Cyanogen bromide on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cyanogen bromide is the
2 NaCN + Br2 -> (CN)2 + 2 NaBr
:(CN)2 + Br2 -> 2 (CN)Br
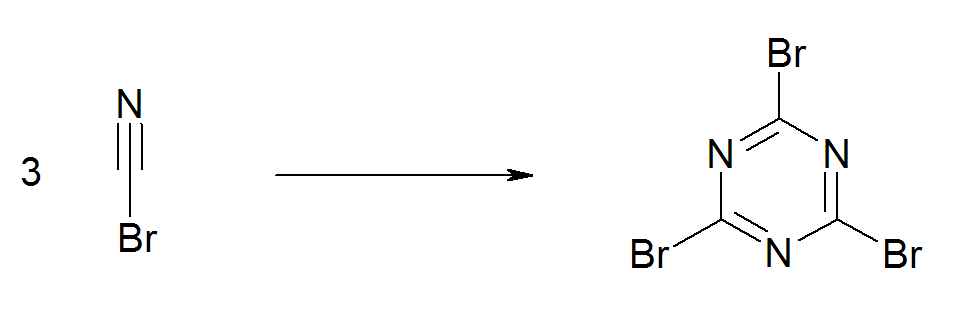
When refrigerated the material has an extended shelflife. Like some other cyanogen compounds, cyanogen bromide undergoes an exothermic trimerisation to cyanuric bromide (). This reaction is catalyzed by traces of bromine, metal salts, acids and bases. For this reason, experimentalists avoid brownish samples.
: Cyanogen bromide is hydrolyzed to release hydrogen cyanide and
Cyanogen bromide is hydrolyzed to release hydrogen cyanide and (CN)Br + H2O -> HCN + HOBr
 The
The
inorganic compound
In chemistry, an inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bonds, that is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as '' inorganic chemis ...
with the formula
In science, a formula is a concise way of expressing information symbolically, as in a mathematical formula or a ''chemical formula''. The informal use of the term ''formula'' in science refers to the general construct of a relationship betwe ...
(CN)Br or BrCN. It is a colorless solid that is widely used to modify biopolymer
Biopolymers are natural polymers produced by the cells of living organisms. Like other polymers, biopolymers consist of monomeric units that are covalently bonded in chains to form larger molecules. There are three main classes of biopolymers, ...
s, fragment protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
s and peptide
Peptides (, ) are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Long chains of amino acids are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides. ...
s (cuts the C-terminus of methionine), and synthesize other compounds. The compound is classified as a pseudohalogen
Pseudohalogens are polyatomic analogues of halogens, whose chemistry, resembling that of the true halogens, allows them to substitute for halogens in several classes of chemical compounds. Pseudohalogens occur in pseudohalogen molecules, inorganic ...
.
Synthesis, basic properties, and structure
Thecarbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon ma ...
atom in cyanogen bromide is bonded to bromine
Bromine is a chemical element with the symbol Br and atomic number 35. It is the third-lightest element in group 17 of the periodic table ( halogens) and is a volatile red-brown liquid at room temperature that evaporates readily to form a simi ...
by a single bond and to nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at se ...
by a triple bond
A triple bond in chemistry is a chemical bond between two atoms involving six bonding electrons instead of the usual two in a covalent single bond. Triple bonds are stronger than the equivalent single bonds or double bonds, with a bond order o ...
(i.e. ). The compound is linear and polar, but it does not spontaneously ionize in water. It dissolves in both water and polar organic solvent
A solvent (s) (from the Latin '' solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas, or a supercritical fluid. Water is a solvent for ...
s.
Cyanogen bromide can be prepared by oxidation
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a ...
of sodium cyanide
Sodium cyanide is a poisonous compound with the formula Na C N. It is a white, water-soluble solid. Cyanide has a high affinity for metals, which leads to the high toxicity of this salt. Its main application, in gold mining, also exploits its hi ...
with bromine
Bromine is a chemical element with the symbol Br and atomic number 35. It is the third-lightest element in group 17 of the periodic table ( halogens) and is a volatile red-brown liquid at room temperature that evaporates readily to form a simi ...
, which proceeds in two steps via the intermediate cyanogen
Cyanogen is the chemical compound with the formula ( C N)2. It is a colorless and highly toxic gas with a pungent odor. The molecule is a pseudohalogen. Cyanogen molecules consist of two CN groups – analogous to diatomic halogen molecu ...
():
:hypobromous acid
Hypobromous acid is a weak, unstable acid with chemical formula of HOBr. It is mainly produced and handled in an aqueous solution. It is generated both biologically and commercially as a disinfectant. Salts of hypobromite are rarely isolated a ...
:Biochemical applications
The main uses of cyanogen bromide are to immobilize proteins, fragment proteins by cleaving peptide bonds, and synthesizecyanamide
Cyanamide is an organic compound with the formula C N2 H2. This white solid is widely used in agriculture and the production of pharmaceuticals and other organic compounds. It is also used as an alcohol-deterrent drug. The molecule features a ...
s and other molecules.
Protein immobilization
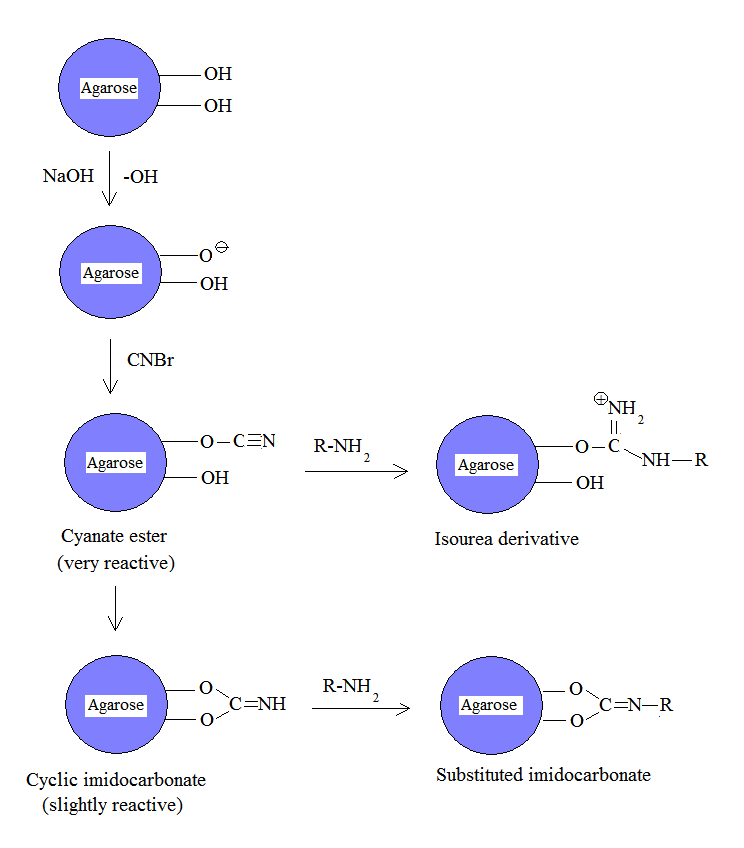
Cyanogen bromide is often used to immobilize proteins by coupling them to reagents such asagarose
Agarose is a heteropolysaccharide, generally extracted from certain red seaweed. It is a linear polymer made up of the repeating unit of agarobiose, which is a disaccharide made up of D-galactose and 3,6-anhydro-L-galactopyranose. Agarose is ...
for affinity chromatography
Affinity chromatography is a method of separating a biomolecule from a mixture, based on a highly specific macromolecular binding interaction between the biomolecule and another substance. The specific type of binding interaction depends on the ...
. Because of its simplicity and mild pH conditions, cyanogen bromide activation is the most common method for preparing affinity gels. Cyanogen bromide is also often used because it reacts with the hydroxyl
In chemistry, a hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group with the chemical formula and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. In organic chemistry, alcohols and carboxylic acids contain one or more hydro ...
groups on agarose to form cyanate
Cyanate is an anion with the structural formula , usually written . It also refers to any salt containing it, such as ammonium cyanate.
It is an isomer of the much less stable fulminate anion .William R. Martin and David W. Ball (2019): "Sma ...
ester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an oxoacid (organic or inorganic) in which at least one hydroxyl group () is replaced by an alkoxy group (), as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides a ...
s and imidocarbonates. These groups are reacted with primary amine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such ...
s in order to couple the protein onto the agarose matrix, as shown in the figure. Because cyanate esters are more reactive than are cyclic imidocarbonates, the amine will react mostly with the ester, yielding isourea derivatives, and partially with the less reactive imidocarbonate, yielding substituted imidocarbonates.
The disadvantages of this approach include the toxicity of cyanogen bromide and its sensitivity to oxidation. Also, cyanogen bromide activation involves the attachment of a ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule ( functional group) that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's elec ...
to agarose by an isourea bond, which is positively charged at neutral pH and thus unstable. Consequently, isourea derivatives may act as weak anion exchanger
Ion exchange is a reversible interchange of one kind of ion present in an insoluble solid with another of like charge present in a solution surrounding the solid with the reaction being used especially for softening or making water demineralised, ...
s.
Protein cleavage
Cyanogen bromide hydrolyzes peptide bonds at the C-terminus of methionine residues. This reaction is used to reduce the size of polypeptide segments for identification and sequencing.Mechanism
 The
The electron density
In quantum chemistry, electron density or electronic density is the measure of the probability of an electron being present at an infinitesimal element of space surrounding any given point. It is a scalar quantity depending upon three spatial va ...
in cyanogen bromide is shifted away from the carbon atom, making it unusually electrophilic, and towards the more electronegative
Electronegativity, symbolized as , is the tendency for an atom of a given chemical element to attract shared electrons (or electron density) when forming a chemical bond. An atom's electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the d ...
bromine and nitrogen. This leaves the carbon particularly vulnerable to attack by a nucleophile, and the cleavage reaction begins with a nucleophilic acyl substitution
Nucleophilic acyl substitution describe a class of substitution reactions involving nucleophiles and acyl compounds. In this type of reaction, a nucleophile – such as an alcohol, amine, or enolate – displaces the leaving group of an acyl deriv ...
reaction in which bromine is ultimately replaced by the sulfur in methionine. This attack is followed by the formation of a five-membered ring as opposed to a six-membered ring, which would entail the formation of a double bond
In chemistry, a double bond is a covalent bond between two atoms involving four bonding electrons as opposed to two in a single bond. Double bonds occur most commonly between two carbon atoms, for example in alkenes. Many double bonds exist betwee ...
in the ring between nitrogen and carbon. This double bond would result in a rigid ring conformation, thereby destabilizing the molecule. Thus, the five-membered ring is formed so that the double bond is outside the ring, as shown in the figure.
Although the nucleophilic sulfur in methionine is responsible for attacking BrCN, the sulfur in cysteine does not behave similarly. If the sulfur in cysteine attacked cyanogen bromide, the bromide ion would deprotonate the cyanide adduct
An adduct (from the Latin ''adductus'', "drawn toward" alternatively, a contraction of "addition product") is a product of a direct addition of two or more distinct molecules, resulting in a single reaction product containing all atoms of all co ...
, leaving the sulfur uncharged and the beta carbon of the cysteine not electrophilic. The strongest electrophile would then be the cyanide nitrogen, which, if attacked by water, would yield cyanic acid
Isocyanic acid is a chemical compound with the structural formula HNCO, which is often written as . It is a colourless, volatile and poisonous substance, with a boiling point of 23.5 °C. It is the predominant tautomer of cyanic acid ().
...
and the original cysteine.
Reaction conditions
Cleaving proteins with BrCN requires using abuffer
Buffer may refer to:
Science
* Buffer gas, an inert or nonflammable gas
* Buffer solution, a solution used to prevent changes in pH
* Buffering agent, the weak acid or base in a buffer solution
* Lysis buffer, in cell biology
* Metal ion buffer
* ...
such as 0.1M HCl (hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride. It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungent smell. It is classified as a strong acid
Acid strength is the tendency of an acid, symbol ...
) or 70% ( formic acid). These are the most common buffers for cleavage. An advantage to HCl is that formic acid causes the formation of formyl esters, which complicates protein characterization. However, formic is still often used because it dissolves most proteins. Also, the oxidation of methionine to methionine sulfoxide, which is inert to BrCN attack, occurs more readily in HCl than in formic acid, possibly because formic acid is a reducing acid. Alternative buffers for cleavage include guanidine
Guanidine is the compound with the formula HNC(NH2)2. It is a colourless solid that dissolves in polar solvents. It is a strong base that is used in the production of plastics and explosives. It is found in urine predominantly in patients experie ...
or urea
Urea, also known as carbamide, is an organic compound with chemical formula . This amide has two amino groups (–) joined by a carbonyl functional group (–C(=O)–). It is thus the simplest amide of carbamic acid.
Urea serves an important ...
in HCl because of their ability to unfold proteins, thereby making methionine more accessible to BrCN.
Note that water is required for normal peptide bond cleavage of the iminolactone intermediate. In formic acid, cleavage of Met-Ser
Ser or SER may refer to:
Places
* Ser, a village in Bogdand Commune, Satu Mare County, Romania
* Serpens (Ser), an astronomical constellation of the northern hemisphere
* Serres, known as Ser in Serbian, a city in Macedonia, Greece
Organization ...
and Met- Thr bonds is enhanced with increased water concentration because these conditions favor the addition of water across the imine
In organic chemistry, an imine ( or ) is a functional group or organic compound containing a carbon–nitrogen double bond (). The nitrogen atom can be attached to a hydrogen or an organic group (R). The carbon atom has two additional single bon ...
rather than reaction of the side chain hydroxyl with the imine. Lowered pH tends to increase cleavage rates by inhibiting methionine side chain oxidation.
Side reactions
When methionine is followed by serine or threonine, side reactions can occur that destroy the methionine without peptide bond cleavage. Normally, once the iminolactone is formed (refer to figure), water and acid can react with the imine to cleave the peptide bond, forming a homoserine lactone and new C-terminal peptide. However, if the adjacent amino acid to methionine has ahydroxyl
In chemistry, a hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group with the chemical formula and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. In organic chemistry, alcohols and carboxylic acids contain one or more hydro ...
or sulfhydryl group, this group can react with the imine to form a homoserine without peptide bond cleavage. These two cases are shown in the figure.
Organic synthesis
Cyanogen bromide is a common reagent in organic synthesis. As stated earlier, the reagent is prone to attack by nucleophiles such as amines and alcohols because of the electrophilic carbon. In the synthesis ofcyanamide
Cyanamide is an organic compound with the formula C N2 H2. This white solid is widely used in agriculture and the production of pharmaceuticals and other organic compounds. It is also used as an alcohol-deterrent drug. The molecule features a ...
s and dicyanamide
Dicyanamide, also known as dicyanamine, is an anion having the formula . It contains two cyanide groups bound to a central nitrogen anion. The chemical is formed by decomposition of 2-cyanoguanidine. It is used extensively as a counterion of org ...
s, primary and secondary amines react with BrCN to yield mono- and dialkylcyanamides, which can further react with amines and hydroxylamine
Hydroxylamine is an inorganic compound with the formula . The material is a white crystalline, hygroscopic compound.Greenwood and Earnshaw. ''Chemistry of the Elements.'' 2nd Edition. Reed Educational and Professional Publishing Ltd. pp. 431–43 ...
to yield guanidine
Guanidine is the compound with the formula HNC(NH2)2. It is a colourless solid that dissolves in polar solvents. It is a strong base that is used in the production of plastics and explosives. It is found in urine predominantly in patients experie ...
s and hydroxyguanidines. In the von Braun reaction
The von Braun reaction is an organic reaction in which a tertiary amine reacts with cyanogen bromide to an organocyanamide.
An example is the reaction of ''N'',''N''-dimethyl-1-naphthylamine:
These days, most chemist have replaced cyanogen ...
, tertiary amines react with BrCN to yield disubstituted cyanamides and an alkyl bromide. Cyanogen bromide can be used to prepare aryl
In organic chemistry, an aryl is any functional group or substituent derived from an aromaticity, aromatic ring, usually an aromatic hydrocarbon, such as phenyl and naphthyl. "Aryl" is used for the sake of abbreviation or generalization, and "Ar ...
nitriles, nitriles, anhydride
An organic acid anhydride is an acid anhydride that is an organic compound. An acid anhydride is a compound that has two acyl groups bonded to the same oxygen atom. A common type of organic acid anhydride is a carboxylic anhydride, where the pa ...
s, and cyanate
Cyanate is an anion with the structural formula , usually written . It also refers to any salt containing it, such as ammonium cyanate.
It is an isomer of the much less stable fulminate anion .William R. Martin and David W. Ball (2019): "Sma ...
s. It can also serve as a cleaving agent.
Cyanogen bromide is used in the synthesis of 4-methylaminorex
4-Methylaminorex (4-MAR, 4-MAX) is a stimulant drug of the 2-amino-5-aryloxazoline class that was first synthesized in 1960 by McNeil Laboratories. It is also known by its street name "U4Euh" ("Euphoria"). It is banned in many countries as a s ...
("ice") and viroxime.
Toxicity, storage, and deactivation
Cyanogen bromide can be stored under dry conditions at 2 to 8 °C for extended periods. Cyanogen bromide is volatile, and readily absorbed through theskin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different de ...
or gastrointestinal tract. Therefore, toxic exposure may occur by inhalation, physical contact, or ingestion. It is acutely toxic, causing a variety of nonspecific symptoms
Signs and symptoms are the observed or detectable signs, and experienced symptoms of an illness, injury, or condition. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than normal, raised or lowered blood pressure or an abnormality showin ...
. Exposure to even small amounts may cause convulsions or death. LD50 orally in rats is reported as 25–50 mg/kg.
The recommended method to deactivate cyanogen bromide is with sodium hydroxide and bleach. The aqueous alkali hydroxide instantly hydrolyzes (CN)Br to alkali cyanide and bromide. The cyanide can then be oxidized by sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na (from Latin ''natrium'') and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable ...
or calcium hypochlorite to the less toxic cyanate ion. Note that deactivation is extremely exothermic and may be explosive.
References
Further reading
* *External links
* * {{Cyanides Bromine compounds Cyano compounds Nonmetal halides Blood agents Lachrymatory agents Pseudohalogens