoken in Malenadu and coastal region of Karnataka.
Usage
Havigannada uses similar verbs and words as mainstream Kannada. However, it has more in common ...
, spoken by the Havyaka Brahmin community. Deccani Urdu and Tamil are spoken by small minorities in Mangalore city. Marathi and Hindi
Hindi ( Devanāgarī: or , ), or more precisely Modern Standard Hindi (Devanagari: ), is an Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in the Hindi Belt region encompassing parts of northern, central, eastern, and western India. Hindi has been ...
are also spoken by significant numbers. Koraga is an indigenous tribal language still spoken by some individuals in the district.
Education and research
 In Dakshina Kannada, primary and secondary education have reached every section of the society. Some of them are St Agnes CBSE school, St Theresa ICSE School and St Aloysius School, Vivekananda collage, A host of educational institutes offering courses in
In Dakshina Kannada, primary and secondary education have reached every section of the society. Some of them are St Agnes CBSE school, St Theresa ICSE School and St Aloysius School, Vivekananda collage, A host of educational institutes offering courses in Medicine
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care pr ...
, Engineering
Engineering is the use of scientific principles to design and build machines, structures, and other items, including bridges, tunnels, roads, vehicles, and buildings. The discipline of engineering encompasses a broad range of more speciali ...
, Pharmacy, Nursing, Hotel and Catering, Law and Management are in this district.
Dakshina Kannada is home to the National Institute of Technology Karnataka (NITK) Surathkal, one of India's top engineering colleges. The College of Fisheries is located at Yekkur near Kankanady. Mangalore University
Mangalore University commonly known as, MU is a public university in Konaje, Mangaluru, Karnataka, India. In 2021, National Assessment and Accreditation Council (NAAC) awarded Mangalore University 'B' grade.
History
Mangalore University was e ...
is a public university in Konaje
Konaje is a locality in Mangalore generally known as the educational hub. Konaje is governed by Dakshina Kannada zilla Panchayath.
It is home to the vast campus of the Mangalore University which is also known as Mangalagangothri. The university ...
near Mangalore
Mangalore (), officially known as Mangaluru, is a major port city of the Indian state of Karnataka. It is located between the Arabian Sea and the Western Ghats about west of Bangalore, the state capital, 20 km north of Karnataka–Ke ...
. It has jurisdiction over the districts of Dakshina Kannada, Udupi and Kodagu
Kodagu (also known by its former name Coorg) is an administrative district in the Karnataka state of India. Before 1956, it was an administratively separate Coorg State, at which point it was merged into an enlarged Mysore State.
It occupies ...
.
The district is home to research institutes such as the Directorate of Cashew Research at Puttur. The Central Plantation Crops Research Institute is in Vitla
Vitla (ವಿಟ್ಲ) also Vittal is a town in Bantwal taluk of Dakshina Kannada district, India, around 18 km from Bantwal in Bantwal Taluk. It is also 14 km from Puttur and 40 km from Mangalore. Vitla was an assembly constit ...
in the Bantwal
Bantwal () is a taluk in Dakshina Kannada district, Karnataka, India. It is located East of Mangalore city center. BC Road-Kaikamba of Bantwal is one of the fastest developing areas in Dakshina Kannada district of Karnataka.
Along with BC ...
taluk. The engineering colleges in the district include St. Joseph Engineering College,
The engineering colleges in the district include St. Joseph Engineering College, KVG College of Engineering
KVG College of Engineering (KVGCE) is one of many engineering colleges in Karnataka, India. It was established in 1986 based on one of the government aided initiatives in technical education in Southern Karnataka State. It is located in Kurunjib ...
, Mangalore Institute of Technology & Engineering, Canara Engineering College, P A College of Engineering, Srinivas Institute of Technology, Srinivas School of Engineering, Vivekananda College of Engineering & Technology, Shree Devi Institute of Technology, Alvas Institute of Engineering & Technology, Karavali Institute of Technology, Sahyadri College of Engineering and Management, Yenepoya Institute of Technology, A J Institute of Engineering and Technology, SDM Institute of Technology, Bearys Institute of Technology and Prasanna College of Engineering & Technology.
The medical colleges in the district include A J Institute of Medical Science, Father Muller Medical College
Father Muller Medical College, () located about a kilometre from the National Highway-66 (the Mumbai-Mangalore highway) at Kankanady in Mangalore, is a religious minority educational institution forming a part of the Father Muller Charitable ...
, KS Hegde Medical Academy, Kasturba Medical College, Srinivas Institute of Medical Sciences and Research Centre
Srinivas Institute of Medical Sciences and Research Centre is a medical college and medical centre outside Surathkal in Mukka, Mangalore, India.
Srinivas was started by the A. Shama Rao Foundation inr 2009.
Description
Srinivas is affil ...
, Yenepoya Medical College & Research Institute and KVG Medical College. Manipal College of Dental Sciences Mangalore
Manipal College of Dental Sciences, Mangalore was founded in 1987 and recognised by the Dental Council of India in 1992 and by the Malaysian Dental Council in 2003. It was certified for ISO9001:2000 in 2006 and was re-certified for ISO9001:200 ...
, A B Shetty Memorial Institute of Dental Sciences, A J Institute of Dental Sciences, Yenepoya Dental College & Research Institute and Srinivas Institute of Dental Sciences are some of the dental colleges.
The Degree colleges in the district include St Aloysius College (Autonomous), St Agnes College (Autonomous), SDM College, Canara College, Besant College, Govinda Dasa College etc
Cultures, traditions and rituals
 Most people of this district follow traditions, customs and rituals. The district has many temples of Hindu gods and goddesses, which are ancient and have deep spiritualism attached to them. The people of Dakshina Kannada worship the Serpent God Subramanya. According to legend, the district was reclaimed by Parashurama from the sea. According to the 17th-century
Most people of this district follow traditions, customs and rituals. The district has many temples of Hindu gods and goddesses, which are ancient and have deep spiritualism attached to them. The people of Dakshina Kannada worship the Serpent God Subramanya. According to legend, the district was reclaimed by Parashurama from the sea. According to the 17th-century Malayalam
Malayalam (; , ) is a Dravidian languages, Dravidian language spoken in the Indian state of Kerala and the union territories of Lakshadweep and Puducherry (union territory), Puducherry (Mahé district) by the Malayali people. It is one of 2 ...
work '' Keralolpathi'', the lands of Kerala
Kerala ( ; ) is a state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile regions of Cochin, Malabar, South ...
and Tulu Nadu were recovered from the sea by the axe-wielding warrior sage Parasurama, the sixth avatar of Vishnu
Vishnu ( ; , ), also known as Narayana and Hari, is one of the principal deities of Hinduism. He is the supreme being within Vaishnavism, one of the major traditions within contemporary Hinduism.
Vishnu is known as "The Preserver" withi ...
(hence, Kerala is also called ''Parasurama Kshetram'' 'The Land of Parasurama'). Parasurama threw his axe across the sea, and the water receded as far as it reached. According to legend, this new area of land extended from Gokarna to
According to legend, this new area of land extended from Gokarna to Kanyakumari
Kanniyakumari (; , referring to Devi Kanya Kumari), also known as Cape Comorin, is a city in Kanniyakumari district in the state of Tamil Nadu, India. It is the southern tip of the Indian subcontinent and the southernmost city in mainland Ind ...
. The land which rose from sea was filled with salt and unsuitable for habitation; so Parasurama invoked the Snake King Vasuki
Vasuki (IAST: ) is the second king of the nagas in Hinduism. He is described as having a gem called ''Nagamani'' (serpent's ornament) on his head. Adishesha, the first king of the serpents and the mount of Narayana, is his elder brother, and ...
, who spat holy poison and converted the soil into fertile lush green land. Out of respect, Vasuki and all snakes were appointed as protectors and guardians of the land. P. T. Srinivasa Iyengar theorised, that Senguttuvan
Cheran Chenkuttuvan ( ml, ചേരൻ ചെങ്കുട്ടുവൻ ; ta, சேரன் செங்குட்டுவன்) (''c.'' 2nd century CE), literally 'the Alluring Kuttuvan Chera', identified with Katal Pirakottiya Vel ...
may have been inspired by the Parasurama legend, which was brought by early Aryan settlers. '' Nagaradhane'' or ''snake worship'' is practiced according to the popular belief of the ''Naga Devatha
Naga or NAGA may refer to:
Mythology
* Nāga, a serpentine deity or race in Hindu, Buddhist and Jain traditions
* Naga Kingdom, in the epic ''Mahabharata''
* Phaya Naga, mythical creatures believed to live in the Laotian stretch of the Mekong Ri ...
'' to go underground and guard the species on the top. Rituals such as Bhuta Kola
Būta Kōlā,/buːt̪ʌ/ is the local pronunciation while the standardised Kannada pronunciation is /bʱuːt̪ʌ koːlɑː/ also referred to as daiva kōlā or nēmā, is a ritual dance performance prevalent among the Hindus of Tulu Nadu an ...
are performed to satisfy the spirits. Kambala
Kambala (or Kambla/Kambula) is an annual buffalo race held in the southwestern Indian state of Karnataka. Traditionally, it is sponsored by local Tuluva landlords and households in the coastal districts of Dakshina Kannada and Udupi of Karnat ...
, a form of buffalo race on muddy track in the paddy field is organised in 16 sites across the district. Cock fight
A cockfight is a blood sport, held in a ring called a cockpit. The history of raising fowl for fighting goes back 6,000 years. The first documented use of the ''word'' gamecock, denoting use of the cock as to a "game", a sport, pastime or ente ...
(Kori Katta in Tulu) is another pastime of the rural agrarian people.
Yakshagana
Yakshagaana is a traditional theatre, developed in Dakshina Kannada, Udupi, Uttara Kannada, Shimoga and western parts of Chikmagalur districts, in the state of Karnataka and in Kasaragod district in Kerala that combines dance, music, dialogue, ...
is the popular folk art of this district. The Yakshagana
Yakshagaana is a traditional theatre, developed in Dakshina Kannada, Udupi, Uttara Kannada, Shimoga and western parts of Chikmagalur districts, in the state of Karnataka and in Kasaragod district in Kerala that combines dance, music, dialogue, ...
is a night-long dance and drama performance practiced in Tulu Nadu with great fanfare. Pilivesha (literally, tiger dance) is a unique form of folk dance in the region fascinating the young and the old alike, which is performed during Dasara and Krishna Janmashtami. Karadi Vesha (literally, bear dance) is another popular dance performed during Dasara. The people of Dakshina Kannada also celebrate traditional Hindu festivals like Bisu, Yugadi (Ugadi
Ugadi or Yugadi, also known as Samvatsarādi (), is New Year's Day according to the Hindu calendar and is celebrated in the states of Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, and Karnataka in India. It is festively observed in these regions on the first ...
), Krishna Janmashtami, Ganesha Chaturthi, Navaratri ( Dasara), Deepavali
Diwali (), Dewali, Divali, or Deepavali (IAST: ''dīpāvalī''), also known as the Festival of Lights, related to Jain Diwali, Bandi Chhor Divas, Tihar, Swanti, Sohrai, and Bandna, is a religious celebration in Indian religions. It is on ...
, Aati Hunime, etc.
According to Kerala Muslim tradition, the Masjid Zeenath Baksh at Mangalore
Mangalore (), officially known as Mangaluru, is a major port city of the Indian state of Karnataka. It is located between the Arabian Sea and the Western Ghats about west of Bangalore, the state capital, 20 km north of Karnataka–Ke ...
is one of the oldest mosques in the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian O ...
. According to the Legend of Cheraman Perumals
The legend of Cheraman Perumals is the medieval tradition associated with the Cheraman Perumals (Chera kings) of Kerala.Narayanan, M. G. S. ''Perumāḷs of Kerala.'' Thrissur (Kerala): CosmoBooks, 2013. 31-32. The sources of the legend include p ...
, the first Indian mosque was built in 624 AD at Kodungallur with the mandate of the last the ruler (the Cheraman Perumal) of Chera dynasty, who left from Dharmadom to Mecca
Mecca (; officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, commonly shortened to Makkah ()) is a city and administrative center of the Mecca Province of Saudi Arabia, and the holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow ...
and converted to Islam during the lifetime of Prophet Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the monoth ...
(c. 570–632). According to ''Qissat Shakarwati Farmad
''Qissat Shakarwati Farmad'' (alternatively ''Qissat Shakruti Firmad'', literally ''"Tale of the Great Chera Ruler"'') is an Arabic manuscript of anonymous authorship, apparently written in Malabar Coast, south India.O. Loth, ''Arabic Manuscripts ...
'', the ''Masjids'' at Kodungallur, Kollam, Madayi
Madayi (a.k.a. Madai). is a Census Town and Grama panchayat in Kannur district of Kerala state, India. Bhagavathy shrine, Madayi Kavu (Thiruvar Kadu Bhagavathi Temple) where devotees worship Bhadrakali, is located here. The Goddess is on ...
, Barkur
Barkur (also spelt Barcoor) is an area in the Brahmavara taluk, Udupi district of Karnataka state in India, comprising three villages, Hosala, Hanehalli, and Kachoor. The area is located on the bank of River Seetha. It is also referred to ...
, Mangalore
Mangalore (), officially known as Mangaluru, is a major port city of the Indian state of Karnataka. It is located between the Arabian Sea and the Western Ghats about west of Bangalore, the state capital, 20 km north of Karnataka–Ke ...
, Kasaragod, Kannur, Dharmadam
Dharmadom or Dharmadam is a census town in Thalassery taluk of Kannur district in the state of Kerala, India. This town is located in between Anjarakandi River and Ummanchira river, and Palayad town and Arabian sea. It is known for the 100-yea ...
, Panthalayani ( Koyilandy), and Chaliyam, were built during the era of Malik Dinar
Malik Dinar ( ar-at, مالك دينار, Mālik b. Dīnār, Malayalam: മാലിക് ദീനാര്) (died 748 CE)Al-Hujwiri, "Kashf al-Mahjoob", 89 was a Muslim scholar and traveller. He was one of the first known Muslims to have co ...
, and they are among the oldest ''Masjid''s in the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian O ...
. It is believed that Malik Dinar
Malik Dinar ( ar-at, مالك دينار, Mālik b. Dīnār, Malayalam: മാലിക് ദീനാര്) (died 748 CE)Al-Hujwiri, "Kashf al-Mahjoob", 89 was a Muslim scholar and traveller. He was one of the first known Muslims to have co ...
died at Thalangara
Thalangara is a part of Kasaragod Town, the district headquarters of the Kasaragod district in the South Indian state of Kerala. Malik Deenar Jama Masjid and Dargah is located here. Its economy is dependent on remittance from expatriate workers ...
in Kasaragod town.Pg 58, Cultural heritage of Kerala
Kerala ( ; ) is a state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile regions of Cochin, Malabar, South ...
: an introduction, A. Sreedhara Menon, East-West Publications, 1978 Two of them, Mangalore and Barkur
Barkur (also spelt Barcoor) is an area in the Brahmavara taluk, Udupi district of Karnataka state in India, comprising three villages, Hosala, Hanehalli, and Kachoor. The area is located on the bank of River Seetha. It is also referred to ...
lie in Tulu Nadu.
The 16th century work '' Tuhfat Ul Mujahideen'' written by Zainuddin Makhdoom II appears to be the first historical work written in detail about the contemporary history of Mangalore. It is written in Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
and contains pieces of information about the resistance put up by the navy of Kunjali Marakkar
Kunjali Marakkar (alternatively spelled Kunhali Marakkar) was the title inherited by the Admiral of the fleet of the Samoothiri / Zamorin, the king of Kozhikode / Calicut, in present-day Kerala, India. There were four Marakkars whose war tacti ...
alongside the Zamorin of Calicut
Kozhikode (), also known in English as Calicut, is a city along the Malabar Coast in the state of Kerala in India. It has a corporation limit population of 609,224 and a metropolitan population of more than 2 million, making it the second l ...
from 1498 to 1583 against Portuguese attempts to colonize Tulu Nadu and Malabar coast.A. Sreedhara Menon. ''Kerala History and its Makers''. D C Books (2011)A G Noorani. Islam in Kerala.
Book/ref>Roland E. Miller. ''Mappila Muslim Culture'' SUNY Press, 2015
Transport
 The district is connected by air through the Mangaluru Airport, Mangalore International Airport at
The district is connected by air through the Mangaluru Airport, Mangalore International Airport at Bajpe
Bajpe is a locality in Mangalore city of Dakshina Kannada district in the state of Karnataka, now also known as Bajpe Town, India. It is around from the city of Mangalore. The Mangalore International Airport is located at Bajpe and was p ...
. Airlines such as Air India
Air India is the flag carrier airline of India, headquartered at New Delhi. It is owned by Talace Private Limited, a Special-Purpose Vehicle (SPV) of Tata Sons, after Air India Limited's former owner, the Government of India, completed the ...
, SpiceJet
SpiceJet is an Indian budget airline headquartered in Gurgaon, Haryana. It is the second largest airline in the country by number of domestic passengers carried, with a market share of 13.6% as of March 2019. The airline operates 630 daily fl ...
and IndiGo
Indigo is a deep color close to the color wheel blue (a primary color in the RGB color space), as well as to some variants of ultramarine, based on the ancient dye of the same name. The word "indigo" comes from the Latin word ''indicum'', m ...
offer daily flights to national and international destinations near the Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf ( fa, خلیج فارس, translit=xalij-e fârs, lit=Gulf of Fars, ), sometimes called the ( ar, اَلْخَلِيْجُ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Khalīj al-ˁArabī), is a mediterranean sea in Western Asia. The bod ...
.
Bus services in this district are run by private players namely Dakshina Kannada Bus Operators' Association (DKBOA) and the state-run KSRTC. The district had public limited (public listed) companies running transport business even before the independence of India in 1947.
The district has five national highways connecting parts of Karnataka and India. NH-66 connects the district with Udupi, Karwar, Mumbai
Mumbai (, ; also known as Bombay — List of renamed Indian cities and states#Maharashtra, the official name until 1995) is the capital city of the Indian States and union territories of India, state of Maharashtra and the ''de facto'' fin ...
, Goa, Kannur, Kozhikode
Kozhikode (), also known in English as Calicut, is a city along the Malabar Coast in the state of Kerala in India. It has a corporation limit population of 609,224 and a metropolitan population of more than 2 million, making it the second l ...
, Kochi and Thiruvananthapuram. NH-169 connects Shimoga with Dakshina Kannada. NH-75 connects the district with Vellore, Kolar, Bangalore
Bangalore (), List of renamed places in India, officially Bengaluru (), is the Capital city, capital and largest city of the Indian state of Karnataka. It has a population of more than and a metropolitan area, metropolitan population of a ...
, Kunigal, Hassan and Sakleshpur
Sakleshpur, Sakleshpura or Sakleshapura is a hill station town and headquarters of Sakleshpur taluk in Hassan district in the Indian state of Karnataka.
Economy
The town lies in the Malnad region on the hills of the biodiversity hotspot, the ...
. The NH-73 connects Mangalore to Tumkur
Tumkur, officially renamed as Tumakuru, is a city located in the southern part of Indian state of Karnataka. Tumkur is situated at a distance of northwest of Bangalore, the state capital along NH 48 and NH 73. It is the headquarters of the ...
via Charmadi, Mudigere
Mudigere is a Town Panchayath and Taluk in Chikkamagaluru district in the Indian state of Karnataka. It is 30 km from the district headquarters.
Nearest airport is at Mangalore which is at a distance of . Mudigere is known for coffee and b ...
, Belur and Tiptur
Tiptur is a city in the southern part of the state of Karnataka, India. It is the second largest and the fastest growing city in Tumkur district. It is a sub-divisional headquarters of Tumkur district in Karnataka. Capital city Bengaluru is 1 ...
. Major ghat sections in Dakshina Kannada include Shiradi Ghat ( Nelyadi to Sakleshpura), Charmadi Ghat ( Charmadi to Kottigehara
{{Infobox settlement
, name = Kottigehara
, other_name =
, nickname =
, settlement_type = Village
, image_skyline = File:Kottigehara 2018.jpg
, image_alt =
, ...
), Sampaje Ghat ( Sampaje to Madikeri
Madikeri is a hill station town in Madikeri taluk and headquarters of Kodagu district in Karnataka, India.
Etymology
Madikeri was known as ''Muddu Raja Keri'', which meant Mudduraja's town, was named after the prominent Haleri king Mudduraj ...
) and Bisle Ghat (Subramanya to Sakleshpura, popularly known as Green Route
Green is the color between cyan and yellow on the visible spectrum. It is evoked by light which has a dominant wavelength of roughly 495570 Nanometre, nm. In subtractive color systems, used in painting and color printing, it is created by ...
by trekkers). NH-275 also connects Mangalore with Bangalore via Mysore. It starts at Bantwal
Bantwal () is a taluk in Dakshina Kannada district, Karnataka, India. It is located East of Mangalore city center. BC Road-Kaikamba of Bantwal is one of the fastest developing areas in Dakshina Kannada district of Karnataka.
Along with BC ...
near Mangalore city and passes through Puttur, Madikeri
Madikeri is a hill station town in Madikeri taluk and headquarters of Kodagu district in Karnataka, India.
Etymology
Madikeri was known as ''Muddu Raja Keri'', which meant Mudduraja's town, was named after the prominent Haleri king Mudduraj ...
, Hunsur
Hunsur is a city in Mysore district in the States and territories of India, Indian state of Karnataka. It is the headquarters of the Hunsur Taluk administrative division.
Geography
Hunsur is located at . Hunsur is situated on the western sid ...
, Mysore, Mandya and Channapatna. It ends at Bangalore
Bangalore (), List of renamed places in India, officially Bengaluru (), is the Capital city, capital and largest city of the Indian state of Karnataka. It has a population of more than and a metropolitan area, metropolitan population of a ...
spanning a length of .
In 1907, the Southern Railway connected Mangalore with Calicut (Kozhikode) along the coastline. This railway line helped connect the district with other places of the Madras presidency during the colonial rule
Colonialism is a practice or policy of control by one people or power over other people or areas, often by establishing colony, colonies and generally with the aim of economic dominance. In the process of colonisation, colonisers may impose the ...
. The Konkan Railway (1998) connects Dakshina Kannada with Maharashtra, Goa, Gujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the ninth ...
, Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, primarily its western or right bank, Delhi shares borders ...
, Rajasthan and Kerala
Kerala ( ; ) is a state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile regions of Cochin, Malabar, South ...
by train. There are direct trains from Mangalore
Mangalore (), officially known as Mangaluru, is a major port city of the Indian state of Karnataka. It is located between the Arabian Sea and the Western Ghats about west of Bangalore, the state capital, 20 km north of Karnataka–Ke ...
to Mumbai
Mumbai (, ; also known as Bombay — List of renamed Indian cities and states#Maharashtra, the official name until 1995) is the capital city of the Indian States and union territories of India, state of Maharashtra and the ''de facto'' fin ...
, Thane
Thane (; also known as Thana, the official name until 1996) is a metropolitan city in Maharashtra, India. It is situated in the north-eastern portion of the Salsette Island. Thane city is entirely within Thane taluka, one of the seven taluk ...
, Chennai
Chennai (, ), formerly known as Madras ( the official name until 1996), is the capital city of Tamil Nadu, the southernmost Indian state. The largest city of the state in area and population, Chennai is located on the Coromandel Coast of th ...
, Margao
Margao or Madgaon is the commercial capital of the Indian state of Goa. It stands on banks of the Sal river and is the administrative headquarters of Salcete sub-district and South Goa district. It is Goa's second largest city by population ...
and Trivandrum
Thiruvananthapuram (; ), also known by its former name Trivandrum (), is the capital of the Indian state of Kerala. It is the most populous city in Kerala with a population of 957,730 as of 2011. The encompassing urban agglomeration populatio ...
. Train services operate daily to Bangalore via Hassan and Kukke Subramanya
Kukke Subramanya (IAST: ''Kukke Subrahmaṇya'') is a Hindu temple located in the village Subramanya, of Kadaba taluk (Earlier in Sullia taluk) in Dakshina Kannada district, Karnataka, India. In this temple Kartikeya is worshipped as Subrama ...
after the conversion from metre gauge to broad gauge track.
The Dakshina Kannada district has a seaport
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as H ...
at Panambur named New Mangalore Port. The seaport managed by New Mangalore Port Trust handles cargo, timber, petroleum and coffee exports. It is one of the major seaports of India.
Historic sites and tourism
Dharmasthala
Dharmasthala (earlier known as Kuduma) is an Indian temple town on the banks of the Nethravathi River in the Belthangady taluk of the Dakshina Kannada district in Karnataka, India.
The town is known for its centuries old Dharmasthala Te ...
Image:Kukke Subramanya Swami.jpg, Kukke Subramanya
Kukke Subramanya (IAST: ''Kukke Subrahmaṇya'') is a Hindu temple located in the village Subramanya, of Kadaba taluk (Earlier in Sullia taluk) in Dakshina Kannada district, Karnataka, India. In this temple Kartikeya is worshipped as Subrama ...
Temple
Image:Kateel Durga Parameshwari 0145.JPG, Shree Durgaparameshwari Temple Kateel
Image:Dasara Navaratri decorations Kudroli Temple Mangalore Karnataka.jpg, Kudroli Temple in Mangalore
Image:Mangaladevi temple 1.jpg, Mangaladevi Temple
Image:St Aloysius College Admin block.jpg, St Aloysius College
Shree Amrutheshwara Temple
Vamanjoor: Temple of Lord Shiva. * Moodabidri: Site of the ancient Jain temples and the Bhattaraka seat. *
Krishnapura matha
The Krishnapur Matha ( kn, ಕೃಷ್ಣಾಪುರ ಮಠ कृष्णपुरा मठ ''Kr̥ṣṇāpura maṭha'') or Krishnapur Mutt in some records and literature is a Madhwa Vaishnavism, Vaishnava monastery. It is one of the Ash ...
: One of the matha (monastery) belonging to ashta matha of Udupi.
* Dharmasthala
Dharmasthala (earlier known as Kuduma) is an Indian temple town on the banks of the Nethravathi River in the Belthangady taluk of the Dakshina Kannada district in Karnataka, India.
The town is known for its centuries old Dharmasthala Te ...
: The temple of Lord Sri Manjunatheshwara is here.
* Kateel
Kateel or Kateelu is a temple town in the Dakshina Kannada district of the Indian state of Karnataka. It is considered one of the holiest Hindu temple towns in India. It is situated on the banks of the river Nandini.
Geography
It is about ...
: Temple of Goddess Sri Durga Parameshwari.
* Kadeshivalaya: Kadeshivalaya temple at Bantwal
* Carstreet: Sri Kalikamba Vinayaka Temple Mangaluru
Mangalore (), officially known as Mangaluru, is a major port city of the Indian state of Karnataka. It is located between the Arabian Sea and the Western Ghats about west of Bangalore, the state capital, 20 km north of Karnataka–Ker ...
.
* Kudroli: Gokarnanatheshwars Temple.
* Mundkur
Mundkur is a village in Karkala Taluk, Udupi district, Karnataka, India. The Durga Parameshwari temple located here was built circa 9th century AD.
Deities
The prime deity is Sri Durgaparameshwari in the form of Mahishamardini
Durg ...
: Sri Durga Parameshwari Temple.
* Karinjeshwara Temple
Sri Karinjeshwara Temple (Tulu: ''ಕಾರಿಂಜೇಶ್ವರ'' ''Kārin̄jēśvara'') is religious institution, a famous Lord Shiva temple located Karinja in Bantwala Taluk Dakshina Kannada, Karnataka, India. This temple is situated on ...
: Temple of Lord Shiva Parvati on a huge rock.
* Ullal: Known for the Ullal beach and Someshwara beach.
* Kukke Subramanya
Kukke Subramanya (IAST: ''Kukke Subrahmaṇya'') is a Hindu temple located in the village Subramanya, of Kadaba taluk (Earlier in Sullia taluk) in Dakshina Kannada district, Karnataka, India. In this temple Kartikeya is worshipped as Subrama ...
: Temple of the serpent Lord Subramanya is here.
* Mulki: Durgaparameshwari Temple.
* St Aloysius Chapel, Mangalore.
* Milagres Church, Mangalore
* Sayyed Madani Mosque and Dargah, Ullal.
* Sultan Battery, Mangalore
* Puttur: Temple of Lord Sri Mahalingeshwara is here.
* Uppinangadi: Sahasralingeshwara temple.
* Kepu, Ananthadi, Balnadu: Known for goddess Ullalthi temple and its unique heritage.
* Puttur karavadtha valiyullahi darga shareef
* Somanatheswar Temple: Someshwara, Ullal.
* Summer Sand Beach Resort at Ullal.
* Pilikula Nisargadhama: Pilikula, Moodushedde, Mangalore.
* Kudupu temple: Kudupu, Mangalore.
*Shri Rajarajeshwari Temple
Polali Rajarajeshwari Temple is a temple located in Polali, Dakshina Kannada district in Karnataka. The primary deity of the temple is ''Shri Rajarajeshwari''. The temple was constructed in the 8th century AD by King Suratha and has been develope ...
Polali: Temple of Shri Rajarajeshwari.
* Kumbladi Balasubrahmanya.
* Charvaka Kapileshwara Devasthaana.
* Shri Kshetra Daipila.
* Masjidu Thaqwa Pumpwell Mangalore.
* Bellye Palli (Big Masjid) Bunder Mangalore.
* Manjusha Car Museum, Dharmastala
* Srimanthi Bhai Memorial Government Museum
* Sawthadka Shri Mahaganapathi Temple.
;Nearby hill stations
Some of the hill stations in close proximity to this district corresponding to their elevation above sea level are Kudremukh peak , Pushpagiri , Madikeri
Madikeri is a hill station town in Madikeri taluk and headquarters of Kodagu district in Karnataka, India.
Etymology
Madikeri was known as ''Muddu Raja Keri'', which meant Mudduraja's town, was named after the prominent Haleri king Mudduraj ...
, Mudigere
Mudigere is a Town Panchayath and Taluk in Chikkamagaluru district in the Indian state of Karnataka. It is 30 km from the district headquarters.
Nearest airport is at Mangalore which is at a distance of . Mudigere is known for coffee and b ...
and Sakleshpur
Sakleshpur, Sakleshpura or Sakleshapura is a hill station town and headquarters of Sakleshpur taluk in Hassan district in the Indian state of Karnataka.
Economy
The town lies in the Malnad region on the hills of the biodiversity hotspot, the ...
.
Agriculture


Agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people t ...
, which was once a major occupation of the people of Dakshina Kannada, has taken a backseat because of the influx of money from natives settled in other cities, states and countries. Significant number of people from this district work in the Gulf (Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Province), East Thrace (Europ ...
) countries and other states of India. Farms and fields have been converted into residential plots and commercial (shopping) complexes around Mangalore city. Horticulture
Horticulture is the branch of agriculture that deals with the art, science, technology, and business of plant cultivation. It includes the cultivation of fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, herbs, sprouts, mushrooms, algae, flowers, seaweeds and no ...
, though, has made some strides, and measures have been taken to improve the fruit plantation sector. The main crops of Dakshina Kannada are Paddy, Coconut, Arecanut, Black Pepper
Black pepper (''Piper nigrum'') is a flowering vine in the family Piperaceae, cultivated for its fruit, known as a peppercorn, which is usually dried and used as a spice and seasoning. The fruit is a drupe (stonefruit) which is about in dia ...
, Cashew and Cocoa. Rice is generally cultivated three seasons in a year, ''Karthika'' or ''Yenel'' (May–October), ''Suggi'' (October to January) and ''Kolake'' (January to April). '' Urad'' (Black gram) is grown in some areas during the season of Suggi. The Karnataka Milk Federation
The Karnataka Milk Federation (KMF) is a dairy cooperative from Karnataka, India, which sells products such as milk, curds, ghee, butter, ice cream, cholocates, and sweets under the brand name Nandini.
It is a federation of milk producers under ...
has a milk processing plant at Kulshekar in Mangalore
Mangalore (), officially known as Mangaluru, is a major port city of the Indian state of Karnataka. It is located between the Arabian Sea and the Western Ghats about west of Bangalore, the state capital, 20 km north of Karnataka–Ke ...
. This plant processes milk procured from the cattle
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, cloven-hooved, herbivores. They are a prominent modern member of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus ''Bos''. Adult females are referred to as cows and adult ma ...
owned by farmers of the district.
Cuisine
 Some of the well-known
Some of the well-known Tuluva
The Tulu people or Tuluvas are an ethno-linguistic group from Southern India. They are native speakers of the Tulu language and the region they traditionally inhabit is known as Tulu Nadu. This region comprises the districts of Dakshina Kannada ...
community dishes in this district include Kori Rotti
Kori rotti is a spicy dish of Tulu Udupi- Mangalorean cuisine, a combination of red-chili and coconut milk based chicken curry and crisp, dry wafers made from boiled rice. ''Kori'' means chicken in Tulu.
See also
* List of chicken dishes
* ...
(dry rice flakes dipped in chicken gravy), Bangude Pulimunchi (spicy sour silver-grey mackerels), Beeja-Manoli Upkari, Neer dosa
Neer dosa, literally meaning water dosa in Tulu is a crêpe prepared from rice batter. Neer dosa is a delicacy from Tulu Nadu and part of Mangalorean cuisine.
Overview
''Neer'' is the word for water in Tulu and Kannada.
Unlike other dosas n ...
, Boothai Gasi and Kadubu. In Coastal Karnataka, the Mangalorean Fish Curry is a popular dish. The Konkani community's specialties include Daali thoy, Bibbe-upkari (cashew based), Val val, Avnas ambe sasam, Kadgi chakko, Paagila podi, Malpuri, Patrode
Patrode/Patrodo/Patra/Patrodu originally a vegetarian dish from India. It is also adapted in the Himachal Pradesh region, UP & Bihar as "Rikvach" and some other names in other parts of India. It is known as ,"Patrodé" in 'Tulunadu' region, Patr ...
and Chane gashi. Mangalore bajji
Golibaje (in Tulu) or Mangalore bajji (in Kannada) is an Indian fried food made from various flours and curd. In Tulu Nadu region, it is known as golibaje. Other names for the dish include Mangalore baje. This is widely famous in Andhra Pradesh a ...
, also known as Golibaje, is a popular snack made from maida, curd, rice flour
Rice flour (also rice powder) is a form of flour made from finely milled rice. It is distinct from rice starch, which is usually produced by steeping rice in lye. Rice flour is a common substitute for wheat flour. It is also used as a thickening ...
, chopped onion
An onion (''Allium cepa'' L., from Latin ''cepa'' meaning "onion"), also known as the bulb onion or common onion, is a vegetable that is the most widely cultivated species of the genus ''Allium''. The shallot is a botanical variety of the onio ...
, coriander leaves, coconut, cumin, green chillies, and salt
Salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl), a chemical compound belonging to the larger class of salts; salt in the form of a natural crystalline mineral is known as rock salt or halite. Salt is present in vast quant ...
. Tulu vegetarian cuisine in Mangalore, also known as Udupi cuisine
Udupi cuisine is a cuisine of South India. It forms an important part of Tuluva cuisine and takes its name from Udupi, a city on the southwest coast of India in the Tulunadu region. Udupi cuisine is strictly vegetarian and has its origin in th ...
, is known and liked throughout the state and the coastal region. Being a coastal district, fish forms the staple diet of most people.
The Beary community have their own unique dishes. ''Pattir'', ''Pole'', ''Pulchepole'', ''Kalthappa'', ''Aapa'', ''Neyyappa'', ''Neypathir'', ''Irmandappa'', ''Pindi'', ''Erchi pindi'', ''Kunji pindi'', and ''Vodupole'' are some of the traditional breakfasts and are primarily made from rice. Various dishes made from fresh or dried fish are also extensively consumed. Molavtanni made from lentils or sprouted pulses is the traditional soup usually eaten along with rice. Kakka is the traditional gravy made from fish,chicken,egg or mutton. Like in other coastal cuisine, coconut and its products form integral part of the Beary cuisine.
Mangalorean Catholics' Sanna-Dukra Maas ("Sanna" means Idli
Idli or idly () is a type of savoury rice cake, originating from the South India,popular as breakfast foods in Southern India and in Sri Lanka. The cakes are made by steaming a batter consisting of fermented black lentils (de-husked) and ric ...
fluffed with toddy or yeast and "Dukra Maas" means Pork) Pork Bafat and Sorpotel . Pickles such as Happala, Sandige and Puli munchi are unique to Mangalore.
Commerce and industry


 The district along with Udupi district is known as "The Cradle of Indian banking". Major nationalised banks of India such as Canara Bank, Corporation Bank,
The district along with Udupi district is known as "The Cradle of Indian banking". Major nationalised banks of India such as Canara Bank, Corporation Bank, Syndicate Bank
Syndicate Bank was one of the oldest and major commercial banks of India. It was founded by Upendra Ananth Pai, T. M. A. Pai and Vaman Srinivas Kudva. At the time of its establishment, the bank was known as Canara Industrial and Banking Syndi ...
, Vijaya Bank
Vijaya Bank was a PSU bank which was merged with Bank of Baroda on 1 April 2019 with its head office in Bangalore, Karnataka, India. It was one of the nationalised banks in India. The bank offered a wide range of financial products and service ...
and private sector Karnataka Bank evolved from these two districts.
Red clay tiles ( Mangalore Tiles), Cashew processing factories and Beedi
A beedi (also spelled bidi or biri) is a thin cigarette or mini-cigar filled with tobacco flake and commonly wrapped in a tendu (''Diospyros melanoxylon'') or ''Piliostigma racemosum'' leaf tied with a string or adhesive at one end. It origi ...
industry once flourished in this district.
Dakshina Kannada district has a per capita income of Rs. which is second only to Bangalore Urban district. Despite ranking 8th in the list of most populous districts in Karnataka, the district is the second largest contributor to the state's GSDP, with a contribution of 5.8%. In other words, despite a low population share of 3.4%, the district's share in state GSDP stands at 5.8%.
As the district is on the shore of the Arabian sea, fishing
Fishing is the activity of trying to catch fish. Fish are often caught as wildlife from the natural environment, but may also be caught from stocked bodies of water such as ponds, canals, park wetlands and reservoirs. Fishing techniques inclu ...
is one of the major occupation of many people. The major fishing places are Bunder (Old harbour), Panambur, Surathkal, Kotekar
Kotekar is a Town in Dakshina Kannada district of Karnataka state, India. It is on the way from Mangalore
Mangalore (), officially known as Mangaluru, is a major port city of the Indian state of Karnataka. It is located between the Arab ...
and Sasihitlu.
The major industries in Dakshina Kannada concentrated around Mangalore are Mangalore Chemical and Fertilizers Ltd. (MCF), Kudremukh Iron Ore Company Ltd. (KIOCL), The Canara Workshops Limited (manufacturers of Canara Springs), Mangalore Refinery and Petrochemicals Ltd. (MRPL), HPCL, BPCL, BASF
BASF SE () is a German multinational chemical company and the largest chemical producer in the world. Its headquarters is located in Ludwigshafen, Germany.
The BASF Group comprises subsidiaries and joint ventures in more than 80 countries ...
, TOTAL GAZ, Bharati Shipyard Limited (BSL) etc. There is a chocolate manufacturing plant at Puttur run by CAMPCO. Major information technology and outsourcing companies have their facilities in Mangalore namely Infosys, Cognizant
Cognizant is an American multinational information technology services and consulting company. It is headquartered in Teaneck, New Jersey, United States. Cognizant is part of the NASDAQ-100 and trades under CTSH. It was founded as an in-hous ...
, Atlantic Data Bureau Services Pvt. Ltd., Lasersoft infosystems Ltd., Mphasis BPO and Endurance International Group. Two IT parks have been constructed, one Export Promotion Industrial Park (EPIP) at Ganjimutt
Ganjimutt or Ganjimata is a town in Mangalore, Mangalore Taluk, central government will establish plastic park total coast 62.77 crores in 104 acreDakshina Kannada district, Karnataka state, West coast of India. It is almost 18 km east of M ...
and a second IT SEZ near Mangalore University
Mangalore University commonly known as, MU is a public university in Konaje, Mangaluru, Karnataka, India. In 2021, National Assessment and Accreditation Council (NAAC) awarded Mangalore University 'B' grade.
History
Mangalore University was e ...
. The Oil and Natural Gas Corporation (ONGC) plans to set up a multiproduct SEZ
A special economic zone (SEZ) is an area in which the business and trade laws are different from the rest of the country. SEZs are located within a country's national borders, and their aims include increasing trade balance, employment, increas ...
(Special Economic Zone) with an investment of over Rs. 350 billion.
Villages
See also
*Mangalore
Mangalore (), officially known as Mangaluru, is a major port city of the Indian state of Karnataka. It is located between the Arabian Sea and the Western Ghats about west of Bangalore, the state capital, 20 km north of Karnataka–Ke ...
* Economy of Mangalore
* Swami Vivekananda Planetarium
Swami Vivekananda Planetarium at Pilikula in Mangalore is the first 3D planetarium in India. It is also the first planetarium in the country with 8K digital and opto-mechanical (hybrid) projection system. The planetarium is at the Pilikula Reg ...
* U S Mallya Indoor Stadium
U S Mallya Indoor Stadium is situated at Mangalore in India. It offers sporting facilities for Badminton and Basketball
Basketball is a team sport in which two teams, most commonly of five players each, opposing one another on a rectangul ...
* Karnataka Urban Development and Coastal Environment Management Project (KUDCEMP)
* Centre for Entrepreneurship Opportunities and Learning (CEOL)
* South Kanara District Chess Association (SKDCA)
References
Further reading
* * * * * * * *External links
Official web site
DK Zilla Parishad
{{Karnataka topics Districts of Karnataka Tulu Nadu