Daimler-Benz DB 605 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Daimler-Benz DB 605 is a German aircraft engine built during
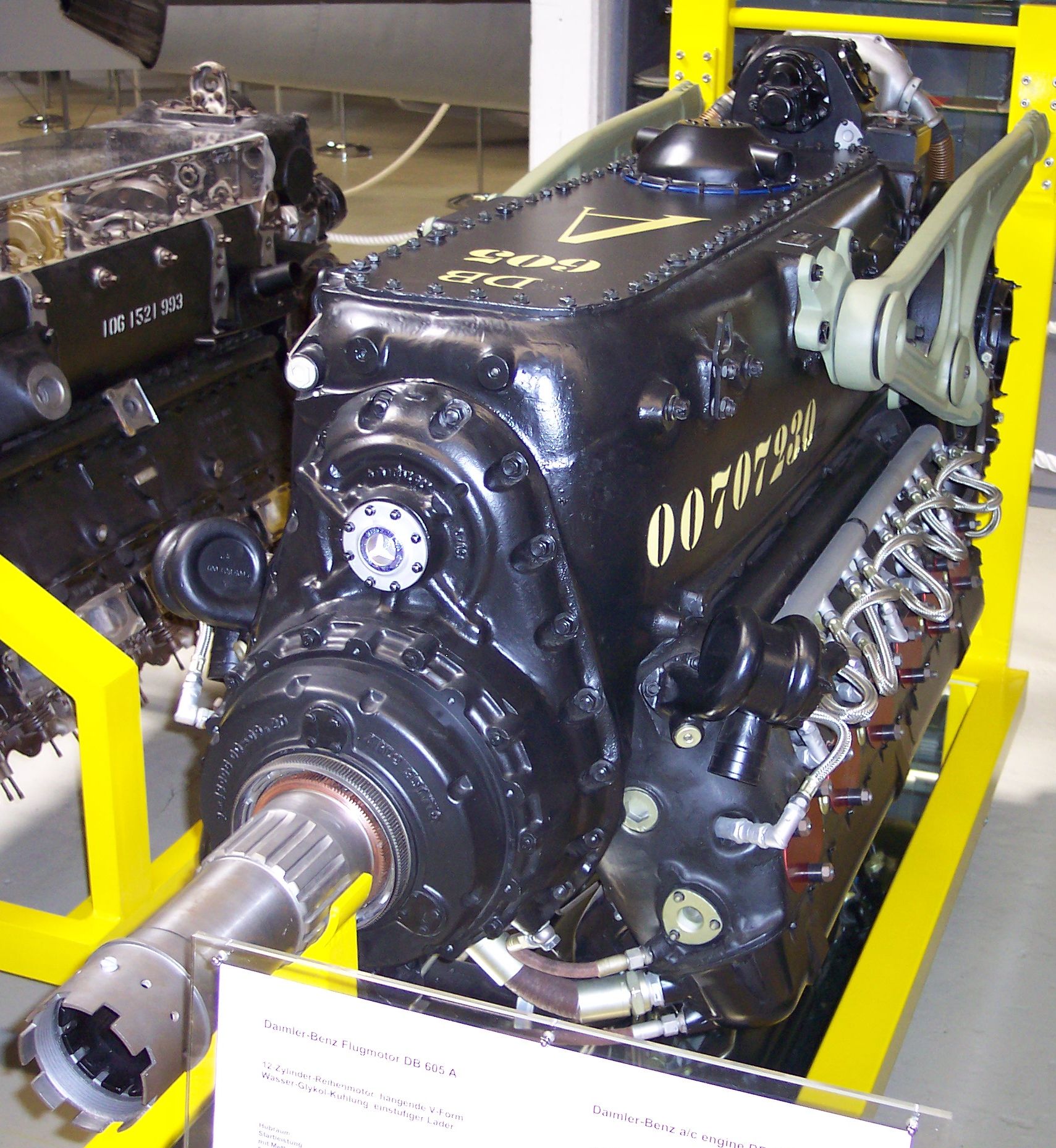 In other ways the engine was essentially identical to the 601, being an inverted V-12 (with the crankshaft above the cylinders). Both used dual Bosch
In other ways the engine was essentially identical to the 601, being an inverted V-12 (with the crankshaft above the cylinders). Both used dual Bosch  One major design difference was the switch from
One major design difference was the switch from

 ;DB 605A:Standard fighter engine, up to 1475 PS, B4 fuel
;DB 605AM:605 A with
;DB 605A:Standard fighter engine, up to 1475 PS, B4 fuel
;DB 605AM:605 A with
National Air and Space Museum

Aviation History.com, DB 600 series page
Website on Messerschmitt Bf 109 performance.
{{Daimler-Benz aeroengines Daimler-Benz aircraft engines 1940s aircraft piston engines Inverted V12 aircraft engines
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
. Developed from the DB 601, the DB 605 was used from 1942 to 1945 in the Messerschmitt Bf 109 fighter, and the Bf 110
The Messerschmitt Bf 110, often known unofficially as the Me 110,Because it was built before ''Bayerische Flugzeugwerke'' became Messerschmitt AG in July 1938, the Bf 110 was never officially given the designation Me 110. is a twin-engine (Des ...
and Me 210C heavy fighters.
The DB 610, a pair of DB 605s geared to turn a single output shaft that replaced the similar DB 606, was used in the A-3 and all A-5 variants of Germany's only operational heavy bomber, the Heinkel He 177
The Heinkel He 177 ''Greif'' (Griffin) was a long-range heavy bomber flown by the ''Luftwaffe'' during World War II. The introduction of the He 177 to combat operations was significantly delayed, by both problems with the development of its ...
A.
License-built versions of the DB 605 were used in the Macchi C.205
The Macchi C.205 ''Veltro'' ( it, Greyhound) (also known as MC.205, "MC" standing for "Macchi Castoldi") was an Italian World War II fighter aircraft built by the Aeronautica Macchi. Along with the Reggiane Re.2005 and Fiat G.55, the Macchi C.205 ...
, Fiat G.55
The Fiat G.55 ''Centauro'' (Italian: " Centaur") was a single-engine single-seat World War II fighter aircraft used by the '' Regia Aeronautica'' and the ''Aeronautica Nazionale Repubblicana'' in 1943–1945. It was designed and built in Turin b ...
, Reggiane 2005 and some other Italian aircraft. It was also used in the Swedish SAAB B 18B and initially in the pusher-design SAAB J 21. Approximately 42,400 DB 605s of all kinds were built.
Design and development
The primary differences between the 605 and 601 were greater displacement, higher revolutions, higher compression ratio and a more powerful supercharger. Engineers determined that the cylinders could be bored out to a larger diameter without seriously affecting the strength of the existing block. The change was small, increasing the cylinder bore from the 601's 150 mm to the 605's 154 mm, but this increased the overall displacement from 33.9 litres to 35.7. Altered valve timing increased the inlet period and improved the scavenging to give greatervolumetric efficiency Volumetric efficiency (VE) in internal combustion engine engineering is defined as the ratio of the mass density of the air-fuel mixture drawn into the cylinder at atmospheric pressure (during the intake stroke) to the mass density of the same volu ...
at higher speeds, which improved the maximum allowable RPM from 2,600 in the 601 to 2,800 in the 605. The combination of these changes raised power output from 1,350 PS (1,332 hp) to 1,475 PS (1,455 hp). Engine weight increased from 700 to 756 kg.
 In other ways the engine was essentially identical to the 601, being an inverted V-12 (with the crankshaft above the cylinders). Both used dual Bosch
In other ways the engine was essentially identical to the 601, being an inverted V-12 (with the crankshaft above the cylinders). Both used dual Bosch magneto
A magneto is an electrical generator that uses permanent magnets to produce periodic pulses of alternating current. Unlike a dynamo, a magneto does not contain a commutator to produce direct current. It is categorized as a form of alternator, ...
s firing twin spark plugs for ignition. Bosch direct fuel injection was powered by a pump supplying up to 90 bar. The oil system used three pumps with a separate 35-litre oil tank. The supercharger was advanced for the era in that it used a barometrically controlled hydraulic clutch (fluid coupling
A fluid coupling or hydraulic coupling is a hydrodynamic or 'hydrokinetic' device used to transmit rotating mechanical power.
) which allowed the system automatically to compensate for changes in altitude.
 One major design difference was the switch from
One major design difference was the switch from ball bearing
A ball bearing is a type of rolling-element bearing that uses balls to maintain the separation between the bearing races.
The purpose of a ball bearing is to reduce rotational friction and support radial and axial loads. It achieves this ...
s to plain bearing
A plain bearing, or more commonly sliding contact bearing and slide bearing (in railroading sometimes called a solid bearing, journal bearing, or friction bearing), is the simplest type of bearing, comprising just a bearing surface and no roll ...
s which, when combined with increasingly poor grades of lubricants, led to serious problems in service, including engine fires; initially, for example, the use of emergency power was forbidden. Although Daimler-Benz redesigned the bearings and added oil slingers and their associated coolers, the RLM considered the DB 605 to be a "sick engine" and the problems had not been fully resolved by the end of the war.
Along with bearing difficulties, the DB 605 suffered particularly badly from the materials shortages in wartime Germany. From the outbreak of war onwards critical shortages of elements such as nickel and cobalt meant that the DB 605 had its exhaust valves reduced in nickel content from about 13.5% to 8%. This resulted in them becoming insufficiently corrosion resistant, and they began to scale in use. This scale then caused pre-ignition, which led to catastrophic detonation and eventually engine failure. This was the primary reason that the full 1.42 ata manifold pressure was not permitted, although the problems occurred for a long time before the official order restricting the power level was given (Jumo and BMW suffered exactly the same problem for some time). This was eventually fixed by applying a very heavy chrome plating to the exhaust valves, which rendered them just sufficiently resistant to scaling while still using less of a critical element than the original nickel alloy. BMW had developed this plating technique first, as the BMW 801 in the Fw 190 had also been suffering from a spate of detonation induced engine failures.
Like the 601, the 605 was designed to run on "B4" fuel with an octane rating of 87. In 1944 a series of newer engines was introduced, allowing the engine to run on the 100 octane "C3" fuel and optionally including fittings for various optional power-boosting agent dispensing systems, such as the MW50
MW 50 (Methanol-''Wasser'' 50) was a 50-50 mixture of methanol and water (German: ''Wasser'') that was often sprayed into the supercharger of World War II aircraft engines primarily for its anti-detonation effect, allowing the use of increased ...
methanol-water injection system, and GM-1
{{unreferenced, date=September 2008
GM-1 (''Göring Mischung'' 1) was a system for injecting nitrous oxide (laughing gas) into aircraft engines that was used by the ''Luftwaffe'' in World War II. This increased the amount of oxygen in the fuel mi ...
nitrous oxide
Nitrous oxide (dinitrogen oxide or dinitrogen monoxide), commonly known as laughing gas, nitrous, or nos, is a chemical compound, an oxide of nitrogen with the formula . At room temperature, it is a colourless non-flammable gas, and has ...
injection system. The DB 605AM, running initially on C3 and MW-50, saw power improved to 1,800 PS (1775 hp) for takeoff. In mid-1944, the requirement for C3 was dropped and standard B4 fuel with MW-50 was used. The DB 605AS(M) improved the maximum rated altitude by using a larger supercharger taken from the DB 603
The Daimler-Benz DB 603 was a German aircraft engine used during World War II. It was a liquid-cooled 12-cylinder inverted V12 enlargement of the DB 601, which was in itself a development of the DB 600. Production of the DB 603 commenced in ...
but was otherwise similar to the A(M). The DB 605ASB's takeoff power was also rated at 1,800 PS (1,775 hp), while maintaining the high-altitude performance of the ASM. The final version of the A-series was the DB 605ASC of 1945, which improved takeoff power to 2,000 PS (1,973 hp).
As early as 1942 Daimler had also been working on an upgraded D-series engine that could run on either C2 or C3 fuel. The first of these, which appeared in late 1944, was a small series of DB 605DM, followed by the main production series, the DB 605DB/DC.Mermet 1999, p. 19. These engines were fitted with an adjustable screw stop which allowed the use of either B4 fuel with MW-50, or C-3 fuel without MW-50, in which case the engine was designated DB 605DB, or the use of C-3 fuel with MW-50, in which case the engine was given the -DC suffix instead. In its DB-suffix form the engine generated 1,800 PS (1,775 hp) for take-off at 1.8 ata, while the DC was capable of 2,000 PS (1,973 hp) at 1.98 ata.Hitchcock 1979, p. 34 If MW-50 was not available for use with the B4 fuel the throttle was limited to 1.45 ata for the entire flight. Thus, this series was ideally suited to catering for the chaotic fuel supply situation prevalent during the last months of the Third Reich. These engines were mainly used in the Bf 109G-10 and K-4 series.
An unusual application of the DB 605 was its installation in a captured Supermarine Spitfire. In November 1942, Spitfire VB ''EN830'' ''NX-X'' of 131 Squadron made a forced landing in a turnip field in German-occupied Jersey
Jersey ( , ; nrf, Jèrri, label= Jèrriais ), officially the Bailiwick of Jersey (french: Bailliage de Jersey, links=no; Jèrriais: ), is an island country and self-governing Crown Dependency near the coast of north-west France. It is the l ...
. The plane was repaired by German forces and re-engined with a DB 605A, amongst other modifications. The aircraft was operated by the Luftwaffe until 14 August 1944, when it was destroyed during a USAAF
The United States Army Air Forces (USAAF or AAF) was the major land-based aerial warfare service component of the United States Army and ''de facto'' aerial warfare service branch of the United States during and immediately after World War II ...
bombing raid.
Variants
;Production versions
 ;DB 605A:Standard fighter engine, up to 1475 PS, B4 fuel
;DB 605AM:605 A with
;DB 605A:Standard fighter engine, up to 1475 PS, B4 fuel
;DB 605AM:605 A with MW-50
MW 50 (Methanol-''Wasser'' 50) was a 50-50 mixture of methanol and water (German: ''Wasser'') that was often sprayed into the supercharger of World War II aircraft engines primarily for its anti-detonation effect, allowing the use of increased ...
system, up to 1800 PS, C3 fuel
;DB 605AS:Altitude optimized version of 605A using the larger DB 603
The Daimler-Benz DB 603 was a German aircraft engine used during World War II. It was a liquid-cooled 12-cylinder inverted V12 enlargement of the DB 601, which was in itself a development of the DB 600. Production of the DB 603 commenced in ...
supercharger, up to 1435 PS, B4 fuel
;DB 605ASM:605 AS with MW-50 system, up to 1800 PS, C3 fuel
;DB 605ASB/605AB:late-war version, first version up to 1850 PS, later reduced to 1800 PS, B4 fuel with MW-50 or C3 fuel without MW-50
;DB 605ASC:late-war version, up to 2000 PS with MW-50, C3 fuel
;DB 605B:Same as 605 A but for use in twin-engined aircraft like Messerschmitt Bf 110
The Messerschmitt Bf 110, often known unofficially as the Me 110,Because it was built before ''Bayerische Flugzeugwerke'' became Messerschmitt AG in July 1938, the Bf 110 was never officially given the designation Me 110. is a twin-engine (Des ...
, Me 210
The Messerschmitt Me 210 was a German heavy fighter and ground-attack aircraft of World War II. Design started before the war, as a replacement for the Bf 110. The first examples were ready in 1939, but they proved to have unacceptably poor f ...
(different prop/gear ratio)
;DB 605BS:proposed version for twin-engined aircraft, derived from DB 605 AS
;DB 605DB:Improved 605 DM, standard MW-50 equipment, first version up to 1850 PS, later reduced to 1800 PS, B4 fuel with MW-50 or C3 fuel without MW-50
;DB 605DC:Improved 605 DM, standard MW-50 equipment, up to 2000 PS, C3 fuel
;DB 605DM:First DB 605 D version, standard MW-50 equipment, up to 1700 PS
;DB 605E:proposed version for twin-engined aircraft, derived from DB 605 D
;DB 605T: Developed to drive the HZ Anlage supercharger for the Henschel Hs 130
;DB 605 L:Similar to 605 D but with two-stage supercharger, 1700 PS, development stopped in December 1944
;Fiat RA.1050 R.C.58 Tifone:Licence built / developed DB 605A-1 engines, built by Fiat in Italy.
;DB 610:Two DB 605s "coupled" (geared together) as a "power system" (71.53L / 4364.8in3), to turn a single propeller shaft, used in the Heinkel He 177
The Heinkel He 177 ''Greif'' (Griffin) was a long-range heavy bomber flown by the ''Luftwaffe'' during World War II. The introduction of the He 177 to combat operations was significantly delayed, by both problems with the development of its ...
A Mirror-imaged starboard component engine supercharger.
::DB 610A - Propeller RH rotation - Reduction ratio 0.413: 1.
:::Take-off and emergency power of at 2,800 rpm with 1.2 atmos. boost at sea level.
:::: at 2,800 rpm with 1.42 atmos. boost at .
:::Climbing at 2,600 rpm with 1.3 atmos. boost at sea level.
:::: at 2,600 rpm with 1.3 atmos. boost at .
:::Maximum cruising at 2,300 rpm with 1.15 atmos. boost at sea level.
:::: at 2,300 rpm with 1.15 atmos. boost at .
:::Fuel consumption (max cruise at sea level).
:::Total length ; width ; height ; weight .
::DB 610B - Propeller LH rotation - Weight
::DB 610C - Propeller RH rotation
:::Take-off and emergency power of at 2,800 rpm at sea level.
:::: at 2,800 rpm at .
:::Climbing at 2,600 rpm at sea level.
:::: at 2,600 rpm at .
:::Maximum cruising at 2,300 rpm at sea level.
:::: at 2,300 rpm at .
::DB 610D - Propeller LH rotation
;DB 616:A development of the DB 605.
;DB 620:Coupled DB628 engines.
;DB 621:A projected two-stage supercharged DB605
;DB 625:A turbocharged DB605
;DB 628:The DB 605, fitted with a two-stage supercharger, abandoned in March 1944.
;IAR DB605:Licence production in Romania by Industria Aeronautică Română
Industria Aeronautică Română (IAR) (now IAR S.A. Brașov) or Romanian Aeronautic Industry in English, is a Romanian aerospace manufacturer. It is based in Ghimbav, near Brașov, Romania.
IAR was founded in 1925 with the aid of the Romanian g ...
(IAR).
Note: All power ratings in PS (metric horsepower). Unless otherwise noted takeoff/emergency power at sea level.
Survivors
AHispano Aviación HA-1112
The Hispano Aviación HA-1109 and HA-1112 are licence-built versions of the Messerschmitt Bf 109G-2 developed in Spain during and after World War II.
Design and development
In 1942, the Spanish government arranged a manufacturing licence with ...
, a license-built Messerschmitt Bf 109 G-2, has been rebuilt by EADS/ Messerschmitt Foundation in Germany with a Daimler-Benz DB 605 engine.
Applications
DB 605 *Caproni Campini Ca.183bis
The Caproni-Campini Ca.183bis was an Italian projected high-altitude fighter intended to have both piston and jet propulsion.
Design and development
The Ca.183bis was intended to have a Daimler-Benz DB 605 in the nose driving a six-bladed contr ...
(intended)
*Fiat G.55
The Fiat G.55 ''Centauro'' (Italian: " Centaur") was a single-engine single-seat World War II fighter aircraft used by the '' Regia Aeronautica'' and the ''Aeronautica Nazionale Repubblicana'' in 1943–1945. It was designed and built in Turin b ...
* IAR 471
*Macchi C.205
The Macchi C.205 ''Veltro'' ( it, Greyhound) (also known as MC.205, "MC" standing for "Macchi Castoldi") was an Italian World War II fighter aircraft built by the Aeronautica Macchi. Along with the Reggiane Re.2005 and Fiat G.55, the Macchi C.205 ...
* Messerschmitt Bf 109G/K
* Messerschmitt Bf 110G
*Messerschmitt Me 210
The Messerschmitt Me 210 was a German heavy fighter and ground-attack aircraft of World War II. Design started before the war, as a replacement for the Bf 110. The first examples were ready in 1939, but they proved to have unacceptably poor ...
*Reggiane Re.2005
The Reggiane Re.2005 ' ( en, Archer, Sagittarius) was an Italian monoplane fighter and fighter-bomber produced for the ''Regia Aeronautica'' during the later years of World War II. Along with the Macchi C.202/ C.205 and Fiat G.55, the Reggiane ...
* Saab 18B, T
* Saab 21
* Savoia-Marchetti SM.91
* Savoia-Marchetti SM.92
*Savoia-Marchetti SM.93
The Savoia-Marchetti SM.93 was an Italian dive bomber designed and produced in Italy from 1943.
Design
The SM-93 was an all-wood single-engined low-wing monoplane with retractable undercarriage. The fuselage had a monocoque structure, with a si ...
*VL Pyörremyrsky
The VL Pyörremyrsky ("Hurricane") was a Finnish fighter, designed by DI Torsti Verkkola at the State Aircraft Factory ('' Valtion lentokonetehdas'') for service with the Finnish Air Force in World War II. The war ended before the type's first fli ...
DB 610
* Dornier Do 317B
*Heinkel He 177
The Heinkel He 177 ''Greif'' (Griffin) was a long-range heavy bomber flown by the ''Luftwaffe'' during World War II. The introduction of the He 177 to combat operations was significantly delayed, by both problems with the development of its ...
A-3 and A-5
* Messerschmitt Me 261V3
* SNCAC NC.3021 Belphégor
Engines on display
Preserved DB 605 engines are on display at theRoyal Air Force Museum
The Royal Air Force Museum is a museum dedicated to the Royal Air Force in the United Kingdom. The museum is a non-departmental public body of the Ministry of Defence and is a registered charity.
The museum is split into two separate sites:
* ...
, London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
and thNational Air and Space Museum
Washington D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, Na ...
Specifications (DB 605AM)

See also
References
Notes
Bibliography
* * * Gregor, Neil ''Daimler-Benz in the Third Reich''. Yale University Press, 1998 * * ''Jane's Fighting Aircraft of World War II''. London. Studio Editions Ltd, 1989. * Hermann, Dietmar and Ringlstetter, Herbert. ''Messerschmitt Bf 109 : Vom Prototyp bis zur Bf 109 K''. München, GER: GeraMond Verlag, 2017. * Hitchcock, Thomas. ''Bf 109K: Monogram Close-Up 16''.Boylston MA: Monogram Aviation Publications, 1979. * Mankau, Heinz and Peter Petrick. ''Messerschmitt Bf 110/Me 210/Me 410: An Illustrated History''. Atglen PA: Schiffer Publishing Ltd., 2003. * Mermet, Jean-Claude. ''Messerschmitt Bf 109G-1 through K-4: Engines and Fittings''. Marnaz, France: Jean-Claude Mermet SA, 1999. * Smith, J Richard and Eddie J. Creek. ''Heinkel He 177 Greif: Heinkel's Strategic Bomber''. Hersham, Surrey, UK: Ian Allan Publishing, 2012.External links
Aviation History.com, DB 600 series page
Website on Messerschmitt Bf 109 performance.
{{Daimler-Benz aeroengines Daimler-Benz aircraft engines 1940s aircraft piston engines Inverted V12 aircraft engines