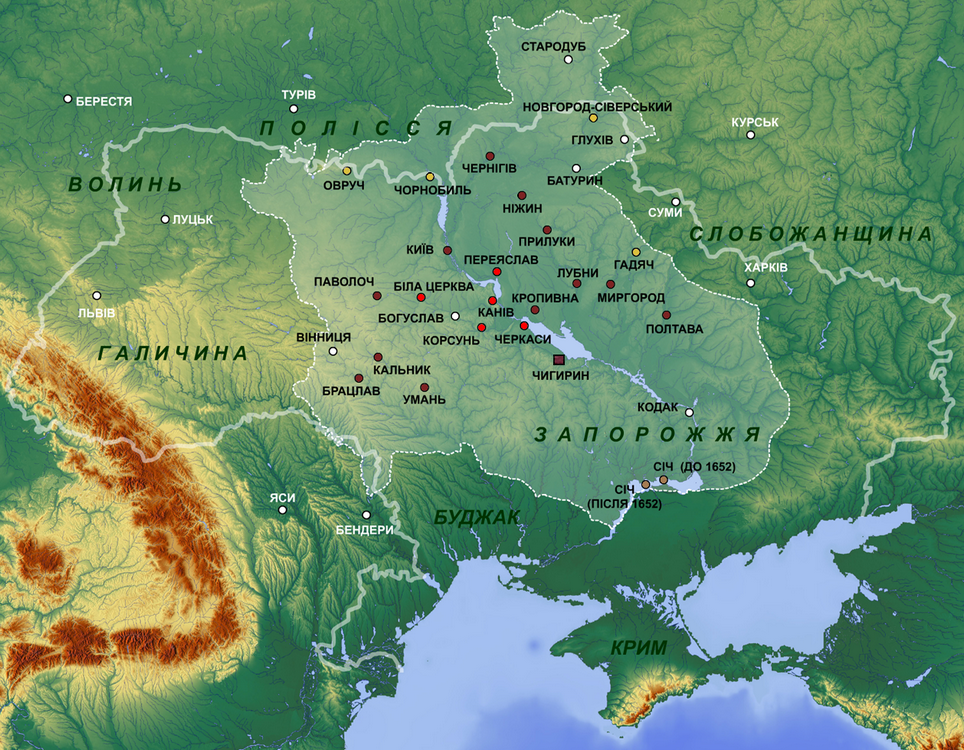
Cossack Hetmanate on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Cossack Hetmanate ( uk, Гетьманщина, Hetmanshchyna; or ''Cossack state''), officially the Zaporizhian Host or Army of Zaporizhia ( uk, Військо Запорозьке, Viisko Zaporozke, links=no; la, Exercitus Zaporoviensis), was a Ukrainian Cossack state in the region of what is today Central Ukraine between 1648 and 1764 (although its administrative-judicial system persisted until 1782).
The Hetmanate was founded by the Hetman of Zaporizhian Host Bohdan Khmelnytsky during the Uprising of 1648–57 in the eastern territories of the
at the Encyclopedia of Ukraine as well as a general name of Ukrainian Cossacks as a political and military organization. The Constitution of Pylyp Orlyk refers to it as Ukraine ( uk, Україна, la, Ucraina), which also is the name found in various Polish, Ottoman and Arab sources. The Cossack Hetmanate was called the Country of Ukraine ('' tr, Ukrayna memleketi'') by the
Grand Principality of Ruthenia was the proposed name of the Cossack Hetmanate as part of the Polish–Lithuanian–Ruthenian Commonwealth.


 When the delegation returned and informed
When the delegation returned and informed
 On September 16, 1658 in Hadyach, an official document was signed between representatives of the Cossack Hetmanate and Poland. Under the conditions of the treaty, Ukraine would become a third and autonomous component of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, under the ultimate sovereignty of the King of Poland but with its own military, courts, and treasury. But the treaty, although ratified by the Diet in May 1659, was never implemented because it was unpopular among the lower classes of the Ruthenian society, where more rebellions occurred. Eventually Vyhovsky surrendered the office of hetman and fled to Poland. The newly re-installed Yurii Khmelnytsky signed the newly composed
On September 16, 1658 in Hadyach, an official document was signed between representatives of the Cossack Hetmanate and Poland. Under the conditions of the treaty, Ukraine would become a third and autonomous component of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, under the ultimate sovereignty of the King of Poland but with its own military, courts, and treasury. But the treaty, although ratified by the Diet in May 1659, was never implemented because it was unpopular among the lower classes of the Ruthenian society, where more rebellions occurred. Eventually Vyhovsky surrendered the office of hetman and fled to Poland. The newly re-installed Yurii Khmelnytsky signed the newly composed
 The period of the Ruin effectively ended when
The period of the Ruin effectively ended when
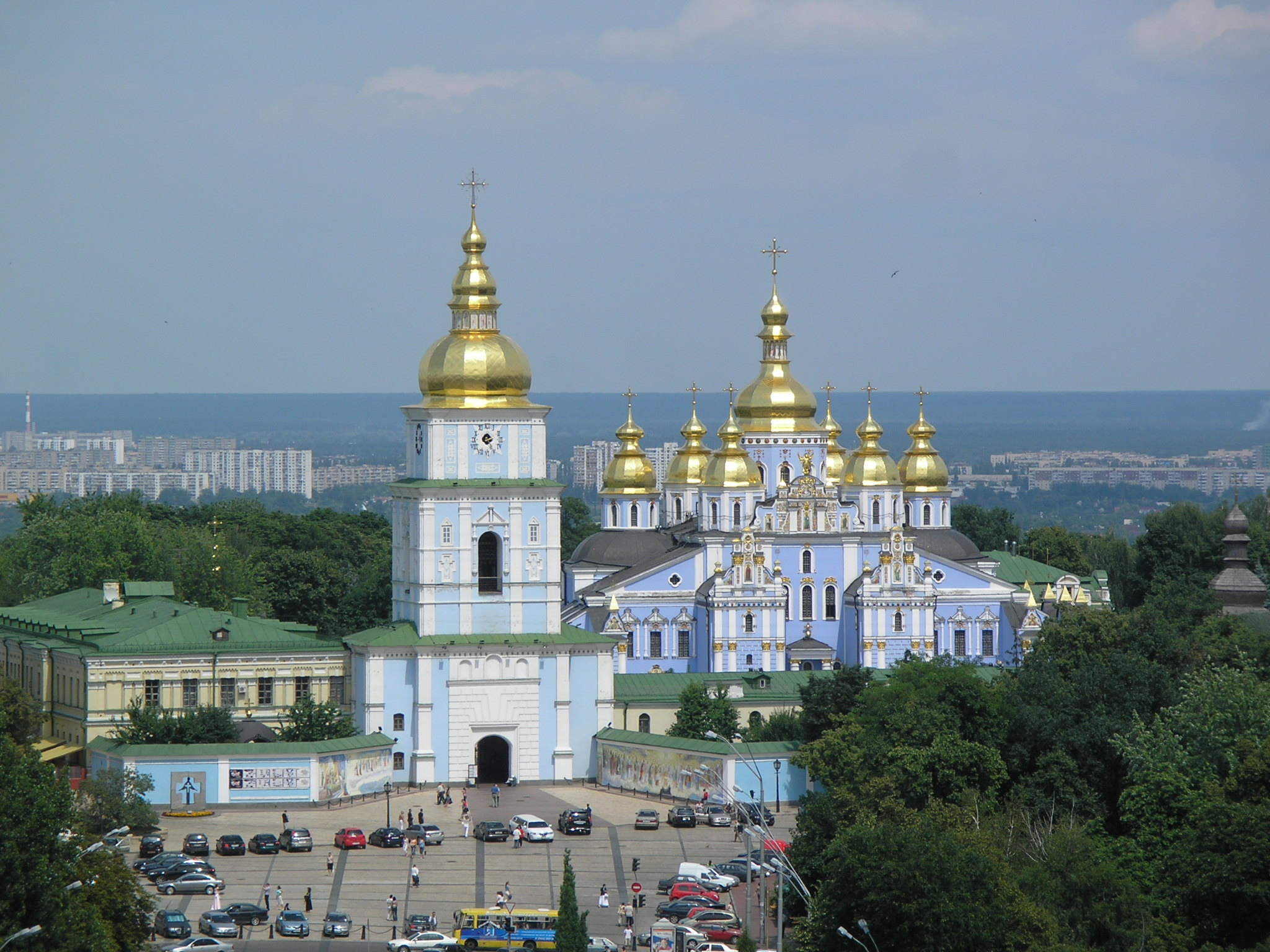
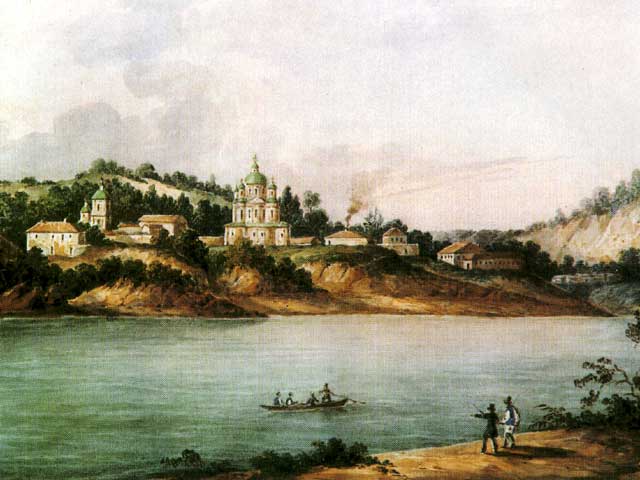 In 1620 The Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople reestablished the Kyiv Metropolis for the Eastern Orthodox communities that refused to join the Union of Brest. In 1686 the Orthodox Church in Ukraine changed from being under the jurisdiction of the Patriarch in Constantinople to being under the authority of the Patriarch of Moscow. Nevertheless, before and after this date local Church leaders pursued a policy of independence. Hetman Ivan Mazepa established very close relations with Metropolitan Varlaam Iasynsky (reigned 1690–1707). Mazepa provided donations of land, money and entire villages to the Church. He also financed the building of numerous churches in Kyiv, including the Church of the Epiphany and the cathedral of St. Michael's Golden-Domed Monastery, and restoration of older churches such as
In 1620 The Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople reestablished the Kyiv Metropolis for the Eastern Orthodox communities that refused to join the Union of Brest. In 1686 the Orthodox Church in Ukraine changed from being under the jurisdiction of the Patriarch in Constantinople to being under the authority of the Patriarch of Moscow. Nevertheless, before and after this date local Church leaders pursued a policy of independence. Hetman Ivan Mazepa established very close relations with Metropolitan Varlaam Iasynsky (reigned 1690–1707). Mazepa provided donations of land, money and entire villages to the Church. He also financed the building of numerous churches in Kyiv, including the Church of the Epiphany and the cathedral of St. Michael's Golden-Domed Monastery, and restoration of older churches such as
File:08. Shlahetna ukr panna.jpg,
File:04. Polkovnik ukr polku.jpg,
File:11. Ukr divchyna-mischanka.jpg,
File:01. Divchyna selanka.jpg,
 The state supreme power belonged to the General Cossack (Military) Council, while the office of head of state was presided by the Hetman. There also was an important advising body Council of Officers ( Starshyna). The hetman was initially chosen by the General Council, consisting of all cossacks, townspeople, clergy and even peasants. By the end of the 17th century, however, its role became more ceremonial as the hetman came to be chosen by the Council of Officers and the Hetmanate itself was turning into an authoritarian state. After 1709, the Battle of Poltava, hetman nomination was to be confirmed by the tsar. Hetman presided until he either died or was forced out by the General Cossack Council. The office of hetman had complete power over the administration, the judiciary, the finances, and the army. His cabinet functioned simultaneously as both the general staff and as the
The state supreme power belonged to the General Cossack (Military) Council, while the office of head of state was presided by the Hetman. There also was an important advising body Council of Officers ( Starshyna). The hetman was initially chosen by the General Council, consisting of all cossacks, townspeople, clergy and even peasants. By the end of the 17th century, however, its role became more ceremonial as the hetman came to be chosen by the Council of Officers and the Hetmanate itself was turning into an authoritarian state. After 1709, the Battle of Poltava, hetman nomination was to be confirmed by the tsar. Hetman presided until he either died or was forced out by the General Cossack Council. The office of hetman had complete power over the administration, the judiciary, the finances, and the army. His cabinet functioned simultaneously as both the general staff and as the
 In 1722 the governmental branch responsible for the Hetmanate was changed from the College of Foreign Affairs to the imperial Senate. That same year, the hetman's authority was undermined by the establishment of the Little Russian Collegium. It was appointed in Moscow and consisted of six Russian military officers stationed in the Hetmanate who acted as a parallel government. Its duty was ostensibly to protect the rights of rank-and-file Cossacks peasants against repression at the hands of the Cossack officers. The president of the collegiate was
In 1722 the governmental branch responsible for the Hetmanate was changed from the College of Foreign Affairs to the imperial Senate. That same year, the hetman's authority was undermined by the establishment of the Little Russian Collegium. It was appointed in Moscow and consisted of six Russian military officers stationed in the Hetmanate who acted as a parallel government. Its duty was ostensibly to protect the rights of rank-and-file Cossacks peasants against repression at the hands of the Cossack officers. The president of the collegiate was
Pereyaslav Agreement
Britannica. Despite this treaty, Khmelnystky continued to correspond with the Ottomans in order to pit the Russians and the Ottomans against each other. He told each side that they had allied with the other only for tactical reasons.
The battle of Poltava and the decline of Cossack Ukraine
in light of Russian and English methods of rule in their borderlands 1707-1914." {{History of Europe Former Slavic countries Historical regions in Ukraine Russian Empire 17th century in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth 17th century in the Zaporozhian Host 18th century in the Zaporozhian Host States and territories established in 1649 States and territories disestablished in 1764 1649 establishments in Russia 1764 disestablishments in the Russian Empire Geography of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth Vassal states of the Ottoman Empire Former Russian protectorates
Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi- confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Poland and Lithuania ru ...
. Establishment of vassal relations with the Tsardom of Russia
The Tsardom of Russia or Tsardom of Rus' also externally referenced as the Tsardom of Muscovy, was the centralized Russian state from the assumption of the title of Tsar by Ivan IV in 1547 until the foundation of the Russian Empire by Peter I ...
in the Treaty of Pereyaslav of 1654 is considered a benchmark of the Cossack Hetmanate in Soviet, Ukrainian, and Russian historiography
Historiography is the study of the methods of historians in developing history as an academic discipline, and by extension is any body of historical work on a particular subject. The historiography of a specific topic covers how historians ha ...
. The second Pereyaslav Council
The Pereiaslav AgreementPereyaslav Agreement
Britannica. ( uk, Пе ...
in 1659 further restricted the independence of the Hetmanate, and from the Russian side there were attempts to declare agreements reached with Yurii Khmelnytsky in 1659 as nothing more than the "former Bohdan's agreements" of 1654. The 1667 Britannica. ( uk, Пе ...
Treaty of Andrusovo
The Truce of Andrusovo ( pl, Rozejm w Andruszowie, russian: Андрусовское перемирие, ''Andrusovskoye Pieriemiriye'', also sometimes known as Treaty of Andrusovo) established a thirteen-and-a-half year truce, signed in 1667 bet ...
– conducted without any representation from the Cossack Hetmanate – established borders between the Polish and Russian states, dividing the Hetmanate in half along the Dnieper
}
The Dnieper () or Dnipro (); , ; . is one of the major transboundary rivers of Europe, rising in the Valdai Hills near Smolensk, Russia, before flowing through Belarus and Ukraine to the Black Sea. It is the longest river of Ukraine and ...
and putting the Zaporozhian Sich under a formal joint Russian-Polish administration.
After a failed attempt to break the union with Russia by Ivan Mazepa
Ivan Stepanovych Mazepa (also spelled Mazeppa; uk, Іван Степанович Мазепа, pl, Jan Mazepa Kołodyński; ) was a Ukrainian military, political, and civic leader who served as the Hetman of Zaporizhian Host in 1687–1708. ...
in 1708, the whole area was included into the Government of Kiev and Cossack autonomy was severely restricted. Catherine II of Russia officially abolished the institute of the Hetman in 1764, and in 1764-1781 the Cossack Hetmanate was incorporated as the Little Russia Governorate headed by Pyotr Rumyantsev
Count Pyotr Alexandrovich Rumyantsev-Zadunaisky (russian: Пётр Алекса́ндрович Румя́нцев-Задунайский; – ) was one of the foremost Russian generals of the 18th century. He governed Little Russia in the na ...
, with the last remnants of the Hetmanate's administrative system abolished in 1781.
Name
The official name of the Cossack Hetmanate was the ''Zaporizhian Host'' or ''Army of Zaporizhia'' ( uk, Військо Запорозьке, Viiskо Zaporozkе). The historiographic term Hetmanate ( uk, Гетьманщина, Hetmanshchyna, "Hetman state") was coined in the late 19th century, deriving from the word '' hetman'', the title of the general of the Zaporizhian Army. Despite not being centered in Zaporizhia, the region's name (meaning "beyond the rapids" in Ukrainian) was derived from cossacks in Southern Ukraine centered on the Zaporizhian Sich,The Zaporizhiaat the Encyclopedia of Ukraine as well as a general name of Ukrainian Cossacks as a political and military organization. The Constitution of Pylyp Orlyk refers to it as Ukraine ( uk, Україна, la, Ucraina), which also is the name found in various Polish, Ottoman and Arab sources. The Cossack Hetmanate was called the Country of Ukraine ('' tr, Ukrayna memleketi'') by the
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
. In the text of Treaty of Buchach
The Treaty of Buchach was signed on 18 October 1672 in Buczacz (now '' Buchach, Ukraine'') between the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth under King Michał Korybut Wiśniowiecki, who had been unable to raise a suitable army, on the one side and t ...
, it is mentioned as the Ukrainian State ( pl, Państwo Ukraińskie). Map of Ukraine, made by Johann Homann, refers to it as Ukraine, or the Land of Cossacks ( la, Ukrania quae et Terra Cosaccorum). In Russian diplomatic correspondence, it was called Little Russia (russian: Малороссия, Malorossiya'').
The founder of the Hetmanate, Bohdan Khmelnytsky, declared himself the ruler of the Ruthenian state to the Polish representative Adam Kysil in February 1649. His contemporary Metropolitan Sylvestr Kosiv recognized him as "the leader and the commander of our land". In his letter to Constantin Șerban (1657), he referred to himself as '.Encyclopedia of UkraineGrand Principality of Ruthenia was the proposed name of the Cossack Hetmanate as part of the Polish–Lithuanian–Ruthenian Commonwealth.
History
Establishment
After many successful military campaigns against the Poles, Hetman Bohdan Khmelnytsky made a triumphant entry intoKyiv
Kyiv, also spelled Kiev, is the capital and most populous city of Ukraine. It is in north-central Ukraine along the Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2021, its population was 2,962,180, making Kyiv the seventh-most populous city in Europe.
Kyi ...
on Christmas 1648, where he was hailed as a liberator of the people from Polish captivity. In February 1649, during negotiations in Pereiaslav with a Polish delegation, Khmelnytsky made it clear to the Poles that he wanted to be the Hetman of a Ruthenia stretching to Chelm and Halych
Halych ( uk, Га́лич ; ro, Halici; pl, Halicz; russian: Га́лич, Galich; german: Halytsch, ''Halitsch'' or ''Galitsch''; yi, העליטש) is a historic city on the Dniester River in western Ukraine. The city gave its name to the P ...
, and build with the Tatar's help. He warned them he intended to resume his military campaign.


 When the delegation returned and informed
When the delegation returned and informed John II Casimir
John II Casimir ( pl, Jan II Kazimierz Waza; lt, Jonas Kazimieras Vaza; 22 March 1609 – 16 December 1672) was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1648 until his abdication in 1668 as well as titular King of Sweden from 1648 ...
of Khmelnytsky's new campaign, the king called for an all szlachta volunteer army, and sent regular troops against the cossacks in southern Volhynia. However, after obtaining intelligence of superior cossack forces, the Polish troops retreated to Zbarazh to set up a defense. The forces of Jeremi Wiśniowiecki
Prince Jeremi Wiśniowiecki ( uk, Ярема Вишневецький – Yarema Vyshnevetsky; 1612 – 20 August 1651) nicknamed ''Hammer on the Cossacks'' ( pl, Młot na Kozaków), was a notable member of the aristocracy of the Polish–Lith ...
reinforced the Zbarazh defenders while he took the lead of all Polish forces. Khmelnytsky besieged the city, wearing it down through a series of random attacks and bombardments. The king, while rushing to help Wiśniowiecki, was ambushed with his newly gathered forces. Khmelnytsky, leaving part of his army with Ivan Cherniata near Zbarazh, moved together with İslâm III Giray to intercept the Polish reinforcements and block their way at a river crossing near Zboriv
Zboriv ( uk, Зборів, pl, Zborów, yi, זבאָרעוו, Zbarav, russian: Зборов) is a town in Ternopil Raion of Ternopil Oblast, west Ukraine. It is located in the historical region of Galicia. Local government is administered by Zb ...
. Caught by some degree of surprise, John Casimir started negotiations with the Tatar's khan. With the khan at his side, he forced Khmelnytsky to start peace negotiations. Khmelnytsky signed the Treaty of Zboriv in August 1649, with a result somewhat less than the Cossack leader had anticipated from his campaign.
As ruler of the Hetmanate, Khmelnytsky engaged in state-building across multiple spheres: military, administration, finance, economics, and culture. He invested the Zaporozhian Host under the leadership of its hetman with supreme power in the new Ruthenian state, and he unified all the spheres of Ukrainian society under his authority. This involved building a government system and a developed military and civilian administration out of Cossack officers and Ruthenian nobles, as well as the establishment of an elite within the Cossack Hetman state.
The Hetmanate used Polish currency, and Polish as an administrative language and language of command. However, after the Truce of Andrusovo
The Truce of Andrusovo ( pl, Rozejm w Andruszowie, russian: Андрусовское перемирие, ''Andrusovskoye Pieriemiriye'', also sometimes known as Treaty of Andrusovo) established a thirteen-and-a-half year truce, signed in 1667 be ...
in 1667, the "simple language" ( uk, проста мова), or the commonly spoken vernacular language of Ukraine, began to be written down and widely used in official documents of the Cossack Hetmanate.
Russian protectorate
After theCrimean Tatars
, flag = Flag of the Crimean Tatar people.svg
, flag_caption = Flag of Crimean Tatars
, image = Love, Peace, Traditions.jpg
, caption = Crimean Tatars in traditional clothing in front of the Khan's Palace ...
betrayed the Cossacks for the third time in 1653, Khmelnytsky realized he could no longer rely on Ottoman support against Poland, and he was forced to turn to Tsardom of Russia
The Tsardom of Russia or Tsardom of Rus' also externally referenced as the Tsardom of Muscovy, was the centralized Russian state from the assumption of the title of Tsar by Ivan IV in 1547 until the foundation of the Russian Empire by Peter I ...
for help. Final attempts to negotiate took place in January 1654 in the town of Pereyaslav
Pereiaslav ( uk, Перея́слав, translit=Pereiaslav, yi, פּרעיאַסלעוו, Periyoslov) is a historical city in the Boryspil Raion, Kyiv Oblast (province) of central Ukraine, located near the confluence of Alta and Trubizh rivers ...
between Khmelnytsky with Cossack leaders and the Tsar's ambassador, Vasiliy Buturlin. The treaty was concluded in April in Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 millio ...
by the Cossacks Samiilo Bohdanovych-Zarudny and Pavlo Teteria
Pavlo Teteria ( uk, Павло́ Тете́ря; russian: Па́вел Ива́нович Тете́ря, pl, Paweł Morzkowski herbu Ślepowron) (1620s–1670) was Hetman of Right-bank Ukraine (1663–1665). His real name is Pavlo Morzhkovsky. ...
, and by Aleksey Trubetskoy, Vasilii Buturlin, and other boyars
A boyar or bolyar was a member of the highest rank of the feudal nobility in many Eastern European states, including Kievan Rus', Bulgaria, Russia, Wallachia and Moldavia, and later Romania, Lithuania and among Baltic Germans. Boyars wer ...
. As a result of the treaty, the Zaporozhian Host became an autonomous Hetmanate within the Russian state. The treaty also led to the Russo-Polish War of 1654–1667.
The Ruin
The period of Hetmanate history known as "theRuin
Ruins () are the remains of a civilization's architecture. The term refers to formerly intact structures that have fallen into a state of partial or total disrepair over time due to a variety of factors, such as lack of maintenance, deliberate ...
", lasting from 1657 to 1687, was marked by constant civil wars throughout the state. After Bohdan Khmelnytsky died in 1657, his sixteen-year-old son Yurii Khmelnytsky was elected as successor. However, the son was not only too young and inexperienced, but also clearly lacked the charisma and leadership qualities of his father.
In response, Ivan Vyhovsky
Ivan Vyhovsky ( uk, Іван Виговський; pl, Iwan Wyhowski / Jan Wyhowski; date of birth unknown, died 1664), a Ukrainian military and political figure and statesman, served as hetman of the Zaporizhian Host and of the Cossack Hetma ...
, the general scribe (''pysar'') of the Hetmanate and an adviser to Bohdan Khmelnytsky, was elected hetman in 1657 by the Starshyna council. His election caused widespread discontent among other regiments and the Zaporizhian Host, who sent runners to Moscow with complaints. As a result, new elections were called that same year at which Vyhovsky was reelected at the General Military Council. This election was also confirmed by Russian authorities who were informed according to the Pereyaslav treaty. Moscow continued to accept runners from the regions of Cossack Hetmanate completely disregarding the authority of hetman and spreading rumors that in truth Russia did not support the candidacy of Vyhovsky. Hrushevsky, M. ''Illustrated History of Ukraine''. "BAO". Donetsk, 2003. page 340 Vyhovsky, seeing the situation turning out of his control, went on to extinguish the revolt led by the Zaporozhian Kosh Otaman
Kish otaman ( uk, Кошовий отаман, ; russian: Кошевой атаман, ; pl, Ataman koszowy; also known as of the Zaporizhian Host) was a chief officer of the ''Kish'' (central body of government) of the Zaporozhian Host in the 1 ...
Yakiv Barabash
Yakiv Federovych Barabash ( uk, Яків Федорович Барабаш) died in September 1658) was a Zaporozhian Cossack Otaman (1657–58) who opposed Hetman Ivan Vyhovsky.
In 1657 he and Poltava polkovnyk Martyn Pushkar led a pro-Tsardom of ...
and Poltava Colonel Martyn Pushkar
Martyn Pushkar (; died 1 June 1658) was a Ukrainian Cossack military leader. From 1648 he was polkovnik of Poltava regiment. After Bohdan Khmelnytsky's death, Pushkar, being one of the senior colonels in the Hetman State, was considered a candida ...
. In the spring of 1658 Vyhovsky crossed Dnieper
}
The Dnieper () or Dnipro (); , ; . is one of the major transboundary rivers of Europe, rising in the Valdai Hills near Smolensk, Russia, before flowing through Belarus and Ukraine to the Black Sea. It is the longest river of Ukraine and ...
and confronted mutineers near Poltava with the help of Tatars. During the battle Pushkar was killed and replaced with a new colonel, while the leaders of the uprising were strictly repressed.
After this, Vyhovsky and General Starshyna considered the relationship with Russia to be broken. The newly elected Metropolitan Dionisi Balaban was transferred to Chyhyryn
Chyhyryn ( uk, Чигирин, ) is a city and historic site located in Cherkasy Raion of Cherkasy Oblast of central Ukraine. From 1648 to 1669 the city was a Hetman residence. After a forced relocation of the Ruthenian Orthodox metropolitan see ...
, away from Kyiv. A manifest nullifying the union with Russia was sent throughout Europe, mainly because it was conducting friendly relationships with Poland and supporting internal opposition within the Hetmanate. Negotiations with Sweden had frozen, while he had military support from the Crimean Khanate
The Crimean Khanate ( crh, , or ), officially the Great Horde and Desht-i Kipchak () and in old European historiography and geography known as Little Tartary ( la, Tartaria Minor), was a Crimean Tatar state existing from 1441 to 1783, the long ...
, so Vyhovsky decided to renegotiate with Poland, with whom talks continued for quite some time.
 On September 16, 1658 in Hadyach, an official document was signed between representatives of the Cossack Hetmanate and Poland. Under the conditions of the treaty, Ukraine would become a third and autonomous component of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, under the ultimate sovereignty of the King of Poland but with its own military, courts, and treasury. But the treaty, although ratified by the Diet in May 1659, was never implemented because it was unpopular among the lower classes of the Ruthenian society, where more rebellions occurred. Eventually Vyhovsky surrendered the office of hetman and fled to Poland. The newly re-installed Yurii Khmelnytsky signed the newly composed
On September 16, 1658 in Hadyach, an official document was signed between representatives of the Cossack Hetmanate and Poland. Under the conditions of the treaty, Ukraine would become a third and autonomous component of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, under the ultimate sovereignty of the King of Poland but with its own military, courts, and treasury. But the treaty, although ratified by the Diet in May 1659, was never implemented because it was unpopular among the lower classes of the Ruthenian society, where more rebellions occurred. Eventually Vyhovsky surrendered the office of hetman and fled to Poland. The newly re-installed Yurii Khmelnytsky signed the newly composed Pereyaslav Articles
The Pereyaslav Articles ( uk, Переяславські статті, translit=Pereiaslavski statti, russian: Переяславские статьи) were concluded on October 27, 1659 between Yurii Khmelnytsky, the son of Bohdan Khmelnytsky, and ...
that were increasingly unfavorable for the Hetmanate and later led to introduction of serfdom
Serfdom was the status of many peasants under feudalism, specifically relating to manorialism, and similar systems. It was a condition of debt bondage and indentured servitude with similarities to and differences from slavery, which deve ...
rights.
In 1667, the Russo-Polish war ended with the Treaty of Andrusovo
The Truce of Andrusovo ( pl, Rozejm w Andruszowie, russian: Андрусовское перемирие, ''Andrusovskoye Pieriemiriye'', also sometimes known as Treaty of Andrusovo) established a thirteen-and-a-half year truce, signed in 1667 bet ...
, which split the Cossack Hetmanate along the Dnieper River: Left-bank Ukraine enjoyed a degree of autonomy within the Tsardom of Russia, while Right-bank Ukraine remained part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, and was temporarily occupied by the Ottoman Empire in the period of 1672-1699 (''see'' the Treaty of Buchach
The Treaty of Buchach was signed on 18 October 1672 in Buczacz (now '' Buchach, Ukraine'') between the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth under King Michał Korybut Wiśniowiecki, who had been unable to raise a suitable army, on the one side and t ...
and the Treaty of Karlowitz). For a short time, Petro Doroshenko
Petro Doroshenko ( uk, Петро Дорофійович Дорошенко, russian: Пётр Дорофе́евич Дороше́нко, pl, Piotr Doroszenko; 1627–1698) was a Cossack political and military leader, Hetman of Right-bank Ukr ...
became the hetman of both banks. After treason by Demian Mnohohrishny and a new Polish offensive, Dorosenko concluded an alliance with the Ottomans, who granted him Ukraine, while the hetman agreed to support Ottoman military action with his army. "By 1669 the Porte issued a patent (berat, nişan) granting Doroshenko all of Cossack Ukraine as an Ottoman sancak or province". After the defeat of the Ottomans at the Battle of Vienna in 1683, Poland managed to recover right-bank Ukraine by 1690, except for the city of Kyiv
Kyiv, also spelled Kiev, is the capital and most populous city of Ukraine. It is in north-central Ukraine along the Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2021, its population was 2,962,180, making Kyiv the seventh-most populous city in Europe.
Kyi ...
, and reincorporated it into their respective voivodeship
A voivodeship is the area administered by a voivode (Governor) in several countries of central and eastern Europe. Voivodeships have existed since medieval times and the area of extent of voivodeship resembles that of a duchy in western medieval ...
s of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, while all the Hetmanate administration was abolished between 1699 and 1704.
The time of Mazepa
Ivan Mazepa
Ivan Stepanovych Mazepa (also spelled Mazeppa; uk, Іван Степанович Мазепа, pl, Jan Mazepa Kołodyński; ) was a Ukrainian military, political, and civic leader who served as the Hetman of Zaporizhian Host in 1687–1708. ...
was elected hetman, serving from 1687 to 1708. He brought stability to the Hetmanate, which was again united under a single hetman. The Hetmanate flourished under his rule, particularly in literature and architecture. The architectural style that developed during his reign was called the Cossack Baroque style.
During his reign, the Great Northern War broke out between Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
and Sweden. Mazepa's alliance with Peter I caused heavy losses of cossacks and Russian interference in the Hetmanate's internal affairs. When the tsar
Tsar ( or ), also spelled ''czar'', ''tzar'', or ''csar'', is a title used by East and South Slavic monarchs. The term is derived from the Latin word ''caesar'', which was intended to mean "emperor" in the European medieval sense of the ter ...
refused to defend Ukraine against the Polish King Stanislaus Leszczynski, an ally of Charles XII of Sweden, Mazepa and some Zaporozhian Cossacks allied themselves with the Swedes on October 28, 1708. The decisive battle of Poltava (in 1709) was won by Russia, putting an end to Mazepa's goal of independence, promised in an earlier treaty with Sweden.
Following the Battle of Poltava, the Hetmanate's autonomy became nominal and the governorate of Kyiv
Kyiv, also spelled Kiev, is the capital and most populous city of Ukraine. It is in north-central Ukraine along the Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2021, its population was 2,962,180, making Kyiv the seventh-most populous city in Europe.
Kyi ...
was established. The Russian Empire also began to purge all suspected allies of Mazepa, culminating in the executions of Cossacks in Lebedin. This resulted in the death of over 900 cossack officials, accused of treason.
End of the Zaporozhian Host
During the reign of Catherine II of Russia, the Cossack Hetmanate's autonomy was progressively destroyed. After several earlier attempts, the office of hetman was finally abolished by the Russian government in 1764, and his functions were assumed by the Little Russian Collegium, thus fully incorporating the Hetmanate into theRussian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
.
On May 7, 1775, Empress Catherine II issued a direct order that the Zaporozhian Sich was to be destroyed. On June 5, 1775, Russian artillery and infantry surrounded the Sich and razed it to the ground. The Russian troops disarmed the Cossacks, and the treasury archives were confiscated. The Koshovyi Otaman
Kish otaman ( uk, Кошовий отаман, ; russian: Кошевой атаман, ; pl, Ataman koszowy; also known as of the Zaporizhian Host) was a chief officer of the ''Kish'' (central body of government) of the Zaporozhian Host in the 1 ...
, Petro Kalnyshevsky
Petro Kalnyshevsky (20 June 1690? – 31 October 1803) was the last Koshovyi Otaman of the Zaporozhian Host, serving in 1762 and from 1765 to 1775. Kalnyshevsky was a hero in the Russo-Turkish War of 1768–1774 for which he was awarded the Gold ...
, was arrested and incarcerated in exile at Solovetsky Monastery
The Solovetsky Monastery ( rus, Солове́цкий монасты́рь, p=səlɐˈvʲɛtskʲɪj mənɐˈstɨrʲ) is a fortified monastery located on the Solovetsky Islands in the White Sea in northern Russia. It was one of the largest Chris ...
. This marked the end of the Zaporozhian Cossacks.
Culture
The Hetmanate coincided with a period of cultural flowering in Ukraine, particularly during the reign of hetmanIvan Mazepa
Ivan Stepanovych Mazepa (also spelled Mazeppa; uk, Іван Степанович Мазепа, pl, Jan Mazepa Kołodyński; ) was a Ukrainian military, political, and civic leader who served as the Hetman of Zaporizhian Host in 1687–1708. ...
.
Education
Visitors from abroad commented on the high level of literacy, even among commoners, in the Hetmanate. There was a higher number of elementary schools per population in the Hetmanate than in either neighboring Russia or Poland. In the 1740s, of 1,099 settlements within seven regimental districts, as many as 866 had primary schools. The German visitor to the Hetmanate, writing in 1720, commented on how the son of Hetman Danylo Apostol, who had never left Ukraine, was fluent in the Latin, Italian, French, German, Polish and Russian languages Under Mazepa, the Kyiv collegium was transformed into an academy and attracted some of the leading scholars of the Orthodox world. It was the largest educational institution in lands ruled by Russia.Timothy Snyder. (2003). ''The Reconstruction of Nations.'' New Haven: Yale University Press. pp. 120-122 Mazepa established another collegium in Chernihiv. These schools largely used the Polish and Latin languages and provided a classic western education to their students. Many of those trained in Kyiv – such asFeofan Prokopovich
Feofan/Theophan Prokopovich (18 June 168119 September 1736) was a Russian Imperial Orthodox theologian, writer, poet, mathematician, and philosopher of Ukrainian origin. Rector of the Academia Mohileana in Kiev (now Kyiv, Ukraine), and Archbish ...
– would later move to Moscow, so that Ivan Mazepa's patronage not only raised the level of culture in Ukraine but also in Moscow itself. A musical academy was established in 1737 in the Hetmanate's then-capital of Hlukhiv. Among its graduates were Maksym Berezovsky (the first composer from the Russian Empire to be recognized in Europe) and Dmitry Bortniansky.
In addition to traditional printing press
A printing press is a mechanical device for applying pressure to an inked surface resting upon a print medium (such as paper or cloth), thereby transferring the ink. It marked a dramatic improvement on earlier printing methods in which the ...
es in Kyiv
Kyiv, also spelled Kiev, is the capital and most populous city of Ukraine. It is in north-central Ukraine along the Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2021, its population was 2,962,180, making Kyiv the seventh-most populous city in Europe.
Kyi ...
, new printing shops were established in Novhorod-Siverskyi
Novhorod-Siverskyi ( uk, Новгород-Сіверський ) is a historic city in Chernihiv Oblast (province) of Ukraine. It is the administrative center of Novhorod-Siverskyi Raion, although until 18 July 2020 it was incorporated as a city ...
and Chernihiv
Chernihiv ( uk, Черні́гів, , russian: Черни́гов, ; pl, Czernihów, ; la, Czernihovia), is a city and municipality in northern Ukraine, which serves as the administrative center of Chernihiv Oblast and Chernihiv Raion within ...
. Most of the books published were religious in nature, such as the ''Peternik'', a book about the lives of the monks of the Kyiv-Pechersk monasatary. Books on local history were compiled. In a book written by Inokentiy Gizel in 1674, the theory that Moscow was the heir of ancient Kyiv was developed and elaborated for the first time.
Religion
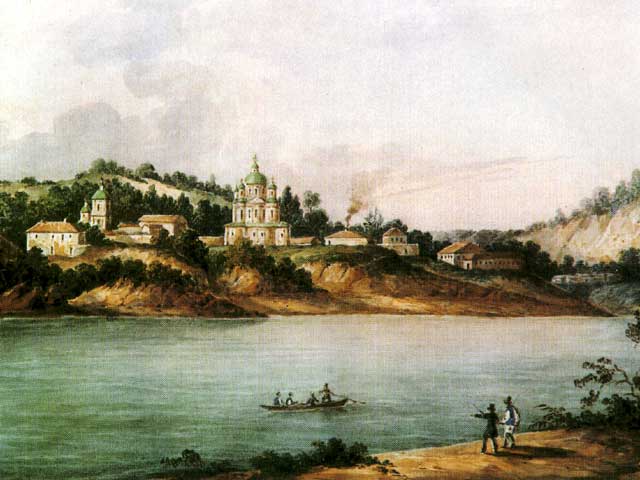 In 1620 The Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople reestablished the Kyiv Metropolis for the Eastern Orthodox communities that refused to join the Union of Brest. In 1686 the Orthodox Church in Ukraine changed from being under the jurisdiction of the Patriarch in Constantinople to being under the authority of the Patriarch of Moscow. Nevertheless, before and after this date local Church leaders pursued a policy of independence. Hetman Ivan Mazepa established very close relations with Metropolitan Varlaam Iasynsky (reigned 1690–1707). Mazepa provided donations of land, money and entire villages to the Church. He also financed the building of numerous churches in Kyiv, including the Church of the Epiphany and the cathedral of St. Michael's Golden-Domed Monastery, and restoration of older churches such as
In 1620 The Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople reestablished the Kyiv Metropolis for the Eastern Orthodox communities that refused to join the Union of Brest. In 1686 the Orthodox Church in Ukraine changed from being under the jurisdiction of the Patriarch in Constantinople to being under the authority of the Patriarch of Moscow. Nevertheless, before and after this date local Church leaders pursued a policy of independence. Hetman Ivan Mazepa established very close relations with Metropolitan Varlaam Iasynsky (reigned 1690–1707). Mazepa provided donations of land, money and entire villages to the Church. He also financed the building of numerous churches in Kyiv, including the Church of the Epiphany and the cathedral of St. Michael's Golden-Domed Monastery, and restoration of older churches such as Saint Sophia Cathedral in Kyiv
Saint Sophia Cathedral in Kyiv, Ukraine, is an architectural monument of Kyivan Rus. The former cathedral is one of the city's best known landmarks and the first heritage site in Ukraine to be inscribed on the World Heritage List along with the K ...
, which had deteriorated to near ruin by the mid-17th century, in a style known as Ukrainian Baroque
Ukrainian Baroque, or Cossack Baroque or Mazepa Baroque ( uk, Українське бароко або Козацьке бароко), is an architectural style that was widespread in the Ukrainian lands in the 17th and 18th centuries. It was th ...
.
Society
The social structure of the Hetmanate consisted of five groups: the nobility, the Cossacks, the clergy, the townspeople, and the peasants.Nobles
As had been the case under Poland, the nobility continued to be the dominant social class during the Hetmanate, although its composition and source of legitimacy within the new society had changed radically. During the Khmelnytsky Uprising, thePolish nobles
The ''szlachta'' (Polish: endonym, Lithuanian language, Lithuanian: šlėkta) were the nobility, noble Estates of the realm, estate of the realm in the Kingdom of Poland (1025–1385), Kingdom of Poland, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and the ...
and Polonized
Polonization (or Polonisation; pl, polonizacja)In Polish historiography, particularly pre-WWII (e.g., L. Wasilewski. As noted in Смалянчук А. Ф. (Smalyanchuk 2001) Паміж краёвасцю і нацыянальнай ідэя� ...
Ruthenian magnates fled the territory of the Hetmanate. As a result, the noble estate now consisted of a merger between the nobility that had stayed in the territory of the Hetmanate (old noble families that did not succumb to Polonization and lesser nobles who had participated in the uprising on the side of the Cossacks against Poland) with members of the emergent Cossack officer class. Unlike the Polish nobles whose lands were redistributed, the nobles loyal to the Hetmanate retained their privileges, their lands, and the services of the peasants. Together, the old nobles and the new Cossack officers became known as the Distinguished Military Fellows (). Thus, the nature of noble status was fundamentally changed. It no longer depended on ancient heredity, but instead on loyalty to the Hetmanate. Over time, however, Cossack officer lands and privileges too became hereditary, and the Cossack noble and officer class acquired huge landed estates comparable to those of the Polish magnates whom they had replaced and emulated.Timothy Snyder. (2003). ''The Reconstruction of Nations.'' New Haven: Yale University Press. pp 116-119.
Noble girl
File:06. Shlahetna panna z starshinskogo rodu.jpg, Noble lady
File:17. Znatna ukr pani.jpg, Noble lady
File:18. Ukr shlachtych.jpg, Nobleman
Cossacks
Most Cossacks failed to enter the noble estate and continued their role as free soldiers. The lower rank Cossacks often resented their wealthier brethren and were responsible for frequent rebellions, particularly duringthe Ruin
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things already mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the m ...
, a period of instability and civil war in the 17th century. These resentments were frequently exploited by Russia. The Zaporizhian Sich served as a refuge for Cossacks fleeing the Hetmanate as it had been prior to Khmelnytsky's uprising.
Cossack colonel
File:09. Sotnyk.jpg, Cossack captain
File:05. Pysar.jpg, Cossack secretary
File:12. Ukr kozak.jpg, Cossack private
Clergy
During the Hetmanate, theRoman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
and Uniate
The Eastern Catholic Churches or Oriental Catholic Churches, also called the Eastern-Rite Catholic Churches, Eastern Rite Catholicism, or simply the Eastern Churches, are 23 Eastern Christian autonomous (''sui iuris'') particular churches of t ...
clergy were driven from Ukraine. The "black", or monastic
Monasticism (from Ancient Greek , , from , , 'alone'), also referred to as monachism, or monkhood, is a religion, religious way of life in which one renounces world (theology), worldly pursuits to devote oneself fully to spiritual work. Monastic ...
, Orthodox clergy enjoyed a very high status in the Hetmanate, controlling 17% of the Hetmanate's land. Monasteries were exempt from taxes and at no times were peasants bound to monasteries allowed to forgo their duties. The Orthodox hierarchy became as wealthy and powerful as the most powerful nobles. The "white", or married, Orthodox clergy were also exempt from paying taxes. Priests' sons often entered the clergy or the Cossack civil service. It was not uncommon for nobles or Cossacks to become priests and vice versa.
Townspeople
Twelve cities within the Hetmanate enjoyed Magdeburg rights, in which they were self-governing and controlled their own courts, finances and taxes. Wealthy townsmen were able to hold office within the Hetmanate or even to buy titles of nobility. Because the towns were generally small (the largest towns ofKyiv
Kyiv, also spelled Kiev, is the capital and most populous city of Ukraine. It is in north-central Ukraine along the Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2021, its population was 2,962,180, making Kyiv the seventh-most populous city in Europe.
Kyi ...
and Nizhyn
Nizhyn ( uk, Ні́жин, Nizhyn, ) is a city located in Chernihiv Oblast of northern Ukraine along the Oster River. The city is located north-east of the national capital Kyiv. Nizhyn serves as the administrative center of Nizhyn Raion. It ...
had no more than 15,000 inhabitants), this social group was not very significant relative to other social groups.
City girl
File:13. Ukr mischanka.jpg, City woman
File:14. Ukr mischanyn.jpg, Townsman
Peasants
Peasants comprised the majority of the Hetmanate's population. Although the institution of forced labor by the peasants was reduced significantly by the Khmelnytsky Uprising, in which the Polish landlords and magnates were expelled from the territory controlled by the Hetman, those nobles loyal to the Hetman as well as the Orthodox Church expected the peasants under their control to continue to provide their services. Thus as a result of the uprising, approximately 50% of the territory consisted of lands given to Cossack officers or free self-governing villages controlled by the peasants, 33% of the land was owned by Cossack officers and nobles, and 17% of the land was owned by the Church. With time, the amount of territory owned by the nobles and officers gradually grew at the expense of the lands owned by peasants and rank-and-file Cossacks, and the peasants were forced to work increasingly more days for their landlords. Nevertheless, their obligations remained lighter than they had been prior to the uprising; and until the end of the Hetmanate, peasants were never fully enserfed and retained the right to move.Peasant girl
File:10. Ukr divchyna selanka.jpg, Peasant girl
File:16. Ukr selanka .jpg, Peasant woman
File:19. Ukr selanyn.jpg, Peasant man
Administrative divisions
The Hetmanate was divided into military-administrative districts known as regimental districts (''polki'') whose number fluctuated with the size of the Hetmanate's territory. In 1649, when the Hetmanate controlled the Right and the Left Banks, it included 16 such districts. After the loss of the Right Bank, this number was reduced to ten. The regimental districts were further divided into companies (''sotnia
Sotnia ( Ukrainian and ) was a military unit and administrative division in many Slavic countries.
Sotnia, deriving back to 1948, has been used in a variety of contexts in both Ukraine and Russia to this day. It is a helpful word to create s ...
s''), which were administered by captains ('' sotnyk''). Companies were named either by a toponym
Toponymy, toponymics, or toponomastics is the study of '' toponyms'' (proper names of places, also known as place names and geographic names), including their origins, meanings, usage and types. Toponym is the general term for a proper name of ...
of their origin or their leader and greatly varied in numbers up to 16.
It is known that the first who introduced the regimental division was Prince Ostafiy Ruzhynsky in 1515. Initially created 20 regiments consisting of 2,000 Cossacks each, were reduced by the King of Poland Stephen Báthory
Stephen Báthory ( hu, Báthory István; pl, Stefan Batory; ; 27 September 1533 – 12 December 1586) was Voivode of Transylvania (1571–1576), Prince of Transylvania (1576–1586), King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania (1576–1586) ...
in 1576 to 10.
List of regiments
The first regimental districts were confirmed by theTreaty of Kurukove
The Treaty of Kurukove ( uk, Куруківський Договір) was an agreement between Hetman Stanisław Koniecpolski of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and Mykhailo Doroshenko of the Ukrainian Cossacks. After four days of negotiatio ...
in 1625, among which were Bila Tserkva Regiment
The Bila Tserkva Regiment ( uk, Білоцерківський полк, russian: Белоцерковский полк) was one of the seventeen territorial-administrative subdivisions of the Hetman State. The regiment's capital was the city of Bi ...
, Kaniv Regiment
Kaniv ( uk, Канів, ) city located in Cherkasy Raion, Cherkasy Oblast (province) in central Ukraine. The city rests on the Dnieper River, and is also one of the main inland river ports on the Dnieper. It hosts the administration of Kaniv u ...
, Korsun Regiment, Kyiv Regiment, Pereyaslav Regiment, Cherkasy Regiment
Cherkasy ( uk, Черка́си, ) is a city in central Ukraine. Cherkasy is the Capital city, capital of Cherkasy Oblast (Oblast, province), as well as the administrative center of Cherkasky Raion (Raion, district) within the oblast. The c ...
. All of them were situated within the Kiev Voivodship. According to the Treaty of Zboriv, there were 23 regiments. In 1667 the signing of Truce of Andrusovo
The Truce of Andrusovo ( pl, Rozejm w Andruszowie, russian: Андрусовское перемирие, ''Andrusovskoye Pieriemiriye'', also sometimes known as Treaty of Andrusovo) established a thirteen-and-a-half year truce, signed in 1667 be ...
between the Tsardom of Russia
The Tsardom of Russia or Tsardom of Rus' also externally referenced as the Tsardom of Muscovy, was the centralized Russian state from the assumption of the title of Tsar by Ivan IV in 1547 until the foundation of the Russian Empire by Peter I ...
and Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi- confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Poland and Lithuania ru ...
secured 10 regiments of the Left-bank Ukraine for Russia, including Kyiv, while the other six stayed at the Right-bank Ukraine as part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi- confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Poland and Lithuania ru ...
.
The capital was the city of Chyhyryn
Chyhyryn ( uk, Чигирин, ) is a city and historic site located in Cherkasy Raion of Cherkasy Oblast of central Ukraine. From 1648 to 1669 the city was a Hetman residence. After a forced relocation of the Ruthenian Orthodox metropolitan see ...
. After the Treaty of Andrusovo
The Truce of Andrusovo ( pl, Rozejm w Andruszowie, russian: Андрусовское перемирие, ''Andrusovskoye Pieriemiriye'', also sometimes known as Treaty of Andrusovo) established a thirteen-and-a-half year truce, signed in 1667 bet ...
, in 1669 the capital was transferred to Baturyn
Baturyn ( uk, Бату́рин, ), is a historic city in Chernihiv Oblast (province) of northern Ukraine. It is located in Nizhyn Raion (district) on the banks of the Seym River. Baturyn lost its city status in 1923 and received it back only in ...
, as Chyhyryn became part of Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (locate at the Right-bank Ukraine). After the Baturyn's tragedy of 1708 conducted by the Russian army of Aleksandr Menshikov, the area was incorporated into the Kiev Governorate
Kiev Governorate, r=Kievskaya guberniya; uk, Київська губернія, Kyivska huberniia (, ) was an administrative division of the Russian Empire from 1796 to 1919 and the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic from 1919 to 1925. It wa ...
the city of Hlukhiv nominally served as the residence of Hetman.
Within the Hetmanate, Polish was frequently used as the language of administration and even of command.
In 1764-65 both Cossack Hetmante and Sloboda Ukraine were liquidated and transformed into Malorossiya Governorate and Sloboda Ukraine Governorate. On the territory of Zaporizhian Sich was created the Novorossiya Governorate
Novorossiya Governorate (russian: Новороссийская губерния, Novorossiyskaya guberniya, New Russia Governorate; uk, Новоросійська губернія), was a governorate of the Russian Empire in the previously O ...
. The general-governor of all Ukrainian territories became Pyotr Rumyantsev
Count Pyotr Alexandrovich Rumyantsev-Zadunaisky (russian: Пётр Алекса́ндрович Румя́нцев-Задунайский; – ) was one of the foremost Russian generals of the 18th century. He governed Little Russia in the na ...
-Zadunaisky.
Government
Leadership
cabinet of ministers
A cabinet is a body of high-ranking state officials, typically consisting of the executive branch's top leaders. Members of a cabinet are usually called cabinet ministers or secretaries. The function of a cabinet varies: in some countrie ...
. The Hetman also had the right to conduct foreign policy, although this right was increasingly limited by Russia in the 18th century.
Each of the regimental districts making up the Hetmanate was administered by a colonel who had dual roles as supreme military and civil authority on his territory. Initially elected by that regimental district's Cossacks, by the 18th century the colonels were appointed by the Hetman. After 1709, the colonels were frequently chosen by Moscow. Each colonel's staff consisted of a quartermaster
Quartermaster is a military term, the meaning of which depends on the country and service. In land armies, a quartermaster is generally a relatively senior soldier who supervises stores or barracks and distributes supplies and provisions. In ...
(second-in-command), judge, chancellor, aide-de-camp, and flag-bearer.
Throughout the 18th century, local autonomy was gradually eroded within the Hetmanate. After the Baturyn's tragedy the autonomy was abolished, incorporating it into the Kiev Governorate
Kiev Governorate, r=Kievskaya guberniya; uk, Київська губернія, Kyivska huberniia (, ) was an administrative division of the Russian Empire from 1796 to 1919 and the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic from 1919 to 1925. It wa ...
. After the Battle of Poltava, hetmans elected by the Council of Officers were to be confirmed by the tsar. They served more as a military administrators and have little influence over the domestic policies. The tsar also frequently appointed the colonels of each regimental district.
First Little Russian Collegiate
 In 1722 the governmental branch responsible for the Hetmanate was changed from the College of Foreign Affairs to the imperial Senate. That same year, the hetman's authority was undermined by the establishment of the Little Russian Collegium. It was appointed in Moscow and consisted of six Russian military officers stationed in the Hetmanate who acted as a parallel government. Its duty was ostensibly to protect the rights of rank-and-file Cossacks peasants against repression at the hands of the Cossack officers. The president of the collegiate was
In 1722 the governmental branch responsible for the Hetmanate was changed from the College of Foreign Affairs to the imperial Senate. That same year, the hetman's authority was undermined by the establishment of the Little Russian Collegium. It was appointed in Moscow and consisted of six Russian military officers stationed in the Hetmanate who acted as a parallel government. Its duty was ostensibly to protect the rights of rank-and-file Cossacks peasants against repression at the hands of the Cossack officers. The president of the collegiate was Brigadier
Brigadier is a military rank, the seniority of which depends on the country. In some countries, it is a senior rank above colonel, equivalent to a brigadier general or commodore, typically commanding a brigade of several thousand soldiers. I ...
Stepan Veliaminov Stepan Lukich Velyaminov (russian: Степан Лукич Вельяминов; 1670–1737) was a Russian military and state figure, Major General#Russia, President of Collegium of Little Russia (1722–1727), privy councilor, senator.
He parti ...
. When the Cossacks responded by electing as Hetman Pavlo Polubotok, opposed to these reforms, he was arrested and died in prison without having been confirmed by the tsar. The Little Russian Collegium then ruled the Hetmanate until 1727, when it was abolished and a new Hetman, Danylo Apostol, was elected.
A code consisting of twenty-eight articles was adopted in 1659 that regulated the relationship between the Hetmanate and Russia. It continued to be in force until the Hetmanate's dissolution. With election of the new Hetman new set of "Pereyaslav Articles
The Pereyaslav Articles ( uk, Переяславські статті, translit=Pereiaslavski statti, russian: Переяславские статьи) were concluded on October 27, 1659 between Yurii Khmelnytsky, the son of Bohdan Khmelnytsky, and ...
" was signed by Danylo Apostol. The new document, known as the 28 Authoritative Ordinances, stipulated that:
* The Hetmanate would not conduct its own foreign relations, although it could deal directly with Poland, the Crimean Khanate
The Crimean Khanate ( crh, , or ), officially the Great Horde and Desht-i Kipchak () and in old European historiography and geography known as Little Tartary ( la, Tartaria Minor), was a Crimean Tatar state existing from 1441 to 1783, the long ...
, and the Ottoman Empire about border problems as long as these agreements did not contradict Russian treaties.
* The Hetmanate continued to control ten regiments, although it was limited to three mercenary regiments.
* During war, the Cossacks were required to serve under the resident Russian commander.
*A court was established consisting of three Cossacks and three government appointees.
*Russians and other non-local landlords were allowed to remain in the Hetmate, but no new peasants from the north could be brought in.
Second Little Russian Collegiate
In 1764, the office of Hetman was abolished by Catherine II, and its authority replaced by the second ''Little Russian Collegiate'' that was transformed out of the Little-RussiaPrikaz
A prikaz (russian: прика́з, ''prikaz''; , plural: ) was an administrative, judicial, territorial, or executive office functioning on behalf of palace, civil, military, or church authorities in Muscovy and in Russia from the 15th to the 1 ...
(Office of Ukrainian Affairs) subordinated to the Ambassadorial Office of the Russian Tsardom. The collegiate consisted of four Russian appointees and four Cossack representatives headed by a president, Pyotr Rumyantsev
Count Pyotr Alexandrovich Rumyantsev-Zadunaisky (russian: Пётр Алекса́ндрович Румя́нцев-Задунайский; – ) was one of the foremost Russian generals of the 18th century. He governed Little Russia in the na ...
, who proceeded to cautiously but firmly eliminate the vestiges of local autonomy. In 1781, the regimental system was dismantled and the Little Russian Collegiate abolished. Two years later, peasants' freedom of movement was restricted and the process of enserfment was completed. Cossack soldiers were integrated into the Russian army, while the Cossack officers were granted status as Russian nobles. As had previously been the practice elsewhere in the Russian Empire, lands were confiscated from the Church (during the times of the Hetmanate monasteries alone controlled 17% of the region's lands) and distributed to the nobility. The territory of the Hetmanate was reorganized into three Russian provinces ( governorates) whose administration was no different from that of any other provinces within the Russian Empire.
Foreign relations
Bohdan Khmelnytsky
Bohdan Khmelnytsky pursued a multi-vectored foreign policy for the newly created Ukrainian Cossack state. "The hetman and his colleagues began to think in terms of establishing a Cossack or Ukrainian state, either independent or allied with some other state." One system of opposition to Poland, who was waging war against the Hetmanate, was an "anti-Catholic block of Orthodox and Protestant states" that includedRussia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
, Moldavia
Moldavia ( ro, Moldova, or , literally "The Country of Moldavia"; in Romanian Cyrillic alphabet, Romanian Cyrillic: or ; chu, Землѧ Молдавскаѧ; el, Ἡγεμονία τῆς Μολδαβίας) is a historical region and for ...
, Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ro, Țara Românească, lit=The Romanian Land' or 'The Romanian Country, ; archaic: ', Romanian Cyrillic alphabet: ) is a historical and geographical region of Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and s ...
, Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the Ap ...
, and Sweden. Another option was to incorporate the Cossack Hetmanate into the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth as an equal partner to Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state that existed from the 13th century to 1795, when the territory was partitioned among the Russian Empire, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Habsburg Empire of Austria. The state was founded by Lit ...
and to Poland. Another system would include Ukraine into the Ottoman orbit, similar to Wallachia, Transylvania, Moldavia, and the Crimean Khanate
The Crimean Khanate ( crh, , or ), officially the Great Horde and Desht-i Kipchak () and in old European historiography and geography known as Little Tartary ( la, Tartaria Minor), was a Crimean Tatar state existing from 1441 to 1783, the long ...
. Finally, Khmelnytsky developed another possibility that would have involved pitting the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth against Russia and the Don Cossacks or, alternatively, to get Poland join Venice in their fight against the Ottomans.
In the early days of the uprising, Khmelnytsky recruited the military support of the Crimean Khanate, which was crucial in opposing the Polish forces for the Hetmanate. However, the Crimean Tatars proved to be an unreliable ally because their actions prevented Cossack victories in potentially decisive battles. It was in the interest of the khanate to keep the Cossack uprising alive so that the Poland would be weakened, but a strong rival Ukrainian state was also not favorable for the khanate.
From the beginning of the uprising, Khmelnytsky also appealed to Russia, which denied giving any military aid to Khmelnytsky for almost six years. Between fall 1648 and spring 1651, Khmelnytsky frequently corresponded with Ottomans, who made vague promises of military aid to the Khmelnytsky. The hetman repeatedly asked the sultan to take him as his subject, but the Ottomans never explicitly acknowledged him as such. The sultan did say that "if the hetman remains faithful", and '' ‘ahdname'', will be granted, meaning that the sultan would guarantee peace and protection. However, by 1653, it became clear to Khmelnytsky that no ''‘ahdname'' would be granted. Khmelnytsky would show his letters from the sultan to the tsar to blackmail him into accepting the hetman into his suzerainty. The Pereyaslav Agreement, signed in March 1654, was a deal to incorporate Ukraine under Russian protection as an autonomous duchy and led to a war between Poland and Russia.Britannica.
Vyhovsky and Doroshenko
After Bohdan Khmelnytsky died in 1657, Ukraine become more instable, leading to conflicts between pro-Polish and pro-Russian factions of Cossacks. In 1658, hetmanIvan Vyhovsky
Ivan Vyhovsky ( uk, Іван Виговський; pl, Iwan Wyhowski / Jan Wyhowski; date of birth unknown, died 1664), a Ukrainian military and political figure and statesman, served as hetman of the Zaporizhian Host and of the Cossack Hetma ...
negotiated the Union of Hadiach, which would set up a three-part Commonwealth, incorporating the Cossack Hetmanate as the "Grand Duchy of Ruthenia" on equal footing with the current members: the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. However, the fall of Vyhovsky meant that this wouldn't come to fruition, as conflicts continued within the Cossack state. By 1660, the state was essentially divided along the Dnieper river, with a Polish-controlled west and a Russian-controlled east. In 1663, Cossacks rebelled against the Commonwealth and with the help of the Crimean Tatars in 1665, Hetman Petro Doroshenko
Petro Doroshenko ( uk, Петро Дорофійович Дорошенко, russian: Пётр Дорофе́евич Дороше́нко, pl, Piotr Doroszenko; 1627–1698) was a Cossack political and military leader, Hetman of Right-bank Ukr ...
took power, with the hopes of taking Ukraine out from under both Russia and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. The two powers had completely ignored the Hetmanate's interests and partitioned the Hetmanate along the Dnieper in the Truce of Andrusovo
The Truce of Andrusovo ( pl, Rozejm w Andruszowie, russian: Андрусовское перемирие, ''Andrusovskoye Pieriemiriye'', also sometimes known as Treaty of Andrusovo) established a thirteen-and-a-half year truce, signed in 1667 be ...
. In 1666, Doroshenko restarted Cossack correspondence with the Ottomans.
The Ottoman Empire perceived the Truce of Andrusovo
The Truce of Andrusovo ( pl, Rozejm w Andruszowie, russian: Андрусовское перемирие, ''Andrusovskoye Pieriemiriye'', also sometimes known as Treaty of Andrusovo) established a thirteen-and-a-half year truce, signed in 1667 be ...
as a threat and began to engage in a more active policy in the region. On 8 June 1668, Doroshenko became the sole hetman of all Ukraine and returned to the idea of putting Ukraine under Ottoman protection, knowing that it would be difficult to survive. Following negotiations, both parties agreed that 1,000 janissaries wouldn't be stationed in Kodak
The Eastman Kodak Company (referred to simply as Kodak ) is an American public company that produces various products related to its historic basis in analogue photography. The company is headquartered in Rochester, New York, and is incorpor ...
and Ukraine would not have to pay any tribute. Doroshenko also drafted 17 articles on the basis of which he would accept Ottoman protection. Doroshenko issued a letter of submission to the sultan on December 24, 1668, which was confirmed by the Sublime Porte
The Sublime Porte, also known as the Ottoman Porte or High Porte ( ota, باب عالی, Bāb-ı Ālī or ''Babıali'', from ar, باب, bāb, gate and , , ), was a synecdoche for the central government of the Ottoman Empire.
History
The name ...
by June 1669. When the Commonwealth attempted to unseat Doroshenko and take over the Hetmanate, the Ottomans declared war in 1672 and marched north on Kamianets-Podilskyi, with Doroshenko's Cossacks and the Crimean Tatars on their side. Following the war, the Ottomans signed a treaty with the Commonwealth, which handed the region of Podolia
Podolia or Podilia ( uk, Поділля, Podillia, ; russian: Подолье, Podolye; ro, Podolia; pl, Podole; german: Podolien; be, Падолле, Padollie; lt, Podolė), is a historic region in Eastern Europe, located in the west-central ...
over to the Ottomans. Continued fighting with the Commonwealth resulted in the Ottomans ceding the province of Podolia back to the Commonwealth in the Treaty of Karlowitz. In 1674, Russia invaded the Hetmanate and besieged the capital of Chyhyryn
Chyhyryn ( uk, Чигирин, ) is a city and historic site located in Cherkasy Raion of Cherkasy Oblast of central Ukraine. From 1648 to 1669 the city was a Hetman residence. After a forced relocation of the Ruthenian Orthodox metropolitan see ...
, leading the Ottomans and Crimean Tatars to send their armies to confront the Russians. The Russians withdrew before any confrontation happened, but the Ottomans razed and plundered the settlements in the Hetmanate that had been friendly to the Russians in accordance with ''Darü’l-İslam''. Doroshenko surrendered to the Russians 2 years later, in 1676.
Although the Ottomans, Poles and Russians all had evidence that the Cossack Hetmanate swore allegiance to multiple parties simultaneously, "they chose to pretend they were not aware of any dual loyalty". The Ottomans did not consolidate their position in Ukraine with a strong military presence, because a frontier buffer zone suited their interests. The Ottomans referred to the Cossack Hetmanate in multiple ways. The Hetmanate under Khmelnytsky was called an eyalet; under Doroshenko, it was called a sancak (province) by June 1669. The Ottomans called the Cossack Hetmanate "the country of Ukraine" (). Historian Viktor Ostapchuk discusses the Ukrainian-Ottoman relationship in the following way:
See also
*Hetmans of Ukrainian Cossacks
Hetman of Zaporizhian Cossacks is a historical term that has multiple meanings.
Officially the post was known as Hetman of the Zaporizhian Host ( uk, Гетьман Війська Запорозького, ''Hetman Viyska Zaporozkoho'').Mytsyk, ...
* Sloboda Ukraine
* Zaporozhian Cossacks
* Zaporizhian Sich
* Zaporozhia (region)
* List of Ukrainian rulers
* List of voivodes of Nizhyn
Notes
References
Bibliography
* * *External links
* * * * Stephen Velychenko,The battle of Poltava and the decline of Cossack Ukraine
in light of Russian and English methods of rule in their borderlands 1707-1914." {{History of Europe Former Slavic countries Historical regions in Ukraine Russian Empire 17th century in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth 17th century in the Zaporozhian Host 18th century in the Zaporozhian Host States and territories established in 1649 States and territories disestablished in 1764 1649 establishments in Russia 1764 disestablishments in the Russian Empire Geography of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth Vassal states of the Ottoman Empire Former Russian protectorates