Crawley on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Crawley () is a large town and
 In the 5th century, Saxon settlers named the area Crow's Leah—meaning a crow-infested clearing, or Crow's Wood. This name evolved over time, and the present spelling appeared by the early 14th century. By this time, nearby settlements were more established: the Saxon church at Worth, for example, dates from between 950 and 1050 AD.
Although Crawley itself is not mentioned in the
In the 5th century, Saxon settlers named the area Crow's Leah—meaning a crow-infested clearing, or Crow's Wood. This name evolved over time, and the present spelling appeared by the early 14th century. By this time, nearby settlements were more established: the Saxon church at Worth, for example, dates from between 950 and 1050 AD.
Although Crawley itself is not mentioned in the
 The Brighton Main Line was the first railway line to serve the Crawley area. A station was opened at Three Bridges (originally known as East Crawley) in the summer of 1841. Crawley railway station, at the southern end of the High Street, was built in 1848 when the Horsham branch was opened from Three Bridges to Horsham. A line was built eastwards from Three Bridges to East Grinstead in 1855. Three Bridges had become the hub of transport in the area by this stage: one-quarter of its population was employed in railway jobs by 1861 (mainly at the
The Brighton Main Line was the first railway line to serve the Crawley area. A station was opened at Three Bridges (originally known as East Crawley) in the summer of 1841. Crawley railway station, at the southern end of the High Street, was built in 1848 when the Horsham branch was opened from Three Bridges to Horsham. A line was built eastwards from Three Bridges to East Grinstead in 1855. Three Bridges had become the hub of transport in the area by this stage: one-quarter of its population was employed in railway jobs by 1861 (mainly at the
 Extended shopping facilities to the east of the existing high street were provided. The first stage to open was The Broadwalk in 1954, following by the opening of the Queen's Square development by
Extended shopping facilities to the east of the existing high street were provided. The first stage to open was The Broadwalk in 1954, following by the opening of the Queen's Square development by  By April 1960, when Thomas Bennett made his last presentation as chairman of the Development Corporation, the town's population had reached 51,700; of the factory and other industrial space had been provided; 21,800 people were employed, nearly 60% of whom worked in manufacturing industries, and only seventy people were registered as unemployed. The corporation had built 10,254 houses, and private builders provided around 1,500 more. Tenants were by then permitted to buy their houses and 440 householders had chosen to do so by April 1960.
A new plan was put forward by West Sussex County Council in 1961. This proposed new neighbourhoods at Broadfield and
By April 1960, when Thomas Bennett made his last presentation as chairman of the Development Corporation, the town's population had reached 51,700; of the factory and other industrial space had been provided; 21,800 people were employed, nearly 60% of whom worked in manufacturing industries, and only seventy people were registered as unemployed. The corporation had built 10,254 houses, and private builders provided around 1,500 more. Tenants were by then permitted to buy their houses and 440 householders had chosen to do so by April 1960.
A new plan was put forward by West Sussex County Council in 1961. This proposed new neighbourhoods at Broadfield and


 Crawley became a parish in the sixteenth century, having previously been a chapelry in the parish of Slaugham. When district and parish councils were established under the
Crawley became a parish in the sixteenth century, having previously been a chapelry in the parish of Slaugham. When district and parish councils were established under the

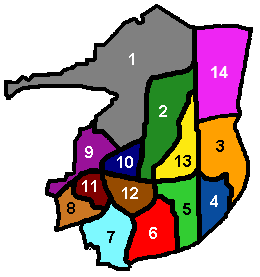
 There are 14 residential neighbourhoods, each with a variety of housing types: terraced, semi-detached and detached houses, low-rise flats and bungalows. There are no residential tower blocks, apart from the 8-storey Milton Mount Flats at the North end of Pound Hill. Many houses have their own gardens and are set back from roads. The hub of each neighbourhood is a shopping parade, community centre and church, and each has a school and recreational open spaces as well. Crawley Development Corporation's intention was for neighbourhood shops to cater only to basic needs, and for the town centre to be used for most shopping requirements. The number of shop units provided in the neighbourhood parades reflected this: despite the master plan making provision for at least 20 shops in each neighbourhood, the number actually built ranged from 19 in the outlying Langley Green neighbourhood to just seven in West Green, close to the town centre.
Each of the 14 residential neighbourhoods is identified by a colour, which is shown on street name signs in a standard format throughout the town: below the street name, the neighbourhood name is shown in white text on a coloured background.
There are areas which are not defined as neighbourhoods but which are closely associated with Crawley:
* The Manor Royal industrial estate is in the north of the town. Although it is part of the Northgate ward, it is allocated a colour: its street name signs feature the word "Industrial" on a black background.
* Crawley's town centre is in the southernmost part of Northgate. Its street name signs do not follow the standard format of the neighbourhood signs but display only the street name.
*
There are 14 residential neighbourhoods, each with a variety of housing types: terraced, semi-detached and detached houses, low-rise flats and bungalows. There are no residential tower blocks, apart from the 8-storey Milton Mount Flats at the North end of Pound Hill. Many houses have their own gardens and are set back from roads. The hub of each neighbourhood is a shopping parade, community centre and church, and each has a school and recreational open spaces as well. Crawley Development Corporation's intention was for neighbourhood shops to cater only to basic needs, and for the town centre to be used for most shopping requirements. The number of shop units provided in the neighbourhood parades reflected this: despite the master plan making provision for at least 20 shops in each neighbourhood, the number actually built ranged from 19 in the outlying Langley Green neighbourhood to just seven in West Green, close to the town centre.
Each of the 14 residential neighbourhoods is identified by a colour, which is shown on street name signs in a standard format throughout the town: below the street name, the neighbourhood name is shown in white text on a coloured background.
There are areas which are not defined as neighbourhoods but which are closely associated with Crawley:
* The Manor Royal industrial estate is in the north of the town. Although it is part of the Northgate ward, it is allocated a colour: its street name signs feature the word "Industrial" on a black background.
* Crawley's town centre is in the southernmost part of Northgate. Its street name signs do not follow the standard format of the neighbourhood signs but display only the street name.
*
 At the
At the
 While most of the jobs created in the new town's early years were in manufacturing, the tertiary sector developed strongly from the 1960s. The Manor Royal estate, with its space, proximity to Gatwick Airport and good transport links, attracted airport-related services such as logistics, catering, distribution and warehousing; and the corporation and private companies built offices throughout the town. Office floorspace in the town increased from in 1965 to a conservative estimate of in 1984. Major schemes during that period included premises for the Westminster Bank British Caledonian and The Office of the Paymaster-General. The five-storey Overline House above the railway station, completed in 1968, is used by Crawley's NHS primary care trust and various other companies.
While most of the jobs created in the new town's early years were in manufacturing, the tertiary sector developed strongly from the 1960s. The Manor Royal estate, with its space, proximity to Gatwick Airport and good transport links, attracted airport-related services such as logistics, catering, distribution and warehousing; and the corporation and private companies built offices throughout the town. Office floorspace in the town increased from in 1965 to a conservative estimate of in 1984. Major schemes during that period included premises for the Westminster Bank British Caledonian and The Office of the Paymaster-General. The five-storey Overline House above the railway station, completed in 1968, is used by Crawley's NHS primary care trust and various other companies.
 Companies headquartered in Crawley include Doosan Babcock Energy, WesternGeco, Virgin Atlantic, Virgin Atlantic's associated travel agency
Companies headquartered in Crawley include Doosan Babcock Energy, WesternGeco, Virgin Atlantic, Virgin Atlantic's associated travel agency

 Even before the new town was planned, Crawley was a retail centre for the surrounding area: there were 177 shops in the town in 1948, 99 of which were on the High Street. Early new town residents relied on these shopping facilities until the Corporation implemented the master plan's designs for a new shopping area on the mostly undeveloped land east of the High Street and north of the railway line. The Broadwalk and its 23 shops were built in 1954, followed by the Queen's Square complex and surrounding streets in the mid-1950s. Queen's Square, a pedestrianised plaza surrounded by large shops and linked to the High Street by The Broadwalk, was officially opened in 1958 by Queen Elizabeth II. The town centre was completed by 1960, by which time Crawley was already recognised as an important regional, rather than merely local, shopping centre.
In the 1960s and 1970s, large branches of Tesco,
Even before the new town was planned, Crawley was a retail centre for the surrounding area: there were 177 shops in the town in 1948, 99 of which were on the High Street. Early new town residents relied on these shopping facilities until the Corporation implemented the master plan's designs for a new shopping area on the mostly undeveloped land east of the High Street and north of the railway line. The Broadwalk and its 23 shops were built in 1954, followed by the Queen's Square complex and surrounding streets in the mid-1950s. Queen's Square, a pedestrianised plaza surrounded by large shops and linked to the High Street by The Broadwalk, was officially opened in 1958 by Queen Elizabeth II. The town centre was completed by 1960, by which time Crawley was already recognised as an important regional, rather than merely local, shopping centre.
In the 1960s and 1970s, large branches of Tesco,
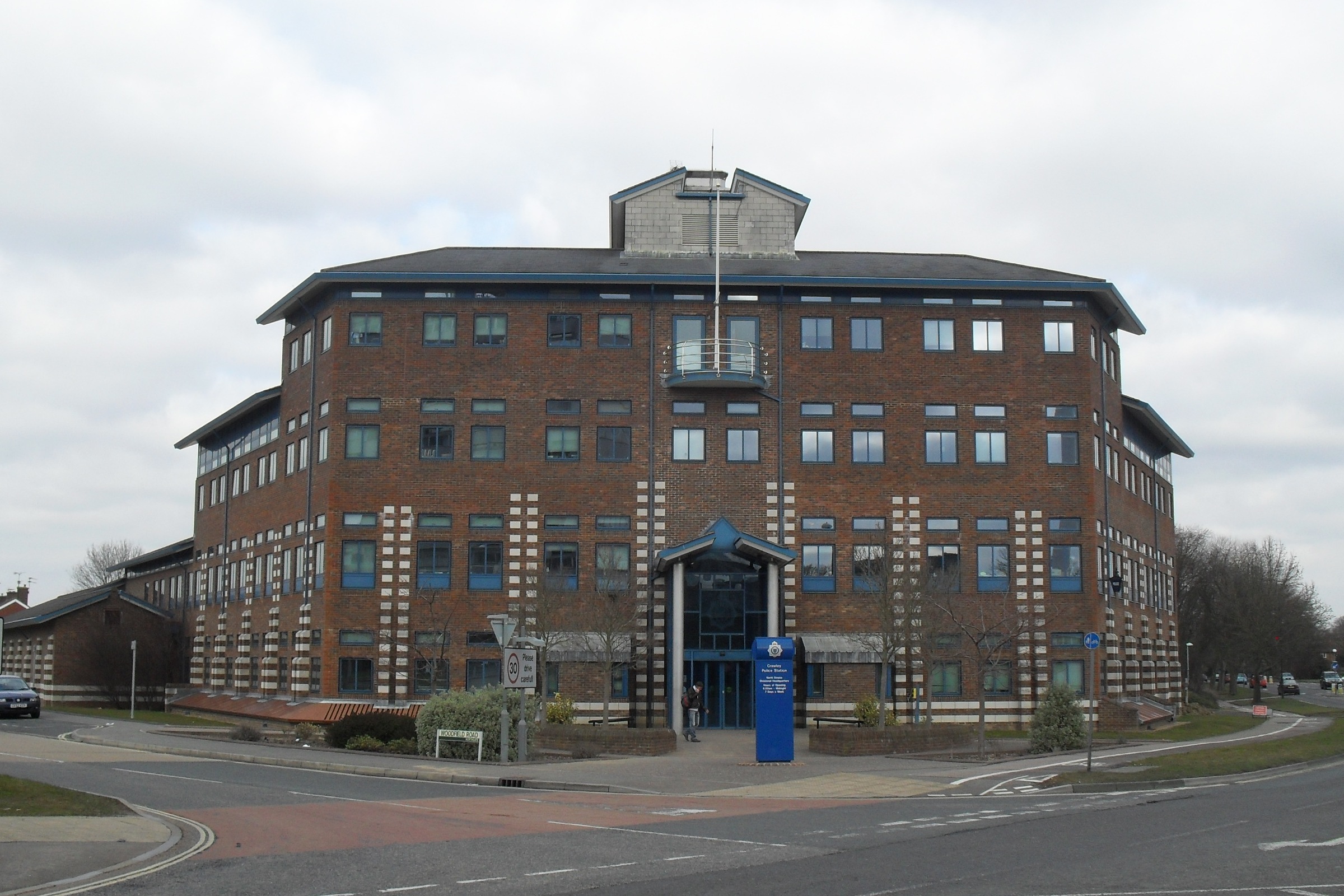

 Policing in Crawley is provided by Sussex Police; the British Transport Police are responsible for the rail network. The borough is the police headquarters for the West Sussex division, and is itself divided into three areas for the purposes of neighbourhood policing: Crawley East, Crawley West, and Crawley Town Centre. A separate division covers Gatwick Airport. There is a police station in the town centre; it is open 24 hours a day, and the front desk is staffed for 16 hours each day except Christmas Day. Statutory emergency fire and rescue services are provided by the
Policing in Crawley is provided by Sussex Police; the British Transport Police are responsible for the rail network. The borough is the police headquarters for the West Sussex division, and is itself divided into three areas for the purposes of neighbourhood policing: Crawley East, Crawley West, and Crawley Town Centre. A separate division covers Gatwick Airport. There is a police station in the town centre; it is open 24 hours a day, and the front desk is staffed for 16 hours each day except Christmas Day. Statutory emergency fire and rescue services are provided by the
 The first railway line in the area was the Brighton Main Line, which opened as far as Haywards Heath on 12 July 1841 and reached Brighton on 21 September 1841. It ran through Three Bridges, which was then a small village east of Crawley, and
The first railway line in the area was the Brighton Main Line, which opened as far as Haywards Heath on 12 July 1841 and reached Brighton on 21 September 1841. It ran through Three Bridges, which was then a small village east of Crawley, and
 Crawley was one of several towns where the boundaries of
Crawley was one of several towns where the boundaries of
 Gatwick Airport was licensed as a private airfield in August 1930. It was used during the Second World War as an RAF base, and returned to civil use in 1946. There were proposals to close the airport in the late 1940s, but in 1950 the government announced that it was to be developed as London's second airport. It was closed between 1956 and 1958 for rebuilding.
Gatwick Airport was licensed as a private airfield in August 1930. It was used during the Second World War as an RAF base, and returned to civil use in 1946. There were proposals to close the airport in the late 1940s, but in 1950 the government announced that it was to be developed as London's second airport. It was closed between 1956 and 1958 for rebuilding.


 Crawley Town F.C. is Crawley's main football team. Formed in 1896, it moved in 1949 to a ground at Town Mead adjacent to the West Green playing fields. Demand for land near the town centre led to the club moving in 1997 to the new Broadfield Stadium, now owned by the borough council. As of the 2019/2020 season, Crawley Town play in League Two, the fourth tier of league football in England. Perhaps the pinnacle of the club's history was in February 2011 when they played against Manchester United at Old Trafford in the
Crawley Town F.C. is Crawley's main football team. Formed in 1896, it moved in 1949 to a ground at Town Mead adjacent to the West Green playing fields. Demand for land near the town centre led to the club moving in 1997 to the new Broadfield Stadium, now owned by the borough council. As of the 2019/2020 season, Crawley Town play in League Two, the fourth tier of league football in England. Perhaps the pinnacle of the club's history was in February 2011 when they played against Manchester United at Old Trafford in the
 The high street becomes an annual focus of motoring heritage in November as one of the official stops on the London to Brighton Veteran Car Run.
The high street becomes an annual focus of motoring heritage in November as one of the official stops on the London to Brighton Veteran Car Run.
 Maintained primary and secondary schools were reorganised in 2004 following the Local Education Authority's decision to change the town's three-tier system of first, middle and secondary schools to a more standard primary/secondary divide. Since the restructuring, Crawley has had 17 primary schools (including two
Maintained primary and secondary schools were reorganised in 2004 following the Local Education Authority's decision to change the town's three-tier system of first, middle and secondary schools to a more standard primary/secondary divide. Since the restructuring, Crawley has had 17 primary schools (including two
File:Erin Doherty in 2020.png, Erin Doherty
File:Ms Dynamite (4663812211).jpg,
* Akala (Kingslee James McLean Daley), British rapper voted the Best Hip Hop Act at the MOBO Awards 2006
*Sir Charles Court, the 21st Premier of Western Australia, was born in Crawley, but migrated to Australia with his family before his first birthday.
* Erin Doherty, actress, known for roles in '' Call the Midwife'' (2017), ''
Crawley Borough Council
{{authority control Towns in West Sussex New towns in England Non-metropolitan districts of West Sussex Populated places established in the 5th century New towns started in the 1940s Unparished areas in West Sussex Boroughs in England
borough
A borough is an administrative division in various English-speaking countries. In principle, the term ''borough'' designates a self-governing walled town, although in practice, official use of the term varies widely.
History
In the Middle Ag ...
in West Sussex, England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe ...
. It is south of London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
, north of Brighton and Hove, and north-east of the county town of Chichester
Chichester () is a cathedral city and civil parish in West Sussex, England.OS Explorer map 120: Chichester, South Harting and Selsey Scale: 1:25 000. Publisher:Ordnance Survey – Southampton B2 edition. Publishing Date:2009. It is the only ...
. Crawley covers an area of and had a population of 106,597 at the time of the 2011 Census.
The area has been inhabited since the Stone Age
The Stone Age was a broad prehistoric period during which stone was widely used to make tools with an edge, a point, or a percussion surface. The period lasted for roughly 3.4 million years, and ended between 4,000 BC and 2,000 BC, with t ...
, and was a centre of ironworking in Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
* Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lett ...
times. Crawley developed slowly as a market town
A market town is a settlement most common in Europe that obtained by custom or royal charter, in the Middle Ages, a market right, which allowed it to host a regular market; this distinguished it from a village or city. In Britain, small rural ...
from the 13th century, serving the surrounding villages in the Weald. Its location on the main road from London to Brighton brought passing trade, which encouraged the development of coaching inn
The coaching inn (also coaching house or staging inn) was a vital part of Europe's inland transport infrastructure until the development of the railway, providing a resting point ( layover) for people and horses. The inn served the needs of tr ...
s. A rail link to London opened in 1841.
Gatwick Airport
Gatwick Airport (), also known as London Gatwick , is a major international airport near Crawley, West Sussex, England, south of Central London. In 2021, Gatwick was the third-busiest airport by total passenger traffic in the UK, after ...
, nowadays one of Britain's busiest international airports, opened on the edge of the town in the 1940s, encouraging commercial and industrial growth. After the Second World War, the British Government planned to move large numbers of people and jobs out of London and into new towns
A planned community, planned city, planned town, or planned settlement is any community that was carefully planned from its inception and is typically constructed on previously undeveloped land. This contrasts with settlements that evolve ...
around South East England. The New Towns Act 1946 designated Crawley as the site of one of these. A master plan was developed for the establishment of new residential, commercial, industrial and civic areas, and rapid development greatly increased the size and population of the town over a few decades.
The town contains 14 residential neighbourhoods radiating out from the core of the old market town, and separated by main roads and railway lines. The nearby communities of Ifield, Pound Hill
Pound Hill is one of 14 neighbourhoods within the town of Crawley in West Sussex, England. Pound Hill is located on the east of Crawley. It is bordered by Three Bridges and Manor Royal to the west and Maidenbower to the south.
It is the larges ...
and Three Bridges were absorbed into the new town at various stages in its development. In 2009, expansion was being planned in the west and north-west of the town, in cooperation with Horsham District Council
Horsham is a market town on the upper reaches of the River Arun on the fringe of the Weald in West Sussex, England. The town is south south-west of London, north-west of Brighton and north-east of the county town of Chichester. Nearby tow ...
, which has now become a new neighbourhood named Kilnwood Vale
Kilnwood Vale is a village in the Horsham district of West Sussex, England. It borders the High Weald Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty along the A264 east of Faygate between Horsham and Crawley. The development first opened in 2016 which when ...
, but it is not in Crawley. Economically, the town has developed into the main centre of industry and employment between London and the south coast. Its large industrial area supports manufacturing and service companies, many of them connected with the airport. The commercial and retail sectors continue to expand.
History
Origins
The area may have been settled during the Mesolithic period: locally manufacturedflint
Flint, occasionally flintstone, is a sedimentary cryptocrystalline form of the mineral quartz, categorized as the variety of chert that occurs in chalk or marly limestone. Flint was widely used historically to make stone tools and start ...
s of the Horsham Culture type have been found to the southwest of the town. Tools and burial mounds from the Neolithic period, and burial mounds and a sword from the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
, have also been discovered. Crawley is on the western edge of the High Weald, which produced iron for more than 2,000 years from the Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age ( Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly ...
onwards. Goffs Park—now a recreational area in the south of the town—was the site of two late Iron Age furnaces. Ironworking and mineral extraction continued throughout Roman times, particularly in the Broadfield area where many furnaces were built.
Domesday Book
Domesday Book () – the Middle English spelling of "Doomsday Book" – is a manuscript record of the "Great Survey" of much of England and parts of Wales completed in 1086 by order of King William I, known as William the Conqueror. The manusc ...
of 1086, the nearby settlements of Ifield and Worth are recorded. The first written record of Crawley dates from 1202, when a licence was issued by King John for a weekly market on Wednesdays. Crawley grew slowly in importance over the next few centuries, but was boosted in the 18th century by the construction of the turnpike
Turnpike often refers to:
* A type of gate, another word for a turnstile
* In the United States, a toll road
Turnpike may also refer to:
Roads United Kingdom
* A turnpike road, a principal road maintained by a turnpike trust, a body with powe ...
road between London and Brighton. When this was completed in 1770, travel between the newly fashionable seaside resort and London became safer and quicker, and Crawley (located approximately halfway between the two) prospered as a coaching halt. By 1839 it offered almost an hourly service to both destinations. The George, a timber-framed house dating from the 15th century, expanded to become a large coaching inn, taking over adjacent buildings. Eventually an annexe had to be built in the middle of the wide High Street; this survived until the 1930s. The original building has become the George Hotel, with conference facilities and 84 bedrooms; it retains many period features including an iron fireback.
Crawley's oldest church is St John the Baptist's, between the High Street and the Broadway. It is said to have 13th-century origins, but there has been much rebuilding (especially in the 19th century) and the oldest part remaining is the south wall of the nave
The nave () is the central part of a church, stretching from the (normally western) main entrance or rear wall, to the transepts, or in a church without transepts, to the chancel. When a church contains side aisles, as in a basilica-typ ...
, which is believed to be 14th century. The church has a 15th-century tower
A tower is a tall structure, taller than it is wide, often by a significant factor. Towers are distinguished from masts by their lack of guy-wires and are therefore, along with tall buildings, self-supporting structures.
Towers are specific ...
(rebuilt in 1804) which originally contained four bells cast in 1724. Two were replaced by Thomas Lester of London in 1742; but in 1880 a new set of eight bells were cast and installed by the Croydon-based firm Gillett, Bland & Company.
Railway age and Victorian era
London, Brighton and South Coast Railway
The London, Brighton and South Coast Railway (LB&SCR; known also as the Brighton line, the Brighton Railway or the Brighton) was a railway company in the United Kingdom from 1846 to 1922. Its territory formed a rough triangle, with London at its ...
's railway works near the station). The Longley company—one of South East England's largest building firms in the late 19th century, responsible for buildings including Christ's Hospital school and King Edward VII Sanatorium
A sanatorium (from Latin '' sānāre'' 'to heal, make healthy'), also sanitarium or sanitorium, are antiquated names for specialised hospitals, for the treatment of specific diseases, related ailments and convalescence. Sanatoriums are often ...
in Midhurst—moved to a site next to Crawley station in 1881. In 1898 more than 700 people were employed at the site.
There was a major expansion in house building in the late 19th century. An area known as "New Town" (unrelated to the postwar developments) was created around the railway level crossing
A level crossing is an intersection where a railway line crosses a road, path, or (in rare situations) airport runway, at the same level, as opposed to the railway line crossing over or under using an overpass or tunnel. The term a ...
and down the Brighton Road; the West Green area, west of the High Street on the way to Ifield, was built up; and housing spread south of the Horsham line for the first time, into what is now Southgate. The population reached 4,433 in 1901, compared to 1,357 a century earlier. In 1891, a racecourse was opened on farmland at Gatwick. Built to replace a steeplechase
Steeplechase may refer to:
* Steeplechase (horse racing), a type of horse race in which participants are required to jump over obstacles
* Steeplechase (athletics), an event in athletics that derives its name from the steeplechase in horse racing ...
course at Waddon
Waddon () is a neighbourhood in the London Borough of Croydon, at the western end of the town of Croydon. The area borders the London Borough of Sutton.
History
It is not known when the manor of Croydon was granted to the See of Canterbury, ...
near Croydon
Croydon is a large town in south London, England, south of Charing Cross. Part of the London Borough of Croydon, a local government district of Greater London. It is one of the largest commercial districts in Greater London, with an exten ...
in Surrey, it was used for both steeplechase and flat racing, and held the Grand National during the years of the First World War. The course had its own railway station on the Brighton Main Line.
In the early 20th century, many of the large country estates in the area, with their mansions and associated grounds and outbuildings, were split up into smaller plots of land, attracting haphazard housing development and small farms. By the outbreak of the First World War in 1914 Crawley had grown into a small but prosperous town, serving a wide rural area and those passing through on the A23 London–Brighton road. Three-quarters of the population had piped water supplies, all businesses and homes had electricity, and piped gas and street lighting had been in place for 50 years. An airfield was opened in 1930 on land near the racecourse. This was a private concern until the Second World War when it was claimed by the Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the United Kingdom's air and space force. It was formed towards the end of the First World War on 1 April 1918, becoming the first independent air force in the world, by regrouping the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) an ...
.
New Town
In May 1946, the New Towns Act of 1946 identified Crawley as a suitable location for a New Town; but it was not officially designated as such until . The of land set aside for the new town were split across the county borders between East Sussex, West Sussex andSurrey
Surrey () is a ceremonial county, ceremonial and non-metropolitan county, non-metropolitan counties of England, county in South East England, bordering Greater London to the south west. Surrey has a large rural area, and several significant ur ...
. Architect Thomas Bennett was appointed chairman of Crawley Development Corporation. A court challenge to the designation order meant that plans were not officially confirmed until December 1947. By this time, an initial plan for the development of the area had been drawn up by Anthony Minoprio
Sir Charles Anthony Minoprio (1900–1988) was a British architect and town planner. Much of his early work was in partnership with Hugh Spencely (1900–1983), a friend since they attended Harrow School together. Later he worked more as a town ...
. This proposed filling in the gaps between the villages of Crawley, Ifield and Three Bridges. Bennett estimated that planning, designing and building the town, and increasing its population from the existing 9,500 to 40,000, would take 15 years.
Work began almost immediately to prepare for the expansion of the town. A full master plan was in place by 1949. This envisaged an increase in the population of the town to 50,000, residential properties in nine neighbourhoods radiating from the town centre, and a separate industrial area to the north. The neighbourhoods would consist mainly of three-bedroom family homes, with a number of smaller and larger properties. Each would be built around a centre with shops, a church, a public house
A pub (short for public house) is a kind of drinking establishment which is licensed to serve alcoholic drinks for consumption on the premises. The term ''public house'' first appeared in the United Kingdom in late 17th century, and wa ...
, a primary school and a community centre
Community centres, community centers, or community halls are public locations where members of a community tend to gather for group activities, social support, public information, and other purposes. They may sometimes be open for the whole c ...
. Secondary education was to be provided at campuses at Ifield Green, Three Bridges and Tilgate
Tilgate is one of 14 neighbourhoods within the town of Crawley in West Sussex, England. The area contains a mixture of privately developed housing, self-build groups and ex-council housing. It is bordered by the districts of Furnace Green to th ...
. Later, a fourth campus, in Southgate, was added to the plans.
At first, little development took place in the town centre, and residents relied on the shops and services in the existing high street. The earliest progress was in West Green, where new residents moved in during the late 1940s. In 1950 the town was visited by the then heir to the throne, Princess Elizabeth, when she officially opened the Manor Royal industrial area. Building work continued throughout the 1950s in West Green, Northgate and Three Bridges, and later in Langley Green, Pound Hill
Pound Hill is one of 14 neighbourhoods within the town of Crawley in West Sussex, England. Pound Hill is located on the east of Crawley. It is bordered by Three Bridges and Manor Royal to the west and Maidenbower to the south.
It is the larges ...
and Ifield. In 1956, land at "Tilgate East" was allocated for housing use, eventually becoming the new neighbourhood of Furnace Green.
Expectations of the eventual population of the town were revised upwards several times. The 1949 master plan had allowed for 50,000 people, but this was amended to 55,000 in 1956 after the Development Corporation had successfully resisted pressure from the Minister for Town and Country Planning to accommodate 60,000. Nevertheless, plans dated 1961 anticipated growth to 70,000 by 1980, and by 1969 consideration was given to an eventual expansion of up to 120,000.
Her Majesty The Queen
The precise style of British sovereigns has varied over the years. style is officially proclaimed in two languages:UK ParliamentRoyal Titles Act 1953(1 & 2 Eliz. 2 c. 9) Proclamation of 28 May 1953 made in accordance with the Royal Titles Act 195 ...
in 1958. Crawley railway station was moved eastwards towards the new development.
Bewbush
Bewbush is one of 14 neighbourhoods in Crawley in West Sussex, England. Bewbush is located in south west Crawley and is bordered by Broadfield to the south, Ifield to the north, Kilnwood Vale to the west and Gossops Green to the north east. ...
, both of which extended outside the administrative area of the then Urban District Council. Detailed plans were made for Broadfield in the late 1960s; by the early 1970s building work had begun. Further expansion at Bewbush was begun in 1974, although development there was slow. The two neighbourhoods were both larger than the original nine: together, their proposed population was 23,000. Work also took place in the area now known as Ifield West on the western fringes of the town.
By 1980, the council identified land at Maidenbower
Maidenbower is one of 14 neighbourhoods within the town of Crawley in West Sussex, England. Maidenbower is located in the south east corner of the town, bordering the M23 motorway. It is bordered by Pound Hill to the north and Furnace Green to ...
, south of the Pound Hill neighbourhood, as being suitable for another new neighbourhood, and work began in 1986. However, all of this development was undertaken privately, unlike the earlier neighbourhoods in which most of the housing was owned by the council.
In 1999, plans were announced to develop the 14th neighbourhood on land at Tinsley Green to the northeast of the town; this was given the go ahead in 2011 and is officially the town's 14th neighbourhood, named Forge Wood after the ancient woodland that is enclosed within the development. After a temporary halt to the proposals when a possible expansion at Gatwick Airport was announced, construction started in 2015. Forge Wood is to have a maximum of 1900 homes. Development of another neighbourhood began in 2012 on the western side of Crawley in the Horsham district, named Kilnwood Vale
Kilnwood Vale is a village in the Horsham district of West Sussex, England. It borders the High Weald Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty along the A264 east of Faygate between Horsham and Crawley. The development first opened in 2016 which when ...
. A plan for a new railway station fell through.
Governance
Local government

 Crawley became a parish in the sixteenth century, having previously been a chapelry in the parish of Slaugham. When district and parish councils were established under the
Crawley became a parish in the sixteenth century, having previously been a chapelry in the parish of Slaugham. When district and parish councils were established under the Local Government Act 1894
The Local Government Act 1894 (56 & 57 Vict. c. 73) was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that reformed local government in England and Wales outside the County of London. The Act followed the reforms carried out at county level un ...
, Crawley was given a parish council and included in the Horsham Rural District. The parish was significantly enlarged in 1933, when it absorbed the neighbouring parish of Ifield.
Following the designation as a New Town in 1947, the parish of Crawley was enlarged in 1953 to take in territory from the parishes of Slaugham and Worth. Three years later, on 1 April 1956, the parish of Crawley was made an urban district
Urban district may refer to:
* District
* Urban area
* Quarter (urban subdivision)
* Neighbourhood
Specific subdivisions in some countries:
* Urban districts of Denmark
* Urban districts of Germany
* Urban district (Great Britain and Ireland) (his ...
, making it independent from Horsham Rural District. The Local Government Act 1972 led to the district being reformed as a borough in April 1974, gaining a mayor for the first time. The new borough in 1974 also saw its boundaries enlarged, gaining other areas which had been included in the designated area of the New Town as well as the area north of the town including Gatwick Airport
Gatwick Airport (), also known as London Gatwick , is a major international airport near Crawley, West Sussex, England, south of Central London. In 2021, Gatwick was the third-busiest airport by total passenger traffic in the UK, after ...
, which had previously been in Surrey
Surrey () is a ceremonial county, ceremonial and non-metropolitan county, non-metropolitan counties of England, county in South East England, bordering Greater London to the south west. Surrey has a large rural area, and several significant ur ...
.
The Urban District Council received its coat of arms
A coat of arms is a heraldic visual design on an escutcheon (i.e., shield), surcoat, or tabard (the latter two being outer garments). The coat of arms on an escutcheon forms the central element of the full heraldic achievement, which in its ...
from the College of Heralds
The College of Arms, or Heralds' College, is a royal corporation consisting of professional officers of arms, with jurisdiction over England, Wales, Northern Ireland and some Commonwealth realms. The heralds are appointed by the British Sovere ...
in 1957. After the change to borough status a modified coat of arms, based on the original, was awarded in 1976 and presented to the council on 24 March 1977. It features a central cross on a shield, representing the town's location at the meeting point of North-South and East-West roads. The shield bears nine martlets representing both the county of Sussex
Sussex (), from the Old English (), is a historic county in South East England that was formerly an independent medieval Anglo-Saxon kingdom. It is bounded to the west by Hampshire, north by Surrey, northeast by Kent, south by the Englis ...
and the new town's original nine neighbourhoods. Supporters, of an eagle and a winged lion, relate to the significance of the airport to the locality. The motto featured is ''I Grow and I Rejoice''—a translation of a phrase from the ''Epistulae'' of Seneca the Younger
Lucius Annaeus Seneca the Younger (; 65 AD), usually known mononymously as Seneca, was a Stoic philosopher of Ancient Rome, a statesman, dramatist, and, in one work, satirist, from the post-Augustan age of Latin literature.
Seneca was born ...
. Despite a petition to save it, the old Crawley Town Hall, which was built in the 1960s, was demolished in 2020 and a new Crawley Town Hall is due to be completed in late 2022.
Initially, the district (and then borough) council worked with the Commission for New Towns
English Partnerships (EP) was the national regeneration agency for England, performing a similar role on a national level to that fulfilled by regional development agencies on a regional level. On 1 December 2008 its powers passed to a successo ...
on many aspects of development; but in 1978 many of the commission's assets, such as housing and parks, were surrendered to the council. The authority's boundaries were extended in 1983 to accommodate the Bewbush and Broadfield neighbourhoods.
The borough remains part of the local two-tier arrangements, with services shared with West Sussex County Council. The authority is divided into 13 wards, each of which is represented by two or three local councillors, forming a total council of 36 members. Most wards are coterminous with the borough's neighbourhoods, but three neighbourhoods are divided: Broadfield, Northgate, and Pound Hill into "Pound Hill North and Forge Wood" and "Pound Hill South and Worth". The council is elected in thirds.
As of the 2021 local elections, the council is run by Labour in coalition with the sole independent councillor, with seats held as follows:
United Kingdom government
Crawley Borough is coterminous with the parliamentary constituency of Crawley. Henry Smith won the seat at the 2010 general election and was re-elected at the 2015, 2017 and 2019 general elections. Laura Moffatt, a member of the Labour Party, was the MP for Crawley from 1997 to 2010; she was the Parliamentary Private Secretary to the Secretary of State for Health, Alan Johnson. In the 2005 general election, the winning margin was the slimmest of any UK constituency: Moffatt won by just 37 votes. Brook House andTinsley House Tinsley House may refer to:
* Tinsley House Immigration Removal Centre, a UK IRC in Gatwick
* Tinsley House (museum), a living history museum, part of the Museum of the Rockies
Museum of the Rockies is a museum in Bozeman, Montana. Originally af ...
Immigration Removal Centre
Immigration detention is the policy of holding individuals suspected of visa violations, illegal entry or unauthorized arrival, as well as those subject to deportation and removal until a decision is made by immigration authorities to grant a vi ...
s, operated by UK Visas and Immigration, are within the grounds of Gatwick Airport in Crawley.
Data from the Home Office's national identity database at Doncaster
Doncaster (, ) is a city in South Yorkshire, England. Named after the River Don, it is the administrative centre of the larger City of Doncaster. It is the second largest settlement in South Yorkshire after Sheffield. Doncaster is situated in ...
, South Yorkshire, was backed up to servers in Crawley for disaster recovery and business continuity
Business continuity may be defined as "the capability of an organization to continue the delivery of products or services at pre-defined acceptable levels following a disruptive incident", and business continuity planning (or business continuity a ...
purposes. The Identity Documents Bill 2010
The Identity Documents Act 2010 (c. 40) is an Act of Parliament in the United Kingdom which reverses the introduction of identity cards, and requires the destruction of the information held on the National Identity Register.
As a bill, it was pr ...
, proposed in May 2010 and passed in September 2010, authorised the destruction of all data stored for the identity card scheme brought about by the Identity Cards Act 2006
The Identity Cards Act 2006 (c. 15) was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that was repealed in 2011. It created national identity cards, a personal identification document and European Economic Area travel document, linked to a ...
.
Geography
At (51.1092, −0.1872), Crawley is in the northeastern corner of West Sussex in South East England, south of London and north of Brighton and Hove. It is surrounded by towns including Horley, Redhill, Reigate,Oxted
Oxted is a town and civil parish in the Tandridge district of Surrey, England, at the foot of the North Downs. It is south south-east of Croydon in Greater London, west of Sevenoaks in Kent, and north of East Grinstead in West Sussex.
Oxt ...
, Dorking, Horsham, Haywards Heath, Burgess Hill
Burgess Hill is a town and civil parish in West Sussex, England, close to the border with East Sussex, on the edge of the South Downs National Park, south of London, north of Brighton and Hove, and northeast of the county town, Chichester. It ...
and East Grinstead. The borough of Crawley is bordered by the districts of Mid Sussex and Horsham in West Sussex as well as the districts of Mole Valley and Tandridge
Tandridge is a village and civil parish in the Tandridge District, in the county of Surrey, England. Its nucleus is on a rise of the Greensand Ridge between Oxted and Godstone. It includes, towards its middle one named sub-locality (hamlet), ...
and the borough of Reigate and Banstead in Surrey
Surrey () is a ceremonial county, ceremonial and non-metropolitan county, non-metropolitan counties of England, county in South East England, bordering Greater London to the south west. Surrey has a large rural area, and several significant ur ...
.
Crawley lies in the Weald between the North
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography.
Etymology
The word ''north ...
and South Downs
The South Downs are a range of chalk hills that extends for about across the south-eastern coastal counties of England from the Itchen valley of Hampshire in the west to Beachy Head, in the Eastbourne Downland Estate, East Sussex, in the eas ...
. Two beds of sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic particles at Earth's surface, followed by cementation. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause these particles ...
meet beneath the town: the eastern neighbourhoods and the town centre lie largely on the sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks.
Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicat ...
Hastings Beds, while the rest of the town is based on Weald Clay
Weald Clay or the Weald Clay Formation is a Lower Cretaceous sedimentary rock unit underlying areas of South East England, between the North and South Downs, in an area called the Weald Basin. It is the uppermost unit of the Wealden Group of ...
. A geological fault running from east to west has left an area of Weald Clay (with a ridge of limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms w ...
) jutting into the Hastings Beds around Tilgate
Tilgate is one of 14 neighbourhoods within the town of Crawley in West Sussex, England. The area contains a mixture of privately developed housing, self-build groups and ex-council housing. It is bordered by the districts of Furnace Green to th ...
. The highest point in the borough is above sea level. The town has no major waterways, although a number of smaller brooks and streams are tributaries for the River Mole which rises near Gatwick Airport and flows northwards to the River Thames
The River Thames ( ), known alternatively in parts as the The Isis, River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At , it is the longest river entirely in England and the Longest rivers of the United Kingdom, se ...
near Hampton Court Palace. There are several lakes at Tilgate Park and a mill pond at Ifield which was stopped to feed the Ifield Water Mill
Ifield Water Mill is a 19th-century weatherboarded watermill in the Ifield neighbourhood of Crawley, a town and borough in West Sussex, England. Built on the site of an earlier, smaller flour mill, which itself replaced an iron forge—one ...
.
In 1822 Gideon Mantell, an amateur fossil collector and palaeontologist
Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of foss ...
, discovered teeth, bones and other remains of what he described as "an animal of the lizard tribe of enormous magnitude", in Tilgate Forest on the edge of Crawley. He announced his discovery in an 1825 scientific paper, giving the creature the name Iguanodon. In 1832 he discovered and named the Hylaeosaurus genus of dinosaurs after finding a fossil in the same forest.
Climate
Crawley lies within the Sussex Weald, an area of highly variable terrain so that many microclimates of frost hollows, sun traps and windswept hilltops will be encountered over a short distance. During calm, clear periods of weather this allows for some interesting temperature variations, although most of the time, when mobile westerly airstreams persist, the weather is typically Oceanic like the rest of the British Isles. Gatwick is the nearest weather station that publishes long-term averages that give an accurate description of the climate of the Crawley area, although more recently the Met Office has also published data for its nearby weather station at Charlwood. Both weather stations are about 3 miles north of Crawley town centre and at similar altitudes. Generally, Crawley's inland and southerly position within the UK means temperatures in summer are amongst the highest in the British Isles, Charlwood recording 36.3C (97.3F) and Gatwick recording 36.4C (97.5F) on 19 July 2006, just 0.2C and 0.1C lower, respectively, than the UK monthly record for that day set at Wisley, 20 miles to the west. The overall maximum stands at 36.5C (97.7F) at Charlwood, set on 10 August 2003. The absolute record for Gatwick is the aforementioned 36.4C. Before this, the highest temperature recorded at Gatwick was 35.6C (96.1F), also in August 2003. The maximum temperature was 25.1C (77.2F) or higher on 15.9 days of the year on average (1971-00) and the warmest day will typically rise to 29.4C (84.9F). The overall minimum for Gatwick Airport for the period from 1960 is −16.7C (1.9F), set in January 1963. More recently, Charlwood fell to −11.2C (11.8F) and Gatwick −11.1C (12.0F) on 20 December 2010. Typically the coldest night at Gatwick will fall to −8.9C (16.0F). Air frost is recorded on 58.2 nights at Gatwick (1971-00) Sunshine totals in Crawley are higher than many inland areas due to its southerly location: Gatwick averaged 1,574 hours per year over 1961–90. No data is available for 1971 to 2000, but given increases at comparable sites nearby, annual averages are likely to be over 1,600 hours. Snowfall is often heavier in the Sussex Weald than in many other low-lying parts of central and southern England due to the proximity of moisture-laden southerly tracking low-pressure systems bringing easterly winds and snow to areas from South London southwards. However, again due to the southerly location of the area, with warmer air from the nearby English Channel, the snow is often temporary as low-pressure systems track north bringing in milder air; areas immediately north of London tend to have less accumulation, but lying for a longer duration. Rainfall is lower than the English average, but higher than many other areas of the South East. 1mm of rain or more falls on 116.7 days of the year.Neighbourhoods and areas

Gatwick Airport
Gatwick Airport (), also known as London Gatwick , is a major international airport near Crawley, West Sussex, England, south of Central London. In 2021, Gatwick was the third-busiest airport by total passenger traffic in the UK, after ...
was built on the site of a manor house, Gatwick Manor, close to the village of Lowfield Heath. Most of the village was demolished when the airport expanded, but the Grade II*-listed St Michael and All Angels Church
St Michael and All Angels Church may refer to:
Africa
* St Michael and All Angels Church, Blantyre Malawi
* St. Michael and All Angels' Anglican Church, Weltevreden Park, Johannesburg, South Africa
America
* Cathedral Church of Saint Michael a ...
, remains. The site of Lowfield Heath village, now occupied by warehouses and light industrial units, is on the airport's southern boundary, between the perimeter road and the A23 close to Manor Royal.
* Worth was originally a village with its own civil parish, lying just beyond the eastern edge of the Crawley urban area and borough boundary; but the development of the Pound Hill and Maidenbower neighbourhoods has filled in the gaps, and the borough boundary has been extended to include the whole of the village. The civil parish of Worth remains, albeit reduced in size, as part of the Mid Sussex district.
* Tinsley Green, a hamlet
''The Tragedy of Hamlet, Prince of Denmark'', often shortened to ''Hamlet'' (), is a tragedy written by William Shakespeare sometime between 1599 and 1601. It is Shakespeare's longest play, with 29,551 words. Set in Denmark, the play depicts ...
in Worth parish, is now within the Forge Wood neighbourhood. Its houses, farms and public house, the Greyhound (at which the British and World Marbles Championship has been held annually since 1932), lie on or around an east–west minor road running from the main Balcombe
Balcombe is a village and civil parish in the Mid Sussex District of West Sussex, England. It lies south of London, north of Brighton, and east north east of the county town of Chichester. Nearby towns include Crawley to the north west and ...
– Horley road to the Manor Royal estate.
* The hamlet of Fernhill is east of Gatwick Airport and the same distance south of Horley. It has been wholly within the borough since 1990, when the borough and county boundary was moved eastwards to align exactly with the M23 motorway. Until then, its houses and farms straddled the boundary. Fernhill was the site of a fatal aeroplane crash in 1969: 50 people (including two residents) died when Ariana Afghan Airlines Flight 701 crashed into a house on Fernhill Road.
Demography
 At the
At the census
A census is the procedure of systematically acquiring, recording and calculating information about the members of a given population. This term is used mostly in connection with national population and housing censuses; other common censuses inc ...
in 2011 the population of Crawley was recorded as 106,597. The 2001 census data showed that population then accounted for 13.2% of the population of the county of West Sussex. The growth in population of the new town—around 1,000% between 1951 and 2001—has outstripped that of most similar-sized settlements. For example, in the same period, the population of the neighbouring district of Horsham grew by just 99%.
Approximately 64.5% of the population is aged below 45, compared to 55% of the population of West Sussex. White British
White British is an ethnicity classification used for the native white population identifying as English, Scottish, Welsh, Cornish, Northern Irish, or British in the United Kingdom Census. In the 2011 census, the White British population wa ...
account for 84.5% of the population and 15.5% of people are from other ethnic backgrounds. People of Indian and Pakistani origin account for 4.5% and 3% of the population respectively. Many inhabitants of Crawley work locally at Gatwick Airport as either air or ground crew.
Many Chagossians expelled from the Chagos Archipelago
The Chagos Archipelago () or Chagos Islands (formerly the Bassas de Chagas, and later the Oil Islands) is a group of seven atolls comprising more than 60 islands in the Indian Ocean about 500 kilometres (310 mi) south of the Maldives arc ...
in the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by ...
settled in Crawley in the 1960s and 1970s, and it was reported in 2016 that the town's Chagossian community numbered approximately 3,000 people. Crawley MP Henry Smith stated that Crawley "is home to perhaps the largest Chagossian population in the world".
The borough has a population density of around 22 persons per hectare (9 persons per acre), making it the second most densely populated district in West Sussex, after Worthing. The social mix is similar to the national norm: around 50% are in the ABC1 social category
A social class is a grouping of people into a set of hierarchical social categories, the most common being the upper, middle and lower classes. Membership in a social class can for example be dependent on education, wealth, occupation, incom ...
, although this varies by ward, with just 44% in Broadfield North compared to 75% in Maidenbower.
The proportion of people in the borough with higher education qualifications is lower than the national average. Around 14% have a qualification at level 4 or above, compared to 20% nationally.
Economy
Crawley originally traded as a market town. TheDevelopment Corporation
Development corporations or development firms are organizations established by governments in several countries for the purpose of urban development. They often are responsible for the development of new suburban areas or the redevelopment of ex ...
intended to develop it as a centre for manufacturing and light engineering, with an industrial zone. The rapid growth of Gatwick Airport provided opportunities for businesses in the aviation, transport, warehousing and distribution industries. The significance of the airport to local employment and enterprise was reflected by the formation of the Gatwick Diamond partnership. This venture, supported by local businesses, local government and SEEDA, South East England's Regional Development Agency, aims to maintain and improve the Crawley and Gatwick area's status as a region of national and international economic importance.
Since the Second World War, unemployment in Crawley has been low: the rate was 1.47% of the working-age population in 2003. During the boom of the 1980s the town boasted the lowest level of unemployment in the UK. Continuous growth and investment have made Crawley one of the most important business and employment centres in the South East England region.
In April 2020, the Centre for Cities thinktank identified Crawley as the place in Britain at the highest risk of widespread job losses due to the coronavirus' effect on the economy; classing 56% of jobs in the town as either vulnerable or very vulnerable of being furloughed or lost.
Manufacturing industry
Crawley was already a modest industrial centre by the end of the Second World War. Building was an important trade: 800 people were employed by building and joinery firms, and two—Longley's and Cook's—were large enough to have their own factories. In 1949, 1,529 people worked in manufacturing: the main industries were light andprecision engineering
Precision engineering is a subdiscipline of electrical engineering, software engineering, electronics engineering, mechanical engineering, and optical engineering concerned with designing machines, fixtures, and other structures that have excep ...
and aircraft repair. Many of the jobs in these industries were highly skilled.
Industrial development had to take place relatively soon after the new town was established because part of the Corporation's remit was to move people and jobs out of an overcrowded and war-damaged London. Industrial jobs were needed as well as houses and shops to create a balanced community where people could settle. The Development Corporation wanted the new town to support a large and mixed industrial base, with factories and other buildings based in a single zone rather than spread throughout the town. A site in the northeastern part of the development area was chosen. Its advantages included flat land with no existing development; proximity to the London–Brighton railway line, the A23 and the planned M23; space for railway sidings (which were eventually built on a much smaller scale than envisaged); and an adjacent site reserved for future expansion, on the other side of the railway line (again, not used for this purpose in the end). Princess Elizabeth (later Queen Elizabeth II) opened the first part of the industrial area on 25 January 1950; its main road was named Manor Royal, and this name eventually came to refer to the whole estate.
The Corporation stipulated that several manufacturing industries should be developed, rather than allowing one sector or firm to dominate. It did not seek to attract companies by offering financial or other incentives; instead, it set out to create the ideal conditions for industrial development to arise naturally, by providing large plots of land with room for expansion, allowing firms to build their own premises or rent ready-made buildings, and constructing a wide range of building types and sizes.
Despite the lack of direct incentives, many firms applied to move to the Manor Royal estate: it was considered such an attractive place to relocate to that the Development Corporation was able to choose between applicants to achieve the ideal mix of firms, and little advertising or promotion had to be undertaken. One year after Manor Royal was opened, eighteen firms were trading there, including four with more than 100 employees and one with more than 1,000. By 1964, businesses which had moved to the town since 1950 employed 16,000 people; the master plan had anticipated between 8,000 and 8,500. In 1978 there were 105 such firms, employing nearly 20,000 people.
Thales Group opened a new manufacturing and office complex in Crawley in 2009. The site consolidated manufacturing and offices in the Crawley area and the south-east of England.
Service industry and commerce
 While most of the jobs created in the new town's early years were in manufacturing, the tertiary sector developed strongly from the 1960s. The Manor Royal estate, with its space, proximity to Gatwick Airport and good transport links, attracted airport-related services such as logistics, catering, distribution and warehousing; and the corporation and private companies built offices throughout the town. Office floorspace in the town increased from in 1965 to a conservative estimate of in 1984. Major schemes during that period included premises for the Westminster Bank British Caledonian and The Office of the Paymaster-General. The five-storey Overline House above the railway station, completed in 1968, is used by Crawley's NHS primary care trust and various other companies.
While most of the jobs created in the new town's early years were in manufacturing, the tertiary sector developed strongly from the 1960s. The Manor Royal estate, with its space, proximity to Gatwick Airport and good transport links, attracted airport-related services such as logistics, catering, distribution and warehousing; and the corporation and private companies built offices throughout the town. Office floorspace in the town increased from in 1965 to a conservative estimate of in 1984. Major schemes during that period included premises for the Westminster Bank British Caledonian and The Office of the Paymaster-General. The five-storey Overline House above the railway station, completed in 1968, is used by Crawley's NHS primary care trust and various other companies.
 Companies headquartered in Crawley include Doosan Babcock Energy, WesternGeco, Virgin Atlantic, Virgin Atlantic's associated travel agency
Companies headquartered in Crawley include Doosan Babcock Energy, WesternGeco, Virgin Atlantic, Virgin Atlantic's associated travel agency Virgin Holidays
Virgin Holidays Limited, trading as Virgin Atlantic Holidays, is a company within the Virgin Group that offers holidays worldwide with destinations including the US and Canada, the Caribbean, Africa, the Middle East, the Indian Ocean and the Fa ...
, William Reed Business Media
William Reed is a digital, high value data and events business serving the food and drinks sector. In 2021, it had offices in five locations - in Crawley, London, Montpellier, Singapore and Chicago.
Early history
In 1862, William Reed foun ...
, Dualit
Dualit is a British manufacturer of coffee and tea capsules, kitchen and catering equipment and is best known for its range of heavy-duty toasters. Although it was primarily designed for the commercial catering market, its domestic usage increa ...
and the Office of the Paymaster-General. Danish company Novo Nordisk
Novo Nordisk A/S is a Danish multinational pharmaceutical company headquartered in Bagsværd, Denmark, with production facilities in nine countries, and affiliates or offices in five countries. Novo Nordisk is controlled by majority shareholder ...
, which manufactures much of the world's insulin supply, has its UK headquarters at the Broadfield Business Park, and BDO Global has an office in Crawley. The UK headquarters of Nestlé is in the Manor Royal area of Crawley. In addition the registered offices of TUI UK and Thomson Airways Thomson may refer to:
Names
* Thomson (surname), a list of people with this name and a description of its origin
* Thomson baronets, four baronetcies created for persons with the surname Thomson
Businesses and organizations
* SGS-Thomson M ...
are located in Crawley.
British Airways
British Airways (BA) is the flag carrier airline of the United Kingdom. It is headquartered in London, England, near its main hub at Heathrow Airport.
The airline is the second largest UK-based carrier, based on fleet size and passengers ...
took over British Caledonian's former headquarters near the Manor Royal estate, renamed it "Astral Towers" and based its British Airways Holidays and Air Miles divisions there. Other companies formerly headquartered in Crawley include Astraeus Airlines
Astraeus Limited, trading as Astraeus Airlines, was a British airline based at Astraeus House in Crawley, West Sussex, England. Founded in 2002, and named after the Greek God of the dusk, it entered administration on 21 November 2011, ceasi ...
, British United Airways, "Head Office: Gatwick Airport, Horley. Surrey." CityFlyer Express, CP Ships
CP Ships was a large Canadian shipping company established in the 19th century. From the late 1880s until after World War II, the company was Canada's largest operator of Atlantic and Pacific steamships. Many immigrants travelled on CP ships f ...
, First Choice Airways, GB Airways, Laker Airways, Tradewinds Airways
Tradewinds Airways Ltd was a British all-cargo airline. Its head office was located in Timberham House, on the property of London Gatwick Airport in Crawley, England.
History
Tradewinds was founded in November 1968 after the collapse of ...
, and Air Europe.
Crawley has numerous hotels, including The George Hotel, dated to 1615. It is reputedly haunted.
Shopping and retail

Sainsbury's
J Sainsbury plc, trading as Sainsbury's, is the second largest chain of supermarkets in the United Kingdom, with a 14.6% share of UK supermarket sales.
Founded in 1869 by John James Sainsbury with a shop in Drury Lane, London, the company ...
and Marks & Spencer
Marks and Spencer Group plc (commonly abbreviated to M&S and colloquially known as Marks's or Marks & Sparks) is a major British multinational retailer with headquarters in Paddington, London that specialises in selling clothing, beauty, home ...
were opened (the Tesco superstore was the largest in Britain at the time). The shopping area was also expanded southeastwards from Queen's Square: although the original plans of 1975 were not implemented fully, several large shop units were built and a new pedestrianised link—The Martlets—was provided between Queen's Square and Haslett Avenue, the main road to Three Bridges. The remaining land between this area and the railway line was sold for private development by 1982; in 1992 a shopping centre named County Mall and anchored by an Owen Owen department store was opened there. Its stores includes major retailers such as The Entertainer, Boots, WHSmith and Superdry as well as over 80 smaller outlets. The town's main bus station was redesigned, roads including the main A2220 Haslett Avenue were rerouted, and some buildings at the south end of The Martlets were demolished to accommodate the mall.
A regeneration strategy for the town centre, "Centre Vision 2000", was produced in 1993. Changes brought about by the scheme have included of additional retail space in Queen's Square and The Martlets, and a mixed-use development at the southern end of the High Street on land formerly occupied by Robinson Road (which was demolished) and Spencers Road (shortened and severed at one end). An ASDA superstore, opened in September 2003, forms the centrepiece. Robinson Road, previously named Church Road, had been at the heart of the old Crawley: a century before its demolition, its buildings included two chapels, a school, a hospital and a post office.
Public services
West Sussex Fire and Rescue Service
The West Sussex Fire and Rescue Service is the statutory fire and rescue service for the administrative county of West Sussex, England. It is part of West Sussex County Council. , the county has 25 fire stations.
Performance
In 2018/2019, ...
which operates a fire station in the town centre. The South East Coast Ambulance Service is responsible for ambulance and paramedic services.
Crawley Hospital in West Green is operated by West Sussex Primary Care Trust. Some services are provided by the Surrey and Sussex Healthcare NHS Trust, including a 24-hour Urgent Treatment Centre for semi-life-threatening injuries. The Surrey and Sussex was judged as "weak" by the Healthcare Commission in 2008, however in 2015 both the hospital and the Surrey and Sussex Trust were rated good by the Care Quality Commission.
Thames Water
Thames Water Utilities Ltd, known as Thames Water, is a large private utility company responsible for the public water supply and waste water treatment in most of Greater London, Luton, the Thames Valley, Surrey, Gloucestershire, north W ...
is responsible for all waste water and sewerage provision. Residents in most parts of Crawley receive their drinking water from Southern Water; areas in the north of the town around Gatwick Airport are provided by Sutton & East Surrey Water; and South East Water supplies Maidenbower.
UK Power Networks is the distribution network operator responsible for electricity. Gas is supplied by Southern Gas Networks who own and manage the South East Local Distribution Zone.
The provision of public services was made in co-operation with the local authorities as the town grew in the 1950s and 1960s. They oversaw the opening of a fire station in 1958, the telephone exchange, police station and town centre health clinic in 1961 and an ambulance station in 1963. Plans for a new hospital on land at The Hawth were abandoned, however, and the existing hospital in West Green was redeveloped instead. Gas was piped from Croydon, away, and a gasworks at Redhill, while the town's water supply came from the Weir Wood reservoir south of East Grinstead and another at Pease Pottage.
In December 2008, a new three-storey library was opened in new buildings at Southgate Avenue, replacing the considerably undersized establishment formerly at County Buildings.
The Civil Aviation Authority
A civil aviation authority (CAA) is a national or supranational statutory authority that oversees the regulation of civil aviation, including the maintenance of an aircraft register.
Role
Due to the inherent dangers in the use of flight vehicles, ...
Regulation Safety Group is in the Aviation House in Gatwick Airport
Gatwick Airport (), also known as London Gatwick , is a major international airport near Crawley, West Sussex, England, south of Central London. In 2021, Gatwick was the third-busiest airport by total passenger traffic in the UK, after ...
in Crawley.
Transport
Crawley's early development as a market town was helped by its location on the London–Brighton turnpike. The area was joined to the railway network in the mid-19th century; and since the creation of the new town, there have been major road upgrades (including a motorway link), a guided bus transit system and the establishment of an airport which has become one of Britain's largest and busiest.Road
The London–Brighton turnpike ran through the centre of Crawley, forming the High Street and Station Road. When Britain's major roads were classified by the British government's Ministry of Transport between 1919 and 1923, it was given the number A23. It was bypassed by a new dual carriageway in 1938 (which forms the A23's current route through the town), and then later to the east side of the town by the M23 motorway, which was opened in 1975. This connects London's orbital motorway, the M25, to the A23 at Pease Pottage, at the southern edge of Crawley's built-up area. The original single-carriageway A23 became the A2219. The M23 has junctions in the Crawley area at the A2011/A264
A, or a, is the first letter and the first vowel of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''a'' (pronounced ), plural ''aes ...
(Junction 10) and Maidenbower (area of Crawley) (Junction 10A). The end of the motorway at Pease Pottage is Junction 11. The A2011, another dual-carriageway, joins the A23 in West Green and provides a link, via the A2004, to the town centre. The A2220 follows the former route of the A264 through the town, linking the A23 directly to the A264 at Copthorne, from where it then runs to East Grinstead.
Rail
a station
, known professionally as , is a Japanese actor, creative director, and writer. He appeared in a number of Japanese TV dramas, including '' Mei-chan no Shitsuji'', '' Hanazakari no Kimitachi e'' and '' Zettai Kareshi''. Additionally, he was well ...
was built to serve it.
A line to Horsham, now part of the Arun Valley Line, was opened on 14 February 1848. A station
, known professionally as , is a Japanese actor, creative director, and writer. He appeared in a number of Japanese TV dramas, including '' Mei-chan no Shitsuji'', '' Hanazakari no Kimitachi e'' and '' Zettai Kareshi''. Additionally, he was well ...
was provided next to Crawley High Street from that date. A new station was constructed slightly to the east, in conjunction with the Overline House commercial development, and replaced the original station which closed on 28 July 1968. The ticket office and Up (London-bound) platform waiting areas form the ground floor of the office building.
The urban area of Crawley is served by a total of three rail stations including Ifield railway station. Due to Crawley's expansion this station is now surrounded by the town's western areas. Opened as ''Lyons Crossing Halt'' on 1 June 1907 to serve the village of Ifield, it was soon renamed ''Ifield Halt'', dropping the "Halt" suffix in 1930.
Regular train services run from Crawley, and also Ifield, to London Victoria and London Bridge stations, Gatwick Airport
Gatwick Airport (), also known as London Gatwick , is a major international airport near Crawley, West Sussex, England, south of Central London. In 2021, Gatwick was the third-busiest airport by total passenger traffic in the UK, after ...
, East Croydon
East Croydon is a railway station and tram stop in Croydon, Greater London, England, and is located in Travelcard Zone 5. At from , it is one of the busiest non-terminal stations in London, and in the United Kingdom as a whole. It is one of th ...
, Horsham, Bognor Regis, Chichester
Chichester () is a cathedral city and civil parish in West Sussex, England.OS Explorer map 120: Chichester, South Harting and Selsey Scale: 1:25 000. Publisher:Ordnance Survey – Southampton B2 edition. Publishing Date:2009. It is the only ...
, Portsmouth
Portsmouth ( ) is a port and city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. The city of Portsmouth has been a unitary authority since 1 April 1997 and is administered by Portsmouth City Council.
Portsmouth is the most d ...
and Southampton. Three Bridges has direct Thameslink trains to Bedford
Bedford is a market town in Bedfordshire, England. At the 2011 Census, the population of the Bedford built-up area (including Biddenham and Kempston) was 106,940, making it the second-largest settlement in Bedfordshire, behind Luton, whilst t ...
and Brighton.
Bus and Fastway
Southdown Motor Services
Southdown Motors Services Ltd (although this was the legal name of the company (until 1992) it was normally referred to as Southdown Motor Services) was a bus and coach operator in East and West Sussex and parts of Hampshire, in southern En ...
and London Transport bus services met. In 1958 the companies reached an agreement which allowed them both to provide services in all parts of the town. When the National Bus Company was formed in 1969, its London Country Bus Services subsidiary took responsibility for many routes, including Green Line Coaches cross-London services which operated to distant destinations such as Watford, Luton
Luton () is a town and unitary authority with borough status, in Bedfordshire, England. At the 2011 census, the Luton built-up area subdivision had a population of 211,228 and its built-up area, including the adjacent towns of Dunstable an ...
and Amersham. A coach station was opened by Southdown in 1931 on the A23 at County Oak, near Lowfield Heath: it was a regular stopping point for express coaches between London and towns on the Sussex coast. This traffic started to serve Gatwick when the airport began to grow, however. When the National Bus Company was broken up, local services were provided by the new South West division of London Country Bus Services, which later became part of the Arriva group. Metrobus acquired these routes from Arriva in March 2001, and is now Crawley's main operator. It provides local services between the neighbourhoods and town centre, and longer-distance routes to Horsham, Redhill, Tunbridge Wells, Worthing and Brighton.
In September 2003 a guided bus service, Fastway, began operating between Bewbush
Bewbush is one of 14 neighbourhoods in Crawley in West Sussex, England. Bewbush is located in south west Crawley and is bordered by Broadfield to the south, Ifield to the north, Kilnwood Vale to the west and Gossops Green to the north east. ...
and Gatwick Airport
Gatwick Airport (), also known as London Gatwick , is a major international airport near Crawley, West Sussex, England, south of Central London. In 2021, Gatwick was the third-busiest airport by total passenger traffic in the UK, after ...
. A second route, from Broadfield to the Langshott area of Horley, north of Gatwick Airport, was added on 27 August 2005.
Gatwick Airport
Her Majesty The Queen
The precise style of British sovereigns has varied over the years. style is officially proclaimed in two languages:UK ParliamentRoyal Titles Act 1953(1 & 2 Eliz. 2 c. 9) Proclamation of 28 May 1953 made in accordance with the Royal Titles Act 195 ...
reopened it on 9 June 1958. A second terminal, the North Terminal, was built in 1988.
An agreement exists between BAA and West Sussex County Council preventing the building of a second runway before 2019. Nevertheless, consultations were launched in 2002 by the Department for Transport, at which proposals for additional facilities and runways were considered. It was agreed that there would be no further expansion at Gatwick unless it became impossible to meet growth targets at London Heathrow Airport
Heathrow Airport (), called ''London Airport'' until 1966 and now known as London Heathrow , is a major international airport in London, England. It is the largest of the six international airports in the London airport system (the others be ...
within existing pollution limits.
Sport and leisure

fifth round
Fifth is the ordinal form of the number five.
Fifth or The Fifth may refer to:
* Fifth Amendment to the United States Constitution, as in the expression "pleading the Fifth"
* Fifth column, a political term
* Fifth disease, a contagious rash tha ...
of the F.A. Cup, a match which saw 9,000 Crawley fans make the trip to Manchester; the game was lost 1–0. The women's football club, Crawley Wasps F.C., plays in the FA Women's National League South, the third tier of women's football. It formed a parnership with Crawley Town in 2021. Three other local men's teams play in the Sussex County Football League: Three Bridges F.C.
Three Bridges Football Club is a football club based in Three Bridges in Crawley, West Sussex, England. The club is affiliated to the Sussex County Football Association. They were established in 1901 and were founding members of the Sussex Cou ...
, Oakwood F.C.
Oakwood Football Club are a football club based in Crawley, England. They were established in 1962 and joined the Sussex County League Division Three in 1984. In 2005–06 season, they were champions of the Sussex County League Division Two and ...
and Ifield Galaxy F.C.. Crawley Rugby Club is based in Ifield, and a golf course was constructed in 1982 at Tilgate Park. Crawley Hockey Club plays their home matches at Hazelwick School, Three Bridges. Three Bridges Cricket Club is a founding member of the Sussex Cricket League
The Sussex Cricket League, founded in 1971, is the top level of competition for recreational club cricket in Sussex, England, and since 1999 the Premier Division has been a designated ECB Premier League
The Premier League (legal name: T ...
and in 2018 were promoted back to the Premier Division.
The new town's original leisure centre was in Haslett Avenue in the Three Bridges neighbourhood. Building work started in the early 1960s, and a large swimming pool opened in 1964. The site was extended to include an athletics arena by 1967, and an additional large sports hall was opened by the town mayor, Councillor Ben Clay and Prime Minister Harold Wilson in 1974. However, the facilities became insufficient for the growing town, even though an annexe was opened in Bewbush in 1984. Athlete Zola Budd had been asked to take part in a 1,500-metre race as part of the opening celebrations, but her invitation was withdrawn at short notice because of concerns raised by council members about possible "political connotations and anti-apartheid demonstrators".
In 2005, Crawley Leisure Centre was closed and replaced by a new facility, the K2 Leisure Centre, on the campus of Thomas Bennett Community College near the Broadfield Stadium. Opened to the public on 14 November 2005, and officially by Lord Coe
Sebastian Newbold Coe, Baron Coe, (born 29 September 1956), often referred to as Seb Coe, is a British politician and former track and field athlete. As a middle-distance runner, Coe won four Olympic medals, including 1500 metres gold medals ...
on 24 January 2006, the centre includes the only Olympic-sized swimming pool in South East England. In March 2008 the centre was named as a training site for the 2012 Olympics in London.
Crawley Development Corporation made little provision for the arts in the plans for the new town, and a proposed arts venue in the town centre was never built. Neighbourhood community centres and the Tilgate Forest Recreational Centre were used for some cultural activities, but it was not until 1988 that the town had a dedicated theatre and arts venue, at the Hawth Theatre
The Hawth Theatre is an arts and entertainment complex located in of woodland about from the town centre of the English town of Crawley. It is wholly owned by Crawley Borough Council and is currently operated by Parkwood Theatres.
History
The ...
. (The name derives from a local corruption of the word " heath", which came to refer specifically to the expanse of wooded land, south of the town centre, in which the theatre was built.) Crawley's earliest cinema, the Imperial Picture House on Brighton Road, lasted from 1909 until the 1940s; the Embassy Cinema on the High Street (opened in 1938) replaced it. A large Cineworld
Cineworld Group plc is a British cinema operator headquartered in London, England. It is the world's second-largest cinema chain (after AMC Theatres), with 9,518 screens across 790 sites in 10 countries: Bulgaria, Czech Republic, Hungary, Irel ...
cinema has since opened in the Crawley Leisure Park, which itself also includes ten-pin bowling
Ten-pin bowling is a type of bowling in which a bowler rolls a bowling ball down a wood or synthetic lane toward ten pins positioned evenly in four rows in an equilateral triangle. The objective is to knock down all ten pins on the first roll ...
, various restaurants and bars and a fitness centre. The Moka nightclub on Station Way opened in October 2012.
Each neighbourhood has self-contained recreational areas, and there are other larger parks throughout the town. The Memorial Gardens, on the eastern side of Queen's Square, feature art displays, children's play areas and lawns, and a plaque commemorating those who died in two Second World War bombing incidents in 1943 and 1944. Goffs Park in Southgate covers , and has lakes, boating ponds, a model railway and many other features. Tilgate Park and Nature Centre has walled gardens, lakes, large areas of woodland with footpaths and bridleways, a golfing area and a collection of animals and birds.
Heritage
Crawley Museum is based in the town centre. Stone Age and Bronze Age remains discovered in the area are on display, as well as more recent artefacts including parts of Vine Cottage, an old timber-framed building on the High Street which was once home to former ''Punch'' editor Mark Lemon and which was demolished when the ASDA development was built. Crawley has threeGrade I listed buildings
In the United Kingdom, a listed building or listed structure is one that has been placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Historic Environment Scotland in Scotland, in Wales, and the Northern Irel ...
( the parish church of St Margaret in Ifield, the parish church of St Nicholas, Worth, and the Friends Meeting House in Langley Lane, Ifield), 12 Grade II* listed buildings and 85 Grade II listed buildings. The borough council has also awarded locally listed building
In the United Kingdom, a listed building or listed structure is one that has been placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Historic Environment Scotland in Scotland, in Wales, and the Northern Ir ...
status to 58 buildings.
 The high street becomes an annual focus of motoring heritage in November as one of the official stops on the London to Brighton Veteran Car Run.
The high street becomes an annual focus of motoring heritage in November as one of the official stops on the London to Brighton Veteran Car Run.
Education

 Maintained primary and secondary schools were reorganised in 2004 following the Local Education Authority's decision to change the town's three-tier system of first, middle and secondary schools to a more standard primary/secondary divide. Since the restructuring, Crawley has had 17 primary schools (including two
Maintained primary and secondary schools were reorganised in 2004 following the Local Education Authority's decision to change the town's three-tier system of first, middle and secondary schools to a more standard primary/secondary divide. Since the restructuring, Crawley has had 17 primary schools (including two Church of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the established Christian church in England and the mother church of the international Anglican Communion. It traces its history to the Christian church recorded as existing in the Roman province of Brit ...
and two Roman Catholic) and four pairs of infant and junior School
A Junior school is a type of school which provides primary education to children, often in the age range from 8 and 13, following attendance at Infant school which covers the age range 5–7. (As both Infant and Junior schools are giving Primary ...
s. Most of these were opened in 2004; others changed their status at this date (for example, from a middle to a junior school). Secondary education is provided at one of six secondary schools:
* Ifield Community College
Ifield Community College (ICC) is a maintained comprehensive secondary school in Crawley, England, for pupils aged 11 to 18.
Admissions
It caters for around 1000 pupils in years 7 to 13, including over 100 in its sixth form. It is situated in ...
* Hazelwick School
* Holy Trinity Church of England School
* Oriel High School
Oriel High School is a maintained community secondary school for pupils aged 11 to 18. It opened in September 2004 as part of a reorganisation of secondary education in Crawley, catering for just 370 pupils in years 7 and 8. It was expected t ...
* St Wilfrid's Catholic School
St Wilfrid's Catholic School is a voluntary aided comprehensive Catholic secondary school in Crawley, West Sussex, England for pupils aged 11 to 18. It caters for 936 pupils in years 7 to 13, including 181 in its sixth form.
History
St Wilfrid ...
* Thomas Bennett Community College
All six of these have a sixth form
In the education systems of England, Northern Ireland, Wales, Jamaica, Trinidad and Tobago and some other Commonwealth countries, sixth form represents the final two years of secondary education, ages 16 to 18. Pupils typically prepare for ...
, the newest opening at Oriel High in September 2008.
There is also a primary / secondary School called The Gatwick School, which is a Free School that opened in 2014. It currently has 4 years, R, 1, 7 and 8. The schools at Ifield and Thomas Bennett are also bases for the Local Authority
Local government is a generic term for the lowest tiers of public administration within a particular sovereign state. This particular usage of the word government refers specifically to a level of administration that is both geographically-l ...
's adult education programmes.
Pupils with special needs
In clinical diagnostic and functional development, special needs (or additional needs) refers to individuals who require assistance for disabilities that may be medical, mental, or psychological. Guidelines for clinical diagnosis are given in b ...
are educated at the two special schools in the town, each of which covers the full spectrum of needs: Manor Green Primary School and Manor Green College.
Desmond Anderson, based in Tilgate
Tilgate is one of 14 neighbourhoods within the town of Crawley in West Sussex, England. The area contains a mixture of privately developed housing, self-build groups and ex-council housing. It is bordered by the districts of Furnace Green to th ...
converted to Academy status in February 2017 and is now part of the University of Brighton Academies Trust. The Atelier 21 Future School for up to 120 pupils aged 4 to 14 years, based in Broadfield House, opened on 24 August 2020.
Further education is provided by Central Sussex College. Opened in 1958 as Crawley Technical College, it merged with other local colleges to form the new institute in August 2005. The college also provides higher education courses in partnership with the universities at Chichester
Chichester () is a cathedral city and civil parish in West Sussex, England.OS Explorer map 120: Chichester, South Harting and Selsey Scale: 1:25 000. Publisher:Ordnance Survey – Southampton B2 edition. Publishing Date:2009. It is the only ...
and Sussex
Sussex (), from the Old English (), is a historic county in South East England that was formerly an independent medieval Anglo-Saxon kingdom. It is bounded to the west by Hampshire, north by Surrey, northeast by Kent, south by the Englis ...
. In 2004, a proposal was made for an additional campus of the University of Sussex
, mottoeng = Be Still and Know
, established =
, type = Public research university
, endowment = £14.4 million (2020)
, budget = £319.6 million (2019–20)
, chancellor = Sanjeev Bhaskar
, vice_chancellor = Sasha Roseneil
, ...
to be created in Crawley, but as of 2008 no conclusion has been reached.
Media
Crawley has three local newspapers, of which two have a long history in the area. The ''Crawley Observer'' began life in 1881 as ''Simmins Weekly Advertiser'', became the ''Sussex & Surrey Courier'' and then the ''Crawley and District Observer'', and took its current name in 1983. The newspaper is now owned by Johnston Press. The ''Crawley News'' was first published in 1979, and later took over the operations of the older ''Crawley Advertiser'' which closed in 1982. The newspaper was taken over by the Trinity Mirror group in 2015 as part of the purchase of Local World but its last edition was published on 26 October 2016. In September 2008 Johnston Press launched a new weekly broadsheet newspaper called the ''Crawley Times'' based on the companies paper produced in Horsham, the ''West Sussex County Times''. Crawley is served by the London regional versions of BBC and ITV television from the Crystal Palace or Reigate transmitters—although, the town is also served byBBC South East
BBC South East is the BBC English region serving Kent, East Sussex, most parts of West Sussex and southern parts of Surrey.
The BBC region was created in September 2001 by the joining of the Heathfield transmitter (formerly part of the BB ...
& ITV Meridian
ITV Meridian (previously Meridian Broadcasting) is the holder of the ITV (TV network), ITV franchise for the South and South East England, South East of England. The station was launched at 12:00 am on 1 January 1993, replacing previous broadca ...
on Freesat. This means the town is served by news and television programs from London and Tunbridge Wells.
Radio Mercury
Mercury FM was a radio station in the Surrey and Sussex area of the United Kingdom that was founded on 20 October 1984 and closed on 25 July 2010. The station broadcast on FM 97.5 MHz in Horsham and 102.7 MHz in East Surrey and Nor ...
began broadcasting on 20 October 1984 from Broadfield House in Broadfield. The station, now owned by Global Radio, broadcasts as Heart South from Brighton, with the studios in Kelvin Way in Crawley closed in August 2010. On 1 February 2011, the local Gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile ...
transmitter on 1521 AM closed and listeners were advised to retune to 1548 AM (Gold London) or 1323 AM (Gold Sussex). Local BBC radio was provided by BBC Radio Sussex from 1983; this became part of BBC Southern Counties Radio following a merger with BBC Radio Surrey in 1994. From March 2009, BBC Southern Counties Radio became BBC Sussex on 104.5FM & BBC Surrey on 104FM. Due to the positioning of their transmitters, when broadcasting separately both stations cover Crawley stories.
Twin town
: Eisenhüttenstadt, German Democratic Republic, 1963–1968 :Dorsten
Dorsten (; Westphalian: ''Dössen'') is a town in the district of Recklinghausen in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany and has a population of about 75,000.
Dorsten is situated on the western rim of Westphalia bordering the Rhineland. Its hist ...
, Germany, since 1973
:, Alytus
Notable people and music groups
Ms. Dynamite
Niomi Arleen McLean-Daley (born 26 April 1981), better known as Ms. Dynamite, is a British singer and rapper. She is the recipient of the Mercury Music Prize, two Brit Awards and three MOBO Awards.
Early years
She was born Niomi Arleen Mc ...
File:Romesh Ranganathan in 2013 (cropped).jpg, Romesh Ranganathan
Jonathan Romesh Ranganathan (born 27 March 1978), is an English actor and comedian. He is known for his deadpan and often self-deprecating comedy.
Ranganathan has made numerous appearances on television comedy panel shows, and in 2016 he co-p ...
File:ENG-PAN (22) 2018-6-69 Gareth Southgate.jpg, Gareth Southgate
Gareth Southgate (born 3 September 1970) is an English professional football manager and former player who played as a defender and midfielder. He has been the manager of the England national team since 2016.
Southgate won the League Cu ...
File:Daley_Thomson_2007_cropped.jpg, Daley Thompson
File:Alan Minter in 2005.png, Alan Minter
Alan Sydney Minter (17 August 19519 September 2020) was a British professional boxer who competed from 1972 to 1981. He held the undisputed middleweight title in 1980, having previously held the British middleweight title from 1975 to 1976, an ...
File:Bethan Leadley 2017 festival.png, Leadley
File:Laura Moffatt 2006-03-06.jpg, Laura Moffatt
File:Robert Smith (musician) crop.jpg, Robert Smith
Les Misérables
''Les Misérables'' ( , ) is a French historical novel by Victor Hugo, first published in 1862, that is considered one of the greatest novels of the 19th century.
In the English-speaking world, the novel is usually referred to by its origin ...
'' (2018) as Princess Anne
Anne, Princess Royal (Anne Elizabeth Alice Louise; born 15 August 1950), is a member of the British royal family. She is the second child and only daughter of Queen Elizabeth II and Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh, and the only sister of ...
in ''The Crown
The Crown is the state in all its aspects within the jurisprudence of the Commonwealth realms and their subdivisions (such as the Crown Dependencies, overseas territories, provinces, or states). Legally ill-defined, the term has differ ...
'' (2019), '' Chloe'' (2022)
*Ms. Dynamite
Niomi Arleen McLean-Daley (born 26 April 1981), better known as Ms. Dynamite, is a British singer and rapper. She is the recipient of the Mercury Music Prize, two Brit Awards and three MOBO Awards.
Early years
She was born Niomi Arleen Mc ...
(Niomi Arleen McLean-Daley, MBE), British rapper, singer, songwriter, record producer, recipient of the Mercury Music Prize and 2 Brit Awards.
*John George Haigh
John George Haigh (; 24 July 1909 – 10 August 1949), commonly known as the Acid Bath Murderer, was an English serial killer convicted for the murder of six people, although he claimed to have killed nine. Haigh battered to death or shot his ...
, the "Acid Bath Murderer", carried out some of his murders at a workshop in the West Green area.
* Caroline Haslett, electrical pioneer, engineer and champion of women's rights.
* Leadley (Bethan Mary Leadley), singer-songwriter, music television presenter for 4Music
4Music is a British music television channel owned and operated by Channel Four Television Corporation. The original incarnation was launched on 15 August 2008, and until 29 June 2022, showed a mix of music and entertainment programming. I ...
and youtuber.
* Mark Lemon, first editor of ''Punch'', lived on the High Street from 1858 until his death in 1870. Commemorated by a blue plaque outside the George Hotel.
*Jordan Maguire-Drew
Jordan Luke Maguire-Drew (born 19 September 1997) is an English professional footballer who plays as a winger for National League South club Yeovil Town.
Beginning his career with Brighton & Hove Albion, he has also played in the Football Lea ...
, professional footballer for Grimsby Town, born in Crawley and played for Oakwood F.C.
Oakwood Football Club are a football club based in Crawley, England. They were established in 1962 and joined the Sussex County League Division Three in 1984. In 2005–06 season, they were champions of the Sussex County League Division Two and ...
before joining Brighton and Hove Albion.
*Alan Minter
Alan Sydney Minter (17 August 19519 September 2020) was a British professional boxer who competed from 1972 to 1981. He held the undisputed middleweight title in 1980, having previously held the British middleweight title from 1975 to 1976, an ...
, boxer won bronze at the 1972 Munich Olympic Games at light middleweight and in 1980 became the undisputed world middleweight champion.
*Ross Minter
Ross Minter (born 10 November 1978) is a former professional boxer. He is the son of Alan Minter, the former undisputed World Middleweight Champion.
Ross "The Boss" won 125 amateur boxing matches before turning professional in 2001 at the age o ...
, boxer was British Boxing Board of Control English Welterweight boxing champion 2005.
* Laura Moffatt, British Labour Party politician who was the Member of Parliament (MP) for Crawley from 1997 until 2010.
* Kevin Muscat, a footballer who has played for Australia since 1994 and had a nine-year spell in Britain, playing for four different clubs, was born in the town.
*Natasha Pyne
Natasha Pyne (born 9 July 1946) is an English actress who starred in ''The Taming of the Shrew'' (1967 film), ''The Breaking of Bumbo'' (1970) and ''Father, Dear Father'' (1973).
Early life
Pyne was born in Crawley, Sussex on 9 July 1946. She i ...
, actress, known for ''The Taming of the Shrew
''The Taming of the Shrew'' is a comedy by William Shakespeare, believed to have been written between 1590 and 1592. The play begins with a framing device, often referred to as the induction, in which a mischievous nobleman tricks a drunk ...
'' (1967), ''The Breaking of Bumbo
''The Breaking of Bumbo'' is a 1970 British comedy film written and directed by Andrew Sinclair, a former Coldstream Guards National service officer that was updated from his 1959 novel of the same name that featured the Suez Crisis. It st ...
'' (1970) and ''Father, Dear Father
''Father, Dear Father'' is a British television sitcom produced by Thames Television for ITV from 1968 to 1973 starring Patrick Cargill. It was subsequently made into a spin-off film of the same title released in 1973.
An Australian sequel ...
'' (1973).
*Romesh Ranganathan
Jonathan Romesh Ranganathan (born 27 March 1978), is an English actor and comedian. He is known for his deadpan and often self-deprecating comedy.
Ranganathan has made numerous appearances on television comedy panel shows, and in 2016 he co-p ...
, comedian and television personality, was a maths teacher at Hazelwick School and lives in the town.
*Grace Saif
Grace Saif (born 7 October 1995) is a British actress known for playing Ani Achola in ''13 Reasons Why''.
Early life and education
Saif was born and grew up in Manchester before she moved to Crawley and attended Hazelwick School. After co ...
, actress, known for '' Doctors'' (2000) and the Netflix
Netflix, Inc. is an American subscription video on-demand over-the-top streaming service and production company based in Los Gatos, California. Founded in 1997 by Reed Hastings and Marc Randolph in Scotts Valley, California, it offers a ...
show '' 13 Reasons Why''.
*Gareth Southgate
Gareth Southgate (born 3 September 1970) is an English professional football manager and former player who played as a defender and midfielder. He has been the manager of the England national team since 2016.
Southgate won the League Cu ...
OBE, England manager (from 2016), former England football player, attended Pound Hill
Pound Hill is one of 14 neighbourhoods within the town of Crawley in West Sussex, England. Pound Hill is located on the east of Crawley. It is bordered by Three Bridges and Manor Royal to the west and Maidenbower to the south.
It is the larges ...
Junior School and Hazelwick School.
* Daley Thompson CBE, athlete, winner of 2 Decathlon Olympic gold medals, trained in Crawley for the Olympics in 1980
Events January
* January 4 – U.S. President Jimmy Carter proclaims a grain embargo against the USSR with the support of the European Commission.
* January 6 – Global Positioning System time epoch begins at 00:00 UTC.
* January 9 – In ...
and 1984.
* Theresa Tomlinson (born 1946), writer for children and young adults, was born in Crawley.
*Peter Vaughan
Peter Vaughan (born Peter Ewart Ohm; 4 April 1923 – 6 December 2016) was an English character actor known for many supporting roles in British film and television productions. He also acted extensively on the stage.
He is perhaps best known ...
, actor, '' Straw Dogs'' (1971), Grouty in '' Porridge'' (1979) and Maester Aemon Targaryen in '' Game of Thrones'' (2011–2015).
* Dan Walker, BBC breakfast presenter, former sports presenter, born and raised in Crawley.
* The Cure were formed in Crawley in 1976 by Robert Smith, Michael Dempsey and Lol Tolhurst, all of whom attended St Wilfrid's RC School.
* The Feeling's drummer Paul Stewart, guitarist Kevin Jeremiah
Kevin () is the anglicized form of the Irish masculine given name (; mga, Caoimhghín ; sga, Cóemgein ; Latinized as ). It is composed of "dear; noble"; Old Irish and ("birth"; Old Irish ).
The variant ''Kevan'' is anglicized from , an ...
and keyboard player Ciaran Jeremiah were also at St Wilfrid's.
*Brett Marvin and the Thunderbolts
Brett Marvin and the Thunderbolts were a British club and touring blues band, formed in 1968 and later, a rarely performing pub band. Under the pseudonym Terry Dactyl and the Dinosaurs they released "Seaside Shuffle", a novelty single that rea ...
were formed in Crawley in 1968 at the Thomas Bennett School.
* 2-D, fictional musician, lead vocalist and keyboardist of Gorillaz
See also
*List of places of worship in Crawley
The borough of Crawley, in West Sussex, England, has 45 churches, chapels and other buildings used specifically for worship. Other religious communities meet in community centres, schools and other buildings whose primary function is secular ...
* Urban planning
Urban planning, also known as town planning, city planning, regional planning, or rural planning, is a technical and political process that is focused on the development and design of land use and the built environment, including air, water, ...
* West Sussex
* Worth Church
* City Place Gatwick
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
Crawley Borough Council
{{authority control Towns in West Sussex New towns in England Non-metropolitan districts of West Sussex Populated places established in the 5th century New towns started in the 1940s Unparished areas in West Sussex Boroughs in England