Cone beam computed tomography on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cone beam computed tomography (or CBCT, also referred to as C-arm CT, cone beam
 In the late 1990s, Dr Yoshinoro Arai in Japan and Dr Piero Mozzo in Italy independently developed Cone Beam Computed Technology for
In the late 1990s, Dr Yoshinoro Arai in Japan and Dr Piero Mozzo in Italy independently developed Cone Beam Computed Technology for
File:Prima Immagine Cone-Beam-1994-07-01 -1.jpg , Axial image obtained from the first Cone-Beam 3D Scan performed on July 1, 1994
File:Prima Immagine Cone-Beam-1994-07-02.jpg , Axial image obtained from the first Cone-Beam 3D Scan performed on July 1, 1994
File:Prima Immagine Cone-Beam-1994-07-01-3.jpg , Axial image obtained from the first Cone-Beam 3D Scan performed on July 1, 1994
File:Prima acquisizione totale 1994-07-01-pag1.jpeg , Original notes about the first Cone-Beam 3D Scan performed on July 1, 1994
 The CBCT has the most important advantage in Endodontics as the 3D demonstrates critical root canal anatomical features that conventional intraoral, or panoramic images cannot.
According to the American Association of Endodontics, there are many specific situations where 3D images produced by CBCT enhances diagnosis and influences treatment and its use can not be disputed over conventional intraoral radiology following the principles of ALARA.
The CBCT has the most important advantage in Endodontics as the 3D demonstrates critical root canal anatomical features that conventional intraoral, or panoramic images cannot.
According to the American Association of Endodontics, there are many specific situations where 3D images produced by CBCT enhances diagnosis and influences treatment and its use can not be disputed over conventional intraoral radiology following the principles of ALARA.
File:DVT-scan-MagoCut-bild1-singlesample.jpg, single sampled (noisy) image
File:DVT-scan-MagoCut-bild2-oversamplefocus.jpg, several samples overlay
File:DVT-scan-MagoCut-bild3-panoramiomodejoined.jpg, joined images to panoramic
File:DVT-scan-MagoCut-bild4-dvtreconstructed.jpg, algorithmic reconstruction
File:CBCT image 03.png, in-vivo image
volume CT
Flat-panel Volume CT is a technique under development to make computed tomography images with improved performance (in particular, with improved spatial resolution). The key difference between volume CT and traditional CT is that volume CT uses a ...
, flat panel CT or Digital Volume Tomography (DVT)) is a medical imaging technique consisting of X-ray computed tomography
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 ...
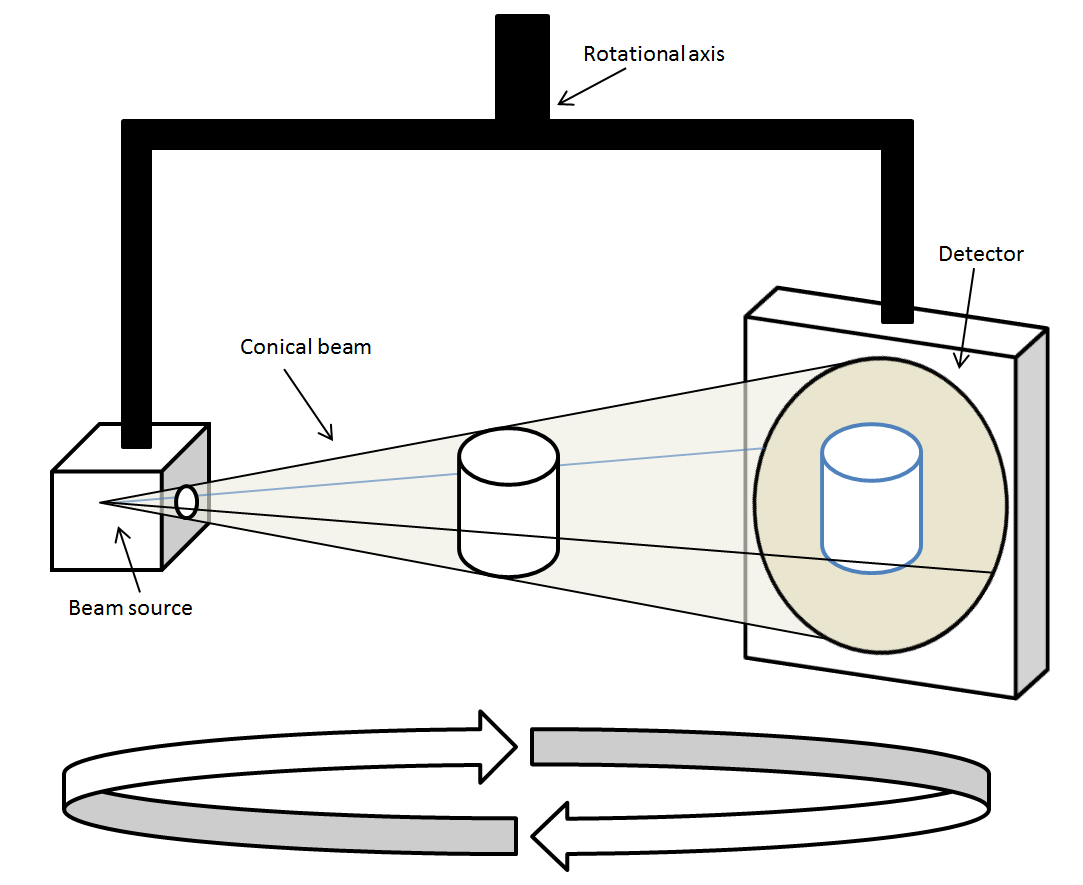
where the X-rays are divergent, forming a cone.
CBCT has become increasingly important in treatment planning and diagnosis in implant dentistry, ENT, orthopedics, and interventional radiology
Interventional radiology (IR) is a medical specialty that performs various minimally-invasive procedures using medical imaging guidance, such as x-ray fluoroscopy, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, or ultrasound. IR performs b ...
(IR), among other things. Perhaps because of the increased access to such technology, CBCT scanners are now finding many uses in dentistry, such as in the fields of oral surgery, endodontics
Endodontics (from the Greek roots ''endo-'' "inside" and ''odont-'' "tooth") is the dental specialty concerned with the study and treatment of the dental pulp.
Overview
Endodontics encompasses the study (practice) of the basic and clinic ...
and orthodontics
Orthodontics is a dentistry specialty that addresses the diagnosis, prevention, management, and correction of mal-positioned teeth and jaws, and misaligned bite patterns. It may also address the modification of facial growth, known as dentofacial ...
. Integrated CBCT is also an important tool for patient positioning and verification in image-guided radiation therapy
Image-guided radiation therapy is the process of frequent imaging, during a course of radiation treatment, used to direct the treatment, position the patient, and compare to the pre-therapy imaging from the treatment plan. Immediately prior to, ...
(IGRT).
During dental/orthodontic imaging, the CBCT scanner rotates around the patient's head, obtaining up to nearly 600 distinct images. For interventional radiology, the patient is positioned offset to the table so that the region of interest is centered in the field of view for the cone beam. A single 200 degree rotation over the region of interest acquires a volumetric data set. The scanning software collects the data and reconstructs it, producing what is termed a ''digital volume'' composed of three-dimensional voxel
In 3D computer graphics, a voxel represents a value on a regular grid in three-dimensional space. As with pixels in a 2D bitmap, voxels themselves do not typically have their position (i.e. coordinates) explicitly encoded with their values. I ...
s of anatomical data that can then be manipulated and visualized with specialized software. CBCT shares many similarities with traditional (fan beam) CT however there are important differences, particularly for reconstruction
Reconstruction may refer to:
Politics, history, and sociology
* Reconstruction (law), the transfer of a company's (or several companies') business to a new company
*''Perestroika'' (Russian for "reconstruction"), a late 20th century Soviet Unio ...
. CBCT has been described as the gold standard for imaging the oral and maxillofacial area.
History
Oral and maxillofacial radiology
 In the late 1990s, Dr Yoshinoro Arai in Japan and Dr Piero Mozzo in Italy independently developed Cone Beam Computed Technology for
In the late 1990s, Dr Yoshinoro Arai in Japan and Dr Piero Mozzo in Italy independently developed Cone Beam Computed Technology for oral and maxillofacial radiology
Oral and maxillofacial radiology, also known as dental and maxillofacial radiology, is the specialty of dentistry concerned with performance and interpretation of diagnostic imaging used for examining the craniofacial, dental and adjacent structur ...
. The first commercial system (the NewTom 9000) was introduced in the European market in 1996 and into the US market in 2001, by Italian company Quantitative Radiology.
Radiotherapy
Cone beam CT using kilovoltageX-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&nb ...
s (as used for diagnostic
Diagnosis is the identification of the nature and cause of a certain phenomenon. Diagnosis is used in many different disciplines, with variations in the use of logic, analytics, and experience, to determine "cause and effect". In systems enginee ...
, rather than therapeutic
A therapy or medical treatment (often abbreviated tx, Tx, or Tx) is the attempted remediation of a health problem, usually following a medical diagnosis.
As a rule, each therapy has indications and contraindications. There are many different ...
purposes) attached to a linear accelerator
A linear particle accelerator (often shortened to linac) is a type of particle accelerator that accelerates charged subatomic particles or ions to a high speed by subjecting them to a series of oscillating electric potentials along a linear ...
treatment machine was first developed in the late 1990s and early 2000s. Such systems have since become common on latest generation linacs. In the late 2010s CBCT also started to become available on-board particle therapy
Particle therapy is a form of external beam radiotherapy using beams of energetic neutrons, protons, or other heavier positive ions for cancer treatment. The most common type of particle therapy as of August 2021 is proton therapy.
In contrast ...
delivery systems.
Interventional radiology
While CBCT withX-ray image intensifier
An X-ray image intensifier (XRII) is an image intensifier that converts X-rays into visible light at higher intensity than the more traditional fluorescent screens can. Such intensifiers are used in X-ray imaging systems (such as fluoroscopes) ...
s was experimented with in the late 1990s, it was not until the adoption of flat-panel X-ray detectors, with improved contrast and spatial resolution, that CBCT became practical for clinical use in interventional radiology procedures. Many fixed, and even mobile, C-arm fluoroscopy systems are now capable of CBCT acquisitions, in addition to traditional planar fluoroscopy.
Applications
Endodontics
Implantology
A dental cone beam scan offers useful information when it comes to the assessment and planning of surgical implants. The American Academy of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology (AAOMR) suggests cone-beam CT as the preferred method for presurgical assessment of dental implant sites.Orthodontics
As a 3D rendition, CBCT offers an undistorted view of thedentition
Dentition pertains to the development of teeth and their arrangement in the mouth. In particular, it is the characteristic arrangement, kind, and number of teeth in a given species at a given age. That is, the number, type, and morpho-physiolo ...
that can be used to accurately visualize both erupted and non-erupted teeth, tooth root orientation and anomalous structures, that conventional 2D radiography cannot.
Processing example using x-ray data from a tooth model:
Orthopedics
The CBCT scanner offers undistorted views of the extremities. One advantage of orthopedic CBCT is the ability to take weight bearing images of thelower extremities
The human leg, in the general word sense, is the entire lower limb of the human body
The human body is the structure of a human being. It is composed of many different types of cells that together create tissues and subsequently organ sys ...
. In the realm of the foot
The foot ( : feet) is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is a separate organ at the terminal part of the leg mad ...
and ankle
The ankle, or the talocrural region, or the jumping bone (informal) is the area where the foot and the leg meet. The ankle includes three joints: the ankle joint proper or talocrural joint, the subtalar joint, and the inferior tibiofibular joi ...
particularly, weight bearing CBCT is gaining momentum due to its ability to combine 3 dimensional and weight bearing information which are of the utmost importance in diagnosis and surgical planning. The preferred term used for CBCT in the lower limb is thus WBCT for Weight Bearing CT following the first scientific publications on the subject.
Image-guided radiation therapy
Image-guided radiation therapy
Image-guided radiation therapy is the process of frequent imaging, during a course of radiation treatment, used to direct the treatment, position the patient, and compare to the pre-therapy imaging from the treatment plan. Immediately prior to, ...
is a form of external beam radiotherapy
External beam radiotherapy (EBRT) is the most common form of radiotherapy (radiation therapy). The patient sits or lies on a couch and an external source of ionizing radiation is pointed at a particular part of the body. In contrast to brachy ...
where the patient is positioned with the organs to be treated accurately matched in position to the treatment field, to reduce the dose to nearby organs which are not being treated. Many organs inside the body move by millimeters relative to the external skin surfaces, and a CBCT scanner mounted on the head of the radiotherapy unit is used immediately before treatment (and sometimes again during treatment) to ensure the patient's organs are in exactly the right position to match the treatment field, and to adjust the position of the treatment table if necessary. The images may also be used to check for other requirements of some types of treatment, such as full or empty bladder, empty rectum, etc. The same cone beam beam source and detector can alternatively be used to take simple X-ray positioning images if the organ shows particularly well on X-ray or if Fiducial marker
A fiducial marker or fiducial is an object placed in the field of view of an imaging system that appears in the image produced, for use as a point of reference or a measure. It may be either something placed into or on the imaging subject, or a ...
s have been inserted into the organ.
Interventional radiology
The CBCT scanner is mounted on a C-armfluoroscopy
Fluoroscopy () is an imaging technique that uses X-rays to obtain real-time moving images of the interior of an object. In its primary application of medical imaging, a fluoroscope () allows a physician to see the internal structure and function ...
unit in the interventional radiology
Interventional radiology (IR) is a medical specialty that performs various minimally-invasive procedures using medical imaging guidance, such as x-ray fluoroscopy, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, or ultrasound. IR performs b ...
(IR) suite, which offers real time imaging with a stationary patient. This eliminates the time needed to transfer a patient from the angiography
Angiography or arteriography is a medical imaging technique used to visualize the inside, or lumen, of blood vessels and organs of the body, with particular interest in the arteries, veins, and the heart chambers. Modern angiography is perfor ...
suite to a conventional computed tomography scanner and facilitates a broad spectrum of applications of CBCT during IR procedures. The clinical applications of CBCT in IR include treatment planning, device or implant positioning and assessment, intra-procedural localization, and assessment of procedure endpoints. CBCT is useful as a primary and supplemental form of imaging. It is an excellent adjunct to DSA and fluoroscopy
Fluoroscopy () is an imaging technique that uses X-rays to obtain real-time moving images of the interior of an object. In its primary application of medical imaging, a fluoroscope () allows a physician to see the internal structure and function ...
for soft tissue
Soft tissue is all the tissue in the body that is not hardened by the processes of ossification or calcification such as bones and teeth. Soft tissue connects, surrounds or supports internal organs and bones, and includes muscle, tendons, ...
and vascular
The blood vessels are the components of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away f ...
visibility during complex procedures. The use of CBCT before fluoroscopy potentially reduces patient radiation exposure.
Clinical applications
* Chemoembolization forHepatocellular Carcinoma
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common type of primary liver cancer in adults and is currently the most common cause of death in people with cirrhosis. HCC is the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide.
It occurs in t ...
: CBCT with contrast confirms that the proper artery is selected to deliver the therapy. The contrast enhances the parenchyma supplied by the selected artery and therefore reveals if the vasculature also supplies the tumor. Post treatment noncontrast CBCT confirms lipiodol
Lipiodol, also known as ethiodized oil, is a poppyseed oil used by injection as a radio-opaque contrast agent that is used to outline structures in radiological investigations. It is used in chemoembolization applications as a contrast agent in ...
staining of the tumor, which improves operator confidence of complete tumor coverage or further treatment.
* Prostatic artery embolization
Prostatic artery embolization (PAE, or prostate artery embolisation) is a developing non-surgical technique for treatment of benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH). Although there is increasing research on PAE, use of the technique remains at an incipi ...
for benign prostatic hypertrophy
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), also called prostate enlargement, is a noncancerous increase in size of the prostate gland. Symptoms may include frequent urination, trouble starting to urinate, weak stream, inability to urinate, or loss o ...
: CBCT provides the soft tissue detail needed to visualize prostatic enhancement, identify duplicated prostatic arteries, and avoid nontarget embolization. CBCT is superior to DSA for this therapy since the enhancement patterns on DSA can be difficult to discern due to the overlapping pelvic structures and variable arterial anatomy.
* Abscess
An abscess is a collection of pus that has built up within the tissue of the body. Signs and symptoms of abscesses include redness, pain, warmth, and swelling. The swelling may feel fluid-filled when pressed. The area of redness often extends ...
drainage: CBCT confirms needle tip location after placement under ultrasound and confirms drain placement by revealing contrast injection into the desired location.
* Adrenal Vein sampling for an adenoma
An adenoma is a benign tumor of epithelial tissue with glandular origin, glandular characteristics, or both. Adenomas can grow from many glandular organs, including the adrenal glands, pituitary gland, thyroid, prostate, and others. Some adenom ...
: contrast enhanced CBCT shows perfusion of the adrenal gland
The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys. Each gland has an outer cortex ...
to confirm catheter placement for obtaining a satisfactory sample.
* Stent
In medicine, a stent is a metal or plastic tube inserted into the lumen of an anatomic vessel or duct to keep the passageway open, and stenting is the placement of a stent. A wide variety of stents are used for different purposes, from expandab ...
placement: CBCT improves the visualization of intracranial and extracranial stents compared to conventional DSA and digital radiography by providing a better depiction of the relationship of the stents to nearby structures (i.e. vascular walls and aneurysm
An aneurysm is an outward bulging, likened to a bubble or balloon, caused by a localized, abnormal, weak spot on a blood vessel wall. Aneurysms may be a result of a hereditary condition or an acquired disease. Aneurysms can also be a nidus ( ...
lumen).
* Lung nodule percutaneous {{More citations needed, date=January 2021
In surgery, a percutaneous procedurei.e. Granger et al., 2012 is any medical procedure or method where access to inner organs or other tissue is done via needle-puncture of the skin, rather than by using ...
transthoracic needle biopsy
Fine-needle aspiration (FNA) is a diagnostic procedure used to investigate lumps or masses. In this technique, a thin (23–25 gauge (0.52 to 0.64 mm outer diameter)), hollow needle is inserted into the mass for sampling of cells that, aft ...
: CBCT guides needle placement and demonstrated a diagnostic accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity of 98.2%, 96.8%, and 100%, respectively. Diagnostic accuracy was unaffected by technically challenging conditions.
* Vascular Anomalies: After correction of arteriovenous malformation
Arteriovenous malformation is an abnormal connection between arteries and veins, bypassing the capillary system. This vascular anomaly is widely known because of its occurrence in the central nervous system (usually cerebral AVM), but can app ...
s with coiling, CBCT sensitively detects small infarcts in tissue that has been "sacrificed" during the procedure to prevent further shunting. The infarcted tissue appears as a small area of contrast retention.
* Peripheral Vascular Interventions
* Biliary
A bile duct is any of a number of long tube-like structures that carry bile, and is present in most vertebrates.
Bile is required for the digestion of food and is secreted by the liver into passages that carry bile toward the hepatic duct. It ...
Interventions
* Spinal Interventions
* Enterostomy An enterostomy ('' entero-'' + '' -stomy''; ) is either (1) a surgical procedure to create a durable opening (called a stoma) through the abdominal wall into an intestine (small intestine or large intestine
The large intestine, also known as the ...
Interventions
Reconstruction
Cone beam reconstruction algorithms are similar to typicaltomographic reconstruction
Tomographic reconstruction is a type of multidimensional inverse problem where the challenge is to yield an estimate of a specific system from a finite number of projections. The mathematical basis for tomographic imaging was laid down by Johann ...
algorithms, and methods such as filtered backprojection
In mathematics, the Radon transform is the integral transform which takes a function ''f'' defined on the plane to a function ''Rf'' defined on the (two-dimensional) space of lines in the plane, whose value at a particular line is equal to the ...
or iterative reconstruction
Iterative reconstruction refers to iterative algorithms used to reconstruct 2D and 3D images in certain imaging techniques.
For example, in computed tomography an image must be reconstructed from projections of an object. Here, iterative recon ...
may be used. However, since the reconstruction is three-dimensional, modifications such as the FDK algorithm may be needed.
Risks
Oral and maxillofacial radiology
Total radiation doses from 3D dental CBCT exams are 96% lower than conventional CT exams, but deliver more radiation than standard dental 2D x-ray (OPG). The time of exposure in CBCT is also comparatively less when compared to conventional CT. CBCT use is only lightly regulated in the US. The recommended standard of care is to use the smallest possible field of view (FOV), the smallestvoxel
In 3D computer graphics, a voxel represents a value on a regular grid in three-dimensional space. As with pixels in a 2D bitmap, voxels themselves do not typically have their position (i.e. coordinates) explicitly encoded with their values. I ...
size, the lowest mA setting and the shortest exposure time in conjunction with a pulsed exposure mode of acquisition. International organisations such as the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level o ...
and ICRP
The International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) is an independent, international, non-governmental organization, with the mission to protect people, animals, and the environment from the harmful effects of ionising radiation. Its ...
, as well as many local bodies and legislation, encourage the idea of justification for all medical exposures, where risks and benefits must be weighed up before a procedure goes ahead.
Disadvantages
Oral and maxillofacial radiology
There are a number of drawbacks of CBCT technology over that of CT scans, such as increased susceptibility to movement artifacts (in first generation machines) and to the lack of appropriate bone density determination.Bone density and the Hounsfield scale
TheHounsfield scale The Hounsfield scale , named after Sir Godfrey Hounsfield, is a quantitative scale for describing radiodensity. It is frequently used in CT scans, where its value is also termed CT number.
Definition
The Hounsfield unit (HU) scale is a linear tr ...
is used to measure radiodensity
Radiodensity (or radiopacity) is opacity to the radio wave and X-ray portion of the electromagnetic spectrum: that is, the relative inability of those kinds of electromagnetic radiation to pass through a particular material. Radiolucency or hypod ...
and, in reference to CT scans, can provide an accurate absolute density for the type of tissue depicted. The radiodensity, measured in Hounsfield Units (HU, also known as CT number) is inaccurate in CBCT scans because different areas in the scan appear with different greyscale
In digital photography, computer-generated imagery, and colorimetry, a grayscale image is one in which the value of each pixel is a single sample representing only an ''amount'' of light; that is, it carries only intensity information. Gr ...
values depending on their relative positions in the organ being scanned, despite possessing identical densities, because the image value of a voxel
In 3D computer graphics, a voxel represents a value on a regular grid in three-dimensional space. As with pixels in a 2D bitmap, voxels themselves do not typically have their position (i.e. coordinates) explicitly encoded with their values. I ...
of an organ depends on the position in the image volume. HU measured from the same anatomical area with both CBCT and medical-grade CT scanners are not identical and are thus unreliable for determination of site-specific, radiographically-identified bone density for purposes such as the placement of dental implants, as there is "no good data to relate the CBCT HU values to bone quality."
Although some authors have supported the use of CBCT technology to evaluate bone density by measuring HU, such support is provided erroneously because scanned regions of the same density in the skull can have a different grayscale value in the reconstructed CBCT dataset.
Dental CBCT systems do not employ a standardized system for scaling the grey levels that represent the reconstructed density values and, as such, they are arbitrary and do not allow for assessment of bone quality. In the absence of such a standardization, it is difficult to interpret the grey levels or impossible to compare the values resulting from different machines. While there is a general acknowledgment that this deficiency exists with CBCT systems (in that they do not correctly display HU), there has been little research conducted to attempt to correct this deficiency. See also this linear method adapted to different machines (in & citations); and a comparatively unusual neural network
A neural network is a network or circuit of biological neurons, or, in a modern sense, an artificial neural network, composed of artificial neurons or nodes. Thus, a neural network is either a biological neural network, made up of biological ...
approach (in & citations).
With time, further advancements in CBCT reconstruction algorithms will allow for improved area detectors, and this, together with enhanced postprocessing, will likely solve or reduce this problem. A method for establishing attenuation coefficients with which actual HU values can be derived from CBCT "HU" values was published in 2010 and further research is currently underway to perfect this method ''in vivo
Studies that are ''in vivo'' (Latin for "within the living"; often not italicized in English) are those in which the effects of various biological entities are tested on whole, living organisms or cells, usually animals, including humans, and p ...
''.
Interventional radiology
While the practicality of CBCT fosters its increasing application in IR, technical limitations hinder its integration into the field. The two most significant factors that affect successful integration are image quality and time (for set up, image acquisition, and image reconstruction). Compared to multidetector computed tomography (MDCT), the wider collimation in CBCT leads to increased scatter radiation and degradation of image quality as demonstrated by artifacts and decreasedcontrast-to-noise ratio
Contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR) is a measure used to determine image quality. CNR is similar to the metric signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), but subtracts a term before taking the ratio. This is important when there is a significant bias in an image, su ...
. The temporal resolution of cesium iodide
Caesium iodide or cesium iodide (chemical formula CsI) is the ionic compound of caesium and iodine. It is often used as the input phosphor of an X-ray image intensifier tube found in fluoroscopy equipment. Caesium iodide photocathodes are highly ...
detectors in CBCT slows data acquisition time to approximately 5 to 20 seconds, which increases motion artifacts. The time required for image reconstruction takes longer for CBCT (1 minute) compared to MDCT (real time) due to the computationally demanding cone beam reconstruction algorithms.
See also
* Computed tomography *Cone beam reconstruction
In microtomography X-ray scanners, cone beam reconstruction is one of two common scanning methods, the other being Fan beam reconstruction.
Cone beam reconstruction uses a 2-dimensional approach for obtaining projection data. Instead of utilizi ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Cone Beam Computed Tomography Dentistry X-ray computed tomography