Current sea-level rise on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Globally,
Globally,
Summary for Policymakers
In
IPCC Special Report on the Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate
.-O. Pörtner, D.C. Roberts, V. Masson-Delmotte, P. Zhai, M. Tignor, E. Poloczanska, K. Mintenbeck, A. Alegría, M. Nicolai, A. Okem, J. Petzold, B. Rama, N.M. Weyer (eds.) Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK and New York, NY, USA. https://doi.org/10.1017/9781009157964.001. This rate is accelerating, with sea levels now rising by 3.7 mm per year.
Summary for Policymakers
In
Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
[Masson-Delmotte, V., P. Zhai, A. Pirani, S.L. Connors, C. Péan, S. Berger, N. Caud, Y. Chen, L. Goldfarb, M.I. Gomis, M. Huang, K. Leitzell, E. Lonnoy, J.B.R. Matthews, T.K. Maycock, T. Waterfield, O. Yelekçi, R. Yu, and B. Zhou (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 3−32, doi:10.1017/9781009157896.001. Sea level rise has a substantial lag in its response to Earth temperature changes. This means that it is virtually certain to continue for a long time, and that its extent in the short term (i.e. around 2050) is insensitive to temperature changes between now and then. Thus, there's confidence that 2050 levels of sea level rise combined with the 2010 population distribution (i.e. absent the effects of
Chapter 15: Small islands
I
Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability
.-O. Pörtner, D.C. Roberts, M. Tignor, E.S. Poloczanska, K. Mintenbeck, A. Alegría, M. Craig, S. Langsdorf, S. Löschke,V. Möller, A. Okem, B. Rama (eds.) Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 2043–2121 , doi=10.1017/9781009325844.017 Societies can adapt to sea level rise in three different ways: implement managed retreat, accommodate coastal change, or protect against sea level rise through hard-construction practices like seawalls or soft approaches such as dune rehabilitation and beach nourishment. Sometimes these adaptation strategies go hand in hand, but at other times choices have to be made among different strategies. For instance, a managed retreat strategy is difficult if the population in the area is quickly increasing: this is a particularly acute problem for Africa, where the population of low-lying coastal areas is projected to increase by around 100 million people within the next 40 years.Trisos, C.H., I.O. Adelekan, E. Totin, A. Ayanlade, J. Efitre, A. Gemeda, K. Kalaba, C. Lennard, C. Masao, Y. Mgaya, G. Ngaruiya, D. Olago, N.P. Simpson, and S. Zakieldeen 2022
Chapter 9: Africa
I
Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability
.-O. Pörtner, D.C. Roberts, M. Tignor, E.S. Poloczanska, K. Mintenbeck, A. Alegría, M. Craig, S. Langsdorf, S. Löschke,V. Möller, A. Okem, B. Rama (eds.) Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 2043–2121 , doi=10.1017/9781009325844.011 Poorer nations may also struggle to implement the same approaches to adapt to sea level rise as richer states, and sea level rise at some locations may be compounded by other environmental issues, such as
 There are broadly two ways of modelling sea level rise and making future projections. In one approach, scientists use process-based modelling, where all relevant and well-understood physical processes are included in a global physical model. An
There are broadly two ways of modelling sea level rise and making future projections. In one approach, scientists use process-based modelling, where all relevant and well-understood physical processes are included in a global physical model. An
Chapter 9: Ocean, Cryosphere and Sea Level Change
I
Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
[Masson-Delmotte, V., P. Zhai, A. Pirani, S.L. Connors, C. Péan, S. Berger, N. Caud, Y. Chen, L. Goldfarb, M.I. Gomis, M. Huang, K. Leitzell, E. Lonnoy, J.B.R. Matthews, T.K. Maycock, T. Waterfield, O. Yelekçi, R. Yu, and B. Zhou (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 1211–1362, doi:10.1017/9781009157896.011. This could lead to a faster-than-projected collapse of marine ice shelves and the abrupt, widespread onset of
 There is a widespread consensus among climate scientists that sea level rise lags well behind the temperature increase that triggers it, and that substantial long-term sea level rise will continue for centuries to come even if the temperature stabilizes.
Models are able to reproduce paleo records of sea level rise, which provides confidence in their application to long-term future change.
Both the Greenland ice sheet and Antarctica have tipping points for warming levels that could be reached before the end of the 21st century. Crossing such tipping points would mean that ice-sheet changes are potentially irreversible: a decrease to pre-industrial temperatures may not stabilize the ice sheet once the tipping point has been crossed. Quantifying the exact temperature change for which this tipping point is crossed remains controversial. For Greenland, estimates roughly range between 1 and 4 °C (2 to 7 °F) above pre-industrial. , the lower of these values has already been passed. A 2021 analysis of sub-glacial sediment at the bottom of a 1.4 km Greenland ice core finds that the Greenland ice sheet melted away at least once during the last million years. Since the maximum positive temperature excursion over that period is 2.5 °C, this strongly suggests that its tipping point is below that value and therefore within the lower half of its range of estimates. Melting of the
There is a widespread consensus among climate scientists that sea level rise lags well behind the temperature increase that triggers it, and that substantial long-term sea level rise will continue for centuries to come even if the temperature stabilizes.
Models are able to reproduce paleo records of sea level rise, which provides confidence in their application to long-term future change.
Both the Greenland ice sheet and Antarctica have tipping points for warming levels that could be reached before the end of the 21st century. Crossing such tipping points would mean that ice-sheet changes are potentially irreversible: a decrease to pre-industrial temperatures may not stabilize the ice sheet once the tipping point has been crossed. Quantifying the exact temperature change for which this tipping point is crossed remains controversial. For Greenland, estimates roughly range between 1 and 4 °C (2 to 7 °F) above pre-industrial. , the lower of these values has already been passed. A 2021 analysis of sub-glacial sediment at the bottom of a 1.4 km Greenland ice core finds that the Greenland ice sheet melted away at least once during the last million years. Since the maximum positive temperature excursion over that period is 2.5 °C, this strongly suggests that its tipping point is below that value and therefore within the lower half of its range of estimates. Melting of the
 The three main reasons warming causes global sea level to rise are: oceans expand, ice sheets lose ice faster than it forms from snowfall, and glaciers at higher altitudes also melt. Sea level rise since the start of the 20th century has been dominated by retreat of glaciers and expansion of the ocean, but the contributions of the two large ice sheets (Greenland and Antarctica) are expected to increase in the 21st century. The ice sheets store most of the land ice (∼99.5%), with a sea-level equivalent (SLE) of for Greenland and for Antarctica.
Each year about of precipitation (liquid equivalent) falls on the ice sheets in Antarctica and Greenland, mostly as snow, which accumulates and over time forms glacial ice. Much of this precipitation began as water vapor evaporated from the ocean surface. Some of the snow is blown away by wind or disappears from the ice sheet by melt or by
The three main reasons warming causes global sea level to rise are: oceans expand, ice sheets lose ice faster than it forms from snowfall, and glaciers at higher altitudes also melt. Sea level rise since the start of the 20th century has been dominated by retreat of glaciers and expansion of the ocean, but the contributions of the two large ice sheets (Greenland and Antarctica) are expected to increase in the 21st century. The ice sheets store most of the land ice (∼99.5%), with a sea-level equivalent (SLE) of for Greenland and for Antarctica.
Each year about of precipitation (liquid equivalent) falls on the ice sheets in Antarctica and Greenland, mostly as snow, which accumulates and over time forms glacial ice. Much of this precipitation began as water vapor evaporated from the ocean surface. Some of the snow is blown away by wind or disappears from the ice sheet by melt or by
 Most of the additional heat trapped in the Earth's climate system by climate change is stored in oceans. They store more than 90% of the extra heat and act as a buffer against the effects of climate change. The heat needed to raise an average temperature increase of the entire world ocean by 0.01 °C would increase the atmospheric temperature by approximately 10 °C: a small change in the mean temperature of the ocean represents a very large change in the total heat content of the climate system.
When the ocean gains heat, the water expands and sea level rises. The amount of expansion varies with both water temperature and pressure. For each degree, warmer water and water under great pressure (due to depth) expand more than cooler water and water under less pressure. Consequently cold Arctic Ocean water will expand less than warm tropical water. Because different climate models present slightly different patterns of ocean heating, their predictions do not agree fully on the contribution of ocean heating to sea level rise. Heat gets transported into deeper parts of the ocean by winds and currents, and some of it reaches depths of more than .
Considering an increase in average global temperature of 2 °C above preindustrial levels, and not considering the potential contributions from ice-sheet processes with limited agreement (low confidence) among modeling approaches, the probability of exceeding 0.5 m rise of sea level globally (0.7 m along the CONUS coastline) by 2100 is about 50%. With 3–5 °C of warming under high emissions pathways, this probability rises to >80% to >99%.
Most of the additional heat trapped in the Earth's climate system by climate change is stored in oceans. They store more than 90% of the extra heat and act as a buffer against the effects of climate change. The heat needed to raise an average temperature increase of the entire world ocean by 0.01 °C would increase the atmospheric temperature by approximately 10 °C: a small change in the mean temperature of the ocean represents a very large change in the total heat content of the climate system.
When the ocean gains heat, the water expands and sea level rises. The amount of expansion varies with both water temperature and pressure. For each degree, warmer water and water under great pressure (due to depth) expand more than cooler water and water under less pressure. Consequently cold Arctic Ocean water will expand less than warm tropical water. Because different climate models present slightly different patterns of ocean heating, their predictions do not agree fully on the contribution of ocean heating to sea level rise. Heat gets transported into deeper parts of the ocean by winds and currents, and some of it reaches depths of more than .
Considering an increase in average global temperature of 2 °C above preindustrial levels, and not considering the potential contributions from ice-sheet processes with limited agreement (low confidence) among modeling approaches, the probability of exceeding 0.5 m rise of sea level globally (0.7 m along the CONUS coastline) by 2100 is about 50%. With 3–5 °C of warming under high emissions pathways, this probability rises to >80% to >99%.
 The large volume of ice on the Antarctic continent stores around 70% of the world's fresh water. The Antarctic ice sheet mass balance is affected by snowfall accumulations, and ice discharge along the periphery. Under the influence of global warming, melt at the base of the ice sheet increases. Simultaneously, the capacity of the atmosphere to carry precipitation increases with temperature so that precipitation, in the form of snowfall, increases in global and regional models. The additional snowfall causes increased ice flow of the ice sheet into the ocean, so that the mass gain due to snowfall is partially compensated. Snowfall increased over the last two centuries, but no increase was found in the interior of Antarctica over the last four decades. Based on changes of Antarctica's ice mass balance over millions of years, due to natural climate fluctuations, researchers concluded that the sea-ice acts as a barrier for warmer waters surrounding the continent. Consequently, the loss of sea ice is a major driver of the instability of the entire ice sheet.
The large volume of ice on the Antarctic continent stores around 70% of the world's fresh water. The Antarctic ice sheet mass balance is affected by snowfall accumulations, and ice discharge along the periphery. Under the influence of global warming, melt at the base of the ice sheet increases. Simultaneously, the capacity of the atmosphere to carry precipitation increases with temperature so that precipitation, in the form of snowfall, increases in global and regional models. The additional snowfall causes increased ice flow of the ice sheet into the ocean, so that the mass gain due to snowfall is partially compensated. Snowfall increased over the last two centuries, but no increase was found in the interior of Antarctica over the last four decades. Based on changes of Antarctica's ice mass balance over millions of years, due to natural climate fluctuations, researchers concluded that the sea-ice acts as a barrier for warmer waters surrounding the continent. Consequently, the loss of sea ice is a major driver of the instability of the entire ice sheet.
 Different satellite methods for measuring ice mass and change are in good agreement, and combining methods leads to more certainty about how the East Antarctic Ice Sheet, the West Antarctic Ice Sheet, and the
Different satellite methods for measuring ice mass and change are in good agreement, and combining methods leads to more certainty about how the East Antarctic Ice Sheet, the West Antarctic Ice Sheet, and the
 Most ice on Greenland is part of the
Most ice on Greenland is part of the
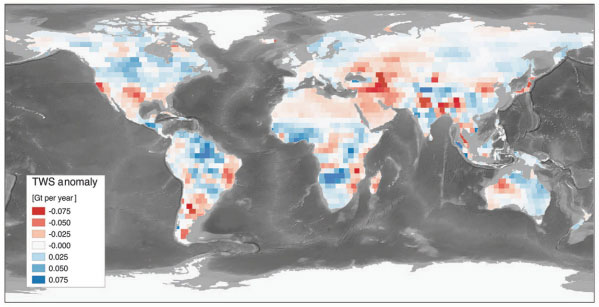 Humans impact how much water is stored on land. Building dams prevents large masses of water from flowing into the sea and therefore increases the storage of water on land. On the other hand, humans extract water from lakes, wetlands and underground reservoirs for food production leading to rising seas. Furthermore, the
Humans impact how much water is stored on land. Building dams prevents large masses of water from flowing into the sea and therefore increases the storage of water on land. On the other hand, humans extract water from lakes, wetlands and underground reservoirs for food production leading to rising seas. Furthermore, the
 Since the launch of
Since the launch of
 The global network of tide gauges is another important source of sea-level observations. Compared to the satellite record, this record has major spatial gaps but covers a much longer period of time. Coverage of tide gauges started primarily in the Northern Hemisphere, with data for the Southern Hemisphere remaining scarce up to the 1970s. The longest running sea-level measurements, NAP or Amsterdam Ordnance Datum established in 1675, are recorded in Amsterdam, the Netherlands. In Australia record collection is also quite extensive, including measurements by an amateur meteorologist beginning in 1837 and measurements taken from a sea-level benchmark struck on a small cliff on the Isle of the Dead near the Port Arthur convict settlement in 1841.
This network was used, in combination with satellite altimeter data, to establish that global mean sea-level rose between 1870 and 2004 at an average rate of about 1.44 mm/yr (1.7 mm/yr during the 20th century). Data collected by the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO) in
The global network of tide gauges is another important source of sea-level observations. Compared to the satellite record, this record has major spatial gaps but covers a much longer period of time. Coverage of tide gauges started primarily in the Northern Hemisphere, with data for the Southern Hemisphere remaining scarce up to the 1970s. The longest running sea-level measurements, NAP or Amsterdam Ordnance Datum established in 1675, are recorded in Amsterdam, the Netherlands. In Australia record collection is also quite extensive, including measurements by an amateur meteorologist beginning in 1837 and measurements taken from a sea-level benchmark struck on a small cliff on the Isle of the Dead near the Port Arthur convict settlement in 1841.
This network was used, in combination with satellite altimeter data, to establish that global mean sea-level rose between 1870 and 2004 at an average rate of about 1.44 mm/yr (1.7 mm/yr during the 20th century). Data collected by the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO) in
 Current and future sea level rise is set to have a number of impacts, particularly on coastal systems. Such impacts include higher and more frequent high-tide and storm-surge flooding, increased coastal erosion, inhibition of primary production processes, more extensive coastal inundation, changes in surface water quality and groundwater characteristics. This is projected in turn to increase loss of property and coastal habitats, increased flood risk and potential loss of life, loss of non-monetary cultural resources and values, impacts on agriculture and
Current and future sea level rise is set to have a number of impacts, particularly on coastal systems. Such impacts include higher and more frequent high-tide and storm-surge flooding, increased coastal erosion, inhibition of primary production processes, more extensive coastal inundation, changes in surface water quality and groundwater characteristics. This is projected in turn to increase loss of property and coastal habitats, increased flood risk and potential loss of life, loss of non-monetary cultural resources and values, impacts on agriculture and
 Coastal ecosystems are facing drastic changes as a consequence of rising sea levels. Many systems might ultimately be lost when sea levels rise too much or too fast. Some ecosystems can move land inward with the high-water mark, but many are prevented from migrating due to natural or artificial barriers. This coastal narrowing, sometimes called 'coastal squeeze' when considering human-made barriers, could result in the loss of habitats such as
Coastal ecosystems are facing drastic changes as a consequence of rising sea levels. Many systems might ultimately be lost when sea levels rise too much or too fast. Some ecosystems can move land inward with the high-water mark, but many are prevented from migrating due to natural or artificial barriers. This coastal narrowing, sometimes called 'coastal squeeze' when considering human-made barriers, could result in the loss of habitats such as

 In Africa, risk from sea level rise is amplified by the future
In Africa, risk from sea level rise is amplified by the future  In the longer term, Egypt, Mozambique and Tanzania are also projected to have the largest number of people affected by annual flooding amongst all African countries if global warming reaches 4 °C by the end of the century (a level associated with the RCP 8.5 scenario). Under RCP 8.5, 10 important cultural sites (
In the longer term, Egypt, Mozambique and Tanzania are also projected to have the largest number of people affected by annual flooding amongst all African countries if global warming reaches 4 °C by the end of the century (a level associated with the RCP 8.5 scenario). Under RCP 8.5, 10 important cultural sites (
 Globally,
Globally, sea levels
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical datuma standardised g ...
are rising due to human-caused climate change. Between 1901 and 2018, the globally averaged sea level rose by , or 1–2 mm per year on average.IPCC, 2019Summary for Policymakers
In
IPCC Special Report on the Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate
.-O. Pörtner, D.C. Roberts, V. Masson-Delmotte, P. Zhai, M. Tignor, E. Poloczanska, K. Mintenbeck, A. Alegría, M. Nicolai, A. Okem, J. Petzold, B. Rama, N.M. Weyer (eds.) Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK and New York, NY, USA. https://doi.org/10.1017/9781009157964.001. This rate is accelerating, with sea levels now rising by 3.7 mm per year.
Climate scientists
This list of climate scientists contains famous or otherwise notable persons who have contributed to the study of climate science. The list is compiled manually, so will not be complete, up to date, or comprehensive. See also :Climatologists. ...
expect further acceleration during the 21st century. Climate change heats (and therefore expands) the ocean and melts land-based ice sheets and glaciers. Between 1993 and 2018, the thermal expansion of water contributed 42% to sea level rise; melting of temperate glacier
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such as ...
s, 21%; Greenland, 15%; and Antarctica, 8%. Over the next 2000 years, the sea level is predicted to rise by if global warming is limited to 1.5°C, by if it peaks at 2°C and by if it peaks at 5 °C.IPCC, 2021Summary for Policymakers
In
Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
[Masson-Delmotte, V., P. Zhai, A. Pirani, S.L. Connors, C. Péan, S. Berger, N. Caud, Y. Chen, L. Goldfarb, M.I. Gomis, M. Huang, K. Leitzell, E. Lonnoy, J.B.R. Matthews, T.K. Maycock, T. Waterfield, O. Yelekçi, R. Yu, and B. Zhou (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 3−32, doi:10.1017/9781009157896.001. Sea level rise has a substantial lag in its response to Earth temperature changes. This means that it is virtually certain to continue for a long time, and that its extent in the short term (i.e. around 2050) is insensitive to temperature changes between now and then. Thus, there's confidence that 2050 levels of sea level rise combined with the 2010 population distribution (i.e. absent the effects of
population growth
Population growth is the increase in the number of people in a population or dispersed group. Actual global human population growth amounts to around 83 million annually, or 1.1% per year. The global population has grown from 1 billion in 1800 to ...
and human migration) would result in ~150 million people under the water line during high tide and ~300 million in places which are flooded every year – an increase of 40 and 50 million people relative to 2010 values for the same. At the same time, the impact on temperature from changes in greenhouse gas emissions over the longer term would greatly influence longer-term sea level rise: by 2100, the spread between the lowest and the highest plausible emission trajectories would result in the sea level rise of when using the best-understood median estimates. When compared to 2050 levels, the difference between the low and high end of that range is equivalent to the difference between ~40 million more people under the water line during high tide and ~50 million more in places which are flooded every year (190 and 350 million people) and ~80 and ~90 million more for the same metrics (230 and 390 million people), respectively. Under the highest emission scenario
Climate change scenarios or socioeconomic scenarios are projections of future greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions used by analysts to assess future vulnerability to climate change. Scenarios and pathways are created by scientists to survey any long ...
, less-understood processes may also lead to sea level rise of well over by 2100, and the levels of cannot be excluded. Applying this extent of sea level rise to the 2010 population distribution could mean as many as 520 million more people under the water line during high tide and 640 million in places which are flooded every year.
While the rise in sea levels ultimately impacts every coastal and island population on Earth and leads to higher storm surge
A storm surge, storm flood, tidal surge, or storm tide is a coastal flood or tsunami-like phenomenon of rising water commonly associated with low-pressure weather systems, such as cyclones. It is measured as the rise in water level above the n ...
s, more dangerous tsunamis, damage in cities, loss and degradation of agricultural
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating Plant, plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of Sedentism, sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of Domestication, domesticated species created food ...
land and ultimately permanent loss of land and the displacement of populations, it does not occur uniformly due to local factors like tides, currents, storms, tectonic effects and land subsidence
Subsidence is a general term for downward vertical movement of the Earth's surface, which can be caused by both natural processes and human activities. Subsidence involves little or no horizontal movement, which distinguishes it from slope move ...
. For instance, sea level rise along US coasts (and along the US East Coast in particular) is already higher than the global average, and it is expected to be 2 to 3 times greater than the global average by the end of the century. At the same time, Asia will be the region where sea level rise would impact the most people: eight Asian countries – Bangladesh, China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
, India, Indonesia, Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
, the Philippines, Thailand and Vietnam – account for 70% of the global population exposed to sea level rise and land subsidence. Altogether, out of the 20 countries with the greatest exposure to sea level rise, 12 are in Asia. Finally, the greatest near-term impact on human populations will occur in the low-lying Caribbean
The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean Se ...
and Pacific islands
Collectively called the Pacific Islands, the islands in the Pacific Ocean are further categorized into three major island groups: Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Depending on the context, the term ''Pacific Islands'' may refer to one of se ...
– many of those would be rendered uninhabitable by sea level rise later this century.Mycoo, M., M. Wairiu, D. Campbell, V. Duvat, Y. Golbuu, S. Maharaj, J. Nalau, P. Nunn, J. Pinnegar, and O. Warrick, 2022Chapter 15: Small islands
I
Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability
.-O. Pörtner, D.C. Roberts, M. Tignor, E.S. Poloczanska, K. Mintenbeck, A. Alegría, M. Craig, S. Langsdorf, S. Löschke,V. Möller, A. Okem, B. Rama (eds.) Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 2043–2121 , doi=10.1017/9781009325844.017 Societies can adapt to sea level rise in three different ways: implement managed retreat, accommodate coastal change, or protect against sea level rise through hard-construction practices like seawalls or soft approaches such as dune rehabilitation and beach nourishment. Sometimes these adaptation strategies go hand in hand, but at other times choices have to be made among different strategies. For instance, a managed retreat strategy is difficult if the population in the area is quickly increasing: this is a particularly acute problem for Africa, where the population of low-lying coastal areas is projected to increase by around 100 million people within the next 40 years.Trisos, C.H., I.O. Adelekan, E. Totin, A. Ayanlade, J. Efitre, A. Gemeda, K. Kalaba, C. Lennard, C. Masao, Y. Mgaya, G. Ngaruiya, D. Olago, N.P. Simpson, and S. Zakieldeen 2022
Chapter 9: Africa
I
Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability
.-O. Pörtner, D.C. Roberts, M. Tignor, E.S. Poloczanska, K. Mintenbeck, A. Alegría, M. Craig, S. Langsdorf, S. Löschke,V. Möller, A. Okem, B. Rama (eds.) Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 2043–2121 , doi=10.1017/9781009325844.011 Poorer nations may also struggle to implement the same approaches to adapt to sea level rise as richer states, and sea level rise at some locations may be compounded by other environmental issues, such as
subsidence
Subsidence is a general term for downward vertical movement of the Earth's surface, which can be caused by both natural processes and human activities. Subsidence involves little or no horizontal movement, which distinguishes it from slope move ...
in so-called sinking cities. Coastal ecosystems
A marine coastal ecosystem is a marine ecosystem which occurs where the land meets the ocean. Marine coastal ecosystems include many different types of marine habitats, such as estuaries and lagoons, salt marshes and mangrove forests, seagrass m ...
typically adapt to rising sea levels by moving inland; however, they might not always be able to do so, due to natural or artificial barriers.
Observations
Between 1901 and 2018, the globally averaged sea level rose by . More precise data gathered from satellite radar measurements reveal an accelerating rise of from 1993 to 2017, accelerating gradually to a rate of per year as of 2021.Regional variations
Sea level rise is not uniform around the globe. Some land masses are moving up or down as a consequence of subsidence (land sinking or settling) or post-glacial rebound (land rising due to the loss of the weight of ice after melting), so that local relative sea level rise may be higher or lower than the global average. There are even regions near current and former glaciers and ice sheets where sea level falls. Furthermore, gravitational effects of changing ice masses and spatially varying patterns of warming lead to differences in the distribution of sea water around the globe. The gravitational effects comes into play when a large ice sheet melts. With the loss of mass, the gravitational pull becomes less and local water levels might drop. Further away from the ice sheet water levels will increase more than average. In this light, melt in Greenland has a different fingerprint on regional sea level than melt in Antarctica. Many ports, urban conglomerations, and agricultural regions are built on river deltas, where subsidence of land contributes to a substantially increased ''relative'' sea level rise. This is caused by both unsustainable extraction of groundwater (in some places also by extraction of oil and gas), and bylevee
A levee (), dike (American English), dyke (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English), embankment, floodbank, or stop bank is a structure that is usually soil, earthen and that often runs parallel (geometry), parallel to ...
s and other flood management practices that prevent accumulation of sediments from compensating for the natural settling of deltaic soils. Total human-caused subsidence in the Rhine-Meuse-Scheldt delta (Netherlands) is estimated at , over in urban areas of the Mississippi River Delta
The Mississippi River Delta is the confluence of the Mississippi River with the Gulf of Mexico in Louisiana, southeastern United States. The river delta is a area of land that stretches from Vermilion Bay on the west, to the Chandeleur Isla ...
( New Orleans), and over in the Sacramento–San Joaquin River Delta. On the other hand, post-glacial isostatic rebound causes relative sea level fall around the Hudson Bay
Hudson Bay ( crj, text=ᐐᓂᐯᒄ, translit=Wînipekw; crl, text=ᐐᓂᐹᒄ, translit=Wînipâkw; iu, text=ᑲᖏᖅᓱᐊᓗᒃ ᐃᓗᐊ, translit=Kangiqsualuk ilua or iu, text=ᑕᓯᐅᔭᕐᔪᐊᖅ, translit=Tasiujarjuaq; french: b ...
in Canada and the northern Baltic
Baltic may refer to:
Peoples and languages
* Baltic languages, a subfamily of Indo-European languages, including Lithuanian, Latvian and extinct Old Prussian
*Balts (or Baltic peoples), ethnic groups speaking the Baltic languages and/or originati ...
.
The Atlantic is set to warm at a faster pace than the Pacific. This has consequences for Europe and the U.S. East Coast
The East Coast of the United States, also known as the Eastern Seaboard, the Atlantic Coast, and the Atlantic Seaboard, is the coastline along which the Eastern United States meets the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean. The eastern seaboard ...
, which received a sea level rise 3–4 times the global average. The downturn of the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation (AMOC) has been also tied to extreme regional sea level rise on the US Northeast Coast.
Projections
ice-sheet model
In climate modelling, Ice-sheet models use numerical methods to simulate the evolution, dynamics and thermodynamics of ice sheets, such as the Greenland ice sheet, the Antarctic ice sheet or the large ice sheets on the northern hemisphere during t ...
is used to calculate the contributions of ice sheets and a general circulation model
A general circulation model (GCM) is a type of climate model. It employs a mathematical model of the general circulation of a planetary atmosphere or ocean. It uses the Navier–Stokes equations on a rotating sphere with thermodynamic terms f ...
is used to compute the rising sea temperature and its expansion. A disadvantage of this method is that not all relevant processes might be understood to a sufficient level, but it can predict non-linearities and long delays in the response which studies of the recent past will miss.
In the other approach, scientists use semi-empirical techniques that use geological data from the past to determine likely sea level responses to a warming world in addition to some basic physical modelling. These semi-empirical sea level models rely on statistical techniques, using relationships between observed past (contributions to) global mean sea level and global mean temperature. This type of modelling was partially motivated by most physical models in previous literature assessments by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) is an intergovernmental body of the United Nations. Its job is to advance scientific knowledge about climate change caused by human activities. The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) a ...
(IPCC) having underestimated the amount of sea level rise compared to observations of the 20th century.
Projections for the 21st century
In its fifth assessment report (2013) theIntergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) is an intergovernmental body of the United Nations. Its job is to advance scientific knowledge about climate change caused by human activities. The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) a ...
(IPCC) estimated how much sea level is likely to rise in the 21st century based on different levels of greenhouse gas emissions. These were conservative projections based on well-known factors which contribute to sea level rise, but exclude other processes which are less well understood. If emissions remain very high, the IPCC projected sea level would rise by . In August 2020 scientists reported that observed ice-sheet losses in Greenland and Antarctica were tracking worst-case scenarios of those IPCC projections. In 2021, the IPCC Sixth Assessment Report had barely changed its worst-case scenario (updating it to 0.6–1 m), whereas most other reports since 2020 have increased their upper estimates to at least 2 m in the very high emissions scenario.
Other attempts have been made to include more physical processes and to develop models that can project sea level rise using paleoclimate data. This typically led to higher estimates of sea level rise. A 2016 study led by Jim Hansen
James Edward Hansen (born March 29, 1942) is an American adjunct professor directing the Program on Climate Science, Awareness and Solutions of the Earth Institute at Columbia University. He is best known for his research in climatology, his ...
concluded that based on past climate change data, sea level rise could accelerate exponentially in the coming decades, with a doubling time of 10, 20 or 40 years, respectively, raising the ocean by several metres in 50, 100 or 200 years. However, Greg Holland from the National Center for Atmospheric Research, who reviewed the study, noted: "There is no doubt that the sea level rise, within the IPCC, is a very conservative number, so the truth lies somewhere between IPCC and Jim''.''"
In addition, one 2017 study's scenario, assuming high fossil fuel
A fossil fuel is a hydrocarbon-containing material formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the remains of dead plants and animals that is extracted and burned as a fuel. The main fossil fuels are coal, oil, and natural gas. Fossil fuels m ...
use for combustion and strong economic growth during this century, projects sea level rise of up to on average—and an extreme scenario with as much as , by 2100. This could mean rapid sea level rise of up to per year by the end of the century. The study also concluded that the Paris climate agreement emissions scenario, if met, would result in a median of sea level rise by 2100.
The Fourth (2017) National Climate Assessment (NCA) of the United States found that it is very likely sea level will rise between 30 and 130 cm (1.0–4.3 feet) in 2100 compared to the year 2000. A rise of 2.4 m (8 feet) is physically possible under a high emission scenario but the authors were unable to say how likely. This worst-case scenario can only come about with a large contribution from Antarctica; a region that is difficult to model.
The possibility of a collapse of the West Antarctic ice sheet and subsequent rapid sea level rise was suggested back in the 1970s. For instance, Mercer published a study in 1978 predicting that anthropogenic carbon dioxide warming and its potential effects on climate in the 21st century could cause a sea level rise of around from melting of the West Antarctic ice-sheet alone.
In 2019, a study projected that in low emission scenario, sea level will rise 30 cm by 2050 and 70 cm by 2100, relative to the level in 2000. In high emission scenario, it will be roughly 35 cm by 2050 and 110 cm by 2100. There is the probability that the rise will be beyond 2 metres by 2100 in the high emission scenario, which would cause displacement of 187 million people. Long before then, current projections of sea level rise for 2050 will generate an intense rise in the frequency of coastal flooding (a baseline of four "moderate" flooding events per year in the US), even without storms and/or heavy rainfall.
In September 2019 the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) is an intergovernmental body of the United Nations. Its job is to advance scientific knowledge about climate change caused by human activities. The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) a ...
published SROCC
The United Nations' Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change's (IPCC) Special Report on the Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate (SROCC) is a report about the effects of climate change on the Ocean, world's seas, sea ice, Ice cap, icecaps ...
, a report about the impact of climate change on the oceans including sea level rise. In February 2021, a paper suggested that the projections for global sea level rise by 2100 reported in the IPCC Fifth Assessment Report
The Fifth Assessment Report (AR5) of the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) is the fifth in a series of such reports and was completed in 2014.IPCC (2014The IPCC’s Fifth Assessment Report (AR5) leaflet/ref> As h ...
were well below what one can expect from an extrapolation of past sea level trends, as well as below the combined projections of an expert elicitation, and thus are likely to have been too conservative. The authors noted that the projections in SROCC were substantially closer to the extrapolated trends, but still appeared too conservative and less plausible than the combined expert elicitation. The projections in the August 2021 IPCC Sixth Assessment Report were ultimately slightly larger than those in SROCC for the low-level warming, but much larger at the upper-end for the high-level warming, due to the addition of a "low-confidence" narrative involving marine ice cliff instability.
High-end 21st-century sea level rise
Sea level rise by 2100 that is much higher than the likely range of projection by the IPCC Sixth Assessment Report (AR6) is possible. In particular, AR6 models do not take into consideration many positive feedback loops that would lead to accelerated melting over time. AR6 does offer a speculative narrative about how more extreme melting could occur. It would probably involve a high warming scenario, in which urgent climate action is not taken and strong warming continues.Fox-Kemper, B., H.T. Hewitt, C. Xiao, G. Aðalgeirsdóttir, S.S. Drijfhout, T.L. Edwards, N.R. Golledge, M. Hemer, R.E. Kopp, G. Krinner, A. Mix, D. Notz, S. Nowicki, I.S. Nurhati, L. Ruiz, J.-B. Sallée, A.B.A. Slangen, and Y. Yu, 2021Chapter 9: Ocean, Cryosphere and Sea Level Change
I
Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
[Masson-Delmotte, V., P. Zhai, A. Pirani, S.L. Connors, C. Péan, S. Berger, N. Caud, Y. Chen, L. Goldfarb, M.I. Gomis, M. Huang, K. Leitzell, E. Lonnoy, J.B.R. Matthews, T.K. Maycock, T. Waterfield, O. Yelekçi, R. Yu, and B. Zhou (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 1211–1362, doi:10.1017/9781009157896.011. This could lead to a faster-than-projected collapse of marine ice shelves and the abrupt, widespread onset of
marine ice cliff instability
Marine ice sheet instability (MISI) describes the potential for ice sheets grounded below sea level to destabilize in a runaway fashion. The mechanism was first proposed in the 1970s by Johannes Weertman and was quickly identified as a means by wh ...
(a process in which ice cliffs collapse under their own weight) and ice sheet instability (a positive feedback loop that leads to runaway melting) in Antarctica, and a faster than projected ice loss in Greenland including reduced albedo as its ice melts. Other processes in Antarctica such as hydrofracturing (in which meltwater collects in ice sheet fractures, forcing them open), increased contact of warm ocean water with ice shelves due to climate change induced ocean circulations changes or changes in the weather over Antarctica leading to lower precipitation and ice deposition, could all be contributing factors. The combination of such processes could lead to sea level rise as high as 2.3 metres by 2100.
Long-term sea level rise
 There is a widespread consensus among climate scientists that sea level rise lags well behind the temperature increase that triggers it, and that substantial long-term sea level rise will continue for centuries to come even if the temperature stabilizes.
Models are able to reproduce paleo records of sea level rise, which provides confidence in their application to long-term future change.
Both the Greenland ice sheet and Antarctica have tipping points for warming levels that could be reached before the end of the 21st century. Crossing such tipping points would mean that ice-sheet changes are potentially irreversible: a decrease to pre-industrial temperatures may not stabilize the ice sheet once the tipping point has been crossed. Quantifying the exact temperature change for which this tipping point is crossed remains controversial. For Greenland, estimates roughly range between 1 and 4 °C (2 to 7 °F) above pre-industrial. , the lower of these values has already been passed. A 2021 analysis of sub-glacial sediment at the bottom of a 1.4 km Greenland ice core finds that the Greenland ice sheet melted away at least once during the last million years. Since the maximum positive temperature excursion over that period is 2.5 °C, this strongly suggests that its tipping point is below that value and therefore within the lower half of its range of estimates. Melting of the
There is a widespread consensus among climate scientists that sea level rise lags well behind the temperature increase that triggers it, and that substantial long-term sea level rise will continue for centuries to come even if the temperature stabilizes.
Models are able to reproduce paleo records of sea level rise, which provides confidence in their application to long-term future change.
Both the Greenland ice sheet and Antarctica have tipping points for warming levels that could be reached before the end of the 21st century. Crossing such tipping points would mean that ice-sheet changes are potentially irreversible: a decrease to pre-industrial temperatures may not stabilize the ice sheet once the tipping point has been crossed. Quantifying the exact temperature change for which this tipping point is crossed remains controversial. For Greenland, estimates roughly range between 1 and 4 °C (2 to 7 °F) above pre-industrial. , the lower of these values has already been passed. A 2021 analysis of sub-glacial sediment at the bottom of a 1.4 km Greenland ice core finds that the Greenland ice sheet melted away at least once during the last million years. Since the maximum positive temperature excursion over that period is 2.5 °C, this strongly suggests that its tipping point is below that value and therefore within the lower half of its range of estimates. Melting of the Greenland ice sheet
The Greenland ice sheet ( da, Grønlands indlandsis, kl, Sermersuaq) is a vast body of ice covering , roughly near 80% of the surface of Greenland. It is sometimes referred to as an ice cap, or under the term ''inland ice'', or its Danish equiva ...
would contribute of sea level rise.
A 2013 study estimated that each degree of temperature rise translates to a commitment to sea level rise within the next 2,000 years. More recent research, especially into Antarctica, indicates that this is probably a conservative estimate and that the true long-term sea level rise might be higher. Warming beyond the 2 °C (3.6 °F) target potentially leads to rates of sea level rise dominated by ice loss from Antarctica. Continued carbon dioxide emissions from fossil fuel sources could cause additional tens of metres of sea level rise, over the next millennia, and the available fossil fuel on Earth is even enough to ultimately melt the entire Antarctic ice sheet, causing about of sea level rise. After 500 years, sea level rise from thermal expansion alone may have reached only half of its eventual level, which models suggest may lie within ranges of .
In the next 2,000 years the sea level is predicted to rise by 2–3 metres if the temperature rise peaks at 1.5 °C, by 2–6 metres if it peaks at 2 °C and by 19–22 metres if it peaks at 5 °C. If temperature rise stops at 2 °C or at 5 °C, the sea level would still continue to rise for about 10,000 years. In the first case it will reach 8–13 metres above pre-industrial level, and in the second 28–37 metres.
Causes
 The three main reasons warming causes global sea level to rise are: oceans expand, ice sheets lose ice faster than it forms from snowfall, and glaciers at higher altitudes also melt. Sea level rise since the start of the 20th century has been dominated by retreat of glaciers and expansion of the ocean, but the contributions of the two large ice sheets (Greenland and Antarctica) are expected to increase in the 21st century. The ice sheets store most of the land ice (∼99.5%), with a sea-level equivalent (SLE) of for Greenland and for Antarctica.
Each year about of precipitation (liquid equivalent) falls on the ice sheets in Antarctica and Greenland, mostly as snow, which accumulates and over time forms glacial ice. Much of this precipitation began as water vapor evaporated from the ocean surface. Some of the snow is blown away by wind or disappears from the ice sheet by melt or by
The three main reasons warming causes global sea level to rise are: oceans expand, ice sheets lose ice faster than it forms from snowfall, and glaciers at higher altitudes also melt. Sea level rise since the start of the 20th century has been dominated by retreat of glaciers and expansion of the ocean, but the contributions of the two large ice sheets (Greenland and Antarctica) are expected to increase in the 21st century. The ice sheets store most of the land ice (∼99.5%), with a sea-level equivalent (SLE) of for Greenland and for Antarctica.
Each year about of precipitation (liquid equivalent) falls on the ice sheets in Antarctica and Greenland, mostly as snow, which accumulates and over time forms glacial ice. Much of this precipitation began as water vapor evaporated from the ocean surface. Some of the snow is blown away by wind or disappears from the ice sheet by melt or by sublimation
Sublimation or sublimate may refer to:
* ''Sublimation'' (album), by Canvas Solaris, 2004
* Sublimation (phase transition), directly from the solid to the gas phase
* Sublimation (psychology), a mature type of defense mechanism
* Sublimate of mer ...
(directly changing into water vapor). The rest of the snow slowly changes into ice. This ice can flow to the edges of the ice sheet and return to the ocean by melting at the edge or in the form of iceberg
An iceberg is a piece of freshwater ice more than 15 m long that has broken off a glacier or an ice shelf and is floating freely in open (salt) water. Smaller chunks of floating glacially-derived ice are called "growlers" or "bergy bits". The ...
s. If precipitation, surface processes and ice loss at the edge balance each other, sea level remains the same. However scientists have found that ice is being lost, and at an accelerating rate.
Ocean heating
 Most of the additional heat trapped in the Earth's climate system by climate change is stored in oceans. They store more than 90% of the extra heat and act as a buffer against the effects of climate change. The heat needed to raise an average temperature increase of the entire world ocean by 0.01 °C would increase the atmospheric temperature by approximately 10 °C: a small change in the mean temperature of the ocean represents a very large change in the total heat content of the climate system.
When the ocean gains heat, the water expands and sea level rises. The amount of expansion varies with both water temperature and pressure. For each degree, warmer water and water under great pressure (due to depth) expand more than cooler water and water under less pressure. Consequently cold Arctic Ocean water will expand less than warm tropical water. Because different climate models present slightly different patterns of ocean heating, their predictions do not agree fully on the contribution of ocean heating to sea level rise. Heat gets transported into deeper parts of the ocean by winds and currents, and some of it reaches depths of more than .
Considering an increase in average global temperature of 2 °C above preindustrial levels, and not considering the potential contributions from ice-sheet processes with limited agreement (low confidence) among modeling approaches, the probability of exceeding 0.5 m rise of sea level globally (0.7 m along the CONUS coastline) by 2100 is about 50%. With 3–5 °C of warming under high emissions pathways, this probability rises to >80% to >99%.
Most of the additional heat trapped in the Earth's climate system by climate change is stored in oceans. They store more than 90% of the extra heat and act as a buffer against the effects of climate change. The heat needed to raise an average temperature increase of the entire world ocean by 0.01 °C would increase the atmospheric temperature by approximately 10 °C: a small change in the mean temperature of the ocean represents a very large change in the total heat content of the climate system.
When the ocean gains heat, the water expands and sea level rises. The amount of expansion varies with both water temperature and pressure. For each degree, warmer water and water under great pressure (due to depth) expand more than cooler water and water under less pressure. Consequently cold Arctic Ocean water will expand less than warm tropical water. Because different climate models present slightly different patterns of ocean heating, their predictions do not agree fully on the contribution of ocean heating to sea level rise. Heat gets transported into deeper parts of the ocean by winds and currents, and some of it reaches depths of more than .
Considering an increase in average global temperature of 2 °C above preindustrial levels, and not considering the potential contributions from ice-sheet processes with limited agreement (low confidence) among modeling approaches, the probability of exceeding 0.5 m rise of sea level globally (0.7 m along the CONUS coastline) by 2100 is about 50%. With 3–5 °C of warming under high emissions pathways, this probability rises to >80% to >99%.
Antarctica
 The large volume of ice on the Antarctic continent stores around 70% of the world's fresh water. The Antarctic ice sheet mass balance is affected by snowfall accumulations, and ice discharge along the periphery. Under the influence of global warming, melt at the base of the ice sheet increases. Simultaneously, the capacity of the atmosphere to carry precipitation increases with temperature so that precipitation, in the form of snowfall, increases in global and regional models. The additional snowfall causes increased ice flow of the ice sheet into the ocean, so that the mass gain due to snowfall is partially compensated. Snowfall increased over the last two centuries, but no increase was found in the interior of Antarctica over the last four decades. Based on changes of Antarctica's ice mass balance over millions of years, due to natural climate fluctuations, researchers concluded that the sea-ice acts as a barrier for warmer waters surrounding the continent. Consequently, the loss of sea ice is a major driver of the instability of the entire ice sheet.
The large volume of ice on the Antarctic continent stores around 70% of the world's fresh water. The Antarctic ice sheet mass balance is affected by snowfall accumulations, and ice discharge along the periphery. Under the influence of global warming, melt at the base of the ice sheet increases. Simultaneously, the capacity of the atmosphere to carry precipitation increases with temperature so that precipitation, in the form of snowfall, increases in global and regional models. The additional snowfall causes increased ice flow of the ice sheet into the ocean, so that the mass gain due to snowfall is partially compensated. Snowfall increased over the last two centuries, but no increase was found in the interior of Antarctica over the last four decades. Based on changes of Antarctica's ice mass balance over millions of years, due to natural climate fluctuations, researchers concluded that the sea-ice acts as a barrier for warmer waters surrounding the continent. Consequently, the loss of sea ice is a major driver of the instability of the entire ice sheet.
 Different satellite methods for measuring ice mass and change are in good agreement, and combining methods leads to more certainty about how the East Antarctic Ice Sheet, the West Antarctic Ice Sheet, and the
Different satellite methods for measuring ice mass and change are in good agreement, and combining methods leads to more certainty about how the East Antarctic Ice Sheet, the West Antarctic Ice Sheet, and the Antarctic Peninsula
The Antarctic Peninsula, known as O'Higgins Land in Chile and Tierra de San Martín in Argentina, and originally as Graham Land in the United Kingdom and the Palmer Peninsula in the United States, is the northernmost part of mainland Antarctic ...
evolve. A 2018 systematic review
A systematic review is a Literature review, scholarly synthesis of the evidence on a clearly presented topic using critical methods to identify, define and assess research on the topic. A systematic review extracts and interprets data from publ ...
study estimated that ice loss across the entire continent was 43 gigatons (Gt) per year on average during the period from 1992 to 2002, but has accelerated to an average of 220 Gt per year during the five years from 2012 to 2017.
* Most of the melt comes from the West Antarctic Ice Sheet, but the Antarctic Peninsula and East Antarctic Ice Sheet also contribute. The sea level rise due to Antarctica has been estimated to be 0.25 mm per year from 1993 to 2005, and 0.42 mm per year from 2005 to 2015. All datasets generally show an acceleration of mass loss from the Antarctic ice-sheet, but with year-to-year variations.
A May 2021 study projected that limiting global warming to 1.5 °C would reduce the land ice contribution to sea level rise by 2100 from 25 cm to 13 cm (from 10 to 6 in.) compared to current mitigation pledges, with glaciers responsible for half the sea level rise contribution. The physical uncertainty of the Antarctic contribution was more significant than the uncertainty due to the choice of mitigation pathway. Alt URL https://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/173870/ By 2019, several studies have attempted to estimate 2300 sea level rise caused by ice loss in Antarctica alone: they suggest 16 cm median and 37 cm maximum values under the low-emission scenario but a median of 1.46 metres (with a minimum of 60 cm and a maximum of 2.89 metres) under the highest-emission scenario.
East Antarctica
The world's largest potential source of sea level rise is the East Antarctic Ice Sheet, which holds enough ice to raise global sea levels by . The ice sheet has historically been considered to be relatively stable and has therefore attracted less scientific attention and observations compared to West Antarctica. A combination of satellite observations of its changing volume, flow and gravitational attraction with modelling of its surface mass balance suggests the overall mass balance of the East Antarctic Ice Sheet was relatively steady or slightly positive for much of the period 1992–2017. A 2019 study, however, using different methodology, concluded thatEast Antarctica
East Antarctica, also called Greater Antarctica, constitutes the majority (two-thirds) of the Antarctic continent, lying on the Indian Ocean side of the continent, separated from West Antarctica by the Transantarctic Mountains. It lies almost ...
is losing significant amounts of ice mass. The lead scientist Eric Rignot
Eric J. Rignot is a chancellor professor of Earth system science at the University of California, Irvine, and senior research scientist for the Radar Science and Engineering Section at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory.
Education
In 1985, Rigno ...
told CNN: "melting is taking place in the most vulnerable parts of Antarctica ... parts that hold the potential for multiple metres of sea level rise in the coming century or two."
Methods agree that the Totten Glacier
Totten Glacier is a large glacier draining a major portion of the East Antarctic Ice Sheet, through the Budd Coast of Wilkes Land in the Australian Antarctic Territory. The catchment drained by the glacier is estimated at , extending approximate ...
has lost ice in recent decades in response to ocean warming and possibly a reduction in local sea ice cover. Totten Glacier is the primary outlet of the Aurora Subglacial Basin Aurora Subglacial Basin is a large subglacial basin of Wilkes Land to the west of Dome Charlie and trending northwest toward the coast in the vicinity of Shackleton Ice Shelf. The basin was delineated by the SPRI-NSF- TUD airborne radio echo sound ...
, a major ice reservoir in East Antarctica that could rapidly retreat due to hydrological processes. The global sea level potential of flowing through Totten Glacier alone is of similar magnitude to the entire probable contribution of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet.
The other major ice reservoir on East Antarctica that might rapidly retreat is the Wilkes Basin which is subject to marine ice sheet instability
Marine ice sheet instability (MISI) describes the potential for ice sheets grounded below sea level to destabilize in a runaway fashion. The mechanism was first proposed in the 1970s by Johannes Weertman and was quickly identified as a means by whi ...
. Ice loss from these outlet glaciers is possibly compensated by accumulation gains in other parts of Antarctica. In 2022, it was estimated that the Wilkes Basin, Aurora Basin and other nearby subglacial basins are likely to have a collective tipping point around 3 °C of global warming, although it may be as high as 6 °C, or as low as 2 °C. Once this tipping point is crossed, the collapse of these subglacial basins could take place as little as 500 or as much as 10,000 years: the median timeline is 2000 years. On the other hand, the entirety of the EAIS would not be committed to collapse until global warming reaches 7.5 °C (range between 5 and 10 °C), and would take at least 10,000 years to disappear. It is also suggested that the loss of two-thirds of its volume may require at least 6 °C of warming.
West Antarctica
Even though East Antarctica contains the largest potential source of sea level rise, it isWest Antarctica
West Antarctica, or Lesser Antarctica, one of the two major regions of Antarctica, is the part of that continent that lies within the Western Hemisphere, and includes the Antarctic Peninsula. It is separated from East Antarctica by the Transant ...
that currently experiences a net outflow of ice, causing sea levels to rise. Using different satellites from 1992 to 2017 shows melt is increasing significantly over this period. Antarctica as a whole has caused a total of of sea level rise. Considering the mass balance of the East Antarctic Ice Sheet which was relatively steady, the major contributor was West Antarctica. Significant acceleration of outflow glaciers in the Amundsen Sea Embayment
The Amundsen Sea, an arm of the Southern Ocean off Marie Byrd Land in western Antarctica, lies between Cape Flying Fish (the northwestern tip of Thurston Island) to the east and Cape Dart on Siple Island to the west. Cape Flying Fish marks th ...
may have contributed to this increase. In contrast to East Antarctica and the Antarctic Peninsula
The Antarctic Peninsula, known as O'Higgins Land in Chile and Tierra de San Martín in Argentina, and originally as Graham Land in the United Kingdom and the Palmer Peninsula in the United States, is the northernmost part of mainland Antarctic ...
, temperatures on West Antarctica have increased significantly with a trend between per decade and per decade between 1976 and 2012.
In 2021, it was estimated that while the *median* increase in sea level rise from the West Antarctic ice sheet melt by 2100 is ~11 cm under all emission scenarios (since the increased warming would intensify the water cycle and increase snowfall
Snow comprises individual ice crystals that grow while suspended in the atmosphere—usually within clouds—and then fall, accumulating on the ground where they undergo further changes.
It consists of frozen crystalline water throughout ...
accumulation over the ice sheet at about the same rate as it would increase ice loss), the multiple types of instability affecting West Antarctica ice sheet mean that it can conceivably contribute as much as 41 cm by 2100 under the low-emission scenario and 57 cm under the highest-emission one. One is marine ice sheet instability
Marine ice sheet instability (MISI) describes the potential for ice sheets grounded below sea level to destabilize in a runaway fashion. The mechanism was first proposed in the 1970s by Johannes Weertman and was quickly identified as a means by whi ...
, where the bedrock on which parts of the ice sheet rest is deeper inland. This means that when a part of the ice sheet melts, a thicker part of the ice sheet is exposed to the ocean, which may lead to additional ice loss. Secondly, melting of the ice shelve
Ice is water frozen into a solid state, typically forming at or below temperatures of 0 degrees Celsius or Depending on the presence of impurities such as particles of soil or bubbles of air, it can appear transparent or a more or less opaqu ...
s, the floating extensions of the ice sheet, leads to a process named the Marine Ice Cliff Instability''.'' Because they function as a buttress to the ice sheet, their melt leads to additional ice flow (see animation one minute into video). Melt of ice shelves is accelerated when surface melt creates crevasses and these crevasses cause fracturing.
The Thwaites and Pine Island glaciers have been identified to be potentially prone to these processes, since both glaciers bedrock topography gets deeper farther inland, exposing them to more warm water intrusion into the grounding zone. With continued melt and retreat they contribute to raising global sea levels. The Thwaites glacier itself will cause a rise of sea level by 65 centimetres if it will completely collapse, but this can also destabilize other glaciers in west Antarctica. The Thwaites Ice Shelf
Thwaites Ice Shelf (), is an Antarctic ice shelf in the Amundsen Sea. It was named by ACAN
after Fredrik T. Thwaites, a glacial geologist and geomorphologist. The Thwaites Ice Shelf is one of the biggest ice shelves in West Antarctica, though ...
can collapse in three to five years, which would then make the destabilization of the entire Thwaites glacier inevitable.
The melting of these two glaciers had accelerated at the beginning of the 21st century. It can destabilize the entire West Antarctic Ice Sheet. However, the process will probably not be finished in this century. Most of the bedrock
In geology, bedrock is solid Rock (geology), rock that lies under loose material (regolith) within the crust (geology), crust of Earth or another terrestrial planet.
Definition
Bedrock is the solid rock that underlies looser surface mater ...
underlying the West Antarctic Ice Sheet lies well below sea level. A rapid collapse of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet could raise sea level by . In 2022, the collapse of the entire West Antarctica was estimated to unfold over a period of about 2000 years, with the absolute minimum of 500 years (and a potential maximum of 13,000 years.) At the same time, this collapse was considered likely to be triggered at around 1.5°C of global warming and would become absolutely unavoidable at 3°C: at worst, it may have even been triggered by now, after the warming passed 1°C in the recent years. Even though the process takes a long time to finish, it has been suggested that the only way to stop it once triggered is by lowering the global temperature to 1°C ''below'' the preindustrial levels (about 2°C below the current levels).
Greenland
 Most ice on Greenland is part of the
Most ice on Greenland is part of the Greenland ice sheet
The Greenland ice sheet ( da, Grønlands indlandsis, kl, Sermersuaq) is a vast body of ice covering , roughly near 80% of the surface of Greenland. It is sometimes referred to as an ice cap, or under the term ''inland ice'', or its Danish equiva ...
which is at its thickest. The rest of the ice on Greenland is part of isolated glaciers and ice caps. The sources contributing to sea level rise from Greenland are from ice sheet melting (70%) and from glacier calving (30%). Dust, soot, and microbe
A microorganism, or microbe,, ''mikros'', "small") and ''organism'' from the el, ὀργανισμός, ''organismós'', "organism"). It is usually written as a single word but is sometimes hyphenated (''micro-organism''), especially in olde ...
s and algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular mic ...
living on parts of the ice sheet further enhance melting by darkening its surface and thus absorbing more thermal radiation; these regions grew by 12% between 2000 and 2012, and are likely to expand further. Average annual ice loss in Greenland more than doubled in the early 21st century compared to the 20th century. Some of Greenland's largest outlet glaciers, such as Jakobshavn Isbræ
Jakobshavn Glacier ( da, Jakobshavn Isbræ), also known as Ilulissat Glacier ( kl, Sermeq Kujalleq), is a large outlet glacier in West Greenland. It is located near the Greenlandic town of Ilulissat (colonial name in da, Jakobshavn) and ends a ...
and Kangerlussuaq Glacier
Kangerlussuaq Glacier ( kl, Kangerlussuaq, meaning 'large fjord'; old spelling ''Kangerdlugssuaq'') is the largest glacier on the east coast of the Greenland ice sheet. It flows into the head of the Kangerlussuaq Fjord, the second largest fjord i ...
, are flowing faster into the ocean.
A study published in 2017 concluded that Greenland's peripheral glaciers and ice caps crossed an irreversible tipping point around 1997, and will continue to melt.
A study published in 2020 estimated that the Greenland Ice Sheet had lost a total of 3,902 gigatons (Gt) of ice between 1992 and 2018, corresponding to a contribution to sea level rise of 10.8 mm. The sea level rise due to the Greenland Ice Sheet has generally increased over time, rising from 0.07 mm per year between 1992 and 1997 to 0.68 mm per year between 2012 and 2017. The contribution for the 2012–2016 period was equivalent to 37% of sea level rise from ''land ice'' sources (excluding thermal expansion). This rate of ice sheet melting is also associated with the higher end of the predictions from the past IPCC assessment reports.
As of 2021, it is estimated that under the SSP1-2.6 emission scenario which largely fulfils the Paris Agreement
The Paris Agreement (french: Accord de Paris), often referred to as the Paris Accords or the Paris Climate Accords, is an international treaty on climate change. Adopted in 2015, the agreement covers climate change mitigation, Climate change a ...
goals, Greenland ice sheet melt adds around 6 cm to global sea level rise by the end of the century, with a plausible maximum of 15 cm (and even a very small chance of the ice sheet gaining mass through the increased surface mass balance
Crucial to the survival of a glacier is its mass balance or surface mass balance (SMB), the difference between glacier ice accumulation, accumulation and Ablation zone, ablation (sublimation and melting). Climate change (general concept), Clim ...
feedback and thus reducing the sea levels by around 2 cm). On the other hand, the scenario associated with the highest global warming, SSP5-8.5, would see Greenland add a minimum of 5 cm to sea level rise, a likely median of 13 cm and a plausible maximum of 23 cm.
There is also a threshold in surface warming beyond which a partial or near-complete melting of the Greenland ice sheet occurs. Different research has put this threshold value as low as 1 °C (2 °F), and definitely 4 °C (7 °F), above pre-industrial temperatures. A 2021 analysis of sub-glacial sediment at the bottom of a 1.4 km Greenland ice core finds that the Greenland ice sheet melted away at least once during the last million years, and therefore strongly suggests that its tipping point is below the 2.5 °C maximum positive temperature excursion over that period. In 2022, it was estimated that the tipping point of the Greenland Ice Sheet may have been as low as 0.8 °C, and is certainly no higher than 3 °C: there's a high chance that it will be crossed around 1.5 °C. Once crossed, it would take between 1000 and 15,000 years for the ice sheet to disintegrate entirely, with the most likely estimate of 10,000 years.
Glaciers
Less than 1% of glacier ice is in mountain glaciers, compared to 99% in Greenland and Antarctica. However, this small size also makes them more vulnerable to melting than the larger ice sheets, and it means that mountain glaciers have had a disproportionate contribution to historical sea level rise and are set to contribute a smaller, but still significant fraction of sea level rise in the 21st century. The roughly 200,000 glaciers on earth are spread out across all continents. Different glaciers respond differently to increasing temperatures. For instance, valley glaciers that have a shallow slope retreat under even mild warming. Every glacier has a height above which there is net gain in mass and under which the glacier loses mass. If that height changes a bit, this has large consequences for glaciers with a shallow slope. Many glaciers drain into the ocean and ice loss can therefore increase when ocean temperatures increase. Observational and modelling studies of mass loss from glaciers and ice caps indicate a contribution to sea level rise of 0.2-0.4 mm per year, averaged over the 20th century. The contribution for the 2012–2016 period was nearly as large as that of Greenland: 0.63 mm of sea level rise per year, equivalent to 34% of sea level rise from ''land ice'' sources. Over the 21st century, this is expected to rise, with glaciers contributing to global sea levels. Glaciers contributed around 40% to sea level rise during the 20th century, with estimates for the 21st century of around 30%. In 2022, it was estimated that in general, mountain glaciers are likely to disappear around the world once the warming crosses 2 °C, and this would become largely inevitable around 3 °C: there's even a chance most glaciers would be lost around 1.5 °C. Because mountain glaciers contain much less ice than the other ice masses, their disappearance may require as little as 50 years after the tipping point is crossed, although 200 years is the most likely value, and the maximum is around 1000 years.Sea ice
Sea ice melt contributes very slightly to global sea level rise. If the melt water from ice floating in the sea was exactly the same as sea water then, according to Archimedes' principle, no rise would occur. However melted sea ice contains less dissolved salt than sea water and is therefore less dense: in other words, although the melted sea ice weighs the same as the sea water it was displacing when it was ice, its volume is still slightly greater. If all floating ice shelves andicebergs
An iceberg is a piece of freshwater ice more than 15 m long that has broken off a glacier or an ice shelf and is floating freely in open (salt) water. Smaller chunks of floating glacially-derived ice are called "growlers" or "bergy bits". The ...
were to melt sea level would only rise by about .
Land water storage
 Humans impact how much water is stored on land. Building dams prevents large masses of water from flowing into the sea and therefore increases the storage of water on land. On the other hand, humans extract water from lakes, wetlands and underground reservoirs for food production leading to rising seas. Furthermore, the
Humans impact how much water is stored on land. Building dams prevents large masses of water from flowing into the sea and therefore increases the storage of water on land. On the other hand, humans extract water from lakes, wetlands and underground reservoirs for food production leading to rising seas. Furthermore, the hydrological cycle
The water cycle, also known as the hydrologic cycle or the hydrological cycle, is a biogeochemical cycle that describes the continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the Earth. The mass of water on Earth remains fairly cons ...
is influenced by climate change and deforestation, which can lead to further positive and negative contributions to sea level rise. In the 20th century, these processes roughly balanced, but dam building has slowed down and is expected to stay low for the 21st century.
Measurement
Sea level changes can be driven either by variations in the amount of water in the oceans, the volume of the ocean or by changes of the land compared to the sea surface. Over a consistent time period, conducting assessments can source contributions to sea level rise and provide early indications of change in trajectory. This type of surveillance can inform plans of prevention. The different techniques used to measure changes in sea level do not measure exactly the same level. Tide gauges can only measure relative sea level, whilst satellites can also measure absolute sea level changes. To get precise measurements for sea level, researchers studying the ice and the oceans on our planet factor in ongoing deformations of the solid Earth, in particular due to landmasses still rising from past ice masses retreating, and also the Earth's gravity androtation
Rotation, or spin, is the circular movement of an object around a '' central axis''. A two-dimensional rotating object has only one possible central axis and can rotate in either a clockwise or counterclockwise direction. A three-dimensional ...
.
Satellites
 Since the launch of
Since the launch of TOPEX/Poseidon
TOPEX/Poseidon was a joint satellite altimeter mission between NASA, the U.S. space agency; and CNES, the French space agency, to map ocean surface topography. Launched on August 10, 1992, it was the first major oceanographic research satellite. ...
in 1992, an overlapping series of altimetric satellites has been continuously recording the sea level and its changes. Those satellites can measure the hills and valleys in the sea caused by currents and detect trends in their height. To measure the distance to the sea surface, the satellites send a microwave pulse which reflects on the ocean's surface and record the time it takes to return. Microwave radiometers correct the additional delay caused by water vapor in the atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gas or layers of gases that envelop a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A s ...
. Combining these data with the precisely known location of the spacecraft determines the sea-surface height to within a few centimetres (about one inch). Current rates of sea level rise from satellite altimetry have been estimated to be per year for the period 1993–2017. Earlier satellite measurements were previously slightly at odds with tide gauge measurements. A small calibration error for the Topex/Poseidon satellite was eventually identified as having caused a slight overestimation of the 1992–2005 sea levels, which masked in the satellite measurements the ongoing sea level rise acceleration that was visible in the tide gauge timeseries.
Satellites are useful for measuring regional variations in sea level, such as the substantial rise between 1993 and 2012 in the western tropical Pacific. This sharp rise has been linked to increasing trade winds, which occur when the Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO) and the El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) change from one state to the other. The PDO is a basin-wide climate pattern consisting of two phases, each commonly lasting 10 to 30 years, while the ENSO has a shorter period of 2 to 7 years.
Tide gauges
 The global network of tide gauges is another important source of sea-level observations. Compared to the satellite record, this record has major spatial gaps but covers a much longer period of time. Coverage of tide gauges started primarily in the Northern Hemisphere, with data for the Southern Hemisphere remaining scarce up to the 1970s. The longest running sea-level measurements, NAP or Amsterdam Ordnance Datum established in 1675, are recorded in Amsterdam, the Netherlands. In Australia record collection is also quite extensive, including measurements by an amateur meteorologist beginning in 1837 and measurements taken from a sea-level benchmark struck on a small cliff on the Isle of the Dead near the Port Arthur convict settlement in 1841.
This network was used, in combination with satellite altimeter data, to establish that global mean sea-level rose between 1870 and 2004 at an average rate of about 1.44 mm/yr (1.7 mm/yr during the 20th century). Data collected by the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO) in
The global network of tide gauges is another important source of sea-level observations. Compared to the satellite record, this record has major spatial gaps but covers a much longer period of time. Coverage of tide gauges started primarily in the Northern Hemisphere, with data for the Southern Hemisphere remaining scarce up to the 1970s. The longest running sea-level measurements, NAP or Amsterdam Ordnance Datum established in 1675, are recorded in Amsterdam, the Netherlands. In Australia record collection is also quite extensive, including measurements by an amateur meteorologist beginning in 1837 and measurements taken from a sea-level benchmark struck on a small cliff on the Isle of the Dead near the Port Arthur convict settlement in 1841.
This network was used, in combination with satellite altimeter data, to establish that global mean sea-level rose between 1870 and 2004 at an average rate of about 1.44 mm/yr (1.7 mm/yr during the 20th century). Data collected by the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO) in Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
show that the global mean sea level currently rises by per year, at double the average 20th century rate. This is an important confirmation of climate change simulations which predicted that sea level rise would accelerate in response to climate change.
Some regional differences are also visible in the tide gauge data. Some of the recorded regional differences are due to differences in the actual sea level, while other are due to vertical land movements. In Europe for instance, considerable variation is found because some land areas are rising while others are sinking. Since 1970, most tidal stations have measured higher seas, but sea levels along the northern Baltic Sea have dropped due to post-glacial rebound.
Impacts
 Current and future sea level rise is set to have a number of impacts, particularly on coastal systems. Such impacts include higher and more frequent high-tide and storm-surge flooding, increased coastal erosion, inhibition of primary production processes, more extensive coastal inundation, changes in surface water quality and groundwater characteristics. This is projected in turn to increase loss of property and coastal habitats, increased flood risk and potential loss of life, loss of non-monetary cultural resources and values, impacts on agriculture and
Current and future sea level rise is set to have a number of impacts, particularly on coastal systems. Such impacts include higher and more frequent high-tide and storm-surge flooding, increased coastal erosion, inhibition of primary production processes, more extensive coastal inundation, changes in surface water quality and groundwater characteristics. This is projected in turn to increase loss of property and coastal habitats, increased flood risk and potential loss of life, loss of non-monetary cultural resources and values, impacts on agriculture and aquaculture
Aquaculture (less commonly spelled aquiculture), also known as aquafarming, is the controlled cultivation ("farming") of aquatic organisms such as fish, crustaceans, mollusks, algae and other organisms of value such as aquatic plants (e.g. lot ...
through decline in soil and water quality, and loss of tourism, recreation, and transportation functions. Many of these impacts are detrimental. Owing to the great diversity of coastal environments; regional and local differences in projected relative sea level and climate changes; and differences in the resilience and adaptive capacity of ecosystems, sectors, and countries, the impacts will be highly variable in time and space. River deltas in Africa and Asia and small island states are particularly vulnerable to sea level rise.
Globally tens of millions of people will be exposed in the latter decades of the century if greenhouse gases are not reduced drastically. Many coastal areas have large population growth, which results in more people at risk from sea level rise. While modest increases in sea level are likely to be offset when cities adapt by constructing sea walls or through relocating, millions of people will be affected in cities such as Miami, Rio de Janeiro, Osaka and Shanghai if following the current trajectory of 3 °C (5.4 °F).
The rising seas pose both a direct risk of flooding unprotected areas and indirect threats of higher storm surges, tsunamis and king tides. They are also associated with the highly detrimental second-order effects such as the loss of coastal ecosystems like mangroves or the increased risk from tsunamis in the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" of Africa, Europe and ...
. Coastal flooding impacts are exacerbated by land use changes such as urbanisation or deforestation of low-lying coastal zones. Regions that are already vulnerable to the rising sea level also struggle with coastal flooding washing away land and altering the landscape. People in these areas struggle increasingly because of these different effects of climate change. Climate change influenced storms also create greater frequency of coastal flooding. Addressing the flooding issues that a region, city, or country is experiencing will be based on the efforts of the affected country. Without much effort these coastal regions could continuously degrade and thus greatly affect the size and influence of a country.
Food production in coastal areas is affected by rising sea levels as well. Due to flooding and salt water intrusion into the soil, the salinity of agricultural lands near the sea increases, posing problems for crops that are not salt-resistant. Furthermore, salt intrusion in fresh irrigation water poses a second problem for crops that are irrigated. Newly developed salt-resistant crop variants are currently more expensive than the crops they are set to replace. The farmland in the Nile Delta
The Nile Delta ( ar, دلتا النيل, or simply , is the delta formed in Lower Egypt where the Nile River spreads out and drains into the Mediterranean Sea. It is one of the world's largest river deltas—from Alexandria in the west to Po ...
is affected by salt water flooding, and there is now more salt in the soil and irrigation water in the Red River Delta and the Mekong Delta
The Mekong Delta ( vi, Đồng bằng Sông Cửu Long, lit=Nine Dragon River Delta or simply vi, Đồng Bằng Sông Mê Kông, lit=Mekong River Delta, label=none), also known as the Western Region ( vi, Miền Tây, links=no) or South-weste ...
in Vietnam. Bangladesh and China are affected in a similar way, particularly their rice production.
Sea trade is the dominant form of resource and good trade throughout the world. When talking about the rising sea level there is the possibility for major issues to arise for sea-based trade and the ports that are utilized. What is also of importance for these ports is that we do not yet know how the rising sea level will continue to impact them over time. A variety of factors play into the investment of seaports for this means. Factors that are important for seaports in reference to the rising sea level are where will the important trade ports be in the future, can we alter and protect the ports that are currently being used, how much is needed to protect trade without wasting time or money. The rising sea level for seaports is a concern, but is hard to decipher what changes need to be made since sea levels do not rise at the same rate all over the world.
The long-term cumulative effects of rising sea levels pose a serious threat in coastal areas. Coastal areas are sensitive to rising sea levels, changes in the frequency and intensity of storms, increased precipitation, and rising ocean temperatures. Ten percent of the world's population live in coastal areas that are less than above sea level. Furthermore, two thirds of the world's cities with over five million people are located in these low-lying coastal areas. In total, approximately 600 million people live directly on the coast around the world. Using remote laser scanning called LiDAR
Lidar (, also LIDAR, or LiDAR; sometimes LADAR) is a method for determining ranges (variable distance) by targeting an object or a surface with a laser and measuring the time for the reflected light to return to the receiver. It can also be ...
to measure elevation on the Earth's surface, researchers found that in the year 2021, 267 million people worldwide lived on land less than 2 metres above sea level and that with a 1-metre sea level rise and zero population growth, that number could increase to 410 million people.
Populations that move from the coasts because of the effects of rising sea levels could be impacted by loss of livelihoods and could become a heavy strain on the regions or cities that they come to inhabit. Further, both their original government or the receiving countries may lack or withhold resources to help these climate migrants, which compounds their level of poverty.
Ecosystems
 Coastal ecosystems are facing drastic changes as a consequence of rising sea levels. Many systems might ultimately be lost when sea levels rise too much or too fast. Some ecosystems can move land inward with the high-water mark, but many are prevented from migrating due to natural or artificial barriers. This coastal narrowing, sometimes called 'coastal squeeze' when considering human-made barriers, could result in the loss of habitats such as
Coastal ecosystems are facing drastic changes as a consequence of rising sea levels. Many systems might ultimately be lost when sea levels rise too much or too fast. Some ecosystems can move land inward with the high-water mark, but many are prevented from migrating due to natural or artificial barriers. This coastal narrowing, sometimes called 'coastal squeeze' when considering human-made barriers, could result in the loss of habitats such as mudflat
Mudflats or mud flats, also known as tidal flats or, in Ireland, slob or slobs, are coastal wetlands that form in intertidal areas where sediments have been deposited by tides or rivers. A global analysis published in 2019 suggested that tidal fl ...
s and marshes.
The mangrove ecosystem is one of the ecosystems affected by rising sea levels. It is an ecological whole composed of mangrove plants growing in and around the mudflats of the tropical coast. Its ecological value is high because it is an ideal home for many species. In recent years, mangroves have been moving inland, but their success depends on various environmental information such as topography and geology. The warmer the climate, the bigger they grow. The mangrove's breathing roots or pneumatophores might grow to be half a metre tall. Mangroves and tidal marshes adjust to rising sea levels by building vertically using accumulated sediment and organic matter
Organic matter, organic material, or natural organic matter refers to the large source of carbon-based compounds found within natural and engineered, terrestrial, and aquatic environments. It is matter composed of organic compounds that have c ...
. If sea level rise is too rapid, they will not be able to keep up and will instead be submerged. More specifically, if the rate of mangrove deposition does not keep up with sea level rise, the key to the extinction of the mangrove ecosystem is the relationship between the rate of inland migration and the rate of sea level rise. If sea levels rise faster than the mangroves can move to land, this can lead to the loss of ecosystems. The ability of mangroves to survive sea level rise events depend on their ability to migrate inland. As both ecosystems protect against storm surges, waves and tsunamis, losing them makes the effects of sea level rise worse. Human activities, such as dam building, may restrict sediment supplies to wetlands, and thereby prevent natural adaptation processes. The loss of some tidal marshes is unavoidable as a consequence.
When seawater reaches inland, problems related to contaminated soils may occur. Also, fish, birds, and coastal plants could lose parts of their habitat. Coral, important for bird and fish life, needs to grow vertically to remain close to the sea surface in order to get enough energy from sunlight. It has so far been able to keep up the vertical growth with the rising seas, but might not be able to do so in the future. In 2016, it was reported that the Bramble Cay melomys
The Bramble Cay melomys, or Bramble Cay mosaic-tailed rat (''Melomys rubicola''), is a recently extinct species of rodent in the family Muridae and subfamily Murinae. It was an endemic species of the isolated Bramble Cay, a low-lying vegetate ...
, which lived on a Great Barrier Reef island, had probably become extinct because of inundation due to sea level rises. This report was confirmed by the federal government of Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
when it declared the Bramble Cay melomys
The Bramble Cay melomys, or Bramble Cay mosaic-tailed rat (''Melomys rubicola''), is a recently extinct species of rodent in the family Muridae and subfamily Murinae. It was an endemic species of the isolated Bramble Cay, a low-lying vegetate ...
extinct as of February 2019, making this species the first known mammal to go extinct as a result of sea level rise.
Adaptation

Adaptation
In biology, adaptation has three related meanings. Firstly, it is the dynamic evolutionary process of natural selection that fits organisms to their environment, enhancing their evolutionary fitness. Secondly, it is a state reached by the po ...
options to sea level rise can be broadly classified into ''retreat, accommodate'' and ''protect''. Retreating is moving people and infrastructure
Infrastructure is the set of facilities and systems that serve a country, city, or other area, and encompasses the services and facilities necessary for its economy, households and firms to function. Infrastructure is composed of public and priv ...
to less exposed areas and preventing further development in areas that are at risk. This type of adaptation is potentially disruptive, as displacement of people might lead to tensions. Accommodation options are measurements that make societies more flexible to sea level rise. Examples are the cultivation of food crops that tolerate a high salt content in the soil and making new building standards which require building to be built higher and have less damage in the case a flood does occur. Finally, areas can be protected by the construction of dams, dikes and by improving natural defenses. In more detail, the existing problems are divided into two parts: one is water pollution, and the other is storm surges and floods. Besides, storm surges and flooding can be instantaneous and devastating to cities, and some coastal areas have begun investing in storm water valves to cope with more frequent and severe flooding during high tides.
These adaptation options can be further divided into ''hard'' and ''soft''. Hard adaptation relies mostly on capital-intensive human-built infrastructure and involves large-scale changes to human societies and ecological systems. Because of its large scale, it is often not flexible. Soft adaptation involves strengthening natural defenses and adaptation strategies in local communities and the use of simple and modular technology, which can be locally owned. The two types of adaptation might be complementary or mutually exclusive.
Cutting greenhouse gas emissions (or climate change mitigation) can stabilize sea level rise rates beyond 2050, but can not prevent sea levels from rising. Thus, mitigation gives more time for adaptation and it leaves more options open, such as nature-based solutions.
Regional examples
Africa
 In Africa, risk from sea level rise is amplified by the future
In Africa, risk from sea level rise is amplified by the future population growth
Population growth is the increase in the number of people in a population or dispersed group. Actual global human population growth amounts to around 83 million annually, or 1.1% per year. The global population has grown from 1 billion in 1800 to ...
. It is believed that 54.2 million people lived in the highly exposed low elevation coastal zones (LECZ) around 2000, but this number will effectively double to around 110 million people by 2030, and by 2060 it'll be in the range between 185 and 230 million people, depending on the extent of population growth. While the average regional sea level rise by 2060 will be around 21 cm (with climate change scenarios making little difference at that point), local geography and population trends interact to increase the exposure to hazards like 100-year flood
A 100-year flood is a flood event that has a 1 in 100 chance (1% probability) of being equaled or exceeded in any given year.
The 100-year flood is also referred to as the 1% flood, since its annual exceedance probability is 1%.Holmes, R.R., Jr. ...
s in a complex manner.
In the near term, some of the largest displacement is projected to occur in the East Africa
East Africa, Eastern Africa, or East of Africa, is the eastern subregion of the African continent. In the United Nations Statistics Division scheme of geographic regions, 10-11-(16*) territories make up Eastern Africa:
Due to the historical ...
region, where at least 750,000 people are likely to be displaced from the coasts between 2020 and 2050. It was also estimated that by 2050, 12 major African cities ( Abidjan, Alexandria, Algiers
Algiers ( ; ar, الجزائر, al-Jazāʾir; ber, Dzayer, script=Latn; french: Alger, ) is the capital and largest city of Algeria. The city's population at the 2008 Census was 2,988,145Census 14 April 2008: Office National des Statistiques ...
, Cape Town, Casablanca
Casablanca, also known in Arabic as Dar al-Bayda ( ar, الدَّار الْبَيْضَاء, al-Dār al-Bayḍāʾ, ; ber, ⴹⴹⴰⵕⵍⴱⵉⴹⴰ, ḍḍaṛlbiḍa, : "White House") is the largest city in Morocco and the country's econom ...
, Dakar, Dar es Salaam
Dar es Salaam (; from ar, دَار السَّلَام, Dâr es-Selâm, lit=Abode of Peace) or commonly known as Dar, is the largest city and financial hub of Tanzania. It is also the capital of Dar es Salaam Region. With a population of over s ...
, Durban, Lagos, Lomé, Luanda and Maputo) would collectively sustain cumulative damages of USD 65 billion for the "moderate" climate change scenario RCP 4.5 and USD 86.5 billion for the high-emission scenario RCP 8.5: the version of the high-emission scenario with additional impacts from high ice sheet instability would involve up to 137.5 billion USD in damages. Additional accounting for the "low-probability, high-damage events" may increase aggregate risks to USD 187 billion for the "moderate" RCP4.5, USD 206 billion for RCP8.5 and USD 397 billion under the high-end instability scenario. In all of these estimates, the Egyptian city of Alexandria alone amounts for around half of this figure: hundreds of thousands of people in its low-lying areas may already have to be relocated in the coming decade. Across sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is, geographically, the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lies south of the Sahara. These include West Africa, East Africa, Central Africa, and Southern Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the List of sov ...
as a whole, damages from sea level rise could reach 2–4% of GDP by 2050, although this is strongly affected by the extent of future economic growth
Economic growth can be defined as the increase or improvement in the inflation-adjusted market value of the goods and services produced by an economy in a financial year. Statisticians conventionally measure such growth as the percent rate of ...
and adaptation
In biology, adaptation has three related meanings. Firstly, it is the dynamic evolutionary process of natural selection that fits organisms to their environment, enhancing their evolutionary fitness. Secondly, it is a state reached by the po ...
.
 In the longer term, Egypt, Mozambique and Tanzania are also projected to have the largest number of people affected by annual flooding amongst all African countries if global warming reaches 4 °C by the end of the century (a level associated with the RCP 8.5 scenario). Under RCP 8.5, 10 important cultural sites (
In the longer term, Egypt, Mozambique and Tanzania are also projected to have the largest number of people affected by annual flooding amongst all African countries if global warming reaches 4 °C by the end of the century (a level associated with the RCP 8.5 scenario). Under RCP 8.5, 10 important cultural sites (Casbah of Algiers
The Casbah ( ar, قصبة, ''qaṣba'', meaning citadel) is the citadel of Algiers in Algeria and the traditional quarter clustered around it. In 1992, the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) proclaimed ' ...
, Carthage Archaeological site, Kerkouane, Leptis Magna Archaeological site, Medina of Sousse, Medina of Tunis, Sabratha Archaeological site, Robben Island, Island of Saint-Louis
The Island of Saint-Louis is the historic part of the city of Saint-Louis, Senegal, Saint-Louis in Senegal. In 2000, it was inscribed by the UNESCO on the World Heritage Site, World Heritage list.
History
Founded as a French colonial settlement ...
and Tipasa) would be at risk of flooding and erosion by the end of the century, along with a total of 15 Ramsar site
A Ramsar site is a wetland site designated to be of international importance under the Ramsar Convention,8 ha (O)
*** Permanent 8 ha (P)
*** Seasonal Intermittent < 8 ha(Ts)
**
 As of 2022, it is estimated that 63 million people in the East and South Asia are already at risk from a
As of 2022, it is estimated that 63 million people in the East and South Asia are already at risk from a
Chapter 10: Asia
I
Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability
.-O. Pörtner, D.C. Roberts, M. Tignor, E.S. Poloczanska, K. Mintenbeck, A. Alegría, M. Craig, S. Langsdorf, S. Löschke,V. Möller, A. Okem, B. Rama (eds.) Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 1457–1579 , doi=10.1017/9781009325844.012 One estimate finds that Asia will suffer direct economic damages of 167.6 billion USD at 0.47 meters of sea level rise, 272.3 billion USD at 1.12 meters and 338.1 billion USD at 1.75 meters (along with the indirect impact of 8.5, 24 or 15 billion USD from population displacement at those levels), with
 In
In
Chapter 11: Australasia
I
Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability
.-O. Pörtner, D.C. Roberts, M. Tignor, E.S. Poloczanska, K. Mintenbeck, A. Alegría, M. Craig, S. Langsdorf, S. Löschke,V. Möller, A. Okem, B. Rama (eds.) Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 1581–1688, , doi=10.1017/9781009325844.013
 By 2100, a minimum of 3-4 million people in South America would be directly affected by coastal flooding and erosion. 6% of the population of Venezuela, 56% of the population of
By 2100, a minimum of 3-4 million people in South America would be directly affected by coastal flooding and erosion. 6% of the population of Venezuela, 56% of the population of
Chapter 12: Central and South America
I
Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability
.-O. Pörtner, D.C. Roberts, M. Tignor, E.S. Poloczanska, K. Mintenbeck, A. Alegría, M. Craig, S. Langsdorf, S. Löschke,V. Möller, A. Okem, B. Rama (eds.) Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 1689–1816 , doi=10.1017/9781009325844.014

Chapter 14: North America
I
Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability
.-O. Pörtner, D.C. Roberts, M. Tignor, E.S. Poloczanska, K. Mintenbeck, A. Alegría, M. Craig, S. Langsdorf, S. Löschke,V. Möller, A. Okem, B. Rama (eds.) Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 1929–2042 , doi=10.1017/9781009325844.016 Sea level rise causes the mixing of sea water into the coastal groundwater, rendering it unusable once it amounts to more than 2-3% of the reservoir. Along an estimated 15% of the US coastline, the majority of local groundwater levels are already below the sea level. It also favors chronic flooding at high tide, as evidenced e.g. in the US East Coast. Similarly, Florida, which is extremely vulnerable to climate change, is already experiencing substantial
 Atolls,
Atolls,  Some island nations, such as the
Some island nations, such as the
 Understanding past sea level is an important guide to current and future changes. In the recent geological past, thermal expansion from increased temperatures and changes in land ice are the dominant reasons of sea level rise. The last time that the Earth was warmer than pre-industrial temperatures was 120 thousand years ago, when warming because of changes in the amount of sunlight due to slow changes in the Earth's orbit caused the
Understanding past sea level is an important guide to current and future changes. In the recent geological past, thermal expansion from increased temperatures and changes in land ice are the dominant reasons of sea level rise. The last time that the Earth was warmer than pre-industrial temperatures was 120 thousand years ago, when warming because of changes in the amount of sunlight due to slow changes in the Earth's orbit caused the
NASA Satellite Data 1993-presentFourth National Climate Assessment Sea Level Rise Key MessageIncorporating Sea Level Change Scenarios at the Local Level
Outlines eight steps a community can take to develop site-appropriate scenarios
The Global Sea Level Observing System (GLOSS)USA Sea Level Rise Viewer (NOAA)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Sea Level Rise Oceanography
Bao Bolong Wetland Reserve
Bao Bolong (also ''Baobolong'', ''Bao Bolon'' or ''Baobolon'') Wetland Reserve is a national park in The Gambia. Established in 1996 it covers 220 square kilometres.
The Wetland Reserve is located on the north bank of the River Gambia, approxima ...
, Delta du Saloum National Park, Diawling National Park
The Diawling National Park lies in south west Mauritania around the Senegal River delta. During the rainy season, much of the park consists of large lakes. It is known for having over 220 species of identified birds, including pelicans, black sto ...
, Golfe de Boughrara
Golfe is a Prefecture located in the Maritime Region of Togo. The prefecture's seat is Lomé which is also the administrative capital of the Togolese Republic.
Cantons
A canton is a type of administrative division of a country. In general, cant ...
, Kalissaye
Kalissaye Avifaunal Reserve (KAR) is a small nature reserve in Senegal, located at the mouth of Kalissaye Pond in the middle of the Casamance River.
Like Basse Casamance National Park 35 km away, KAR is currently closed due to the Casamance ...
, Lagune de Ghar el Melh et Delta de la Mejerda, Marromeu Game Reserve
The Marromeu Game Reserve is a protected swath of of floodplain in the Zambezi, the only such area along the river. It was dedicated on 1 January 1969. It is located near Beira.
The area is an open grassland with many rivers and streams in the ...
, Parc Naturel des Mangroves du Fleuve Cacheu
The Cacheu River Mangroves Natural Park ( pt, Parque Natural dos Tarrafes do Rio Cacheu) is a national park situated on the Cacheu River in Guinea-Bissau. It was established on 1 December 2000. This site is 886 km. The park has been designa ...
, Seal Ledges Provincial Nature Reserve
Seal may refer to any of the following:
Common uses
* Pinniped, a diverse group of semi-aquatic marine mammals, many of which are commonly called seals, particularly:
** Earless seal, or "true seal"
** Fur seal
* Seal (emblem), a device to impr ...
, Sebkhet Halk Elmanzel et Oued Essed, Sebkhet Soliman, Réserve Naturelle d'Intérêt Communautaire de la Somone, Songor Biosphere Reserve, Tanbi Wetland Complex and Watamu Marine National Park).
Asia
 As of 2022, it is estimated that 63 million people in the East and South Asia are already at risk from a
As of 2022, it is estimated that 63 million people in the East and South Asia are already at risk from a 100-year flood
A 100-year flood is a flood event that has a 1 in 100 chance (1% probability) of being equaled or exceeded in any given year.
The 100-year flood is also referred to as the 1% flood, since its annual exceedance probability is 1%.Holmes, R.R., Jr. ...
, in large part due to inadequate coastal protection in many countries. This will be greatly exacerbated in the future: Asia has the largest population at risk from sea level and Bangladesh, China, India, Indonesia, Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
, Philippines, Thailand and Vietnam alone account for 70% number of people exposed to sea level rise during the 21st century. This is entirely due to the region's densely populated coasts, as the rate of sea level rise in Asia is generally similar to the global average. Exceptions include the Indo-Pacific
The Indo-Pacific is a vast biogeographic region of Earth.
In a narrow sense, sometimes known as the Indo-West Pacific or Indo-Pacific Asia, it comprises the tropical waters of the Indian Ocean, the western and central Pacific Ocean, and the ...
region, where it had been around 10% faster since the 1990s, and the coast of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
, where globally "extreme" sea level rise had been detected since the 1980s, and it is believed that the difference between and of global warming would have a disproportionate impact on flood frequency. It is also estimated that future sea level rise along the Japanese Honshu Island
, historically called , is the largest and most populous island of Japan. It is located south of Hokkaidō across the Tsugaru Strait, north of Shikoku across the Inland Sea, and northeast of Kyūshū across the Kanmon Straits. The island sep ...
would be up to 25 cm faster than the global average under RCP 8.5, the intense climate change scenario. RCP 8.5 is additionally associated with the loss of at least a third of the Japanese beaches and 57–72% of Thai beaches.Shaw, R., Y. Luo, T.S. Cheong, S. Abdul Halim, S. Chaturvedi, M. Hashizume, G.E. Insarov, Y. Ishikawa, M. Jafari, A. Kitoh, J. Pulhin, C. Singh, K. Vasant, and Z. Zhang, 2022Chapter 10: Asia
I
Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability
.-O. Pörtner, D.C. Roberts, M. Tignor, E.S. Poloczanska, K. Mintenbeck, A. Alegría, M. Craig, S. Langsdorf, S. Löschke,V. Möller, A. Okem, B. Rama (eds.) Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 1457–1579 , doi=10.1017/9781009325844.012 One estimate finds that Asia will suffer direct economic damages of 167.6 billion USD at 0.47 meters of sea level rise, 272.3 billion USD at 1.12 meters and 338.1 billion USD at 1.75 meters (along with the indirect impact of 8.5, 24 or 15 billion USD from population displacement at those levels), with
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
, India, the Republic of Korea, Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
, Indonesia and Russia experiencing the largest economic losses. Out of the 20 coastal cities expected to see the highest flood losses by 2050, 13 are in Asia. For nine of those ( Bangkok, Guangzhou, Ho Chi Minh City
, population_density_km2 = 4,292
, population_density_metro_km2 = 697.2
, population_demonym = Saigonese
, blank_name = GRP (Nominal)
, blank_info = 2019
, blank1_name = – Total
, blank1_ ...
, Jakarta
Jakarta (; , bew, Jakarte), officially the Special Capital Region of Jakarta ( id, Daerah Khusus Ibukota Jakarta) is the capital and largest city of Indonesia. Lying on the northwest coast of Java, the world's most populous island, Jakarta ...
, Kolkata, Nagoya, Tianjin , Xiamen and Zhanjiang) sea level rise would be compounded by subsidence. By 2050, Guangzhou would see 0.2 meters of sea level rise and the estimated ''annual'' economic losses of 254 million USD - the highest in the world. One estimate calculates that in the absence of adaptation, cumulative economic losses caused by sea level rise in Guangzhou under RCP8.5 would reach ~331 billion USD by 2050, ~660 billion USD by 2070 and 1.4 trillion USD by 2100, while the impact of high-end ice sheet instability would increase these figures to ~420 billion USD, ~840 billion USD and ~1.8 trillion USD, respectively. In Shanghai, coastal inundation amounts to ~0.03% of local GDP; but would increase to 0.8% (confidence interval
In frequentist statistics, a confidence interval (CI) is a range of estimates for an unknown parameter. A confidence interval is computed at a designated ''confidence level''; the 95% confidence level is most common, but other levels, such as 9 ...
of 0.4–1.4%) by 2100 even under the "moderate" RCP 4.5 scenario in the absence of adaptation. Likewise, failing to adapt to sea level rise in Mumbai would result in the damages of 112–162 billion USD by 2050, which would nearly triple by 2070. As the result, efforts like the Mumbai Coastal Road are being implemented, although they are likely to affect coastal ecosystems and fishing livelihoods.
It is estimated that sea level rise in Bangladesh may force the relocation of up to one-third of power plants as early as 2030, while a similar proportion would have to deal with the increased salinity of their cooling water by then. Research from 2010s indicates that by 2050, between 0.9 and 2.1 million people would be displaced by sea level rise alone: this would likely necessitate the creation of ~594,000 additional jobs and ~197,000 housing units in the areas receiving the displaced persons, as well as to secure the supply of additional ~783 billion calorie
The calorie is a unit of energy. For historical reasons, two main definitions of "calorie" are in wide use. The large calorie, food calorie, or kilogram calorie was originally defined as the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of on ...
s worth of food. in 2021, another paper estimated that 816,000 would be directly displaced by sea level rise by 2050, but this would be increased to 1,3 million when the indirect effects are taken into account. Both studies assume that the majority of the displaced people would travel to the other areas of Bangladesh, and attempt to estimate population changes in different localities.
In an attempt to address these challenges, the Bangladesh Delta Plan 2100 has been launched in 2018. As of 2020, it was seen falling short of most of its initial targets. The progress is being monitored. Sea level rise also disrupts freshwater fisheries in Bangladesh by making the waters too saline for many fish species.
In 2019, the president of Indonesia, Joko Widodo
Joko Widodo (; born 21 June 1961), popularly known as Jokowi, is an Indonesian politician and businessman who is the 7th and current president of Indonesia. Elected in July 2014, he was the first Indonesian president not to come from an elite ...
, declared that the city of Jakarta
Jakarta (; , bew, Jakarte), officially the Special Capital Region of Jakarta ( id, Daerah Khusus Ibukota Jakarta) is the capital and largest city of Indonesia. Lying on the northwest coast of Java, the world's most populous island, Jakarta ...
is sinking to a degree that requires him to move the capital to another city. A study conducted between 1982 and 2010 found that some areas of Jakarta have been sinking by as much as 28 cm (11 inches) per year due to ground water drilling and the weight of its buildings, and the problem is now exacerbated by sea level rise. However, there are concerns that building in a new location will increase tropical deforestation
Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. The most concentrated d ...
. Other so called sinking cities, such as Bangkok or Tokyo, are vulnerable to these compounding subsidence with sea level rise.
Australasia
 In
In Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
, erosion and flooding of Queensland's Sunshine Coast Sunshine Coast may refer to:
* Sunshine Coast, Queensland, Australia
**Sunshine Coast Region, a local government area of Queensland named after the region
**Sunshine Coast Stadium
* Sunshine Coast (British Columbia), geographic subregion of the Br ...
beaches is projected to intensify by 60% by 2030, with severe impacts on tourism in the absence of adaptation. Adaptation costs to sea level rise under the high-emission RCP 8.5 scenario are projected to be three times greater than the adaptation costs to low-emission RCP 2.6 scenario. For 0.2- to 0.3-m sea level rise (set to occur by 2050), what is currently a 100-year flood
A 100-year flood is a flood event that has a 1 in 100 chance (1% probability) of being equaled or exceeded in any given year.
The 100-year flood is also referred to as the 1% flood, since its annual exceedance probability is 1%.Holmes, R.R., Jr. ...
would occur every year in New Zealand cities of Wellington and Christchurch. Under 0.5 m sea level rise, the current 100-year flood in Australia would be likely to occur several times a year, while in New Zealand, buildings with a collective worth of NZ$12.75 billion would become exposed to new 100-year floods. A meter or so of sea level rise would threaten assets in New Zealand with a worth of NZD$25.5 billion (with a disproportionate impact on Maori-owned holdings and cultural heritage objects), and Australian assets with a worth of AUD$164–226 billion (including many unsealed road
A road is a linear way for the conveyance of traffic that mostly has an improved surface for use by vehicles (motorized and non-motorized) and pedestrians. Unlike streets, the main function of roads is transportation.
There are many types of ...
s and railway lines). The latter represents a 111% rise in Australia's inundation costs between 2020 and 2100.Lawrence, J., B. Mackey, F. Chiew, M.J. Costello, K. Hennessy, N. Lansbury, U.B. Nidumolu, G. Pecl, L. Rickards, N. Tapper,
A. Woodward, and A. Wreford, 2022Chapter 11: Australasia
I
Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability
.-O. Pörtner, D.C. Roberts, M. Tignor, E.S. Poloczanska, K. Mintenbeck, A. Alegría, M. Craig, S. Langsdorf, S. Löschke,V. Möller, A. Okem, B. Rama (eds.) Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 1581–1688, , doi=10.1017/9781009325844.013
Central and South America
 By 2100, a minimum of 3-4 million people in South America would be directly affected by coastal flooding and erosion. 6% of the population of Venezuela, 56% of the population of
By 2100, a minimum of 3-4 million people in South America would be directly affected by coastal flooding and erosion. 6% of the population of Venezuela, 56% of the population of Guyana
Guyana ( or ), officially the Cooperative Republic of Guyana, is a country on the northern mainland of South America. Guyana is an indigenous word which means "Land of Many Waters". The capital city is Georgetown. Guyana is bordered by the ...
(including in the capital, Georgetown, much of which is already below the sea level) and 68% of the population of Suriname
Suriname (; srn, Sranankondre or ), officially the Republic of Suriname ( nl, Republiek Suriname , srn, Ripolik fu Sranan), is a country on the northeastern Atlantic coast of South America. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north ...
are already living in low-lying areas exposed to sea level rise. In Brazil, the coastal ecoregion of Caatinga is responsible for 99% of its shrimp
Shrimp are crustaceans (a form of shellfish) with elongated bodies and a primarily swimming mode of locomotion – most commonly Caridea and Dendrobranchiata of the decapod order, although some crustaceans outside of this order are refer ...
production, yet its unique conditions are threatened by a combination of sea level rise, ocean warming and ocean acidification. The port complex of Santa Catarina had been interrupted by extreme wave or wind behavior 76 times in one 6-year period in 2010s, with a 25,000-50,000 USD loss for each idle day. In Port of Santos, storm surge
A storm surge, storm flood, tidal surge, or storm tide is a coastal flood or tsunami-like phenomenon of rising water commonly associated with low-pressure weather systems, such as cyclones. It is measured as the rise in water level above the n ...
s were three times more frequent between 2000 and 2016 than between 1928 and 1999.Castellanos, E., M.F. Lemos, L. Astigarraga, N. Chacón, N. Cuvi, C. Huggel, L. Miranda, M. Moncassim Vale, J.P. Ometto,
P.L. Peri, J.C. Postigo, L. Ramajo, L. Roco, and M. Rusticucci, 2022Chapter 12: Central and South America
I
Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability
.-O. Pörtner, D.C. Roberts, M. Tignor, E.S. Poloczanska, K. Mintenbeck, A. Alegría, M. Craig, S. Langsdorf, S. Löschke,V. Möller, A. Okem, B. Rama (eds.) Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 1689–1816 , doi=10.1017/9781009325844.014
Europe

Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 ...
is one of the cities which had been the most threatened by flooding. The city is located on islands in the delta of the Po and Piave rivers. Sea level rise causes an increase in frequency and magnitude of floodings in the city which had already spent more than $6 billion on the flood barrier system.
Netherlands is a country that sits partially below sea level and is subsiding. It has responded to that reality by extending its Delta Works program. In 2008, the Dutch ''Delta Commission'', advised in a report that the Netherlands would need a massive new building program to strengthen the country's water defenses against the rising sea for the following 190 years. This included drawing up worst-case plans for evacuations. The plan also included between €1.0 and €1.5 billion in annual spending through to the year 2100 for precautionary measures, such as broadening coastal dunes and strengthening sea and river dikes
Dyke (UK) or dike (US) may refer to:
General uses
* Dyke (slang), a slang word meaning "lesbian"
* Dike (geology), a subvertical sheet-like intrusion of magma or sediment
* Dike (mythology), ''Dikē'', the Greek goddess of moral justice
* Dikes, ...
. The commission said the country must plan for a rise in the North Sea up to by 2100 and plan for a rise by 2200.
Analysis of the impacts of Hurricane Sandy determined that communities located behind wetlands
experienced 20% less damage (Narayan et al., 2016). Coral reefs are providing 544 million USD yr−1 (Beck et al., 2018a) and mangroves
22 billion USD yr−1 in property protection for coastal communities in the USA and Mexico
North America
As of 2017, around 95 million Americans lived on the coast: for Canada and Mexico, this figure amounts to 6.5 million and 19 million people. Northern Gulf of Mexico,Atlantic Canada
Atlantic Canada, also called the Atlantic provinces (french: provinces de l'Atlantique), is the region of Eastern Canada comprising the provinces located on the Atlantic coast, excluding Quebec. The four provinces are New Brunswick, Newfoundlan ...
and the Pacific coast of Mexico would experience the greatest sea level rise. By 2030, flooding along the US Gulf Coast may result in economic losses of up to 176 billion USD: around 50 billion USD could be potentially avoided through nature-based solutions such as wetland restoration
A wetland is a distinct ecosystem that is flooded or saturated by water, either permanently (for years or decades) or seasonally (for weeks or months). Flooding results in oxygen-free (anoxic) processes prevailing, especially in the soils. The ...
and oyster reef restoration. By 2050, 20 million people in the greater New York City area would be threatened, as 40% of the existing water treatment facilities would be compromised and 60% of power plants will need to be relocated. By 2100, sea level rise of 0.9 metres and 1.8 metres would threaten 4.2 and 13.1 million people in the US, respectively. In California alone, 2 metres of SLR could affect 600,000 people and threaten over 150 billion USD in property with inundation, potentially representing more than 6% of the state's GDP. In North Carolina, a meter of SLR inundates 42% of the Albemarle-Pamlico Peninsula
Albemarle-Pamlico Peninsula is a large peninsula (about 3,200 square miles) on the North Carolina coast, lying between the Albemarle Sound to the north and the Pamlico Sound to the south. The 5 counties of Dare, Hyde, Beaufort, Tyrrell, and Was ...
, incurring losses of up to 14 billion USD (at 2016 value of the currency). In nine southeast US states, the same level of sea level rise would amount to the loss over 1000 sites eligible for inclusion in the National Register for Historic Places
The National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) is the United States federal government's official list of districts, sites, buildings, structures and objects deemed worthy of preservation for their historical significance or "great artistic v ...
and up to 13,000 historical and archaeological sites overall.Hicke, J.A., S. Lucatello, L.D., Mortsch, J. Dawson, M. Domínguez Aguilar, C.A.F. Enquist, E.A. Gilmore, D.S. Gutzler,
S. Harper, K. Holsman, E.B. Jewett, T.A. Kohler, and KA. Miller, 2022Chapter 14: North America
I
Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability
.-O. Pörtner, D.C. Roberts, M. Tignor, E.S. Poloczanska, K. Mintenbeck, A. Alegría, M. Craig, S. Langsdorf, S. Löschke,V. Möller, A. Okem, B. Rama (eds.) Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 1929–2042 , doi=10.1017/9781009325844.016 Sea level rise causes the mixing of sea water into the coastal groundwater, rendering it unusable once it amounts to more than 2-3% of the reservoir. Along an estimated 15% of the US coastline, the majority of local groundwater levels are already below the sea level. It also favors chronic flooding at high tide, as evidenced e.g. in the US East Coast. Similarly, Florida, which is extremely vulnerable to climate change, is already experiencing substantial
nuisance flooding
Tidal flooding, also known as sunny day flooding or nuisance flooding, is the temporary inundation of low-lying areas, especially streets, during exceptionally high tide events, such as at Full moon, full and new moons. The highest tides of the ...
and king tide flooding. Nonpartisan think tank '' Resources for the Future'' describes Miami as "the most vulnerable major coastal city in the world" to damages associated with storm-related coastal flooding and sea level rise. Storm surge
A storm surge, storm flood, tidal surge, or storm tide is a coastal flood or tsunami-like phenomenon of rising water commonly associated with low-pressure weather systems, such as cyclones. It is measured as the rise in water level above the n ...
s can cause the largest loss of life and property in the world's coastal areas, and their frequency and intensity has increased in the recent years. New York City is one of the worst affected areas, and simulations show that the current 100-year flood
A 100-year flood is a flood event that has a 1 in 100 chance (1% probability) of being equaled or exceeded in any given year.
The 100-year flood is also referred to as the 1% flood, since its annual exceedance probability is 1%.Holmes, R.R., Jr. ...
would occur once in 19–68 years by 2050 and 40–60 years by 2080. U.S. coastal cities conduct beach nourishment, also known as ''beach replenishment'', where mined sand is trucked in and added, in addition to other adaptation measures such as zoning, restrictions on state funding, and building code standards. In Mexico, the damages from SLR to tourism hotspots like Cancun, Isla Mujeres, Playa del Carmen, Puerto Morelos and Cozumel could amount to 1.4–2.3 billion USD. The damages are also widespread in Canada and will affect both major cities like Halifax and the more remote locations like Lennox Island, whose Mi'kmaq community is already considering relocation due to widespread coastal erosion.
Island nations
 Atolls,
Atolls, low islands
The Low Islands are one of the many uninhabited Canadian arctic island groups in Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut. They are located in Ungava Bay, stretching between Young Island to the south and Lookout Island to the north.
References
Externa ...
and low-lying coastal areas on islands are particularly vulnerable to sea level rise. Possible impacts include coastal erosion, flooding and salt intrusion into soils and freshwater. None are more vulnerable than small island nations, particularly those with population concentrations on atolls. Atolls on average reach above sea level. This type of island is a final stage in the geologic history of an island of volcanic origin (all volcanic islands usually become an atoll, eventually). With climate change causing sea levels rise, the process of atoll formation has sped up.
Since atolls are low-lying islands, they are vulnerable to rising waters or storms covering them in water. Atolls are vital because they are the home to many distinct cultures and sovereign nations. As ocean water prematurely covers atolls, saltwater can intrude into drinking water supplies and undermine the ecosystems that the population utilizes to survive. Sea level rise has the potential to devastate tourism and local economies; a sea level rise of would cause partial or complete inundation of 29% of coastal resorts in the Caribbean
The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean Se ...
. A further 49–60% of coastal resorts would be at risk from resulting coastal erosion. It is difficult to assess how much of past erosion and floods have been caused by sea level change, compared to other environmental events such as hurricanes. Adaptation to sea level rise is costly for small island nations as a large portion of their population lives in areas that are at risk.
Maldives, Tuvalu, and other low-lying countries are among the areas that are at the highest level of risk. At current rates, sea level would be high enough to make the Maldives uninhabitable by 2100. The Island nation of Fiji is being impacted by sea level rise. Five of the Solomon Islands have disappeared due to the combined effects of sea level rise and stronger trade winds that were pushing water into the Western Pacific. Countries becoming uninhabitable could exacerbate the humanitarian crisis of climate refugees.
 Some island nations, such as the
Some island nations, such as the Republic of Maldives
Maldives (, ; dv, ދިވެހިރާއްޖެ, translit=Dhivehi Raajje, ), officially the Republic of Maldives ( dv, ދިވެހިރާއްޖޭގެ ޖުމްހޫރިއްޔާ, translit=Dhivehi Raajjeyge Jumhooriyyaa, label=none, ), is an archipelag ...
, Kiribati and Tuvalu are considering international migration of their population in response to rising seas. Moving to different countries is not an easy solution, as those who move need to have a steady income and social network in their new country. It might be easier to adapt locally by moving further inland and increasing sediment supply needed for natural erosion protection. In the island nation of Fiji
Fiji ( , ,; fj, Viti, ; Fiji Hindi: फ़िजी, ''Fijī''), officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consists ...
, residents are restoring coral reefs and mangroves to protect themselves against flooding and erosion, which is estimated to be more cost-efficient than building sea-walls.
Of interest is how the rising sea level will affect children in these communities. Children without stability at home and their communities can experience a variety of issues in their development. Already, children in small island states are encountering hampered access to food and water, displacement, and resulting mental and social disorders from these stressors.
In the case all islands of an island nation become uninhabitable or completely submerged by the sea, the states themselves would theoretically also become dissolved. Once this happens, all rights on the surrounding area (sea) are removed. This area can be significant as rights extend to a radius of around the entire island state. Any resources, such as fossil oil, minerals and metals, within this area can be freely dug up by anyone and sold without needing to pay any commission to the (now dissolved) island state.
Changes in other geologic periods
 Understanding past sea level is an important guide to current and future changes. In the recent geological past, thermal expansion from increased temperatures and changes in land ice are the dominant reasons of sea level rise. The last time that the Earth was warmer than pre-industrial temperatures was 120 thousand years ago, when warming because of changes in the amount of sunlight due to slow changes in the Earth's orbit caused the
Understanding past sea level is an important guide to current and future changes. In the recent geological past, thermal expansion from increased temperatures and changes in land ice are the dominant reasons of sea level rise. The last time that the Earth was warmer than pre-industrial temperatures was 120 thousand years ago, when warming because of changes in the amount of sunlight due to slow changes in the Earth's orbit caused the Eemian
The Eemian (also called the last interglacial, Sangamonian, Sangamonian Stage, Ipswichian, Mikulin, Kaydaky, penultimate,NOAA - Penultimate Interglacial Period http://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/global-warming/penultimate-interglacial-period Valdivia or Ri ...
interglacial
An interglacial period (or alternatively interglacial, interglaciation) is a geological interval of warmer global average temperature lasting thousands of years that separates consecutive glacial periods within an ice age. The current Holocene in ...
; sea levels during that warmer interglacial were at least higher than now. The Eemian warming was sustained over a period of thousands of years, and the magnitude of the rise in sea level implies a large contribution from the Antarctic and Greenland ice sheets. Further into the past, a report by the Royal Netherlands Institute for Sea Research states that, around three million years ago, levels of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere similar to today's levels increased temperature by two to three degrees Celsius and melted one third of Antarctica's ice sheets. This in turn caused sea-levels to rise 20 metres over their present values.
Since the last glacial maximum
The Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), also referred to as the Late Glacial Maximum, was the most recent time during the Last Glacial Period that ice sheets were at their greatest extent.
Ice sheets covered much of Northern North America, Northern Eur ...
about 20,000 years ago, the sea level has risen by more than , with rates varying from less than a mm/year during the pre-industrial era to 40+ mm/year when major ice sheets over Canada and Eurasia melted. Rapid disintegration of these ice sheets led to so called ' meltwater pulses', periods during which sea level rose rapidly. The rate of rise started to slow down about 8,200 years before present; the sea level was then almost constant in the last 2,500 years, before the recent rising trend that started at the end of the 19th century or in the beginning of the 20th.
See also
*Climate emergency declaration
A climate emergency declaration or ''declaring a climate emergency'' is an action taken by governments and scientists to acknowledge humanity is in a climate emergency. The first such declaration was made by a local government in December 2016. ...
* Climate engineering
* Coastal development hazards
* Coastal sediment supply
* Effects of climate change on oceans
Among the effects of climate change on oceans are: an increase in sea surface temperature as well as ocean temperatures at greater depths, more frequent marine heatwaves, a reduction in pH value, a rise in sea level from ocean warming and ice ...
* Effects of climate change on small island countries
The effect of climate change on small island countries can be extreme because of low-lying coasts, relatively small land masses, and exposure to extreme weather. The effects of climate change, particularly sea level rise and increasingly intense ...
* Hydrosphere
* Islands First
Islands First is a non-governmental organization working on behalf of the Small Island Developing States to confront the challenges of climate change, the depletion of ocean resources (including ocean acidification and biodiversity loss), and oce ...
* List of countries by average elevation
References
External links
NASA Satellite Data 1993-present
Outlines eight steps a community can take to develop site-appropriate scenarios
The Global Sea Level Observing System (GLOSS)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Sea Level Rise Oceanography
Rise
Rise or RISE may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional entities
* '' Rise: The Vieneo Province'', an internet-based virtual world
* Rise FM, a fictional radio station in the video game ''Grand Theft Auto 3''
* Rise Kujikawa, a video ...
Effects of climate change
Coastal geography
Climate change adaptation
Articles containing video clips