Computer case screws on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Computer case
Computer case
 The #6-32 UNC is a UTS screw specifying a major thread diameter of which is defined as ; and (threads per inch) which equates to a thread pitch of . The optional UNC specification indicates the standard coarse thread is used which is defined for #6 screws as 32 tpi rendering 'UNC' redundant, however it may be seen when other specifications such as plating or other treatments are also specified. It is by far the most common screw found inside computer cases.Rutter, Daniel
The #6-32 UNC is a UTS screw specifying a major thread diameter of which is defined as ; and (threads per inch) which equates to a thread pitch of . The optional UNC specification indicates the standard coarse thread is used which is defined for #6 screws as 32 tpi rendering 'UNC' redundant, however it may be seen when other specifications such as plating or other treatments are also specified. It is by far the most common screw found inside computer cases.Rutter, Daniel
Dan's Data - Letters 53
"Screwed"'', 2006-02-26 It commonly appears in lengths of () and () or less often (). Non-standard metricized lengths such as are also sometimes encountered. Nearly every brand new computer case comes with a bag of these. They are commonly used for the following purposes, however there are many exceptions: * securing a power supply to the case * securing a 3.5-inch hard disk drive to the case * holding an
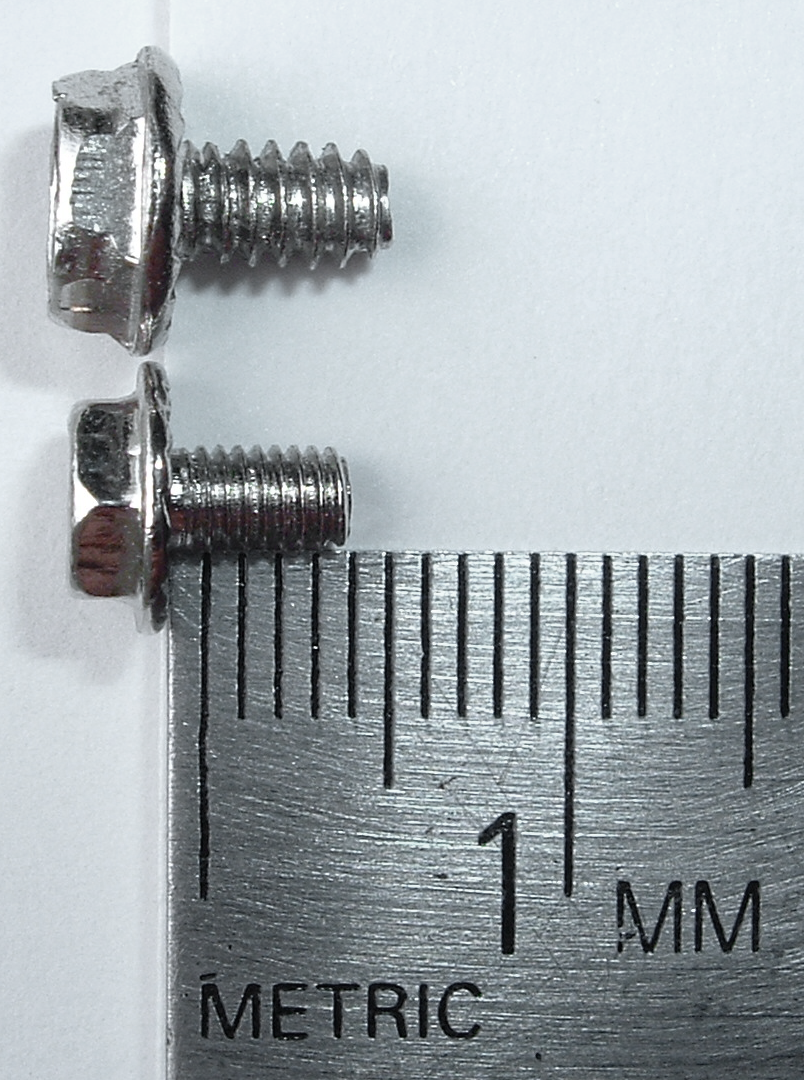 The M3 is a metric screw specifying a nominal diameter of ; and standard coarse thread pitch defined as . The M3 is the second most common screw found in PCs. It commonly appears in many lengths from 1 to 20 mm. Nearly every brand-new computer case comes with a bag of these. Notwithstanding many exceptions, they are commonly used for securing the following devices:
* 5.25-inch optical disc drives
* 2.5-inch hard disks and
The M3 is a metric screw specifying a nominal diameter of ; and standard coarse thread pitch defined as . The M3 is the second most common screw found in PCs. It commonly appears in many lengths from 1 to 20 mm. Nearly every brand-new computer case comes with a bag of these. Notwithstanding many exceptions, they are commonly used for securing the following devices:
* 5.25-inch optical disc drives
* 2.5-inch hard disks and
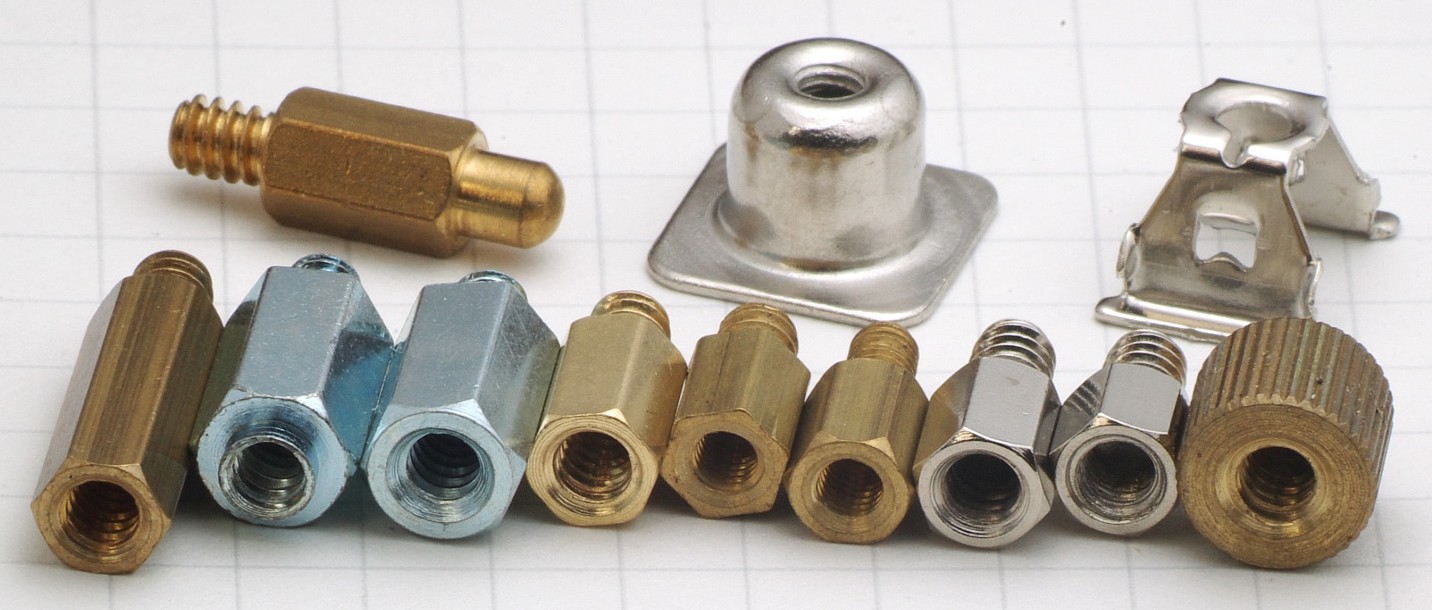 Most cases use threaded brass standoffs (Jack Screw Standoffs) for attaching the motherboard to the case chassis. Because the case material is usually a conductive metal, attaching the motherboard directly to it can cause a
Most cases use threaded brass standoffs (Jack Screw Standoffs) for attaching the motherboard to the case chassis. Because the case material is usually a conductive metal, attaching the motherboard directly to it can cause a
File:Cross slot screw.jpg, Close-up of a #6-32 UNC screw with a flanged hex/Phillips head, commonly provided in PC cases
File:PCscrew6-32-large.jpg, Close-up of a #6-32 UNC screw with a Phillips pan head, commonly provided in PC cases
File:Thumbscrews pc.jpg, Thumbscrews from an ATX PC case
The 11 Tools Every System Builder Should Own
' (and screws) from crn.com Computer enclosure Screws
 Computer case
Computer case screw
A screw and a bolt (see '' Differentiation between bolt and screw'' below) are similar types of fastener typically made of metal and characterized by a helical ridge, called a ''male thread'' (external thread). Screws and bolts are used to f ...
s are the hardware used to secure parts of a PC to the case. Although there are numerous manufacturers of computer cases, they have generally used three thread sizes. The Unified Thread Standard
The Unified Thread Standard (UTS) defines a standard thread form and series—along with allowances, tolerances, and designations—for screw threads commonly used in the United States and Canada. It is the main standard for bolts, nuts, and a w ...
(UTS) originates from the United States, while the ISO metric screw thread
The ISO metric screw thread is the most commonly used type of general-purpose screw thread worldwide. They were one of the first international standards agreed when the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) was set up in 1947.
Th ...
is standardized worldwide. In turn, these thread standards
Thread may refer to:
Objects
* Thread (yarn), a kind of thin yarn used for sewing
** Thread (unit of measurement), a cotton yarn measure
* Screw thread, a helical ridge on a cylindrical fastener
Arts and entertainment
* ''Thread'' (film), 2016 ...
define preferred size combinations that are based on generic units—some on the inch and others on the millimetre.
The #6-32 UNC screws are often found on 3.5" hard disk drive
A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive, or fixed disk is an electro-mechanical data storage device that stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage with one or more rigid rapidly rotating platters coated with magne ...
s and the case's body to secure the covers. The M3 threaded holes are often found on 5.25" optical disc drives, 3.5" floppy drives, and 2.5" drives. Motherboards
A motherboard (also called mainboard, main circuit board, mb, mboard, backplane board, base board, system board, logic board (only in Apple computers) or mobo) is the main printed circuit board (PCB) in general-purpose computers and other expand ...
and other circuit boards often use a #6-32 UNC standoff. #4-40 UNC thumb screws are often found on the ends of DVI, VGA
Video Graphics Array (VGA) is a video display controller and accompanying de facto graphics standard, first introduced with the IBM PS/2 line of computers in 1987, which became ubiquitous in the PC industry within three years. The term can no ...
, serial and parallel
Parallel is a geometric term of location which may refer to:
Computing
* Parallel algorithm
* Parallel computing
* Parallel metaheuristic
* Parallel (software), a UNIX utility for running programs in parallel
* Parallel Sysplex, a cluster of ...
connectors.
More modern cases from certain manufacturers ( Dell, Gateway) and enthusiast cases will lack screws altogether, instead utilizing a tool-less design.
#6-32 UNC screw
 The #6-32 UNC is a UTS screw specifying a major thread diameter of which is defined as ; and (threads per inch) which equates to a thread pitch of . The optional UNC specification indicates the standard coarse thread is used which is defined for #6 screws as 32 tpi rendering 'UNC' redundant, however it may be seen when other specifications such as plating or other treatments are also specified. It is by far the most common screw found inside computer cases.Rutter, Daniel
The #6-32 UNC is a UTS screw specifying a major thread diameter of which is defined as ; and (threads per inch) which equates to a thread pitch of . The optional UNC specification indicates the standard coarse thread is used which is defined for #6 screws as 32 tpi rendering 'UNC' redundant, however it may be seen when other specifications such as plating or other treatments are also specified. It is by far the most common screw found inside computer cases.Rutter, Daniel Dan's Data - Letters 53
"Screwed"'', 2006-02-26 It commonly appears in lengths of () and () or less often (). Non-standard metricized lengths such as are also sometimes encountered. Nearly every brand new computer case comes with a bag of these. They are commonly used for the following purposes, however there are many exceptions: * securing a power supply to the case * securing a 3.5-inch hard disk drive to the case * holding an
expansion card
In computing, an expansion card (also called an expansion board, adapter card, peripheral card or accessory card) is a printed circuit board that can be inserted into an electrical connector, or expansion slot (also referred to as a bus sl ...
in place by its metal slot cover
* fastening case components to one another
* usually, one or more #6-32 UNC screws hold the main cover on the case
They are almost always provided with a #2 Phillips drive. Sometimes a Green Robertson
Robertson may refer to:
People
* Robertson (surname) (includes a list of people with this name)
* Robertson (given name)
* Clan Robertson, a Scottish clan
* Robertson, stage name of Belgian magician Étienne-Gaspard Robert (1763–1837)
Places ...
or Torx
Torx (pronounced ) is a trademark for a type of screw drive characterized by a 6-point star-shaped pattern, developed in 1967, Bernard F. Reiland, "Coupling arrangement and tools for same", filed 1967-03-21 by Camcar Textron. A popular generic ...
drive is used instead. All three patterns may also be combined with a slot for a flat-blade screwdriver. Usually they are provided with a 1/4 in () flanged hex head. Non-standard metricized flanged hex heads can also be encountered. Also common are ''pan head'' screws - a low disk with a chamfered outer edge. Because they are used in places where high torque is not required and easy removal and replacement may be desirable (such as on the side panels of the PC case), they are frequently available as thumbscrews with larger, knurled heads that can be removed with one's fingers or tools.
M3 screw
 The M3 is a metric screw specifying a nominal diameter of ; and standard coarse thread pitch defined as . The M3 is the second most common screw found in PCs. It commonly appears in many lengths from 1 to 20 mm. Nearly every brand-new computer case comes with a bag of these. Notwithstanding many exceptions, they are commonly used for securing the following devices:
* 5.25-inch optical disc drives
* 2.5-inch hard disks and
The M3 is a metric screw specifying a nominal diameter of ; and standard coarse thread pitch defined as . The M3 is the second most common screw found in PCs. It commonly appears in many lengths from 1 to 20 mm. Nearly every brand-new computer case comes with a bag of these. Notwithstanding many exceptions, they are commonly used for securing the following devices:
* 5.25-inch optical disc drives
* 2.5-inch hard disks and solid-state drive
A solid-state drive (SSD) is a solid-state storage device that uses integrated circuit assemblies to store data persistently, typically using flash memory, and functioning as secondary storage in the hierarchy of computer storage. It is a ...
* 3.5-inch floppy drives
M3 screws typically accept a #2 Phillips screwdriver tip.
Motherboard standoff
 Most cases use threaded brass standoffs (Jack Screw Standoffs) for attaching the motherboard to the case chassis. Because the case material is usually a conductive metal, attaching the motherboard directly to it can cause a
Most cases use threaded brass standoffs (Jack Screw Standoffs) for attaching the motherboard to the case chassis. Because the case material is usually a conductive metal, attaching the motherboard directly to it can cause a short circuit
A short circuit (sometimes abbreviated to short or s/c) is an electrical circuit that allows a current to travel along an unintended path with no or very low electrical impedance. This results in an excessive current flowing through the circui ...
. Sometimes threaded or snap-lock plastic standoffs are used, which are less secure, but equally useful in a stationary computer. The standoff provides a margin of space between the motherboard and the case to keep the multiple solder points below from grounding and short-circuiting.
Usually, the standoff has a #6-32 UNC male thread on one end which screws into a threaded hole in the case or motherboard backplate and a #6-32 UNC female thread in the other end which accepts a screw to retain the motherboard. Less often, the standoff has a female thread in both ends and a second screw is used to attach it to the case. Some standoffs use the M3 female thread (which faces the motherboard) instead of #6-32 UNC, and on a rare occasion a mixture of types can be used in the same case.
All-metric standoffs are stated as threading x hex length x threaded length. For example, M3 x 10 x 6 means a standoff with M3 male and female threading, 10 mm hex length, and 6 mm threaded length. M6 x 10 x 8 means M6 male and female threading, 10 mm hex length, and 8 mm threaded length. Typically, M2.5 and M3 standoffs tighten with a 5 mm socket, M4 standoffs with a 6 mm socket, M5 standoffs with a 7 mm socket, and M6 standoffs with an 8 mm socket, but this is not always the case.
Version 2.1 of the ATX
ATX (Advanced Technology eXtended) is a motherboard and power supply configuration specification developed by Intel in 1995 to improve on previous de facto standards like the AT design. It was the first major change in desktop computer enclo ...
specification states that the length of standoffs needs to be at least , with their cross sections fitting within square areas centered around each mounting hole on ATX motherboards.
#4-40 UNC thumbscrews
Pairs of #4-40 UNC thumbscrews are used to fasten certain connectors to hardware ports. The screws are typically located on either side ofD-subminiature
The D-subminiature or D-sub is a common type of electrical connector. They are named for their characteristic D-shaped metal shield. When they were introduced, D-subs were among the smallest connectors used on computer systems.
Description, no ...
connectors such as on VGA, serial, parallel and legacy game controller ports. They are also more recently used on DVI connectors. The typical length for a #4-40 screw used in PCs is (). Occasionally the 4-40 hexagonal standoffs come loose when loosening the 4-40 screws to remove a cable, gender changer, or adapter. The 4-40 standoffs typically tighten with a 5 mm or 3/16-inch socket. Care should be taken not to overtighten them as they are somewhat delicate and will snap off at the base with excessive torque.
Material
Steel is by far the most common material used, frequently with a plated or anodized finish. Other materials including brass, aluminum, nylon and various plastics are also used for applications with particular physical or aesthetic requirements.Comparison
The #6-32 UNC is a thicker screw with a more coarse thread. This makes it more suitable for fastening larger parts and thicker materials requiring increased holding strength. Its larger size and coarse thread make it easier to work with during assembly, with less risk of cross threading. The integrated flange provides greater holding strength with less risk of pull through. The hex head makes it easier to work with during assembly with powered torque screwdrivers. The M3 is a thinner screw with a finer thread than the #6-32 UNC. This makes it more suitable for fastening into smaller parts and thinner materials requiring good strength in a limited space. Its size and fine thread make it appropriate for applications where a #6-32 UNC would be excessively bulky without providing any other benefits versus the smaller M3.Gallery
Example
A regular computer case may require/include * 7 thumb screw 6-32 × 6 mm for 2.5” drive tray, expansion slots * 4 hexagon screw 6-32 × 6 mm for psu * 21 phillips screw 6-32 × 5 mm for motherboard, 3.5” harddisk tray * 12 phillips screw M3 × 5 mm for 2.5” harddrive * 16 KB5 x 10 mm for fans * 9 standoff 6-32 × 6.5 + 4 mm for motherboard * 1 positioning standoff 6-32 × 6.5 + 4 mm for motherboardSee also
*Torx
Torx (pronounced ) is a trademark for a type of screw drive characterized by a 6-point star-shaped pattern, developed in 1967, Bernard F. Reiland, "Coupling arrangement and tools for same", filed 1967-03-21 by Camcar Textron. A popular generic ...
References
{{ReflistExternal links
*The 11 Tools Every System Builder Should Own
' (and screws) from crn.com Computer enclosure Screws