Cyanogen on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cyanogen is the
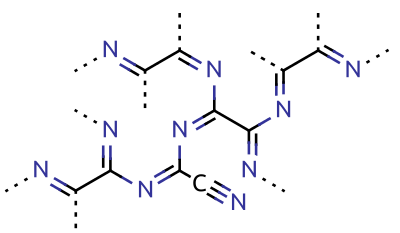 Paracyanogen is a polymer of cyanogen. It can be best prepared by heating mercuric cyanide. It can also be prepared by heating silver cyanide,
Paracyanogen is a polymer of cyanogen. It can be best prepared by heating mercuric cyanide. It can also be prepared by heating silver cyanide,
National Pollutant Inventory - Cyanide compounds fact sheet
{{Authority control Alkanedinitriles Pseudohalogens Blood agents Lachrymatory agents
chemical compound
A chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules (or molecular entities) containing atoms from more than one chemical element held together by chemical bonds. A molecule consisting of atoms of only one element ...
with the formula ( C N)2. It is a colorless and highly toxic
Toxicity is the degree to which a chemical substance or a particular mixture of substances can damage an organism. Toxicity can refer to the effect on a whole organism, such as an animal, bacterium, or plant, as well as the effect on a subs ...
gas
Gas is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, liquid, and plasma).
A pure gas may be made up of individual atoms (e.g. a noble gas like neon), elemental molecules made from one type of atom (e.g. oxygen), or ...
with a pungent
Pungency () refers to the taste of food commonly referred to as spiciness, hotness or heat, found in foods such as chili peppers. Highly pungent tastes may be experienced as unpleasant. The term piquancy () is sometimes applied to foods with a l ...
odor. The molecule is a pseudohalogen. Cyanogen molecules consist of two CN groups – analogous to diatomic halogen molecules, such as Cl2, but far less oxidizing. The two cyano groups are bonded together at their carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon mak ...
atoms: N≡C‒ C≡N, although other isomers have been detected. The name is also used for the CN radical, and hence is used for compounds such as cyanogen bromide
Cyanogen bromide is the inorganic compound with the formula (CN)Br or BrCN. It is a colorless solid that is widely used to modify biopolymers, fragment proteins and peptides (cuts the C-terminus of methionine), and synthesize other compounds. ...
(NCBr) (but see also '' Cyano radical''.)
Cyanogen is the anhydride
An organic acid anhydride is an acid anhydride that is an organic compound. An acid anhydride is a compound that has two acyl groups bonded to the same oxygen atom. A common type of organic acid anhydride is a carboxylic anhydride, where the pa ...
of oxamide:
:H2NC(O)C(O)NH2 → NCCN + 2 H2O
although oxamide is manufactured from cyanogen by hydrolysis:
:NCCN + 2 H2O → H2NC(O)C(O)NH2
Preparation
Cyanogen is typically generated from cyanide compounds. One laboratory method entails thermal decomposition of mercuric cyanide: :2 Hg(CN)2 → (CN)2 + Hg2(CN)2 Alternatively, one can combine solutions of copper(II) salts (such ascopper(II) sulfate
Copper(II) sulfate, also known as copper sulphate, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It forms hydrates , where ''n'' can range from 1 to 7. The pentahydrate (''n'' = 5), a bright blue crystal, is the most commonly encountered h ...
) with cyanides; an unstable copper(II) cyanide is formed which rapidly decomposes into copper(I) cyanide
Copper(I) cyanide is an inorganic compound with the formula CuCN. This off-white solid occurs in two polymorphs; impure samples can be green due to the presence of Cu(II) impurities. The compound is useful as a catalyst, in electroplating copper ...
and cyanogen.
:2 CuSO4 + 4 KCN → (CN)2 + 2 CuCN + 2 K2SO4
Industrially, it is created by the oxidation
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a ...
of hydrogen cyanide, usually using chlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element with the symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between them. Chlorine i ...
over an activated silicon dioxide
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is one ...
catalyst
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recyc ...
or nitrogen dioxide
Nitrogen dioxide is a chemical compound with the formula . It is one of several nitrogen oxides. is an intermediate in the industrial synthesis of nitric acid, millions of tons of which are produced each year for use primarily in the productio ...
over a copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkis ...
salt. It is also formed when nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at se ...
and acetylene are reacted by an electrical spark or discharge.
Isomers
Cyanogen is NCCN. There are less stable isomers in which the order of the atoms differs. Isocyanogen (or cyanoisocyanogen) is NCNC, diisocyanogen is CNNC, and diazodicarbon is CCNN.Paracyanogen
 Paracyanogen is a polymer of cyanogen. It can be best prepared by heating mercuric cyanide. It can also be prepared by heating silver cyanide,
Paracyanogen is a polymer of cyanogen. It can be best prepared by heating mercuric cyanide. It can also be prepared by heating silver cyanide, silver cyanate
Silver cyanate is the cyanate salt of silver
Silver is a chemical element with the symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transit ...
, cyanogen iodide
Cyanogen iodide or iodine cyanide (ICN) is a pseudohalogen composed of iodine and the cyanide group. It is a highly toxic inorganic compound. It occurs as white crystals that react slowly with water to form hydrogen cyanide.
Synthesis
Cyanogen io ...
or cyanuric iodide. It can also be prepared by the polymerization of cyanogen at in the presence of trace impurities. Paracyanogen can also be converted back to cyanogen by heating to . Based on experimental evidence, the structure of this polymeric material is thought to be rather irregular, with most of the carbon atoms being of sp2 type and localized domains of π conjugation.
History
Cyanogen was first synthesized in 1815 byJoseph Louis Gay-Lussac
Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac (, , ; 6 December 1778 – 9 May 1850) was a French chemist and physicist. He is known mostly for his discovery that water is made of two parts hydrogen and one part oxygen (with Alexander von Humboldt), for two laws ...
, who determined its empirical formula and named it. Gay-Lussac coined the word "cyanogène" from the Greek words κυανός (kyanos, blue) and γεννάω (gennao, I create), because cyanide was first isolated by the Swedish chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele
Carl Wilhelm Scheele (, ; 9 December 1742 – 21 May 1786) was a Swedish German pharmaceutical chemist.
Scheele discovered oxygen (although Joseph Priestley published his findings first), and identified molybdenum, tungsten, barium, hyd ...
from the pigment "Prussian blue
Prussian blue (also known as Berlin blue, Brandenburg blue or, in painting, Parisian or Paris blue) is a dark blue pigment produced by oxidation of ferrous ferrocyanide salts. It has the chemical formula Fe CN)">Cyanide.html" ;"title="e(Cyani ...
".
By the 1850s, cyanogen soap
Soap is a salt of a fatty acid used in a variety of cleansing and lubricating products. In a domestic setting, soaps are surfactants usually used for washing, bathing, and other types of housekeeping. In industrial settings, soaps are use ...
was used by photographers
A photographer (the Greek φῶς (''phos''), meaning "light", and γραφή (''graphê''), meaning "drawing, writing", together meaning "drawing with light") is a person who makes photographs.
Duties and types of photographers
As in other ...
to remove silver
Silver is a chemical element with the symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical ...
stains from their hands.
It attained importance with the growth of the fertilizer
A fertilizer (American English) or fertiliser (British English; see spelling differences) is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from ...
industry in the late 19th century and remains an important intermediate in the production of many fertilizers. It is also used as a stabilizer in the production of nitrocellulose
Nitrocellulose (also known as cellulose nitrate, flash paper, flash cotton, guncotton, pyroxylin and flash string, depending on form) is a highly flammable compound formed by nitrating cellulose through exposure to a mixture of nitric acid and ...
.
In 1910 a spectroscopic
Spectroscopy is the field of study that measures and interprets the electromagnetic spectra that result from the interaction between electromagnetic radiation and matter as a function of the wavelength or frequency of the radiation. Matter wa ...
analysis of Halley's Comet
Halley's Comet or Comet Halley, officially designated 1P/Halley, is a short-period comet visible from Earth every 75–79 years. Halley is the only known short-period comet that is regularly visible to the naked eye from Earth, and thus the on ...
found cyanogen in the comet's tail, which led to public fear that the Earth would be poisoned as it passed through the tail. Because of the extremely diffuse nature of the tail, there was no effect when the planet passed through it.
Safety
Like othercyanide
Cyanide is a naturally occurring, rapidly acting, toxic chemical that can exist in many different forms.
In chemistry, a cyanide () is a chemical compound that contains a functional group. This group, known as the cyano group, consists of ...
s, cyanogen is very toxic, as it readily undergoes reduction to cyanide, which poisons the cytochrome c oxidase
The enzyme cytochrome c oxidase or Complex IV, (was , now reclassified as a translocasEC 7.1.1.9 is a large transmembrane protein complex found in bacteria, archaea, and mitochondria of eukaryotes.
It is the last enzyme in the respiratory elect ...
complex, thus interrupting the mitochondrial electron transfer chain
An electron transport chain (ETC) is a series of protein complexes and other molecules that transfer electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors via redox reactions (both reduction and oxidation occurring simultaneously) and couples thi ...
. Cyanogen gas is an irritant to the eyes and respiratory system. Inhalation can lead to headache, dizziness, rapid pulse, nausea, vomiting, loss of consciousness, convulsions, and death, depending on exposure.
Lethal dose through inhalation typically ranges from .
Cyanogen produces the second-hottest-known natural flame (after carbon subnitride) with a temperature of over when it burns in oxygen.
In popular culture
In the '' Doctor Who'' serial "The Brain of Morbius
''The Brain of Morbius'' is the fifth serial of the 13th season of the British science fiction television series ''Doctor Who'', which was first broadcast in four weekly parts on BBC1 from 3 to 24 January 1976. The screenwriter credit is given ...
" (the 5th serial of season 13), the Doctor synthesizes cyanogen using hydrogen cyanide as a starting material and vents it through a pipe to stop Solon from performing surgery on the brain of Morbius's body, however he completes it but shortly after dies of cyanogen poisoning.
In '' Dragnet'' (1987) Friday (Dan Aykroyd) and Streebek (Tom Hanks) are tracking down the villain who stole "the pseudohalogenic compound cyanogen".
See also
* PseudohalogenReferences
External links
National Pollutant Inventory - Cyanide compounds fact sheet
{{Authority control Alkanedinitriles Pseudohalogens Blood agents Lachrymatory agents