Core rope memory on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Core rope memory is a form of
Core rope memory is a form of
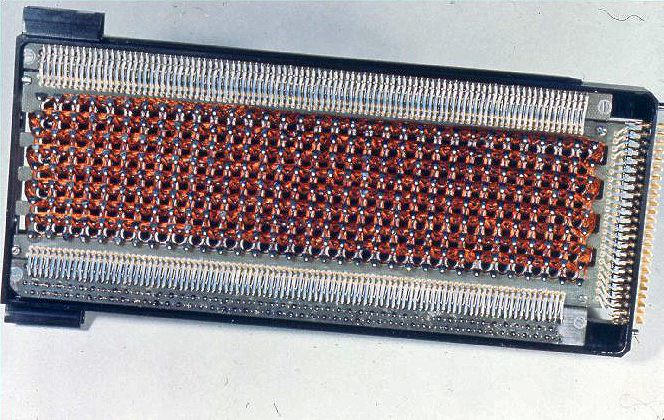 By the standards of the time, a relatively large amount of data could be stored in a small installed volume of core rope memory: 72 kilobytes per cubic foot, or roughly 2.5 megabytes per cubic meter. This was about 18 times the amount of data per volume compared to standard read-write core memory: the Block II Apollo Guidance Computer used 36,864 sixteen-bit words of core rope memory (placed within one cubic foot) and 2,048 sixteen-bit words (15 data bits+1
By the standards of the time, a relatively large amount of data could be stored in a small installed volume of core rope memory: 72 kilobytes per cubic foot, or roughly 2.5 megabytes per cubic meter. This was about 18 times the amount of data per volume compared to standard read-write core memory: the Block II Apollo Guidance Computer used 36,864 sixteen-bit words of core rope memory (placed within one cubic foot) and 2,048 sixteen-bit words (15 data bits+1
"Computer for Apollo"
NASA/MIT film from 1965 which demonstrates how rope memory was manufactured.
– By Raytheon; hosted by the Library of the California Institute of Technology's History of Recent Science & Technology site (originally hosted by the Dibner Institute)
''Computers in Spaceflight: The NASA Experience''
– By James Tomayko (Chapter 2, Part 5, "The Apollo guidance computer: Hardware")
has a detailed explanation of how core rope memory works.
extensive blog post by computer restoration expert Ken Shirriff {{DEFAULTSORT:Core Rope Memory Computer memory Non-volatile memory
 Core rope memory is a form of
Core rope memory is a form of read-only memory
Read-only memory (ROM) is a type of non-volatile memory used in computers and other electronic devices. Data stored in ROM cannot be electronically modified after the manufacture of the memory device. Read-only memory is useful for storing ...
(ROM) for computer
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations ( computation) automatically. Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as programs. These prog ...
s, first used in the 1960s by early NASA Mars space probes and then in the Apollo Guidance Computer
The Apollo Guidance Computer (AGC) was a digital computer produced for the Apollo program that was installed on board each Apollo command module (CM) and Apollo Lunar Module (LM). The AGC provided computation and electronic interfaces for guidanc ...
(AGC) and programmed by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a private land-grant research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Established in 1861, MIT has played a key role in the development of modern technology and science, and is one of th ...
(MIT) Instrumentation Lab and built by Raytheon.
Software written by MIT programmers was woven into core rope memory by female workers in factories. Some programmers nicknamed the finished product ''LOL memory'', for ''Little Old Lady'' memory.
Memory density
 By the standards of the time, a relatively large amount of data could be stored in a small installed volume of core rope memory: 72 kilobytes per cubic foot, or roughly 2.5 megabytes per cubic meter. This was about 18 times the amount of data per volume compared to standard read-write core memory: the Block II Apollo Guidance Computer used 36,864 sixteen-bit words of core rope memory (placed within one cubic foot) and 2,048 sixteen-bit words (15 data bits+1
By the standards of the time, a relatively large amount of data could be stored in a small installed volume of core rope memory: 72 kilobytes per cubic foot, or roughly 2.5 megabytes per cubic meter. This was about 18 times the amount of data per volume compared to standard read-write core memory: the Block II Apollo Guidance Computer used 36,864 sixteen-bit words of core rope memory (placed within one cubic foot) and 2,048 sixteen-bit words (15 data bits+1 parity bit
A parity bit, or check bit, is a bit added to a string of binary code. Parity bits are a simple form of error detecting code. Parity bits are generally applied to the smallest units of a communication protocol, typically 8-bit octets (bytes), ...
) of magnetic core memory (within two cubic feet).
Popular culture
In somemoon landing conspiracy theories
Moon landing conspiracy theories claim that some or all elements of the Apollo program and the associated Moon landings were hoaxes staged by NASA, possibly with the aid of other organizations. The most notable claim is that the six crewed ...
, confusion between core rope and regular core memory is used to advance the claim that the Apollo mission computer memory system could never have passed through the Earth's magnetic field undisturbed. Regular core memory would likely be susceptible to transiting magnetic fields of this magnitude, whereas core rope is not.
References
External links
"Computer for Apollo"
NASA/MIT film from 1965 which demonstrates how rope memory was manufactured.
– By Raytheon; hosted by the Library of the California Institute of Technology's History of Recent Science & Technology site (originally hosted by the Dibner Institute)
''Computers in Spaceflight: The NASA Experience''
– By James Tomayko (Chapter 2, Part 5, "The Apollo guidance computer: Hardware")
has a detailed explanation of how core rope memory works.
extensive blog post by computer restoration expert Ken Shirriff {{DEFAULTSORT:Core Rope Memory Computer memory Non-volatile memory