Coosa chiefdom on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
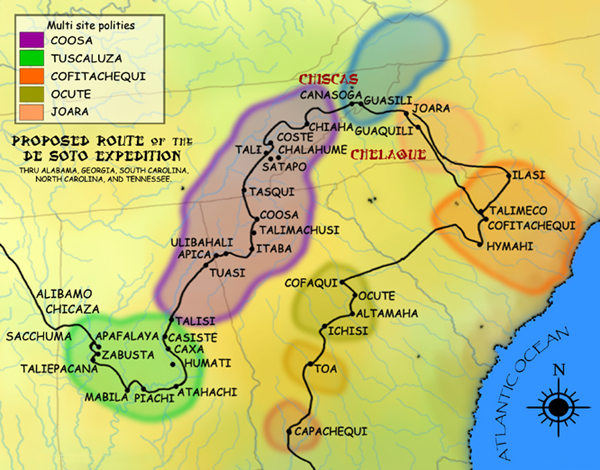 The Coosa chiefdom was a powerful Native American paramount chiefdom in what are now
The Coosa chiefdom was a powerful Native American paramount chiefdom in what are now
''
 The Coosa chiefdom was a powerful Native American paramount chiefdom in what are now
The Coosa chiefdom was a powerful Native American paramount chiefdom in what are now Gordon
Gordon may refer to:
People
* Gordon (given name), a masculine given name, including list of persons and fictional characters
* Gordon (surname), the surname
* Gordon (slave), escaped to a Union Army camp during the U.S. Civil War
* Clan Gordon, ...
and Murray counties in Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
, in the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
."Late Prehistoric/Early Historic Chiefdoms (ca. A.D. 1300-1850)"''
New Georgia Encyclopedia
The ''New Georgia Encyclopedia'' (NGE) is a web-based encyclopedia containing over 2,000 articles about the state of Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia. It is a program of Georgia Humanities (GH), in partnership with the University of Georgia Press, t ...
''. Retrieved July 22, 2010. It was inhabited from about 1400 until about 1600, and dominated several smaller chiefdoms. The total population of Coosa's area of influence, reaching into present-day Tennessee and Alabama, has been estimated at 50,000.
Hernando de Soto and his conquistadors visited Coosa on their expedition through the Southeast United States in 1539–1541, as did participants in Tristán de Luna's expedition in 1560, and Juan Pardo's 1566–1568 expedition. The Europeans recorded descriptions and impressions of the various chiefdoms they visited, describing Coosa as a series of communities and fertile gardens containing much food, rather than a town or city.
Coosa was also the name of one of the four mother towns of the Muscogee Creek confederacy
The Muscogee, also known as the Mvskoke, Muscogee Creek, and the Muscogee Creek Confederacy ( in the Muscogee language), are a group of related indigenous (Native American) peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands
 The Coosa chiefdom was centered at a site along the
The Coosa chiefdom was centered at a site along the
 The Coosa chiefdom was centered at a site along the
The Coosa chiefdom was centered at a site along the Coosawattee River
The Coosawattee River is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed April 27, 2011 river located in northwestern Georgia, United States.
Description
The river is noted as beg ...
in present-day Gordon
Gordon may refer to:
People
* Gordon (given name), a masculine given name, including list of persons and fictional characters
* Gordon (surname), the surname
* Gordon (slave), escaped to a Union Army camp during the U.S. Civil War
* Clan Gordon, ...
and Murray counties in northwestern Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
. The capital of Coosa, it had a large plaza
A town square (or square, plaza, public square, city square, urban square, or ''piazza'') is an open public space, commonly found in the heart of a traditional town but not necessarily a true geometric square, used for community gatherings. ...
and three platform mound
Platform may refer to:
Technology
* Computing platform, a framework on which applications may be run
* Platform game, a genre of video games
* Car platform, a set of components shared by several vehicle models
* Weapons platform, a system or ...
s, as well as residential dwellings. Researchers have found various Mississippian culture pottery
Mississippian culture pottery is the ceramic tradition of the Mississippian culture (800 to 1600 CE) found as artifacts in archaeological sites in the American Midwest and Southeast. It is often characterized by the adoption and use of riverine ( ...
types, the most substantial of which reflect the site's Middle and Late South Appalachian Mississippian culture (a regional variation of the Mississippian culture) habitation from 1300 to 1600.
Archeologists
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscape ...
, who nicknamed this settlement as " Little Egypt", have defined these as the Dallas
Dallas () is the List of municipalities in Texas, third largest city in Texas and the largest city in the Dallas–Fort Worth metroplex, the List of metropolitan statistical areas, fourth-largest metropolitan area in the United States at 7.5 ...
, Lamar, and Mouse Creek phases of pottery. These type variations could indicate that the chiefdom underwent three archaeological phases and changes in culture, each with distinct pottery and artifact styles. Only one other village had a mound; the others associated with the chiefdom had only residential dwellings.
Hernando de Soto and his expedition entered the Coosa chiefdom in 1540. Chroniclers recorded that the chiefdom consisted of eight villages. Archaeologists have identified the remains of seven of these, including the capital. The population of the Coosa is thought to have been between about 2,500 to 4,650 people. The chief of Coosa ruled over a significantly wider confederation of other chiefdoms, whose territory spread 400 miles along the Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, (french: Appalaches), are a system of mountains in eastern to northeastern North America. The Appalachians first formed roughly 480 million years ago during the Ordovician Period. They ...
across present-day northern Georgia into eastern Tennessee
Tennessee ( , ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked state in the Southeastern region of the United States. Tennessee is the 36th-largest by area and the 15th-most populous of the 50 states. It is bordered by Kentucky to th ...
and central Alabama
(We dare defend our rights)
, anthem = "Alabama"
, image_map = Alabama in United States.svg
, seat = Montgomery
, LargestCity = Huntsville
, LargestCounty = Baldwin County
, LargestMetro = Greater Birmingham
, area_total_km2 = 135,765 ...
. These populations totaled in the tens of thousands. This "paramount chiefdom consisted of seven or more smaller chiefdoms, representing about 50,000 people."
Following contact with Europeans and the associated introduction of endemic Old World diseases, the populations of the Coosa and other local chiefdoms suffered extensive fatalities from the new diseases. The societies went into precipitous decline and suffered great disruption by the loss of so much life. By the close of the 16th century, most of the core area of the Coosa was abandoned. The surviving population withdrew to a few villages along the Coosa River in Alabama. One such settlement was the King site, a small heavily fortified village of 277 to 517 people and 47 houses.
Linguistics
The chroniclers of the de Soto Expedition recorded the name of the Coosa as ''Coça''. The early French maps recorded several member towns of the Creek Confederacy as being occupied by the Cousha or Coushetta, in their transliterated form of the name as they heard it. The Cherokee first appeared to use the word ''kusa'' to mean the Muskogee Creek people of the Upper Towns, who were competitors and enemies. According to James Mooney, they called the Muskogee Creek "Ani'-Ku'sa or Ani'-Gu'sa, from Kusa, their principal town". English speakers adopted "Coosa" as a frontier English version of the early Cherokee word. The contemporary Cherokee name for all Creek Indians is ''ani-kusa''. This is also the name for Muskogee, Oklahoma: ᎫᏐᎢ, guso'i. The name for the Muskogee Creek people, in the revisedCherokee syllabary
The Cherokee syllabary is a syllabary invented by Sequoyah in the late 1810s and early 1820s to write the Cherokee language. His creation of the syllabary is particularly noteworthy as he was illiterate until the creation of his syllabary. He ...
of ᎦᎳᎩᎾ/Elias Boudinot
Elias Boudinot ( ; May 2, 1740 – October 24, 1821) was a lawyer and statesman from Elizabeth, New Jersey who was a delegate to the Continental Congress (more accurately referred to as the Congress of the Confederation) and served as President ...
, is spelled ᎠᏂᎫᏌ. A singular Muskogee Creek person is ᎠᎫᏌ, "agusa," according to the ''Cherokee-English Dictionary'' (Cherokee Nation of Oklahoma: Feeling & Pulte,1975).
See also
*List of sites and peoples visited by the Hernando de Soto Expedition
This is a list of sites and peoples visited by the Hernando de Soto Expedition in the years 1539–1543. In May 1539, de Soto left Havana, Cuba, with nine ships, over 620 men and 220 surviving horses and landed at Charlotte Harbor, Florida. This ...
* Cusabo
The Cusabo or Cosabo were a group of American Indian tribes who lived along the coast of the Atlantic Ocean in what is now South Carolina, approximately between present-day Charleston and south to the Savannah River, at the time of European colon ...
* Mississippian culture
* Southeastern Ceremonial Complex
The Southeastern Ceremonial Complex (formerly the Southern Cult), aka S.E.C.C., is the name given to the regional stylistic similarity of artifacts, iconography, ceremonies, and mythology of the Mississippian culture. It coincided with their ado ...
* Four Mothers Society
The Four Mothers Society or Four Mothers Nation is a religious, political, and traditionalist organization of Muscogee Creek, Cherokee, Choctaw and Chickasaw people, as well as the Natchez people enrolled in these tribes, in Oklahoma. It was forme ...
* Abihka
* Tuckabutche
* Tallapoosas
The Tallapoosas were a division of the Upper Creeks in the Muscogee Confederacy. Prior to Removal to Indian Territory, Tallapoosa lived along the Tallapoosa River in Alabama.
They are also called the Cadapouches or Canapouches, which was mistak ...
Notes
References
* Fagan, Brian. ''Ancient North America: The Archaeology of a Continent''. London: Thames and Hudson, 2005. pp. 487–488 * Hudson, Charles M., ''Knights of Spain, Warriors of the Sun: Hernando De Soto and the South's Ancient Chiefdoms'', University of Georgia Press, 1997. * Hudson, Charles M., ''Conversations with the High Priest of Coosa'', Chapel Hill, NC: University of North Carolina Press, 2003. {{authority control Native American tribes in Georgia (U.S. state) South Appalachian Mississippian culture Late Mississippian culture Muscogee tribal towns Former chiefdoms in North America Gordon County, Georgia Murray County, Georgia